HPV Strain Predicts Severity of Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis with Implications for Disease Screening
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Biopsy of RRP Lesions and Primary Cell Culture
2.3. HPV Genotyping
2.4. Fluorescent RNA In Situ Hybridization (RNA-ISH) for HPV Gene Expression
2.5. Statistical Methods
2.6. DNA In Situ Hybridization (DNA-ISH) for Research
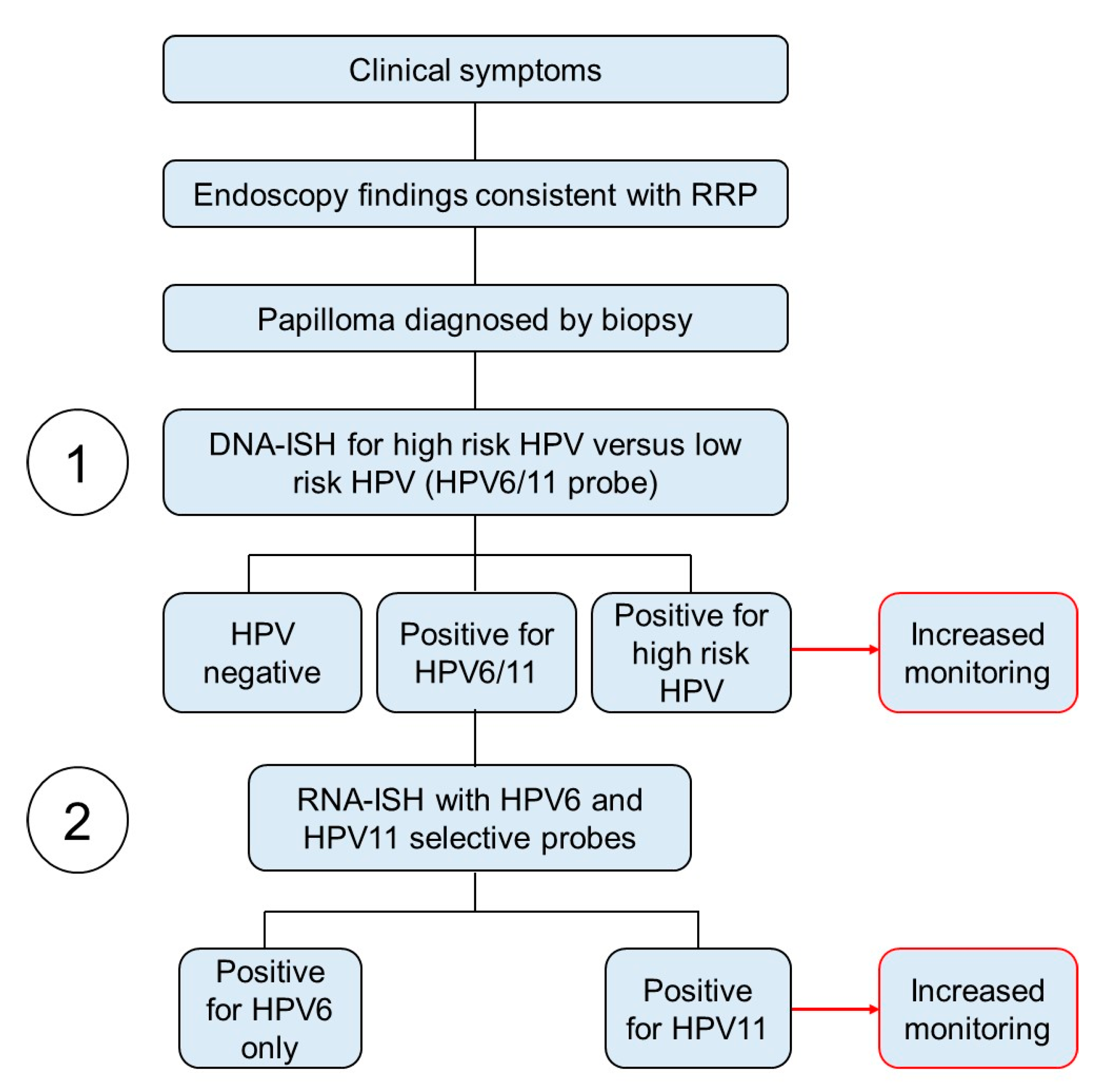
2.7. DNA-ISH Assay for Screening Low-Risk HPV6/11
2.8. RNA-ISH Assay for Screening HPV6 vs. HPV11
3. Results
3.1. Summary of the Published Literature on Risk Factors of Severe RRP Disease
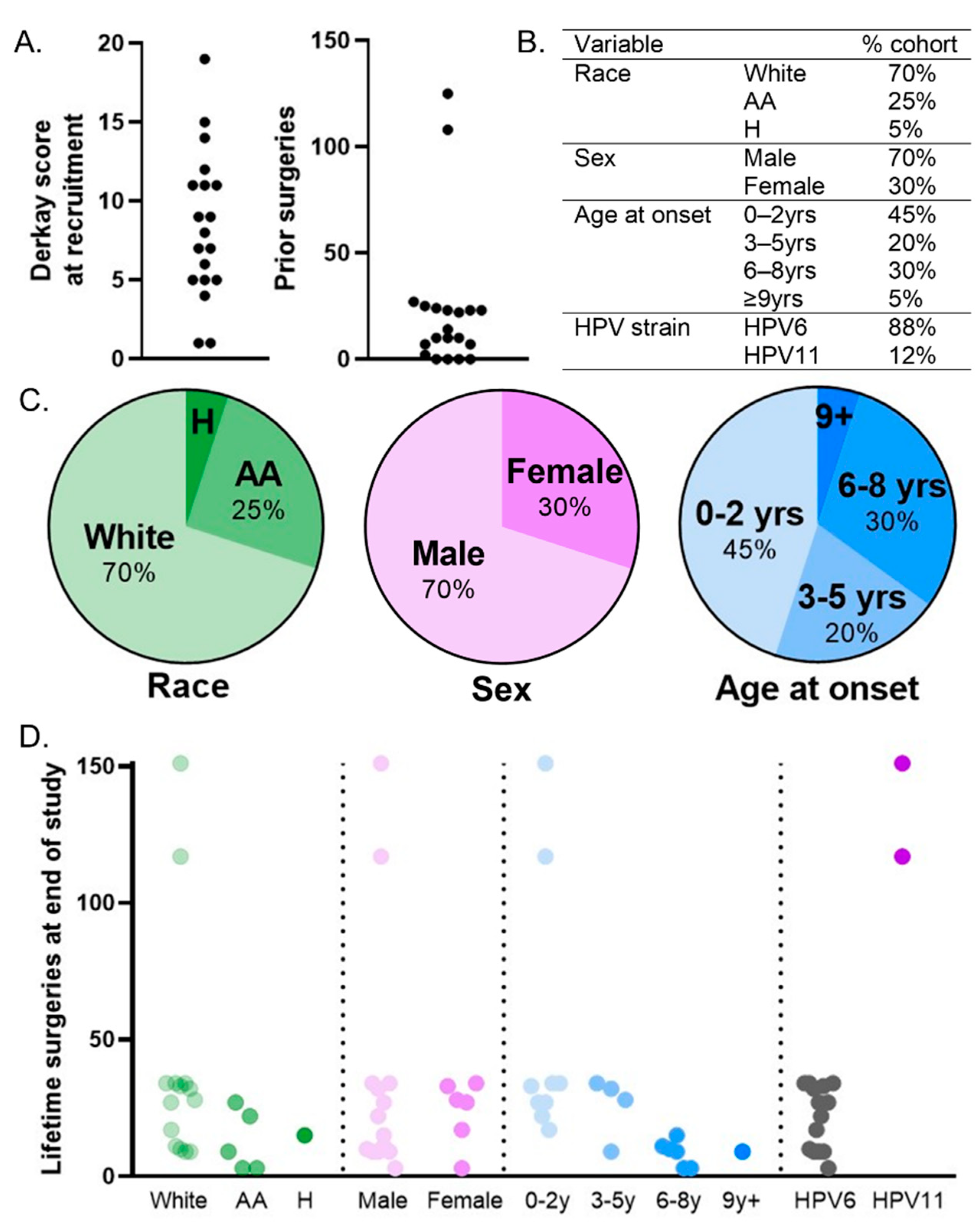
3.2. Cohort Recruitment and Characteristics
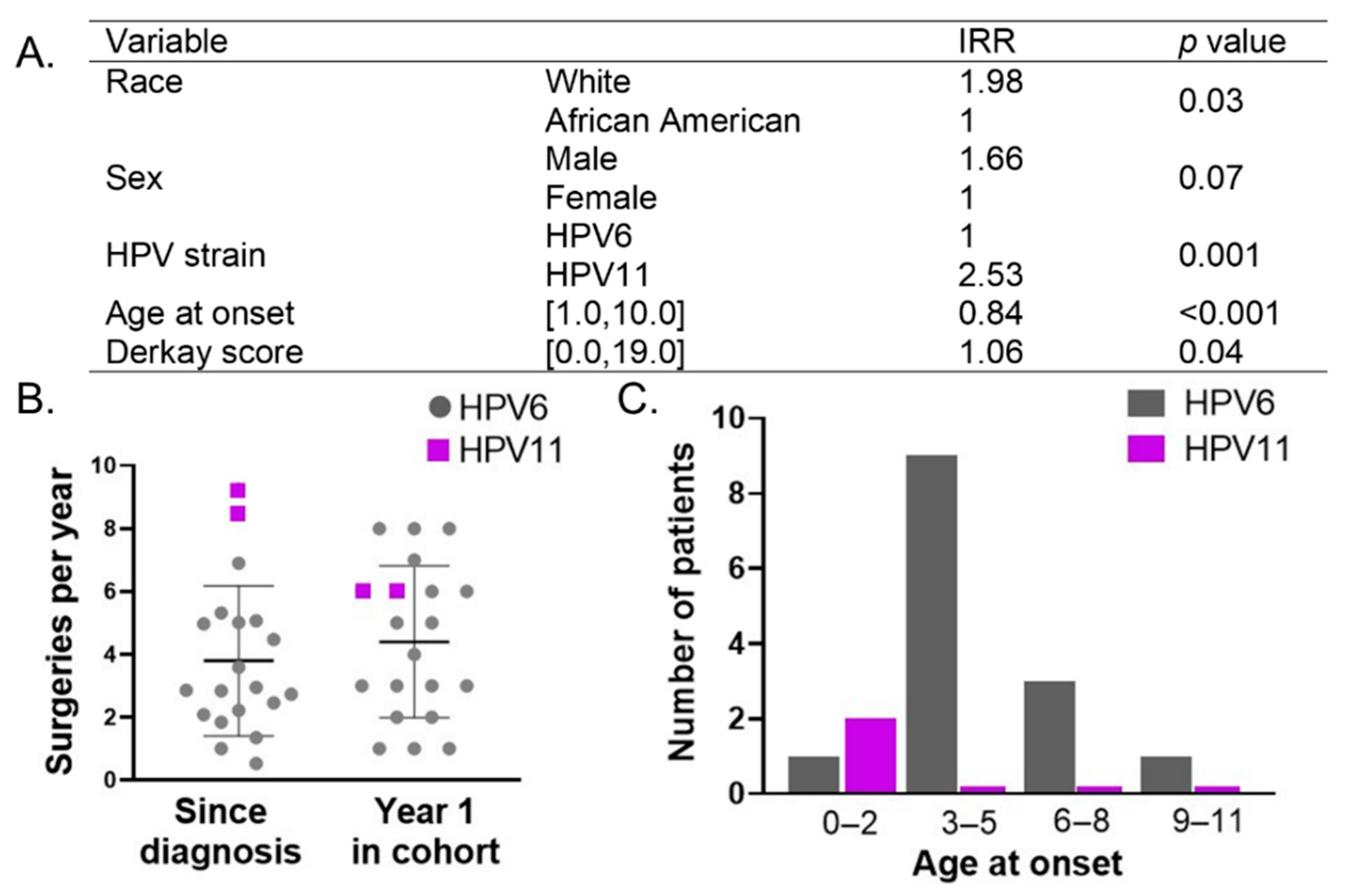
3.3. Analysis of Predictive Factors Reveals Importance of HPV Type
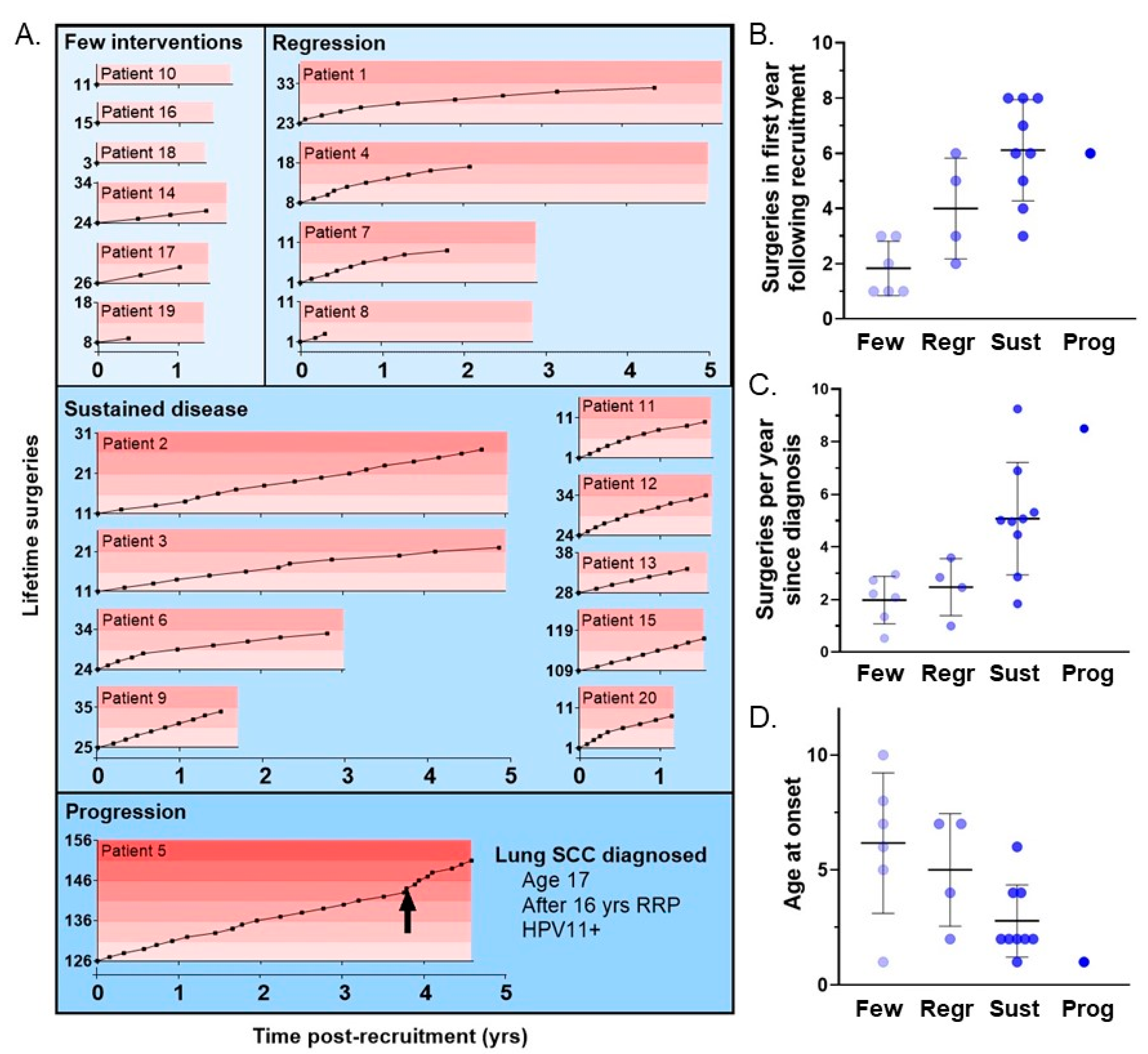
3.4. Clinical Course Categories Show Differences in Age of Onset and Disease Severity
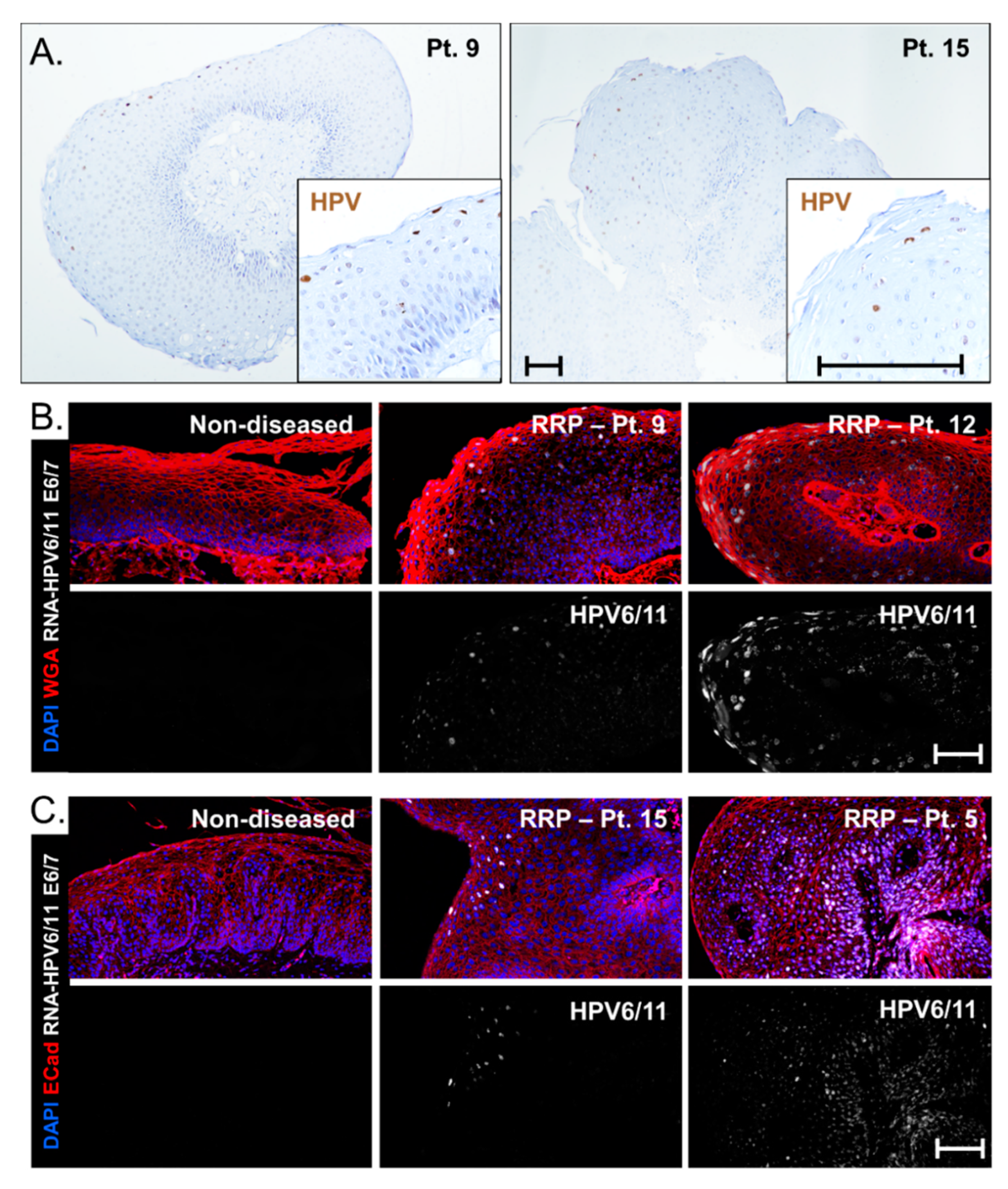
3.5. Viral Gene Expression Levels Do Not Account for Disease Severity Differences between HPV6 and HPV 11 Cohorts
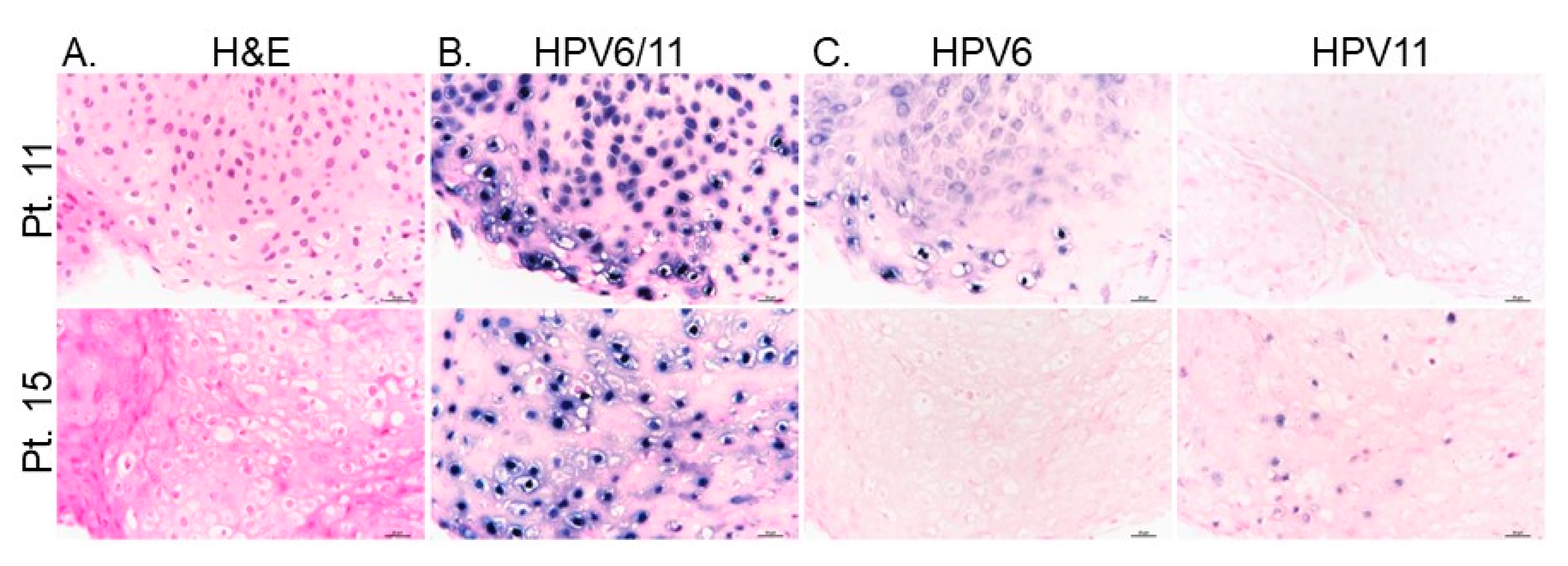
3.6. HPV Strain-Selective Probes for RNA-ISH to Enable HPV6 versus HPV11 Screening
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derkay, C.S.; Wiatrak, B. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Review. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkay, C.S. Task Force on Recurrent Respiratory Papillomas: A Preliminary Report. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 121, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.R.; Derkay, C.S.; Reeves, W.C. Initial Results from the National Registry for Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1999, 125, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, T.; Lie, K.A.; Akre, H.; Sandlie, L.E.; Jebsen, P.; Sandvik, L.; Nymoen, D.A.; Bzhalava, D.; Dillner, J.; Brøndbo, K. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: HPV Genotypes and Risk of High-Grade Laryngeal Neoplasia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Myers, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, D.; Woo, J.A.; Kallakury, B.; Ju, A.; Bazylewicz, M.; Carter, Y.M.; Albanese, C.; et al. Use of reprogrammed cells to identify therapy for respiratory papillomatosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goon, P.; Sonnex, C.; Jani, P.; Stanley, M.; Sudhoff, H. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: An overview of current thinking and treatment. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2007, 265, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, R.D.; Rimell, F.L.; Adams, G.L.; Derkay, C.S.; Hester, R. Diagnosis and Management of Pulmonary Metastasis from Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2003, 129, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, B.M.; DiLorenzo, T.P. A possible role for human papillomaviruses in head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1996, 15, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraff, S.; Derkay, C.S.; Burke, B.; Lawson, L. American Society of Pediatric Otolaryngology Members’ Experience with Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis and the Use of Adjuvant Therapy. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkay, C.S.; Bluher, A.E. Update on Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 52, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Bishop, J.A.; Akpeng, B.; Pai, S.I.; Best, S.R. Xenograft Model for Therapeutic Drug Testing in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2015, 124, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saumet, L.; Damay, A.; Jeziorski, E.; Cartier, C.; Rouleau, C.; Margueritte, G.; Rodière, M.; Segondy, M. Papillomatose laryngée sévère évoluant vers un carcinome bronchopulmonaire associé à HPV 11 chez une enfant de 15 ans: À propos d’un cas. Arch. Pédiatr. 2011, 18, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauz, P.-S.; Zago, M.; Kurth, R.; Pawlita, M.; Holderried, M.; Thiericke, J.; Iftner, A.; Stubenrauch, F.; Sotlar, K.; Iftner, T. A case of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with malignant transformation, HPV11 DNAemia, high L1 antibody titre and a fatal papillary endocardial lesion. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lin, H.W.; Richmon, J.D.; Emerick, K.S.; De Venecia, R.K.; Zeitels, S.M.; Faquin, W.C.; Lin, D.T. Malignant transformation of a highly aggressive human papillomavirus type 11–associated recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2010, 31, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rady, P.L.; Schnadig, V.J.; Weiss, R.L.; Hughes, T.K.; Tyring, S.K. Malignant Transformation of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Associated With Integrated Human Papillomavirus Type 11 DNA and Mutation of p53. Laryngoscope 1998, 108, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magid, M.S.; Chen, Y.-T.; Soslow, R.A.; Boulad, F.; Kernan, N.A.; Szabolcs, P. Juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis involving the lung: A case report and review of the literature. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 1998, 1, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeberg, H.; Syrjänen, S.; Kärjä, J.; Syrjänen, K. Human Papillomavirus Type 11 DNA in Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Pre-existing Multiple Laryngeal Papillomas. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1989, 107, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerein, V.; Rastorguev, E.; Gerein, J.; Draf, W.; Schirren, J. Incidence, age at onset, and potential reasons of malignant transformation in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis patients: 20 years experience. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatrak, B.J.; Wiatrak, D.W.; Broker, T.R.; Lewis, L. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Longitudinal Study Comparing Severity Associated With Human Papilloma Viral Types 6 and 11 and Other Risk Factors in a Large Pediatric Population. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pou, A.M.; Rimell, F.L.; Jordan, J.A.; Barua, P.; Shoemaker, D.L.; Post, J.C.; Johnson, J.T.; Ehrlich, G.D. Adult Respiratory Papillomatosis: Human Papillomavirus Type and Viral Coinfections as Predictors of Prognosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1995, 104, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, P.; Todorov, S.; Todorov, I.; Karchev, T.; Kalvatchev, Z. Identification of HPV DNA in patients with juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis using SYBR® Green real-time PCR. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 70, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabah, R.; Lancaster, W.; Thomas, R.; Gregoire, L. Human papillomavirus-11-associated recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is more aggressive than human papillomavirus-6-associated disease. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2001, 4, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gi, R.E.A.T.P.; Giorgi, M.R.M.S.; Slagter-Menkema, L.; Van Hemel, B.M.; Van Der Laan, B.F.A.M.; Heuvel, E.R.V.D.; Dikkers, F.G.; Schuuring, E.M.D. Clinical course of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: Comparison between aggressiveness of human papillomavirus-6 and human papillomavirus-11. Head Neck 2014, 37, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.L.; Küpper, D.S.; Bonfim, C.M.D.; Aragon, D.C.; Damico, T.A.; Miura, C.S.; Passos, I.M.; Nogueira, M.L.; Rahal, P.; Valera, F.C.P. HPV genotype is a prognosticator for recurrence of respiratory papillomatosis in children. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2021, 46, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñaloza-Plascencia, M.; Montoya-Fuentes, H.; Flores-Martínez, S.E.; Fierro-Velasco, F.J.; Peñaloza-González, J.M.; Sánchez-Corona, J. Molecular Identification of 7 Human Papillomavirus Types in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 126, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padayachee, A.; Prescott, C. Relationship between the clinical course and HPV typing of recurrent laryngeal papillomatosis. The Red Cross War Memorial Children’s Hospital Experience 1982–1988. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1993, 26, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounts, P.; Kashima, H. Association of human papillomavirus subtype and clinical course in respiratory papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 1984, 94, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donne, A.; Hampson, L.; Homer, J.; Hampson, I. The role of HPV type in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbott, M.; Cossart, Y.; Kan, A.; Konopka, M.; Chan, R.; Rose, B.R. Human papillomavirus and host variables as predictors of clinical course in patients with juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3098–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchinsky, F.J.; Donfack, J.; Derkay, C.S.; Choi, S.S.; Conley, S.F.; Myer, C.M.; McClay, J.E.; Campisi, P.; Wiatrak, B.J.; Sobol, S.E.; et al. Age of Child, More than HPV Type, Is Associated with Clinical Course in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, T.; Akre, H.; Lie, K.A.; Jebsen, P.; Sandvik, L.; Brøndbo, K. Risk Factors for Aggressive Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in Adults and Juveniles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchinsky, F.J.; Valentino, W.L.; Ruszkay, N.; Powell, E.; Derkay, C.S.; Seedat, R.Y.; Uloza, V.; Dikkers, F.G.; Tunkel, D.E.; Choi, S.S.; et al. Age at diagnosis, but not HPV type, is strongly associated with clinical course in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lépine, C.; Voron, T.; Berrebi, D.; Mandavit, M.; Nervo, M.; Outh-Gauer, S.; Péré, H.; Tournier, L.; Teissier, N.; Tartour, E.; et al. Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Aggressiveness: In Situ Study of the Level of Transcription of HPV E6 and E7. Cancers 2020, 12, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkay, C.S.; Malis, D.J.; Zalzal, G.; Wiatrak, B.J.; Kashima, H.K.; Coltrera, M.D. A Staging System for Assessing Severity of Disease and Response to Therapy in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 1998, 108, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, R.P.; Derkay, C.S.; Burke, B.L.; Lawson, M.L. Reliability of a staging assessment system for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2003, 67, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, M.C.; Brusadelli, M.G.; Carlile, A.; Ruiz-Torres, S.; Lodin, H.; Lee, D.; Kofron, M.; Lambert, P.F.; Lane, A.; Ameziane, N.; et al. Patient-Derived Organotypic Epithelial Rafts Model Phenotypes in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Viruses 2021, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimell, F.L.; Shoemaker, D.L.; Pou, A.M.; Jordan, J.A.; Post, J.C.; Ehrlich, G.D. Pediatric Respiratory Papillomatosis: Prognostic Role of Viral Typing and Cofactors. Laryngoscope 1997, 107, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Maunoury, S.; Croissant, O.; Orth, G. Integration of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequences: A possible early event in the progression of genital tumors. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 3295–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbitt, G.; Zarod, A.P.; Arrand, J.R.; Longson, M.; Farrington, W.T. Human papillomavirus (HPV) genotypes associated with laryngeal papilloma. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, P.M.; Dedo, H.H.; Rabah, R.; Field, J.B.; Mathog, R.H.; Gregoire, L.; Lancaster, W.D. Integration of Human Papillomavirus Type 11 in Recurrent Respiratory Papilloma-Associated Cancer. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Cohort Composition * | Method of HPV Genotyping ** | Risk Factors for Severe Disease | Is HPV11+ Disease More Severe? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mounts, 1984 [27] | 21; AoRRP + JoRRP | HPV6 subtype c | Unknown 1 | |
| Padayachee, 1993 [26] | 20; JoRRP | ISH | HPV6 | No |
| Pou, 1995 [20] | 29 (24); AoRRP | PCR | HPV11/16; HSV, EBV, or CMV coinfection | Unknown 2 |
| Rimell, 1997 [37] | 24; JoRRP | PCR | HPV11 | Yes |
| Gabbott, 1997 [29] | 47; JoRRP | PCR | Early age at diagnosis | No |
| Peñaloza-Plascencia, 2000 [25] | 47; JoRRP | PCR | None | No |
| Rabah, 2001 [22] | 61; JoRRP | PCR | HPV11 | Yes |
| Wiatrak, 2004 [19] | 73 (58); JoRRP | ISH, PCR | HPV11, age at onset ≤3, Medicaid insurance, C-section | Yes |
| Draganov, 2005 [21] | 23; JoRRP | PCR, RT-qPCR | HPV11 | Yes |
| Buchinisky, 2008 [30] | 118; JoRRP | PCR, RFLP | Early age at onset, HPV11 | Yes |
| Omland, 2014 [4] | 221; JoRRP + AoRRP | PCR | HPV negative in AoRRP | No |
| Tjon Pian Gi, 2015 [23] | 55; JoRRP + AoRRP | PCR | Early age of onset, HPV11 in JoRRP, HPV6 in AoRRP | In JoRRP only |
| Buckinisky, 2019 [32] | 339; JoRRP + AoRRP | PCR, RFLP, linear array | Early age at onset | No |
| Nogueira, 2021 [24] | 15 JoRRP, 26 AoRRP | Sequencing | Early age at onset, HPV11 in JoRRP | Yes |
| Patient ID | Gender | Race 1 | Age at Onset | Years since Diagnosis | Derkay Score | Prior Surgeries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt. 01 | Male | White | 4 | 9 | 12 | 22 |
| Pt. 02 | Male | White | 2 | 6 | 5 | 10 |
| Pt. 03 | Male | AA | 2 | 8 | 1 | 10 |
| Pt. 04 | Female | White | 2 | 7 | 9 | 7 |
| Pt. 05 | Male | White | 1 | 18 | 11 | 125 |
| Pt. 06 | Female | White | 2 | 18 | 4 | 23 |
| Pt. 07 | Male | White | 7 | 3 | 6 | 0 |
| Pt. 08 | Male | AA | 7 | 3 | 5 | 0 |
| Pt. 09 | Female | White | 4 | 7 | 19 | 24 |
| Pt. 10 | Male | White | 6 | 5 | 1 | 10 |
| Pt. 11 | Male | White | 6 | 2 | 11 | 0 |
| Pt. 12 | Male | White | 2 | 5 | 8 | 23 |
| Pt. 13 | Male | White | 2 | 7 | 7 | 27 |
| Pt. 14 | Female | AA | 1 | 10 | 9 | 23 |
| Pt. 15 | Male | White | 1 | 13 | 11 | 108 |
| Pt. 16 | Male | Hispanic | 7 | 7 | 0 | 14 |
| Pt. 17 | Female | White | 5 | 9 | 5 | 25 |
| Pt. 18 | Female | AA | 8 | 6 | 7 | 2 |
| Pt. 19 | Male | White | 10 | 7 | 14 | 7 |
| Pt. 20 | Male | AA | 4 | 2 | 15 | 0 |
| Patient ID | Surgeries in First Year of Recruitment | Total Surgeries 1 y Post- Recruitment | Lifetime Surgeries at End of Study | Surgeries per Year Since Diagnosis | HPV Serotype 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt. 01 | 5 | 27 | 32 | 4 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 02 | 3 | 13 | 27 | 4 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 03 | 4 | 14 | 22 | 3 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 04 | 2 | 9 | 17 | 2 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 05 | 6 | 131 | 151 | 8 | HPV11 |
| Pt. 06 | 6 | 29 | 33 | 2 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 07 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 3 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 08 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 09 | 7 | 31 | 34 | 5 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 10 | 1 | 11 | 11 | 2 | - |
| Pt. 11 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 5 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 12 | 8 | 31 | 34 | 7 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 13 | 5 | 32 | 34 | 5 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 14 | 3 | 26 | 27 | 3 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 15 | 6 | 114 | 117 | 9 | HPV11 |
| Pt. 16 | 1 | 15 | 15 | 2 | - |
| Pt. 17 | 3 | 28 | 28 | 3 | - |
| Pt. 18 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | - |
| Pt. 19 | 2 | 9 | 9 | 1 | HPV6 |
| Pt. 20 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 5 | HPV6 |
| Characteristic | Few Surgical Interventions | Regression | Sustained Disease | Progression | Kruskal-Wallis Test 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at onset | 6 ± 3 | 5 ± 2 | 3 ± 2 | 1 | 0.04 |
| Years since diagnosis | 7 ± 2 | 6 ± 3 | 7 ± 5 | 18 | 0.54 |
| Derkay scoreat recruitment | 6 ± 5 | 8 ± 3 | 9 ± 6 | 11 | 0.72 |
| Surgeries prior to recruitment | 14 ± 9 | 7 ± 10 | 25 ± 33 | 125 | 0.12 |
| Surgeries in first year after recruitment | 2 ± 1 | 4 ± 2 | 6 ± 2 | 6 | 0.58 |
| Total surgeries 1y post-recruitment | 15 ± 10 | 11 ± 11 | 31 ± 33 | 131 | 0.06 |
| Lifetime surgeries at end of study | 16 ± 10 | 15 ± 13 | 36 ± 32 | 151 | 0.04 |
| Surgeries per year since diagnosis | 2 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | 5 ± 2 | 8 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bedard, M.C.; de Alarcon, A.; Kou, Y.-F.; Lee, D.; Sestito, A.; Duggins, A.L.; Brusadelli, M.; Lane, A.; Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A.; Wells, S.I.; et al. HPV Strain Predicts Severity of Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis with Implications for Disease Screening. Cancers 2021, 13, 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112556
Bedard MC, de Alarcon A, Kou Y-F, Lee D, Sestito A, Duggins AL, Brusadelli M, Lane A, Wikenheiser-Brokamp KA, Wells SI, et al. HPV Strain Predicts Severity of Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis with Implications for Disease Screening. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112556
Chicago/Turabian StyleBedard, Mary C., Alessandro de Alarcon, Yann-Fuu Kou, David Lee, Alexandra Sestito, Angela L. Duggins, Marion Brusadelli, Adam Lane, Kathryn A. Wikenheiser-Brokamp, Susanne I. Wells, and et al. 2021. "HPV Strain Predicts Severity of Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis with Implications for Disease Screening" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112556
APA StyleBedard, M. C., de Alarcon, A., Kou, Y.-F., Lee, D., Sestito, A., Duggins, A. L., Brusadelli, M., Lane, A., Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K. A., Wells, S. I., & Smith, D. F. (2021). HPV Strain Predicts Severity of Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis with Implications for Disease Screening. Cancers, 13(11), 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112556






