Small Extracellular Vesicles from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Carry a Proteomic Signature for Tumor Hypoxia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2. Isolation of sEVs
2.3. Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)
2.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry (MS)
2.7. Protein Identification and Quantitation by MS
2.8. Wound Healing Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
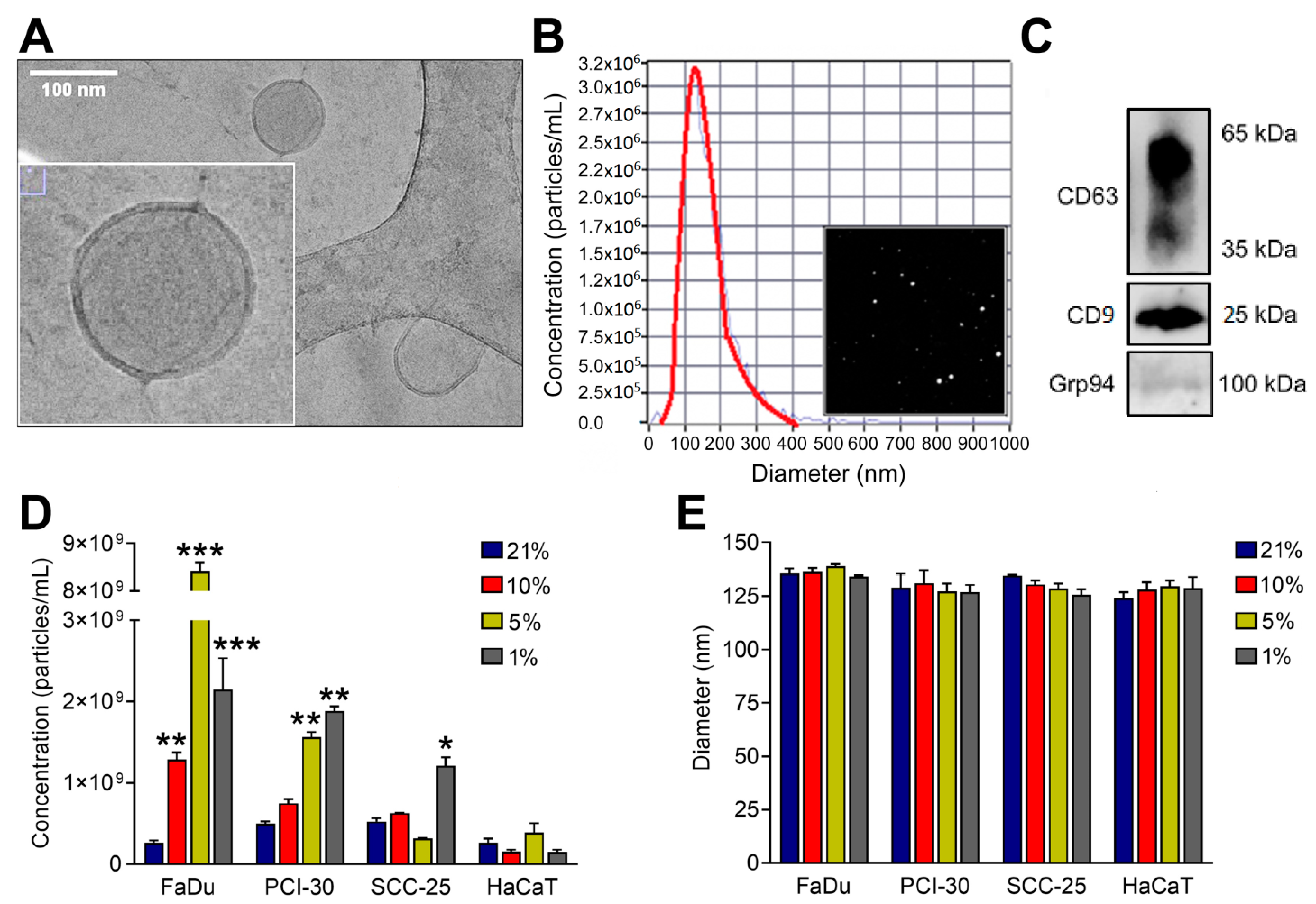
3.1. Characterization of sEVs
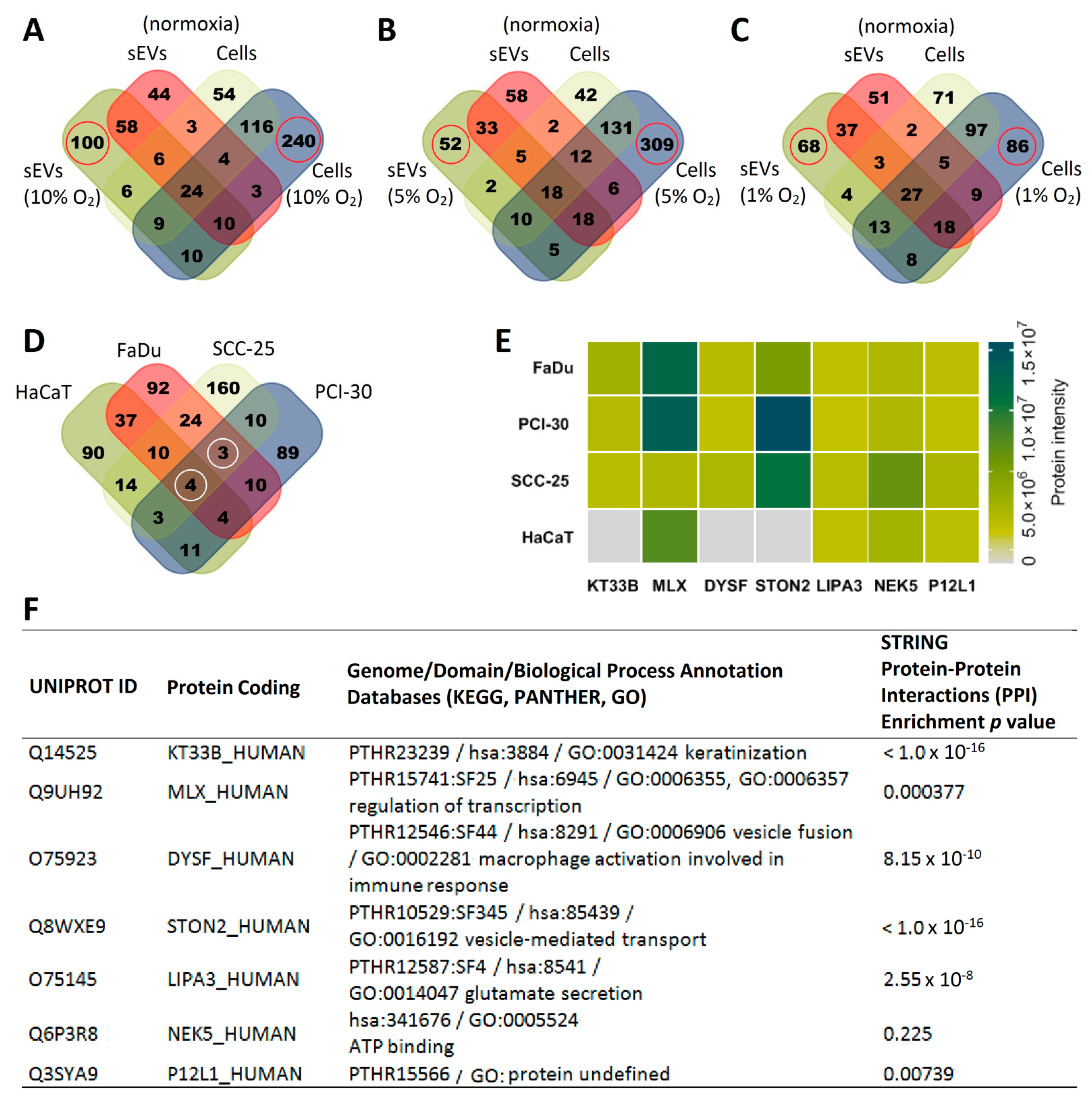
3.2. sEVs Reflect the Hypoxic State of HNSCC Cells and Carry Unique Hypoxia-Related Protein Signatures
3.3. The Degree of Hypoxia in Tumor Cells Is Reflected in the Protein Profile of HNSCC-Derived sEVs
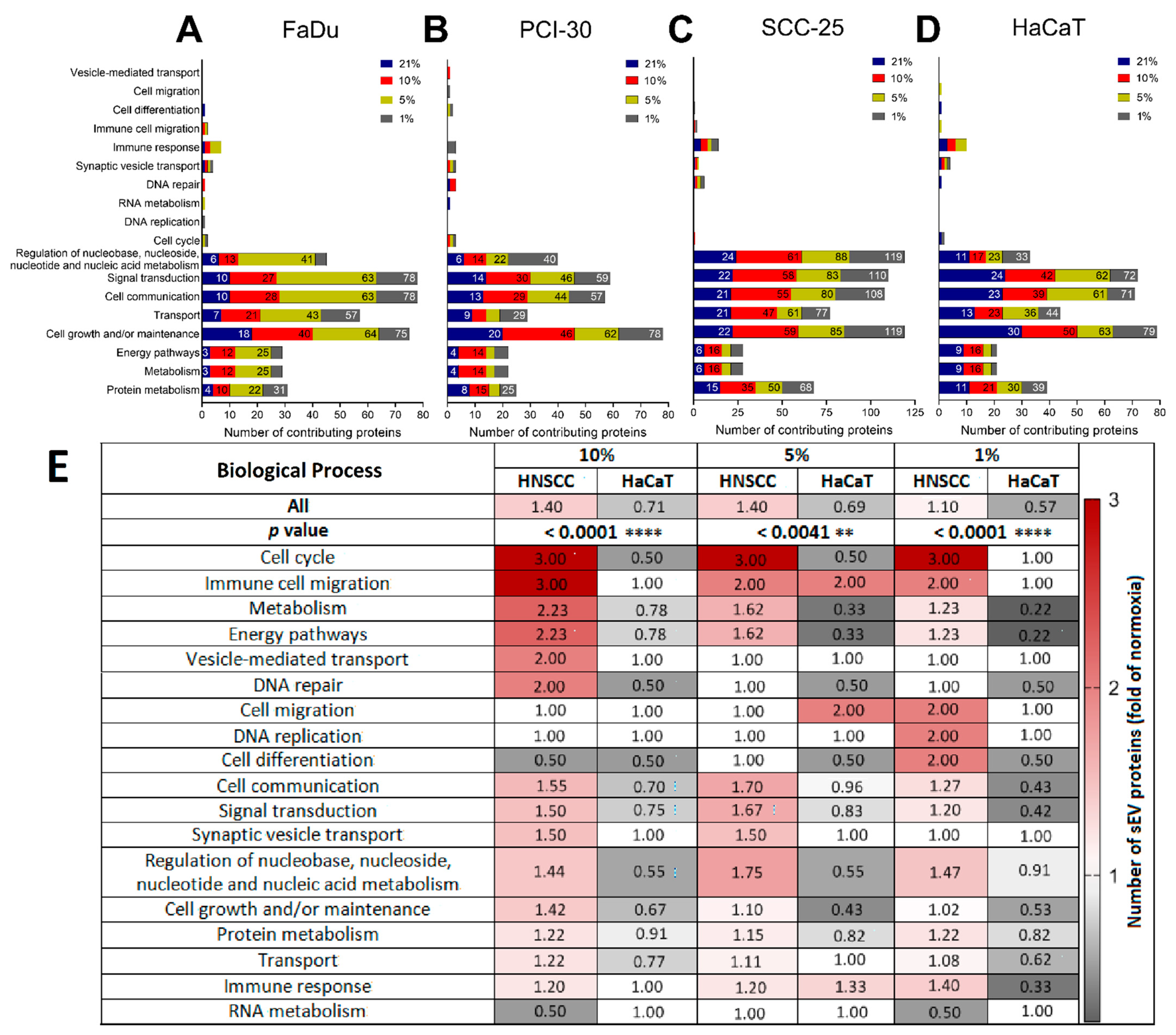
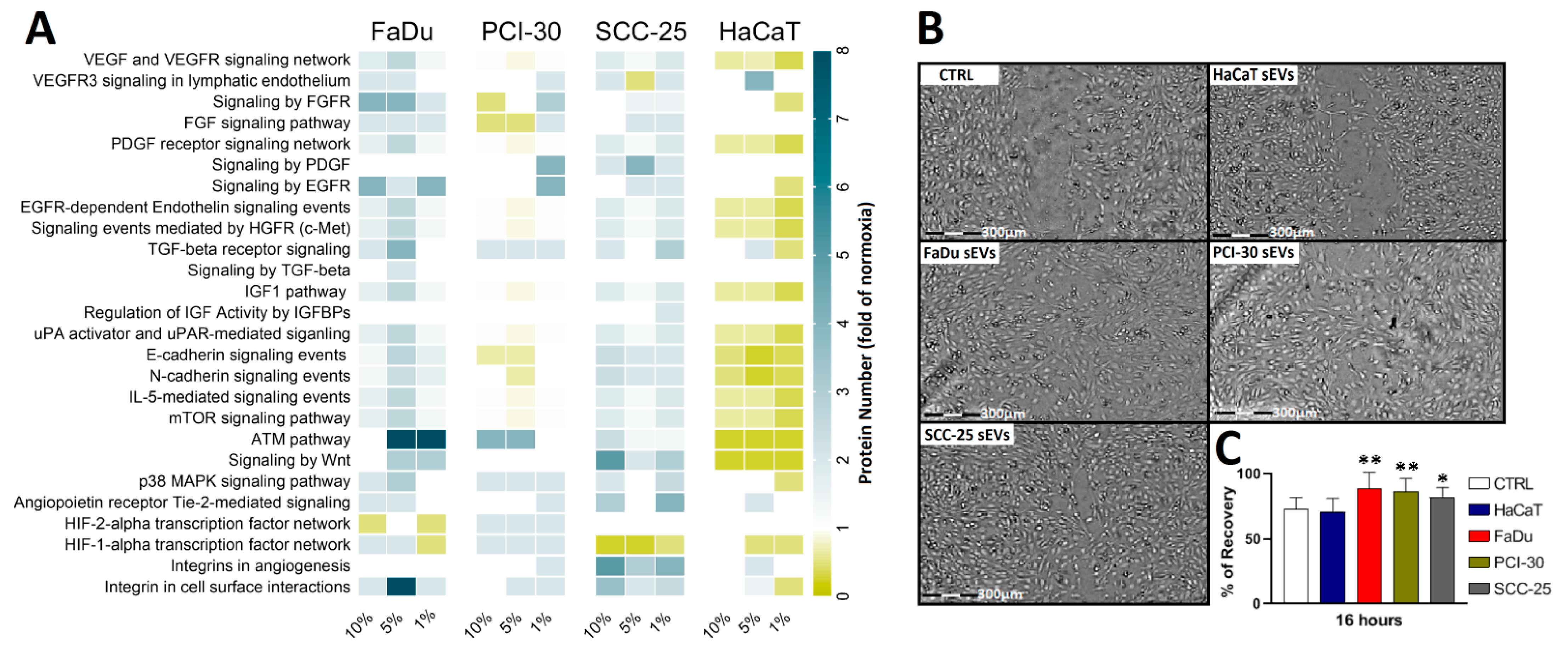
3.4. Functional Gene Designations for the Identified Proteins
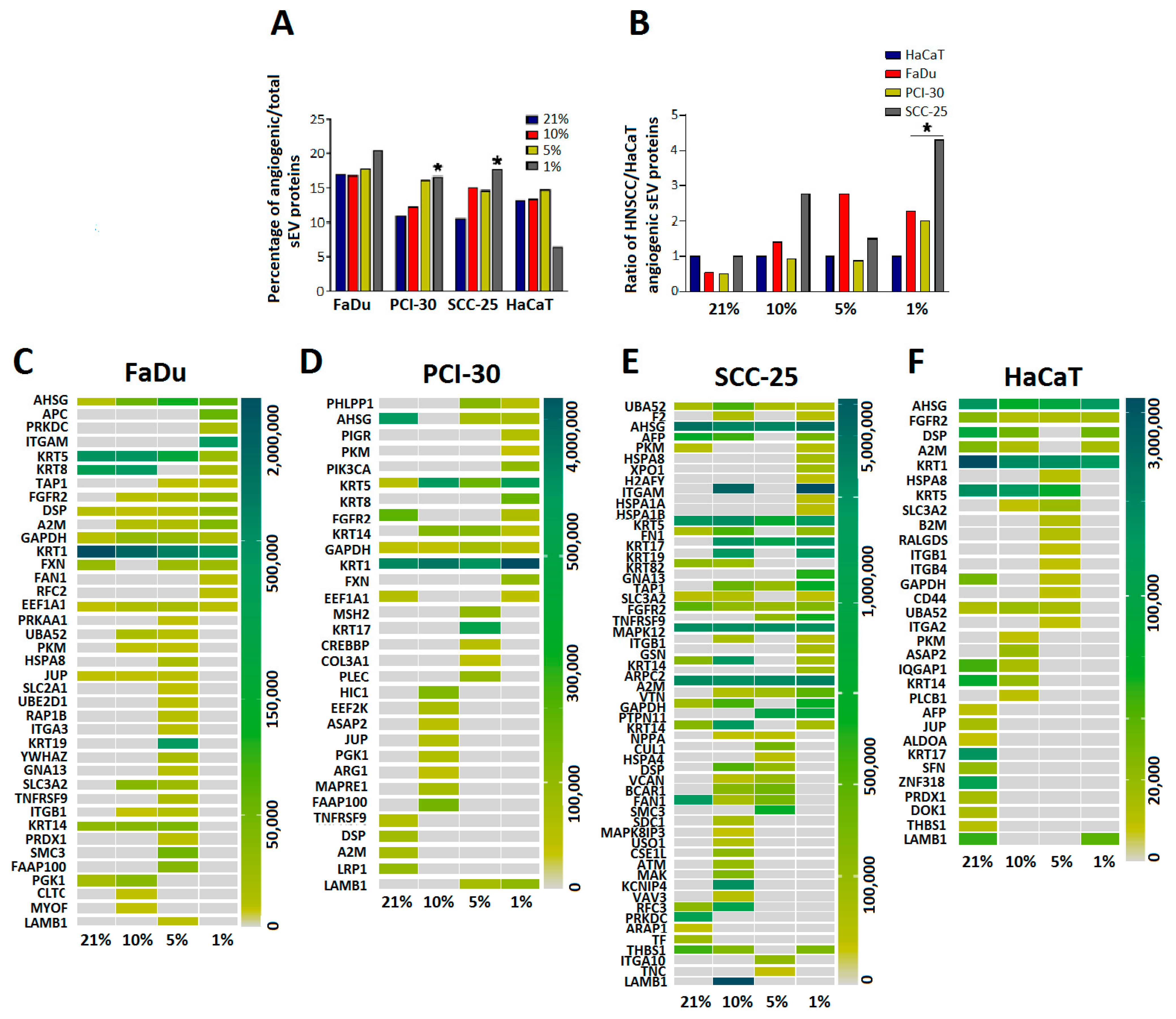
3.5. sEVs Isolated from HNSCC Cells Cultured in Hypoxic Conditions Are Enriched in Angiogenic Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahao, R.; Perdomo, S.; Pinto, L.F.R.; de Nascimento Carvalho, F.; Dias, F.L.; de Podesta, J.R.V.; von Zeidler, S.V.; de Abreu, P.M.; Vilensky, M.; Giglio, R.E.; et al. Predictors of Survival After Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in South America: The InterCHANGE Study. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2020, 6, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadoni, G.; Giraldi, L.; Petrelli, L.; Pandolfini, M.; Giuliani, M.; Paludetti, G.; Pastorino, R.; Leoncini, E.; Arzani, D.; Almadori, G.; et al. Prognostic factors in head and neck cancer: A 10-year retrospective analysis in a single-institution in Italy. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatta, G.; Botta, L.; Sanchez, M.J.; Anderson, L.A.; Pierannunzio, D.; Licitra, L. Prognoses and improvement for head and neck cancers diagnosed in Europe in early 2000s: The EUROCARE-5 population-based study. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2130–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredell, M.G.; Ernst, J.; El-Kochairi, I.; Dahlem, Y.; Ikenberg, K.; Schumann, D.M. Current relevance of hypoxia in head and neck cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50781–50804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanduleanu, S.; Hamming-Vrieze, O.; Wesseling, F.W.R.; Even, A.J.G.; Hoebers, F.J.; Hoeben, A.; Vogel, W.V.; Tesselaar, M.E.T.; Parvin, D.; Bartelink, H.; et al. [(18)F]-HX4 PET/CT hypoxia in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with chemoradiotherapy: Prognostic results from two prospective trials. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 23, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Younis, R.H.; Gutkind, J.S. Hypoxia-induced energy stress inhibits the mTOR pathway by activating an AMPK/REDD1 signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, S.; Faouzi Zaarour, R.; Hassan Venkatesh, G.; Francis, A.; El-Sayed, W.; Buart, S.; Bravo, P.; Thiery, J.; Chouaib, S. Role of Hypoxic Stress in Regulating Tumor Immunogenicity, Resistance and Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.C.; Rathore, A.; Younas, H.; Gilkes, D.; Polotsky, V.Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Cancer. Curr. Sleep Med. Rep. 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, G.N.; Li, W. HIF-1alpha pathway: Role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talks, K.L.; Turley, H.; Gatter, K.C.; Maxwell, P.H.; Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Harris, A.L. The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Potential role of exosomes in the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of hypoxic diseases. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1184–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Praharaj, P.P.; Peak, T.C.; Long, J.; Singh, R.; Rhim, J.S.; Elmageed, Z.Y.A.; Deep, G. Hypoxia-induced exosome secretion promotes survival of African-American and Caucasian prostate cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Gillespie, D.G.; Reichert, T.E.; Jackson, E.K.; Whiteside, T.L. Purine Metabolites in Tumor-Derived Exosomes May Facilitate Immune Escape of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, S.; Floros, T.; Theodoraki, M.N.; Hong, C.S.; Jackson, E.K.; Lang, S.; Whiteside, T.L. Suppression of Lymphocyte Functions by Plasma Exosomes Correlates with Disease Activity in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4843–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, N.; Yerneni, S.S.; Razzo, B.M.; Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes from HNSCC Promote Angiogenesis through Reprogramming of Endothelial Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. Validation of plasma-derived small extracellular vesicles as cancer biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Kim, H.S.; Bojmar, L.; Gyan, K.E.; Cioffi, M.; Hernandez, J.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Rodrigues, G.; Molina, H.; Heissel, S.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle and Particle Biomarkers Define Multiple Human Cancers. Cell 2020, 182, 1044–1061 e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indira Chandran, V.; Welinder, C.; de Goncalves Oliveira, K.; Cerezo-Magana, M.; Mansson, A.S.; Johansson, M.C.; Marko-Varga, G.; Belting, M. Global extracellular vesicle proteomic signature defines U87-MG glioma cell hypoxic status with potential implications for non-invasive diagnostics. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 144, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzewska, P.; Christianson, H.C.; Welch, J.E.; Svensson, K.J.; Fredlund, E.; Ringner, M.; Morgelin, M.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Bengzon, J.; Belting, M.; et al. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Rubenich, D.S.; Zareba, L.; Siewiera, J.; Pieper, J.; Braganhol, E.; Reichert, T.E.; Szczepanski, M.J. Potential Roles of Tumor Cell- and Stroma Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Promoting a Pro-Angiogenic Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Ahmadi, M.; Hassanpour, M.; Rezaie, J. Hypoxic exosomes orchestrate tumorigenesis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walbrecq, G.; Margue, C.; Behrmann, I.; Kreis, S. Distinct Cargos of Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Hypoxic Cells and Their Effect on Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Deep, G. Hypoxia in tumor microenvironment regulates exosome biogenesis: Molecular mechanisms and translational opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2020, 479, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. The effect of extracellular vesicles on the regulation of mitochondria under hypoxia. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, N.; Razzo, B.M.; Yerneni, S.S.; Whiteside, T.L. Optimization of cell culture conditions for exosome isolation using mini-size exclusion chromatography (mini-SEC). Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 378, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, N.; Hong, C.S.; Ludwig, S.; Azambuja, J.H.; Sharma, P.; Theodoraki, M.N.; Whiteside, T.L. Isolation and Analysis of Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2019, 127, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseka, P.; Pathan, M.; Chitti, S.V.; Kang, T.; Mathivanan, S. FunRich enables enrichment analysis of OMICs datasets. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, R.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, R.; Pierson, C.R.; Finlay, J.L.; Yang, F.; Gu, N.; et al. The Antiproliferative and Colony-suppressive Activities of STAT3 Inhibitors in Human Cancer Cells Is Compromised Under Hypoxic Conditions. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Whiteside, T.L. Potential roles of tumor-derived exosomes in angiogenesis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Yang, F.; Miao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Shu, Y.; Shen, H. Role of hypoxia-induced exosomes in tumor biology. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haibe, Y.; Kreidieh, M.; El Hajj, H.; Khalifeh, I.; Mukherji, D.; Temraz, S.; Shamseddine, A. Resistance Mechanisms to Anti-angiogenic Therapies in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, J.E.; Pothen, A.J.; Stegeman, I.; Willems, S.M.; Grolman, W. Clinical implications of hypoxia biomarker expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1101–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvoniemi, A.; Suilamo, S.; Laitinen, T.; Forsback, S.; Loyttyniemi, E.; Vaittinen, S.; Saunavaara, V.; Solin, O.; Gronroos, T.J.; Minn, H. Repeatability of tumour hypoxia imaging using (18)F.EF5 PET/CT in head and neck cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serganova, I.; Humm, J.; Ling, C.; Blasberg, R. Tumor hypoxia imaging. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5260–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schmidt, S.; Linge, A.; Grosser, M.; Lohaus, F.; Gudziol, V.; Nowak, A.; Tinhofer, I.; Budach, V.; Sak, A.; Stuschke, M.; et al. Comparison of GeneChip, nCounter, and Real-Time PCR-Based Gene Expressions Predicting Locoregional Tumor Control after Primary and Postoperative Radiochemotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Dai, W.; Ma, S.; Wang, Q.; Lan, M.; Luo, H.; Chen, T.; Yang, X.; Zhu, G.; Li, Q.; et al. An EV-Associated Gene Signature Correlates with Hypoxic Microenvironment and Predicts Recurrence in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes and tumor-mediated immune suppression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlendieck, K. Proteomic identification of biomarkers of skeletal muscle disorders. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Jeong, H.; Roh, J.S.; Lee, B.; Han, M.E.; Oh, S.O.; Sohn, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. DYSF expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective study of 2 independent cohorts. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Niu, C.; Ou, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y. Stonin 2 Overexpression is Correlated with Unfavorable Prognosis and Tumor Invasion in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inazu, M.; Yamada, T.; Kubota, N.; Yamanaka, T. Functional expression of choline transporter-like protein 1 (CTL1) in small cell lung carcinoma cells: A target molecule for lung cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 76, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Liquid Biopsy in Head and Neck Cancer: Promises and Challenges. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Głuszko, A.; Szczepański, M.J.; Whiteside, T.L.; Reichert, T.E.; Siewiera, J.; Ludwig, N. Small Extracellular Vesicles from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Carry a Proteomic Signature for Tumor Hypoxia. Cancers 2021, 13, 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164176
Głuszko A, Szczepański MJ, Whiteside TL, Reichert TE, Siewiera J, Ludwig N. Small Extracellular Vesicles from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Carry a Proteomic Signature for Tumor Hypoxia. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164176
Chicago/Turabian StyleGłuszko, Alicja, Mirosław J. Szczepański, Theresa L. Whiteside, Torsten E. Reichert, Jacek Siewiera, and Nils Ludwig. 2021. "Small Extracellular Vesicles from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Carry a Proteomic Signature for Tumor Hypoxia" Cancers 13, no. 16: 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164176
APA StyleGłuszko, A., Szczepański, M. J., Whiteside, T. L., Reichert, T. E., Siewiera, J., & Ludwig, N. (2021). Small Extracellular Vesicles from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Carry a Proteomic Signature for Tumor Hypoxia. Cancers, 13(16), 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164176









