Association between Temporal Glycemic Change and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Men: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Assessment of FBG and FBG Change
2.3. Assessment of Covariates
2.4. Outcome Ascertainment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Association of Baseline FBG or the Most Recent FBG with PC
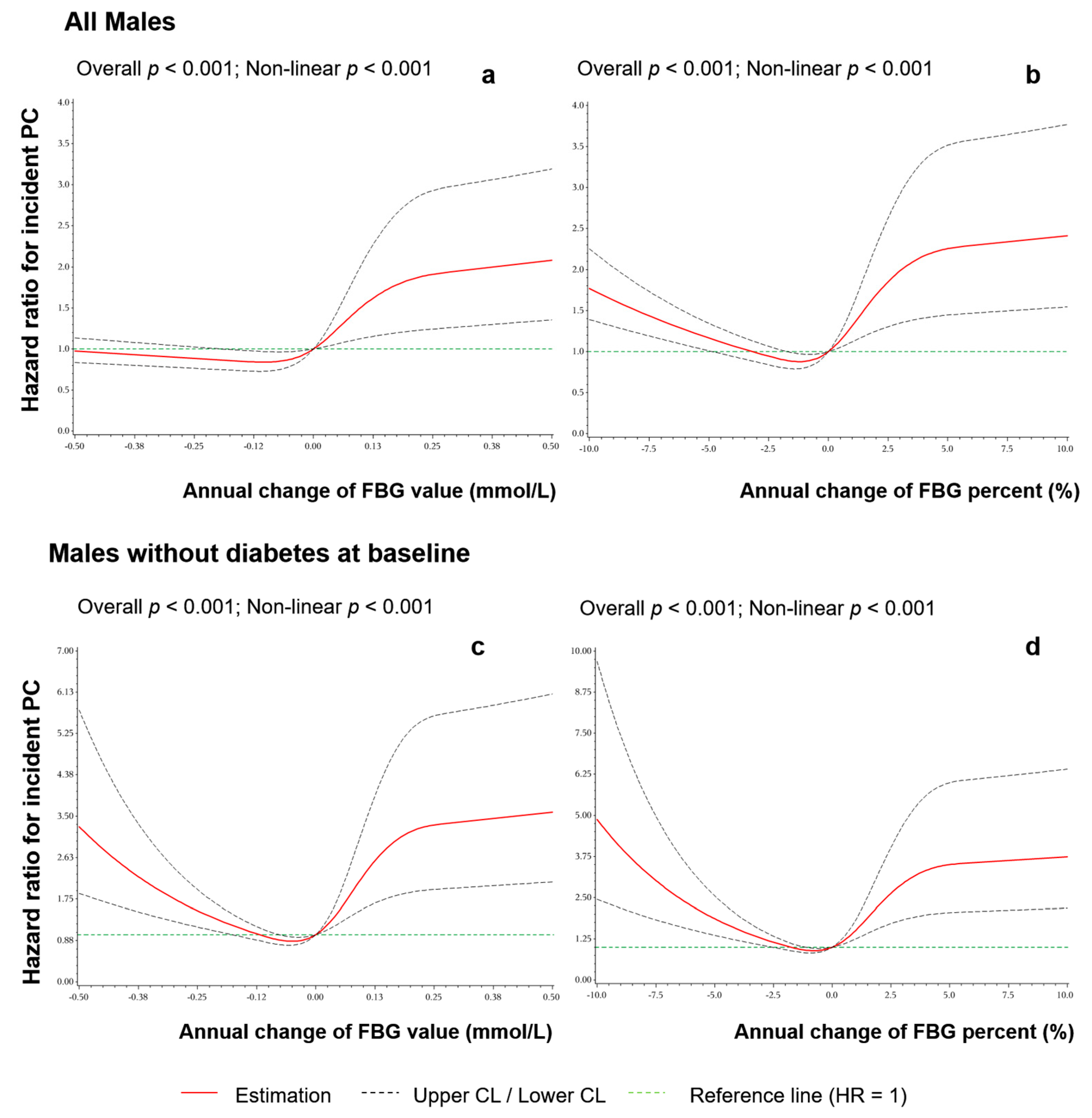
3.3. Association of FBG Change with PC
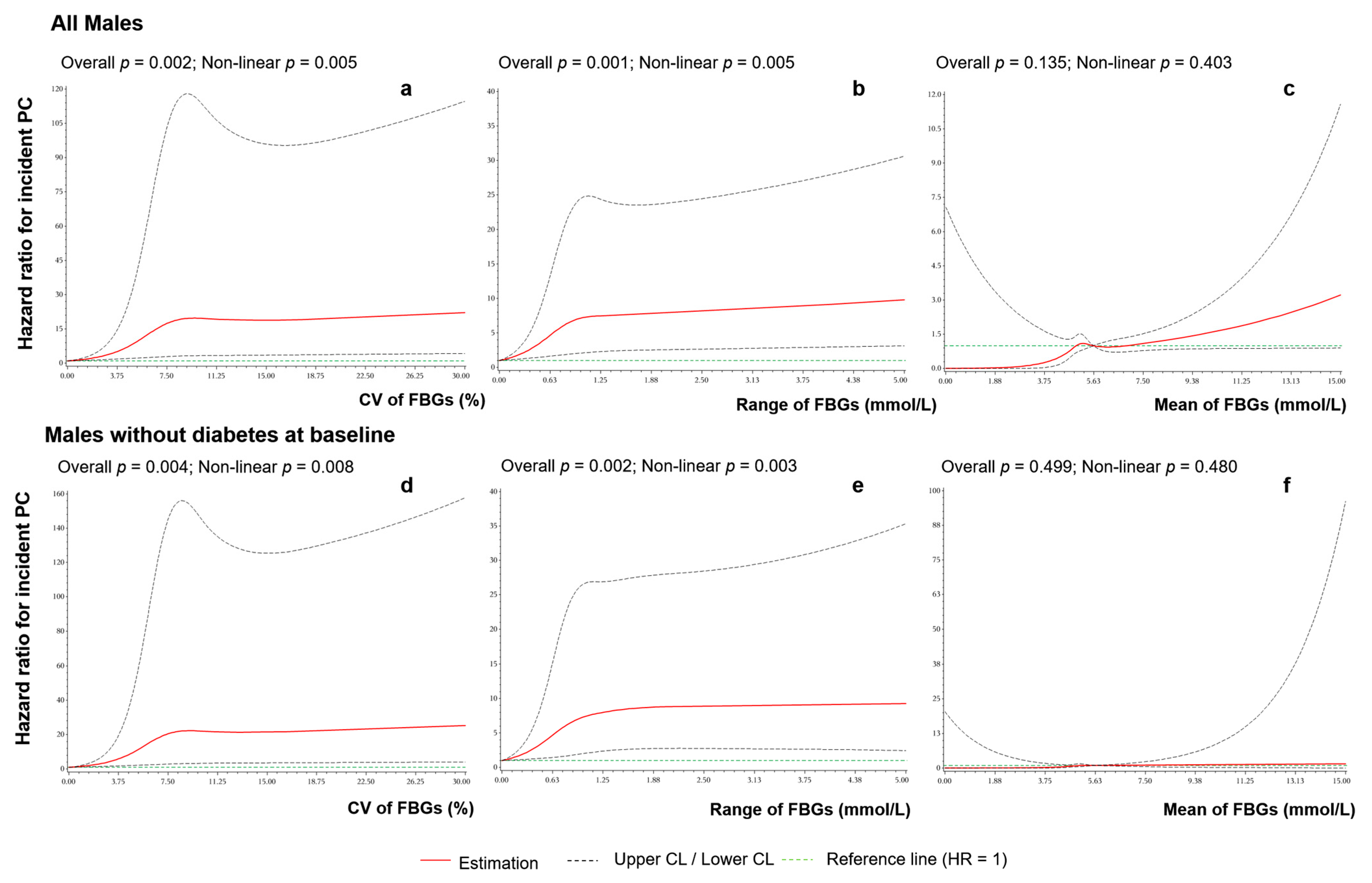
3.4. FBG Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Globocan. Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Huang, J.; Lok, V.; Ngai, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Lao, X.Q.; Ng, K.; Chong, C.; Zheng, Z.J.; Wong, M.C. Worldwide Burden of, Risk Factors for, and Trends in Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIH. Sheets. Pancreas Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Midha, S.; Chawla, S.; Garg, P.K. Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for pancreatic cancer: A review. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; You, L.; Zhang, T.; Dai, M.; Zhao, Y. Advances in the epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Trends, risk factors, screening, and prognosis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto, M.I.; Harinck, F.; Hruban, R.H.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Poley, J.-W.; Kamel, I.; Nio, Y.; Schulick, R.S.; Bassi, C.; Kluijt, I.; et al. International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening (CAPS) Consortium summit on the management of patients with increased risk for familial pancreatic cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrikson, N.B.; Bowles, E.J.A.; Blasi, P.R.; Morrison, C.C.; Nguyen, M.; Pillarisetty, V.G.; Lin, J.S. Screening for Pancreatic Cancer: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2019, 322, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Kandlakunta, H.; Nagpal, S.J.S.; Feng, Z.; Hoos, W.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Model to Determine Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With New-Onset Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 730–739.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Lou, Y.B.; Mu, Y.C.; Kang, M.X.; Wu, Y.L. Predictive Factors for Differentiating Pancreatic Cancer-Associated Diabetes Mellitus from Common Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus for the Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. Digestion 2018, 98, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursi, B.; Finkelman, B.; Giantonio, B.J.; Haynes, K.; Rustgi, A.K.; Rhim, A.D.; Mamtani, R.; Yang, Y.X. A Clinical Prediction Model to Assess Risk for Pancreatic Cancer Among Patients With New-Onset Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 840–850e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.H.; Chang, Y.; Lee, S.R.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.J. Glycemic Status, Insulin Resistance, and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer Mortality in Individuals With and Without Diabetes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, S.H.; Ohrr, H.; Sull, J.W.; Yun, J.E.; Ji, M.; Samet, J.M. Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA 2005, 293, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, W.-C.; Tu, Y.-K.; Wu, M.-S.; Lin, J.-T.; Wang, H.-P.; Chien, K.-L. Blood glucose concentration and risk of pancreatic cancer: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. BMJ 2015, 350, g7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pannala, R.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Timmons, L.J.; Ransom, J.E.; de Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Temporal association of changes in fasting blood glucose and body mass index with diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keum, N.; Ha, K.H.; Bao, Y.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, H.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Long-term patterns of fasting blood glucose levels and pancreatic cancer incidence. Cancer Causes Control. 2018, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Liao, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Associations Between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cancers in a Large Cohort in China. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 788–796.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Song, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, M.; Ma, Y.; Cui, L.; Jonas, J.B. Blood Pressure Classification of 2017 Associated With Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in Young Chinese Adults. Hypertension 2020, 76, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuth, S.; Alberti, K.G.; Bennett, P.; Buse, J.; Defronzo, R.; Kahn, R.; Kitzmiller, J.; Knowler, W.C.; Lebovitz, H.; Lernmark, A.; et al. Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 3160–3167. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Babic, A.; Khalaf, N.; Nowak, J.A.; Brais, L.K.; Rubinson, D.A.; Ng, K.; Aguirre, A.J.; Pandharipande, P.V.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. Diabetes, Weight Change, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e202948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.Z.; Pandol, S.J.; Jeon, C.Y.; Chari, S.T.; Sugar, C.A.; Chao, C.R.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Wu, B.U.; Setiawan, V.W. New-Onset Diabetes, Longitudinal Trends in Metabolic Markers, and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Heterogeneous Population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1812–1821.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapstur, S.M.; Gann, P.H.; Lowe, W.; Liu, K.; Colangelo, L.; Dyer, A. Abnormal Glucose Metabolism and Pancreatic Cancer Mortality. JAMA 2000, 283, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Graubard, B.; Chari, S.; Limburg, P.; Taylor, P.R.; Virtamo, J.; Albanes, D. Insulin, glucose, insulin resistance, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers. JAMA 2005, 294, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inoue, M.; Noda, M.; Kurahashi, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Sasazuki, S.; Iso, H.; Tsugane, S. Impact of metabolic factors on subsequent cancer risk: Results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2009, 18, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Montes, E.; Coscia, C.; Gómez-Rubio, P.; Fernández, A.; Boenink, R.; Rava, M.; Márquez, M.; Molero, X.; Löhr, M.; Sharp, L.; et al. Deciphering the complex interplay between pancreatic cancer, diabetes mellitus subtypes and obesity/BMI through causal inference and mediation analyses. Gut 2021, 70, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannucci, E.; Harlan, D.M.; Archer, M.C.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Habel, L.; Pollak, M.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Yee, D. Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandhu, M.S.; Dunger, D.B.; Giovannucci, E.L. Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF binding proteins, their biologic interactions, and colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Ma, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Ma, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wu, E. High glucose promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation via the induction of EGF expression and transactivation of EGFR. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Q.; Liu, H.; Guo, K.; Li, F.; Li, W.; Han, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, E. Relationship between neural alteration and perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer patients with hyperglycemia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Hu, D.; Chen, H.; Shi, G.; Fetahu, I.; Wu, F.; Rabidou, K.; Fang, R.; Tan, L.; Xu, S.; et al. Glucose-regulated phosphorylation of TET2 by AMPK reveals a pathway linking diabetes to cancer. Nature 2018, 559, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Darmanin, S.; Natsuisaka, M.; Kondo, T.; Asaka, M.; Shindoh, M.; Higashino, F.; Hamuro, J.; Okada, F.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Enhanced expression of asparagine synthetase under glucose-deprived conditions protects pancreatic cancer cells from apoptosis induced by glucose deprivation and cisplatin. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3345–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kittah, N.E.; Vella, A. Management of endocrine disease: Pathogenesis and management of hypoglycemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, R37–R47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total | Times of FBG Measurements | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2~3 | 4~6 | |||
| No. of participants | 138,870 | 32,238 | 44,479 | 62,153 | |
| No. of incident PC | 135 | 42 | 68 | 25 | |
| Follow-up time, y | 11.39 (7.03,13.06) | 6.24 (3.91,10.14) | 9.2 (6.53,12.76) | 12.99 (12.51,13.18) | <0.001 |
| Duration of FBG measurements | 6.26 (1.67,10.1) | - | 4.15 (2.36,6.13) | 10.2 (8.24,10.85) | <0.001 |
| Age(y) | |||||
| M (P25, P75) | 51 (39,59) | 53 (36,63) | 51 (37,60) | 50 (41,56) | <0.001 |
| Age < 40, No. (%) | 35,424 (25.51) | 9417 (29.21) | 12,530 (28.17) | 13,477 (21.68) | <0.001 |
| 40 ≤ Age < 60, No. (%) | 70,763 (50.96) | 11,831 (36.70) | 20,450 (45.98) | 38,482 (61.91) | |
| 60 ≤ Age < 80, No. (%) | 30,003 (21.61) | 9427 (29.24) | 10,551 (23.72) | 10,025 (16.13) | |
| ≥80, No. (%) | 2680 (1.93) | 1563 (4.85) | 948 (2.13) | 169 (0.27) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
| M (P25,P75) | 24.86 (22.71,27.12) | 24.77 (22.49,26.99) | 24.77 (22.53,26.99) | 25.04 (22.89,27.34) | <0.001 |
| BMI<18.5 | 2362 (1.7) | 704 (2.18) | 835 (1.88) | 823 (1.32) | <0.001 |
| 18.5≤BMI<25.0 | 69,563 (50.09) | 16,884 (52.37) | 23,070 (51.87) | 29,609 (47.64) | |
| 25.0≤BMI<30.0 | 56,551 (40.72) | 12,364 (38.35) | 17,371 (39.05) | 26,816 (43.15) | |
| BMI≥30.0 | 10,394 (7.48) | 2286 (7.09) | 3203 (7.20) | 4905 (7.89) | |
| Education status, No. (%) | |||||
| Junior middle school or lower education | 96,143 (69.23) | 16,908 (52.45) | 31,684 (71.23) | 47,551 (76.51) | <0.001 |
| Senior middle school | 19,028 (13.7) | 2808 (8.71) | 6445 (14.49) | 9775 (15.73) | |
| College and above | 11,652 (8.39) | 2391 (7.42) | 4439 (9.98) | 4822 (7.76) | |
| Missing | 12,047 (8.68) | 10,131 (31.43) | 1911 (4.30) | 5 (0.01) | |
| Smoking history, No. (%) | |||||
| Never smoker | 66,660 (48) | 14,633 (45.39) | 22,567 (50.74) | 29,460 (47.40) | <0.001 |
| Ever-smoker | 66,945 (48.21) | 12,686 (39.35) | 21,567 (48.49) | 32,692 (52.60) | |
| Missing | 5265 (3.79) | 4919 (15.26) | 345 (0.78) | 1 (0.00) | |
| Drinking history, No. (%) | |||||
| Never drinker | 66,662 (48) | 13,934 (43.22) | 23,878 (53.68) | 28,850 (46.42) | <0.001 |
| Ever drinker | 63,020 (45.38) | 9654 (29.95) | 20,064 (45.11) | 33,302 (53.58) | |
| Missing | 9188 (6.62) | 8650 (26.83) | 537 (1.21) | 1 (0.00) | |
| Anti-diabetic medications use history, No. (%) | |||||
| No | 118,793 (85.54) | 21,875 (67.85) | 37,157 (83.54) | 59,761 (96.15) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 2755 (1.98) | 689 (2.14) | 910 (2.05) | 1156 (1.86) | |
| Missing | 17,322 (12.47) | 9674 (30.01) | 6412 (14.42) | 1236 (1.99) | |
| Working environment, No. (%) | |||||
| Above the ground | 76,876 (55.36) | 15,178 (47.08) | 25,134 (56.51) | 36,564 (58.83) | <0.001 |
| Underground without dust exposure | 13,138 (9.46) | 2160 (6.70) | 4409 (9.91) | 6569 (10.57) | |
| Underground with dust exposure | 38,965 (28.06) | 5877 (18.23) | 14,068 (31.63) | 19,020 (30.60) | |
| Missing | 9891 (7.12) | 9023 (27.99) | 868 (1.95) | 0 (0.00) | |
| FBG Annual Change | All Males | Males without Diabetes at Baseline | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-Ys (Case) | HR (95% CI) a | Adjusted HR (95% CI) b | P-Ys (Case) | HR (95% CI) a | Adjusted HR (95% CI) b | ||
| Value (mmol/L) per year | −0.05~0.05 | 384,317.27 (10) | Ref | Ref | 372,674.58 (9) | Ref | Ref |
| <−0.05 | 248,300.50 (26) | 4.247 (2.047, 8.810) ** | 4.010 (1.920, 8.375) ** | 199,506.99 (19) | 4.161 (1.882, 9.200) ** | 3.976 (1.797, 8.798) ** | |
| 0.05~0.15 | 298,390.94 (15) | 1.940 (0.872, 4.318) | 1.816 (0.815, 4.045) | 289,282.46 (15) | 2.154 (0.942, 4.921) | 2.022 (0.884, 4.623) | |
| ≥0.15 | 253,207.62 (42) | 6.702 (3.362, 13.361) ** | 5.897 (2.935, 11.848) ** | 221,647.65 (38) | 7.436 (3.595, 15.383) ** | 6.769 (3.254, 14.080) ** | |
| Percent (%) per year | −1%~1% | 400,348.79 (11) | Ref | Ref | 303,446.40 (9) | Ref | Ref |
| <−1% | 233,833.54 (25) | 4.121 (2.027, 8.379) ** | 3.851 (1.883, 7.878) ** | 267,307.19 (19) | 2.498 (1.130, 5.523) * | 2.414 (1.092, 5.340) * | |
| 1%~3% | 290,858.88 (14) | 1.761 (0.799, 3.879) | 1.671 (0.758, 3.682) | 278,220.88 (13) | 1.582 (0.676, 3.702) | 1.502 (0.642, 3.516) | |
| ≥3% | 259,175.13 (43) | 6.332 (3.264, 12.282) ** | 5.512 (2.827, 10.748) ** | 234,137.22 (40) | 6.012 (2.917, 12.394) ** | 5.390 (2.603, 11.162) ** | |
| FBG Stability | All Males | Males without Diabetes at Baseline | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-Ys (Case) | HR (95% CI) a | Adjusted HR (95% CI) b | Linear HR (95% CI) c | P for trend | P-Ys (Case) | HR (95% CI) a | Adjusted HR (95% CI) b | Linear HR (95% CI) c | P for trend | ||
| CV (%) | <5 | 187,842.94 (4) | Ref | Ref | 1.025 (1.009, 1.042) ** | 0.003 | 182,445.65 (4) | Ref | Ref | 1.029 (1.011, 1.049) ** | 0.002 |
| 5~15 | 732,002.46 (55) | 3.317 (1.202, 9.156) * | 6.039 (2.173, 16.783) ** | 701,661.54 (52) | 3.203 (1.158, 8.859) * | 5.918 (2.123, 16.493) ** | |||||
| ≥15 | 264,374.86 (34) | 5.663 (2.009, 15.967) ** | 8.039 (2.815, 22.958) ** | 199,004.5 (25) | 5.414 (1.883, 15.563) ** | 7.939 (2.747, 22.947) ** | |||||
| Range (mmol/L) | <0.5 | 164,305.43 (10) | Ref | Ref | 1.073 (1.021, 1.128) ** | 0.005 | 160,739.67 (10) | Ref | Ref | 1.084 (1.016, 1.157) * | 0.015 |
| 0.5~1.5 | 617,668.22 (48) | 1.167 (0.590, 2.308) | 2.63 (1.314, 5.265) ** | 604,832.99 (46) | 1.127 (0.568, 2.236) | 2.621 (1.304, 5.269) ** | |||||
| ≥1.5 | 402,246.6 (35) | 1.274 (0.630, 2.578) | 3.553 (1.671, 7.555)** | 317,539.03 (25) | 1.138 (0.545, 2.375) | 3.773 (1.74, 8.181) ** | |||||
| Mean (mmol/L) | <5.6 | 775,037.24 (56) | Ref | Ref | 1.074 (0.998, 1.157) | 0.058 | 771,836.29 (56) | Ref | Ref | 1.084 (0.939, 1.252) | 0.272 |
| 5.6~7 | 284,942.69 (25) | 1.209 (0.755, 1.938) | 1.085 (0.668, 1.763) | 265,903.49 (22) | 1.136 (0.694, 1.860) | 1.090 (0.662, 1.794) | |||||
| ≥7 | 124,240.33 (12) | 1.327 (0.711, 2.475) | 0.854 (0.354, 2.058) | 45,371.91 (3) | 0.892 (0.279, 2.848) | 1.151 (0.342, 3.88) | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; Luo, C.; Feng, X.; You, L.; Dai, M.; Zhao, Y. Association between Temporal Glycemic Change and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Men: A Prospective Cohort Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 3403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143403
Cai J, Chen H, Lu M, Zhang Y, Lu B, Luo C, Feng X, You L, Dai M, Zhao Y. Association between Temporal Glycemic Change and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Men: A Prospective Cohort Study. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143403
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Jie, Hongda Chen, Ming Lu, Yuhan Zhang, Bin Lu, Chenyu Luo, Xiaoshuang Feng, Lei You, Min Dai, and Yupei Zhao. 2022. "Association between Temporal Glycemic Change and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Men: A Prospective Cohort Study" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143403
APA StyleCai, J., Chen, H., Lu, M., Zhang, Y., Lu, B., Luo, C., Feng, X., You, L., Dai, M., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Association between Temporal Glycemic Change and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Men: A Prospective Cohort Study. Cancers, 14(14), 3403. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143403






