Serum Epiplakin Might Be a Potential Serodiagnostic Biomarker for Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Measurement of Serum Epiplakin
2.3. Immunohistochemistry and Scoring
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
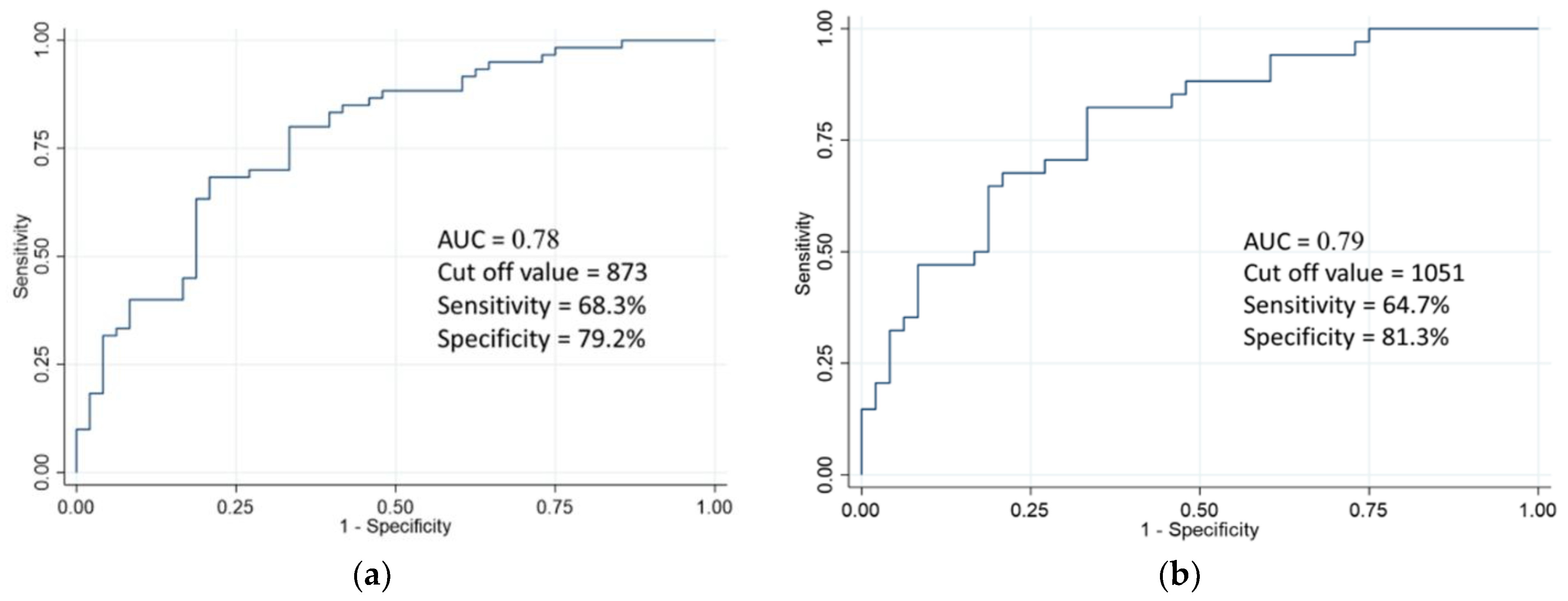
3.1. Validation of Serum Epiplakin Levels
3.2. Association of Serum Epiplakin Levels with Clinicopathological Characteristics
3.3. Association of Serum Epiplakin Level with BC Recurrence
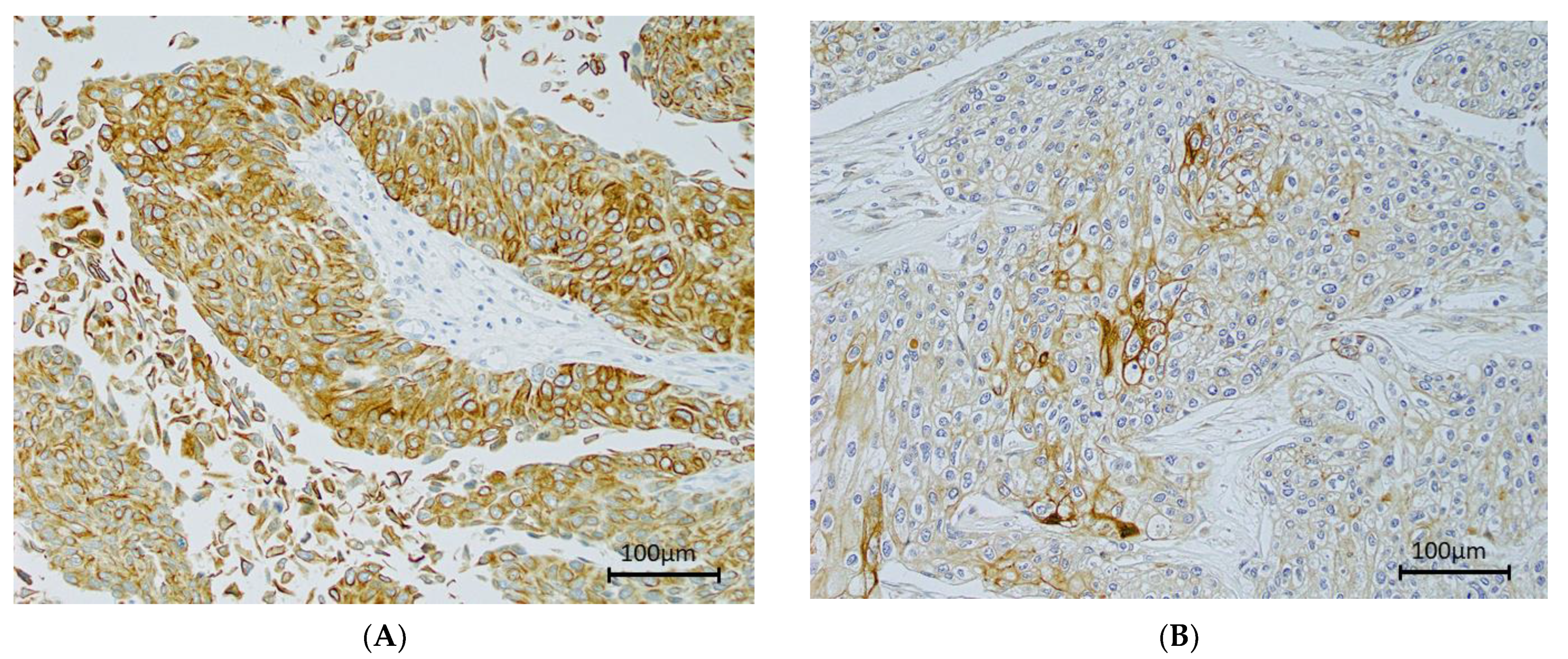
3.4. Immunohistochemistry of Epiplakin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Zanetti, R.; Ferlay, J. Cancer Incidence in Five Continents, Vol. XI (Electronic Version); IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; Available online: https://ci5.iarc.fr (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Babjuk, M.; Bohle, A.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Comperat, E.M.; Hernandez, V.; Kaasinen, E.; Palou, J.; Roupret, M.; et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: Update 2016. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, R.J.; van der Meijden, A.P.; Oosterlinck, W.; Witjes, J.A.; Bouffioux, C.; Denis, L.; Newling, D.W.; Kurth, K. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using eortc risk tables: A combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven eortc trials. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muus Ubago, J.; Mehta, V.; Wojcik, E.M.; Barkan, G.A. Evaluation of atypical urine cytology progression to malignancy. Cancer Cytopathol. 2013, 121, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babjuk, M.; Soukup, V.; Pesl, M.; Kostirova, M.; Drncova, E.; Smolova, H.; Szakacsova, M.; Getzenberg, R.; Pavlik, I.; Droracek, J. Urinary cytology and quantitative BTA and UBC tests in surveillance of patients with ptapt1 bladder urothelial carcinoma. Urology 2008, 71, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Jones, J.S. Defining the Role of Nmp22 in Bladder Cancer Surveillance. World J. Urol. 2008, 26, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okusa, H.; Kodera, Y.; Oh-ishi, M.; Minamida, S.; Tsuchida, M.; Kavoussi, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Sato, T.; Iwamura, M.; Maeda, T.; et al. Searching for new biomarkers of bladder cancer based on proteomics analysis. J. Electrophor. 2008, 52, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jefferson, J.J.; Leung, C.L.; Liem, R.K. Plakins: Goliaths that link cell junctions and the cytoskeleton. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Matsuo, N.; Takeo, N.; Goto, M.; Okamoto, O.; Tatsukawa, S.; Kitamura, H.; Fujikura, Y.; Yoshioka, H.; et al. Epiplakin Accelerates the Lateral Organization of Keratin Filaments During Wound Healing. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 60, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, K.; Lassmann, H.; Bittner, R.; Shorny, S.; Fassler, R.; Propst, F.; Wiche, G. Targeted inactivation of plectin reveals essential function in maintaining the integrity of skin, muscle, and heart cytoarchitecture. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3143–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UALCAN. Available online: http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/index.html (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Greene, F.L.; Page, D.L.; Fleming, I.D.; Fritz, A.G.; Balch, C.M.; Haller, D.G.; Morrow, M. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 6th ed; Springer: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, J.I.; Amin, M.B.; Reuter, V.R.; Mostofi, F.K. The World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology consensus classification of urothelial(transitional cell)neoplasms of the urinary bladder. Bladder Consensus Conference Committee. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1998, 22, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Nagashio, R.; Jiang, S.X.; Saito, K.; Tsuchiya, B.; Ryuge, S.; Katono, K.; Nakashima, H.; Fukuda, E.; Goshima, N.; et al. Calnexin Is a Novel Sero-Diagnostic Marker for Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagita, K.; Nagashio, R.; Jiang, S.X.; Kuchitsu, Y.; Hachimura, K.; Ichinoe, M.; Igawa, S.; Nakashima, H.; Fukuda, E.; Goshima, N.; et al. Cytoskeleton-Associated Protein 4 is a Novel Serodiagnostic Marker for Lung Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchisaka, A.; Numata, S.; Teye, K.; Natsuki, Y.; Kawakami, T.; Takeda, Y.; Wang, W.; Ishikawa, K.; Goto, M.; Koga, H.; et al. Epiplakin Is a Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Autoantigen and Related to Bronchiolitis Obliterans in Japanese Patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.G.; Kim, J.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Bellmunt, J.; Guo, G.; Cherniack, A.D.; Hinoue, T.; Laird, P.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Akbani, R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, G.D.; Winokur, T.S.; Cerfolio, R.J.; Van Tine, B.A.; Chow, L.T.; Okoh, V.; Garver, R.I., Jr. Differential expression and biodistribution of cytokeratin 18 and desmoplakins in non-small cell lung carcinoma subtypes. Lung Cancer 2002, 36, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, N.; Gist, J.; Smith, T.; Tylka, D.; Trogdon, G.; Wahl, J.K. Desmosomal Component Expression in Normal, Dysplastic, and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 649731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Elgehama, A.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Gu, Y.; Guo, W.; Xu, Q. Loss of Periplakin Expression Is Associated with the Tumorigenesis of Colorectal Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 87, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ikeda, M.; Sato, Y.; Kuruma, H.; Kamata, Y.; Nishimori, T.; Tomonaga, T.; Nomura, F.; Egawa, S.; Iwamura, M. Loss of periplakin expression is associated with pathological stage and cancerspecific survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Biomed. Res. 2014, 35, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, I.; Esumi, M.; Kusumi, Y.; Furusaka, T.; Oshima, T. Particular Gene Upregulation and P53 Heterogeneous Expression in Tp53-Mutated Maxillary Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 4633–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Shiraki, N.; Baba, H.; Goto, M.; Fujiwara, S.; Kume, K.; Kume, S. Expression Patterns of Epiplakin1 in Pancreas, Pancreatic Cancer and Regenerating Pancreas. Genes Cells 2008, 13, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Pan, Z.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, X.; Hua, N.; Li, G.H. Klf5-Mediated Eppk1 Expression Promotes Cell Proliferation in Cervical Cancer Via the P38 Signaling Pathway. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spazierer, D.; Fuchs, P.; Reipert, S.; Fischer, I.; Schmuth, M.; Lassmann, H.; Wiche, G. Epiplakin is dispensable for skin barrier function and for integrity of keratin network cytoarchitecture in simple and stratified epithelia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Coulombe, P.A. Intermediate filament scaffolds fulfill mechanical, organizational, and signaling functions in the cytoplasm. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etienne-Manneville, S. Cytoplasmic Intermediate Filaments in Cell Biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 34, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Fujiwara, S. Interactions between Epiplakin and Intermediate Filaments. J. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, M.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Sakai, T.; Fassler, R.; Ohashi, S.; Adachi, E.; Yoshioka, H.; Fujiwara, S. Elimination of Epiplakin by Gene Targeting Results in Acceleration of Keratinocyte Migration in Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilki, D.; Burger, M.; Dalbagni, G.; Grossman, H.B.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Palou, J.; Reich, O.; Roupret, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Zlotta, A.R. Urine Markers for Detection and Surveillance of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; La Civita, E.; Liotti, A.; Cennamo, M.; Tortora, F.; Buonerba, C.; Crocetto, F.; Lucarelli, G.; Busetto, G.M.; Del Giudice, F.; et al. Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Urine: A Route Towards Molecular Diagnosis and Personalized Medicine of Bladder Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Rosser, C.J. Uroseek Gene Panel for Bladder Cancer Surveillance. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eich, M.L.; Rodriguez Pena, M.D.C.; Springer, S.U.; Taheri, D.; Tregnago, A.C.; Salles, D.C.; Bezerra, S.M.; Cunha, I.W.; Fujita, K.; Ertoy, D.; et al. Incidence and Distribution of Uroseek Gene Panel in a Multi-Institutional Cohort of Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogbe, P.H.; Manel, A.; Vian, E.; Durand, G.; Forey, N.; Voegele, C.; Zvereva, M.; Hosen, M.I.; Meziani, S.; De Tilly, B.; et al. Urinary Tert Promoter Mutations as Non-Invasive Biomarkers for the Comprehensive Detection of Urothelial Cancer. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonham, N.; Kreuze, J.; Winter, S.; van der Vlugt, R.; Bergervoet, J.; Tomlinson, J.; Mumford, R. Methods in Virus Diagnostics: From Elisa to Next Generation Sequencing. Virus Res. 2014, 186, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, V.; Dagher, R.; Madjer, T.; Joannes, A.; Jaillet, M.; Kolb, M.; Bonniaud, P.; Murray, L.A.; Sleeman, M.A.; Crestani, B. Identification of Periplakin as a Major Regulator of Lung Injury and Repair in Mice. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e90163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | No. of Pts. | Serum Epiplakin Level | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Mean | Range | |||
| Age(years) | 0.11 | ||||
| ≤65 | 11 | 761.8 | 1136.6 | 373.5–3209 | |
| >65 | 49 | 1302.8 | 1844.2 | 263.8–4955 | |
| Sex | 0.28 | ||||
| Male | 45 | 1192.8 | 1813.4 | 346–6485.8 | |
| Female | 14 | 1181 | 1384 | 263.8–3501 | |
| T stage | 0.50 | ||||
| ≤pT1 | 34 | 1250.9 | 1806.1 | 346–6845.8 | |
| ≥pT2 | 26 | 1175.6 | 1575.2 | 263.8–4955 | |
| Grade | 0.40 | ||||
| G1/2 | 32 | 1430 | 1849.5 | 383.5–6845.8 | |
| G3 | 28 | 1177 | 1542.1 | 263.8–4955 | |
| Urine cytology | 0.51 | ||||
| <classⅢb | 16 | 1171 | 1544.7 | 373.5–3982 | |
| ≥classⅢb | 43 | 1303 | 1800 | 263.8–6845.8 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimura, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Mochizuki, K.; Shiono, Y.; Hirano, S.; Koguchi, D.; Ikeda, M.; Sato, Y.; Iwamura, M. Serum Epiplakin Might Be a Potential Serodiagnostic Biomarker for Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205150
Shimura S, Matsumoto K, Shimizu Y, Mochizuki K, Shiono Y, Hirano S, Koguchi D, Ikeda M, Sato Y, Iwamura M. Serum Epiplakin Might Be a Potential Serodiagnostic Biomarker for Bladder Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(20):5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205150
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimura, Soichiro, Kazumasa Matsumoto, Yuriko Shimizu, Kohei Mochizuki, Yutaka Shiono, Shuhei Hirano, Dai Koguchi, Masaomi Ikeda, Yuichi Sato, and Masatsugu Iwamura. 2021. "Serum Epiplakin Might Be a Potential Serodiagnostic Biomarker for Bladder Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 20: 5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205150
APA StyleShimura, S., Matsumoto, K., Shimizu, Y., Mochizuki, K., Shiono, Y., Hirano, S., Koguchi, D., Ikeda, M., Sato, Y., & Iwamura, M. (2021). Serum Epiplakin Might Be a Potential Serodiagnostic Biomarker for Bladder Cancer. Cancers, 13(20), 5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13205150






