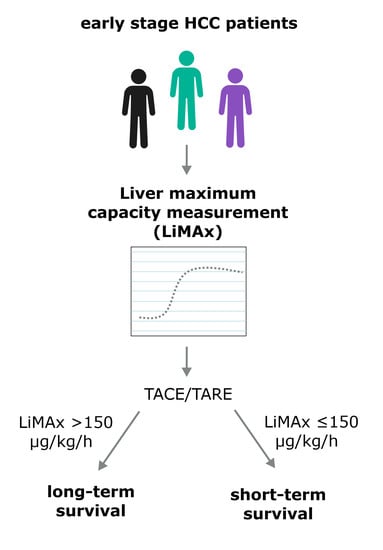
The Liver Maximum Capacity Test (LiMAx) Is Associated with Short-Term Survival in Patients with Early Stage HCC Undergoing Transarterial Treatment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
2.3. Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE)
2.4. LiMAx
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
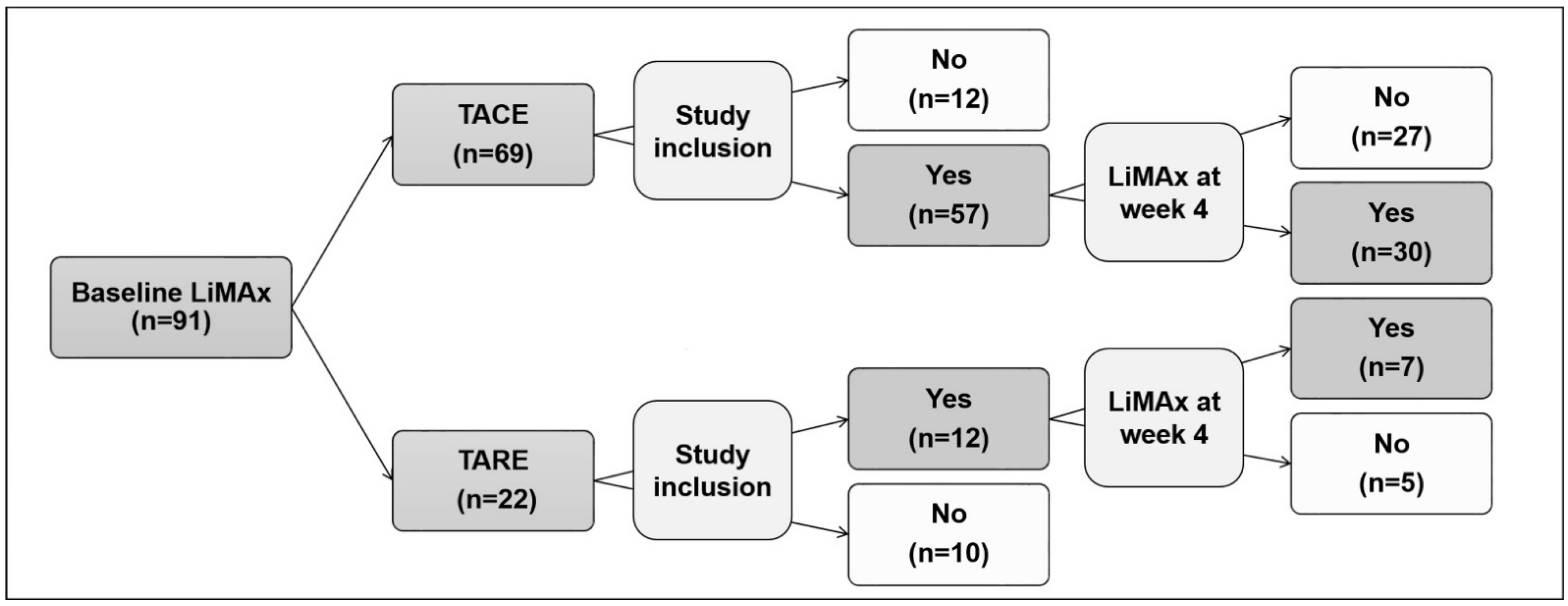
3.1. Study Population
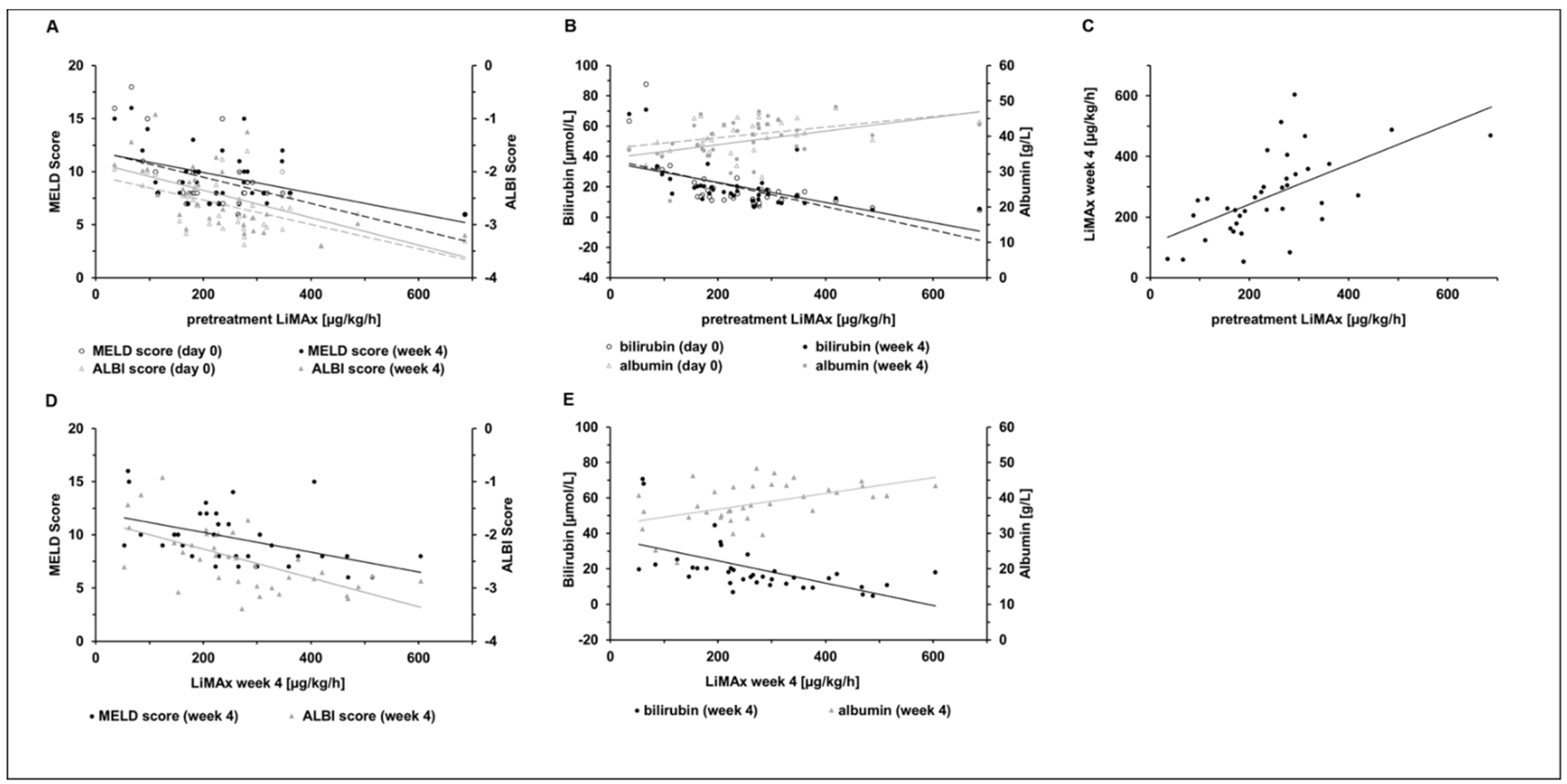
3.2. LiMAx Results and Other Parameters of Liver Function before and after Transarterial Treatment
3.3. LiMAx Results and Adverse Events of Transarterial Treatment
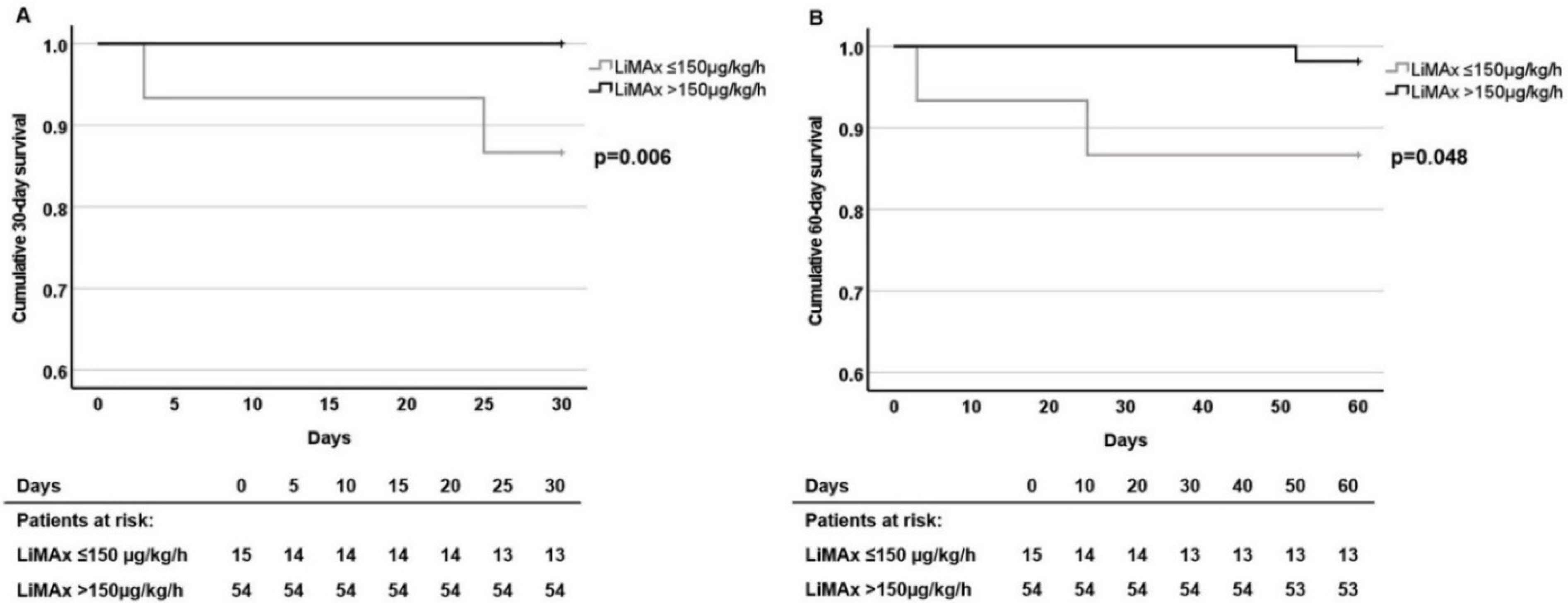
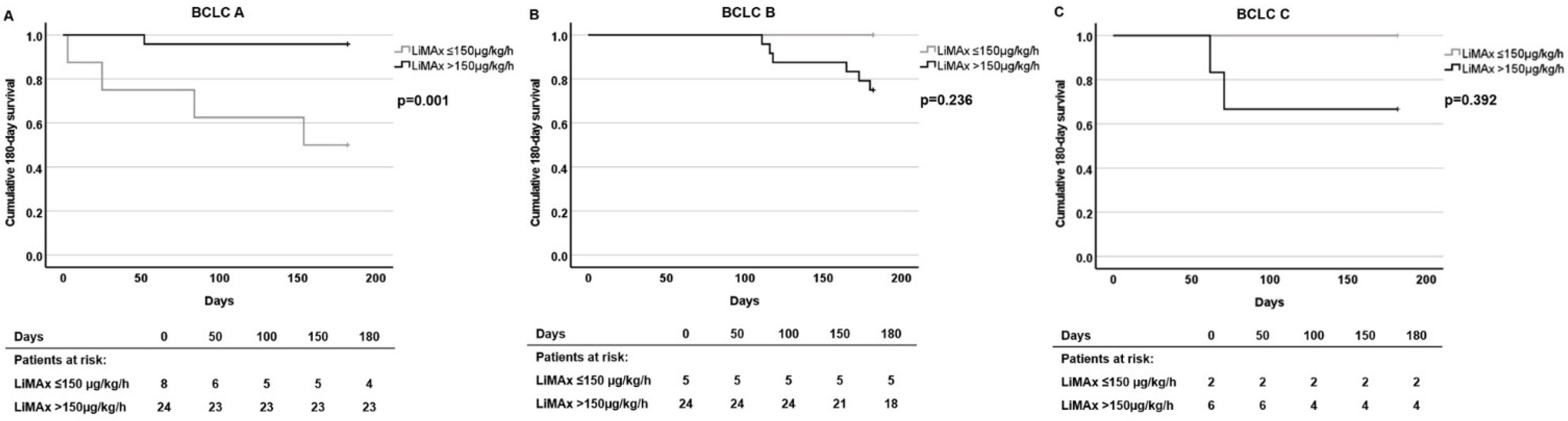
3.4. Association of LiMAx Results with Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global Cancer Statistics, 2002. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.-L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, İ.B. HCC Locoregional Therapies: Yttrium-90 (Y-90) Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT). J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2017, 48, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundram, F.X.; Buscombe, J.R. Selective internal radiation therapy for liver tumours. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, Y.J. Recent Updates of Transarterial Chemoembolilzation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnutzmann, D.; Kortes, N.; Sumkauskaite, M.; Schmitz, A.; Weiss, K.-H.; Radeleff, B. Transvascular therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), status and developments. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2018, 27, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.A.; Bajwa, R.; Madoff, D.C. Embolotherapeutic Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2020 Update. Cancers 2020, 12, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscaglia, F.; Ogasawara, S. Patient Selection for Transarterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Importance of Benefit/Risk Assessment. Liver Cancer 2018, 7, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L.; Hsieh, C.-F.; Chen, T.; Lin, T.-J.; Huang, T.-C.; Lee, H.-C.; Chen, K.-Y.; Liao, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-K. Risk factors for 1-year mortality in patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma treated solely with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Adv. Dig. Med. 2014, 1, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; de Baere, T.; Soulen, M.C.; Rilling, W.S.; Geschwind, J.-F.H. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology 2016, 64, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.; Mismas, V.; Marceglia, S.; Romano, A.; Giacomelli, L.; Bertini, M.; Federici, G.; Metrangolo, S.; Parisi, G.; Tumino, E.; et al. Transarterial radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: An update and perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6518–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaba, R.C.; Lokken, R.P.; Hickey, R.M.; Lipnik, A.J.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Salem, R.; Brown, D.B.; Walker, T.G.; Silberzweig, J.E.; Baerlocher, M.O.; et al. Quality Improvement Guidelines for Transarterial Chemoembolization and Embolization of Hepatic Malignancy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1210–1223.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtas, C.O.; D’Alessio, A.; Rimassa, L.; Sharma, R.; Pinato, D.J. ALBI grade: Evidence for an improved model for liver functional estimation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torimura, T.; Iwamoto, H. Optimizing the management of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Current trends and prospects. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Stoehr, F.; Mähringer-Kunz, A.; Hahn, F.; Weinmann, A.; Kloeckner, R. Current Strategies to Identify Patients That Will Benefit from TACE Treatment and Future Directions a Practical Step-by-Step Guide. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, Z. Establishment of a predictive model for short-term efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical application. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2019, 15, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohla, M.A.S.; Abu Zeid, M.I.; Al-Warraky, M.; Taha, H.; Gish, R.G. Predictors of hepatic decompensation after TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2015, 2, e000032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M. Updated treatment approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.; Weiner, A.A.; Nosher, J.; Lu, S.-E.; Foltz, G.M.; Hasan, O.; Kim, S.K.; Gendel, V.; Mani, N.B.; Carpizo, D.R.; et al. Assessment of the Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) Grade as a Prognostic Indicator for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Radioembolization. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.K.; Yim, S.Y.; Suh, S.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, Y.S.; Yim, H.J.; Yeon, J.E.; Byun, K.S.; Um, S.H. ALBI versus Child-Pugh grading systems for liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescure, C.; Estrade, F.; Pedrono, M.; Campillo-Gimenez, B.; Le Sourd, S.; Pracht, M.; Palard, X.; Bourien, H.; Muzellec, L.; Uguen, T.; et al. ALBI Score Is a Strong Predictor of Toxicity Following SIRT for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delicque, J.; Hermida, M.; Piron, L.; Allimant, C.; Belgour, A.; Pageaux, G.-P.; Bouallegue, F.B.; Assenat, E.; Mariano-Goulart, D.; Guiu, B.; et al. Intra-arterial treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of MELD score variations between radio-embolization and chemo-embolization. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechter, M.; Kersting, S.; Gerken, G.; Kahraman, A. Enzymatic liver function measured by LiMAx–a reliable diagnostic and prognostic tool in chronic liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara, M.; Dziodzio, T.; Malinowski, M.; Lüttgert, K.; Nikolov, R.; Ritschl, P.V.; Öllinger, R.; Pratschke, J.; Stockmann, M. Prospective Assessment of Liver Function by an Enzymatic Liver Function Test to Estimate Short-Term Survival in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, J.F.; Kotobi, A.N.; Malinowski, M.; Schulz, A.; Jara, M.; Neuhaus, P.; Stockmann, M. Predicting the prognosis in acute liver failure: Results from a retrospective pilot study using the LiMAx test. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, M.C.; Schulz, A.; Massmann, A.; Buecker, A.; Glanemann, M.; Lammert, F.; Malinowski, M. Predictive Power of Liver Maximum Function Capacity Test in Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Patients: A Pilot Study. Dig. Dis. 2020, 38, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaffarnik, M.F.; Lock, J.F.; Vetter, H.; Ahmadi, N.; Lojewski, C.; Malinowski, M.; Neuhaus, P.; Stockmann, M. Early diagnosis of sepsis-related hepatic dysfunction and its prognostic impact on survival: A prospective study with the LiMAx test. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, M.; Lock, J.F.; Malinowski, M.; Niehues, S.M.; Seehofer, D.; Neuhaus, P. The LiMAx test: A new liver function test for predicting postoperative outcome in liver surgery. HPB 2010, 12, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, M.; Lock, J.F.; Riecke, B.; Heyne, K.; Martus, P.; Fricke, M.; Lehmann, S.; Niehues, S.M.; Schwabe, M.; Lemke, A.-J.; et al. Prediction of Postoperative Outcome After Hepatectomy With a New Bedside Test for Maximal Liver Function Capacity. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, M.; Malinowski, M.; Lüttgert, K.; Schott, E.; Neuhaus, P.; Stockmann, M. Prognostic value of enzymatic liver function for the estimation of short-term survival of liver transplant candidates: A prospective study with the LiMAx test. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, M.C.; Massmann, A.; Schulz, A.; Buecker, A.; Glanemann, M.; Lammert, F.; Malinowski, M. Volume–Function Analysis (LiMAx Test) in Patients with HCC and Cirrhosis Undergoing TACE—A Feasibility Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzakova, E.S.; Schulze-Hagen, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Lurje, G.; Bednarsch, J.; Pedersoli, F.; Isfort, P.; Kuhl, C.; Bruners, P. Monitoring Liver Function of Patients Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) by a 13C Breath Test (LiMAx). CardioVasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senk, K.; Wilcke, J.; Haimerl, M.; Verloh, N.; Bartulos, C.R.; Bäumler, W.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Prediction of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) outcome by pre- and postinterventional 13C-methacetin breath test. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2021, 79, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jung, Y. Radiation-induced liver disease: Current understanding and future perspectives. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, M.; Bednarsch, J.; Valle, E.; Lock, J.F.; Malinowski, M.; Schulz, A.; Seehofer, D.; Jung, T.; Stockmann, M. Reliable assessment of liver function using LiMAx. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 193, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, C.G.; Turcotte, J.G. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl. Clin. Surg. 1964, 1, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, R.N.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, P.S.; Kim, W.R. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology 2007, 45, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thai, N.; Thinh, N.T.; Ky, T.D.; Bang, M.H.; Giang, D.T.; Le Ha, N.; Son, M.H.; Tien, D.D.; Lee, H.W. Efficacy and safety of selective internal radiation therapy with yttrium-90 for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, A.; Desai, K.; Hickey, R.; Thornburg, B.; Lewandowski, R.; Salem, R. Locoregional Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 19, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R. Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Oncol. 2012, 39, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.-H.; Bai, D.-S.; Jiang, G.-Q.; Jin, S.-J. Review of preoperative transarterial chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyvat, F. Interventional Radiologic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 15, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Overall (n = 69) | TACE (n = 57) | TARE (n = 12) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) † | 65 (48–85) | 65 (48–85) | 67 (56–80) | 0.715 |
| Sex (male) | 54 (78.3%) | 45 (78.9%) | 9 (75.0%) | 0.076 |
| BMI † | 29.0 (19.2–52.7) | 29.4 (19.2–52.7) | 28.5 (23.3–41.6) | 0.845 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 0.288 | |||
| None Child A Child B | 6 (8.7%) 47 (68.1%) 16 (23.2%) | 4 (7.0%) 38 (66.7%) 15 (26.3%) | 2 (16.7%) 9 (75%) 1 (8.3%) | |
| MELD score † | 8 (6–20) | 9 (6–20) | 8 (7–12) | 0.081 |
| ALBI score † | −2.54 (−3.40–0.97) | −2.51 (−3.40–0.97) | −2.81 (−3.38–1.72) | 0.182 |
| ALBI grade | 0.553 | |||
| 1 2 3 | 33 (48.5%) 33 (48.5%) 2 (2.9%) | 25 (43.9%) 29 (50.9%) 2 (3.5%) | 8 (66.7%) 4 (33.3%) 0 | |
| Etiology of liver cirrhosis | 0.805 | |||
| Alcoholic NAFLD Viral Cryptogenic Autoimmune | 38 (60.3%) 12 (19.0%) 3 (4.8%) 9 (14.3%) 1 (1.6%) | 30 (52.6%) 11 (19.3%) 3 (5.3%) 8 (14.0%) 1 (1.8%) | 8 (80.0%) 1 (10.0%) 1 (10.0%) 0 0 | |
| BCLC score | 0.204 | |||
| A B C | 32 (46.4%) 29 (42.0%) 8 (11.6%) | 29 (50.9%) 22 (38.6%) 6 (10.5%) | 3 (25.0%) 7 (58.3%) 2 (16.7%) | |
| Number of noduli | 0.270 | |||
| 1 2 3 >3 | 24 (34.8%) 17 (24.6%) 11 (15.9%) 17 (24.6%) | 17 (29.8%) 16 (28.1%) 10 (17.5%) 14 (24.6%) | 7 (58.3%) 1 (8.3%) 1 (8.3%) 3 (25.0%) | |
| Largest nodule diameter (mm) † | 57 (9–159) | 54 (12–159) | 76 (9–155) | 0.054 |
| Nodules in hepatic lobe | 0.671 | |||
| Right Left Both | 26 (37.7%) 9 (13.0%) 34 (49.3%) | 20 (35.1%) 8 (14.0%) 29 (50.9%) | 6 (50.0%) 1 (8.3%) 5 (41.7%) | |
| Repetitive TACE | 17 (24.6%) | 17 (24.6%) |
| Parameter | Before TACE/TARE (n = 37) | Week 4 after TACE/TARE (n = 37) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Range | Median | Range | p Value | |
| LiMAx (µg/kg/h) | 235 | 35–686 | 255 † | 53–604 | 0.397 |
| ALT (µkat/L) | 0.59 | 0.23–1.03 | 0.48 | 0.25–12.58 | 0.148 |
| AST (µkat/L) | 0.84 | 0.38–1.58 | 0.73 | 0.28–12.93 | 0.608 |
| GGT (µkat/L) | 2.66 | 0.42–10.53 | 2.23 | 0.58–7.45 | 0.837 |
| Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 18.9 | 4.8–87.8 | 16.6 | 4.9–70.8 | 0.709 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 133 | 51–265 | 127 | 40–240 | 0.778 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 40.2 | 28.5–48.0 | 38.3 | 21.7–48.3 | 0.193 |
| INR | 1.2 | 0.9–1.9 | 1.2 | 0.9–2.9 | 0.679 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 79 | 32–124 | 73 | 29–135 | 0.657 |
| ALBI score | −2.69 | −3.40–1.44 | −2.46 | −3.39–0.92 | 0.181 |
| CTP score | 5 | 5–7 | 5 | 5–7 | 0.680 |
| MELD score | 8 | 6–18 | 9 | 6–16 | 0.258 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, J.; Wellhöner, S.; Ebel, S.; Lincke, T.; Böhlig, A.; Gerhardt, F.; Veelken, R.; Goessmann, H.; Steinhoff, K.G.; Denecke, T.; et al. The Liver Maximum Capacity Test (LiMAx) Is Associated with Short-Term Survival in Patients with Early Stage HCC Undergoing Transarterial Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215323
Fischer J, Wellhöner S, Ebel S, Lincke T, Böhlig A, Gerhardt F, Veelken R, Goessmann H, Steinhoff KG, Denecke T, et al. The Liver Maximum Capacity Test (LiMAx) Is Associated with Short-Term Survival in Patients with Early Stage HCC Undergoing Transarterial Treatment. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215323
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, Janett, Stella Wellhöner, Sebastian Ebel, Thomas Lincke, Albrecht Böhlig, Florian Gerhardt, Rhea Veelken, Holger Goessmann, Karen Geva Steinhoff, Timm Denecke, and et al. 2022. "The Liver Maximum Capacity Test (LiMAx) Is Associated with Short-Term Survival in Patients with Early Stage HCC Undergoing Transarterial Treatment" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215323
APA StyleFischer, J., Wellhöner, S., Ebel, S., Lincke, T., Böhlig, A., Gerhardt, F., Veelken, R., Goessmann, H., Steinhoff, K. G., Denecke, T., Sabri, O., Berg, T., & Bömmel, F. v. (2022). The Liver Maximum Capacity Test (LiMAx) Is Associated with Short-Term Survival in Patients with Early Stage HCC Undergoing Transarterial Treatment. Cancers, 14(21), 5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215323