Discovery and Validation of Clinically Relevant Long Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
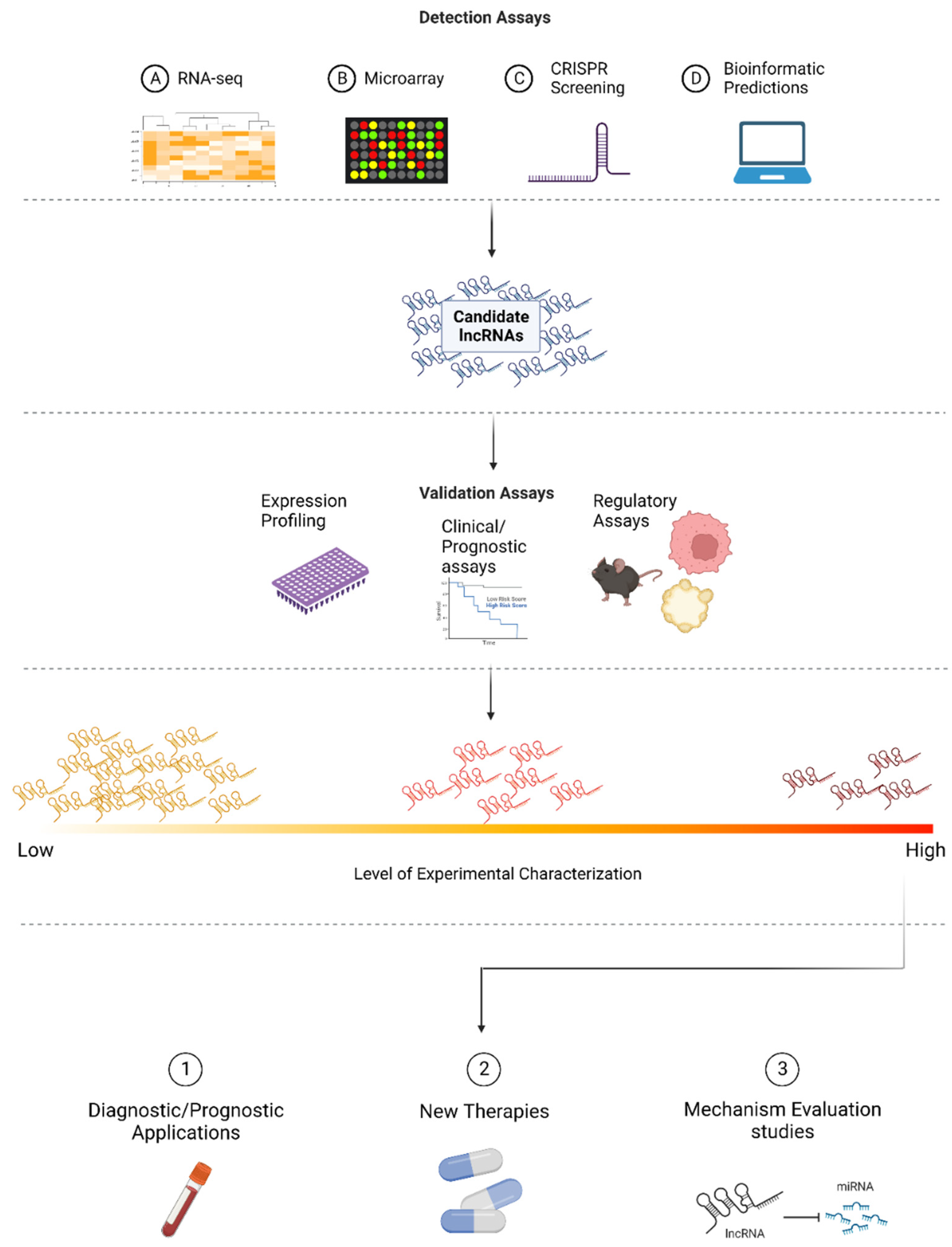
2. Approaches to Identify Relevant lncRNAs in CRC
2.1. RNA Sequencing
2.2. Microarrays
2.3. CRISPR-Cas9 Screening
2.4. Bioinformatic Approaches
3. Experimental Validation of Candidate lncRNAs
3.1. Expression Profiling
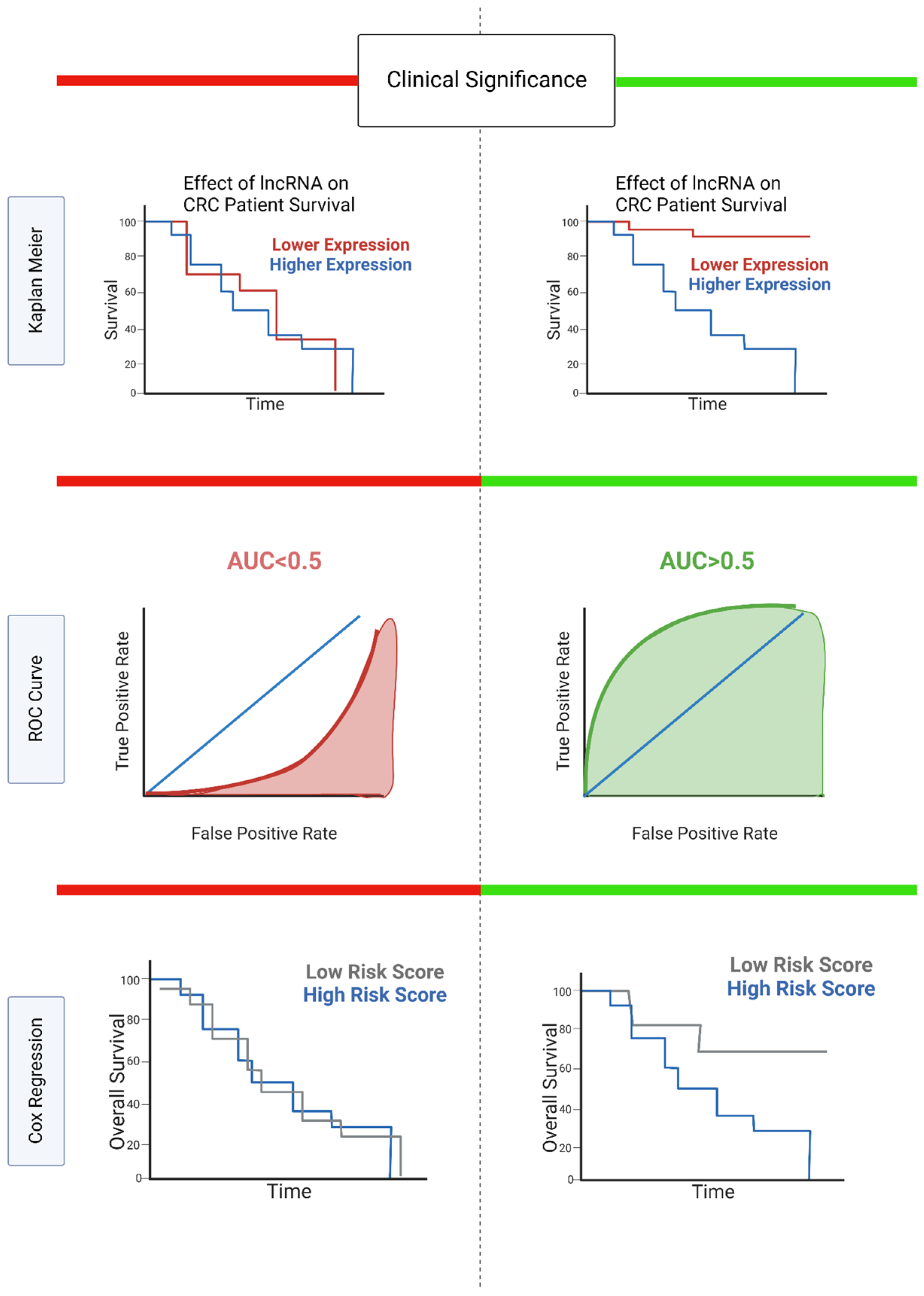
3.2. Clinical Significance
3.3. Regulatory Significance
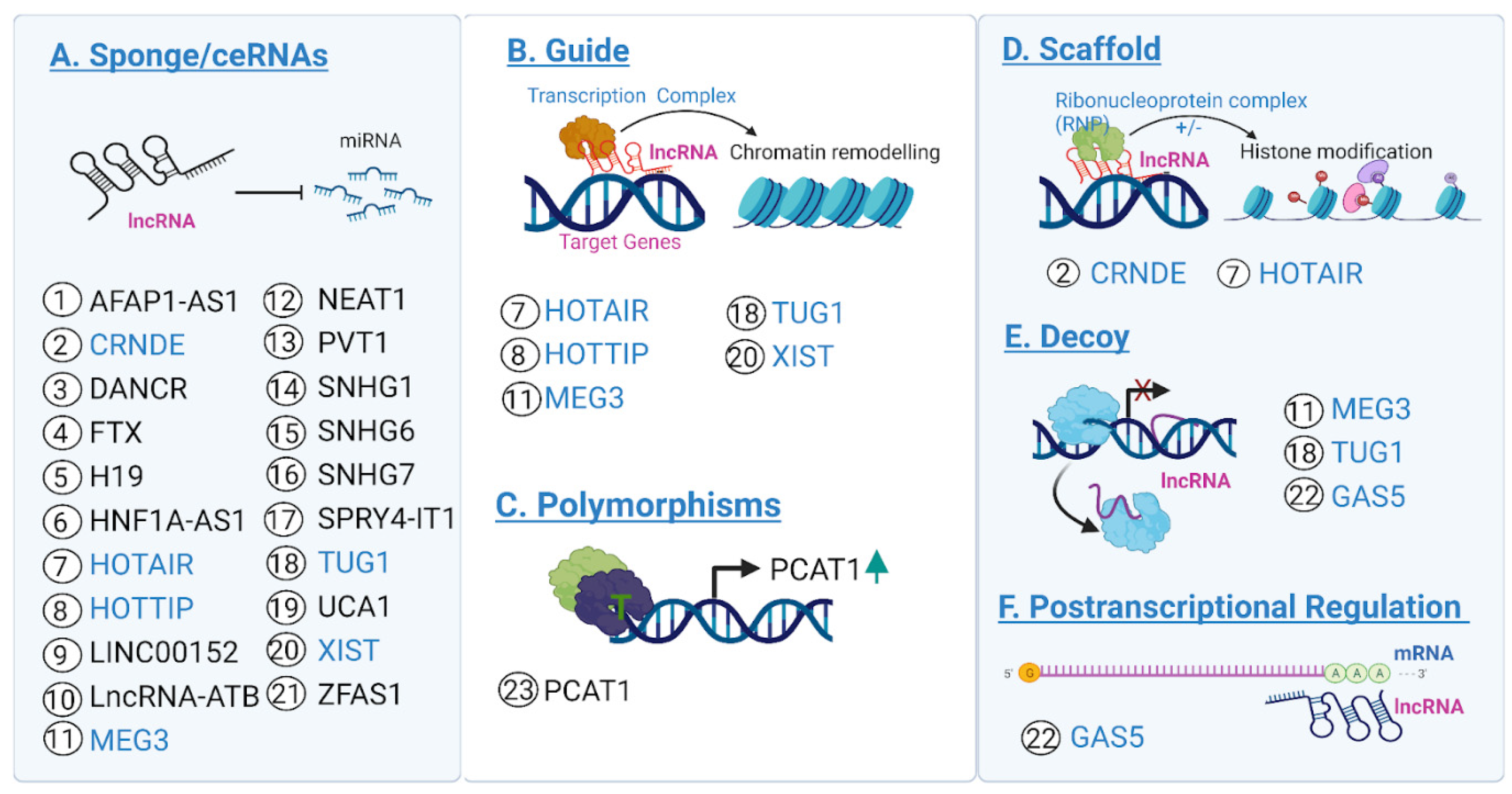
4. Validated lncRNA Candidates in CRC
4.1. LINC01296
4.2. HOTAIR
4.3. Other Promising Candidates
5. Current Use of lncRNAs in Clinical Practice
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jass, J.R. Colorectal Cancer: A Multipathway Disease. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2006, 12, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 9783319406176. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, G.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Russo, A.-G.; Marsoni, S.; Bardelli, A.; Siena, S. Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer in Young Individuals. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fang, Y.; Sun, L.; He, R.; He, B.; Zhang, S. Long Non-Coding RNA: A Potential Strategy for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 762752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.N.; Ingham, S.; Hodson, J.; Lalloo, F.; Bulman, M.; Howell, A.; Evans, D.G. Risk of Contralateral Breast Cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers: A 30-Year Semi-Prospective Analysis. Fam. Cancer 2015, 14, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.; Martinez, P.; Wade, R.; Hockley, S.; Oscier, D.; Matutes, E.; Dearden, C.E.; Richards, S.M.; Catovsky, D.; Morgan, G.J. Mutational Status of the TP53 Gene as a Predictor of Response and Survival in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results from the LRF CLL4 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.E.; Tal-Singer, R.; Rennard, S.I.; Furtwaengler, A.; Leidy, N.; Lowings, M.; Martin, U.J.; Martin, T.R.; Merrill, D.D.; Snyder, J.; et al. Plasma Fibrinogen Qualification as a Drug Development Tool in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Perspective of the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Biomarker Qualification Consortium. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordetsky, J.; Epstein, J. Grading of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma: Current State and Prognostic Implications. Diagn. Pathol. 2016, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groskopf, J.; Aubin, S.M.J.; Deras, I.L.; Blase, A.; Bodrug, S.; Clark, C.; Brentano, S.; Mathis, J.; Pham, J.; Meyer, T.; et al. APTIMA PCA3 Molecular Urine Test: Development of a Method to Aid in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Shi, L.; Luo, Z. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 612393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-H.; Deng, J.-L.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Y.-S. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Prostate Cancer: Functional Roles and Clinical Implications. Cancer Lett. 2019, 464, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 Catalog of Human Long Noncoding RNAs: Analysis of Their Gene Structure, Evolution, and Expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin Signature Reveals over a Thousand Highly Conserved Large Non-Coding RNAs in Mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene Regulation by Long Non-Coding RNAs and Its Biological Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursheikhani, A.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Kerachian, M.A. Mechanisms of Long Non-Coding RNA Function in Colorectal Cancer Tumorigenesis. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, A.; Sayin, V.I.; Van den Eynden, J.; Singh, S.X.; Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Larsson, E. Pan-Cancer Transcriptomic Analysis Associates Long Non-Coding RNAs with Key Mutational Driver Events. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Cen, B.; Ji, A. Regulation of lncRNA Expression. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2014, 19, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Ci, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. The Landscape of DNA Methylation-Mediated Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 51134–51150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, P.; Wu, L.; Guan, W. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of DNA Methylation and Long Non-Coding RNA Expression in Gastric Cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James de Bony, E.; Bizet, M.; Van Grembergen, O.; Hassabi, B.; Calonne, E.; Putmans, P.; Bontempi, G.; Fuks, F. Comprehensive Identification of Long Noncoding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27605–27629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Saus, E.; Brunet-Vega, A.; Iraola-Guzmán, S.; Pegueroles, C.; Gabaldón, T.; Pericay, C. Long Non-Coding RNAs As Potential Novel Prognostic Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatandoost, N.; Ghanbari, J.; Mojaver, M.; Avan, A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Salehi, R. Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer: From Conventional Methods to Novel Biomarkers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kılıç, Ö.; Gültekin, Y.; Biri, İ.; Yılmaz, A.U. The Prognostic Factors on Survival Rates for Patients with Stage II-III Colon Cancer. Turk. J. Colorectal Dis. 2021, 32, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.K.; Covarrubias, S.; Carpenter, S. The How and Why of lncRNA Function: An Innate Immune Perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kikyo, N. Strategies to Identify Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in Gene Regulation. Cell Biosci. 2012, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlion, A.; Everaert, C.; Nuytens, J.; Hulstaert, E.; Vandesompele, J.; Mestdagh, P. Custom Long Non-Coding RNA Capture Enhances Detection Sensitivity in Different Human Sample Types. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraola-Guzmán, S.; Brunet-Vega, A.; Pegueroles, C.; Saus, E.; Hovhannisyan, H.; Casalots, A.; Pericay, C.; Gabaldón, T. Target Enrichment Enables the Discovery of lncRNAs with Somatic Mutations or Altered Expression in Paraffin-Embedded Colorectal Cancer Samples. Cancers 2020, 12, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Łabaj, P.P.; Zumbo, P.; Sykacek, P.; Shi, W.; Shi, L.; Phan, J.; Wu, P.-Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; et al. Detecting and Correcting Systematic Variation in Large-Scale RNA Sequencing Data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneau, J.; Dumontier, S.; Gosselin, R.; Scott, M.S. Current RNA-Seq Methodology Reporting Limits Reproducibility. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szcześniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Survey of Best Practices for RNA-Seq Data Analysis. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X. Statistical Detection of Differentially Expressed Genes Based on RNA-Seq: From Biological to Phylogenetic Replicates. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 17, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toolabi, N.; Daliri, F.S.; Mokhlesi, A.; Talkhabi, M. Identification of Key Regulators Associated with Colon Cancer Prognosis and Pathogenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 16, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, D.; Mu, L.; Zhao, X.; Guo, M.; Xu, A.; Fang, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Microarray Profiling and Co-Expression Network Analysis of lncRNAs and mRNAs in Ovarian Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brittain, W.J.; Brandsetter, T.; Prucker, O.; Rühe, J. The Surface Science of Microarray Generation-A Critical Inventory. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39397–39409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarillo, C.; Swerdel, M.; Hart, R.P. Comparison of Microarray and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Methods for Measuring MicroRNA Levels in MSC Cultures. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 698, 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, F.; Tsuchiya, S.; Terasawa, K.; Tsujimoto, G. Intra-Platform Repeatability and Inter-Platform Comparability of microRNA Microarray Technology. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Barbacioru, C.; Hyland, F.; Xiao, W.; Hunkapiller, K.L.; Blake, J.; Chan, F.; Gonzalez, C.; Zhang, L.; Samaha, R.R. Large Scale Real-Time PCR Validation on Gene Expression Measurements from Two Commercial Long-Oligonucleotide Microarrays. BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, R.; Bosch, N.; Lanzós, A.; Polidori, T.; Pulido-Quetglas, C.; Johnson, R. Hacking the Cancer Genome: Profiling Therapeutically Actionable Long Non-Coding RNAs Using CRISPR-Cas9 Screening. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Quetglas, C.; Johnson, R. Designing Libraries for Pooled CRISPR Functional Screens of Long Noncoding RNAs. Mamm. Genome 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Cho, S.W.; Birk, H.S.; Malatesta, M.; He, D.; Attenello, F.J.; Villalta, J.E.; Cho, M.Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. CRISPRi-Based Genome-Scale Identification of Functional Long Noncoding RNA Loci in Human Cells. Science 2017, 355, aah7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xu, H.; Xiao, T.; Cong, L.; Love, M.I.; Zhang, F.; Irizarry, R.A.; Liu, J.S.; Brown, M.; Liu, X.S. MAGeCK Enables Robust Identification of Essential Genes from Genome-Scale CRISPR/Cas9 Knockout Screens. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Prat, E.; Arnan, C.; Sala, I.; Bosch, N.; Guigó, R.; Johnson, R. DECKO: Single-Oligo, Dual-CRISPR Deletion of Genomic Elements Including Long Non-Coding RNAs. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, G.; Ziyu, X.; Yiting, L.; Zonghang, L.; Lifeng, Z. Construction of Competing Endogenous RNA Network and Identification of Novel Molecular Biomarkers in Colon Cancer: A Bioinformatic Analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e25369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Chai, H.; Zhao, H. Detecting lncRNA-Cancer Associations by Combining miRNAs, Genes, and Prognosis With Matrix Factorization. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 639872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mularoni, L.; Sabarinathan, R.; Deu-Pons, J.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; López-Bigas, N. OncodriveFML: A General Framework to Identify Coding and Non-Coding Regions with Cancer Driver Mutations. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzós, A.; Carlevaro-Fita, J.; Mularoni, L.; Reverter, F.; Palumbo, E.; Guigó, R.; Johnson, R. Discovery of Cancer Driver Long Noncoding RNAs across 1112 Tumour Genomes: New Candidates and Distinguishing Features. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, L.; Chiu, H.-S.; Avila Cobos, F.; Gross, S.; Volders, P.-J.; Cannoodt, R.; Nuytens, J.; Vanderheyden, K.; Anckaert, J.; Lefever, S.; et al. Publisher Correction: The RNA Atlas Expands the Catalog of Human Non-Coding RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeevan, M.S.; Ranamukhaarachchi, D.G.; Vernon, S.D.; Unger, E.R. Use of Real-Time Quantitative PCR to Validate the Results of cDNA Array and Differential Display PCR Technologies. Methods 2001, 25, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickells, R.W.; Pelzel, H.R. Tools and Resources for Analyzing Gene Expression Changes in Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 141, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR--a Perspective. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 34, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, F.; Guertler, R.; Naim, S.; Nixdorf, S.; Fedier, A.; Hacker, N.F.; Heinzelmann-Schwarz, V. Careful Selection of Reference Genes Is Required for Reliable Performance of RT-qPCR in Human Normal and Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayani, J.; Squire, J.A. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH). Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2004, Chapter 22. Unit 22.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselinyová, D.; Mašlanková, J.; Kalinová, K.; Mičková, H.; Mareková, M.; Rabajdová, M. Selected In Situ Hybridization Methods: Principles and Application. Molecules 2021, 26, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamri, A.; Nam, J.Y.; Blancato, J.K. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization of Cells, Chromosomes, and Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1606, 265–279. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Flanagan, J.; Su, N.; Wang, L.-C.; Bui, S.; Nielson, A.; Wu, X.; Vo, H.-T.; Ma, X.-J.; Luo, Y. RNAscope: A Novel in Situ RNA Analysis Platform for Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, M.X.-M.; Su, N.; Wang, L.-C.; Wu, X.; Bui, S.; Nielsen, A.; Vo, H.-T.; Nguyen, N.; Luo, Y.; et al. RNAscope for in Situ Detection of Transcriptionally Active Human Papillomavirus in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, V.; McIlreavey, L.; Greene, C.; O’Doherty, E.; Clarke, R.; Craig, S.; Salto-Tellez, M.; McQuaid, S.; Lewis, C.; James, J. RNAscope Hybridization Confirms mRNA Integrity in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Cancer Tissue Samples. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93392–93403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.-M.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.-M.M.; Jansen, M.; Ma, X.-J.; Kim, J.; Anderson, C.M.; Wu, X.; Pan, L.; Su, N.; et al. Robust RNA-Based in Situ Mutation Detection Delineates Colorectal Cancer Subclonal Evolution. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley-Bunker, A.; Pearson, J.; Currie, M.J.; Morrin, H.; Whitehead, M.R.; Eglinton, T.; Walker, L.C. Assessment of Intra-Tumoural Colorectal Cancer Prognostic Biomarkers Using RNA Hybridisation. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.K.; Zacheaus, C.; Doxtater, K.; Keramatnia, F.; Gao, C.; Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Z Probe, An Efficient Tool for Characterizing Long Non-Coding RNA in FFPE Tissues. Noncoding RNA 2018, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.; Zecchini, H.; Nagarajan, S. Multiplexed Detection and Analysis of Low-Abundance Long Noncoding RNA Using RNAscopeTM in Cultured Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2148, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Jin, K.; Ji, D.; Peng, W.; Tang, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNA CCDC144NL-AS1 Promotes Cell Proliferation by Regulating the miR-363-3p/GALNT7 Axis in Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Wang, C.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L. lncRNA SNHG22 Sponges miR-128-3p to Promote the Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Upregulating E2F3. Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoo, Z.H.; Candlish, J.; Teare, D. What Is an ROC Curve? Emerg. Med. J. 2017, 34, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.; Seals, S.; Aban, I. Survival Analysis and Regression Models. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, Q.-F.; Huang, T.; Wu, P.; Shen, L.; Huang, Z.-L. Identification and Validation of a Prognostic lncRNA Signature for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cai, W.; Yuan, W.; Peng, S. Identification of Key lncRNAs as Prognostic Prediction Models for Colorectal Cancer Based on LASSO. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 675–684. [Google Scholar]
- Bradburn, M.J.; Clark, T.G.; Love, S.B.; Altman, D.G. Survival Analysis Part II: Multivariate Data Analysis—An Introduction to Concepts and Methods. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazi, P.; Carollo, E.; Carter, D.R.F.; Brooks, S.A. A Practical Toolkit to Study Aspects of the Metastatic Cascade in Vitro. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Han, S.; Du, W. Capsule-LPI: A LncRNA-Protein Interaction Predicting Tool Based on a Capsule Network. BMC Bioinformatics 2021, 22, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muppirala, U.K.; Honavar, V.G.; Dobbs, D. Predicting RNA-Protein Interactions Using Only Sequence Information. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Ren, S.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, T. Computational Prediction of Associations between Long Non-Coding RNAs and Proteins. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Tastsoglou, S.; Skoufos, G.; Karavangeli, A.; Pierros, V.; Zacharopoulou, E.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-LncBase v3: Indexing Experimentally Supported miRNA Targets on Non-Coding Transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D101–D110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Jiang, S.; Tao, R.; Ge, H.; Qin, J. Activating Transcription Factor 3-Activated Long Noncoding RNA Forkhead Box P4-Antisense RNA 1 Aggravates Colorectal Cancer Progression by Regulating microRNA-423-5p/nucleus Accumbens Associated 1 Axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 2114–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Jiang, M.; Fan, X. LncRNA FIRRE Functions as a Tumor Promoter by Interaction with PTBP1 to Stabilize BECN1 mRNA and Facilitate Autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Vancura, A.; Lanzós, A.; Bosch-Guiteras, N.; Esteban, M.T.; Gutierrez, A.H.; Haefliger, S.; Johnson, R. Cancer LncRNA Census 2 (CLC2): An Enhanced Resource Reveals Clinical Features of Cancer lncRNAs. NAR Cancer 2021, 3, zcab013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; De, W. Long Noncoding RNA LINC01296 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Colorectal Cancer by Suppressing p15 Expression. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211004414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeneCards. Available online: https://www.genecards.org (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Liu, B.; Pan, S.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Jia, L. LINC01296/miR-26a/GALNT3 Axis Contributes to Colorectal Cancer Progression by Regulating O-Glycosylated MUC1 via PI3K/AKT Pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Shao, B.; Liu, Z.; Dang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Chen, C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, S.; et al. LINC01296/miR-141-3p/ZEB1-ZEB2 Axis Promotes Tumor Metastasis via Enhancing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Process. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.-J.; Yan, J.-B. Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01296 Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 7175–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E.; et al. Functional Demarcation of Active and Silent Chromatin Domains in Human HOX Loci by Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertler, A.A.; Schlossman, D.M.; Borowitz, M.J.; Laurent, G.; Jansen, F.K.; Schmidt, C.; Frankel, A.E. A Phase I Study of T101-Ricin A Chain Immunotoxin in Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Biol. Response Mod. 1988, 7, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, S.; Zhu, H. The Sequence, Structure and Evolutionary Features of HOTAIR in Mammals. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappulla, D.C.; Cech, T.R. Yeast Telomerase RNA: A Flexible Scaffold for Protein Subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10024–10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, J. The Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Activates Autophagy by Upregulating ATG3 and ATG7 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, J. Circulating Long Non-Coding HOX Transcript Antisense Intergenic Ribonucleic Acid in Plasma as a Potential Biomarker for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Thorac Cancer 2016, 7, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Liang, G.-Y.; Yao, W.-Z.; Sui, J.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Peng, H.; Hong, W.-W.; Ye, Y.-C.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; et al. Integrated Analysis of Long Non-Coding RNA Competing Interactions Reveals the Potential Role in Progression of Human Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, M.; Slyskova, J.; Schneiderova, M.; Makovicky, P.; Bielik, L.; Levy, M.; Lipska, L.; Hemmelova, B.; Kala, Z.; Protivankova, M.; et al. HOTAIR Long Non-Coding RNA Is a Negative Prognostic Factor Not Only in Primary Tumors, but Also in the Blood of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogo, R.; Shimamura, T.; Mimori, K.; Kawahara, K.; Imoto, S.; Sudo, T.; Tanaka, F.; Shibata, K.; Suzuki, A.; Komune, S.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Regulates Polycomb-Dependent Chromatin Modification and Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancers. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6320–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Pan, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, P.-G. LncRNA HOTAIR Recruits SNAIL to Inhibit the Transcription of HNF4α and Promote the Viability, Migration, Invasion and EMT of Colorectal Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Gu, D.; Ma, G.; Zhu, L.; Hua, Q.; Chu, H.; Tong, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. Genetic Variants in lncRNA HOTAIR Are Associated with Risk of Colorectal Cancer. Mutagenesis 2015, 30, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; You, L.-H.; Zhou, R.-Z. Significant Association between Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Polymorphisms and Cancer Susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2016, 9, 3335–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, J.O.; Jun, H.H.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Ryu, C.S.; Kim, S.; Oh, D.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, N.K. Genetic Variants of Associated With Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility and Mortality. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, C. lncRNA HOTAIR Contributes to 5FU Resistance through Suppressing miR-218 and Activating NF-κB/TS Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Song, M.; Zhang, J.; Kuerban, M.; Wang, H. Combined Identification of Long Non-Coding RNA CCAT1 and HOTAIR in Serum as an Effective Screening for Colorectal Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14131–14140. [Google Scholar]
- Pardini, B.; Sabo, A.A.; Birolo, G.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNAs in Extracellular Fluids as Cancer Biomarkers: The New Frontier of Liquid Biopsies. Cancers 2019, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Feng, M. Prognostic Value of LncRNA HOTAIR in Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Open Med. 2020, 15, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y. BRAF-Activated Long Non-Coding RNA Contributes to Colorectal Cancer Migration by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, M.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. MALAT-1: A Long Non-Coding RNA and Its Important 3’ End Functional Motif in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jie, D.; Yun, T.; Li, W.; Yan, L.; Wang, K.; Feng, J. Downregulated Long Noncoding RNA BANCR Promotes the Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Downregualtion of p21 Expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, R. LncRNA BANCR Promotes Tumorigenesis and Enhances Adriamycin Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. Aging 2018, 10, 2062–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, Z.H.; Roche, V.; Chew, X.H.; Fadieieva, A.; Tay, Y. A Non-Canonical Tumor Suppressive Role for the Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 in Colon and Breast Cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Y. The Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressive Functions of the Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1: An Emerging Controversy. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials.gov. Available online: www.clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Google Patents. Available online: https://patents.google.com/advanced (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Yu, A.-M.; Choi, Y.H.; Tu, M.-J. RNA Drugs and RNA Targets for Small Molecules: Principles, Progress, and Challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 862–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damase, T.R.; Sukhovershin, R.; Boada, C.; Taraballi, F.; Pettigrew, R.I.; Cooke, J.P. The Limitless Future of RNA Therapeutics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 628137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkle, M.; El-Daly, S.M.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNA Therapeutics—Challenges and Potential Solutions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 629–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S. Long Non-Coding RNAs: From Disease Code to Drug Role. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methodology | Application | Model | Biological Process Tested | Dysregulation of lncRNA of Interest Required | Refs. (PubMed ID) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apoptotic assay | In vitro/in vivo | Cell lines, organoids, animal assays | Cell proliferation | Yes | 32144238 |
| Transwell assay | In vitro | Cell lines, organoids | Cell invasion | Yes | 33328585 |
| CCK-8 assay | In vitro | Cell lines, organoids | Cell proliferation | Yes | 34224294 |
| MTT assay | In vitro | Cell lines, organoids | Cell proliferation | Yes | 33277833 |
| Wound healing assay | In vitro | Cell lines, organoids | Cell migration | Yes | 33570445 |
| Colony formation assay | In vitro | Cell lines | Cell formation | Yes | 34371180 |
| Flow cytometry | In vitro | Cell lines | Cell cycle/apoptosis | Yes | 33099922 |
| Bioinformatic programs (RPIseq, lncPRO, lncBASE, Capsule-LPI) | In silico | N/A | Coexpression networking | No | 35034547 |
| RNA sequencing | In vitro | Cell lines, organoids | Coexpression networking | Yes | 35039060 |
| Western blot | In vitro/in vivo | Cell lines, organoids, animal assays | Protein expression | Yes | 34498706 |
| Dual luciferase assay | In vitro | Cell lines | Interactions | Yes | 35066433 |
| RNA immunoprecipitation | In vivo | Cell lines, organoids, animal assays | Interactions | Yes | 35110535 |
| RNA pull-down | In vitro | Cell lines, organoids | Interactions | Yes | 35107754 |
| Tumor formation assay | In vivo | Organoids, animal assays | Tumor formation | Yes | 34477476 |
| lncRNA | Mechanism of Action | Refs. (Pubmed ID) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| AFAP1-AS1 | Proliferation, migration, invasion through the miR-195-5p/WISP1 axis. Tumor growth and metastasis | 34335760, 27578191 |
| CRNDE | Regulation of apoptosis, proliferation, drug sensitivity via the Akt/mTORC1 pathway. Epigenetic transcriptional regulation of DUSP5 and CDNK1A | 35069879, 28796262 |
| DANCR | Suppression of apoptosis via RNA stabilization of MALAT1 Enhanced growth and metastasis via the DANCR/miR-518a-3p/MDM2 ceRNA network | 33414433, 32423468 |
| FTX | Proliferation, migration, invasion through the FTX-miR-214-5p-JAG1 regulatory axis. Enhanced growth and progression via the miR-192-5p/EIF5A2 axis | 34733921, 32280242 |
| GAS5 | Inhibition of proliferation and migration, induction of apoptosis via the GAS5/miR-10b axis. Suppression of macroautophagy, induction of apoptosis via the mTOR/SIRT1 pathway | 35103069, 33416133 |
| H19 | Migration, invasion, induction of EMT, metastasis via activation of Raf-ERK signaling Proliferation, invasion, metastasis via the H19/miR-29b-3p/PGRN/Wnt axis | 32698890, 29754471 |
| HNF1A-AS1 | Migration, invasion, glycolysis via miR-124/MYO6. Angiogenesis via the PBX3/OTX1/ERK-MAPK pathway | 32110048, 32325080 |
| HOTAIR | Migration, invasion, EMT, cell viability via SNAIL/HNF4α transcriptional regulation. Suppression of miR-218 via the EZH2-targeting miR-218-2 promoter regulatory axis | 33588137, 28918035 |
| HOTTIP | Proliferation, migration, invasion Enhanced susceptibility via rs3807598, rs2067087, and rs17427960 SNPs | 31945724, 30940774 |
| LINC00152 | Proliferation and metastasis via promoter hypomethylation and the YAP1/LINC00152/miR-632/miR-185-3p/FSCN1 axis | 32307642, 32042551 |
| lncRNA-ATB | Proliferation, migration, invasion via sponging miR-141-3p, metastasis Developmental flexibility via transcriptional regulation of β-catenin | 33199986, 32256798 |
| MEG3 | Inhibited proliferation through targeting SOCS3/STAT3 signaling via miR-708 Inhibited proliferation and migration via the miR-376/PRDK1 signal axis | 34934045, 31632544 |
| NEAT1 | Proliferation, invasion, apoptotic suppression via the miR-138/SLC38A1 axis Proliferation via the KDM5A/Cul4A/Wnt axis | 32700988, 34109988 |
| PCAT1 | Proliferation, migration, invasion, drug resistance. Proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptotic suppression via miR-149-5p regulation | 33277833, 31646561 |
| PVT1 | Proliferation, apoptotic regulation via the miR-761/MAPK1 axis. Epigenetic regulation of MYC, regulation of TGFβ/SMAD and Wnt/β-Catenin pathways | 34515320, 33148262 |
| SNHG1 | EMT regulation via miR-497-5p/miR-195-5p modulation. Proliferation, migration, invasion via Wnt/β-catenin signaling | 31276207, 29749530 |
| SPRY4-IT1 | Cell growth and glycolysis via PDK1. Proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT regulation via miR-101-3p modulation | 33029299, 28720069 |
| TUG1 | Proliferation, invasion, migration, apoptotic suppression, tumor growth via the miR-542-3p/TRIB2 axis and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Proliferation, migration, cell viability via the TUG1/miR-145-5p/TRPC6 regulatory axis | 34030715, 32985219 |
| TUSC7 | Inhibition of proliferation, invasion, EMT, enhanced apoptosis via the TUSC7/miR-23b/PDE7A axis | 33370523, 31002365 |
| UCA1 | Proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT, drug resistance via the UCA1/miR-495-SP1/SP3 axis. Proliferation and drug resistance via UCA1/miR-495-HGF/c-MET | 33961855, 34976187 |
| XIST | Proliferation, EMT, drug resistance via the XIST/miR-125b-2-3p/WEE1 axis. Proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptotic suppression via the miR-338-3p/PAX5 axis | 33666372, 32826710 |
| ZEB1-AS1 | Proliferation via miR-141-3p regulation. Cell viability and apoptotic suppression via the MiR-205/YAP1 axis | 32669962, 32190742 |
| ZFAS1 | Tumor size, metastasis, lipogenesis via PABP2/SREBP1. Proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis via miR-34b/SOX4 | 35036050, 33725330 |
| SNHG6 | Proliferation, apoptotic suppression via JAK2/SNHG6 regulation. Proliferation and invasion via miR-101-3p regulation and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | 32840014, 31533634 |
| CCAT2 | Proliferation, apoptotic suppression. Proliferation, migration, invasion via TAF15/RAB14/AKT/GSK3β axis, tumor growth and metastasis | 33099922, 34868956 |
| SNHG7 | Proliferation, migration, invasion, cell viability, and metastasis via miR-216b regulation and GALNT1 expression | 29915311, 33685194 |
| FOXD2-AS1 | Proliferation, cell cycle regulation via miR-4306 regulation. Proliferation, migration, invasion via the miR-25-3p/Sema4C axis | 34396433, 31908535 |
| LINC00460 | Metastasis via miR-149-5p and biglycan regulation. Proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptotic suppression via the miR-613/SphK1 axis | 33472555, 32821121 |
| MIR4435-2HG | Proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis via the miR-206/YAP1 axis. Proliferation, apoptotic suppression | 32154166, 32141545 |
| ELFN1-AS1 | Proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptotic suppression via the miR-1205/MTA1 axis. Proliferation, migration, apoptotic suppression via the miR-4644/TRIM44 axis | 34337713, 31929141 |
| LINC00858 | Suppression of apoptosis, senescence, autophagy. Tumor growth via WNK2 regulation. Proliferation, invasion, migration via the miR-4766-5p/PAK2 axis | 32768499, 31902050 |
| CCAT1 | Proliferation, migration, invasion via the hsa-miR-4679/GNG10 axis. Migration, invasion, cell viability via the CCAT1/VEGF/miR-218 axis | 35005034, 32256733 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Snyder, M.; Iraola-Guzmán, S.; Saus, E.; Gabaldón, T. Discovery and Validation of Clinically Relevant Long Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163866
Snyder M, Iraola-Guzmán S, Saus E, Gabaldón T. Discovery and Validation of Clinically Relevant Long Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(16):3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163866
Chicago/Turabian StyleSnyder, Madison, Susana Iraola-Guzmán, Ester Saus, and Toni Gabaldón. 2022. "Discovery and Validation of Clinically Relevant Long Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 16: 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163866
APA StyleSnyder, M., Iraola-Guzmán, S., Saus, E., & Gabaldón, T. (2022). Discovery and Validation of Clinically Relevant Long Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 14(16), 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14163866






