Targeting the Sphingosine Kinase/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Axis in Drug Discovery for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
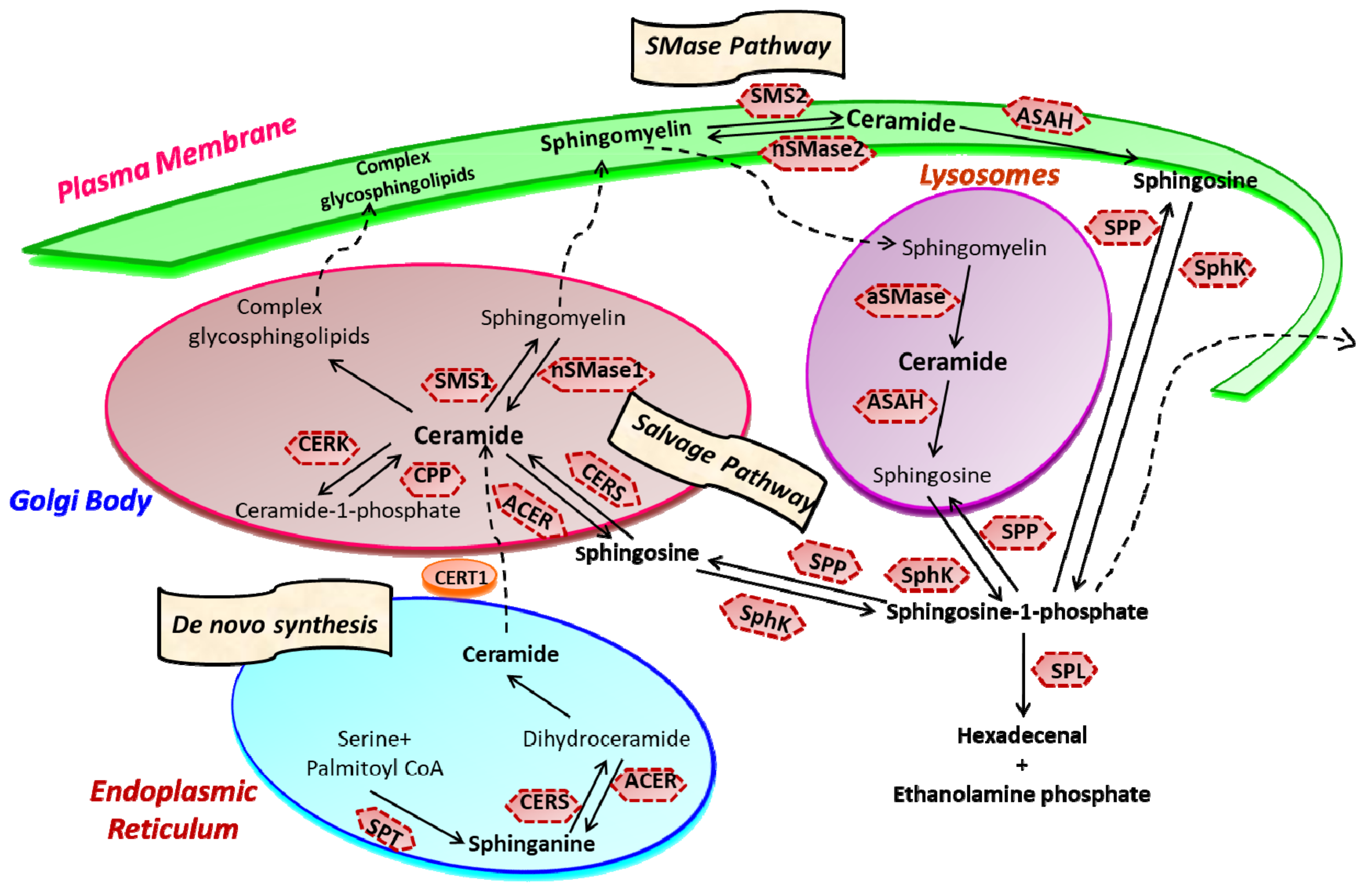
2. Sphingolipid Metabolism
3. Sphingosine Kinase
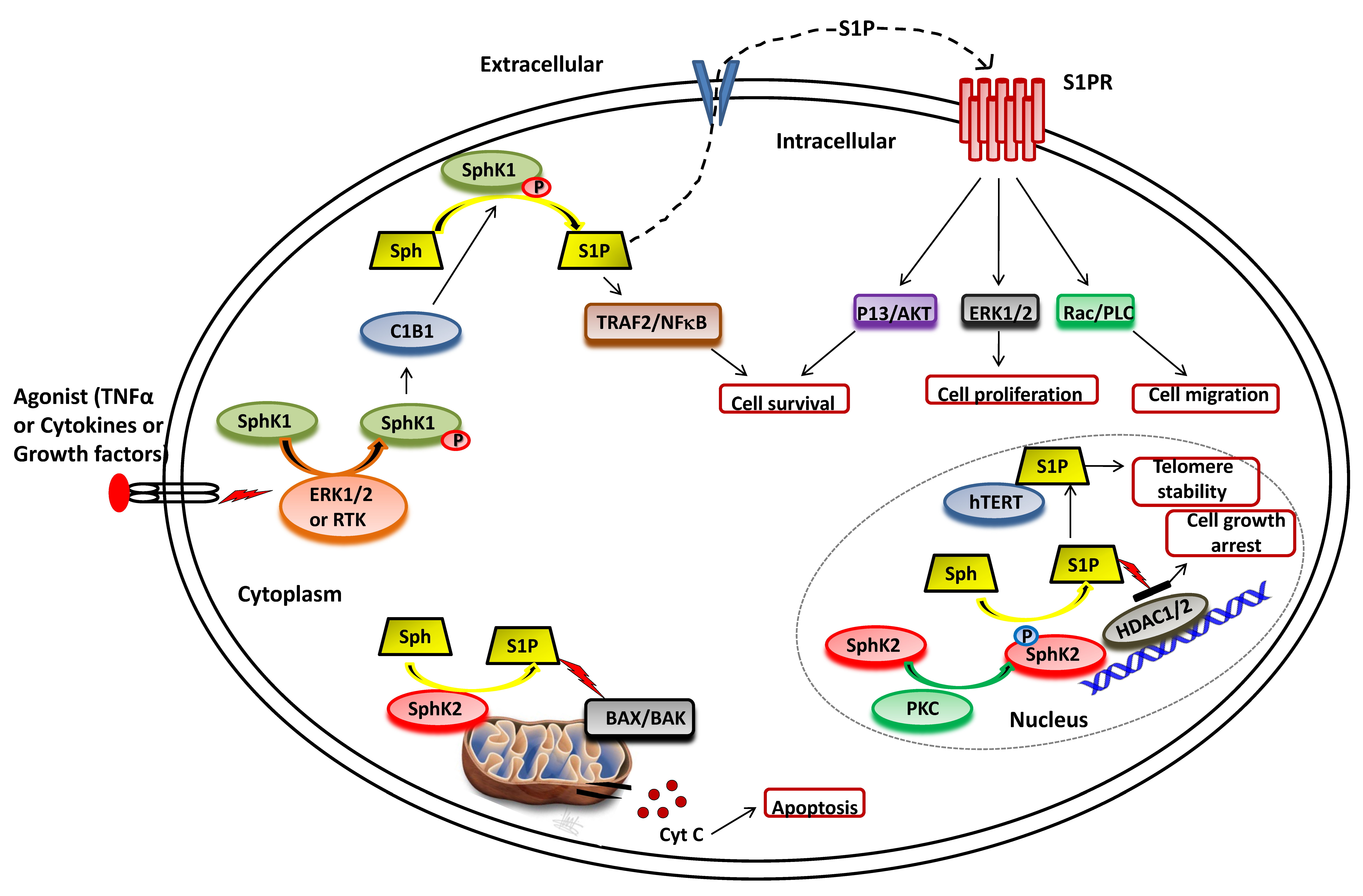
3.1. SphK1 Activation and Functions
3.2. SphK2 Activation and Functions
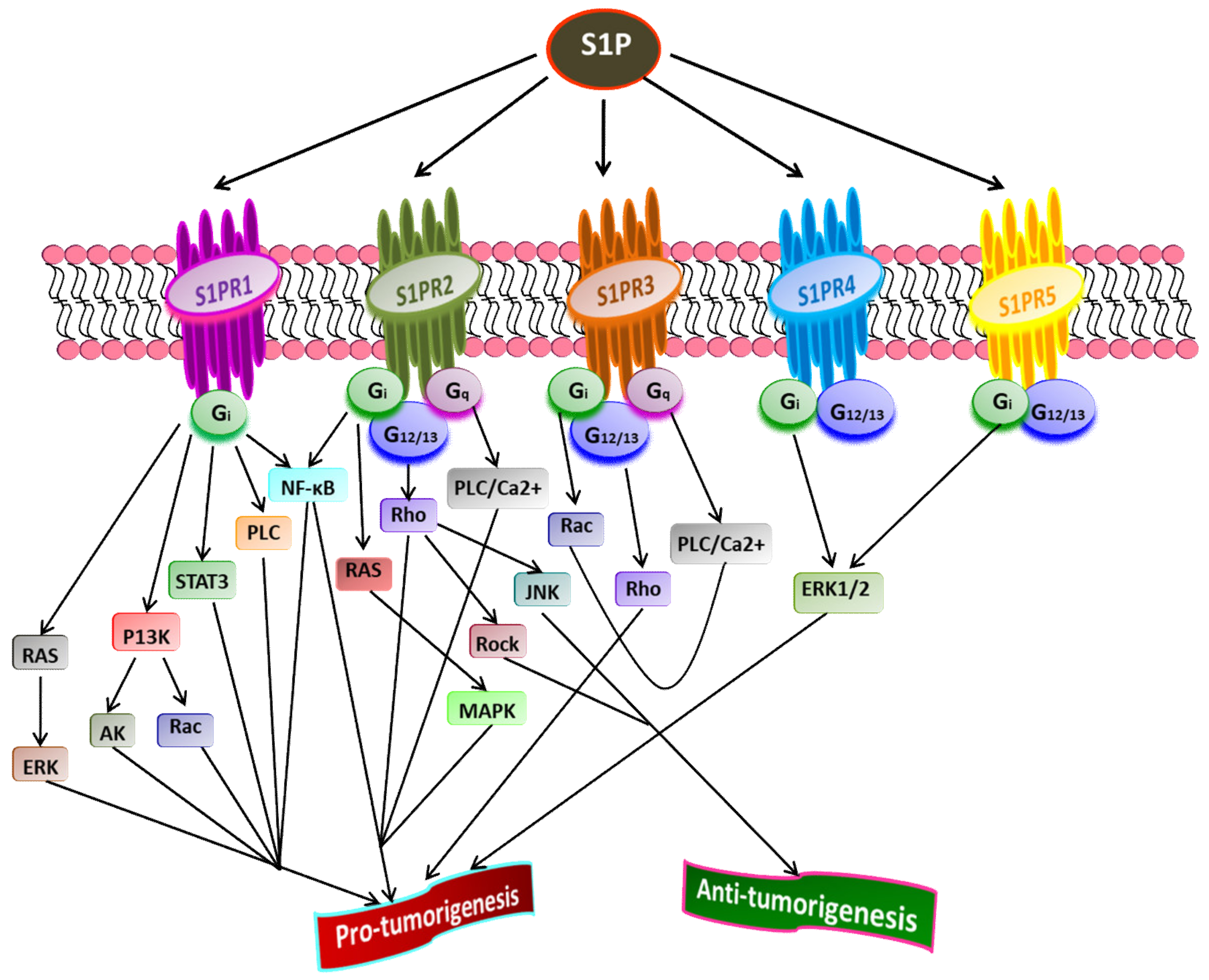
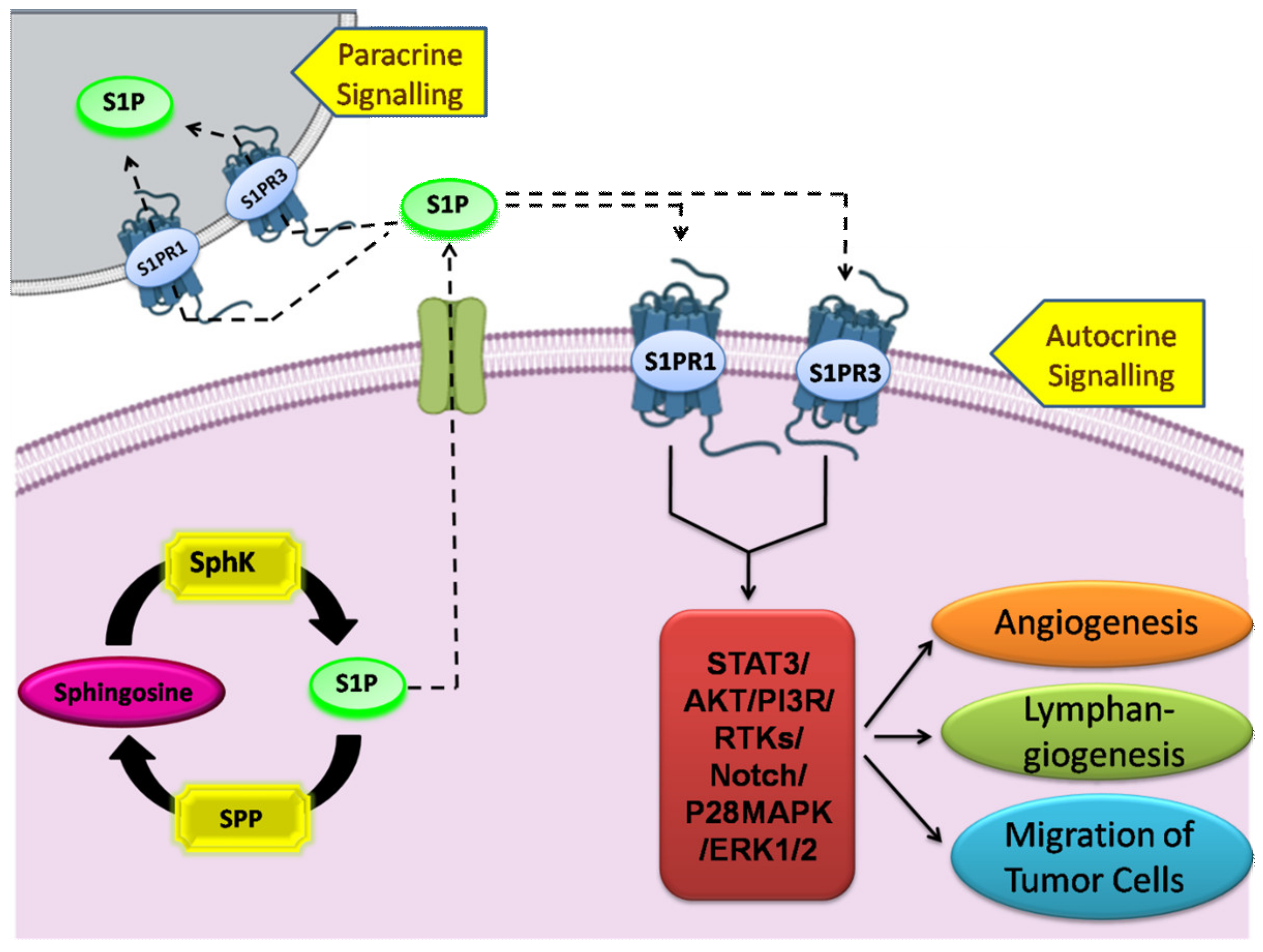
4. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Its Receptors in the Pathophysiology
5. SphK1/S1P Signaling in Human Malignancies
5.1. Breast Cancer
5.2. Lung Cancer
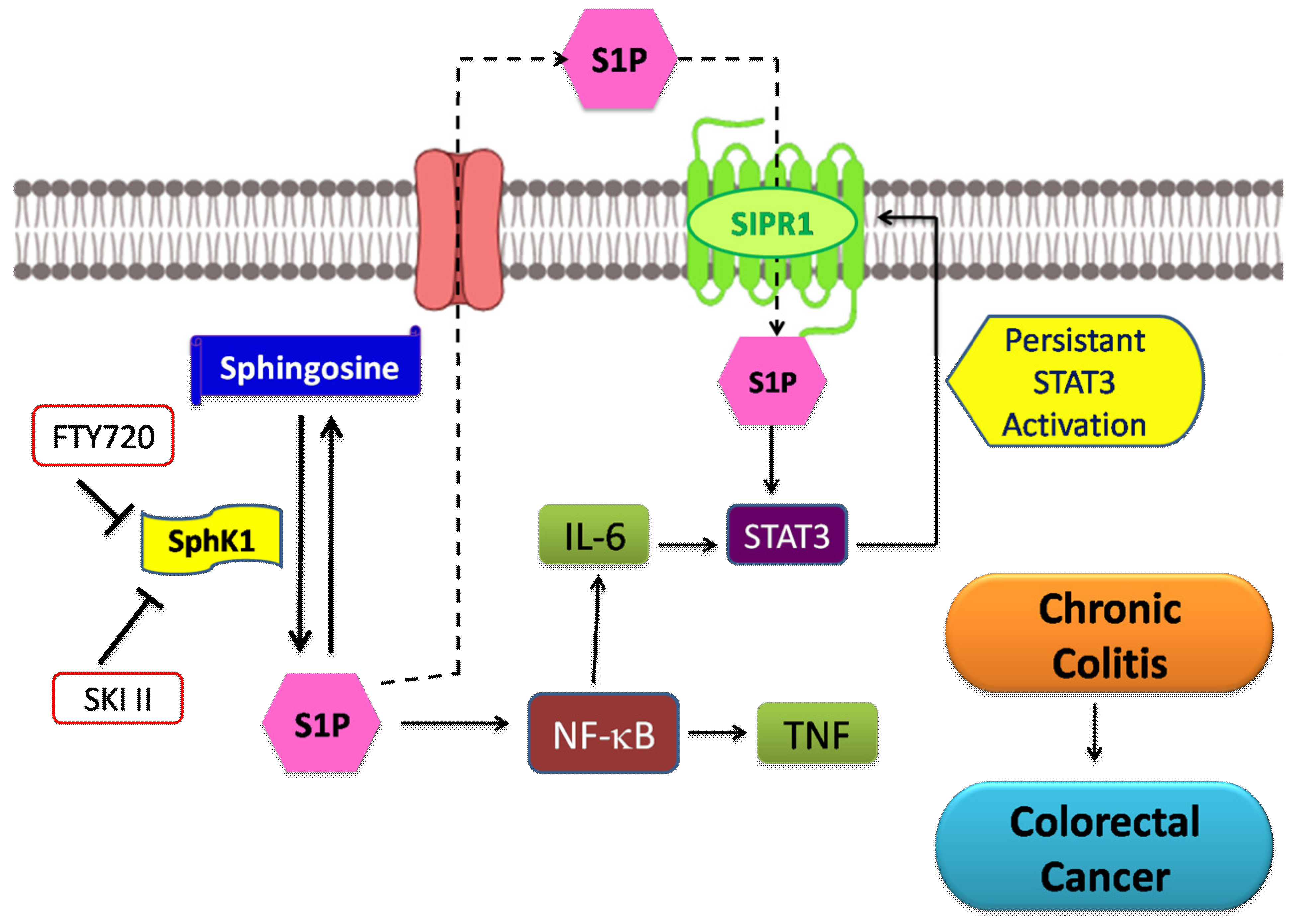
5.3. Colorectal Cancer
5.4. Gastric Cancer
5.5. Glioma
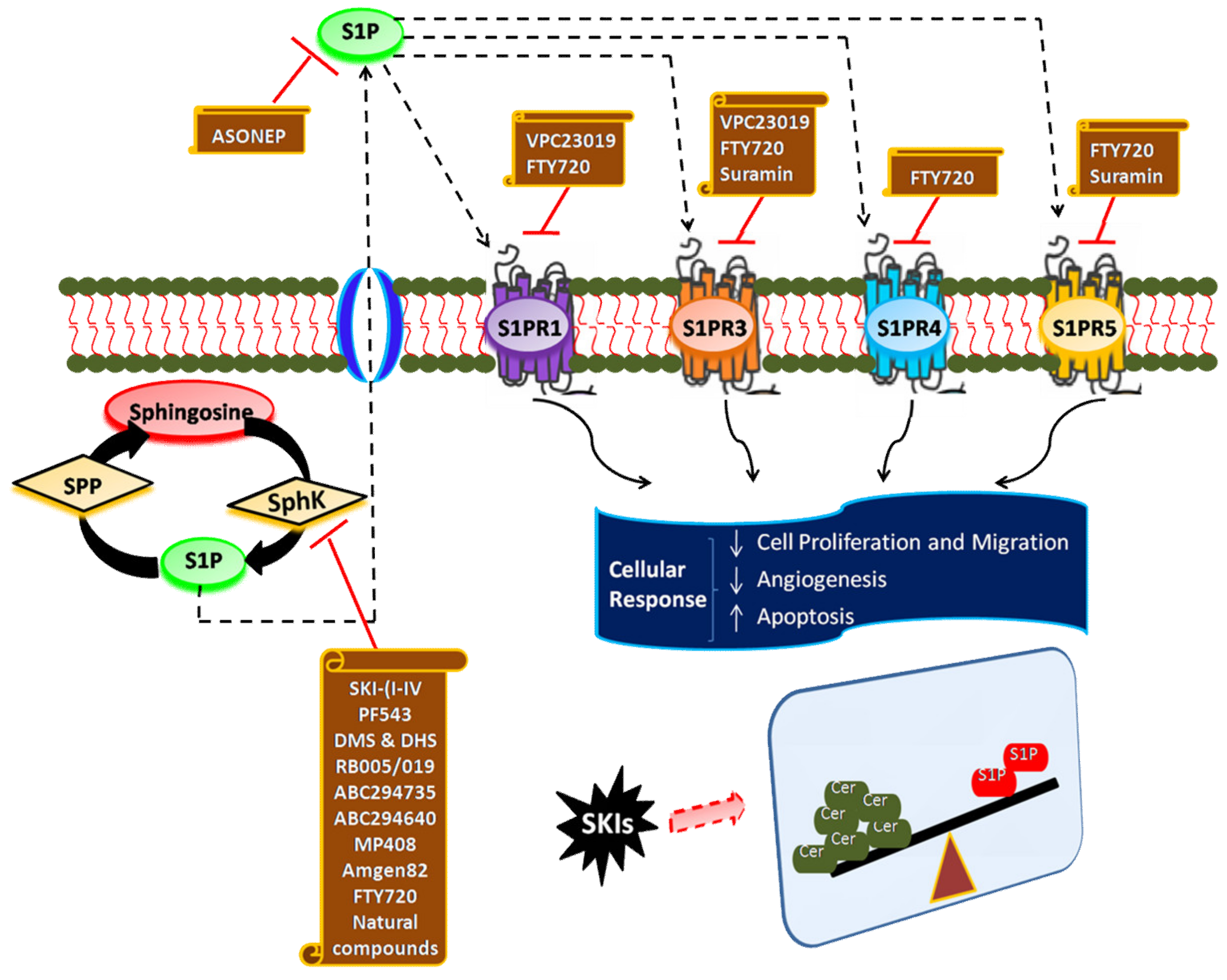
6. Targeting SphK1/S1P Signaling Axis for Cancer Therapy
7. Inhibitors of SphK
7.1. SKI-(I-IV)
7.2. PF543
7.3. N,N-Dimethylsphingosine, and Dihydroxysphingosine
7.4. FTY720
7.5. RB-005 and RB-019
7.6. ABC294735
7.7. ABC294640
7.8. MP-A08
7.9. Amgen-82
7.10. Natural Compounds
8. Antagonists of S1P Receptors
8.1. Suramin
8.2. VPC23019
9. S1P-Blocking Antibodies
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Many ceramides. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 27855–27862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arana, L.; Gangoiti, P.; Ouro, A.; Trueba, M.; Gómez-Muñoz, A. Ceramide and ceramide 1-phosphate in health and disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espaillat, M.P.; Shamseddine, A.A.; Adada, M.M.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in cancer, two faces of the sphinx. Transl. Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 484–499. [Google Scholar]
- Kitatani, K.; Idkowiak-Baldys, J.; Hannun, Y.A. The sphingolipid salvage pathway in ceramide metabolism and signaling. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancevic, B.; Kolesnick, R. Ceramide-rich platforms in transmembrane signaling. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.J.; Tennagels, N. On ceramides, other sphingolipids and impaired glucose homeostasis. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddoughi, S.A.; Ogretmen, B. Diverse functions of ceramide in cancer cell death and proliferation. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 117, pp. 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Nica, A.F.; Tsao, C.C.; Watt, J.C.; Jiffar, T.; Kurinna, S.; Jurasz, P.; Konopleva, M.; Andreeff, M.; Radomski, M.W.; Ruvolo, P.P. Ceramide promotes apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia-derived K562 cells by a mechanism involving caspase-8 and JNK. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3362–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, N.C.; Maiti, A. The Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Ceramide-1-Phosphate in Inflammation and Cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4806541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, J.; Lima, S.; Maceyka, M.; Spiegel, S. Revisiting the sphingolipid rheostat: Evolving concepts in cancer therapy. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 333, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceyka, M.; Spiegel, S. Sphingolipid metabolites in inflammatory disease. Nature 2014, 510, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceyka, M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and its role in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, T.; Hanada, K. Sphingolipid metabolism and interorganellar transport: Localization of sphingolipid enzymes and lipid transfer proteins. Traffic 2015, 16, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, N.; Hannun, Y.A. Bioactive sphingolipids: Metabolism and function. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S91–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevska, G.M.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M.N. The expanding role of sphingolipids in lipid droplet biogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, D.T.; Obeid, M.L. Ceramide and apoptosis: Exploring the enigmatic connections between sphingolipid metabolism and programmed cell death. Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussani, P.; Colleoni, T.; Brioschi, L.; Bassi, R.; Hanada, K.; Tettamanti, G.; Riboni, L.; Viani, P. Ceramide traffic in C6 glioma cells: Evidence for CERT-dependent and independent transport from ER to the Golgi apparatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meer, G.V.; Sprong, H. Membrane lipids and vesicular traffic. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Hill, R.A.; Li, Y.-T. Ceramide glycosylation catalyzed by glucosylceramide synthase and cancer drug resistance. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 117, pp. 59–89. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Han, T.-Y.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cabot, M.C. Ceramide glycosylation potentiates cellular multidrug resistance. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gault, C.R.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. An overview of sphingolipid metabolism: From synthesis to breakdown. In Sphingolipids as Signaling and Regulatory Molecules; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, R.W.; Canals, D.; Hannun, Y.A. Roles and regulation of secretory and lysosomal acid sphingomyelinase. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Saito, M. Involvement of sphingolipids in ethanol neurotoxicity in the developing brain. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 670–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulbins, E. Regulation of death receptor signaling and apoptosis by ceramide. Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 47, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.C.; Wallington-Beddoe, C.T.; Powell, J.A.; Pitson, S.M. Targeting sphingolipid metabolism as an approach for combination therapies in haematological malignancies. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvillier, O.; Pirianov, G.; Kleuser, B.; Vanek, P.G.; Coso, O.A.; Gutkind, J.S.; Spiegel, S. Suppression of ceramide-mediated programmed cell death by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Nature 1996, 381, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pralhada Rao, R.; Vaidyanathan, N.; Rengasamy, M.; Mammen Oommen, A.; Somaiya, N.; Jagannath, M.R. Sphingolipid Metabolic Pathway: An Overview of Major Roles Played in Human Diseases. J. Lipids 2013, 2013, 178910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bionda, C.; Portoukalian, J.; Schmitt, D.; Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C.; Ardail, D. Subcellular compartmentalization of ceramide metabolism: MAM (mitochondria-associated membrane) and/or mitochondria? Biochem. J. 2004, 382, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariä, D.A.; De Sanctis, J.B.; Shah, J.; Dumut, D.C.; Radzioch, D. Biochemistry of very-long-chain and long-chain ceramides in cystic fibrosis and other diseases: The importance of side chain. Prog. Lipid Res. 2019, 74, 130–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hatoum, D.; Haddadi, N.; Lin, Y.; Nassif, N.T.; McGowan, E.M. Mammalian sphingosine kinase (SphK) isoenzymes and isoform expression: Challenges for SphK as an oncotarget. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Min, X.; Xiao, S.-H.; Johnstone, S.; Romanow, W.; Meininger, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.; An, S.; et al. Molecular Basis of Sphingosine Kinase 1 Substrate Recognition and Catalysis. Structure 2013, 21, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavo, A.; Liccardo, D.; Komici, K.; Corbi, G.; de Lucia, C.; Femminella, G.D.; Elia, A.; Bencivenga, L.; Ferrara, N.; Koch, W.J.; et al. Sphingosine Kinases and Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors: Signaling and Actions in the Cardiovascular System. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez, A.J.; Carlos-Dias, E.; Gosink, M.; Allen, J.M.; Takacs, L. Human sphingosine kinase: Molecular cloning, functional characterization and tissue distribution. Gene 2000, 251, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, S.; Lee, S.C.; Long, J.; Pyne, N.J. Role of sphingosine kinases and lipid phosphate phosphatases in regulating spatial sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling in health and disease. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Khan, F.I.; Roy, S.; Anwar, S.; Dahiya, R.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, M.T.; Lai, D.; Hassan, M.I. Functional implications of pH-induced conformational changes in the Sphingosine kinase 1. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 225, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceyka, M.; Sankala, H.; Hait, N.C.; Le Stunff, H.; Liu, H.; Toman, R.; Collier, C.; Zhang, M.; Satin, L.S.; Merrill, A.H. SphK1 and SphK2, sphingosine kinase isoenzymes with opposing functions in sphingolipid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37118–37129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Khan, F.I.; Ambreen, D.; Lai, D.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I. Investigation of guanidinium chloride-induced unfolding pathway of sphingosine kinase 1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitson, S.M.; Moretti, P.A.B.; Zebol, J.R.; Lynn, H.E.; Xia, P.; Vadas, M.A.; Wattenberg, B.W. Activation of sphingosine kinase 1 by ERK1/2-mediated phosphorylation. Embo J. 2003, 22, 5491–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkoski-Gross, M.J.; Obeid, L.M. Molecular mechanisms of regulation of sphingosine kinase 1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, N.C.; Oskeritzian, C.A.; Paugh, S.W.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinases, sphingosine 1-phosphate, apoptosis and diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 2016–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, R.; van Koppen, C.J.; Danneberg, K.; ter Braak, M.; Meyer zu Heringdorf, D. Regulation and functional roles of sphingosine kinases. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 2007, 374, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceyka, M.; Alvarez, S.E.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Activation of Sphingosine Kinase 1. In Sphingolipid Biology; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, S.; Yamashita, H.; Tamori, M.; Mashimo, M.; Yamagata, K.; Nakamura, H.; Murayama, T. Translocation and activation of sphingosine kinase 1 by ceramide-1-phosphate. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 5396–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fan, F.; Yang, W. Sphingosine Kinase 1 and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Quercetin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting SphK1/S1P signaling. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, D.L.; Fu, P.; Natarajan, V. Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in lung diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 168, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zou, X.; Xu, L. Transforming growth factor-b-sphingosine kinase 1/S1P signaling upregulates microRNA-21 to promote fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, M.; Shegogue, D.; Pei, H.; Bu, S.; Bielawska, A.; Bielawski, J.; Pettus, B.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.; Trojanowska, M. Sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) is induced by transforming growth factor-band mediates TIMP-1 up-regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 53994–54001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, S.E.; Rowsey, T.G.; Priyadarsini, S.; Mandal, N.A.; Karamichos, D. Unravelling the interplay of sphingolipids and TGF-b signaling in the human corneal stroma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Wang, L.; Moretti, P.A.B.; Albanese, N.; Chai, F.; Pitson, S.M.; D’Andrea, R.J.; Gamble, J.R.; Vadas, M.A. Sphingosine Kinase Interacts with TRAF2 and Dissects Tumor Necrosis Factor-a Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7996–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; An, J.; Jawadi, H.; Siow, D.L.; Lee, J.-F.; Zhao, J.; Gartung, A.; Maddipati, K.R.; Honn, K.V.; Wattenberg, B.W.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 mediated NFkB activation contributes to tumor necrosis factor-α induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013, 106, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, L.; Kordula, T.; Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Regulation and functions of sphingosine kinases in the brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, F.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. Prolactin upregulates sphingosine kinase-1 expression and activity in the human breast cancer cell line MCF7 and triggers enhanced proliferation and migration. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maczis, M.A.; Maceyka, M.; Waters, M.R.; Newton, J.; Singh, M.; Rigsby, M.F.; Turner, T.H.; Alzubi, M.A.; Harrell, J.C.; Milstien, S.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 activation by estrogen receptor a ± 36 contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitson, S.M.; Xia, P.; Leclercq, T.M.; Moretti, P.A.B.; Zebol, J.R.; Lynn, H.E.; Wattenberg, B.W.; Vadas, M.A. Phosphorylation-dependent translocation of sphingosine kinase to the plasma membrane drives its oncogenic signalling. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarman, K.E.; Moretti, P.A.B.; Zebol, J.R.; Pitson, S.M. Translocation of sphingosine kinase 1 to the plasma membrane is mediated by calcium-and integrin-binding protein 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.S. The Role of Sphingolipids in Cancer Development and Therapy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pitson, S.M. Regulation of sphingosine kinase and sphingolipid signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Chang, W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Depends on Sphingosine Kinase 1 (SphK1)/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P)/Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 3 (S1PR3)/Notch Signaling for Metastasis. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2018, 24, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, Z. Sphingosine kinase 1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and oxaliplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 5371–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.C.; Chiyoda, T.; Liu, X.; Weigert, M.; Curtis, M.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Loth, R.; Lastra, R.; McGregor, S.M.; Locasale, J.W. SPHK1 is a novel target of metformin in ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Brocklyn, J.R.; Jackson, C.A.; Pearl, D.K.; Kotur, M.S.; Snyder, P.J.; Prior, T.W. Sphingosine Kinase-1 Expression Correlates With Poor Survival of Patients With Glioblastoma Multiforme: Roles of Sphingosine Kinase Isoforms in Growth of Glioblastoma Cell Lines. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Ji, C.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, W.; Ni, W.; Tong, X.; Wei, J.-F. Sphingosine kinase inhibitors: A patent review. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelisti, C.; Evangelisti, C.; Buontempo, F.; Lonetti, A.; Orsini, E.; Chiarini, F.; Barata, J.T.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J.; Martelli, A.M. Therapeutic potential of targeting sphingosine kinases and sphingosine 1-phosphate in hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2016, 30, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Mohammad, T.; Dahiya, R.; Roy, S.; Noman, O.M.A.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Hassan, M.I. Evaluation of binding and inhibition mechanism of dietary phytochemicals with sphingosine kinase 1: Towards targeted anticancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Mohammad, T.; Khan, P.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Rehman, M.T.; Hassan, M.I. Evaluation of ellagic acid as an inhibitor of sphingosine kinase 1: A targeted approach towards anticancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, N.; Lin, Y.; Simpson, A.M.; Nassif, N.T.; McGowan, E.M. “Dicing and splicing” sphingosine kinase and relevance to cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan-Stroud, L.A.; Obeid, L.M. Sphingosine kinase 1 in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 117, 201–235. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Zhang, J.; Vessey, D.A.; Honbo, N.; Karliner, J.S. Deletion of the sphingosine kinase-1 gene influences cell fate during hypoxia and glucose deprivation in adult mouse cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 74, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, N.; Okada, T.; Hayashi, S.; Fujita, T.; Jahangeer, S.; Nakamura, S.-I. Sphingosine kinase 2 is a nuclear protein and inhibits DNA synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46832–46839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Sonoda, H.; Yu, H.; Kajimoto, T.; Goparaju, S.K.; Jahangeer, S.; Okada, T.; Nakamura, S.-I. Protein kinase D-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear export of sphingosine kinase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27493–27502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Toman, R.E.; Goparaju, S.K.; Maceyka, M.; Nava, V.E.; Sankala, H.; Payne, S.G.; Bektas, M.; Ishii, I.; Chun, J.; et al. Sphingosine Kinase Type 2 Is a Putative BH3-only Protein That Induces Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40330–40336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Xu, G.; Peng, C.; Chen, G.; Kong, B.; Friess, H.; Shen, S.; Lv, Y.; et al. Targeting sphingosine kinase 2 suppresses cell growth and synergizes with BCL2/BCL-XL inhibitors through NOXA-mediated MCL1 degradation in cholangiocarcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 546–561. [Google Scholar]
- Chipuk, J.E.; McStay, G.P.; Bharti, A.; Kuwana, T.; Clarke, C.J.; Siskind, L.J.; Obeid, L.M.; Green, D.R. Sphingolipid metabolism cooperates with BAK and BAX to promote the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Cell 2012, 148, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, H.A.; Pitson, S.M. Roles, regulation and inhibitors of sphingosine kinase 2. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5317–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Maceyka, M.; Strub, G.M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Singh, S.K.; Luo, C.; Marmorstein, R.; Kordula, T.; Milstien, S.; et al. Regulation of histone acetylation in the nucleus by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 2009, 325, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitai Chand, H.; Jeremy, A.; Michael, M.; Graham, M.S.; Kuzhuvelil, B.H.; Tomasz, K.; Sheldon, M.; Sarah, S. Sphingosine Kinase 2 and S1P in the Nucleus Regulate Histone Acetylation by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, A.; Tzieply, N.; von Knethen, A.; Johann, A.M.; Schmidt, H.; Geisslinger, G.; Brüne, B. Tumor cell apoptosis polarizes macrophages role of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 3810–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Liu, G.; Bao, G.; Cui, D.; Fan, J.; Wang, F.; Jin, H. SphK2 over-expression promotes osteosarcoma cell growth. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, N.; Omori, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Ito, H.; Takagi, A.; Kojima, T.; Nakatochi, M.; Ogiso, H.; Kawamoto, Y.; Nakamura, M. Increased SPHK2 transcription of human colon cancer cells in serum-depleted culture: The involvement of CREB transcription factor. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanifard, L.; Sheervalilou, R.; Majidinia, M.; Yousefi, B. New insights into the roles and regulation of SphK2 as a therapeutic target in cancer chemoresistance. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8162–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, C.; Chen, M.-B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, T.-N.; Peng, X.; Ning, L.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wang, L.-W. Targeting sphingosine kinase 2 (SphK2) by ABC294640 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneer Selvam, S.; De Palma, R.M.; Oaks, J.J.; Oleinik, N.; Peterson, Y.K.; Stahelin, R.V.; Skordalakes, E.; Ponnusamy, S.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Smith, C.D.; et al. Binding of the sphingolipid S1P to hTERT stabilizes telomerase at the nuclear periphery by allosterically mimicking protein phosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strub, G.M.; Paillard, M.; Liang, J.; Gomez, L.; Allegood, J.C.; Hait, N.C.; Maceyka, M.; Price, M.M.; Chen, Q.; Simpson, D.C.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate produced by sphingosine kinase 2 in mitochondria interacts with prohibitin 2 to regulate complex IV assembly and respiration. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, D.-S.; Clemens, J.; Macdonald, T.L.; Lynch, K.R. Characterization of the Human and Mouse Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor, S1P5 (Edg-8): Structure− Activity Relationship of Sphingosine1-Phosphate Receptors. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 14053–14060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Wang, F.; Yoshioka, K.; Takuwa, N.; Takuwa, Y. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate-Specific G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Novel Therapeutic Targets for Atherosclerosis. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.E.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Autocrine and paracrine roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 18, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.I.; Saba, J.D. S1P metabolism in cancer and other pathological conditions. Biochimie 2010, 92, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takabe, K.; Paugh, S.W.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. “Inside-out” signaling of sphingosine-1-phosphate: Therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhong, H.; Xu, K.; Qi, X. Roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, L.; Lee, H.; Armstrong, B.; Scuto, A.; Kowolik, C.; Weiss, L.M.; Forman, S.; Yu, H. S1PR1 is an effective target to block STAT3 signaling in activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BloodJ. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 120, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, H.; Kim, P.-J.; Jeon, Y.K.; Cho, Y.M.; Kim, K.; Park, B.-H.; Ku, J.Y. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) expression in non-muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma: Association with poor clinical outcome and potential therapeutic target. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Cai, T.-T.; Huang, D.-J.; He, J.; Ni, H.-H.; Zhou, F.-J.; Zhang, X.-S.; Li, J. Sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1) promotes tumor-associated regulatory T cell expansion: Leading to poor survival in bladder cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr Gandy, K.A.; Adada, M.; Canals, D.; Carroll, B.; Roddy, P.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Epidermal growth factor-induced cellular invasion requires sphingosine-1-phosphate/sphingosine-1-phosphate 2 receptor-mediated ezrin activation. Faseb J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2012, 27, 3155–3166. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, L.; Alpini, G. Therapeutic Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 2 in the Progression of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petti, L.; Piontini, A.; Arena, V.; Danese, S.; Vetrano, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 is a negative regulator of epithelial cell proliferation and intestinal tumorigenesis. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1046.2. [Google Scholar]
- Stelling, A.; Hashwah, H.; Bertram, K.; Manz, M.G.; Tzankov, A.; Muller, A. The tumor suppressive TGF-b/SMAD1/S1PR2 signaling axis is recurrently inactivated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2018, 131, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, R.J.; Wang, H.-G.; Sung, S.-S.; Loughran, T.P.; Liu, X. Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors in cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, N.; Yamada, S.; Shoda, T.; Kurihara, M.; Sekino, Y.; Kanda, Y. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes expansion of cancer stem cells via S1PR3 by a ligand-independent Notch activation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, J.; et al. S1P/S1PR3 axis promotes aerobic glycolysis by YAP/c-MYC/PGAM1 axis in osteosarcoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siehler, S.; Manning, D.R. Pathways of transduction engaged by sphingosine 1-phosphate through G protein-coupled receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2002, 1582, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin-Nolan, S.M.; Bruning, J.C. The role of ceramides in metabolic disorders: When size and localization matters. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patmanathan, S.N.; Wang, W.; Yap, L.F.; Herr, D.R.; Paterson, I.C. Mechanisms of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor signalling in cancer. Cell. Signal. 2017, 34, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Edwards, J.; Tannahill, C.L.; Tigyi, G.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 4 uses HER2 (ERBB2) to regulate extracellular signal regulated kinase-1/2 in MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 35957–35966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, G.; Ledoux, A.; Branka, S.; Bocquet, M.; Gilhodes, J.; Walzer, T.; Kasahara, K.; Inagaki, M.; Sabbadini, R.A.; Cuvillier, O. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling through its receptor S1P5 promotes chromosome segregation and mitotic progression. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaah4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-L.; Ho, M.-C.; Lee, P.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Huang, W.-P.; Lee, H. S1P5 is required for sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced autophagy in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C451–C458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.-M.; Li, L.; Jing, B.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-S.; Wang, C.-L.; Feng, L.; Xie, Y.-E. Effect of S1P5 on proliferation and migration of human esophageal cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2010, 16, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Aoki, H.; Ramanathan, R.; Hait, N.C.; Takabe, K. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in immune cells and inflammation: Roles and therapeutic potential. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.E.; Harikumar, K.B.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Strub, G.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Maceyka, M.; Jiang, H.; Luo, C.; Kordula, T.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2. Nature 2010, 465, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-S.; Choi, S.; Shin, B.; Yu, J.; Yu, J.; Hwang, J.-M.; Yun, H.; Chung, Y.-H.; Choi, J.-S.; Choi, Y. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor (TRAF)-interacting protein (TRIP) negatively regulates the TRAF2 ubiquitin-dependent pathway by suppressing the TRAF2-sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 9660–9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasugi, N.; Sasaki, T.; Suzuki, K.; Osawa, S.; Isshiki, H.; Hori, Y.; Shimada, N.; Higo, T.; Yokoshima, S.; Fukuyama, T.; et al. BACE1 activity is modulated by cell-associated sphingosine-1-phosphate. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6850–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffken, K.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase 1 in breast cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2018, 67, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Takabe, K.; Hait, N.C. Metastatic triple-negative breast cancer is dependent on SphKs/S1P signaling for growth and survival. Cell. Signal. 2017, 32, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Jemal, A. Lung cancer statistics. In Lung Cancer and Personalized Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Xiong, H.; Li, J.; Liao, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Li, M. Sphingosine kinase-1 enhances resistance to apoptosis through activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Harikumar, K.B. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: A novel target for lung disorders. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachechiladze, M.; Tichý, T.; Kolek, V.; Grygarkova, I.; KLeIN, J.; Mgebrishvili, G.; Kharaishvili, G.; Janíková, M.; Smičková, P.; Cierna, L.; et al. Sphingosine kinase-1 predicts overall survival outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with carboplatin and navelbine. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.S.; Sudhadevi, T.; Fu, P.; Punathil-Kannan, P.-K.; Ebenezer, D.L.; Ramchandran, R.; Putherickal, V.; Cheresh, P.; Zhou, G.; Ha, A.W. Sphingosine Kinase 1/S1P Signaling Contributes to Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating Hippo/YAP Pathway and Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in Lung Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoriti, P.; Carbone, G.; Greco, M.; Pirozzi, F.; Pirozzi, R.E.M.; Corcione, F. Worldwide burden of colorectal cancer: A review. Updates Surg. 2016, 68, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaiher, J.; Ravipati, A.; Grams, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Alatise, O.; Are, C. Colorectal cancer-global burden, trends, and geographical variations. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, W.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, B. SPNS 2 promotes the malignancy of colorectal cancer cells via regulating Akt and ERK pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, S.G.; Sadeghi, H.; Dermani, F.K. Targeting the SPHK1/HIF1 Pathway to Inhibit Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells Niche. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2019, 51, 716–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machala, M.; Procházková, J.; Hofmanová, J.; Králiková, L.; Slavík, J.; Tylichová, Z.; Ovesná, P.; Kozubík, A.; Vondráček, J. Colon Cancer and Perturbations of the Sphingolipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.V.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Lin, E.Y. STAT3 and sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammation-associated colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10279–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya, H.; Tamashiro, P.M.; Shimizu, Y.; Iino, K.; Peres, R.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M.; Kawamori, T. Sphingosine Kinase 1 expression in peritoneal macrophages is required for colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, D.; Kitayama, J.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yamashita, H.; Mori, K.; Watanabe, T.; Yatomi, Y.; Nagawa, H. Sphingosine-1-phosphate transactivates c-Met as well as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in human gastric cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2004, 577, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, D.; Takabe, K.; Kapitonov, D.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Targeting SphK1 as a new strategy against cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, J.; Guan, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, M.; Rong, X.; Huang, K.; Huang, J.; Liao, Q. SphK1 confers resistance to apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by downregulating Bim via stimulating Akt/FoxO3a signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuereder, T.; Hoeflmayer, D.; Jaeger-Lansky, A.; Rasin-Streden, D.; Strommer, S.; Fisker, N.; Hansen, B.J.; Crevenna, R.; Wacheck, V. Sphingosine kinase 1 is a relevant molecular target in gastric cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2011, 22, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qu, H.; Gong, W.; Liu, A. Up-regulation and tumor-promoting role of SPHK1 were attenuated by miR-330-3p in gastric cancer. Iubmb Life 2018, 70, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Miao, Z.; Tan, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Hou, W.; Huang, J.; Xu, H. SPHK1-induced autophagy in peritoneal mesothelial cell enhances gastric cancer peritoneal dissemination. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitonov, D.; Allegood, J.C.; Mitchell, C.; Hait, N.C.; Almenara, J.A.; Adams, J.K.; Zipkin, R.E.; Dent, P.; Kordula, T.; Milstien, S. Targeting sphingosine kinase 1 inhibits Akt signaling, induces apoptosis, and suppresses growth of human glioblastoma cells and xenografts. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6915–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.; Pearl, D.K.; Van Brocklyn, J.R. Sphingosine-1-phosphate regulates glioblastoma cell invasiveness through the urokinase plasminogen activator system and CCN1/Cyr61. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2009, 7, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paugh, B.S.; Bryan, L.; Paugh, S.W.; Wilczynska, K.M.; Alvarez, S.M.; Singh, S.K.; Kapitonov, D.; Rokita, H.; Wright, S.; Griswold-Prenner, I.; et al. Interleukin-1 regulates the expression of sphingosine kinase 1 in glioblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Sun, T.; Chen, H.; Han, M.; Wang, D. Potential sphingosine-1-phosphate-related therapeutic targets in the treatment of cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, I.; van Echten-Deckert, G. Sphingosine 1-phosphate-A double edged sword in the brain. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengst, J.A.; Dick, T.E.; Sharma, A.; Doi, K.; Hegde, S.; Tan, S.-F.; Geffert, L.M.; Fox, T.E.; Sharma, A.K.; Desai, D.; et al. SKI-178: A Multitargeted Inhibitor of Sphingosine Kinase and Microtubule Dynamics Demonstrating Therapeutic Efficacy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Models. Cancer Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, T.E.; Hengst, J.A.; Fox, T.E.; Colledge, A.L.; Kale, V.P.; Sung, S.-S.; Sharma, A.; Amin, S.; Loughran, T.P.; Kester, M. The apoptotic mechanism of action of the sphingosine kinase 1 selective inhibitor SKI-178 in human acute myeloid leukemia cell lines. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbčić, P.; Tomljanović, I.; Klobučar, M.; Pavelić, S.K.; Lučin, K.; Sedić, M. Dual sphingosine kinase inhibitor SKI-II enhances sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppression of osteopontin and FAK/IGF-1R signalling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, B.; Sánchez, D.I.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling as a Target in Hepatic Fibrosis Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, B.; Sánchez, D.I.; Crespo, I.; San-Miguel, B.; Álvarez, M.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. Inhibition of the SphK1/S1P signaling pathway by melatonin in mice with liver fibrosis and human hepatic stellate cells. Biofactors 2017, 43, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.; Gao, D.; Fang, Z.-Y. Targeting colorectal cancer cells by a novel sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor PF-543. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Kameyama, H.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. Induction of autophagy by sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor PF-543 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B. Effect of the Sphingosine Kinase 1 Selective Inhibitor, PF543 on Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis in Mice. Dna Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coward, J.; Ambrosini, G.; Musi, E.; Truman, J.-P.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Allegood, J.C.; Wang, E.; Merrill, J.A.H.; Schwartz, G.K. Safingol (L-threo-sphinganine) induces autophagy in solid tumor cells through inhibition of PKC and the PI3-kinase pathway. Autophagy 2009, 5, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.D.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X.W.; Wang, M.H.; Sun, P.; Jiang, J. Role of Sphk1 in the malignant transformation of breast epithelial cells and breast cancer progression. Indian J. Cancer 2014, 51, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Pan, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Kong, X. DMS triggers apoptosis associated with the inhibition of SPHK1/NF-kB activation and increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration in human cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Y.; He, H.; Mai, C. SPHK1 inhibitor suppresses cell proliferation and invasion associated with the inhibition of NF-kB pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, D.R.; Alvarez, S.E.; Paugh, S.W.; Mitra, P.; Yu, J.; Griffiths, R.; Barbour, S.E.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Apoptosis induces expression of sphingosine kinase 1 to release sphingosine-1-phosphate as a “come-and-get-me” signal. Faseb J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 2629–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, M.A.; Carvajal, R.D.; Merrill, A.H.; Gonen, M.; Cane, L.M.; Schwartz, G.K. A phase I clinical trial of safingol in combination with cisplatin in advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Man, K.; Ho, J.W.; Wang, X.H.; Poon, R.T.P.; Xu, Y.; Ng, K.T.; Chu, A.C.; Sun, C.K.; Ng, I.O. FTY720: A promising agent for treatment of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8458–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, H.; Takahara, S.; Horie, S.; Muto, S.; Otsuki, Y.; Katsuoka, Y. Induction of apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo caused by FTY720 treatment. J. Urol. 2003, 169, 2372–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pchejetski, D.; Bohler, T.; Brizuela, L.; Sauer, L.; Doumerc, N.; Golzio, M.; Salunkhe, V.; Teissié, J.; Malavaud, B.; Waxman, J. FTY720 (fingolimod) sensitizes prostate cancer cells to radiotherapy by inhibition of sphingosine kinase-1. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8651–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qi, Y.; Wadham, C.; Wang, L.; Warren, A.; Di, W.; Xia, P. FTY720 induces necrotic cell death and autophagy in ovarian cancer cells: A protective role of autophagy. Autophagy 2010, 6, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Frissora, F.; Ma, Y.; Santhanam, R.; Jarjoura, D.; Lehman, A.; Perrotti, D.; Chen, C.-S.; Dalton, J.T. FTY720 demonstrates promising preclinical activity for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2008, 111, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Ding, K.; Xu, J. FTY720 reduces migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cell lines via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10707–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymiczek, A.; Pastorino, S.; Larson, D.; Tanji, M.; Pellegrini, L.; Xue, J.; Li, S.; Giorgi, C.; Pinton, P.; Takinishi, Y.; et al. FTY720 inhibits mesothelioma growth in vitro and in a syngeneic mouse model. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.J.; MacRitchie, N.; Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S.; Bittman, R. Synthesis of selective inhibitors of sphingosine kinase 1. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2136–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Peterson, Y.K.; Smith, R.A.; Smith, C.D. Characterization of isoenzyme-selective inhibitors of human sphingosine kinases. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beljanski, V.; Knaak, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Smith, C.D. Combined anticancer effects of sphingosine kinase inhibitors and sorafenib. Investig. New Drugs 2011, 29, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.S.; Voelkel-Johnson, C.; Smith, C.D. Suppression of c-Myc and RRM2 expression in pancreatic cancer cells by the sphingosine kinase-2 inhibitor ABC294640. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60181–60192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.J.; Zhuang, Y.; Maines, L.W.; Gao, P.; Wang, W.; Beljanski, V.; Upson, J.J.; Green, C.L.; Keller, S.N.; Smith, C.D. Pharmacology and antitumor activity of ABC294640, a selective inhibitor of sphingosine kinase-2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 333, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, M.R.; Powell, J.A.; Coolen, C.; Moretti, P.A.B.; Zebol, J.R.; Pham, D.H.; Finnie, J.W.; Don, A.S.; Ebert, L.M.; Bonder, C.S.; et al. A selective ATP-competitive sphingosine kinase inhibitor demonstrates anti-cancer properties. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7065–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, D.J.; Li, Y.; Brown, M.L.; Min, X.; Schmitt, M.J.; Wanska, M.; Wang, X.; Connors, R.; Johnstone, S.; Cardozo, M. Structure guided design of a series of sphingosine kinase (SphK) inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4608–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rex, K.; Jeffries, S.; Brown, M.L.; Carlson, T.; Coxon, A.; Fajardo, F.; Frank, B.; Gustin, D.; Kamb, A.; Kassner, P.D. Sphingosine kinase activity is not required for tumor cell viability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Kumazoe, M.; Huang, Y.; Lesnick, C.; Kay, N.E.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Tachibana, H. SphK1 inhibitor potentiates the anti-cancer effect of EGCG on leukaemia cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 178, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sak, K.; Everaus, H. Established Human Cell Lines as Models to Study Anti-leukemic Effects of Flavonoids. Curr. Genom. 2017, 18, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.-H.; Chen, M.-B.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wu, M.-H.; Li, W.-T.; Wei, M.-X.; Liu, C.-Y.; Qin, S.-K. Identification of sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) as a primary target of icaritin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.-Q.; Gao, H.; Han, M.; Liu, K.-L.; Peng, J.-J.; Han, Y.-T. Hispidulin suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma by modulating ceramide-sphingosine 1-phosphate rheostat. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1501. [Google Scholar]
- Funaki, M.; Kitabayashi, J.; Shimakami, T.; Nagata, N.; Sakai, Y.; Takegoshi, K.; Okada, H.; Murai, K.; Shirasaki, T.; Oyama, T. Peretinoin, an acyclic retinoid, inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis by suppressing sphingosine kinase 1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-O.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, M.-S.; Lee, H.-J. Anti-cancer effect of pristimerin by inhibition of HIF-1a involves the SPHK-1 pathway in hypoxic prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, I.; Musman, M.; Ohtani, I.I.; Ichiba, T.; Tanaka, J.; Gravalos, D.G.; Higa, T. Pachastrissamine, a cytotoxic anhydrophytosphingosine from a marine sponge, Pachastrissa sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1505–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canals, D.; Mormeneo, D.; Fabrià s, G.; Llebaria, A.; Casas, J.; Delgado, A. Synthesis and biological properties of Pachastrissamine (jaspine B) and diastereoisomeric jaspines. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.Y. Pachastrissamine from Pachastrissa sp. Inhibits Melanoma Cell Growth by Dual Inhibition of Cdk2 and ERK-mediated FOXO3 Downregulation. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Yue, S.; Li, L. Involvement of sphingosine 1-phosphate (SIP)/S1P3 signaling in cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustberg, M.B.; Pant, S.; Ruppert, A.S.; Shen, T.; Wei, Y.; Chen, L.; Brenner, L.; Shiels, D.; Jensen, R.R.; Berger, M.; et al. Phase I/II trial of non-cytotoxic suramin in combination with weekly paclitaxel in metastatic breast cancer treated with prior taxanes. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.D.; Clemens, J.J.; Macdonald, T.L.; Lynch, K.R. Sphingosine 1-phosphate analogs as receptor antagonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9833–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L.; Wu, X.; Qiu, L.; Di, W. Sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)/S1P receptor axis is involved in ovarian cancer angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74947–74961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, G.T.; Maceyka, M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer, inflammation and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, F.; Lim, K.G.; Loveridge, C.; Long, J.; Pitson, S.M.; Tigyi, G.; Bittman, R.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J. FTY720 and (S)-FTY720 vinylphosphonate inhibit sphingosine kinase 1 and promote its proteasomal degradation in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle, breast cancer and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Billich, A.; Baumruker, T.; Heining, P.; Schmouder, R.; Francis, G.; Aradhye, S.; Burtin, P. Fingolimod (FTY720): Discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.W.Y.; Man, K.; Sun, C.K.; Lee, T.K.; Poon, R.T.P.; Fan, S.T. Effects of a novel immunomodulating agent, FTY720, on tumor growth and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Ma, D.H.; Han, Y. FTY720 enhances chemosensitivity of colon cancer cells to doxorubicin and etoposide via the modulation of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance protein 1. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.-Y.; Chiu, C.-F.; Chiu, S.-J.; Chu, P.-C.; Weng, J.-R. FTY720 Induces Autophagy-Associated Apoptosis in Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells, in Part, through a Reactive Oxygen Species/Mcl-1-Dependent Mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.; Alshaker, H.; Cooper, C.; Winkler, M.; Pchejetski, D. The emerging role of FTY720 (Fingolimod) in cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 23106–23127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bexiga, C.; Nejo, P.; Oliveira, I.; Rodrigues, P.; Pereira, P.; Fragoso, S.; Mayer, A.; Parreira, J.; Santos, S.; Louro, P.; et al. When BRCA2-breast cancer is more prevalent than BRCA1-breast cancer: Prospective follow-up data from a multidisciplinary program. Cancer Res. 2020, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, Y.N. Ozanimod: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappos, L.; Bar-Or, A.; Cree, B.A.; Fox, R.J.; Giovannoni, G.; Gold, R.; Vermersch, P.; Arnold, D.L.; Arnould, S.; Scherz, T. Siponimod versus placebo in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (EXPAND): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbadini, R.A. Sphingosine-1-phosphate antibodies as potential agents in the treatment of cancer and age-related macular degeneration. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, B.; Vekich, J.A.; Sibbald, B.J.; Cavalli, A.L.; Moreno, K.M.; Matteo, R.G.; Garland, W.A.; Lu, Y.; Yu, S.; Hall, H.S. Validation of an anti-sphingosine-1-phosphate antibody as a potential therapeutic in reducing growth, invasion, and angiogenesis in multiple tumor lineages. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Bullock, A.J.; Callea, M.; Shah, H.; Song, J.; Moreno, K.; Visentin, B.; Deutschman, D.; Alsop, D.C.; et al. Anti-S1P Antibody as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for VEGFR TKI-Resistant Renal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.S.; Pal, S.K.; Drabkin, H.A.; Hainsworth, J.D.; Dorr, A.; Atkins, M.B.; Mier, J.W.; Wang, X.; Sabbadini, R.A.; Paggiarino, D. A multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study of the S1P inhibitor sonepcizumab (LT1009) in patients with previously treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, TPS4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.J.; Schrecengost, R.S.; Lee, B.D.; Zhuang, Y.; Smith, S.N.; Eberly, J.L.; Yun, J.K.; Smith, C.D. Discovery and evaluation of inhibitors of human sphingosine kinase. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5962–5969. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Weng, W.; Sun, Z.-X.; Fu, X.-J.; Ma, J.; Zhuang, W.-F. SphK1 inhibitor II (SKI-II) inhibits acute myelogenous leukemia cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Xin, C.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. A novel mode of action of the putative sphingosine kinase inhibitor 2-(p-hydroxyanilino)-4-(p-chlorophenyl) thiazole (SKI II): Induction of lysosomal sphingosine kinase 1 degradation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sk, U.H.; Gimbor, M.A.; Hengst, J.A.; Wang, X.; Yun, J.; Amin, S. Synthesis and bioactivity of sphingosine kinase inhibitors and their novel aspirinyl conjugated analogs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4149–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.R. Building a better sphingosine kinase-1 inhibitor. Biochem. J. 2012, 444, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnute, M.E.; McReynolds, M.D.; Kasten, T.; Yates, M.; Jerome, G.; Rains, J.W.; Hall, T.; Chrencik, J.; Kraus, M.; Cronin, C.N. Modulation of cellular S1P levels with a novel, potent and specific inhibitor of sphingosine kinase-1. Biochem. J. 2012, 444, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, A.; Kohama, T.; Tu, Z.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Purification and characterization of rat kidney sphingosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12576–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr Gandy, K.A.; Obeid, L.M. Targeting the sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate pathway in disease: Review of sphingosine kinase inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsall, L.C.; Van Brocklyn, J.R.; Cuvillier, O.; Kleuser, B.; Spiegel, S. N, N-Dimethylsphingosine is a potent competitive inhibitor of sphingosine kinase but not of protein kinase C: Modulation of cellular levels of sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 12892–12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coward, J.; Truman, J.-P.; Ambrosini, G.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Schwartz, G.K. Safingol, an inhibitor of sphingosine kinase, stimulates autophagy in a ceramide-independent and phosphatidylinositol (PI)-3 kinase-mediated manner. AACR 2005, 46, 784–785. [Google Scholar]
- Jendiroba, D.B.; Klostergaard, J.; Keyhani, A.; Pagliaro, L.; Freireich, E.J. Effective cytotoxicity against human leukemias and chemotherapy-resistant leukemia cell lines by N-N-dimethylsphingosine. Leuk. Res. 2002, 26, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, E.A.; Sakakura, C.; Shirahama, T.; Masamune, A.; Ohta, H.; Hakomori, S.I.; Igarashi, Y. Sphingosine and its methylated derivative N, N-dimethylsphingosine (DMS) induce apoptosis in a variety of human cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, V.E.; Cuvillier, O.; Edsall, L.C.; Kimura, K.; Milstien, S.; Gelmann, E.P.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine enhances apoptosis of radiation-resistant prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4468–4474. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Li, W.; Ren, L.; Liu, J.; Pang, X.; Chen, X.; Kang, D.; Wang, J.; Du, G. The sphingosine kinase-1/sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer: Potential target for anticancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 195, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sugiura, M.; Nava, V.E.; Edsall, L.C.; Kono, K.; Poulton, S.; Milstien, S.; Kohama, T.; Spiegel, S. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel mammalian sphingosine kinase type 2 isoform. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19513–19520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.L.; Lynch, K.R. Drugging sphingosine kinases. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Tao, Y.-F.; Xu, L.-X.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.-L.; Fang, F.; Wu, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.-H.; Du, W.-W.; et al. A novel sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor (SKI-5C) induces cell death of Wilms’ tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 4548–4563. [Google Scholar]
- Kornienko, A.; Evidente, A.; Vurro, M.; Mathieu, V.R.; Cimmino, A.; Evidente, M.; van Otterlo, W.A.L.; Dasari, R.; Lefranc, F.; Kiss, R. Toward a Cancer Drug of Fungal Origin. Med. Res. Rev. 2015, 35, 937–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Hartung, H.-P. Mechanism of action of oral fingolimod (FTY720) in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 33, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristóbal, I.; Madoz-Gúrpide, J.; Manso, R.; González-Alonso, P.; Rojo, F.; García-Foncillas, J. Potential anti-tumor effects of FTY720 associated with PP2A activation: A brief review. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullershausen, F.; Zecri, F.D.R.; Cetin, C.; Billich, A.; Guerini, D.; Seuwen, K. Persistent signaling induced by FTY720-phosphate is mediated by internalized S1P1 receptors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.-D.; Ji, X.-J.; Cong, Z.-X.; Zhu, J.-H.; Zhou, Y. FTY720 for cancer therapy. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, T.; Hagihara, K.; Satoh, R.; Sugiura, R. More than Just an Immunosuppressant: The Emerging Role of FTY720 as a Novel Inducer of ROS and Apoptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4397159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, H.; Takahara, S.; Ichimaru, N.; Wang, J.D.; Itoh, Y.; Otsuki, Y.; Morimoto, J.; Fukui, R.; Hoshiga, M.; Ishihara, T. Marked prevention of tumor growth and metastasis by a novel immunosuppressive agent, FTY720, in mouse breast cancer models. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patmanathan, S.N.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G.; Paterson, I.C. The antineoplastic properties of FTY720: Evidence for the repurposing of fingolimod. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, H.; Hideshima, T.; Raje, N.; Roccaro, A.M.; Shiraishi, N.; Kumar, S.; Hamasaki, M.; Ishitsuka, K.; Tai, Y.-T.; Podar, K. FTY720 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells and overcomes drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7478–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.M.; Seo, B.R.; Min, K.-J.; Kwon, T.K. FTY720 enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by up-regulating DR5 and down-regulating Mcl-1 in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11614–11626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Liang, Y.; Yin, D.; Song, R.; Pei, T.; Pan, S.; Jiang, H.; Liu, L. FTY720 inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma by inactivating STAT3 signaling. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.A.; Chou, C.C.; Berman-Booty, L.D.; Ma, Y.; Hung, J.H.; Wang, D.; Kogure, T.; Patel, T.; Terracciano, L.; Muthusamy, N. Antitumor effects of OSU-2S, a nonimmunosuppressive analogue of FTY720, in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.J.; MacRitchie, N.; Anthony, N.G.; Mackay, S.P.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J.; Bittman, R. Structure-Activity Relationships and Molecular Modeling of Sphingosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9310–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.S.; Voelkel-Johnson, C.; Smith, C.D. Targeting Sphingosine Kinases for the Treatment of Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 140, 295–325. [Google Scholar]
- Beljanski, V.; Knaak, C.; Smith, C.D. A novel sphingosine kinase inhibitor induces autophagy in tumor cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 333, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Bai, A.; Smith, C.D.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Yu, F.; Qin, Z. ABC294640, A Novel Sphingosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor, Induces Oncogenic Virus-Infected Cell Autophagic Death and Represses Tumor Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Chaiteerakij, R.; Moser, C.D.; Shaleh, H.; Boakye, J.; Chen, G.; Ndzengue, A.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S. Antitumor effect of the novel sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor ABC294640 is enhanced by inhibition of autophagy and by sorafenib in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-C.; Hou, M.-F.; Huang, H.-W.; Chang, F.-R.; Yeh, C.-C.; Tang, J.-Y.; Chang, H.-W. Marine algal natural products with anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L. Natural products in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman, D.J. Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, M.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Roy, S.; Mandal, C. Natural products: Promising resources for cancer drug discovery. Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, Y.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Development of small-molecule inhibitors of sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 132, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Sarkar, J.; Chakraborti, T.; Chakraborti, S. Role of Spm-Cer-S1P signalling pathway in MMP-2 mediated U46619-induced proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: Protective role of epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2015, 33, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, L.A.; Di Vito, C.; Marfia, G.; Ferraretto, A.; Tringali, C.; Viani, P.; Riboni, L. Sphingosine kinase 2 and ceramide transport as key targets of the natural flavonoid luteolin to induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143384. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.C.; Subedi, L.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, K.H. Bioactive compounds from the seeds of Amomum tsaoko Crevost et Lemaire, a Chinese spice as inhibitors of sphingosine kinases, SPHK1/2. Rsc Adv. 2019, 9, 33957–33968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-J.; Yan, Y.-Y.; Sun, H.-M.; Liu, Y.; Su, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-B.; Zhang, J.-Y. Anti-Cancer Effects of Pristimerin and the Mechanisms: A Critical Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Ding, S.-F. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes the proliferation and attenuates apoptosis of Endothelial progenitor cells via S1PR1/S1PR3/PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, Y.; Mathews, T.P.; Gellett, A.M.; Tomsig, J.L.; Kennedy, P.C.; Moyer, M.L.; Macdonald, T.L.; Lynch, K.R. Sphingosine kinase type 1 inhibition reveals rapid turnover of circulating sphingosine 1-phosphate. Biochem. J. 2011, 440, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class | Compound | Target (IC50) | Specificity | Experimental Model | Highest Testing Phase | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitors of SphK1 | SKI-I | SphK1 (10 µM) | Yes | Acute myeloid leukemia cells | Preclinical | Induces apoptotic cell death. Decreases cancer progression, angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis | [140,141] |
| SKI-II | SphK1 (16 µM) SphK2 (8 µM) | No | HepG2 cells BDL or CCl4-treated mice model of hepatic fibrosis | Preclinical | Inhibits tumorigenesis in xenograft and fibrosis mice model. Induces apoptosis with antiproliferative effects in different cancer cell lines | [142,143] | |
| PF-543 | SphK1 (3.6 nM) | Yes | Hepatic fibrosis mice model, Colorectal carcinoma, head, and neck squamous carcinoma and breast cancer cells. | Preclinical | Inhibits fibrogenesis in hepatic fibrosis mice model and human hepatic stellate cells. Inhibits cell proliferation and imparts cytotoxicity in various cancer cell lines | [144,145,146,147] | |
| DMS | SphK1, SphK2 (<1.0 mM) | No | Histiocyticlymphoma, Jurkat and leukemia, lung, breast, hepatocellular carcinoma (SK-Hep1 and MHCCLM3) cells | Preclinical | Induces apoptosis and delays cancer progression in various human cancer cell lines | [148,149,150,151] | |
| DHS (Safingol) | SphK1 (5 μM) | No | Jurkat and leukemia cells (U937), metastatic solid tumor | Phase I clinical trial in combination with cisplatin for solid tumors | Decreases cell proliferation, invasion and inhibits tumorigenesis | [152,153] | |
| FTY720 (Fingolimod) S1P receptor-independent | SphK1 (5.0–12.5 μM) | No | Liver cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, glioblastoma, leukemia, and malignant mesothelioma cells | FDA-approved and launched for clinical use (2010) to treat multiple sclerosis | Decreases colitis and cancer progression Antiproliferative and antimetastatic effects in various cancer cell lines. | [154,155,156,157,158,159,160] | |
| RB-005 and RB-019 | SphK1 (IC50 = 3.6 µM) | Yes | Proliferating human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMC) | Biological testing | Inhibits proliferative diseases, including PAH (pulmonary arterial hypertension) | [161] | |
| ABC294735 | SphK1, SphK2 (10 μM) | No | Pancreatic cancer cell s (BxPC-3) and Renal cancer cells (A498) (combination with Sorafenib) | Preclinical | Delays tumorigenesis in xenograft models. Exerts antiproliferative and cytotoxic activity in cancer cell lines. | [162,163] | |
| ABC294640 | SphK2 (9.0 μM) | Yes | Pancreatic cancer Cholangiocarcinoma cells (HuCCT1, OZ, HuH28, EGI-1, WITT, and LIV27) | Phase I clinical trial for different cancer | Decreases liver transplant graft injury and rheumatoid arthritis. Attenuates tumor proliferation in human cancer cell lines | [164,165] | |
| MP-A08 | SphK1 (6.9 mM) SphK2 (27 mM) | Yes | Human lung adenocarcinoma (A549) xenograft model) | Preclinical | Induces tumor cell apoptosis and inhibits tumor angiogenesis in a mouse xenograft model | [66,166] | |
| Amgen 82 | SphK1 (20 nM) SphK2 (14 nM) | No | Tumor xenograft mice model | Preclinical | Attenuate S1P intracellular levels with no appreciable effect on cell viability at therapeutic concentrations; promotes cell death only at higher concentrations | [167,168] | |
| EGCG | SphK1 (75 μM) | No | Myeloid leukemia cells (K562, HL-60 and Kasumi-3) | Biological testing | Polyphenon E induces cell death in chronic myeloid acute myeloid leukemia cells. EGCG/safingol combination suppresses viable cell number in Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell lines | [169,170] | |
| Icaritin | SphK1 | No | Hepatocellular carcinoma cells (Huh-7, HepG2, and KYN-2) | Biological testing | Imparts cytotoxicity, enhances and hinders tumorigenesis in liver cancer cell lines | [171] | |
| Hispidulin | SphK1 | No | Renal carcinoma cells (A498 and Caki-2) | Biological testing | Inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in kidney cancer cell lines | [172] | |
| Ellagic acid | SphK1 | No | Adenocarcinoma alveolar cells (A549) | Biological testing | Imparts cytotoxicity in NSCLC (Non-small cell lung cancer)cell lines | [69] | |
| Peretinoin | SphK1 | No | Hepatoma cell line (Huh-7) | Biological testing | Suppresses cancer progression in liver cancer cell line | [173] | |
| Pristimerin | SphK1 | Prostate cancer cell line (PC-3), breast cancer stem cells and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) | Biological testing | Inhibits HIF-1α accumulation in a hypoxic prostate cancer cell line. Imparts toxicity in cancer stem cells | [174] | ||
|
Pachastrissa mine | SphK1, SphK2 (4.6 µM) | No | Skin cancer cells (A375 and B16F10 cell), Melanoma tumor xenograft mice model | Biological testing | Imparts cytotoxicity and accelerates apoptosis in melanoma cell lines. Suppresses melanoma cell growth in mice model | [175,176,177] | |
| Antagonists and Agonists of S1P receptors | Suramin | An antagonist of S1PR3 and S1PR5 (50–100 µM) | Yes | CCl4/BDL-induced liver fibrosis in mice | Phase I/II clinical trial | Impedes liver fibrogenesis Elicits anti-tumor activity in breast cancer cells | [178,179] |
| VPC23019 and its analogs | Antagonists of S1PR1 (50 nM) and S1PR3 (100 nM) | Yes | Endothelial progenitor cells, ovarian cancer cells and urinary bladder carcinoma cell line Ovarian cancer xenograft mice model | Preclinical | Inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in endothelial progenitor cells. Inhibit the endothelial cell migration, invasion, tumor growth and angiogenesis in cancer cell lines | [180,181] | |
| FTY720 (Fingolimod) | S1PR1 agonist and functional antagonist, an Agonist of S1PR3, S1PR4, and S1PR5 (=0.2–6 nM) | Yes | Liver, breast, prostate, bladder, leukemia, colon and ovarian cancer cell lines Xenograft mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma, bladder and lung cancer | FDA-approved drug to treat multiple sclerosis | Imparts immunosuppressive effects Arrests growth and induces apoptosis in cancer cell lines. Suppresses tumor growth in various mice xenograft models | [155,158,182,183,184,185,186,187,188] | |
| Ozanimod (RPC1083) | S1PR1 (0.16 nM) and S1PR5 agonist | Yes | LNCaP, PC-3, and DU-145 cellular models of prostate cancer | FDA-approved for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, under evaluation for use in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease in multinational phase III trials, under pre-clinical evaluation for anticancer effects in cellular models of prostate cancer | Inhibits the colony formation and migratory characteristics of PCa cells. Induces apoptosis in PC-3 and DU-145 cells | [189,190] | |
| Siponimod (BAF312) | S1PR1 and S1PR5 modulator | Yes | Recommended for secondary progressive multiple sclerosis | [191] | |||
| S1P-blocking antibodies | ASONEPTM (sonepcizumab/LT1009) | S1P-blocking antibody (IC50 = 100 pM) | Yes | Subcutaneous murine melanoma B16-F10 allograft, human lung A549 and ovarian SKOV3 xenograft models | Phase I clinical trial for solid tumors | Reduces the tumor-associated migration and angiogenesis in murine xenograft and allograft model | [192,193,194,195] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, P.; Taiyab, A.; Hussain, A.; Alajmi, M.F.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Targeting the Sphingosine Kinase/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Axis in Drug Discovery for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081898
Gupta P, Taiyab A, Hussain A, Alajmi MF, Islam A, Hassan MI. Targeting the Sphingosine Kinase/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Axis in Drug Discovery for Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2021; 13(8):1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081898
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Preeti, Aaliya Taiyab, Afzal Hussain, Mohamed F. Alajmi, Asimul Islam, and Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan. 2021. "Targeting the Sphingosine Kinase/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Axis in Drug Discovery for Cancer Therapy" Cancers 13, no. 8: 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081898
APA StyleGupta, P., Taiyab, A., Hussain, A., Alajmi, M. F., Islam, A., & Hassan, M. I. (2021). Targeting the Sphingosine Kinase/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Axis in Drug Discovery for Cancer Therapy. Cancers, 13(8), 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081898








