Pediatric Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Malignancies: From Extramedullary to Medullary Involvement
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. B-Cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma
2.2. B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
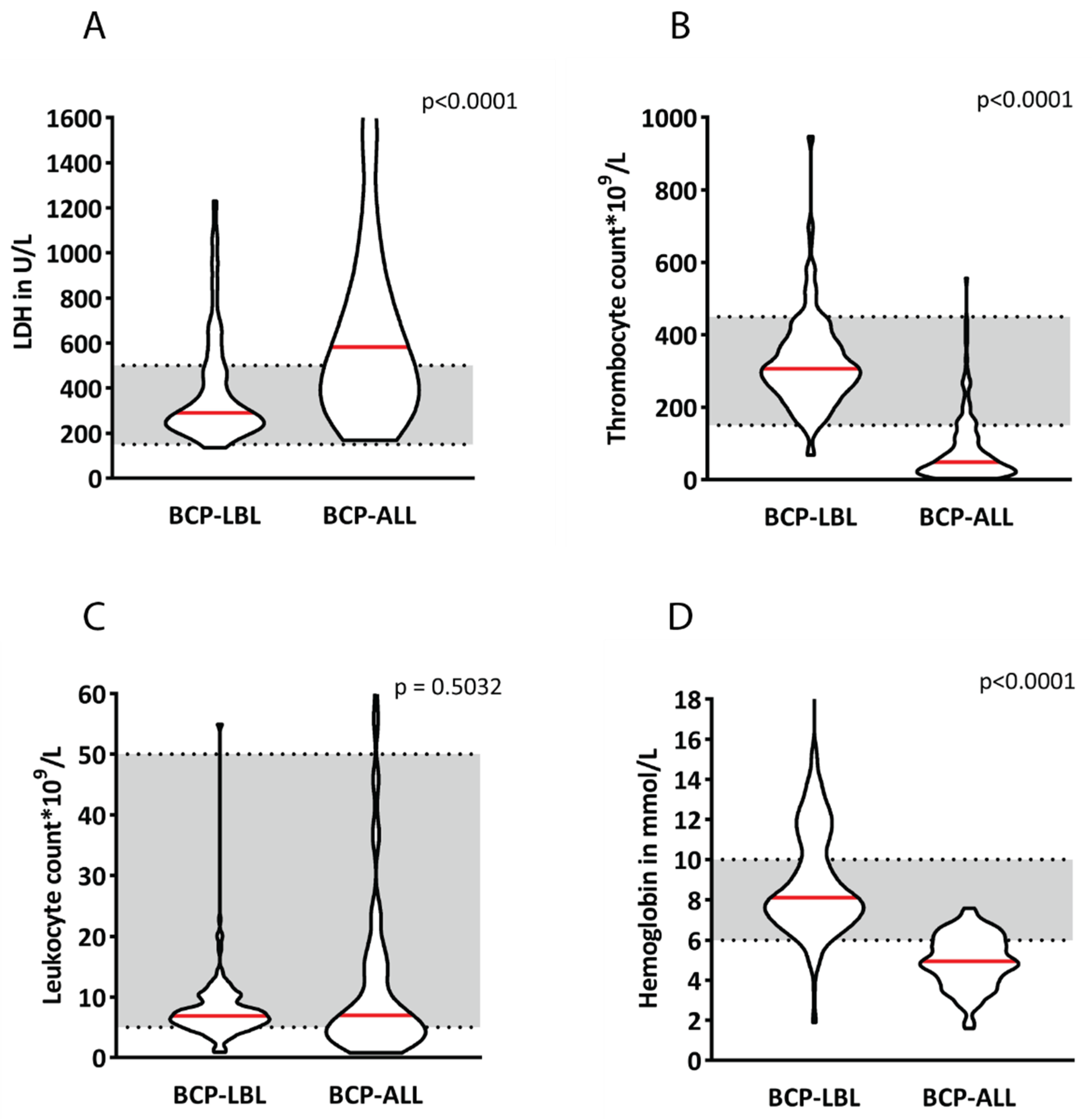
3.1. Patient Characteristics at Diagnosis
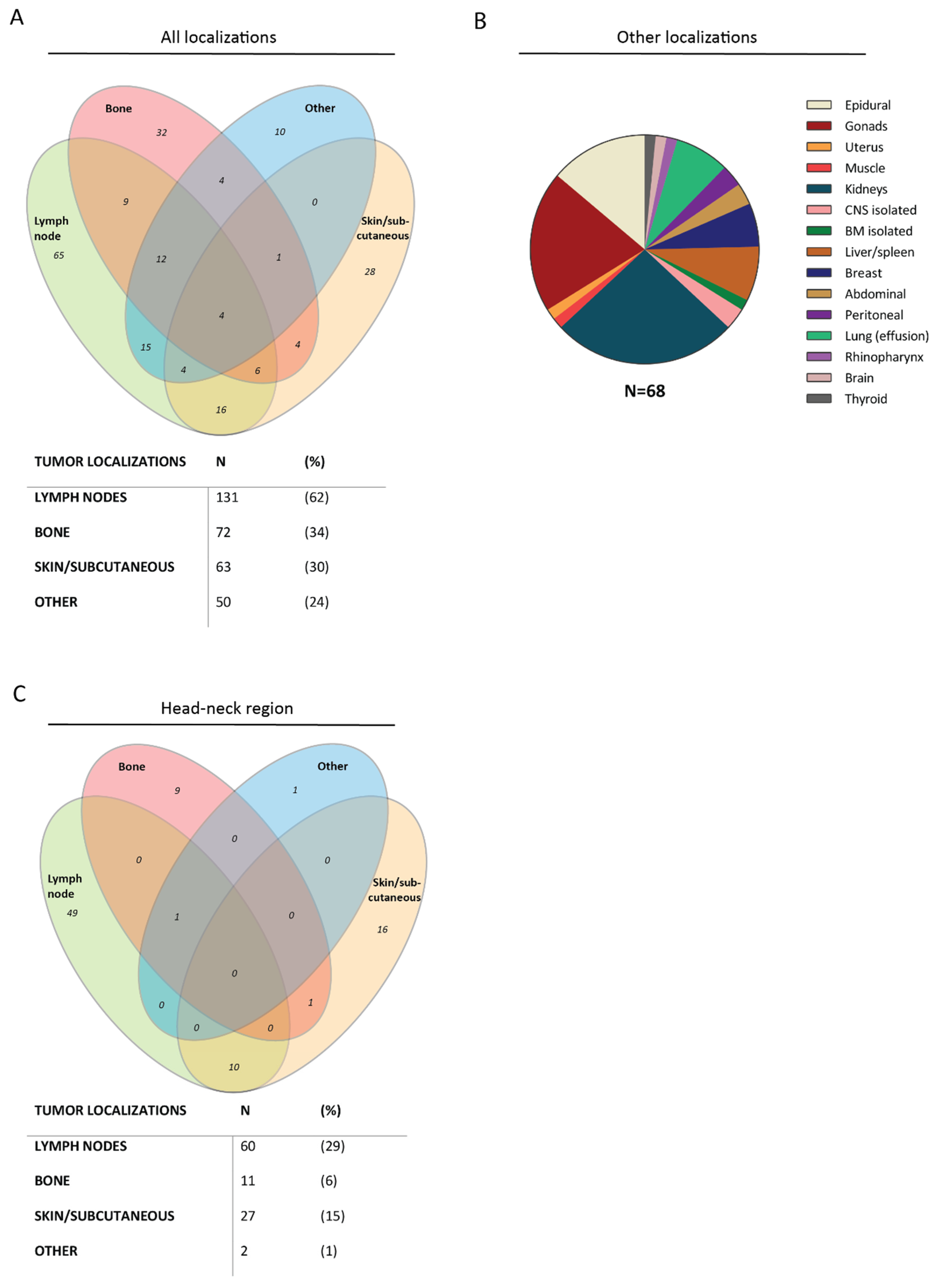
3.2. Localizations of B-Cell Malignancies
3.3. Cytogenetic Aberrations
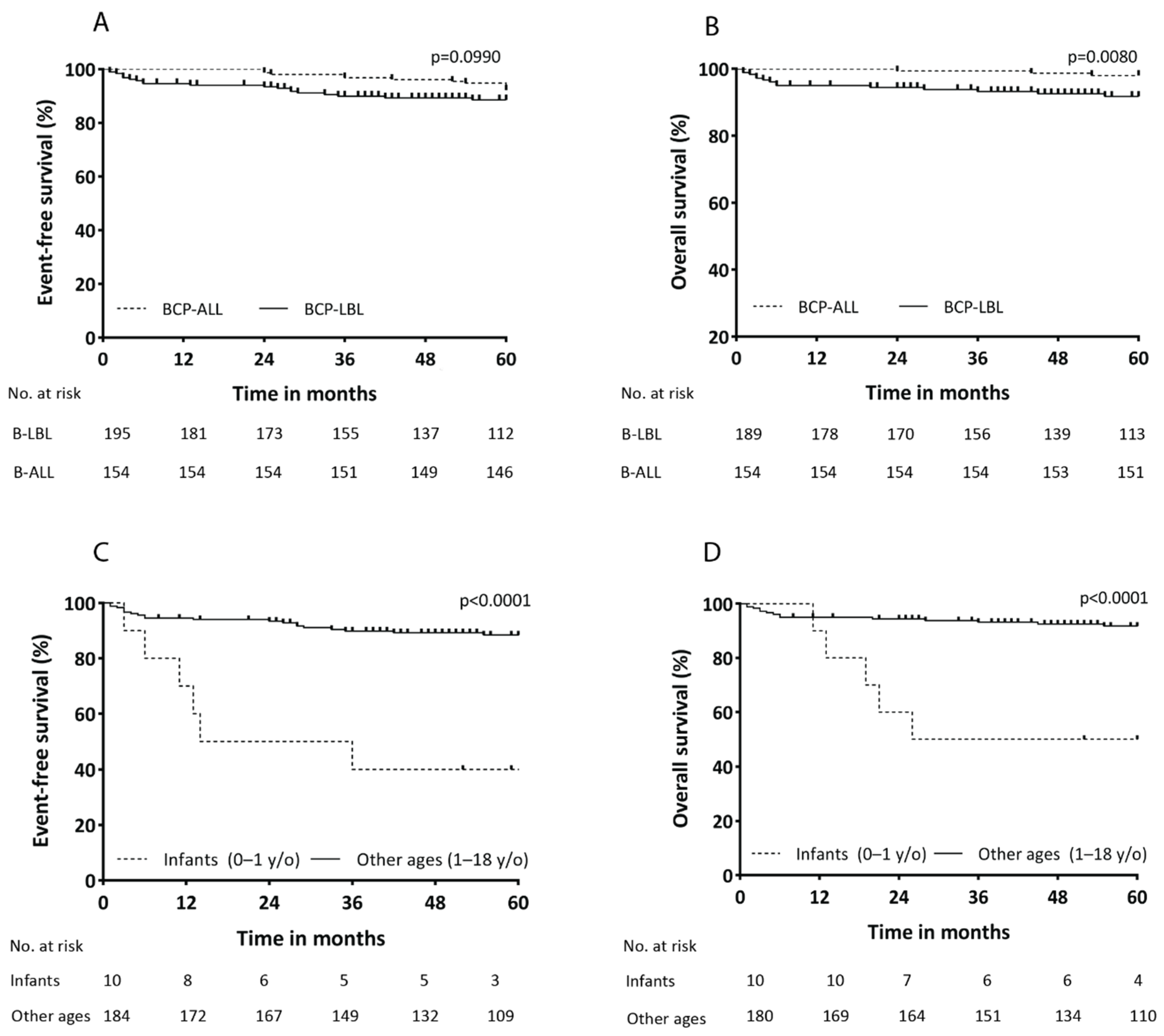
3.4. Differences in Overall Survival between BCP-LBL and BCP-ALL
3.5. Inferior Outcome for Infants with BCP-LBL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reedijk, A.M.J.; Coebergh, J.W.W.; De Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; Van der Sluis, I.M.; Kremer, L.C.; Karim-Kos, H.E.; Pieters, R. Progress against childhood and adolescent acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the Netherlands, 1990–2015. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horibe, K.; Saito, A.M.; Takimoto, T.; Tsuchida, M.; Manabe, A.; Shima, M.; Ohara, A.; Mizutani, S. Incidence and survival rates of hematological malignancies in Japanese children and adolescents (2006–2010): Based on registry data from the Japanese Society of Pediatric Hematology. Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 98, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Lee Harris, N.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Lyon, France; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Knez, V.; Bao, L.; Carstens, B.; Liang, X. Analysis of clinicopathological and cytogenetic differences between B-lymphoblastic lymphoma and B-lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood. Leuk Lymphoma 2020, 61, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Klairmont, M.M.; Holland, A.C.; Choi, J.K.; Mullighan, C.G.; Wang, L.; Sandlund, J.; Pui, C.H.; Inaba, H. Integrative genomic analysis of B-lymphoblastic lymphoma with intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 69, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraders, M.; Van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Kamping, E.J.; Van Krieken, J.H.; Van Kessel, A.G.; Groenen, P.J.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; Kuiper, R.P. High-resolution genomic profiling of pediatric lymphoblastic lymphomas reveals subtle differences with pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemias in the B-lineage. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2009, 191, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmann, E.; Burkhardt, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Meyer, U.; Woessmann, W.; Klapper, W.; Wrobel, G.; Rosolen, A.; Pillon, M.; Escherich, G.; et al. Results and conclusions of the European Intergroup EURO-LB02 trial in children and adolescents with lymphoblastic lymphoma. Haematologica 2017, 102, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaux, K.; Bergeron, C.; Gandemer, V.; Mechinaud, F.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Bertrand, Y.; SFCE and the EORTC children leukemia group. Relapsed or Refractory Lymphoblastic Lymphoma in Children: Results and Analysis of 23 Patients in the EORTC 58951 and the LMT96 Protocols. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, B.; Reiter, A.; Landmann, E.; Lang, P.; Lassay, L.; Dickerhoff, R.; Henzie, G.; Von Stackelberg, A. Poor outcome for children and adolescents with progressive disease or relapse of lymphoblastic lymphoma: A report from the berlin-frankfurt-muenster group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3363–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.B. Classification, staging and end results of treatment of childhood non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: Dissimilarities from lymphomas in adults. Semin. Oncol. 1980, 7, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pieters, R.; De Groot-Kruseman, H.; Van der Velden, V.; Fiocco, M.; Van den Berg, H.; De Bont, E.; Egeler, R.M.; Hoogerbrugge, P.; Kaspers, G.; Van der Schoot, E.; et al. Successful Therapy Reduction and Intensification for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Based on Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring: Study ALL10 From the Dutch Childhood Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2591–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moricke, A.; Reiter, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Gadner, H.; Stanulla, M.; Dordelmann, M.; Löning, L.; Beier, R.; Ludwig, W.D.; Ratei, R.; et al. Risk-adjusted therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia can decrease treatment burden and improve survival: Treatment results of 2169 unselected pediatric and adolescent patients enrolled in the trial ALL-BFM 95. Blood 2008, 111, 4477–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, A.; Goulden, N.; Wade, R.; Mitchell, C.; Hancock, J.; Hough, R.; Rowntree, C.; Richards, S. Treatment reduction for children and young adults with low-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia defined by minimal residual disease (UKALL 2003): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, W.; Pullen, J.; Boyett, J.; Falletta, J.; Van Eys, J.; Borowitz, M.; Jackson, J.; Dowell, B.; Frankel, L.; Quddus, F. Clinical and biologic features predict a poor prognosis in acute lymphoid leukemias in infants: A Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Blood 1986, 67, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaman, G.; Zeltzer, P.; Bleyer, W.A.; Amendola, B.; Level, C.; Sather, H.; Hammond, D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in infants less than one year of age: A cumulative experience of the Children’s Cancer Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1985, 3, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieters, R.; De Lorenzo, P.; Ancliffe, P.; Aversa, L.A.; Brethon, B.; Biondi, A.; Campbell, M.; Escherich, G.; Ferster, A.; Gardner, R.A.; et al. Outcome of infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with the Interfant-06 protocol; results from an international randomised study. Blood 2018, 132, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.; De Lorenzo, P.; Ancliffe, P.; Aversa, L.A.; Brethon, B.; Biondi, A.; Campbell, M.; Escherich, G.; Ferster, A.; Gardner, R.A.; et al. Outcome of Infants Younger Than 1 Year With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated With the Interfant-06 Protocol: Results From an International Phase III Randomized Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2246–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Greaves, M.; Mullighan, C.G. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2013, 381, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odero, M.D. t(6;12)(p21;p13) in lymphoid malignancies. Atlas Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol. 2007, 11, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Conter, V.; Bartram, C.R.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Schrauder, A.; Panzer-Grumayer, R.; Moricke, A.; Aricò, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Mann, G.; De Rossi, G.; et al. Molecular response to treatment redefines all prognostic factors in children and adolescents with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results in 3184 patients of the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 study. Blood 2010, 115, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Feature | BCP-LBL 210 (100%) | BCP-ALL 154 (100%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.4440 | ||
| Males | 120 (57) | 80 (52) | |
| Females | 90 (43) | 74 (48) | |
| Age in years (cat) | <0.0001 | ||
| 0–1 | 10 (5) | - | |
| 1–7 | 95 (45) | 109 (71) | 0.0070 |
| 7–12 | 61 (29) | 21 (14) | 0.0180 |
| 12–18 | 38 (18) | 23 (15) | 0.8770 |
| Unknown | 6 (3) | 0 (0) | |
| Murphy stage | |||
| I | 19 (9) | - | - |
| II | 41 (19) | - | - |
| III | 75 (36) | - | - |
| IV | 69 (33) | - | - |
| Unknown | 6 (3) | - | - |
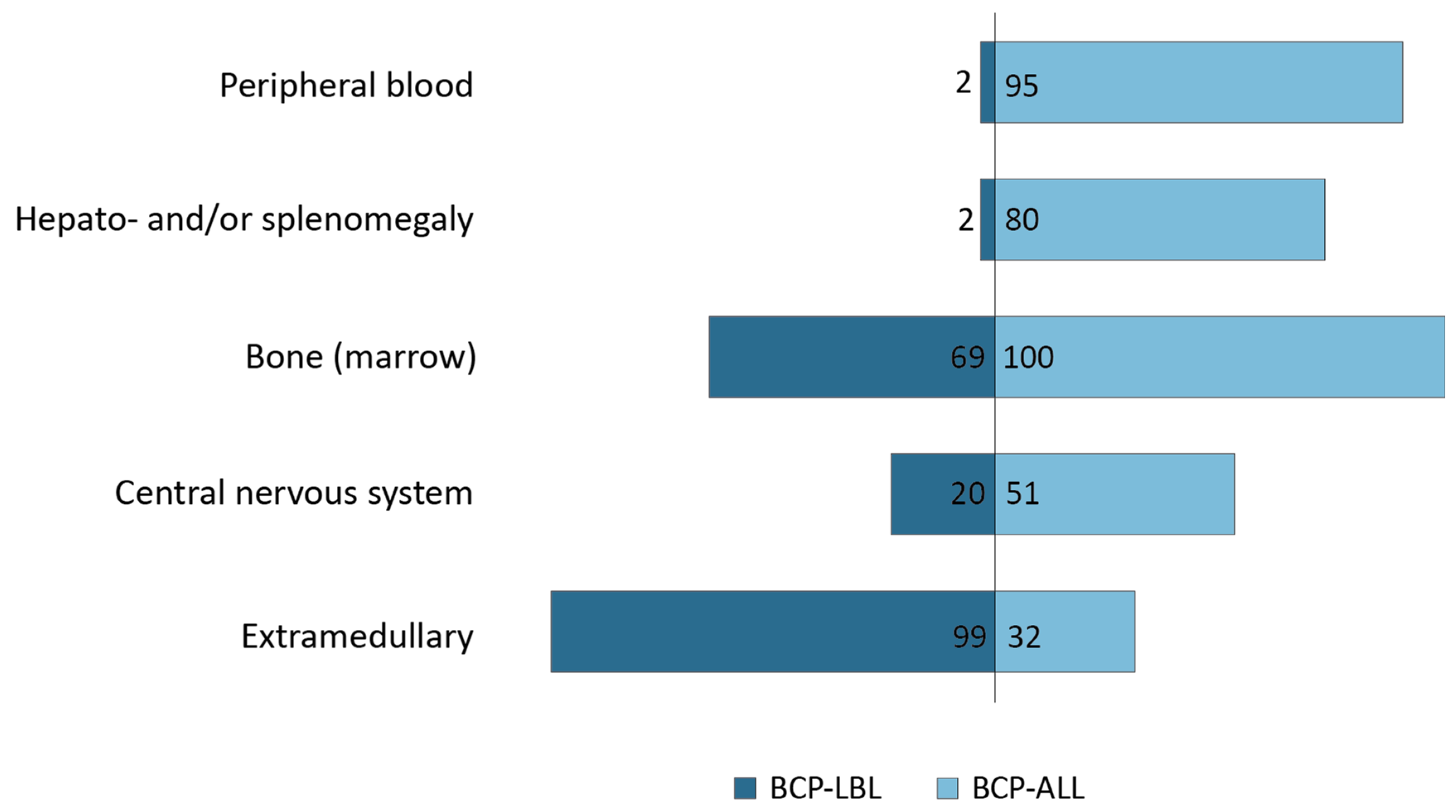
| Bone Marrow | Peripheral Blood | Hepato-and/or Splenomegaly | Central Nervous System | Extramedullary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-ALL | 100% | 95% | 80% | 51% | 32% |
| B-LBL | 26% | 2% | 2% | 20% | 99% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kroeze, E.; Arias Padilla, L.; Bakker, M.; Boer, J.M.; Hagleitner, M.M.; Burkhardt, B.; Mori, T.; Attarbaschi, A.; Verdú-Amorós, J.; Pillon, M.; et al. Pediatric Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Malignancies: From Extramedullary to Medullary Involvement. Cancers 2022, 14, 3895. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163895
Kroeze E, Arias Padilla L, Bakker M, Boer JM, Hagleitner MM, Burkhardt B, Mori T, Attarbaschi A, Verdú-Amorós J, Pillon M, et al. Pediatric Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Malignancies: From Extramedullary to Medullary Involvement. Cancers. 2022; 14(16):3895. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163895
Chicago/Turabian StyleKroeze, Emma, Laura Arias Padilla, Max Bakker, Judith M. Boer, Melanie M. Hagleitner, Birgit Burkhardt, Takeshi Mori, Andishe Attarbaschi, Jaime Verdú-Amorós, Marta Pillon, and et al. 2022. "Pediatric Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Malignancies: From Extramedullary to Medullary Involvement" Cancers 14, no. 16: 3895. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163895
APA StyleKroeze, E., Arias Padilla, L., Bakker, M., Boer, J. M., Hagleitner, M. M., Burkhardt, B., Mori, T., Attarbaschi, A., Verdú-Amorós, J., Pillon, M., Anderzhanova, L., Kabíčková, E., Chiang, A. K. S., Kebudi, R., Mellgren, K., Lazic, J., Jazbec, J., Meijerink, J. P. P., Beishuizen, A., & Loeffen, J. L. C., on behalf of the European Intergroup for Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (EICNHL) and the International Berlin–Frankfurt–Münster (i-BFM) Study. (2022). Pediatric Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Malignancies: From Extramedullary to Medullary Involvement. Cancers, 14(16), 3895. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163895







