Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma Heterotypic 3D Co-Cultures with Immune Cell Subsets
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
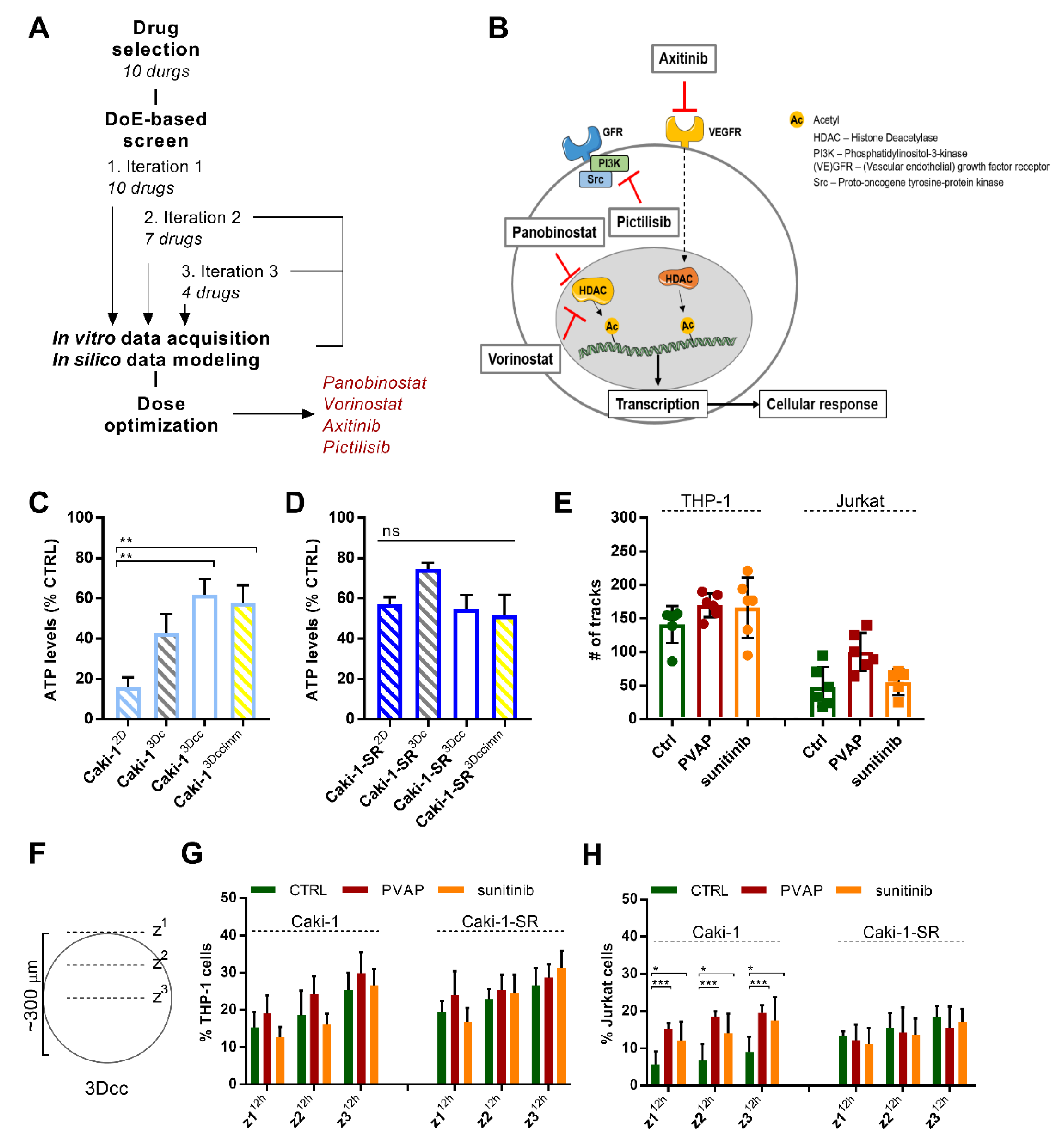
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Generation of Sunitinib-Resistant Caki-1 Cells
2.4. 3D Homo- and Heterotypic Spheroid (co)Cultures
2.5. ATP Measurements
2.6. CellTracker Staining or Ethidium Homodimer and Calcein
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining and Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Infiltration Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Formation of Heterotypic ccRCC 3D Co-Culture Systems Including Immune Cells
3.2. Surface Protein Expression of Cells in the 3Dccimm Models
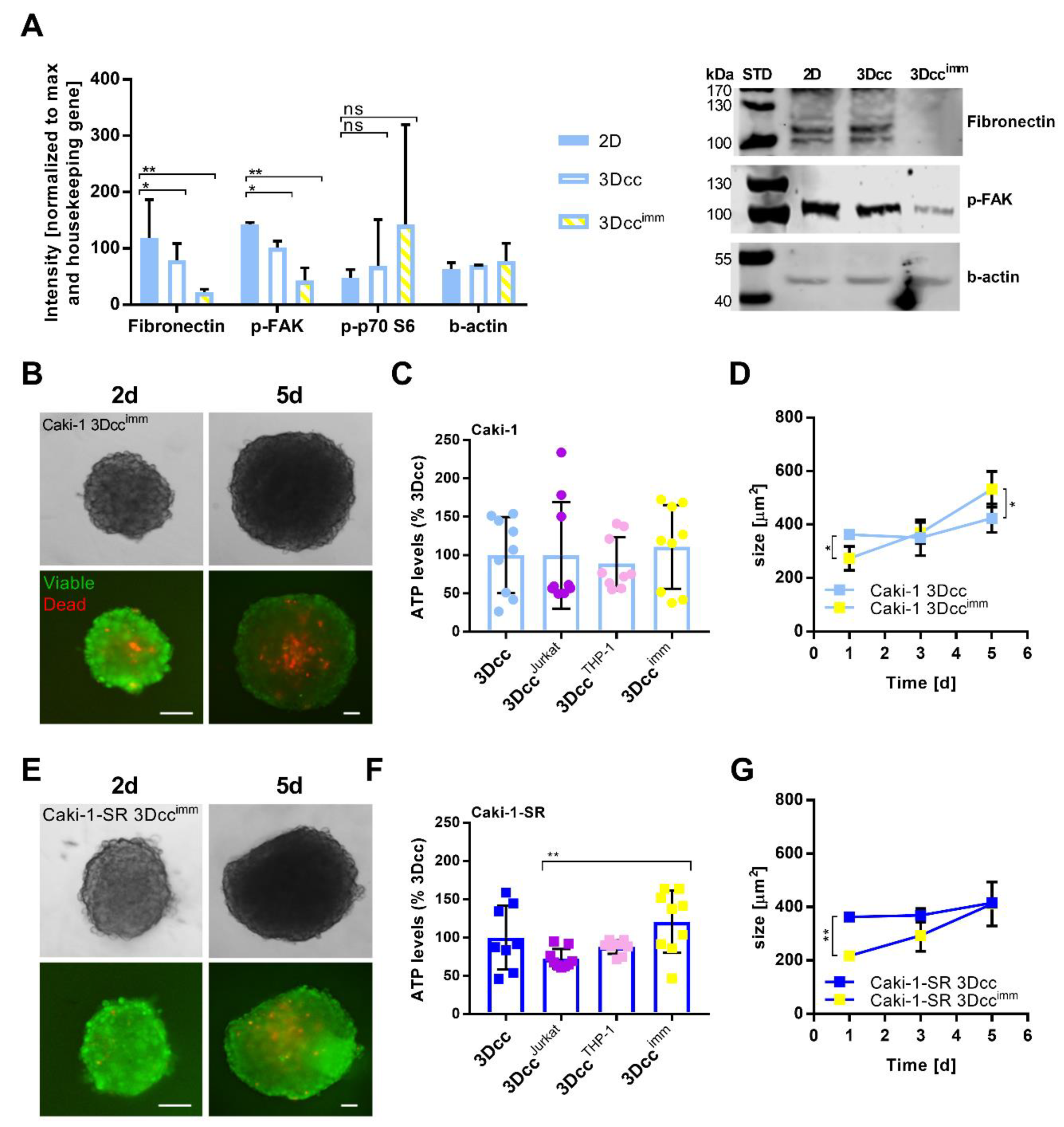
3.3. Features and Maintenance of the Heterotypic ccRCC 3D Co-Culture Systems Including Immune Cells
3.4. Native Immune Cells Have an Impact on Reproducibility and Are Less Compatible with the 3Dcc System
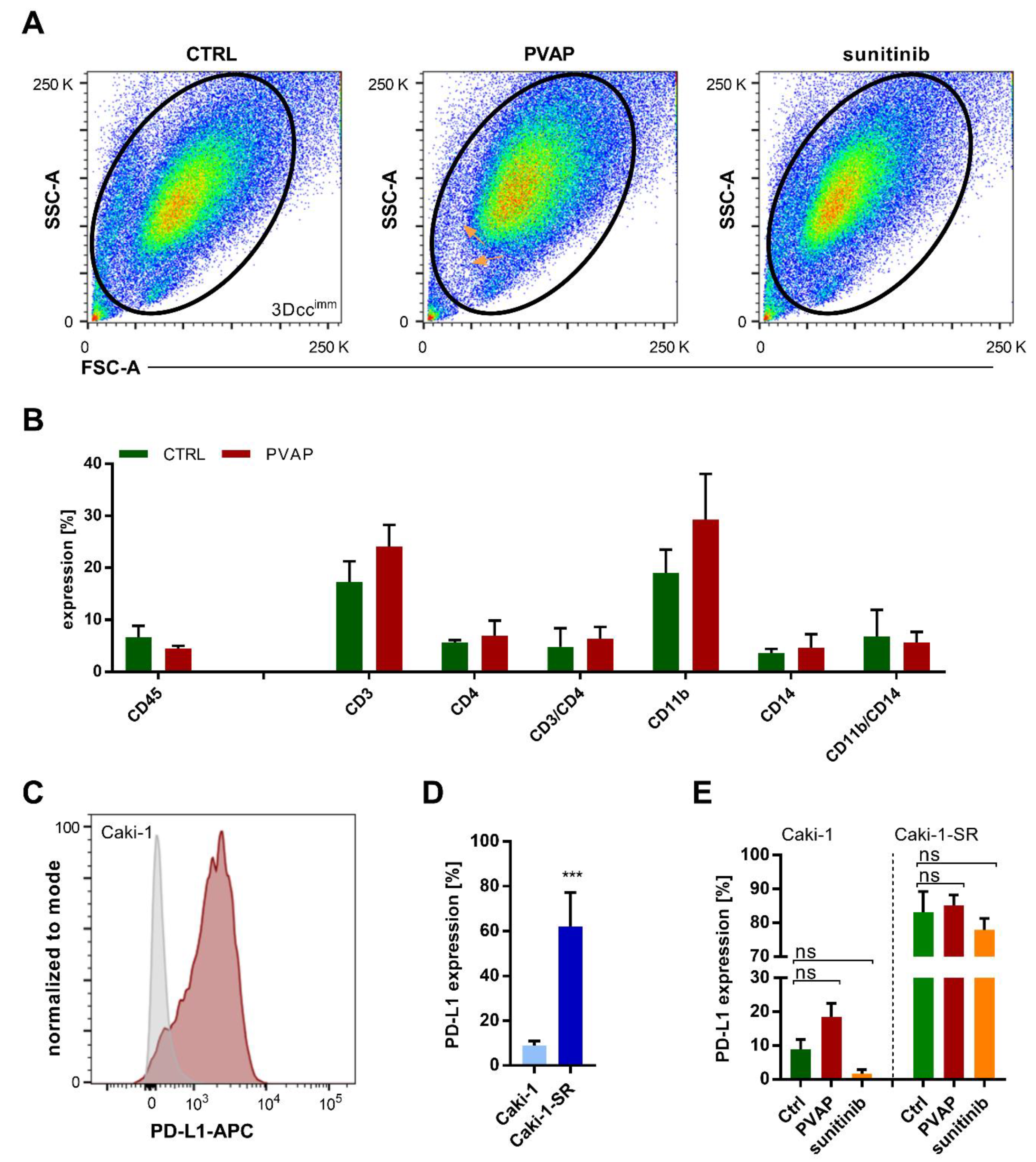
3.5. Infiltration of Immune Cells in 3Dccimm upon Treatments
3.6. Survival of Immune Cells in 3Dccimm upon Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chevrier, S.; Levine, J.H.; Zanotelli, V.R.T.; Silina, K.; Schulz, D.; Bacac, M.; Ries, C.H.; Ailles, L.; Jewett, M.A.S.; Moch, H.; et al. An Immune Atlas of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 736–749.e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Rodriguez, R.; Pruthi, D.; Johnson-Pais, T.; Wang, H.; Mansour, A.; Kaushik, D. Immunogenic Heterogeneity of Renal Cell Carcinoma With Venous Tumor Thrombus. Urology 2019, 124, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F. Tumors: Wounds That Do Not Heal. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.M.; Vétizou, M.; Daillère, R.; Roberti, M.P.; Yamazaki, T.; Routy, B.; Lepage, P.; Boneca, I.G.; Chamaillard, M.; Kroemer, G.; et al. Resistance Mechanisms to Immune-Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer: Tumor-Intrinsic and -Extrinsic Factors. Immunity 2016, 44, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huinen, Z.R.; Huijbers, E.J.M.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Griffioen, A.W. Anti-angiogenic agents—Overcoming tumour endothelial cell anergy and improving immunotherapy outcomes. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, A.W.; Damen, C.A.; Martinotti, S.; Blijham, G.H.; Groenewegen, G. Endothelial intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression is suppressed in human malignancies: The role of angiogenic factors. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, R.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Kim, M.; Ober, R.J.; Ward, E.S. Phagocytosis of antibody-opsonized tumor cells leads to the formation of a discrete vacuolar compartment in macrophages. Traffic 2018, 19, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlung, H.L.; Babes, L.; Zhao, X.W.; van Houdt, M.; Treffers, L.W.; van Rees, D.J.; Franke, K.; Schornagel, K.; Verkuijlen, P.; Janssen, H.; et al. Neutrophils Kill Antibody-Opsonized Cancer Cells by Trogoptosis. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3946–3959.e3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, A.E.; Crawford, J.C.; Thomas, P.G. Hitting the Target: How T Cells Detect and Eliminate Tumors. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.S.; Cox, M.A.; Zajac, A.J. T-cell exhaustion: Characteristics, causes and conversion. Immunology 2010, 129, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perica, K.; Varela, J.C.; Oelke, M.; Schneck, J. Adoptive T cell immunotherapy for cancer. Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2015, 6, e0004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.R.; Maus, M.V. Gene editing for immune cell therapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijbers, E.J.M.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Lê, C.T.; Langman, S.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Mayo, K.H.; Griffioen, A.W. An improved conjugate vaccine technology; induction of antibody responses to the tumor vasculature. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3054–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, D.J.; Chernajovsky, Y. Novel delivery methods to achieve immunomodulation. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Song, W.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Disease Immunotherapy: Immunomodulatory Nanosystems (Adv. Sci. 17/2019). Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2019, 6, 1970100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chan, H.L.; Chen, P. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Basics and Challenges. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 3009–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Maher, V.E.; Zhang, L.; Tang, S.; Sridhara, R.; Ibrahim, A.; Kim, G.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Nivolumab in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma After Anti-Angiogenic Therapy and Exploratory Predictive Biomarker Analysis. Oncologist 2017, 22, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; McDermott, D.F. Ipilimumab in combination with nivolumab for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, C. Checkpoint Inhibitor-TKI Combos Effective in RCC. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebell, P.J.; Ivanyi, P.; Bedke, J.; Bergmann, L.; Berthold, D.; Boegemann, M.; Busch, J.; Doehn, C.; Krege, S.; Retz, M.; et al. Consensus paper: Current state of first- and second-line therapy in advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2020, 16, 2307–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; McDermott, D.F.; Hammers, H.; Bro, W.; Bukowski, R.M.; Faba, B.; Faba, J.; Figlin, R.A.; Hutson, T.; Jonasch, E.; et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garje, R.; An, J.; Greco, A.; Vaddepally, R.K.; Zakharia, Y. The Future of Immunotherapy-Based Combination Therapy in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzy, G.M.; Koessler, T.; Ducrey, E.; McKee, T.; Ris, F.; Buchs, N.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Patient-Derived In Vitro Models for Drug Discovery in Colorectal Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E. Issues with Cancer Spheroid Models in Therapeutic Drug Screening. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerignoli, F.; Abassi, Y.A.; Lamarche, B.J.; Guenther, G.; Santa Ana, D.; Guimet, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Xi, B. In vitro immunotherapy potency assays using real-time cell analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Ahmed, M.; Okoye, I.; Arutyunova, E.; Babu, D.; Turnbull, W.L.; Kundu, J.K.; Shields, J.; Agopsowicz, K.C.; Xu, L.; et al. Comprehensive in vitro characterization of PD-L1 small molecule inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Modugno, F.; Colosi, C.; Trono, P.; Antonacci, G.; Ruocco, G.; Nisticò, P. 3D models in the new era of immune oncology: Focus on T cells, CAF and ECM. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courau, T.; Bonnereau, J.; Chicoteau, J.; Bottois, H.; Remark, R.; Assante Miranda, L.; Toubert, A.; Blery, M.; Aparicio, T.; Allez, M.; et al. Cocultures of human colorectal tumor spheroids with immune cells reveal the therapeutic potential of MICA/B and NKG2A targeting for cancer treatment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, A.; Hedrich, V.; Sommergruber, W. 3D-3 Tumor Models in Drug Discovery for Analysis of Immune Cell Infiltration. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1953, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Luo, Z.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.; Tebon, P.; Feng, Y.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Sengupta, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Organ-on-a-Chip for Cancer and Immune Organs Modeling. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanti, A.; Teo, J.; Stefanini, C. In Vitro Immune Organs-on-Chip for Drug Development: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polini, A.; del Mercato, L.L.; Barra, A.; Zhang, Y.S.; Calabi, F.; Gigli, G. Towards the development of human immune-system-on-a-chip platforms. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoetemelk, M.; Rausch, M.; Colin, D.J.; Dormond, O.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Short-term 3D culture systems of various complexity for treatment optimization of colorectal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, M.; Weiss, A.; Achkhanian, J.; Rotari, A.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Identification of low-dose multidrug combinations for sunitinib-naive and pre-treated renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, M.; Weiss, A.; Zoetemelk, M.; Piersma, S.R.; Jimenez, C.R.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Optimized Combination of HDACI and TKI Efficiently Inhibits Metabolic Activity in Renal Cell Carcinoma and Overcomes Sunitinib Resistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Árnadóttir, S.S.; Jeppesen, M.; Lamy, P.; Bramsen, J.B.; Nordentoft, I.; Knudsen, M.; Vang, S.; Madsen, M.R.; Thastrup, O.; Thastrup, J.; et al. Characterization of genetic intratumor heterogeneity in colorectal cancer and matching patient-derived spheroid cultures. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucinska, M.; Murias, M.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Beyond mouse cancer models: Three-dimensional human-relevant in vitro and non-mammalian in vivo models for photodynamic therapy. Mutat Res. 2017, 773, 242–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beijnum, J.R.; Weiss, A.; Berndsen, R.H.; Wong, T.J.; Reckman, L.C.; Piersma, S.R.; Zoetemelk, M.; De Haas, R.R.; Dormond, O.; Bex, A.; et al. Integrating phenotypic search and phosphoproteomic profiling of active kinases for optimization of drug mixtures for RCC treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, Y.C.; Hsiao, A.Y.; Allen, S.G.; Torisawa, Y.S.; Ho, M.; Takayama, S. High-throughput 3D spheroid culture and drug testing using a 384 hanging drop array. Analyst 2011, 136, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Roman, N.; Stevenson, K.; Gilmour, L.; Hamilton, G.; Chalmers, A.J. A novel 3D human glioblastoma cell culture system for modeling drug and radiation responses. Neuro. Oncol. 2017, 19, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoetemelk, M.; Ramzy, G.M.; Rausch, M.; Koessler, T.; van Beijnum, J.R.; Weiss, A.; Mieville, V.; Piersma, S.R.; de Haas, R.R.; Delucinge-Vivier, C.; et al. Optimized low-dose combinatorial drug treatment boosts selectivity and efficacy of colorectal carcinoma treatment. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2894–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.S.; Shvarts, O.; Leppert, J.T.; Figlin, R.A.; Belldegrun, A.S. Renal cell carcinoma 2005: New frontiers in staging, prognostication and targeted molecular therapy. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferronika, P.; Hof, J.; Kats-Ugurlu, G.; Sijmons, R.H.; Terpstra, M.M.; de Lange, K.; Leliveld-Kors, A.; Westers, H.; Kok, K. Comprehensive Profiling of Primary and Metastatic ccRCC Reveals a High Homology of the Metastases to a Subregion of the Primary Tumour. Cancers 2019, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Le Roux-Bourdieu, M.; Zoetemelk, M.; Ramzy, G.M.; Rausch, M.; Harry, D.; Miljkovic-Licina, M.; Falamaki, K.; Wehrle-Haller, B.; Meraldi, P.; et al. Identification of a Synergistic Multi-Drug Combination Active in Cancer Cells via the Prevention of Spindle Pole Clustering. Cancers 2019, 11, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnappinger, J.; Straub, T.; Lee, S.; Schiergens, T.; Oberneder, R.; Nößner, E. Immune landscape analysis to identify targets for immunotherapy across human carcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 92, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorny, P.J.; Liu, Y.; Dharmani-Khan, P.; Pratt, L.M.; Jamani, K.; Luider, J.; Auer-Grzesiak, I.; Mansoor, A.; Williamson, T.S.; Ugarte-Torres, A.; et al. Immune cell subset counts associated with graft-versus-host disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.; Teng, Y. Is It Time to Start Transitioning From 2D to 3D Cell Culture? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidegger, I.; Pircher, A.; Pichler, R. Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment in Renal Cell Cancer Biology and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Liu, L. The role of collagen in cancer: From bench to bedside. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Yuan, J.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Collagen as a double-edged sword in tumor progression. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 2871–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrousse-Arias, D.; Martínez-Alonso, E.; Corral-Escariz, M.; Bienes-Martínez, R.; Berridy, J.; Serrano-Oviedo, L.; Conde, E.; García-Bermejo, M.L.; Giménez-Bachs, J.M.; Salinas-Sánchez, A.S.; et al. VHL promotes immune response against renal cell carcinoma via NF-κB-dependent regulation of VCAM-1. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östman, A. The tumor microenvironment controls drug sensitivity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Bort, E.; Kieler, M.; Sharma, S.; Candido, J.B.; Loessner, D. 3D approaches to model the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5074–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, B.; Mohr, M.A.; Ponti, A.; Emmert, M.Y.; Weibel, F.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Moll, S.; Certa, U.; Prunotto, M.; Pantazis, P. Monitoring and manipulating cellular crosstalk during kidney fibrosis inside a 3D in vitro co-culture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, S.P.; Pinto, C.; Martins, T.R.; Harrer, N.; Estrada, M.F.; Loza-Alvarez, P.; Cabeçadas, J.; Alves, P.M.; Gualda, E.J.; Sommergruber, W.; et al. 3D-3-culture: A tool to unveil macrophage plasticity in the tumour microenvironment. Biomaterials 2018, 163, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Hir, M.; Hegyi, I.; Cueni-Loffing, D.; Loffing, J.; Kaissling, B. Characterization of renal interstitial fibroblast-specific protein 1/S100A4-positive cells in healthy and inflamed rodent kidneys. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 123, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strutz, F.; Zeisberg, M. Renal Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneval, P.; Rossert, J.; Bariety, J. Renewal of FSP1: A marker of fibrogenesis on human renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1366–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, E.M.; Potenta, S.E.; Sugimoto, H.; Zeisberg, M.; Kalluri, R. Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Yin, X.; Zhai, X.; Wang, L.; Li, K.; Li, Z. Down-regulation of integrin β1 and focal adhesion kinase in renal glomeruli under various hemodynamic conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, N.M.; Ferenbach, D.A.; Isenberg, J.S.; Thomson, A.W.; Hughes, J. Dendritic cells and macrophages in the kidney: A spectrum of good and evil. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurts, C.; Panzer, U.; Anders, H.J.; Rees, A.J. The immune system and kidney disease: Basic concepts and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanput, W.; Peters, V.; Wichers, H. THP-1 and U937 Cells. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health; Verhoeckx, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Hori, S.; Morizawa, Y.; Tatsumi, Y.; Nakai, Y.; Anai, S.; Torimoto, K.; Aoki, K.; Tanaka, N.; Shimada, K.; et al. CXCL1-Mediated Interaction of Cancer Cells with Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Tumor Progression in Human Bladder Cancer. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, W.-K.; Zhang, W.; Hu, B. Vascular endothelial growth factor suppresses dendritic cells function of human prostate cancer. Onco. Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, K.; Kono, K.; Takahashi, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Fujii, H. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits the function of human mature dendritic cells mediated by VEGF receptor-2. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton-Nash, D.K.; Newman, P.J. A New Role for Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (CD31): Inhibition of TCR-Mediated Signal Transduction. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 682. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Vezzani, B.; Khan, N.; Su, J.; Xu, L.; Yan, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Gaur, A.; Diao, Z.; et al. CD10 expression identifies a subset of human perivascular progenitor cells with high proliferation and calcification potentials. Stem Cells 2020, 38, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Moriyama, T.; Onimaru, M.; Nakata, K.; Nabae, T.; Ueki, T.; Sato, N.; Tominaga, Y.; et al. Prospectively isolated cancer-associated CD10+ fibroblasts have stronger interactions with CD133+ colon cancer cells than with CD133− cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedland, S.J.; Seligson, D.B.; Liu, A.Y.; Pantuck, A.J.; Paik, S.H.; Horvath, S.; Wieder, J.A.; Zisman, A.; Nguyen, D.; Tso, C.L.; et al. Loss of CD10 (neutral endopeptidase) is a frequent and early event in human prostate cancer. Prostate 2003, 55, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wennborg, A.; Aurell, E.; Dekel, E.; Zou, J.-Z.; Xu, Y.; Huang, S.; Ernberg, I. Dynamics inside the cancer cell attractor reveal cell heterogeneity, limits of stability, and escape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.M.; Kimryn Rathmell, W.; Beckermann, K.E. Modeling clear cell renal cell carcinoma and therapeutic implications. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3413–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, L.K.; Branchi, V.; Leonardelli, S.; Pelusi, N.; Simon, A.G.; Klümper, N.; Ellinger, J.; Hauser, S.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Ritter, M.; et al. Cultivation of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patient-Derived Organoids in an Air-Liquid Interface System as a Tool for Studying Individualized Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.T.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Giangarra, V.; Grzeskowiak, C.L.; Ju, J.; Liu, I.H.; Chiou, S.-H.; Salahudeen, A.A.; Smith, A.R.; et al. Organoid Modeling of the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cell 2018, 175, 1972–1988.e1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, J.J.; Li, X.; Chou, C.J. Advances and Challenges of HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 138, 183–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, M. HDAC inhibitors still need a home run, despite recent approval. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination Therapy With Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi) for the Treatment of Cancer: Achieving the Full Therapeutic Potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.E.; Jeong, I.G.; Choi, J.; Jang, S.; Lee, J.H.; Ro, S.; Hwang, J.J.; Kim, C.S. HDAC inhibitors synergize antiproliferative effect of sorafenib in renal cell carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar]
- Worthington, R.J.; Melander, C. Combination approaches to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrimali, R.K.; Yu, Z.; Theoret, M.R.; Chinnasamy, D.; Restifo, N.P.; Rosenberg, S.A. Antiangiogenic agents can increase lymphocyte infiltration into tumor and enhance the effectiveness of adoptive immunotherapy of cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6171–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roland, C.L.; Lynn, K.D.; Toombs, J.E.; Dineen, S.P.; Udugamasooriya, D.G.; Brekken, R.A. Cytokine levels correlate with immune cell infiltration after anti-VEGF therapy in preclinical mouse models of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dings, R.P.M.; Vang, K.B.; Castermans, K.; Popescu, F.; Zhang, Y.; oude Egbrink, M.G.A.; Mescher, M.F.; Farrar, M.A.; Griffioen, A.W.; Mayo, K.H. Enhancement of T-cell–Mediated Antitumor Response: Angiostatic Adjuvant to Immunotherapy against Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kuang, X.; Liang, L.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, F.; Tao, J.; Lei, G.; Zhao, S.; et al. The Beneficial Role of Sunitinib in Tumor Immune Surveillance by Regulating Tumor PD-L1. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Soria, J.C.; Kowanetz, M.; Fine, G.D.; Hamid, O.; Gordon, M.S.; Sosman, J.A.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Gettinger, S.N.; et al. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 2014, 515, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, M.; McDermott, D. Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2015, 7, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
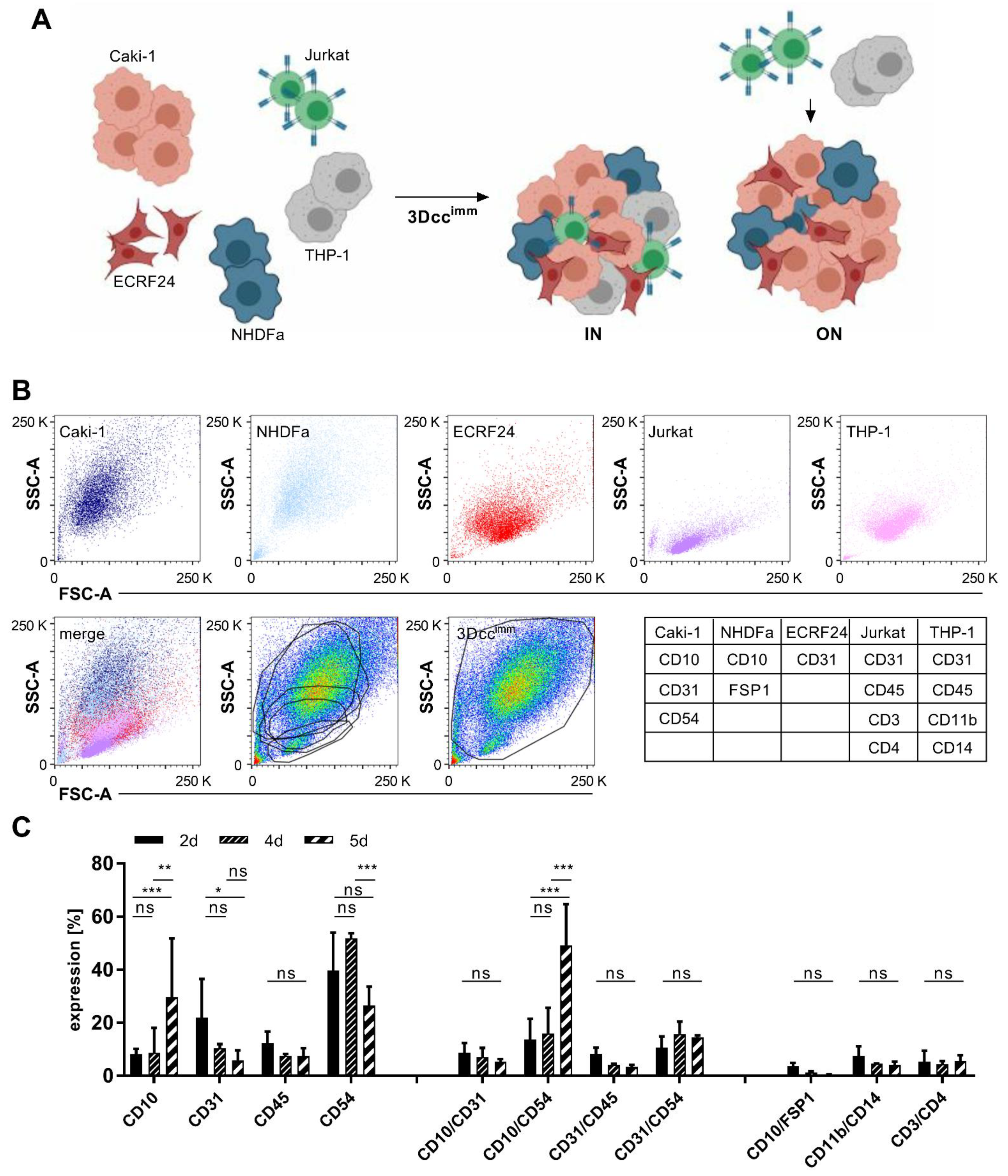
| Cell Type | Markers | Quantity of Cells [%] in Time ± SD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Day 2 | Day 4 | Day 5 | ||
| Caki-1 | CD10 CD54 | 70 | 58.26 ± 14.1 | 64.30 ± 6.1 | 71.76 ± 2.7 |
| Caki-1-SR | CD10 high CD31 CD54 high | 70 | 59.13 ± 13.9 | 59.46 ± 8.5 | 70.32 ± 3.0 |
| NHDFα | CD10 FSP1 | 20 | 5.5 ± 0.7 | 1.38 ± 0.6 | 2.47 ± 1.0 |
| ECRF24 | CD10 CD31 | 10 | 11.56 ± 2.8 | 9.58 ± 3.3 | 8.01 ± 2.6 |
| Jurkat | CD45 CD3 CD4 | 5 | 11.13 ± 3.5 | 4.27 ± 0.7 | 8.83 ± 1.4 |
| THP-1 | CD45 CD11b CD14 | 10 | 11.35 ± 5.5 | 5.81 ± 1.2 | 5.59 ± 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rausch, M.; Blanc, L.; De Souza Silva, O.; Dormond, O.; Griffioen, A.W.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma Heterotypic 3D Co-Cultures with Immune Cell Subsets. Cancers 2021, 13, 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112551
Rausch M, Blanc L, De Souza Silva O, Dormond O, Griffioen AW, Nowak-Sliwinska P. Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma Heterotypic 3D Co-Cultures with Immune Cell Subsets. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112551
Chicago/Turabian StyleRausch, Magdalena, Léa Blanc, Olga De Souza Silva, Olivier Dormond, Arjan W. Griffioen, and Patrycja Nowak-Sliwinska. 2021. "Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma Heterotypic 3D Co-Cultures with Immune Cell Subsets" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112551
APA StyleRausch, M., Blanc, L., De Souza Silva, O., Dormond, O., Griffioen, A. W., & Nowak-Sliwinska, P. (2021). Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma Heterotypic 3D Co-Cultures with Immune Cell Subsets. Cancers, 13(11), 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112551








