STAT3, the Challenge for Chemotherapeutic and Radiotherapeutic Efficacy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
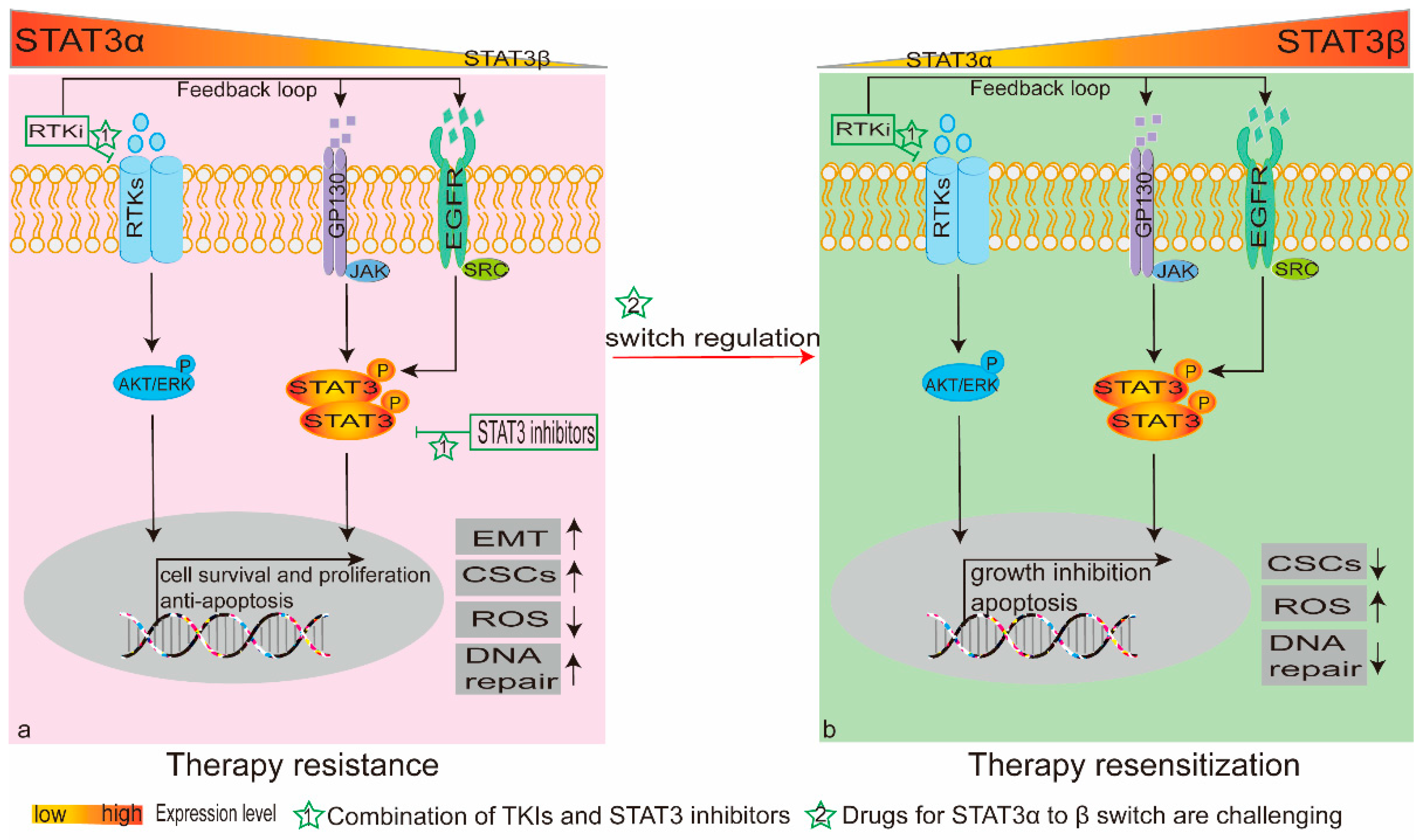
2. Feedback Loop Leading to STAT3 Activation
3. STAT3 Activation by Radiation
| Cancers | Cell Lines | Treatment | Inhibition of STAT3 Activation via Different Methods | In Vitro or In Vivo | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute myeloid leukemia | KG-1/U937 | DNR/Ara-C/IDR | Simvastatin/OPN siRNA | in vitro | Significantly decreases the viability of cells and the expression level of STAT3, which sensitizes cells to chemotherapy. | [45] |
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma | SUP-M2 | crizotinib | Stattic | in vitro | Inhibition of STAT3 can reverse the resistance to crizotinib in IR10RA-overexpressed cells. | [47] |
| B-1 lymphoma | B-1 cells | RT | STAT3−/− mice | in vitro and in vivo | In STAT3−/− mice, B cells are more susceptible to radiation-induced apoptosis. | [56] |
| Lung cancer | A549/H358/H157 | RT | Niclosamide | in vitro and in vivo | Blocks IR-induced activation of the STAT3/Bcl-2/Bcl-xL pathway and enhances apoptosis. | [59] |
| A549 | RT | AZD0530 | in vitro | Inhibits cell migration by blocking Src and enhances sensitivity to IR. | [73] | |
| A549 | RT/cisplatin | shRNA | in vitro and in vivo | Enhances radiosensitivity both in vitro and in vivo and enhances chemosensitivity in vitro. | [74,81] | |
| HCC2429 | RT | TG101209 | in vitro and in vivo | Inhibits STAT3 activation and survivin expression, induces apoptosis and decreases proliferation. | [75] | |
| PC-9 | Erlotinib | STAT3 siRNA/STAT3 shRNA | in vitro and in vivo | Inhibition of STAT3 feedback sensitized lung adenocarcinoma to MEK inhibition. | [35] | |
| Breast cancer | MCF-7 | RT | Xanthohumol | in vitro | Suppresses MDR1, EGFR and STAT3 expression, while increasing death receptor (DR)-4 and DR5 expression, and restores sensitivity to IR and doxorubicin. | [77] |
| MDA-MB-231/MDA-MB-468 | RT | Niclosamide/STAT3 shRNA | in vitro and in vivo | Niclosamide inhibits STAT3 and Bcl-2 and increases ROS generation in vitro and in vivo; it is identified as a radiosensitizer. shRNA of STAT3 sensitizes breast cells to IR. | [68] | |
| SKBR3 | RT | Lapatinib/S3I-201 | in vitro and in vivo | Inhibition of the HER2-STAT3-survivin axis increases sensitivity in SKBR3 cells. | [67] | |
| BT474 | Trastuzumab | S3I-201 | in vitro and in vivo | STAT3 inhibition significantly inhibits tumor growth and sensitizes breast cancer cells to trastuzumab. | [36] | |
| Colorectal cancer | HCT116/LoVo | RT | JAK2 shRNA | in vitro and in vivo | Downregulation of JAK2/STAT3/CCND2 signaling to sensitize cells to radiotherapy and impair cancer stemness. | [78] |
| HCT116/HCT29 | 5-FU/RT | Selumetinib | in vitro and in vivo | Increases mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis and decreases STAT3 activation and survivin expression; it also enhances sensitivity to radiotherapy in vivo. | [79] | |
| HCT116 | Refametinib | 4-IPP | in vitro | Inhibition of 4-IPP sensitizes cancer cells to refametinib. | [38] | |
| Esophageal carcinoma | ECa109 | RT | AG490 | in vitro | Reverses the IR-induced EMT phenotypes and gene expression via regulation of the IL-6/STAT3/Twist signaling pathway. Attenuates radioresistance under AG490 treatment. | [80] |
| ECa109/TE13/KYSE150 | RT | Stattic | in vitro and in vivo | Stattic inhibits STAT3 activation, downregulates HIF-1α and VEGF expression; and confers radiosensitivity in vitro and in vivo. | [87] | |
| ECa109/TE13 | RT | NSC74859 | in vitro and in vivo | Sensitizes cells to radiotherapy in vitro and in vivo via inhibiting STAT3 activation and downregulation of HIF-1α and VEGF expression. | [88] | |
| Glioblastoma | D456 GSCs | RT | Ibrutinib | in vitro | Combines with radiotherapy to disrupt tumor growth and mainly disrupts glioma stem cells by inhibiting bone marrow and X-linked (BMX)/STAT3 activation. | [64] |
| GBM-R212 | RT | STAT3 shRNA | in vitro | Reduces STAT3, decrease Slug expression and suppresses cell invasion; inhibits cancer stem cell properties and enhances radiotherapy. | [82] | |
| GSC-2/ GSC-11 | RT | Stattic/WP1066 | in vitro | Enhances radiosensitivity of GSC lines by inhibition of STAT3 activation, mainly impacting pSTAT3 on Serine727. | [72] | |
| U251/U87 | RT | Cryptotanshinone/WP1066/S3I-201 | in vitro and in vivo | Re-sensitizes radioresistant cells to radiotherapy by inhibition of STAT3; when combined with ERK1/2 inhibitors, it remarkably eliminates resistant cells and inhibits tumor regrowth. | [89] | |
| Head and neck carcinoma | UMSCC-17B | RT | Stattic | in vitro and in vivo | Reduces STAT3-mediated HIF-1α expression in response to Stattic. | [90] |
| UMSCC-22A/UMSCC-22B | RT | Linifanib | in vitro | Cell growth inhibition, G2/M cell cycle arrest and induction of cell death via apoptosis; it overcomes radioresistance by reducing pSTAT3 and expression of its target genes, e.g., cyclin D1, survivin. | [91] | |
| HNSCC-CD44(+)ALDH1(+) cell | RT | Cucurbitacin I | in vitro and in vivo | Combines with radiotherapy to suppress tumorigenesis and metastasis and also reduces CSC-like cells. | [76] | |
| Hepatoblastoma | HepG2.2.15 | RT | STAT3D | Suppresses RT-induced hepatitis B virus DNA replication and impairs hepatobiliary malignancies. | [62] | |
| PLC5/Huh-7/Sk-Hep1/Hep3B | RT | Sorafenib/STAT3 siRNA | In vitro and in vivo | Enhances radiation-induced apoptosis by inhibiting STAT3; it also downregulates Mcl-1, cyclin D1 and survivin expression, overcomes resistance to radiation in cells and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. | [92] |
4. STAT3 Target Genes Impact Chemoresistance and Radioresistance
4.1. Bcl-2 Family
4.2. EMT Regulators
4.3. Survivin
4.4. Cyclin D1
4.5. Immunosuppressive Molecules
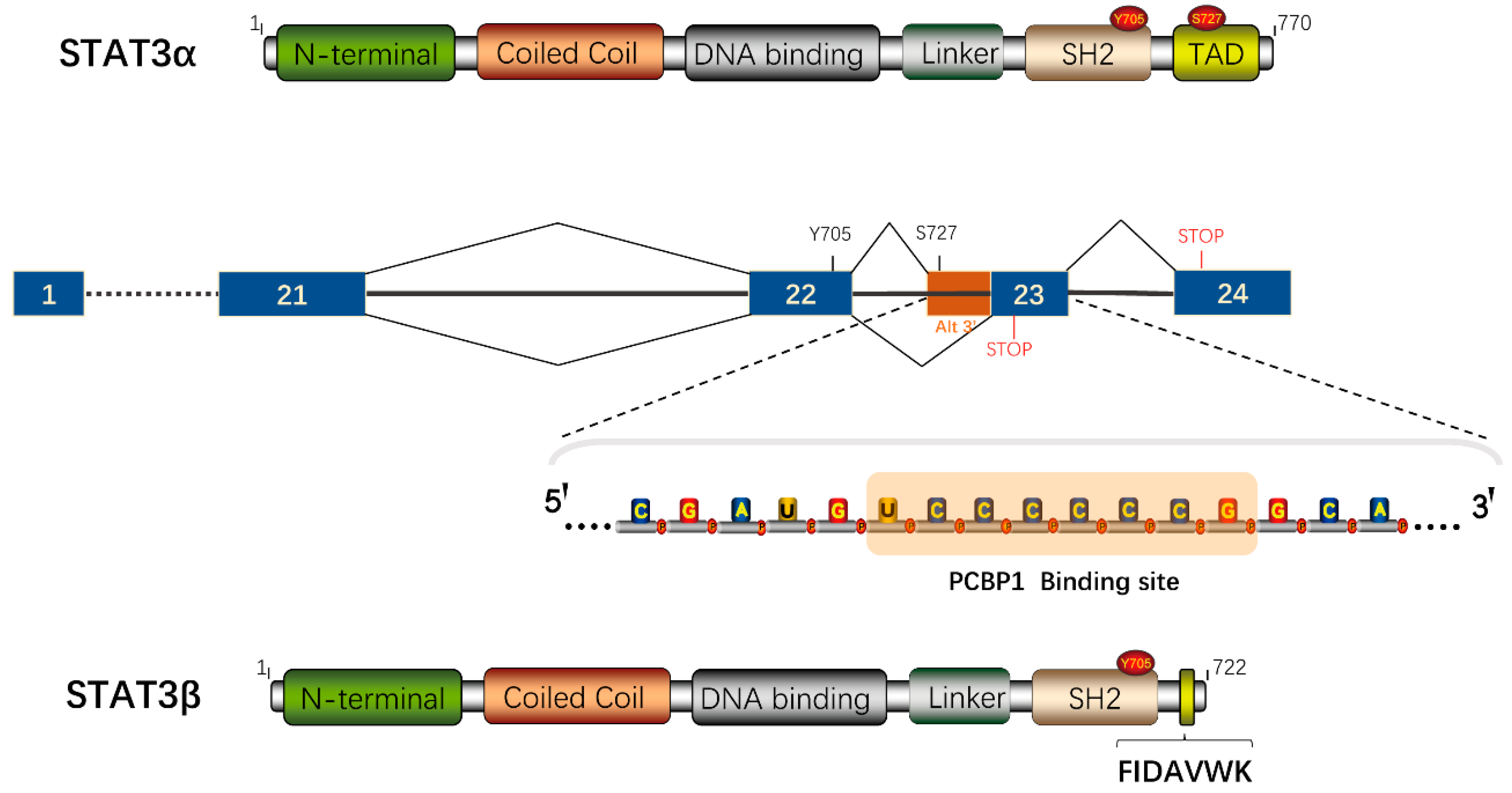
5. The Alternative Splicing Product STAT3β
5.1. Antitumorigenic Potential of STAT3β
5.2. STAT3β Switch Modulates Chemo(Radio)therapy Sensitivity
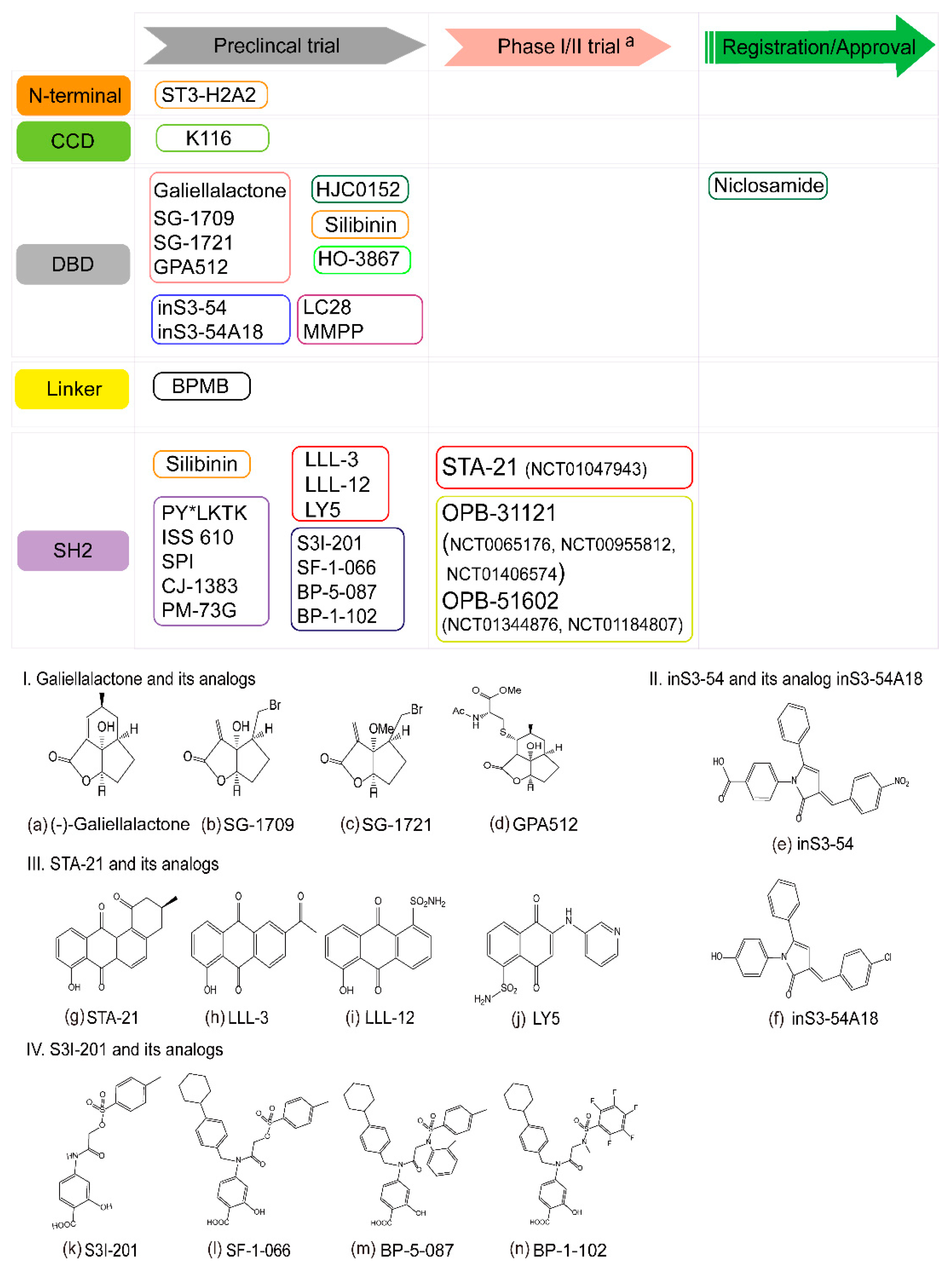
6. STAT3 as a Therapeutic Target
6.1. Targeting the STAT3 N-Terminal Domain
6.2. Targeting the STAT3 DNA-Binding Domain
6.3. Targeting the STAT3 Linker Domain
6.4. Targeting the STAT3 SH2 Domain
6.5. The Challenge of STAT3 Inhibitors
7. Conclusions and future perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | protein kinase B | JAK | Janus kinase |
| Arg | arginine | KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma 2 viral oncogene homolog |
| ATM | ataxia telangiectasia mutated | lncRNA-SRLR | sorafenib resistance-associated lncRNA in RCC |
| Bax | Bcl2 associated X | MEK | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 | NKTL | NK/T-cell lymphoma |
| Bcl-xL | B-cell lymphoma-extra large | MLS | myxoid liposarcoma |
| BLACAT1 | bladder cancer associated transcript 1 | NTD | amino-terminal domain |
| BL | Burkitt lymphoma | NSCLC | non-small-cell lung cancer |
| CCD | coiled-coil domain | PCBP1 | poly-C binding protein-1 |
| CKS1B | cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit 1B | PD-L1 | programmed death ligand 1 |
| CML | chronic myeloid leukemia | PI3K | phosphonosinol-3 kinase |
| CRC | colorectal cancer | PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| CRT | chemoradiotherapy | RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| CSC | cancer stem cell | ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| DAP | diarylidenyl-piperidone | RT | radiation therapy |
| DBD | DNA-binding domain | RTKs | receptor tyrosine kinases |
| DC | dendritic cell | Ser727 | serine 727 |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor | SELL | selectin L |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor | SH2 | Src homology 2 |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition | STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| ESCC | esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma | TAD | transcriptional activation domain |
| FBDD | fragment-based drug design | TGF-β | transforming growth factor β |
| FN | Fibronectin | TKIs | tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| FRET | fluorescence resonance energy transfer | Twist1 | twist basic helix loop helix transcription factor 1 |
| GAS | interferon γ-activated sequence | Val | valine |
| GBM | Glioblastoma | VEGFR | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 | Tyr705 | tyrosine 705 |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 | Ile | isoleucine |
References
- Hoek, J.; Bloemendal, K.M.; van der Velden, L.A.; van Diessen, J.N.; van Werkhoven, E.; Klop, W.M.; Tesselaar, M.E. Nephrotoxicity as a Dose-Limiting Factor in a High-Dose Cisplatin-Based Chemoradiotherapy Regimen for Head and Neck Carcinomas. Cancers 2016, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.A.; Qureshi, M.M.; Logue, J.M.; Cooley, T.P.; Zaner, K.S.; Jalisi, S.; Truong, M.T. Assessing cumulative acute toxicity of chemoradiotherapy in head and neck cancer with or without induction chemotherapy. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 38, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzner, M.; Ebner, R.; Wolff, H.A.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Wienands, J.; Grade, M. STAT3: A Novel Molecular Mediator of Resistance to Chemoradiotherapy. Cancers 2014, 6, 1986–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugase, T.; Takahashi, T.; Serada, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Hiramatsu, K.; Ohkawara, T.; Tanaka, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Makino, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; et al. SOCS1 Gene Therapy Improves Radiosensitivity and Enhances Irradiation-Induced DNA Damage in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6975–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzner, M.; Roesler, B.; Bielfeld, C.; Emons, G.; Gaedcke, J.; Wolff, H.A.; Rave-Frank, M.; Kramer, F.; Beissbarth, T.; Kitz, J.; et al. STAT3 inhibition sensitizes colorectal cancer to chemoradiotherapy in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Tang, W.; Marquez, R.T.; Li, K.; Highfill, C.A.; He, F.; Lian, J.; Lin, J.; Fuchs, J.R.; Ji, M.; et al. Overcoming chemo/radio-resistance of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting STAT3 signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11708–11723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, K.; Stark, G.R.; Kerr, I.M.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science 1993, 261, 1744–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Arya, A.; Naema, A.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Looi, C.Y. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STATs) Proteins in Cancer and Inflammation: Functions and Therapeutic Implication. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.L.; Hoey, T. Cooperative DNA binding and sequence-selective recognition conferred by the STAT amino-terminal domain. Science 1996, 273, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, K.; Horvath, C.M.; Huang, L.H.T.; Qureshi, S.A.; Cowburn, D.; Darnell, J.E. Interferon activation of the transcription factor Stat91 involves dimerization through SH2-phosphotyrosyl peptide interactions. Cell 1994, 76, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kee, W.H.; Seow, K.T.; Fung, W.; Cao, X. The coiled-coil domain of Stat3 is essential for its SH2 domain-mediated receptor binding and subsequent activation induced by epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 7132–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegenka, U.M.; Buschmann, J.; Lutticken, C.; Heinrich, P.C.; Horn, F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Nishio, Y.; Inoue, M.; Wang, X.J.; Wei, S.; Matsusaka, T.; Yoshida, K.; Sudo, T.; Naruto, M.; Kishimoto, T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell 1994, 77, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wen, Z.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stat3: A STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 1994, 264, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.S.; Lamb, P.; Seidel, H.M.; Stein, R.B.; Rosen, J. Rapid activation of the STAT3 transcription factor by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 1994, 84, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisse, C.; Halaas, J.L.; Horvath, C.M.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Stoffel, M.; Friedman, J.M. Leptin activation of Stat3 in the hypothalamus of wild-type and ob/ob mice but not db/db mice. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.P.; Cao, X. Structure, function, and regulation of STAT proteins. Mol. Biosyst. 2006, 2, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Yang, P.L.; Li, E.M.; Xu, L.Y. STAT3beta, a distinct isoform from STAT3. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 110, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkson, J.; Ryan, D.; Kim, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Haura, E.; Laudano, A.; Sebti, S.; Hamilton, A.D.; Jove, R. Phosphotyrosyl peptides block Stat3-mediated DNA binding activity, gene regulation, and cell transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45443–45455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, I.H.; Ng, D.C.; Jans, D.A.; Bogoyevitch, M.A. Selective STAT3-alpha or -beta expression reveals spliceform-specific phosphorylation kinetics, nuclear retention and distinct gene expression outcomes. Biochem. J. 2012, 447, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieblein, J.C.; Ball, S.; Hutzen, B.; Sasser, A.K.; Lin, H.J.; Huang, T.H.; Hall, B.M.; Lin, J. STAT3 can be activated through paracrine signaling in breast epithelial cells. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Jin, X.; Rothman, K.; Lin, H.J.; Tang, H.; Burke, W. Modulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activities by p53 tumor suppressor in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Tang, W.; Wu, X.; Karnak, D.; Meng, X.; Thompson, R.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Qiao, X.T.; Lin, J.; et al. HAb18G/CD147 promotes pSTAT3-mediated pancreatic cancer development via CD44s. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6703–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvinus, F.M.; Orth, C.; Moriggl, R.; Tsareva, S.A.; Wagner, S.; Pfitzner, E.B.; Baus, D.; Kaufmann, R.; Huber, L.A.; Zatloukal, K.; et al. Persistent STAT3 activation in colon cancer is associated with enhanced cell proliferation and tumor growth. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Han, C.R.; Zhao, L.; Willingham, M.C.; Cheng, S.Y. Inhibition of STAT3 activity delays obesity-induced thyroid carcinogenesis in a mouse model. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Wright, K.L.; Huang, M.; Song, L.; Haura, E.; Turkson, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Sinibaldi, D.; Coppola, D.; et al. Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gao, F.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, F.; Yuan, H.H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Jiang, B. JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway activation mediates tumor angiogenesis by upregulation of VEGF and bFGF in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 73, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.L.; Lay, E.J.; Jian, W.; Parra, D.; Chan, K.S. Stat3 activation in urothelial stem cells leads to direct progression to invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haura, E.B.; Zheng, Z.; Song, L.; Cantor, A.; Bepler, G. Activated epidermal growth factor receptor-Stat-3 signaling promotes tumor survival in vivo in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8288–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Noguchi, K.; Shi, W.; Tanaka, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Yoshida, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat3 gene leads to early embryonic lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3801–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, H.; Burdon, T.; Chambers, I.; Smith, A. Self-renewal of pluripotent embryonic stem cells is mediated via activation of STAT3. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2048–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maritano, D.; Sugrue, M.L.; Tininini, S.; Dewilde, S.; Strobl, B.; Fu, X.; Murray-Tait, V.; Chiarle, R.; Poli, V. The STAT3 isoforms alpha and beta have unique and specific functions. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Bernards, R. Feedback and redundancy in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: Relevance to cancer therapies. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Zhuang, G.; Cao, Y.; Du, P.; Kim, H.J.; Settleman, J. Drug resistance via feedback activation of Stat3 in oncogene-addicted cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Fan, K.; Qian, W.; Hou, S.; Wang, H.; Dai, J.; Wei, H.; Guo, Y. Feedback activation of STAT3 mediates trastuzumab resistance via upregulation of MUC1 and MUC4 expression. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8317–8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.K.; Kim, H.P.; Han, S.W.; Oh, D.Y.; Im, S.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, T.Y. KRAS mutant lung cancer cells are differentially responsive to MEK inhibitor due to AKT or STAT3 activation: Implication for combinatorial approach. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 49, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.K.; Kim, H.P.; Park, Y.L.; Jang, J.E.; Lim, Y.; Song, S.H.; Han, S.W.; Kim, T.Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes resistance to MEK blockade in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiring, A.M.; Page, B.D.G.; Kraft, I.L.; Mason, C.C.; Vellore, N.A.; Resetca, D.; Zabriskie, M.S.; Zhang, T.Y.; Khorashad, J.S.; Engar, A.J.; et al. Combined STAT3 and BCR-ABL1 inhibition induces synthetic lethality in therapy-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Liang, G.; Yang, S.; Lin, J. Rational combination of MEK inhibitor and the STAT3 pathway modulator for the therapy in K-Ras mutated pancreatic and colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14472–14487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Kalimutho, M.; Dunne, P.D.; Carson, R.; Allen, W.; Jithesh, P.V.; Redmond, K.L.; Sasazuki, T.; Shirasawa, S.; Blayney, J.; et al. ADAM17-dependent c-MET-STAT3 signaling mediates resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1940–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Naour, A.; Mevel, R.; Thibault, B.; Courtais, E.; Chantalat, E.; Delord, J.P.; Couderc, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Martinez, A. Effect of combined inhibition of p110 alpha PI3K isoform and STAT3 pathway in ovarian cancer platinum-based resistance. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27220–27232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Huang, G.; Wang, R.; Pan, Y.; He, Z.; Chu, X.; Song, H.; Chen, L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts treated with cisplatin facilitates chemoresistance of lung adenocarcinoma through IL-11/IL-11R/STAT3 signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, T.; Nakata, R.; Sheard, M.; Shimada, H.; Buettner, R.; Groshen, S.; Ji, L.; Yu, H.; Jove, R.; Seeger, R.; et al. Critical role of STAT3 in IL-6-mediated drug resistance in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3852–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, A.; Mohammadi, S.; Ghaffari, S.H.; Nikbakht, M.; Bashash, D.; Alimoghaddam, K.; Ghavamzadeh, A. Osteopontin b and c isoforms: Molecular Candidates Associated with Leukemic Stem Cell Chemoresistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sredni, B.; Weil, M.; Khomenok, G.; Lebenthal, I.; Teitz, S.; Mardor, Y.; Ram, Z.; Orenstein, A.; Kershenovich, A.; Michowiz, S.; et al. Ammonium trichloro(dioxoethylene-o,o’)tellurate (AS101) sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy by inhibiting the tumor interleukin 10 autocrine loop. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoph, N.; Probst, N.A.; Lee, L.C.; Monahan, J.M.; Matthews, J.D.; Liang, H.C.; Bahnsen, K.; Montes-Mojarro, I.A.; Karaca Atabay, E.; Sharma, G.G.; et al. IL10RA Modulates Crizotinib Sensitivity in NPM1-ALK-positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, L.; Liu, D.; Sun, L.; Chen, H.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Ma, Y.; Guo, N.; et al. Acquisition of resistance to trastuzumab in gastric cancer cells is associated with activation of IL-6/STAT3/Jagged-1/Notch positive feedback loop. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5072–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokavec, M.; Oner, M.G.; Li, H.; Jackstadt, R.; Jiang, L.; Lodygin, D.; Kaller, M.; Horst, D.; Ziegler, P.K.; Schwitalla, S.; et al. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, H.; Yin, X.; Long, L.; Chen, X.; Feng, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; et al. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-204 feedback loop contributes to cisplatin resistance of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39154–39166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. STAT3 mediates multidrug resistance of Burkitt lymphoma cells by promoting antioxidant feedback. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 488, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roentgen, W.C. [On a new kind of ray (first report)]. Munch. Med. Wochenschr. (1950) 1959, 101, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Thariat, J.; Hannoun-Levi, J.M.; Sun Myint, A.; Vuong, T.; Gerard, J.P. Past, present, and future of radiotherapy for the benefit of patients. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, A.C.; Stewart, F.A.; Vens, C. Strategies to improve radiotherapy with targeted drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.M.; Hong, Y.; Lee, S.; Liu, P.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, T.H.; Chang, K.T.; Hong, Y. Therapeutic Implications for Overcoming Radiation Resistance in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26880–26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, D.C.; Poli, V.; David, M.; Rickert, R.C. Cutting edge: Inherent and acquired resistance to radiation-induced apoptosis in B cells: A pivotal role for STAT3. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6593–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Di, B. Silencing STAT3 with short hairpin RNA enhances radiosensitivity of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in vivo. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.T.; Chen, M.F.; Chen, W.C.; Hsieh, C.C. The role of IL-6 in the radiation response of prostate cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Li, R.; Park, D.; Xie, M.; Sica, G.L.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, Z.Q.; Deng, X. Disruption of STAT3 by niclosamide reverses radioresistance of human lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Kong, Y.; Lei, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Ji, K.; Wang, Q.; et al. MSCs inhibit tumor progression and enhance radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells by down-regulating Stat3 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, F.S.; Chen, X.H.; Liu, Q.W.; Feng, J.B.; Liu, Q.J.; Su, X. Radiation induces phosphorylation of STAT3 in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6161–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.H.; Chen, P.J.; Jeng, Y.M.; Cheng, A.L.; Huang, L.R.; Cheng, J.C. Synergistic effect of radiation and interleukin-6 on hepatitis B virus reactivation in liver through STAT3 signaling pathway. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 75, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.T.; Lu, Q.P. Mucin 1 promotes radioresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7571–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Guryanova, O.A.; Zhou, W.; Liu, C.; Huang, Z.; Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Wu, Q.; He, Z.; et al. Ibrutinib inactivates BMX-STAT3 in glioma stem cells to impair malignant growth and radioresistance. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, K.M.; Opdenaker, L.M.; Flynn, N.J.; Appeah, D.K.; Sims-Mourtada, J. Radiation induces an inflammatory response that results in STAT3-dependent changes in cellular plasticity and radioresistance of breast cancer stem-like cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru, N.; Fan, M.; Candas, D.; Menaa, C.; Liu, H.C.; Nantajit, D.; Wen, Y.; Xiao, K.; Eldridge, A.; Chromy, B.A.; et al. HER2-associated radioresistance of breast cancer stem cells isolated from HER2-negative breast cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.A.; Seong, M.K.; Seol, H.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, E.K.; Chang, J.W.; Hwang, S.G.; Noh, W.C. STAT3-survivin signaling mediates a poor response to radiotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7055–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, D.; Kim, H.; Yin, T.; Fan, S.; Shen, Q. Activation of STAT3 and Bcl-2 and reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) promote radioresistance in breast cancer and overcome of radioresistance with niclosamide. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5292–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweida, A.J.; Darragh, L.; Phan, A.; Binder, D.; Bhatia, S.; Mueller, A.; Court, B.V.; Milner, D.; Raben, D.; Woessner, R.; et al. STAT3 Modulation of Regulatory T Cells in Response to Radiation Therapy in Head and Neck Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, J.G.; Wang, Z.; Huo, L.; Howard, R.G.; Frank, D.A.; Rothstein, T.L. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) is constitutively activated in normal, self-renewing B-1 cells but only inducibly expressed in conventional B lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, Z.G.; Muller-Barthelemy, M.; Kemeny, J.L.; Dedieu, V.; Biau, J.; Khalil, T.; Raoelfils, L.I.; Granzotto, A.; Pereira, B.; Beaudoin, C.; et al. STAT3 Serine 727 Phosphorylation: A Relevant Target to Radiosensitize Human Glioblastoma. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masliantsev, K.; Pinel, B.; Balbous, A.; Guichet, P.O.; Tachon, G.; Milin, S.; Godet, J.; Duchesne, M.; Berger, A.; Petropoulos, C.; et al. Impact of STAT3 phosphorylation in glioblastoma stem cells radiosensitization and patient outcome. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3968–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purnell, P.R.; Mack, P.C.; Tepper, C.G.; Evans, C.P.; Green, T.P.; Gumerlock, P.H.; Lara, P.N.; Gandara, D.R.; Kung, H.J.; Gautschi, O. The Src inhibitor AZD0530 blocks invasion and may act as a radiosensitizer in lung cancer cells. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.J.; Jin, F.G.; Liu, T.G.; Fu, E.Q.; Xie, Y.H.; Sun, R.L. Overexpression of STAT3 potentiates growth, survival, and radioresistance of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 171, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Moretti, L.; Giacalone, N.J.; Schleicher, S.; Speirs, C.K.; Carbone, D.P.; Lu, B. Inhibition of JAK2 signaling by TG101209 enhances radiotherapy in lung cancer models. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Chen, K.H.; Huang, P.I.; Chen, Y.C.; Chiou, G.Y.; Lo, W.L.; Tseng, L.M.; Hsu, H.S.; Chang, K.W.; Chiou, S.H. Cucurbitacin I suppressed stem-like property and enhanced radiation-induced apoptosis in head and neck squamous carcinoma--derived CD44(+)ALDH1(+) cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2879–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Park, M.A.; Heo, S.W.; Park, S.Y.; Kang, K.W.; Park, P.H.; Kim, J.A. The radio-sensitizing effect of xanthohumol is mediated by STAT3 and EGFR suppression in doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2638–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Nam, J.S. The JAK2/STAT3/CCND2 Axis promotes colorectal Cancer stem cell persistence and radioresistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urick, M.E.; Chung, E.J.; Shield, W.P., 3rd; Gerber, N.; White, A.; Sowers, A.; Thetford, A.; Camphausen, K.; Mitchell, J.; Citrin, D.E. Enhancement of 5-fluorouracil-induced in vitro and in vivo radiosensitization with MEK inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5038–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Jing, S.; He, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, B.; Ma, S.; Dai, W.; et al. IL-6/STAT3/TWIST inhibition reverses ionizing radiation-induced EMT and radioresistance in esophageal squamous carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11228–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Prognostic significance of STAT3 expression and its correlation with chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.C.; Tsai, J.T.; Chao, T.Y.; Ma, H.I.; Liu, W.H. The STAT3/Slug Axis Enhances Radiation-Induced Tumor Invasion and Cancer Stem-like Properties in Radioresistant Glioblastoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, S.I.; Kim, R.K.; Cho, E.W.; Kim, I.G. Tescalcin/c-Src/IGF1Rbeta-mediated STAT3 activation enhances cancer stemness and radioresistant properties through ALDH1. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, P.K.; Tsai, W.K.; Chen, M.; Lin, W.R.; Chow, Y.C.; Lee, C.C.; Hsu, J.M.; Chen, Y.J. Zerumbone Regulates DNA Repair Responding to Ionizing Radiation and Enhances Radiosensitivity of Human Prostatic Cancer Cells. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.S.; Hou, M.F.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Lo, S. Role of MRE11 in cell proliferation, tumor invasion, and DNA repair in breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1485–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Ren, Y.; Weng, G.; Xu, L.; Xue, X.; Keng, P.C.; Lee, S.O.; Chen, Y. IL-6 signaling contributes to radioresistance of prostate cancer through key DNA repair-associated molecules ATM, ATR, and BRCA 1/2. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; He, J.; Guo, Q.; Hu, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Kang, Y.; She, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. STAT3 inhibitor stattic enhances radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Q.; He, J.; Qin, Q.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhan, L.; Lu, J.; et al. STAT3 inhibitor NSC74859 radiosensitizes esophageal cancer via the downregulation of HIF-1alpha. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 9793–9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Fan, M.; Jiang, N.; Duan, Y.; Jing, D.; Xiao, W.; Fragoso, R.C.; Lam, K.S.; et al. Dual blockage of STAT3 and ERK1/2 eliminates radioresistant GBM cells. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Cui, C.; Dodge, C.T.; Bhayani, M.K.; Lai, S.Y. Targeting STAT3 inhibits growth and enhances radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.W.; Gridley, D.S.; Kim, P.D.; Hu, S.; de Necochea-Campion, R.; Ferris, R.L.; Chen, C.S.; Mirshahidi, S. Linifanib (ABT-869) enhances radiosensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Tai, W.T.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Shiau, C.W.; Cheng, A.L.; Chen, K.F. Sorafenib enhances radiation-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting STAT3. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, M.; Endo, K.; Furuya, S.; Minami, M.; Fukasawa, A.; Imamura, T.; Miyazawa, K. STAT3 integrates cooperative Ras and TGF-beta signals that induce Snail expression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Chiang, K.Y.; Zhu, N.; Findley, H.W.; Zhou, M. Contribution of STAT3 to the activation of survivin by GM-CSF in CD34+ cell lines. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, K.; Lang, C.; Devgan, G.; Azare, J.; Berishaj, M.; Gerald, W.; Kim, Y.B.; Paz, K.; Darnell, J.E.; Albanese, C.; et al. Cyclin D1 is transcriptionally regulated by and required for transformation by activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2544–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.F.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Tweardy, D.J.; Alshareef, A.; Liao, L.D.; Xue, Y.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Chen, B.; et al. The Opposing Function of STAT3 as an Oncoprotein and Tumor Suppressor Is Dictated by the Expression Status of STAT3beta in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanou, A.; Brar, B.K.; Knight, R.A.; Latchman, D.S. Opposing actions of STAT-1 and STAT-3 on the Bcl-2 and Bcl-x promoters. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.O.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Haque, S.J. Aberrant Stat3 signaling by interleukin-4 in malignant glioma cells: Involvement of IL-13Ralpha2. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2956–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isomoto, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Werneburg, N.W.; Bronk, S.F.; Guicciardi, M.E.; Frank, D.A.; Gores, G.J. Interleukin 6 upregulates myeloid cell leukemia-1 expression through a STAT3 pathway in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, E.H.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, M.K.; Cho, C.H.; Kang, K.W.; Lee, J.W.; Han, W.; Noh, D.Y.; et al. STAT3-RANTES autocrine signaling is essential for tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Yagishita, S.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Fujiwara, T.; Tsuta, K.; Nokihara, H.; Tamura, T.; et al. The clinical relevance of the miR-197/CKS1B/STAT3-mediated PD-L1 network in chemoresistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Feng, J.; Hong, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Liao, S.; Wang, X.; Ji, T.; Wang, S.; Ma, D.; et al. Silencing of the STAT3 signaling pathway reverses the inherent and induced chemoresistance of human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvendiran, K.; Bratasz, A.; Tong, L.; Ignarro, L.J.; Kuppusamy, P. NCX-4016, a nitro-derivative of aspirin, inhibits EGFR and STAT3 signaling and modulates Bcl-2 proteins in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells and xenografts. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Guo, B.Y.; Zhang, S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts attenuate Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells by promoting STAT3 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hira, S.K.; Mondal, I.; Bhattacharya, D.; Gupta, K.K.; Manna, P.P. Downregulation of STAT3 phosphorylation enhances tumoricidal effect of IL-15-activated dendritic cell against doxorubicin-resistant lymphoma and leukemia via TNF-alpha. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 67, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Tang, W.; Dai, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, M.; Ji, Q.; Ji, M.; Pienta, K.; Lawrence, T.; Xu, L. Natural BH3 mimetic (-)-gossypol chemosensitizes human prostate cancer via Bcl-xL inhibition accompanied by increase of Puma and Noxa. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiprianova, I.; Remy, J.; Milosch, N.; Mohrenz, I.V.; Seifert, V.; Aigner, A.; Kogel, D. Sorafenib Sensitizes Glioma Cells to the BH3 Mimetic ABT-737 by Targeting MCL1 in a STAT3-Dependent Manner. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Ni, Z.; Dai, X.; Su, C.; Smith, A.R.; Xu, L.; He, F. Sorafenib sensitizes (-)-gossypol-induced growth suppression in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells via Mcl-1 inhibition and Bak activation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, C.J.; Reyes, A.O.; Vakar-Lopez, F.; Levy, L.B.; Kuban, D.A.; Hoover, D.C.; Lee, A.K.; Pisters, L.L. Bcl-2 is significantly overexpressed in localized radio-recurrent prostate carcinoma, compared with localized radio-naive prostate carcinoma. Inter. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 56, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Xie, D.; Boike, T.; Raghavan, P.; Burma, S.; Chen, D.J.; Habib, A.A.; Chakraborty, A.; Hsieh, J.T.; Saha, D. Downregulation of human DAB2IP gene expression in prostate cancer cells results in resistance to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2829–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Staalduinen, J.; Baker, D.; Ten Dijke, P.; van Dam, H. Epithelial-mesenchymal-transition-inducing transcription factors: New targets for tackling chemoresistance in cancer? Oncogene 2018, 37, 6195–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, K.Y.; Kang, M.; Garofalo, F.; Ueno, D.; Liang, H.; Cady, S.; Madarikan, O.; Pitruzzello, N.; Tsai, C.H.; Hartwich, T.M.P.; et al. Inhibition of Heat Shock Protein 90 suppresses TWIST1 Transcription. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 96, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.; Ren, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Tong, G.; Yang, G. The crosstalk between STAT3 and p53/RAS signaling controls cancer cell metastasis and cisplatin resistance via the Slug/MAPK/PI3K/AKT-mediated regulation of EMT and autophagy. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.K.; Bamodu, O.A.; Tzeng, Y.M.; Hsiao, M.; Yeh, C.T.; Lin, C.M. Ovatodiolide inhibits the oncogenicity and cancer stem cell-like phenotype of glioblastoma cells, as well as potentiate the anticancer effect of temozolomide. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Huang, C.M.; Bamodu, O.A.; Lin, C.S.; Liu, B.L.; Tzeng, Y.M.; Tsai, J.T.; Lee, W.H.; Chen, T.M. Ovatodiolide suppresses nasopharyngeal cancer by targeting stem cell-like population, inducing apoptosis, inhibiting EMT and dysregulating JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Yang, F. Snail expression contributes to temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 4277–4289. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.M.; Wei, W.; Yang, R.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.D.; Jiang, G.M.; Wang, B.L. Regulation of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 by Snail contributes to chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, E.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, A.; Lee, S.B.; Shim, S.; Jang, H.; Myung, J.K.; et al. Effects of metformin and phenformin on apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in chemoresistant rectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2834–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xing, H.; Hong, L.; Lu, D.H.; Li, B.S.; Tang, J.M.; Min, J. STAT3-mediated Twist1 upregulation contributes to epithelial-mesenehymal transition in cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 11, 6749–6757. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Hui, K.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; et al. DAB2IP regulates the chemoresistance to pirarubicin and tumor recurrence of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer through STAT3/Twist1/P-glycoprotein signaling. Cell Signal. 2015, 27, 2515–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, A.C.; Mita, M.M.; Nawrocki, S.T.; Giles, F.J. Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5000–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Vishnoi, K.; Mahata, S.; Tripathi, S.C.; Misra, S.P.; Misra, V.; Mehrotra, R.; Dwivedi, M.; Bharti, A.C. Berberine and Curcumin Target Survivin and STAT3 in Gastric Cancer Cells and Synergize Actions of Standard Chemotherapeutic 5-Fluorouracil. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, X.; Liao, M. Bile salt (glycochenodeoxycholate acid) induces cell survival and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10899–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Jin, P.; Liu, W. Periostin Contributes to Cisplatin Resistance in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells via Activation of Stat3 and Akt and Upregulation of Survivin. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Tian, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, B.; Dong, P.; Watari, H.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Guo, Y.; et al. Ovarian Primary and Metastatic Tumors Suppressed by Survivin Knockout or a Novel Survivin Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 2233–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.K.; Yang, Z.F.; Lam, S.P.; Lam, C.T.; Ngai, P.; Tam, K.H.; Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T. Inhibition of Stat3 activity by YC-1 enhances chemo-sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliran, H., Jr.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Xu, H.; Heng, H.; Thakur, A.; Bollig, A.; Sarkar, F.H.; Liao, J.D. Overexpression of cyclin D1 promotes tumor cell growth and confers resistance to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in an elastase-myc transgene-expressing pancreatic tumor cell line. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6075–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.F.; Liu, T.Q.; Zhi, X.T.; Zou, J.; Zhong, J.T.; Li, T.; Mo, X.L.; Zhou, W.; Guo, W.W.; Liu, X.; et al. COX-2/PGE2 Axis Regulates HIF2alpha Activity to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Hypoxic Response and Reduce the Sensitivity of Sorafenib Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3204–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, T. Targeting the AKT/cyclin D1 pathway to overcome intrinsic and acquired radioresistance of tumors for effective radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, H.; Lv, M.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y. Parthenolide facilitates apoptosis and reverses drug-resistance of human gastric carcinoma cells by inhibiting the STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3572–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Ma, K.; Dong, B.; Zhao, C.; Che, C.; Dong, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Liang, R. The synergistic antitumor effect of Huaier combined with 5-Florouracil in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.; Zhou, S.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, M. STAT3 signaling pathway in drug-resistant bladder cancer cell line. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.T.; Cheng, A.L.; Shiau, C.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Ko, C.H.; Lin, M.W.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, K.F. Dovitinib induces apoptosis and overcomes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through SHP-1-mediated inhibition of STAT3. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, T.; Clayman, G.L. Antisense inhibition of cyclin D1 in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 126, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, E.R.; Nesbit, M.; Litwin, S.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Cheffetz, S.; Herlyn, M. Antisense cyclin D1 induces apoptosis and tumor shrinkage in human squamous carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4876–4881. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, M.; Suzui, M.; Yasumatu, R.; Nakashima, T.; Kuratomi, Y.; Azuma, K.; Tomita, K.; Komiyama, S.; Weinstein, I.B. Constitutive activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 correlates with cyclin D1 overexpression and may provide a novel prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, M.; Toh, S.; Koike, K.; Kuratomi, Y.; Suzui, M.; Deguchi, A.; Komiyama, S.; Weinstein, I.B. The roles of JNK1 and Stat3 in the response of head and neck cancer cell lines to combined treatment with all-trans-retinoic acid and 5-fluorouracil. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2002, 93, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.M.; Fan, M.; Nantajit, D.; Cao, N.; Li, J.J. Cyclin D1 in low-dose radiation-induced adaptive resistance. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6738–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Jin, X.; Shen, L.; Fang, Y.; Fei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, C.; Chen, X. Inhibition of cyclin D1 enhances sensitivity to radiotherapy and reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition for esophageal cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5355–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casimiro, M.C.; Di Sante, G.; Ju, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.; Crosariol, M.; Yaman, I.; Gormley, M.; Meng, H.; Lisanti, M.P.; et al. Cyclin D1 Promotes Androgen-Dependent DNA Damage Repair in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Ba, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, J. Insulinoma-associated protein 1 controls nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiotherapy by modulating cyclin D1-dependent DNA repair machinery. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Kortylewski, M.; Pardoll, D. Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: Role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Niu, G.; Kortylewski, M.; Burdelya, L.; Shain, K.; Zhang, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Gabrilovich, D.; Heller, R.; Coppola, D.; et al. Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortylewski, M.; Kujawski, M.; Wang, T.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.; Pilon-Thomas, S.; Niu, G.; Kay, H.; Mulé, J.; Kerr, W.G.; et al. Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabarro, S.; Himoudi, N.; Papanastasiou, A.; Gilmour, K.; Gibson, S.; Sebire, N.; Thrasher, A.; Blundell, M.; Hubank, M.; Canderan, G.; et al. Coordinated oncogenic transformation and inhibition of host immune responses by the PAX3-FKHR fusion oncoprotein. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedova, Y.; Huang, M.; Kusmartsev, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Cheng, P.; Salup, R.; Jove, R.; Gabrilovich, D. Hyperactivation of STAT3 is involved in abnormal differentiation of dendritic cells in cancer. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larmonier, N.; Marron, M.; Zeng, Y.; Cantrell, J.; Romanoski, A.; Sepassi, M.; Thompson, S.; Chen, X.; Andreansky, S.; Katsanis, E. Tumor-derived CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell suppression of dendritic cell function involves TGF-beta and IL-10. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhart, E.M.; Siedlar, M.; Wedel, A.; Werner, T.; Ziegler-Heitbrock, H.W. Role of Stat3 in lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-10 gene expression. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinjyo, I.; Inoue, H.; Hamano, S.; Fukuyama, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Koga, K.; Takaki, H.; Himeno, K.; Takaesu, G.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Loss of SOCS3 in T helper cells resulted in reduced immune responses and hyperproduction of interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor-beta 1. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzycka, M.; Marzec, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wasik, M.A. Nucleophosmin/anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM/ALK) oncoprotein induces the T regulatory cell phenotype by activating STAT3. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9964–9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Le, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, L.; Frey, J.A.; Gao, A.C.; Peng, Z.; Huang, S.; Xiong, H.Q.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; et al. Stat3 activation regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and human pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene 2003, 22, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Bone, N.D.; Strege, A.K.; Jelinek, D.F.; Kay, N.E. VEGF receptors on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells interact with STAT 1 and 3: Implication for apoptosis resistance. Leukemia 2005, 19, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.L.; Nairismägi, M.L.; Laurensia, Y.; Lim, J.Q.; Tan, J.; Li, Z.M.; Pang, W.L.; Kizhakeyil, A.; Wijaya, G.C.; Huang, D.C.; et al. Oncogenic activation of the STAT3 pathway drives PD-L1 expression in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.J.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Xue, B.X.; Gao, J.; Sun, C.Y.; Zang, Y.C.; Zhou, Y.B.; Yang, D.R.; et al. Combined inhibition of JAK1,2/Stat3-PD-L1 signaling pathway suppresses the immune escape of castration-resistant prostate cancer to NK cells in hypoxia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 8111–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Quintero, A.J.; Tweardy, D.J. Identification and characterization of cis elements in the STAT3 gene regulating STAT3 alpha and STAT3 beta messenger RNA splicing. Blood 2001, 98, 3853–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biethahn, S.; Alves, F.; Wilde, S.; Hiddemann, W.; Spiekermann, K. Expression of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor- and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-associated signal transduction proteins of the JAK/STAT pathway in normal granulopoiesis and in blast cells of acute myelogenous leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 1999, 27, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; White, S.M.; Schaefer, T.S.; Ball, E.D.; Dyer, K.F.; Tweardy, D.J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor activation of Stat3 alpha and Stat3 beta in immature normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Blood 1996, 88, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Wang, L.M.; Jove, R.; Vande Woude, G.F. Requirement of Stat3 signaling for HGF/SF-Met mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Tang, H.; Cao, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Tian, W.; Pang, X.; Li, K.; Chen, T. Strategy of STAT3beta cell-specific expression in macrophages exhibits antitumor effects on mouse breast cancer. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, T.S.; Sanders, L.K.; Nathans, D. Cooperative transcriptional activity of Jun and Stat3 beta, a short form of Stat3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9097–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, T.S.; Sanders, L.K.; Park, O.K.; Nathans, D. Functional differences between Stat3alpha and Stat3beta. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 5307–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, A.V.; Ivanov, S.V.; Zhang, X.; Ivanov, V.N.; Timofeeva, O.A.; Lerman, M.I. STRA13 interacts with STAT3 and modulates transcription of STAT3-dependent targets. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, I.H.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Jans, D.A. Cytokine-induced slowing of STAT3 nuclear import; faster basal trafficking of the STAT3beta isoform. Traffic 2014, 15, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Krasilnikov, M.; Ronai, Z. Regulation of Fas expression by STAT3 and c-Jun is mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4932–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammarchi, F.; de Stanchina, E.; Bournazou, E.; Supakorndej, T.; Martires, K.; Riedel, E.; Corben, A.D.; Bromberg, J.F.; Cartegni, L. Antitumorigenic potential of STAT3 alternative splicing modulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17779–17784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karni, R.; Jove, R.; Levitzki, A. Inhibition of pp60c-Src reduces Bcl-XL expression and reverses the transformed phenotype of cells overexpressing EGF and HER-2 receptors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4654–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. Dominant negative STAT3 suppresses the growth and invasion capability of human lung cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2009, 2, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Shain, K.H.; Huang, M.; Ravi, R.; Bedi, A.; Dalton, W.S.; Jove, R.; Yu, H. Overexpression of a dominant-negative signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 variant in tumor cells leads to production of soluble factors that induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3276–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Aigner, P.; Mizutani, T.; Horvath, J.; Eder, T.; Heber, S.; Lind, K.; Just, V.; Moll, H.P.; Yeroslaviz, A.; Fischer, M.J.M.; et al. STAT3beta is a tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1989–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo-Caspi, Y.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G.; Paret, G. A-to-I RNA editing is induced upon hypoxia. Shock 2011, 35, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, L.; Abutbul-Amitai, M.; Paret, G.; Nevo-Caspi, Y. Alternative Splicing of STAT3 Is Affected by RNA Editing. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Che, X.; Jia, R. PCBP1 inhibits the expression of oncogenic STAT3 isoform by targeting alternative splicing of STAT3 exon 23. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tano, V.; Jans, D.A.; Bogoyevitch, M.A. Oligonucleotide-directed STAT3 alternative splicing switch drives anti-tumorigenic outcomes in MCF10 human breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigner, P.; Just, V.; Stoiber, D. STAT3 isoforms: Alternative fates in cancer? Cytokine 2019, 118, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drubay, V.; Skrypek, N.; Cordiez, L.; Vasseur, R.; Schulz, C.; Boukrout, N.; Duchene, B.; Coppin, L.; Van Seuningen, I.; Jonckheere, N. TGF-betaRII Knock-down in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Promotes Tumor Growth and Gemcitabine Resistance. Importance of STAT3 Phosphorylation on S727. Cancers 2018, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.S.; Pal, A.D.; Banerjee, S. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small non-coding RNAs induce cancer cell chemoresistance and migration. Virology 2013, 443, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Yeh, J.E.; Pinello, L.; Jacob, J.; Chakravarthy, S.; Yuan, G.C.; Chopra, R.; Frank, D.A. Impact of the N-Terminal Domain of STAT3 in STAT3-Dependent Transcriptional Activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 3284–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, O.A.; Gaponenko, V.; Lockett, S.J.; Tarasov, S.G.; Jiang, S.; Michejda, C.J.; Perantoni, A.O.; Tarasova, N.I. Rationally designed inhibitors identify STAT3 N-domain as a promising anticancer drug target. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, O.A.; Tarasova, N.I.; Zhang, X.; Chasovskikh, S.; Cheema, A.K.; Wang, H.; Brown, M.L.; Dritschilo, A. STAT3 suppresses transcription of proapoptotic genes in cancer cells with the involvement of its N-terminal domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidler, M.; Rether, J.; Anke, T.; Erkel, G. Inhibition of interleukin-6 signaling by galiellalactone. FEBS Lett. 2000, 484, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsten, R.; Johansson, M.; Dahlman, A.; Dizeyi, N.; Sterner, O.; Bjartell, A. Galiellalactone is a novel therapeutic candidate against hormone-refractory prostate cancer expressing activated Stat3. Prostate 2008, 68, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellsten, R.; Johansson, M.; Dahlman, A.; Sterner, O.; Bjartell, A. Galiellalactone inhibits stem cell-like ALDH-positive prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Don-Doncow, N.; Escobar, Z.; Johansson, M.; Kjellstrom, S.; Garcia, V.; Munoz, E.; Sterner, O.; Bjartell, A.; Hellsten, R. Galiellalactone is a direct inhibitor of the transcription factor STAT3 in prostate cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15969–15978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaper, D.; Vahid, S.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, S.; Nouruzi, S.; Bishop, J.L.; Johansson, M.; Zoubeidi, A. Galiellalactone inhibits the STAT3/AR signaling axis and suppresses Enzalutamide-resistant Prostate Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, T.; Han, Y.T.; Suh, Y.G.; Chun, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, K.S. Novel Galiellalactone Analogues Can Target STAT3 Phosphorylation and Cause Apoptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, Z.; Bjartell, A.; Canesin, G.; Evans-Axelsson, S.; Sterner, O.; Hellsten, R.; Johansson, M.H. Preclinical Characterization of 3beta-(N-Acetyl l-cysteine methyl ester)-2abeta,3-dihydrogaliellalactone (GPA512), a Prodrug of a Direct STAT3 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4551–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Ding, C.; Chu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Terry, K.; Liu, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J. Discovery of O-Alkylamino Tethered Niclosamide Derivatives as Potent and Orally Bioavailable Anticancer Agents. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Dong, Z.; Wang, F.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.T. A small molecule compound targeting STAT3 DNA-binding domain inhibits cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.J.; Peng, H.; He, Y.; Hangoc, G.; Pollok, K.; Sandusky, G.; et al. Small-molecule inhibitors targeting the DNA-binding domain of STAT3 suppress tumor growth, metastasis and STAT3 target gene expression in vivo. Oncogene 2016, 35, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X.; Jin, H.W.; Zhang, L.R.; Zhang, J.T.; Liu, Z.M.; Cui, J.R. Small-molecule compounds targeting the STAT3 DNA-binding domain suppress survival of cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.J.; Zheng, J.; Jung, Y.Y.; Hwang, C.J.; Lee, H.P.; Woo, J.R.; Baek, S.Y.; Ham, Y.W.; Kang, M.W.; Shong, M.; et al. MMPP Attenuates Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Growth by Inhibiting the STAT3 DNA-Binding Activity via Direct Binding to the STAT3 DNA-Binding Domain. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4632–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvendiran, K.; Ahmed, S.; Dayton, A.; Kuppusamy, M.L.; Rivera, B.K.; Kalai, T.; Hideg, K.; Kuppusamy, P. HO-3867, a curcumin analog, sensitizes cisplatin-resistant ovarian carcinoma, leading to therapeutic synergy through STAT3 inhibition. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mast, J.M.; Tse, D.; Shee, K.; Lakshmi Kuppusamy, M.; Kmiec, M.M.; Kalai, T.; Kuppusamy, P. Diarylidenylpiperidones, H-4073 and HO-3867, Induce G2/M Cell-Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and Inhibit STAT3 Phosphorylation in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 77, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvendiran, K.; Tong, L.; Bratasz, A.; Kuppusamy, M.L.; Ahmed, S.; Ravi, Y.; Trigg, N.J.; Rivera, B.K.; Kalai, T.; Hideg, K.; et al. Anticancer efficacy of a difluorodiarylidenyl piperidone (HO-3867) in human ovarian cancer cells and tumor xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, R.; Corzano, R.; Rashid, R.; Lin, J.; Senthil, M.; Hedvat, M.; Schroeder, A.; Mao, A.; Herrmann, A.; Yim, J.; et al. Alkylation of cysteine 468 in Stat3 defines a novel site for therapeutic development. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, T.; Suehiro, N.; Masuda, Y.; Miyoshi, N.; Muraoka, D.; Ogo, N.; Asai, A. Discovery of a New STAT3 Inhibitor Acting on the Linker Domain. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grab, J.; Berg, A.; Blechschmidt, L.; Kluver, B.; Rubner, S.; Fu, D.Y.; Meiler, J.; Graber, M.; Berg, T. The STAT5b Linker Domain Mediates the Selectivity of Catechol Bisphosphates for STAT5b over STAT5a. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkson, J.; Kim, J.S.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, J.; Huang, M.; Glenn, M.; Haura, E.; Sebti, S.; Hamilton, A.D.; Jove, R. Novel peptidomimetic inhibitors of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 dimerization and biological activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Jaganathan, S.; Turkson, J. A cell-permeable Stat3 SH2 domain mimetic inhibits Stat3 activation and induces antitumor cell effects in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 35855–35865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzenne, E.J.; Klostergaard, J.; Mandal, P.K.; Liao, W.S.; Lu, Z.; Gao, F.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Robertson, F.M.; McMurray, J.S. A phosphopeptide mimetic prodrug targeting the SH2 domain of Stat3 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2012, 10, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gong, A.; Wu, C. Stattic Enhances Radiosensitivity and Reduces Radio-Induced Migration and Invasion in HCC Cell Lines through an Apoptosis Pathway. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1832494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Lin, J. A low-molecular-weight compound discovered through virtual database screening inhibits Stat3 function in breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4700–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, K.; Takaishi, M.; Nakajima, K.; Ikeda, M.; Kanda, T.; Tarutani, M.; Iiyama, T.; Asao, N.; DiGiovanni, J.; Sano, S. Stat3 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of psoriasis: A clinical feasibility study with STA-21, a Stat3 inhibitor. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Kwok, S.K.; Lim, M.A.; Kim, E.K.; Ryu, J.G.; Kim, S.M.; Oh, H.J.; Ju, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. STA-21, a promising STAT-3 inhibitor that reciprocally regulates Th17 and Treg cells, inhibits osteoclastogenesis in mice and humans and alleviates autoimmune inflammation in an experimental model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencalha, A.L.; Du Rocher, B.; Salles, D.; Binato, R.; Abdelhay, E. LLL-3, a STAT3 inhibitor, represses BCR-ABL-positive cell proliferation, activates apoptosis and improves the effects of Imatinib mesylate. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 65, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, B.; Sobo, M.; Cen, L.; Josiah, D.; Hutzen, B.; Cisek, K.; Bhasin, D.; Regan, N.; Lin, L.; Chan, C.; et al. LLL-3 inhibits STAT3 activity, suppresses glioblastoma cell growth and prolongs survival in a mouse glioblastoma model. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hutzen, B.; Li, P.K.; Ball, S.; Zuo, M.; DeAngelis, S.; Foust, E.; Sobo, M.; Friedman, L.; Bhasin, D.; et al. A novel small molecule, LLL12, inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and activities and exhibits potent growth-suppressive activity in human cancer cells. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, W.; Jou, D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Xiao, H.; Qin, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, J.; et al. A novel small molecule STAT3 inhibitor, LY5, inhibits cell viability, colony formation, and migration of colon and liver cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12917–12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiquee, K.; Zhang, S.; Guida, W.C.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Greedy, B.; Lawrence, H.R.; Yip, M.L.; Jove, R.; McLaughlin, M.M.; Lawrence, N.J.; et al. Selective chemical probe inhibitor of Stat3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7391–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, D.P.; Lewis, A.M.; Williams, D.; Resetca, D.; Wilson, D.J.; Gunning, P.T. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) inhibitor, S3I-201, acts as a potent and non-selective alkylating agent. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20669–20679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Pireddu, R.; Yang, H.; Urlam, M.K.; Lawrence, H.R.; Guida, W.C.; Lawrence, N.J.; Sebti, S.M. A novel inhibitor of STAT3 homodimerization selectively suppresses STAT3 activity and malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, S.; Singh, J.; Zhang, X.; Yue, P.; Page, B.D.; Sharmeen, S.; Shahani, V.M.; Zhao, W.; Schimmer, A.D.; Turkson, J.; et al. Disruption of transcriptionally active Stat3 dimers with non-phosphorylated, salicylic acid-based small molecules: Potent in vitro and tumor cell activities. Chembiochem 2009, 10, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yue, P.; Fletcher, S.; Zhao, W.; Gunning, P.T.; Turkson, J. A novel small-molecule disrupts Stat3 SH2 domain-phosphotyrosine interactions and Stat3-dependent tumor processes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yue, P.; Page, B.D.; Li, T.; Zhao, W.; Namanja, A.T.; Paladino, D.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Gunning, P.T.; et al. Orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of transcription factor Stat3 regresses human breast and lung cancer xenografts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9623–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haftchenary, S.; Luchman, H.A.; Jouk, A.O.; Veloso, A.J.; Page, B.D.; Cheng, X.R.; Dawson, S.S.; Grinshtein, N.; Shahani, V.M.; Kerman, K.; et al. Potent Targeting of the STAT3 Protein in Brain Cancer Stem Cells: A Promising Route for Treating Glioblastoma. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, F.; Sugimoto, K.; Harada, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Ohi, N.; Kurahashi, S.; Naoe, T. A novel STAT inhibitor, OPB-31121, has a significant antitumor effect on leukemia with STAT-addictive oncokinases. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Nam, H.J.; Kim, H.P.; Han, S.W.; Im, S.A.; Kim, T.Y.; Oh, D.Y.; Bang, Y.J. OPB-31121, a novel small molecular inhibitor, disrupts the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and exhibits an antitumor activity in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.L.; Soo, R.A.; Tan, D.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lim, J.S.; Marban, P.C.; Kong, L.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Thuya, W.L.; et al. Phase I and biomarker study of OPB-51602, a novel signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Uchida, T.; Terui, Y.; Hayakawa, F.; Kobayashi, Y.; Taniwaki, M.; Takamatsu, Y.; Naoe, T.; Tobinai, K.; Munakata, W.; et al. Phase I study of OPB-51602, an oral inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, in patients with relapsed/refractory hematological malignancies. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, L.; Genini, D.; Laurini, E.; Merulla, J.; Perez, L.; Fermeglia, M.; Carbone, G.M.; Pricl, S.; Catapano, C.V. Hitting the right spot: Mechanism of action of OPB-31121, a novel and potent inhibitor of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genini, D.; Brambilla, L.; Laurini, E.; Merulla, J.; Civenni, G.; Pandit, S.; D’Antuono, R.; Perez, L.; Levy, D.E.; Pricl, S.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by a SH2 domain-targeting STAT3 inhibitor leads to metabolic synthetic lethality in cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4924–E4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, A.; Wagner, C.; de Araujo, E.D.; Bajusz, D.; Neubauer, H.A.; Herling, M.; Gunning, P.T.; Keseru, G.M.; Moriggl, R. Direct Targeting Options for STAT3 and STAT5 in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Han, S.W.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, T.Y.; Heo, D.S.; Yuasa, M.; Yanagihara, Y.; Bang, Y.J. Phase I Study of OPB-31121, an Oral STAT3 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendell, J.C.; Hong, D.S.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Naing, A.; Jones, S.F.; Falchook, G.; Bricmont, P.; Elekes, A.; Rock, E.P.; Kurzrock, R. Phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation, and pharmacokinetic study of STAT3 inhibitor OPB-31121 in subjects with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdura, S.; Cuyas, E.; Llorach-Pares, L.; Perez-Sanchez, A.; Micol, V.; Nonell-Canals, A.; Joven, J.; Valiente, M.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; et al. Silibinin is a direct inhibitor of STAT3. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 116, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, C.; Haripal, B.; Klinge, S.; Darnell, J.E. Mutations in the linker domain affect phospho-STAT3 function and suggest targets for interrupting STAT3 activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14811–14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraskouskaya, D.; Duodu, E.; Arpin, C.C.; Gunning, P.T. Progress towards the development of SH2 domain inhibitors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3337–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Song, K.; Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Shen, Q.; Wang, R.; Gao, J.; Hong, Y.; Li, Q.; Ni, D.; et al. AlloFinder: A strategy for allosteric modulator discovery and allosterome analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W451–W458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Iglesia, N.; Konopka, G.; Lim, K.L.; Nutt, C.L.; Bromberg, J.F.; Frank, D.A.; Mischel, P.S.; Louis, D.N.; Bonni, A. Deregulation of a STAT3-interleukin 8 signaling pathway promotes human glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasiveness. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5870–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Iglesia, N.; Konopka, G.; Puram, S.V.; Chan, J.A.; Bachoo, R.M.; You, M.J.; Levy, D.E.; Depinho, R.A.; Bonni, A. Identification of a PTEN-regulated STAT3 brain tumor suppressor pathway. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneller, D.; Machat, G.; Sousek, A.; Proell, V.; van Zijl, F.; Zulehner, G.; Huber, H.; Mair, M.; Muellner, M.K.; Nijman, S.M.; et al. p19(ARF) /p14(ARF) controls oncogenic functions of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 54, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, P.-L.; Liu, L.-X.; Li, E.-M.; Xu, L.-Y. STAT3, the Challenge for Chemotherapeutic and Radiotherapeutic Efficacy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092459
Yang P-L, Liu L-X, Li E-M, Xu L-Y. STAT3, the Challenge for Chemotherapeutic and Radiotherapeutic Efficacy. Cancers. 2020; 12(9):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092459
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ping-Lian, Lu-Xin Liu, En-Min Li, and Li-Yan Xu. 2020. "STAT3, the Challenge for Chemotherapeutic and Radiotherapeutic Efficacy" Cancers 12, no. 9: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092459
APA StyleYang, P.-L., Liu, L.-X., Li, E.-M., & Xu, L.-Y. (2020). STAT3, the Challenge for Chemotherapeutic and Radiotherapeutic Efficacy. Cancers, 12(9), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092459





