Predicting Malignant Lymph Nodes Using a Novel Scoring System Based on Multi-Endobronchial Ultrasound Features
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. EBUS-TBNA Procedure and Pathological Diagnosis
2.3. EBUS Image Categories
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Lymph Nodes
3.2. Diagnostic Yields of Each EBUS Feature for MLNs
3.3. Diagnostic Test Parameters of Each EBUS Feature and Predictive Scoring System of MLNs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silvestri, G.A.; Gonzalez, A.V.; Jantz, M.A.; Margolis, M.L.; Gould, M.K.; Tanoue, L.T.; Harris, L.J.; Detterbeck, F.C. Methods for staging non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, e211S–e250S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilmann, P.; Clementsen, P.F.; Colella, S.; Siemsen, M.; De Leyn, P.; Dumonceau, J.M.; Herth, F.; Larghi, A.; Vazquez-Sequeiros, E.; Hassan, C.; et al. Combined endobronchial and esophageal endosonography for the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline, in cooperation with the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons (ESTS). Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 48, 545–559. [Google Scholar]
- Postmus, P.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Oudkerk, M.; Senan, S.; Waller, D.A.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Escriu, C.; Peters, S.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv1–iv21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Jiang, L.Y.; Zhang, W.; Xin, Y.; Han, B.H. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for staging of lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.; Shah, P.L.; Edmonds, L.; Lim, E. Test performance of endobronchial ultrasound and transbronchial needle aspiration biopsy for mediastinal staging in patients with lung cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2009, 64, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ibraheem, A.; Hirmas, N.; Fanti, S.; Paez, D.; Abuhijla, F.; Al-Rimawi, D.; Al-Rasheed, U.; Abdeljalil, R.; Hawari, F.; Alrabi, K.; et al. Impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT, CT and EBUS/TBNA on preoperative mediastinal nodal staging of NSCLC. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osarogiagbon, R.U.; Lee, Y.S.; Faris, N.R.; Ray, M.A.; Ojeabulu, P.O.; Smeltzer, M.P. Invasive mediastinal staging for resected non-small cell lung cancer in a population-based cohort. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 158, 1220–1229.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, B.; Park, E.Y.; Yang, B.; Lee, G.K.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.M. Long-term survival according to N stage diagnosed by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 2022, 161, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J.; Chan, H.P.; Soon, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.; Soo, R.A.; Kee, A.C.L. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the adequacy of endobronchial ultrasound transbronchial needle aspiration for next-generation sequencing in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2022, 166, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimura, K.; Yanase, K.; Imabayashi, T.; Takeyasu, Y.; Furuse, H.; Tanaka, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sasada, S.; Tsuchida, T. The impact of core tissues on successful next-generation sequencing analysis of specimens obtained through endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Cancers 2021, 13, 5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylton, D.A.; Turner, S.; Kidane, B.; Spicer, J.; Xie, F.; Farrokhyar, F.; Yasufuku, K.; Agzarian, J.; Hanna, W.C. The Canada Lymph Node Score for prediction of malignancy in mediastinal lymph nodes during endobronchial ultrasound. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, 2499–2507.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid-Bindert, G.; Jiang, H.; Kähler, G.; Saur, J.; Henzler, T.; Wang, H.; Ren, S.; Zhou, C.; Pilz, L.R. Predicting malignancy in mediastinal lymph nodes by endobronchial ultrasound: A new ultrasound scoring system. Respirology 2012, 17, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alici, I.O.; Yılmaz Demirci, N.; Yılmaz, A.; Karakaya, J.; Özaydın, E. The sonographic features of malignant mediastinal lymph nodes and a proposal for an algorithmic approach for sampling during endobronchial ultrasound. Clin. Respir. J. 2016, 10, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evison, M.; Morris, J.; Martin, J.; Shah, R.; Barber, P.V.; Booton, R.; Crosbie, P.A. Nodal staging in lung cancer: A risk stratification model for lymph nodes classified as negative by EBUS-TBNA. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, I.F.; Gatti, A.A.; Hylton, D.A.; Sullivan, K.A.; Patel, Y.S.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Farrokhyar, F.; Hanna, W.C. An artificial intelligence algorithm to predict nodal metastasis in lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 114, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Yasufuku, K.; Nakajima, T.; Chiyo, M.; Yoshida, S.; Suzuki, M.; Shibuya, K.; Hiroshima, K.; Nakatani, Y.; Yoshino, I. The utility of sonographic features during endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for lymph node staging in patients with lung cancer: A standard endobronchial ultrasound image classification system. Chest 2010, 138, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Anayama, T.; Shingyoji, M.; Kimura, H.; Yoshino, I.; Yasufuku, K. Vascular image patterns of lymph nodes for the prediction of metastatic disease during EBUS-TBNA for mediastinal staging of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Mao, X.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yu, Y.F.; Qin, E.; Chen, X.; Shen, J.-X. Endobronchial ultrasound elastography differentiates intrathoracic lymph nodes: A meta-analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 106, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumo, T.; Sasada, S.; Chavez, C.; Matsumoto, Y.; Tsuchida, T. Endobronchial ultrasound elastography in the diagnosis of mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 44, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimura, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Sasada, S.; Hara, S.; Ikushima, I.; Chiba, Y.; Tachiwada, T.; Kawanami, T.; Yatera, K. Quantitative analysis of endobronchial ultrasound elastography in computed tomography-negative mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zheng, X.; Mao, X.; Wang, L.; Xiong, H.; Herth, F.J.F.; Han, B. Endobronchial ultrasound elastography for evaluation of intrathoracic lymph nodes: A pilot study. Respiration 2017, 93, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Udagawa, H.; Kirita, K.; Nomura, S.; Itotani, R.; Tamiya, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Ota, T.; Naito, T.; Izumi, H.; et al. Comparison of the efficiency of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration using a 22G needle versus 25G needle for the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in patients with lung cancer: A prospective randomized, crossover study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3745–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, C.D.; Young, B.; Matta, M. Comparison of specimen adequacy and diagnostic accuracy of a 25-gauge and 22-gauge needle in endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 3643–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delong, E.R.; Delong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1998, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, R.L.J.; Leoncini, F.; Slotman, J.; de Korte, C.; Trisolini, R.; van der Heijden, E.H.F.M.; on behalf of the E-Predict Study Group. Accuracy and reproducibility of endoscopic ultrasound B-mode features for observer-based lymph nodal malignancy prediction. Respiration 2021, 100, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhun, B.W.; Um, S.W.; Suh, G.Y.; Chung, M.P.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.J.; Han, J.; Lee, K.-J. Clinical value of endobronchial ultrasound findings for predicting nodal metastasis in patients with suspected lymphadenopathy: A prospective study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiek, H.; Fiorentino, F.; Peralta, A.D.; Serra, E.; Esteban, B.; Martinez, R.; Noguera, M.A.; Moyano, P.; Sala, E.; Sauleda, J.; et al. Real-time prediction of mediastinal lymph node malignancy by endobronchial ultrasound. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2014, 50, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Nakajima, T.; Inage, T.; Sata, Y.; Sakairi, Y.; Tamura, H.; Wada, H.; Suzuki, H.; Chiyo, M.; Yoshino, I. The combination of endobronchial elastography and sonographic findings during endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for predicting nodal metastasis. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.K.; Yu, K.L.; Chang, L.Y.; Fan, H.J.; Wen, Y.F.; Ho, C.C. Differentiating malignant and benign lymph nodes using endobronchial ultrasound elastography. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, R.L.J.; de Korte, C.L.; van der Heijden, E.H.F.M. Optimal endobronchial ultrasound strain elastography assessment strategy: An explorative study. Respiration 2019, 97, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, R.L.J.; Trisolini, R.; Leoncini, F.; Candoli, P.; Bezzi, M.; Messi, A.; Krasnik, M.; de Korte, C.L.; Annema, J.T.; van der Heijden, E.H. Predictive value of endobronchial ultrasound strain elastography in mediastinal lymph node staging: The E-predict multicenter study results. Respiration 2020, 99, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiina, T. JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: Basics and terminology. J. Med. Ultrason. 2013, 40, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiina, T.; Nitta, N.; Ueno, E.; Bamber, J.C. Real time tissue elasticity imaging using the combined autocorrelation method. J Med. Ultrason. 2002, 29, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, Y.; Yi, A.J.; Cui, X.W.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound elastography for the evaluation of lymph nodes. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 714660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, H.D.; Chien, Y.C.; Huang, C.K.; Wang, H.C. Application of transthoracic shear-wave ultrasound elastography in lung lesions. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Numbers of Patients (N = 301) (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 199 (66.1) |
| Age, years | 66 (16–91) |
| Smoking history | |
| Never | 74 (24.6) |
| Past | 143 (47.5) |
| Current | 84 (27.9) |
| Final diagnosis per patient | |
| Malignant | 271 (90.0) |
| Lung cancer | 233 (77.4) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 117 (38.9) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 39 (13.0) |
| Neuroendocrine tumor | 63 (21.0) |
| Other non-small cell carcinoma | 14 (4.7) |
| Non-pulmonary malignancies | 38 (12.6) |
| Breast cancer | 14 (4.7) |
| Gastrointestinal cancer | 10 (3.3) |
| Hematologic cancer | 4 (1.3) |
| Other cancer | 10 (3.3) |
| Benign | 30 (10.0) |
| Sarcoidosis (definite or suspect) | 15 (5.0) |
| Infection | 2 (0.7) |
| Others | 3 (1.0) |
| Non-specific finding | 10 (3.3) |
| Characteristics | Number of Lymph Nodes (N = 594) (%) |
|---|---|
| Lymph node location | |
| Subcarinal (7) | 162 (27.3) |
| Lower paratracheal (4R, 4L) | 177 (29.8) |
| Hilar (10R, 10L) | 19 (3.2) |
| Interlobar (11s, 11i, 11L) | 131 (22.1) |
| Others (2R, 2L, 3p, 5, 8, 9, 12, 13) | 105 (17.7) |
| Short axis on CT, cm | |
| ≥1 | 327 (55.1) |
| <1 | 267 (44.9) |
| Short axis size on CT, cm | 1.1 (0.3–5.6) |
| SUVmax on PET | |
| ≥2.5 | 359 (60.4) |
| <2.5 | 127 (21.4) |
| Not evaluated | 108 (18.2) |
| Final diagnosis per lymph node | |
| Malignant | 375 (63.1) |
| Benign | 219 (36.9) |
| EBUS Modes and Features | Numbers of Malignant LNs/Total LNs (%) | Univariable p-Value † | Odds Ratio (95% CI) ‡ | Multivariable p-Value ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-mode | ||||
| Short axis | <0.001 | 1.860 (1.090–3.150) | <0.001 | |
| ≤1 cm | 130/275 (47.3) | |||
| >1 cm | 245/319 (76.8) | |||
| Shape | 0.104 | 0.970 (0.518–1.820) | 0.925 | |
| Oval | 283/461 (61.4) | |||
| Round | 92/133 (69.2) | |||
| Margin | <0.001 | 0.561 (0.249–1.260) | 0.163 | |
| Indistinct | 68/85 (80.0) | |||
| Distinct | 307/509 (60.3) | |||
| Echogenicity | <0.001 | 20.40 (11.30–36.50) | <0.001 | |
| Homogeneous | 26/195 (13.3) | |||
| Heterogeneous | 349/399 (87.5) | |||
| CHS | <0.001 | 1.910 (1.020–3.560) | 0.043 | |
| Presence | 41/156 (26.3) | |||
| Absence | 334/438 (76.3) | |||
| CNS | <0.001 | 3.860 (1.370–10.90) | 0.011 | |
| Absence | 273/487 (56.1) | |||
| Presence | 102/107 (95.3) | |||
| Power/color Doppler mode | ||||
| Vascular pattern | <0.001 | 1.060 (0.613–1.840) | 0.827 | |
| Grades 0–1 | 172/334 (51.5) | |||
| Grades 2–3 | 203/260 (78.1) | |||
| Elastography mode | ||||
| Elasticity | <0.001 | 3.460 (1.830–6.560) | <0.001 | |
| Others | 236/431 (54.8) | |||
| Blue dominant | 139/163 (85.3) | |||
| EBUS Features and Scoring Systems | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | Accuracy (%) |
| B-mode | |||||
| Short axis (>1 cm) | 65.3 | 66.2 | 76.8 | 52.7 | 65.7 |
| Shape (round) | 24.5 | 81.3 | 69.2 | 38.6 | 45.5 |
| Margin (distinct) | 81.9 | 7.8 | 60.3 | 20.0 | 54.5 |
| Echogenicity (heterogeneous) | 93.1 | 77.2 | 87.5 | 86.7 | 87.2 |
| CHS (absence) | 89.1 | 52.5 | 76.3 | 73.7 | 75.6 |
| CNS (presence) | 27.2 | 97.7 | 95.3 | 44.2 | 53.2 |
| Power/color Doppler mode | |||||
| Vascular pattern (Grades 2–3) | 54.1 | 74.0 | 78.1 | 48.5 | 61.4 |
| Elastography mode | |||||
| Elasticity (blue) | 37.1 | 89.0 | 85.3 | 45.2 | 56.2 |
| Scoring system | |||||
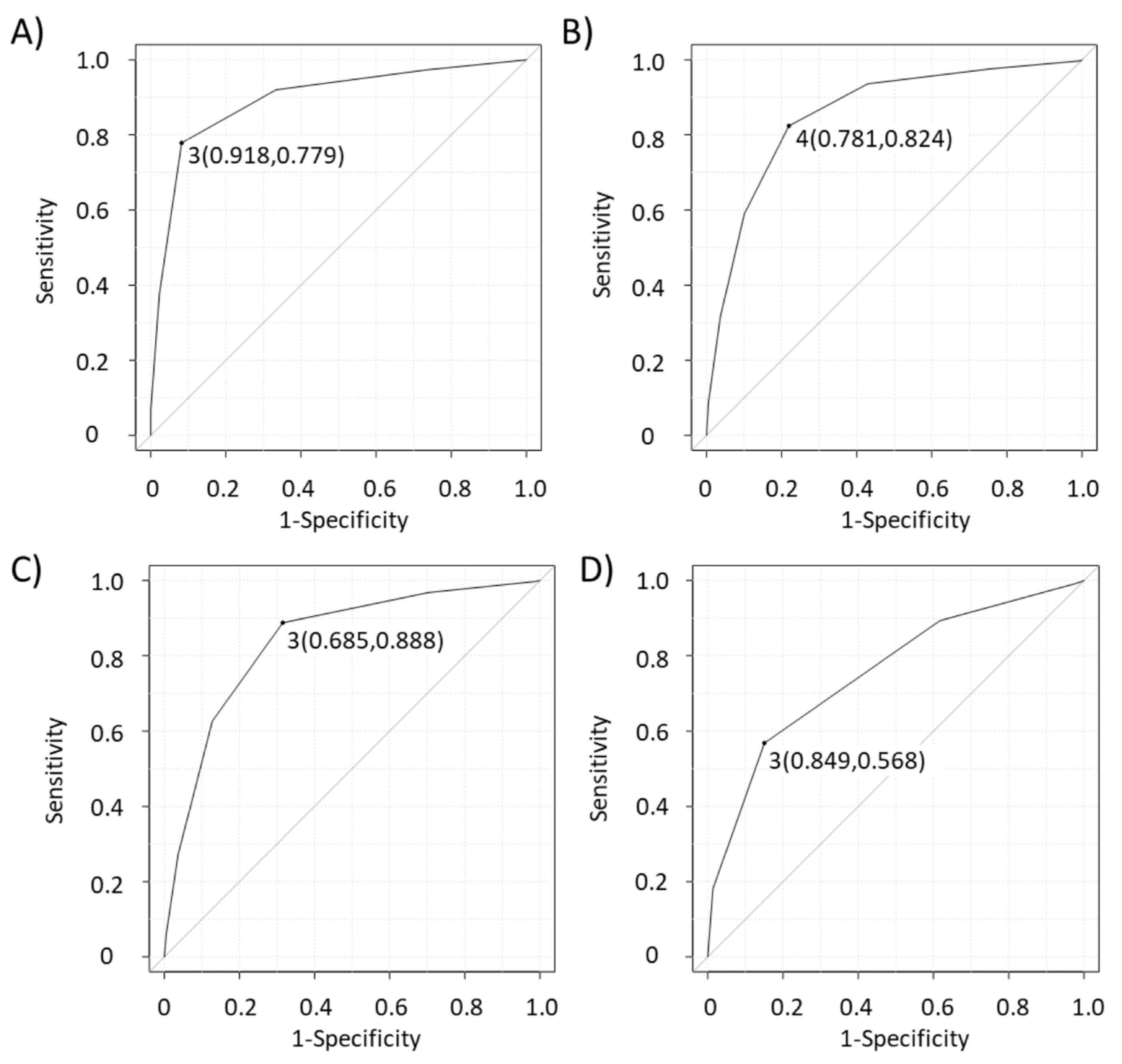
| Novel scoring system | 77.9 | 91.8 | 94.2 | 70.8 | 83.0 |
| Eight EBUS features | 82.4 | 78.1 | 86.6 | 72.2 | 81.0 |
| Six B-mode features | 88.8 | 68.5 | 82.8 | 78.1 | 81.3 |
| Canada lymph node score | 56.8 | 84.9 | 86.6 | 53.4 | 67.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morishita, M.; Uchimura, K.; Furuse, H.; Imabayashi, T.; Tsuchida, T.; Matsumoto, Y. Predicting Malignant Lymph Nodes Using a Novel Scoring System Based on Multi-Endobronchial Ultrasound Features. Cancers 2022, 14, 5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215355
Morishita M, Uchimura K, Furuse H, Imabayashi T, Tsuchida T, Matsumoto Y. Predicting Malignant Lymph Nodes Using a Novel Scoring System Based on Multi-Endobronchial Ultrasound Features. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215355
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorishita, Momoko, Keigo Uchimura, Hideaki Furuse, Tatsuya Imabayashi, Takaaki Tsuchida, and Yuji Matsumoto. 2022. "Predicting Malignant Lymph Nodes Using a Novel Scoring System Based on Multi-Endobronchial Ultrasound Features" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215355
APA StyleMorishita, M., Uchimura, K., Furuse, H., Imabayashi, T., Tsuchida, T., & Matsumoto, Y. (2022). Predicting Malignant Lymph Nodes Using a Novel Scoring System Based on Multi-Endobronchial Ultrasound Features. Cancers, 14(21), 5355. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215355






