Intracellular Autofluorescence as a New Biomarker for Cancer Stem Cells in Glioblastoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.3. Cell Sorting
2.4. Neurosphere Formation Assay
2.5. In Vitro Limiting Dilution Assay (LDA)
2.6. Temozolomide (TMZ) and Radiation Treatment
2.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.8. Riboflavin, Fumitremorgin C, and Basal Medium Treatments
2.9. In Vivo GBM Xenografts
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Autofluorescent Cells in Primary GBM Cultures
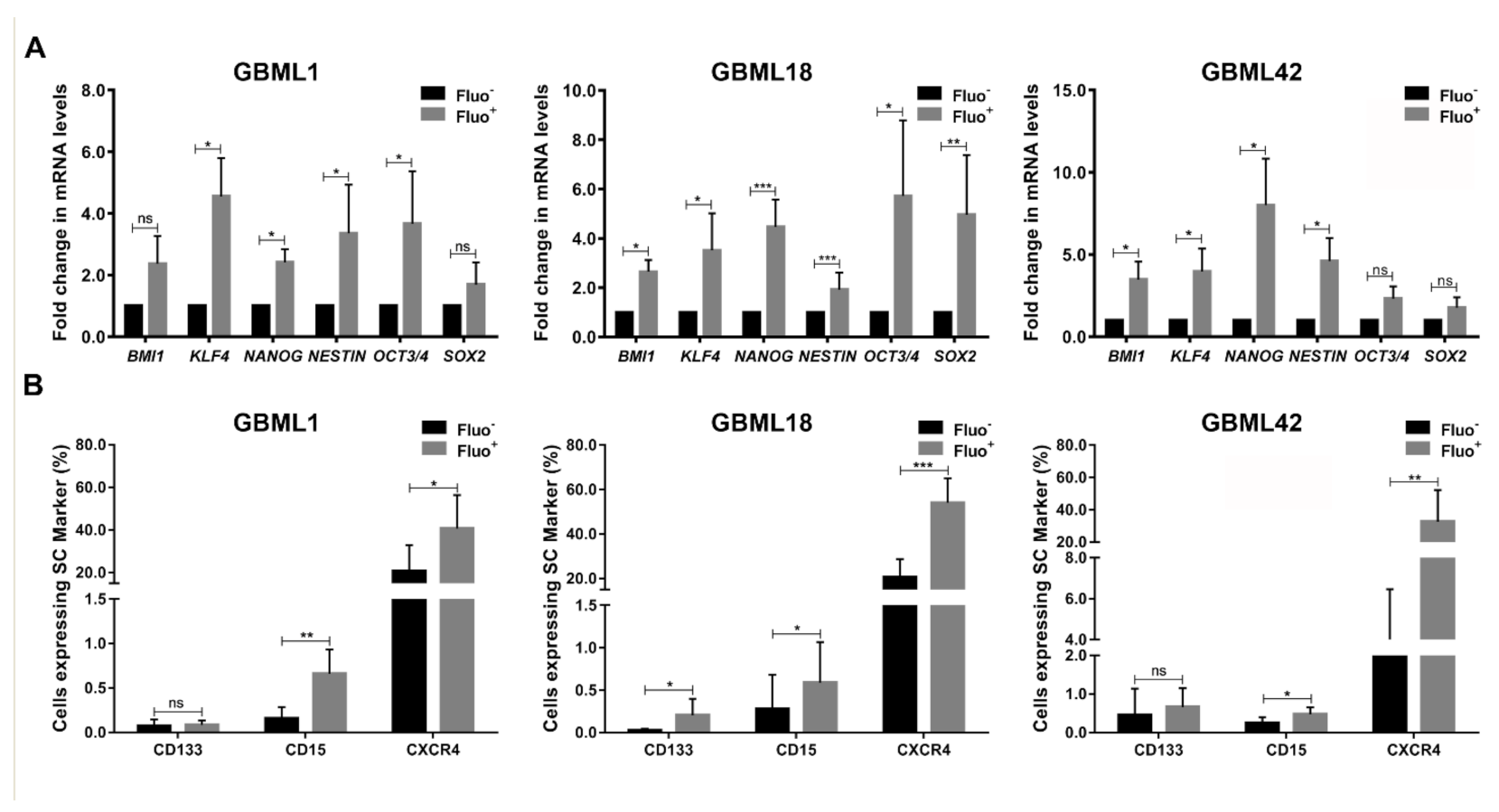
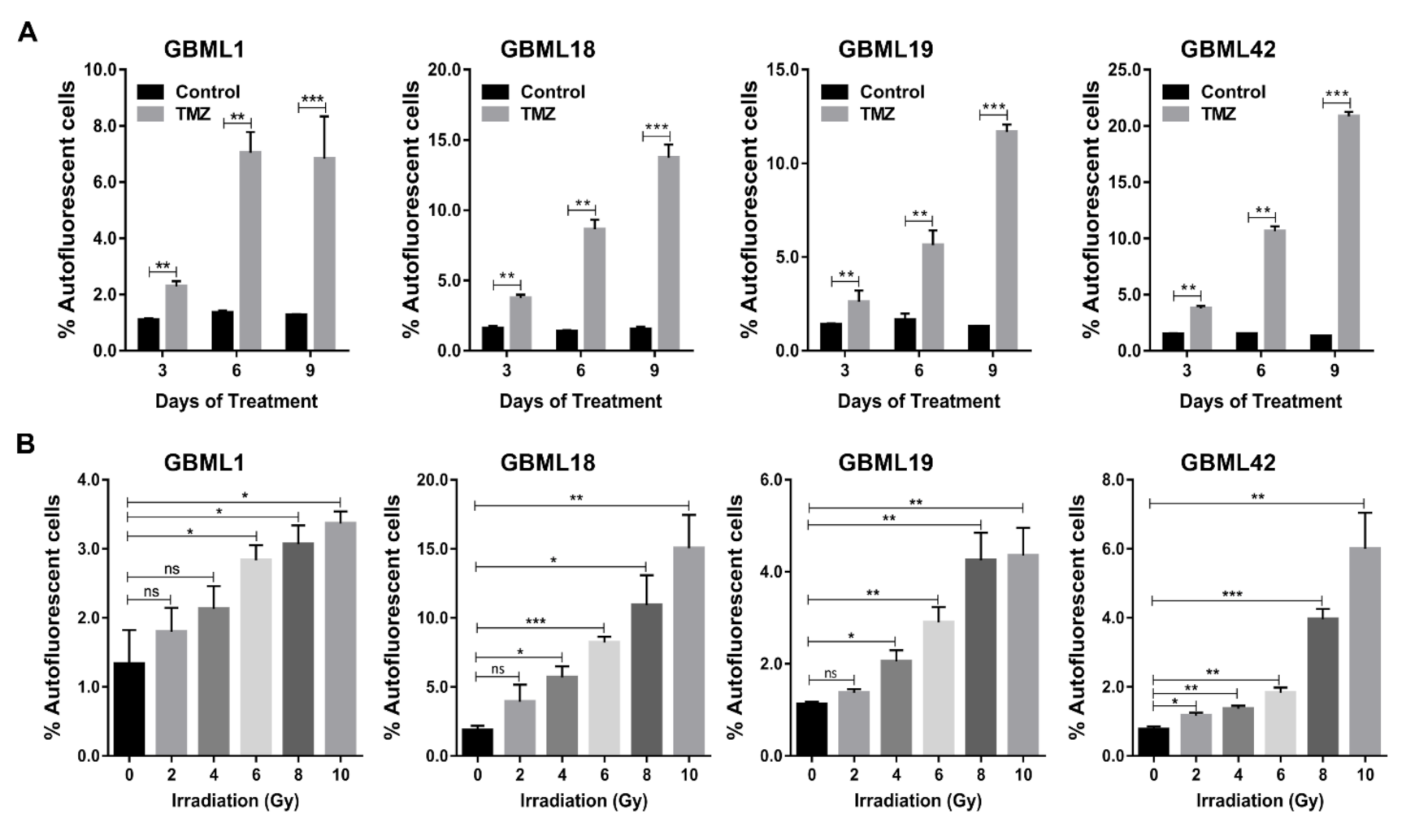
3.2. Autofluorescent Cells Present Hallmark Characteristics of GBM Stem Cells
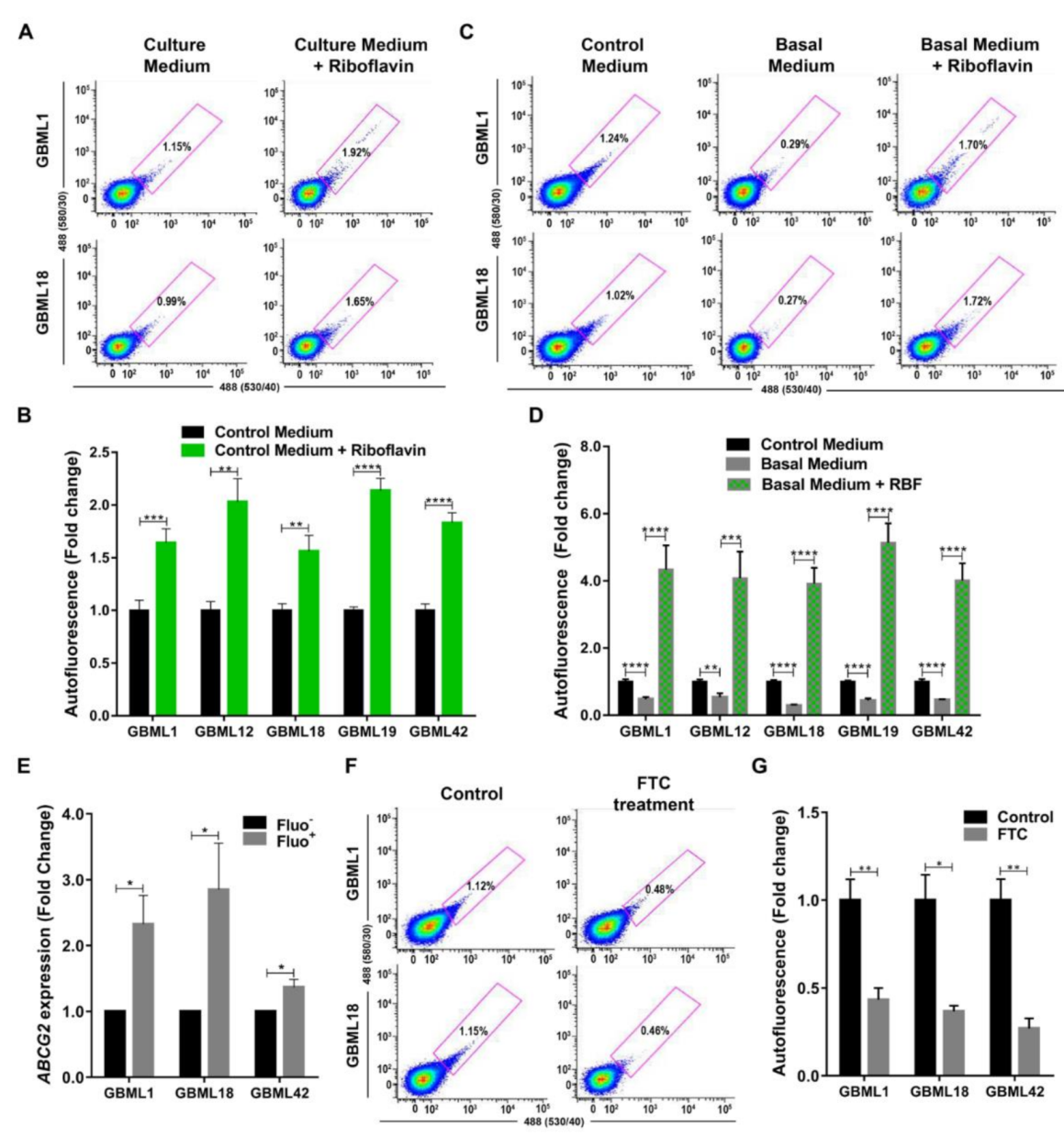
3.3. Riboflavin is a Major Source of Intracellular Autofluorescence in GSCs
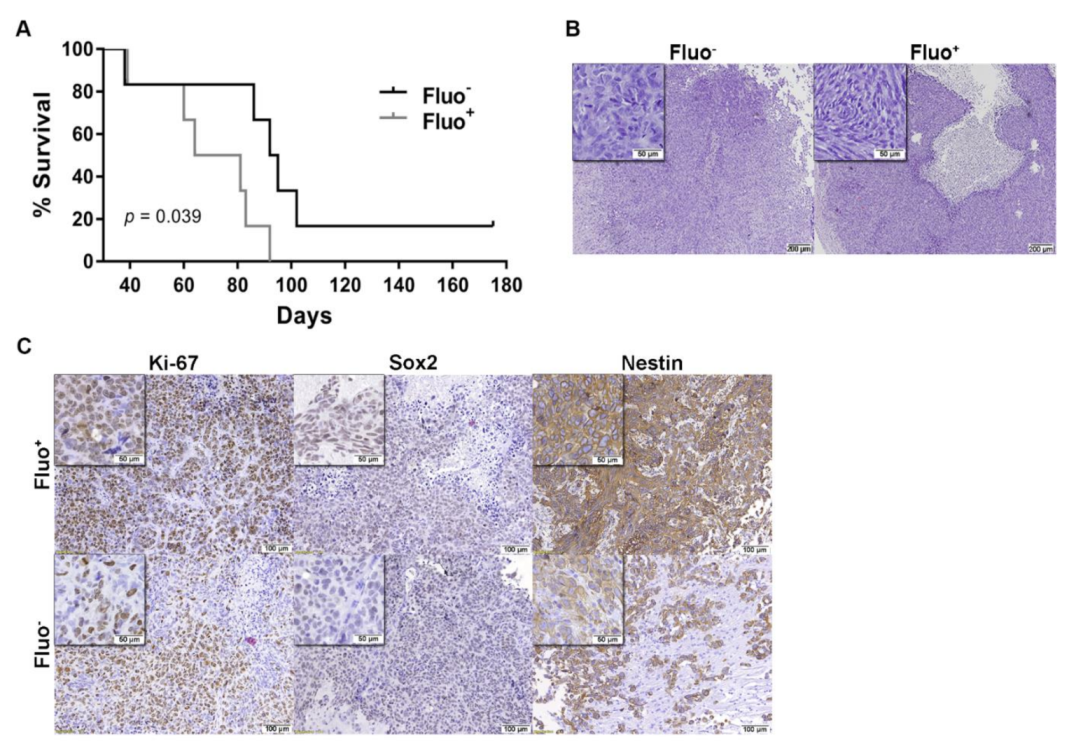
3.4. Autofluorescence GSCs are Associated with Tumor Aggressiveness in GBM Xenografts Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Fisher, J.L.; Aldape, K.D.; Wrensch, M. Epidemiology and molecular pathology of glioma. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006, 2, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnari, F.B.; Fenton, T.; Bachoo, R.M.; Mukasa, A.; Stommel, J.M.; Stegh, A.; Hahn, W.C.; Ligon, K.L.; Louis, D.N.; Brennan, C.; et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2683–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnet, N.G.; Jefferies, S.J.; Benson, R.J.; Hunt, D.P.; Treasure, F.P. Years of life lost (YLL) from cancer is an important measure of population burden--and should be considered when allocating research funds. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Clarke, I.D.; Terasaki, M.; Bonn, V.E.; Hawkins, C.; Squire, J.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5821–5828. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.S.; McKay, R.M.; Burns, D.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 2012, 488, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCord, A.M.; Jamal, M.; Williams, E.S.; Camphausen, K.; Tofilon, P.J. CD133+ glioblastoma stem-like cells are radiosensitive with a defective DNA damage response compared with established cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5145–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y. Inhibition of Autophagy by Chloroquine Enhances the Antitumor Efficacy of Sorafenib in Glioblastoma. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, R.; Binda, E.; Orfanelli, U.; Cipelletti, B.; Gritti, A.; De Vitis, S.; Fiocco, R.; Foroni, C.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A. Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.U.; Auffinger, B.; Lesniak, M.S. Understanding glioma stem cells: Rationale, clinical relevance and therapeutic strategies. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2013, 13, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira de Castro, J.; Gonçalves, C.S.; Hormigo, A.; Costa, B.M. Exploiting the complexities of glioblastoma stem cells: Insights for cancer initiation and therapeutic targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicha, M.S.; Liu, S.; Dontu, G. Cancer stem cells: An old idea—A paradigm shift. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capela, A.; Temple, S. LeX is expressed by principle progenitor cells in the embryonic nervous system, is secreted into their environment and binds Wnt-1. Dev. Biol. 2006, 291, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capela, A.; Temple, S. LeX/ssea-1 is expressed by adult mouse CNS stem cells, identifying them as nonependymal. Neuron 2002, 35, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.C.; Roy, N.S.; Keyoung, H.M.; Goodman, R.R.; McKhann, G., 2nd; Jiang, L.; Kang, J.; Nedergaard, M.; Goldman, S.A. Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the adult human brain. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Van Meir, E.G. Brain cancer propagating cells: Biology, genetics and targeted therapies. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Lorenzo, I.; Dorado, J.; Lonardo, E.; Alcala, S.; Serrano, A.G.; Clausell-Tormos, J.; Cioffi, M.; Megias, D.; Zagorac, S.; Balic, A.; et al. Intracellular autofluorescence: A biomarker for epithelial cancer stem cells. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pojo, M.; Goncalves, C.S.; Xavier-Magalhaes, A.; Oliveira, A.I.; Goncalves, T.; Correia, S.; Rodrigues, A.J.; Costa, S.; Pinto, L.; Pinto, A.A.; et al. A transcriptomic signature mediated by HOXA9 promotes human glioblastoma initiation, aggressiveness and resistance to temozolomide. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7657–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.S.; Vieira de Castro, J.; Pojo, M.; Martins, E.P.; Queirós, S.; Chautard, E.; Taipa, R.; Pires, M.M.; Pinto, A.A.; Pardal, F.; et al. WNT6 is a Novel Oncogenic Prognostic Biomarker in Human Glioblastoma. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4805–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, H.D.; Nakano, I.; Lazareff, J.A.; Masterman-Smith, M.; Geschwind, D.H.; Bronner-Fraser, M.; Kornblum, H.I. Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15178–15183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Porath, I.; Thomson, M.W.; Carey, V.J.; Ge, R.; Bell, G.W.; Regev, A.; Weinberg, R.A. An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suva, M.L.; Rheinbay, E.; Gillespie, S.M.; Patel, A.P.; Wakimoto, H.; Rabkin, S.D.; Riggi, N.; Chi, A.S.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; et al. Reconstructing and reprogramming the tumor-propagating potential of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cell 2014, 157, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunici, P.; Bissola, L.; Lualdi, E.; Pollo, B.; Cajola, L.; Broggi, G.; Sozzi, G.; Finocchiaro, G. Genetic alterations and in vivo tumorigenicity of neurospheres derived from an adult glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2004, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guryanova, O.A.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Lathia, J.D.; Huang, Z.; Yang, J.; MacSwords, J.; Eyler, C.E.; McLendon, R.E.; Heddleston, J.M.; et al. Nonreceptor tyrosine kinase BMX maintains self-renewal and tumorigenic potential of glioblastoma stem cells by activating STAT3. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, Z.; Tunici, P.; Ng, H.; Abdulkadir, I.R.; Lu, L.; Irvin, D.; Black, K.L.; Yu, J.S. Analysis of gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffinger, B.; Spencer, D.; Pytel, P.; Ahmed, A.U.; Lesniak, M.S. The role of glioma stem cells in chemotherapy resistance and glioblastoma multiforme recurrence. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.A.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.J.; Park, K.; Yang, H.; Jin, J.; Joo, K.M.; et al. Wnt activation is implicated in glioblastoma radioresistance. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohsaka, S.; Hinohara, K.; Wang, L.; Nishimura, T.; Urushido, M.; Yachi, K.; Tsuda, M.; Tanino, M.; Kimura, T.; Nishihara, H.; et al. Epiregulin enhances tumorigenicity by activating the ERK/MAPK pathway in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, V.; Marino, D.; Cudalbu, C.; Hamou, M.; Mlynarik, V.; de Tribolet, N.; Dietrich, P.; Gruetter, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Radovanovic, I. Retraction: Marker-independent identification of glioma-initiating cells. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mack, S.C.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Valentim, C.L.; Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Auffinger, B.; Guo, D.; Hasan, T.; Deheeger, M.; Tobias, A.L.; Kim, J.Y.; Atashi, F.; Zhang, L.; Lesniak, M.S.; et al. Dedifferentiation of Glioma Cells to Glioma Stem-like Cells By Therapeutic Stress-induced HIF Signaling in the Recurrent GBM Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 3064–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffinger, B.; Tobias, A.L.; Han, Y.; Lee, G.; Guo, D.; Dey, M.; Lesniak, M.S.; Ahmed, A.U. Conversion of differentiated cancer cells into cancer stem-like cells in a glioblastoma model after primary chemotherapy. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Bin, Z.Q.; Qiang, H.; Liang, C.; Hua, C.; Jun, D.; Dong, W.A.; Qing, L. ABCG2 is related with the grade of glioma and resistance to mitoxantone, a chemotherapeutic drug for glioma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Ji, X.Y.; Huang, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhu, Y.D.; Lan, Q. Differentiation profile of brain tumor stem cells: A comparative study with neural stem cells. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleau, A.M.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Ozawa, T.; Fomchenko, E.I.; Huse, J.T.; Brennan, C.W.; Holland, E.C. PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway regulates the side population phenotype and ABCG2 activity in glioma tumor stem-like cells. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Herwaarden, A.E.; Wagenaar, E.; Merino, G.; Jonker, J.W.; Rosing, H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. Multidrug transporter ABCG2/breast cancer resistance protein secretes riboflavin (vitamin B2) into milk. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifergan, I.; Goler-Baron, V.; Assaraf, Y.G. Riboflavin concentration within ABCG2-rich extracellular vesicles is a novel marker for multidrug resistance in malignant cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 380, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Di, H.; Fan, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, J. Overexpression of riboflavin transporter 2 contributes toward progression and invasion of glioma. Neuroreport 2016, 27, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.R.; Yu, X.Y.; Fan, J.H.; Guo, L.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, W.; Lu, S.H. RFT2 is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis by sustaining cell proliferation and protecting against cell death. Cancer Lett. 2014, 353, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M.; Iqbal, S.; Naseem, I. Ameliorative effect of riboflavin on hyperglycemia, oxidative stress and DNA damage in type-2 diabetic mice: Mechanistic and therapeutic strategies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 584, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, H.J. Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) and health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Robey, R.W.; Bates, S.E.; Ambudkar, S.V. Sunitinib (Sutent, SU11248), a small-molecule receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, blocks function of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and ABCG2. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, P.J.; Germain, G.S.; Harwood, F.C.; Schuetz, J.D.; Stewart, C.F.; Buchdunger, E.; Traxler, P. Imatinib mesylate is a potent inhibitor of the ABCG2 (BCRP) transporter and reverses resistance to topotecan and SN-38 in vitro. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, C.J.; Robey, R.W.; Bokesch, H.R.; Bates, S.E.; Shukla, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Dean, M.; McMahon, J.B. New inhibitors of ABCG2 identified by high-throughput screening. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3271–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohse, M.; Scharenberg, C.; Shukla, S.; Robey, R.W.; Volkmann, T.; Deeken, J.F.; Brendel, C.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Neubauer, A.; Bates, S.E. Comparison of ATP-binding cassette transporter interactions with the tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, W.; Zhang, J.-T. Human ABCG2: Structure, function, and its role in multidrug resistance. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eadie, L.; Hughes, T.; White, D. Interaction of the efflux transporters ABCB1 and ABCG2 with imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, J.; Lovato, D.; Larson, R. ABCG2 inhibitors: Will they find clinical relevance. J. Dev. Drugs 2015, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.M.; Manolaridis, I.; Kowal, J.; Zechner, M.; Taylor, N.M.; Bause, M.; Bauer, S.; Bartholomaeus, R.; Bernhardt, G.; Koenig, B. Structural basis of small-molecule inhibition of human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira de Castro, J.; S. Gonçalves, C.; P. Martins, E.; Miranda-Lorenzo, I.; T. Cerqueira, M.; Longatto-Filho, A.; A. Pinto, A.; L. Reis, R.; Sousa, N.; Heeschen, C.; et al. Intracellular Autofluorescence as a New Biomarker for Cancer Stem Cells in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040828
Vieira de Castro J, S. Gonçalves C, P. Martins E, Miranda-Lorenzo I, T. Cerqueira M, Longatto-Filho A, A. Pinto A, L. Reis R, Sousa N, Heeschen C, et al. Intracellular Autofluorescence as a New Biomarker for Cancer Stem Cells in Glioblastoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040828
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira de Castro, Joana, Céline S. Gonçalves, Eduarda P. Martins, Irene Miranda-Lorenzo, Mariana T. Cerqueira, Adhemar Longatto-Filho, Afonso A. Pinto, Rui L. Reis, Nuno Sousa, Christopher Heeschen, and et al. 2021. "Intracellular Autofluorescence as a New Biomarker for Cancer Stem Cells in Glioblastoma" Cancers 13, no. 4: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040828
APA StyleVieira de Castro, J., S. Gonçalves, C., P. Martins, E., Miranda-Lorenzo, I., T. Cerqueira, M., Longatto-Filho, A., A. Pinto, A., L. Reis, R., Sousa, N., Heeschen, C., & M. Costa, B. (2021). Intracellular Autofluorescence as a New Biomarker for Cancer Stem Cells in Glioblastoma. Cancers, 13(4), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040828







