Association between Immunologic Markers and Cirrhosis in Individuals from a Prospective Chronic Hepatitis C Cohort
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Marker Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
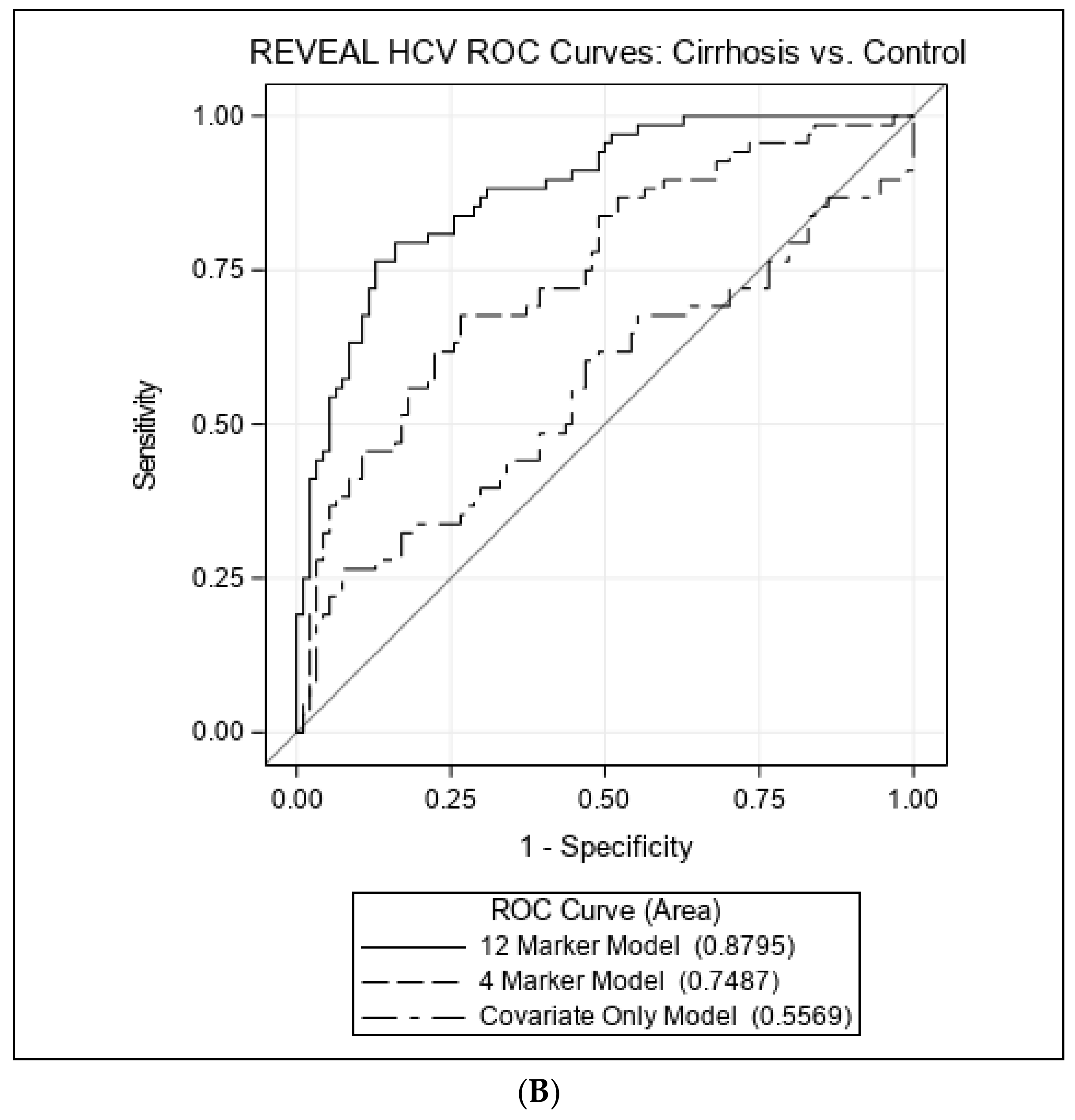
3.2. Associations with Cirrhosis vs. Controls
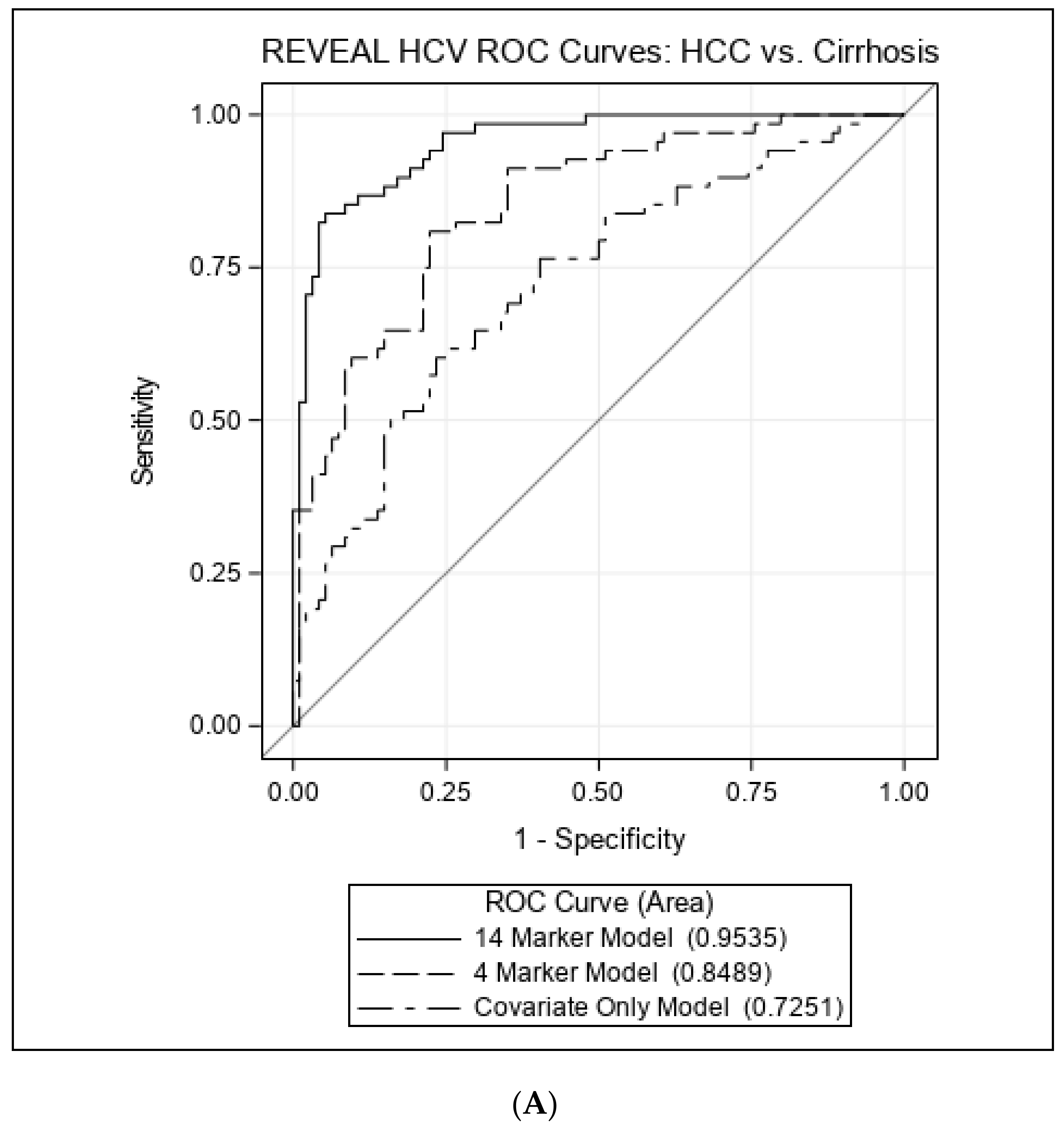
3.3. Associations with HCC vs. Cirrhosis
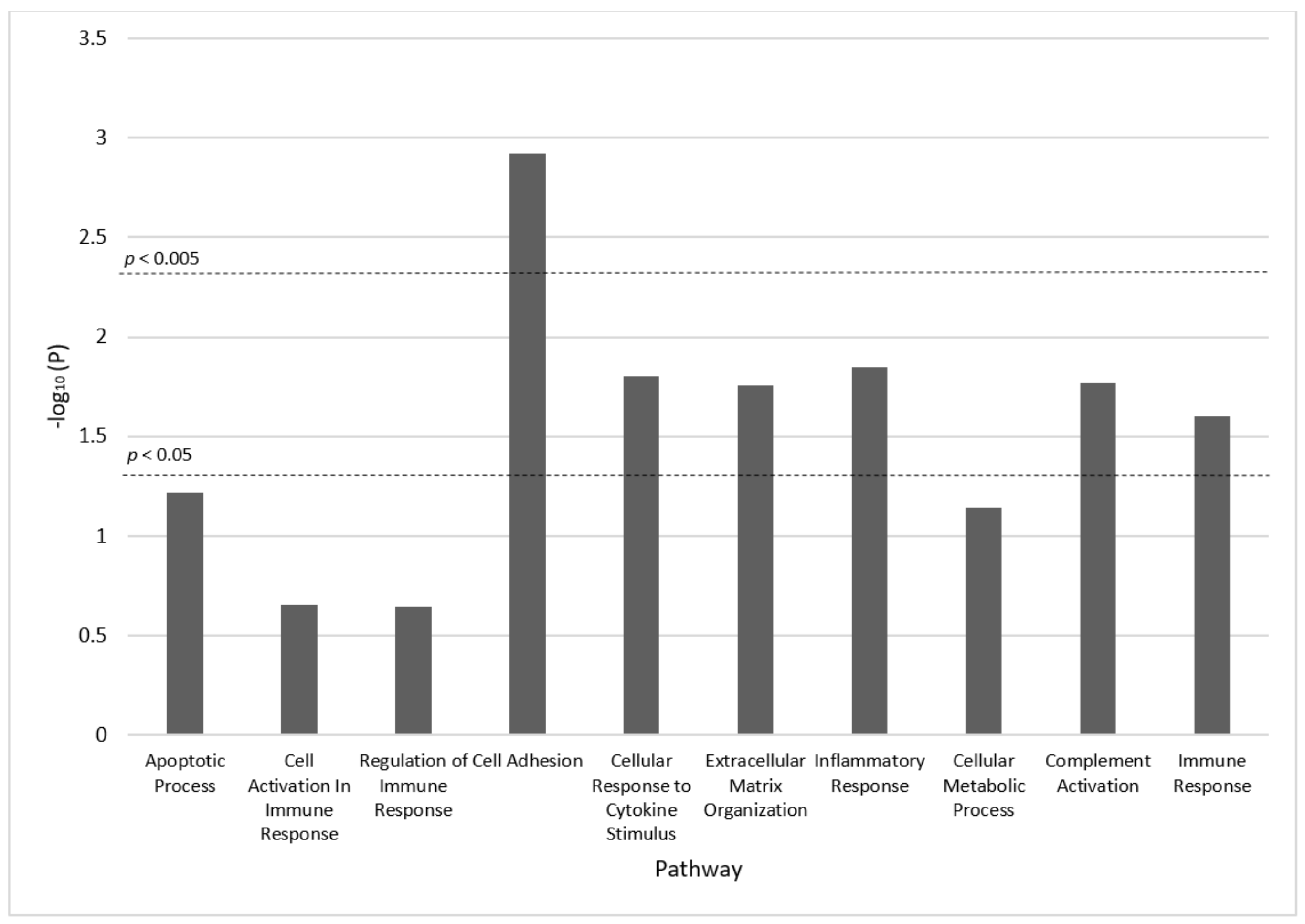
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.H.; Yang, H.I.; Yuan, Y.; L’Italien, G.; Chen, C.J. Epidemiology and natural history of hepatitis C virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9270–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, G.; Gkouvatsos, K.; Pantopoulos, K. Chronic hepatitis C and liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11033–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, A.; Chemello, L.; Benvegnu, L. Natural history of hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 1999, 31 (Suppl. S1), 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzakis, A. Global HCV Burden. In Hepatitis C: Epidemiology, Prevention and Elimination; Hatzakis, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Meredith, L.W.; Wilson, G.K.; Fletcher, N.F.; McKeating, J.A. Hepatitis C virus entry: Beyond receptors. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 22, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Baumert, T.; Blum, H.E. Hepatitis C virus infection and apoptosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 4865–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Fan, X.; Yan, J.; Luan, J. Progress in evaluating the status of hepatitis C infection based on the functional changes of hepatic stellate cells (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4116–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Yang, H.-I.; Lu, S.-N.; Jen, C.-L.; You, S.-L.; Wang, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, C.-J.; for the R.E.V.E.A.L.-HCV Study Group. Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection Increases Mortality from Hepatic and Extrahepatic Diseases: A Community-Based Long-Term Prospective Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiol, J.; Argirion, I.; Liu, Z.; Kim Lam, T.; O’Brien, T.R.; Yu, K.; McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; Pinto, L.; Chen, C.J.; et al. Immunologic markers and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus- and hepatitis C virus-infected individuals. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valva, P.; Casciato, P.; Lezama, C.; Galoppo, M.; Gadano, A.; Galdame, O.; Galoppo, M.C.; Mullen, E.; De Matteo, E.; Preciado, M.V. Serum apoptosis markers related to liver damage in chronic hepatitis C: sFas as a marker of advanced fibrosis in children and adults while M30 of severe steatosis only in children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshad, M.; Gupta, P.; Irshad, K. Immunopathogenesis of Liver Injury During Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Viral Immunol. 2019, 32, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartling, H.J.; Ballegaard, V.C.; Nielsen, N.S.; Gaardbo, J.C.; Nielsen, S.D. Immune regulation in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei-Hsuan, L.; Yang, H.-I.; Lu, S.-N.; Jen, C.-L.; Yeh, S.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Chen, P.-J.; You, S.-L.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chen, W.J.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Seromarkers and Subsequent Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Long-Term Predictors from a Community-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4587–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argirion, I.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Lam, T.K.; O’Brien, T.R.; Yu, K.; McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; Pinto, L.; Chen, C.J.; Lee, M.H.; et al. Association between immunologic markers and cirrhosis in individuals with chronic hepatitis B. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, A.M.; Simon, R.; Pfeiffer, R.M. Prediction error estimation: A comparison of resampling methods. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Li, Q.; Bergen, A.W.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Caporaso, N.; Kraft, P.; Chatterjee, N. Pathway analysis by adaptive combination of p-values. Genet. Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintermann, E.; Christen, U. The Many Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Hepatic Fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichal, T.; Mesnil, C.; Bureau, F. Homeostatic Eosinophils: Characteristics and Functions. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampinen, M.; Carlson, M.; Hakansson, L.D.; Venge, P. Cytokine-regulated accumulation of eosinophils in inflammatory disease. Allergy 2004, 59, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E.; Koyama, S.; Robbins, R.A. Bleomycin stimulates lung fibroblast and epithelial cell lines to release eosinophil chemotactic activity. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 16, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haley, K.J.; Lilly, C.M.; Yang, J.H.; Feng, Y.; Kennedy, S.P.; Turi, T.G.; Thompson, J.F.; Sukhova, G.H.; Libby, P.; Lee, R.T. Overexpression of eotaxin and the CCR3 receptor in human atherosclerosis: Using genomic technology to identify a potential novel pathway of vascular inflammation. Circulation 2000, 102, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. Review article: The eosinophil as a therapeutic target in gastrointestinal disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisset, L.R.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P. Chemokines and their receptors in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma: Progress and perspective. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2005, 11, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, B.; Purbeck, C.A.; Choi, Y.H.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Brenner, D. Replicative senescence of activated human hepatic stellate cells is accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory but less fibrogenic phenotype. Hepatology 2003, 37, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, A.; Weismuller, T.J.; Lankisch, T.O.; Santer, D.M.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Manns, M.P.; Houghton, M. Differential serum levels of eosinophilic eotaxins in primary sclerosing cholangitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and autoimmune hepatitis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownell, J.; Polyak, S.J. Molecular pathways: Hepatitis C virus, CXCL10, and the inflammatory road to liver cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berres, M.-L.; Trautwein, C.; Schmeding, M.; Eurich, D.; Tacke, F.; Bahra, M.; Neuhaus, P.; Neumann, U.P.; Wasmuth, H.E. Serum chemokine CXC ligand 10 (CXCL10) predicts fibrosis progression after liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection. Hepatology 2011, 53, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, Y.H.; Shetty, S.; Adams, D.H. The role of chemokines in the recruitment of lymphocytes to the liver. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, M.S.; Huang, Y.H.; Shieh, B.; Teng, R.H.; Yan, Y.P.; Lee, Y.T.; Liao, K.K.; Li, C. CC chemokines induce neutrophils to chemotaxis, degranulation, and alpha-defensin release. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 41, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, A.W.; Urbanowicz, R.A.; Ball, J.K. The role of humoral innate immunity in hepatitis C virus infection. Viruses 2012, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Chou, Y.-Y.; Chang, T.L. Defensins in viral infections. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, N.H.; Hung, K.; Haribhai, D.; Chu, H.; Karlsson-Sjöberg, J.; Amir, E.; Teggatz, P.; Barman, M.; Hayward, M.; Eastwood, D.; et al. Enteric defensins are essential regulators of intestinal microbial ecology. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehaume, L.M.; Hancock, R.E. Neutrophil-derived defensins as modulators of innate immune function. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceti, A.; Mangoni, M.L.; Pasquazzi, C.; Fiocco, D.; Marangi, M.; Miele, R.; Zechini, B.; Borro, M.; Versace, I.; Simmaco, M. α-Defensin increase in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with hepatitis C virus chronic infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2006, 13, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, E.H.; Almehdar, H.A.; AlJaddawi, A.A.; Abu Zeid, I.E.; Redwan, E.M. Elevated Concentration of Defensins in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 8373819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibusuki, R.; Uto, H.; Arima, S.; Mawatari, S.; Setoguchi, Y.; Iwashita, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Maeda, T.; Tanoue, S.; Kanmura, S.; et al. Transgenic expression of human neutrophil peptide-1 enhances hepatic fibrosis in mice fed a choline-deficient, L-amino acid-defined diet. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotman, M.E.; Chang, T.L. Defensins in innate antiviral immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavakis, T.; Cines, D.B.; Rhee, J.-S.; Liang, O.D.; Schubert, U.; Hammes, H.-P.; Higazi, A.A.-R.; Nawroth, P.P.; Preissner, K.T.; Bdeir, K. Regulation of neovascularization by human neutrophil peptides (α-defensins): A link between inflammation and angiogenesis. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, D.; Freire, J.M.; Pacheco, T.R.; Barata, J.T.; Castanho, M.A. Apoptotic human neutrophil peptide-1 anti-tumor activity revealed by cellular biomechanics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibusuki, R.; Uto, H.; Oda, K.; Ohshige, A.; Tabu, K.; Mawatari, S.; Kumagai, K.; Kanmura, S.; Tamai, T.; Moriuchi, A.; et al. Human neutrophil peptide-1 promotes alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis and hepatocyte apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.S.; Li, D.; Shi, H.S.; Wen, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Xu, N.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, X.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; et al. Intratumoral expression of mature human neutrophil peptide-1 mediates antitumor immunity in mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6901–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Wang, Y.S.; Pan, W.B.; Xiao, B.; Wen, Y.J.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, L.J.; Deng, H.X.; You, J.; Kan, B.; et al. Human alpha-defensin-1 inhibits growth of human lung adenocarcinoma xenograft in nude mice. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Hotchin, N.A. Signalling mechanisms of the leukocyte integrin αMβ2: Current and future perspectives. Biol. Cell 2012, 104, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovjov, D.A.; Pluskota, E.; Plow, E.F. Distinct roles for the alpha and beta subunits in the functions of integrin alphaMbeta2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxon, A.; Rieu, P.; Barkalow, F.J.; Askari, S.; Sharpe, A.H.; von Andrian, U.H.; Arnaout, M.A.; Mayadas, T.N. A Novel Role for the β2 Integrin CD11b/CD18 in Neutrophil Apoptosis: A Homeostatic Mechanism in Inflammation. Immunity 1996, 5, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.C.; Khan, S.Q.; Kaneda, M.M.; Pathria, P.; Shepard, R.; Louis, T.L.; Anand, S.; Woo, G.; Leem, C.; Faridi, M.H.; et al. Integrin CD11b activation drives anti-tumor innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margadant, C.; Sonnenberg, A. Integrin-TGF-beta crosstalk in fibrosis, cancer and wound healing. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiuk, A.; Zak, J.; Maciorkowska, E.; Panasiuk, B.; Prokopowicz, D. Expression of beta2-integrin on leukocytes in liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6193–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondou, H.; Mushiake, S.; Etani, Y.; Miyoshi, Y.; Michigami, T.; Ozono, K. A blocking peptide for transforming growth factor-beta1 activation prevents hepatic fibrosis in vivo. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, J.; Jenkins, G.; Tatler, A.L. Myofibroblast TGF-β Activation Measurement In Vitro. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2299, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Xu, A.; Xu, J. Roles of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: Signaling, Cancer, and Beyond. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1248, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Human hepatic stellate cells express CCR5 and RANTES to induce proliferation and migration. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G949–G958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Zsebo, K.M.; Geissler, E.N. The kit ligand, stem cell factor. Adv. Immunol. 1994, 55, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissler, E.N.; Liao, M.; Brook, J.D.; Martin, F.H.; Zsebo, K.M.; Housman, D.E.; Galli, S.J. Stem cell factor (SCF), a novel hematopoietic growth factor and ligand for c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor, maps on human chromosome 12 between 12q14.3 and 12qter. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 1991, 17, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hogaboam, C.; Carpenter, A.; Colletti, L. Stem cell factor restores hepatocyte proliferation in IL-6 knockout mice following 70% hepatectomy. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.; Hogaboam, C.M.; Kunkel, S.L.; Harrison, D.J.; Bone-Larson, C.; Lukacs, N.W. Stem cell factor attenuates liver damage in a murine model of acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrust, T.; Batusic, D.; Ringe, B.; Ramadori, G. Mast cells distribution in human liver disease and experimental rat liver fibrosis. Indications for mast cell participation in development of liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, L.; Da Silva, C.A.; Frossard, N. Stem cell factor and its receptor c-Kit as targets for inflammatory diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 533, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuroglu, T.; Ramadori, P.; Dudas, J.; Malik, I.; Hammerich, K.; Fuzesi, L.; Ramadori, G. Expression of stem cell factor and its receptor c-Kit during the development of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumoto, K.; Saito, T.; Onodera, M.; Sakamoto, A.; Tanaka, M.; Hattori, E.; Haga, H.; Ito, J.I.; Sugahara, K.; Saito, K.; et al. Serum levels of stem cell factor and thrombopoietin are markedly decreased in fulminant hepatic failure patients with a poor prognosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.H.; Kuo, F.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Hu, T.H.; Lu, S.N.; Wang, J.H.; Hung, C.H. Ultrasound is highly specific in diagnosing compensated cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C patients in real world clinical practice. Medicine 2019, 98, e16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.M.M.; Feldstein, V.A.; Parks, M.; Hudock, R.; Etheridge, D.; Peters, M.G. An Assessment of the Clinical Accuracy of Ultrasound in Diagnosing Cirrhosis in the Absence of Portal Hypertension. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 14, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Brochado-Kith, O.; Martinez, I.; Berenguer, J.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.; Salguero, S.; Sepulveda-Crespo, D.; Diez, C.; Hontanon, V.; Ibanez-Samaniego, L.; Perez-Latorre, L.; et al. HCV Cure with Direct-Acting Antivirals Improves Liver and Immunological Markers in HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 723196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Cirrhosis Cases | HCC Cases | Controls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total N | 68 | 94 | 91 a |
| % Male | 51.5% | 57.5% | 57.1% |
| Median Age at Sample Date (Range) | 54.0 (34–65) | 55.5 (34–65) | 56.0 (30–65) |
| Median Year of Serum Collection (Range) | 1991 (1991–1992) | 1993 (1992–1997) | 1993 (1992–1996) |
| Median Years of Follow-up (Range) * | 19.9 (7.5–20.9) | 15.3 (3.6–20.8) | 19.9 (2.1–20.8) |
| Median BMI (Range) | 24.4 (17.9–32.3) | 25.0 (18.4–37.6) | 23.3 (18.6–33.7) |
| ALT, N (%) | |||
| <15 | 19 (27.9) | 20 (21.3) | 31 (34.1) |
| 15–44 | 36 (52.9) | 40 (42.6) | 42 (46.2) |
| ≥45 | 13 (19.1) | 34 (36.2) | 18 (19.8) |
| Smoking | |||
| No | 51 (75.0) | 54 (57.5) | 64 (70.3) |
| Yes | 17 (25.0) | 40 (42.5) | 27 (29.7) |
| Alcohol drinking | |||
| No | 63 (92.7) | 85 (90.4) | 82 (90.1) |
| Yes | 5 (7.3) | 9 (9.6) | 9 (9.9) |
| Family history of HCC | |||
| No | 67 (98.5) | 93 (98.9) | 88 (96.7) |
| Yes | 1 (1.5) | 1 (1.1) | 3 (3.3) |
| Baseline RNA positivity † | |||
| No | 14 (20.6) | 8 (8.5) | 8 (8.8) |
| Yes | 51 (75.0) | 86 (91.5) | 83 (91.2) |
| Median HCV RNA level at sample date | 17,400 | 40,400 | 25,700 |
| Median time to event in years (Range) | 10.75 (0.37–19.02) | 13.3 (2.29–21.59) | - |
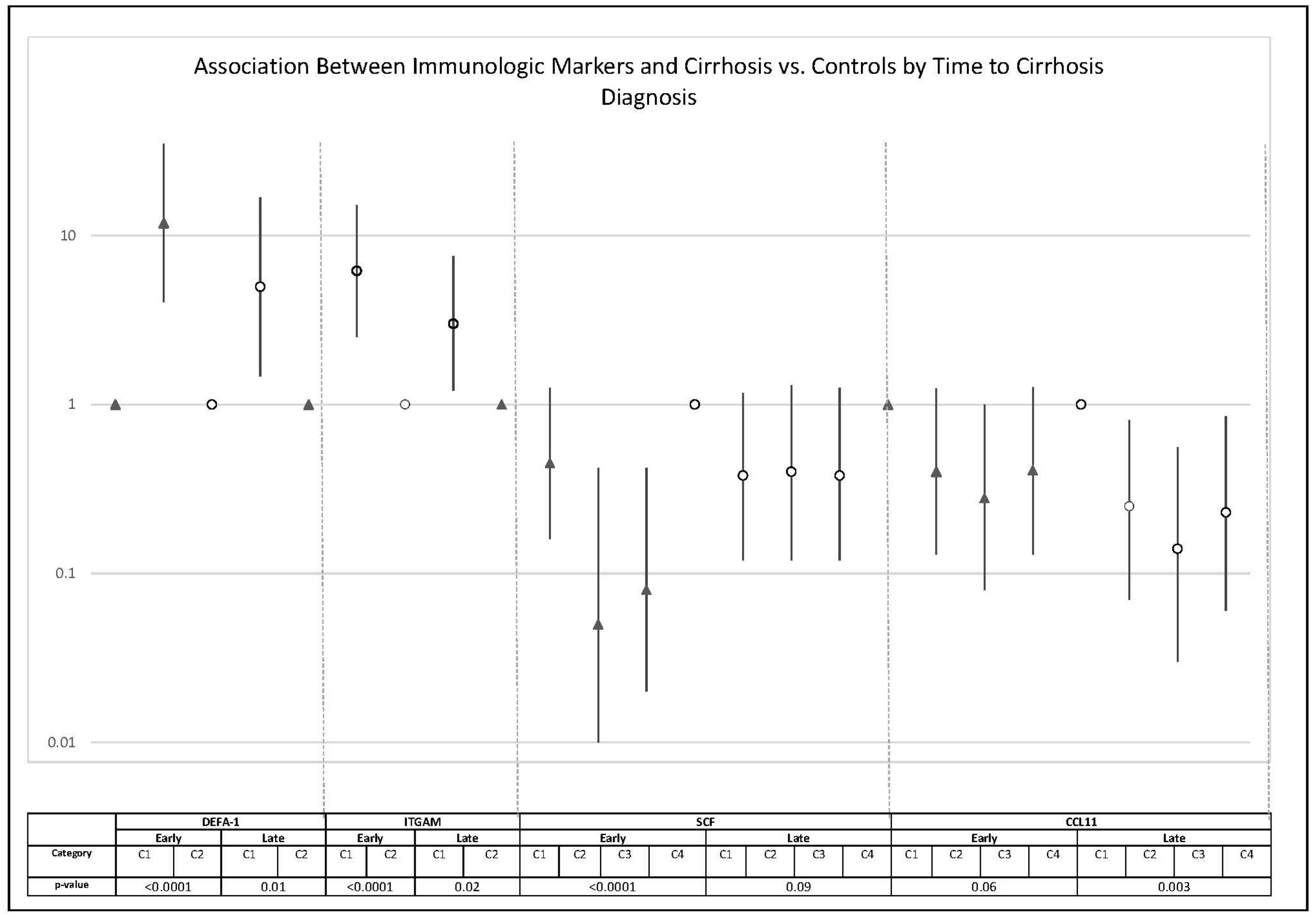
| Analyte | OR (95% CI) | p-Value ‡ | FDR-Corrected p-Value ‡ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 vs. C1 | C3 vs. C1 | C4 vs. C1 | |||
| Cirrhosis vs. Control | |||||
| DEFA-1 | 7.73 (2.96–20.17) | NA | NA | <0.0001 | 0.003 |
| ITGAM | 4.03 (1.94–8.36) | NA | NA | 0.0002 | 0.006 |
| SCF | 0.40 (0.17–0.94) | 0.19 (0.07–0.53) | 0.19 (0.07–0.53) | 0.0001 | 0.006 |
| CCL11 | 0.30 (0.12–0.75) | 0.20 (0.07–0.57) | 0.31 (0.12–0.80) | 0.002 | 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Argirion, I.; Brown, J.; Jackson, S.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Lam, T.K.; O’Brien, T.R.; Yu, K.J.; McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; Pinto, L.A.; et al. Association between Immunologic Markers and Cirrhosis in Individuals from a Prospective Chronic Hepatitis C Cohort. Cancers 2022, 14, 5280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215280
Argirion I, Brown J, Jackson S, Pfeiffer RM, Lam TK, O’Brien TR, Yu KJ, McGlynn KA, Petrick JL, Pinto LA, et al. Association between Immunologic Markers and Cirrhosis in Individuals from a Prospective Chronic Hepatitis C Cohort. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215280
Chicago/Turabian StyleArgirion, Ilona, Jalen Brown, Sarah Jackson, Ruth M. Pfeiffer, Tram Kim Lam, Thomas R. O’Brien, Kelly J. Yu, Katherine A. McGlynn, Jessica L. Petrick, Ligia A. Pinto, and et al. 2022. "Association between Immunologic Markers and Cirrhosis in Individuals from a Prospective Chronic Hepatitis C Cohort" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215280
APA StyleArgirion, I., Brown, J., Jackson, S., Pfeiffer, R. M., Lam, T. K., O’Brien, T. R., Yu, K. J., McGlynn, K. A., Petrick, J. L., Pinto, L. A., Chen, C.-J., Hildesheim, A., Yang, H.-I., Lee, M.-H., & Koshiol, J. (2022). Association between Immunologic Markers and Cirrhosis in Individuals from a Prospective Chronic Hepatitis C Cohort. Cancers, 14(21), 5280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215280








