Prognostic Impact of the SARC-F Score in Gastrointestinal Advanced Cancers
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients and Our Study
2.2. Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS)
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Baseline Features
3.2. The Cumulative OS Rate According to the SARC-F Score and GPS
3.3. The Relationship between the SARC-F Score and ECOG-PS in the Whole Cohort
3.4. Uni- and Multivariate Analysis of the OS
3.5. The Cumulative OS Rate Stratified by the SARC-F Score According to the Primary Origin
3.6. ROC Analysis on the Prognstic Impact of the SARC-F Score
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| OMPU | Osaka medical and pharmaceutical university |
| OS | overall survival |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| GPS | Glasgow Prognostic Score |
| CRP | C reactive protein |
| AUC | area under the ROC |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| OR | odds ratio |
References
- Nishikawa, H.; Fukunishi, S.; Asai, A.; Yokohama, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; Higuchi, K. Pathophysiology and mechanisms of primary sarcopenia (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, A.; Nieves, J.W. Nutrition and Sarcopenia—What Do We Know? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhetri, J.K.; de Souto Barreto, P.; Fougère, B.; Rolland, Y.; Vellas, B.; Cesari, M. Chronic inflammation and sarcopenia: A regenerative cell therapy perspective. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 103, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, C.C. Malnutrition and sarcopenia. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, R.F.; Loh, K.P.; Williams, G.R.; Jatoi, A.; Mustian, K.M.; Mohile, S.G. Cachexia and Sarcopenia in Older Adults with Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2019, 11, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrieri, P.; Ribolsi, M.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Emerenziani, S.; Altomare, A.; Cicala, M. Nutritional Aspects in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, C. Management of diet in gastrointestinal cancer. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, R.; Xu, J.; Fang, K.; Abdelrahim, M.; Chang, L. Sarcopenia as a predictor of postoperative risk of complications, mortality and length of stay following gastrointestinal oncological surgery. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2021, 103, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Goto, M.; Fukunishi, S.; Asai, A.; Nishiguchi, S.; Higuchi, K. Cancer Cachexia: Its Mechanism and Clinical Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.Y.; Chen, Z.J.; Qiu, X.M.; Zhu, D.X.; Tang, X.J.; Zhou, Q. Sarcopenia and prognosis of advanced cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition 2021, 90, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chi, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Hu, K. Impact of preoperative sarcopenia on postoperative complications and prognosis of gastric cancer resection: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2021, 98, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Avila, M.; Bozada-Gutiérrez, K.; Valenzuela-Salazar, C.; Herrera-Esquivel, J.; Moreno-Portillo, M. Sarcopenia predicts worse postoperative outcomes and decreased survival rates in patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2021, 36, 1077–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, H.; Arai, H.; Inui, A. The regulatory approval of anamorelin for treatment of cachexia in patients with non-small cell lung cancer, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, and colorectal cancer in Japan: Facts and numbers. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A symptom score to predict persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, S.; Kaneko, R.; Murata, K. SARC-F for Screening of Sarcopenia among Older Adults: A Meta-analysis of Screening Test Accuracy. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Won, C.W. Validation of the Korean Version of the SARC-F Questionnaire to Assess Sarcopenia: Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 40–45.e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Kamiya, K.; Hamazaki, N.; Matsuzawa, R.; Nozaki, K.; Maekawa, E.; Noda, C.; Yamaoka-Tojo, M.; Matsunaga, A.; Masuda, T.; et al. Utility of SARC-F for Assessing Physical Function in Elderly Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voelker, S.N.; Michalopoulos, N.; Maier, A.B.; Reijnierse, E.M. Reliability and Concurrent Validity of the SARC-F and Its Modified Versions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1864–1876.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.L.; Ding, L.Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, S.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Hua, H.X.; Chen, L.; Xu, H. Screening Accuracy of SARC-F for Sarcopenia in the Elderly: A Diagnostic Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Menezes, A.M.; Bielemann, R.M.; Malmstrom, T.K.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Grupo de Estudos em Composição Corporal e Nutrição (COCONUT). Enhancing SARC-F: Improving Sarcopenia Screening in the Clinical Practice. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, N.; Wakita, T.; Kamitani, T.; Wada, O.; Mizuno, K. SARC-F Validation and SARC-F+EBM Derivation in Musculoskeletal Disease: The SPSS-OK Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Hu, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, D.; et al. Screening Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: SARC-F vs SARC-F Combined With Calf Circumference (SARC-CalF). J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, e1–e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Tian, Z.; Thapa, S.; Sun, H.; Wen, S.; Xiong, H.; Yu, S. Comparing SARC-F with SARC-CalF for screening sarcopenia in advanced cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3337–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behne, T.E.G.; Dock-Nasimento, D.B.; Sierra, J.C.; Rodrigues, H.H.N.P.; Palauro, M.L.; Andreo, F.O.; Silva-The, M.B.; DE-Aguilar-Nascimento, J.E. Association between preoperative potential sarcopenia and survival of cancer patients undergoing major surgical procedures. Rev. Col. Bras Cir. 2020, 47, e20202528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, D.; Paiva, C.E.; Del Fabbro, E.G.; Steer, C.; Naberhuis, J.; van de Wetering, M.; Fernández-Ortega, P.; Morita, T.; Suh, S.Y.; Bruera, E.; et al. Prognostication in advanced cancer: Update and directions for future research. Support Care Cancer 2019, 27, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.P.L.; McMillan, D.C.; McWilliams, K.; Sande, T.A.; Fearon, K.C.; Tuck, S.; Fallon, M.T.; Laird, B.J. Prognostic Tools in Patients With Advanced Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2017, 53, 962–970.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.X.; Bi, X.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Zhao, J.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, H.; Cai, J.Q. Prognostic Role of Glasgow Prognostic Score in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Mohan, C. Immunological Biomarkers of COVID-19. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 40, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Chronic Inflammation as an Immunological Abnormality and Effectiveness of Exercise. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hollingworth, T.W.; Oke, S.M.; Patel, H.; Smith, T.R. Getting to grips with sarcopenia: Recent advances and practical management for the gastroenterologist. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020, 12, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginster, J.Y.; Beaudart, C.; Al-Daghri, N.; Avouac, B.; Bauer, J.; Bere, N.; Bruyère, O.; Cerreta, F.; Cesari, M.; Rosa, M.M.; et al. Update on the ESCEO recommendation for the conduct of clinical trials for drugs aiming at the treatment of sarcopenia in older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuomisto, A.E.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Väyrynen, J.P. Systemic inflammation in colorectal cancer: Underlying factors, effects, and prognostic significance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4383–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Hiraoka, A.; Shiraki, M.; Sugimoto, R.; Taniki, N.; Hiramatsu, A.; Nakamoto, N.; Iwasa, M.; Chayama, K.; Shimizu, M. Utility of the SARC-F Questionnaire for Sarcopenia Screening in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
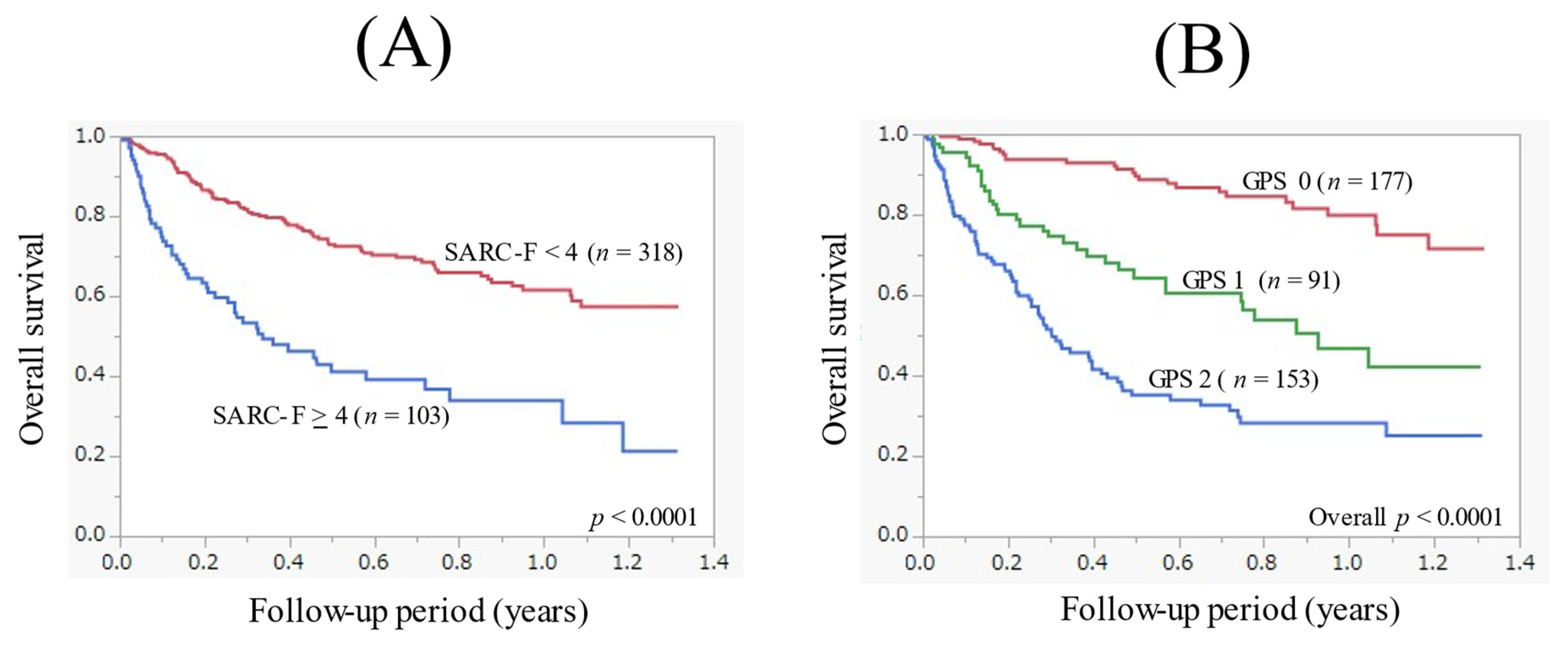

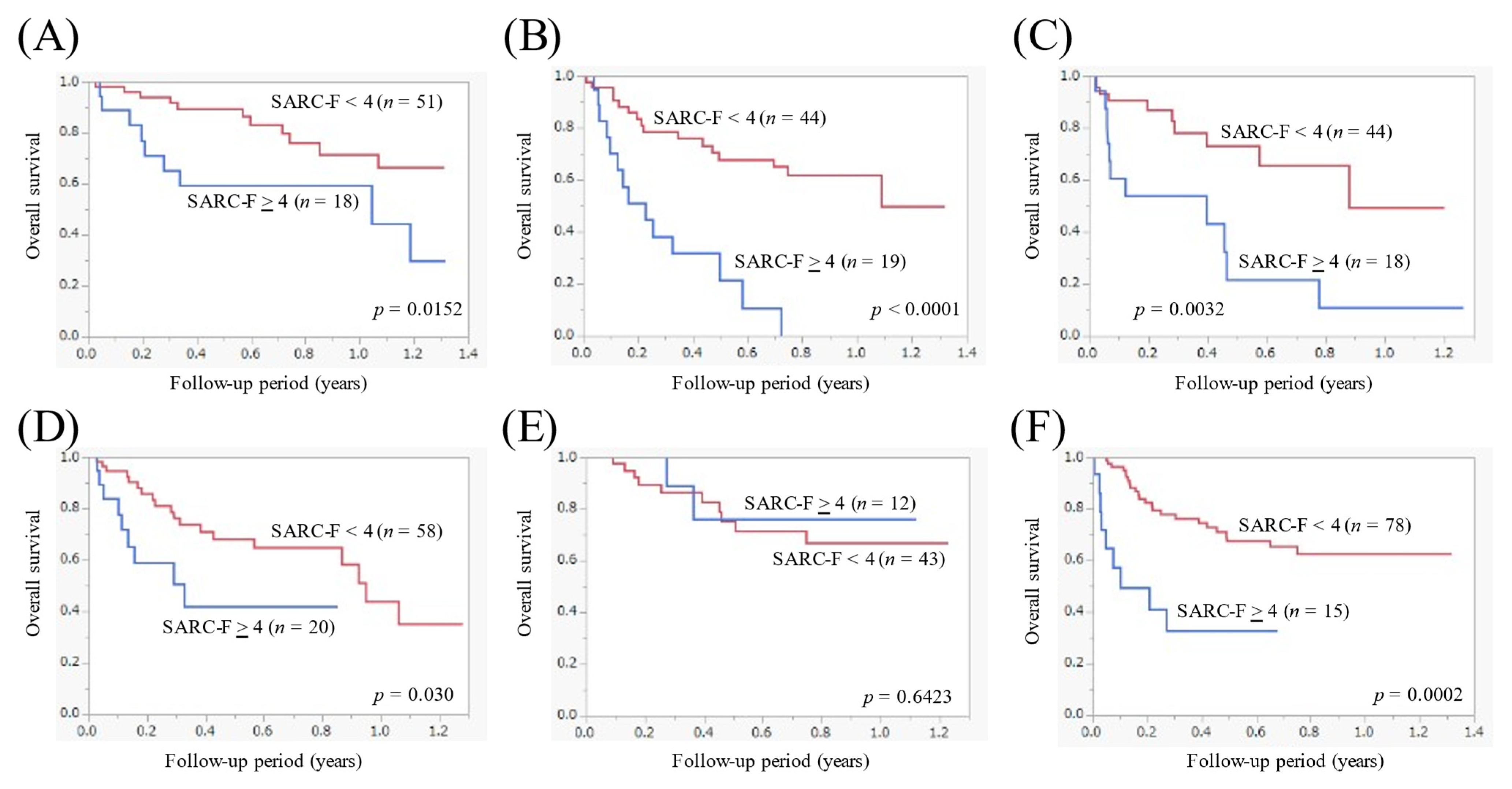

| Variables | Number or Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 73 (66, 79) |
| Gender, male/female | 272/149 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.0 (18.8, 23.6) |
| Hb (g/dL) | 11.9 (10.4, 13.3) |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.5 (3.0, 3.9) |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.75 (0.19, 4.39) |
| GPS, 0/1/2 | 177/91/153 |
| Total lymphocyte count (/μL) | 1081 (767, 1490) |
| ALT (IU/l) | 22 (13, 52.5) |
| Platelet count × 104/mm3 | 21.4 (15.7, 28.0) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2) | 68 (55, 82) |
| ECOG-PS, 0/1/2/3/4 | 201/78/38/61/43 |
| SARC-F score, 0/1/2/3/4 or more | 198/53/38/29/103 |
| Breakdown of advanced cancers (number (%)) | |
| Esophageal cancer | 69 (16.4%) |
| Gastric cancer | 63 (15.0%) |
| Biliary tract cancer | 62 (14.7%) |
| Pancreatic cancer | 78 (18.5%) |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 55 (13.1%) |
| Colorectal cancer | 93 (22.1%) |
| Small intestine cancer | 1 (0.2%) |
| Variables | n | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 73 years, yes/no | 216/205 | 0.0072 |
| Gender, male/female | 272/149 | 0.0626 |
| BMI ≥ 21 kg/m2, yes/no | 210/205 * | 0.1478 |
| Hb ≥ 11.9 g/dL, yes/no | 212/209 | <0.0001 |
| Platelet count ≥ 21.4 × 104/mm3, yes/no | 211/210 | 0.7554 |
| Total lymphocyte count ≥1081/μL, yes/no | 211/210 | <0.0001 |
| ALT ≥ 22 IU/l, yes/no | 216/205 | 0.7103 |
| eGFR ≥ 68 mL/min/1.73m2, yes/no | 213/208 | 0.0910 |
| SARC-F score ≥ 4, yes/no | 103/318 | <0.0001 |
| GPS, 0/1/2 | 177/91/153 | <0.0001 |
| ECOG-PS, 0/1/2/3/4 | 201/78/38/61/43 | <0.0001 |
| Variables | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 73 years | 1.085 | 0.763–1.544 | 0.6491 |
| Hb ≥ 11.9 g/dL | 0.830 | 0.568–1.211 | 0.3324 |
| Total lymphocyte count ≥ 1081/μL | 0.537 | 0.367–0.787 | 0.0014 |
| SARC-F score ≥ 4 | 2.899 | 1.295–6.489 | 0.0096 |
| Glasgow prognostic score | |||
| 0 | Reference | ||
| 1 | 1.953 | 1.141–3.343 | 0.0147 |
| 2 | 3.460 | 2.103–5.691 | <0.0001 |
| ECOG-PS | |||
| 0 | Reference | ||
| 1 | 1.489 | 0.860–2.580 | 0.1555 |
| 2 | 4.622 | 2.691–7.940 | <0.0001 |
| 3 | 6.235 | 2.663–14.601 | <0.0001 |
| 4 | 18.82 | 7.298–48.534 | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsui, M.; Nishikawa, H.; Goto, M.; Asai, A.; Ushiro, K.; Ogura, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Nakamura, S.; Kakimoto, K.; Miyazaki, T.; et al. Prognostic Impact of the SARC-F Score in Gastrointestinal Advanced Cancers. Cancers 2022, 14, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010010
Matsui M, Nishikawa H, Goto M, Asai A, Ushiro K, Ogura T, Takeuchi T, Nakamura S, Kakimoto K, Miyazaki T, et al. Prognostic Impact of the SARC-F Score in Gastrointestinal Advanced Cancers. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsui, Masahiro, Hiroki Nishikawa, Masahiro Goto, Akira Asai, Kosuke Ushiro, Takeshi Ogura, Toshihisa Takeuchi, Shiro Nakamura, Kazuki Kakimoto, Takako Miyazaki, and et al. 2022. "Prognostic Impact of the SARC-F Score in Gastrointestinal Advanced Cancers" Cancers 14, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010010
APA StyleMatsui, M., Nishikawa, H., Goto, M., Asai, A., Ushiro, K., Ogura, T., Takeuchi, T., Nakamura, S., Kakimoto, K., Miyazaki, T., Fukunishi, S., Ohama, H., Yokohama, K., Yasuoka, H., & Higuchi, K. (2022). Prognostic Impact of the SARC-F Score in Gastrointestinal Advanced Cancers. Cancers, 14(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010010






