Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing of Temperature Rise During 110 kV Conductor–Ground Wire Ice-Shedding Discharge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Principle
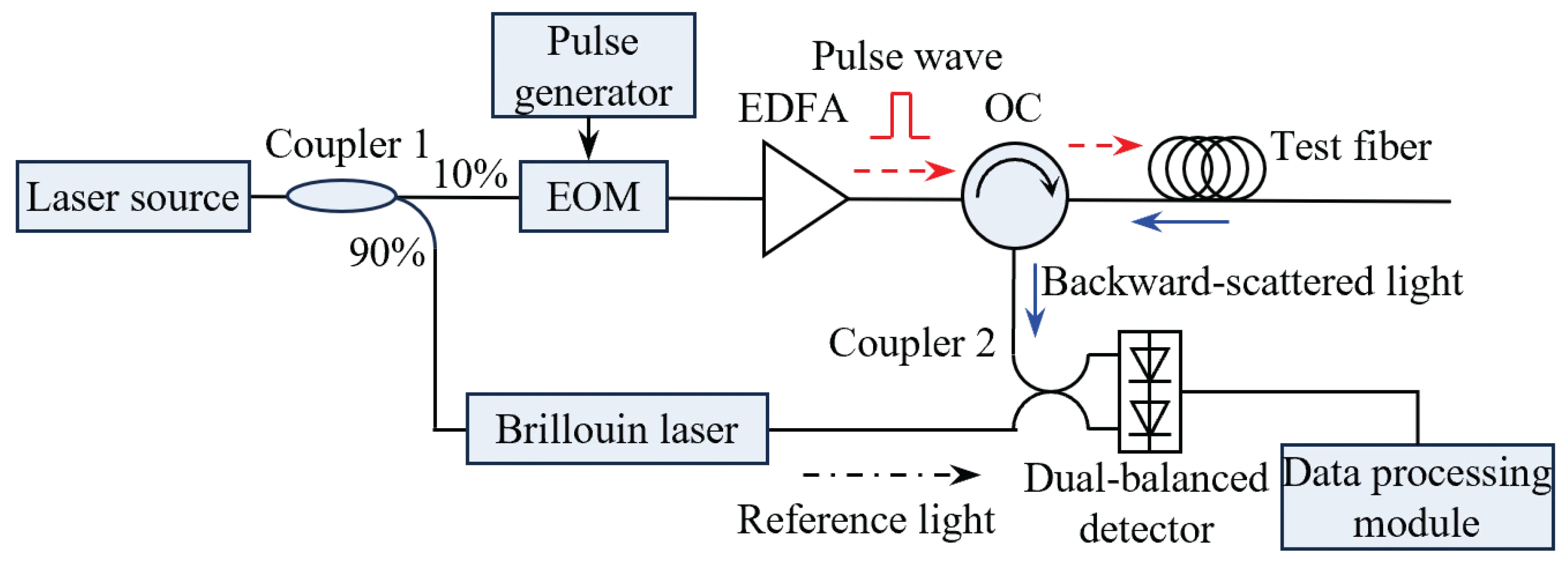
2.1. Brillouin Optical Time-Domain Reflectometry
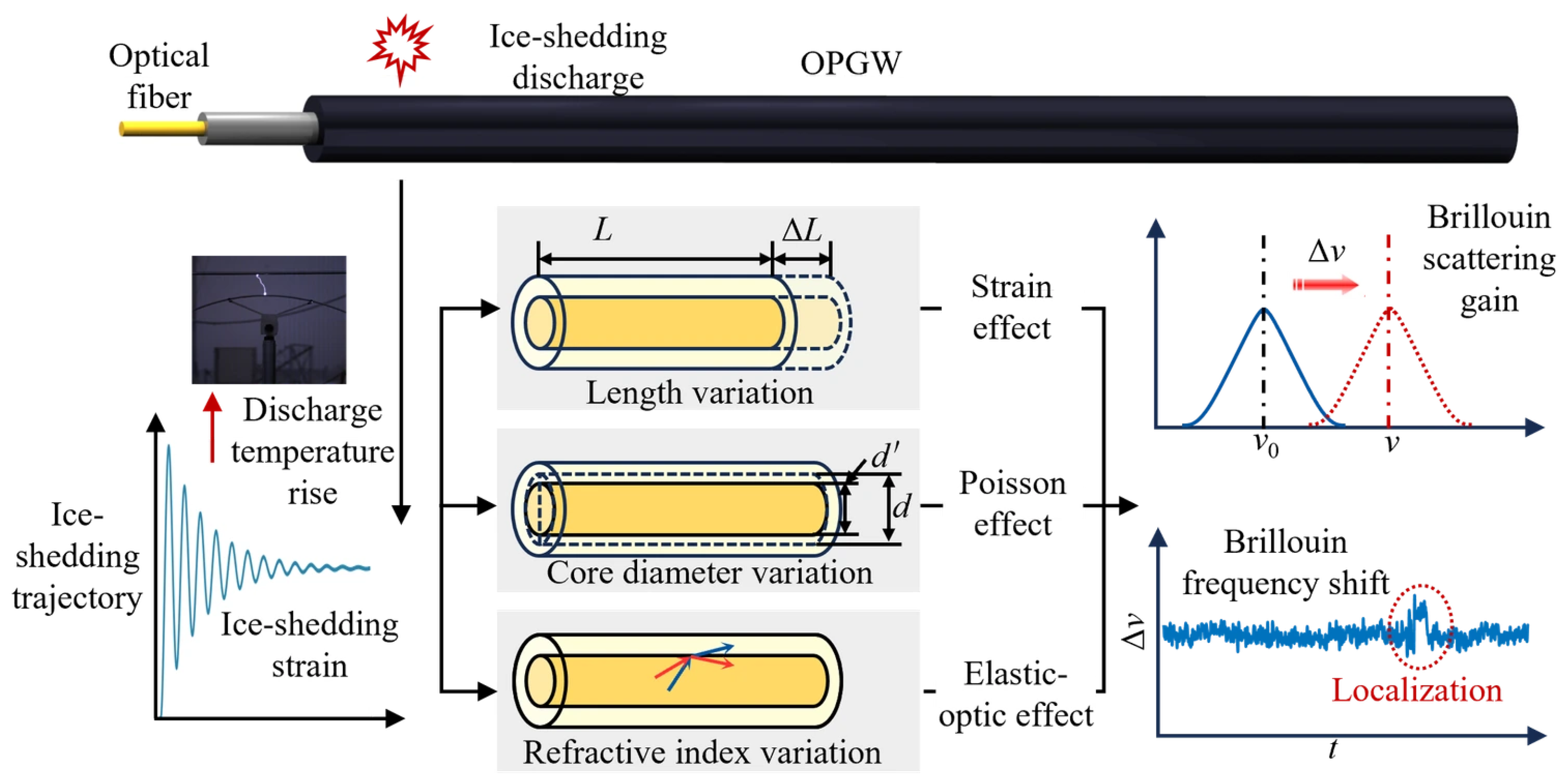
2.2. OPGW Sensing Characteristics and Monitoring Mechanism for Ice-Shedding Discharge
- (1)
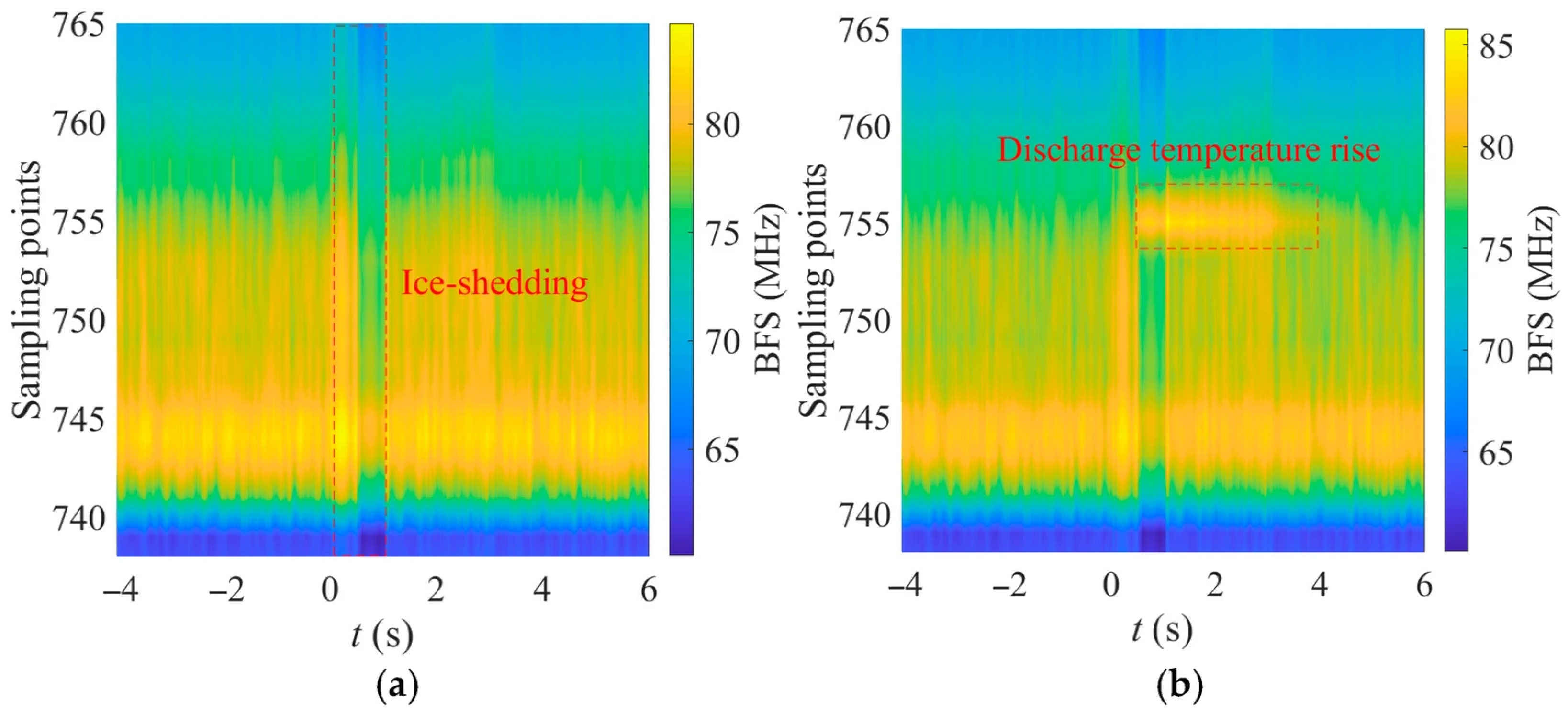
- Ice-shedding strain: Axial stress variations induced by the jump propagate through the aluminum-clad steel strands and the metal tube, eventually reaching the encapsulated fiber. The fiber is subjected to rapid dynamic tensile strain, causing changes in the BFS.
- (2)
- Discharge temperature rise: Gap breakdown produces a high-temperature arc (typically 7000–8000 °C [24]), and both arc heating and Joule heating of the discharge current heat the metal layers of the OPGW through thermal radiation and conduction. The heat is further transferred into the internal fiber, causing a local temperature rise.
3. Experimental System and Methods
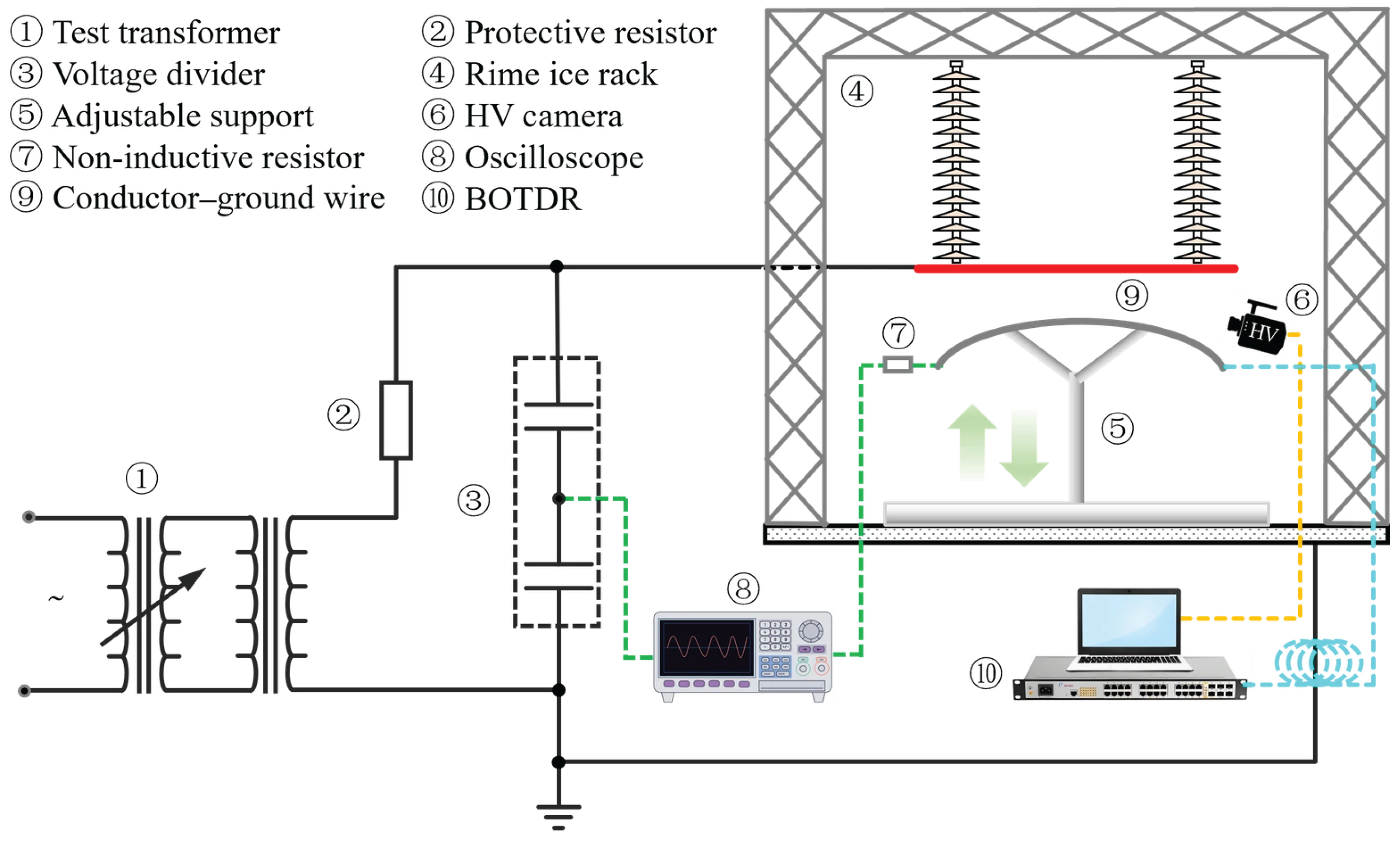
3.1. Experimental System
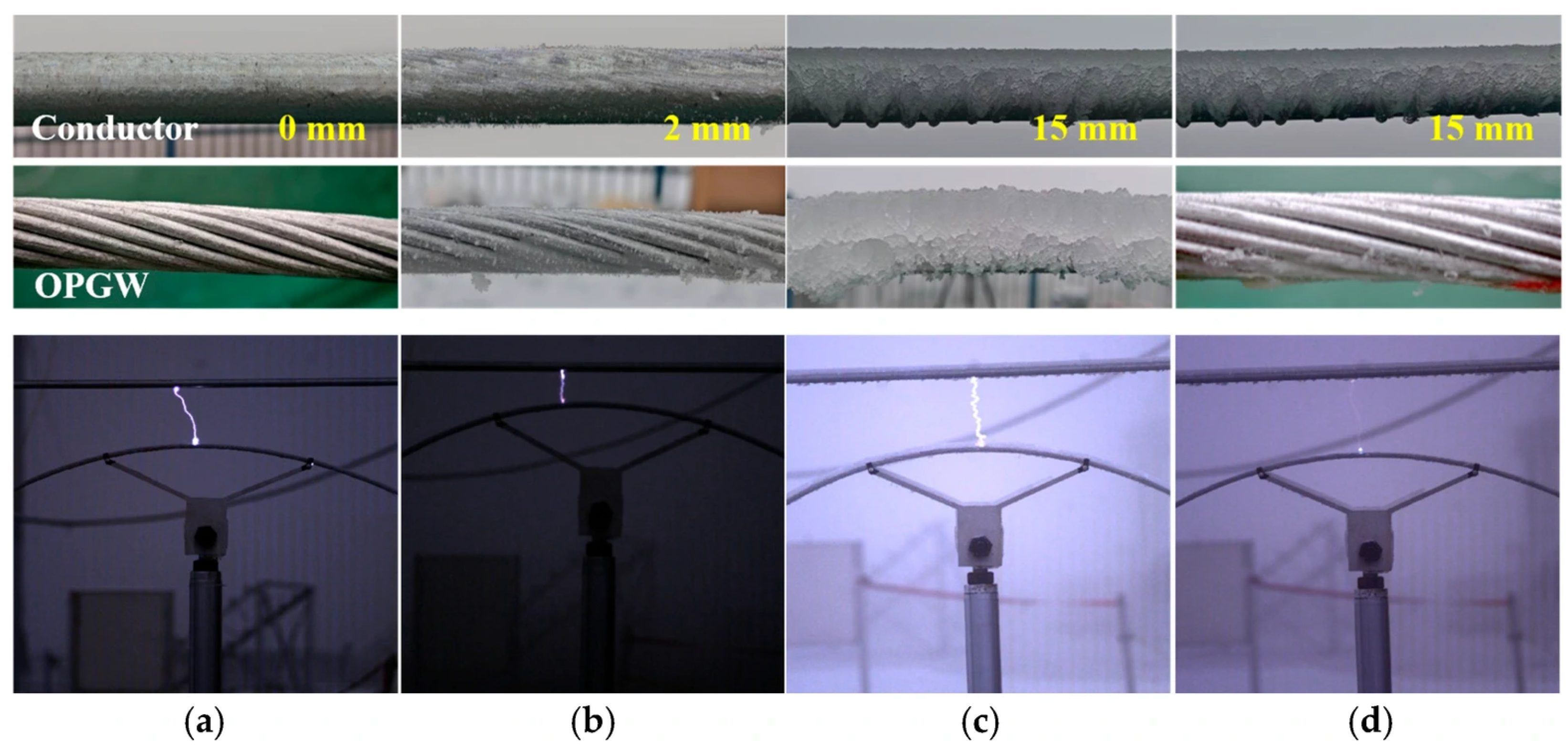
3.2. Icing Conditions
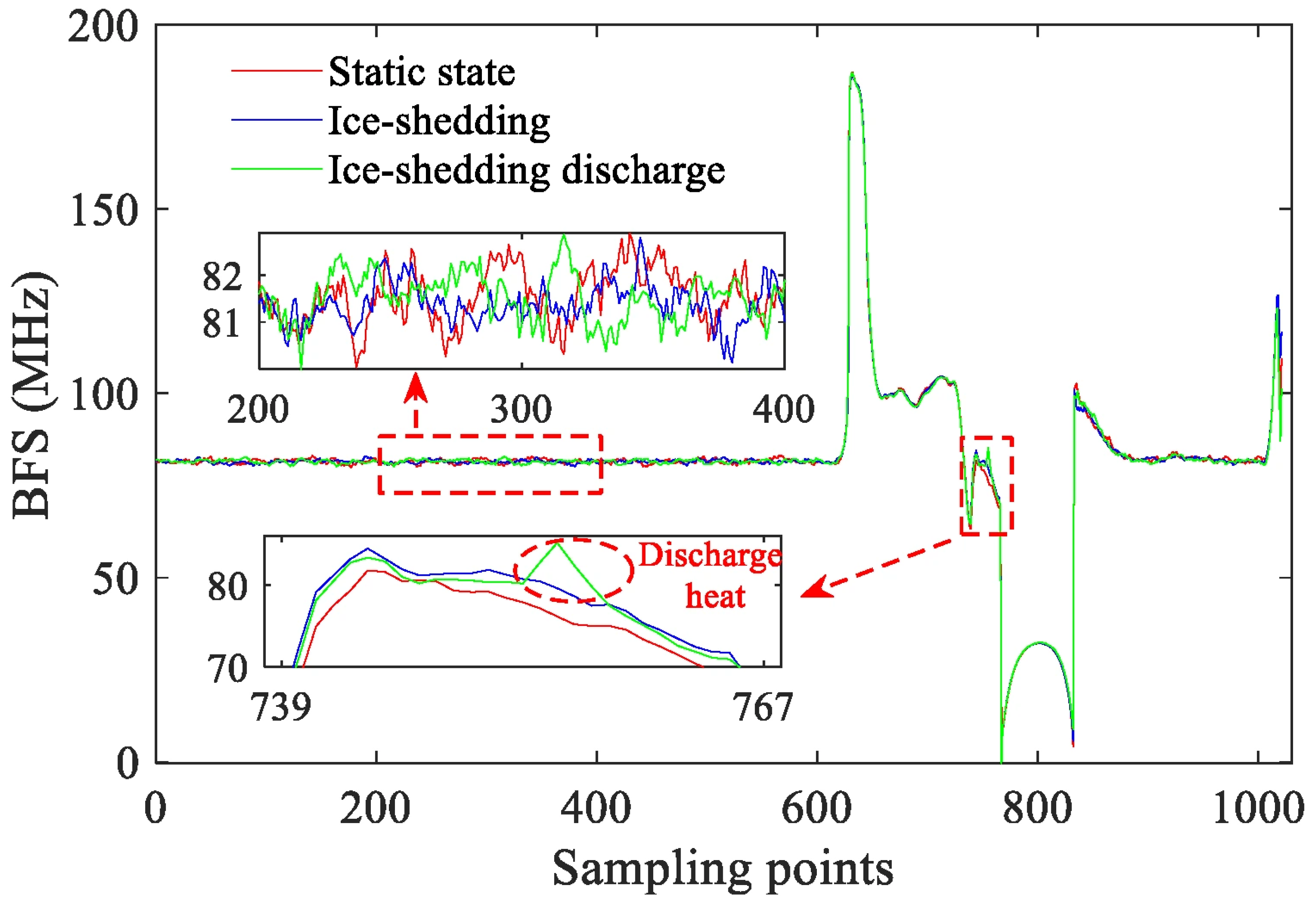
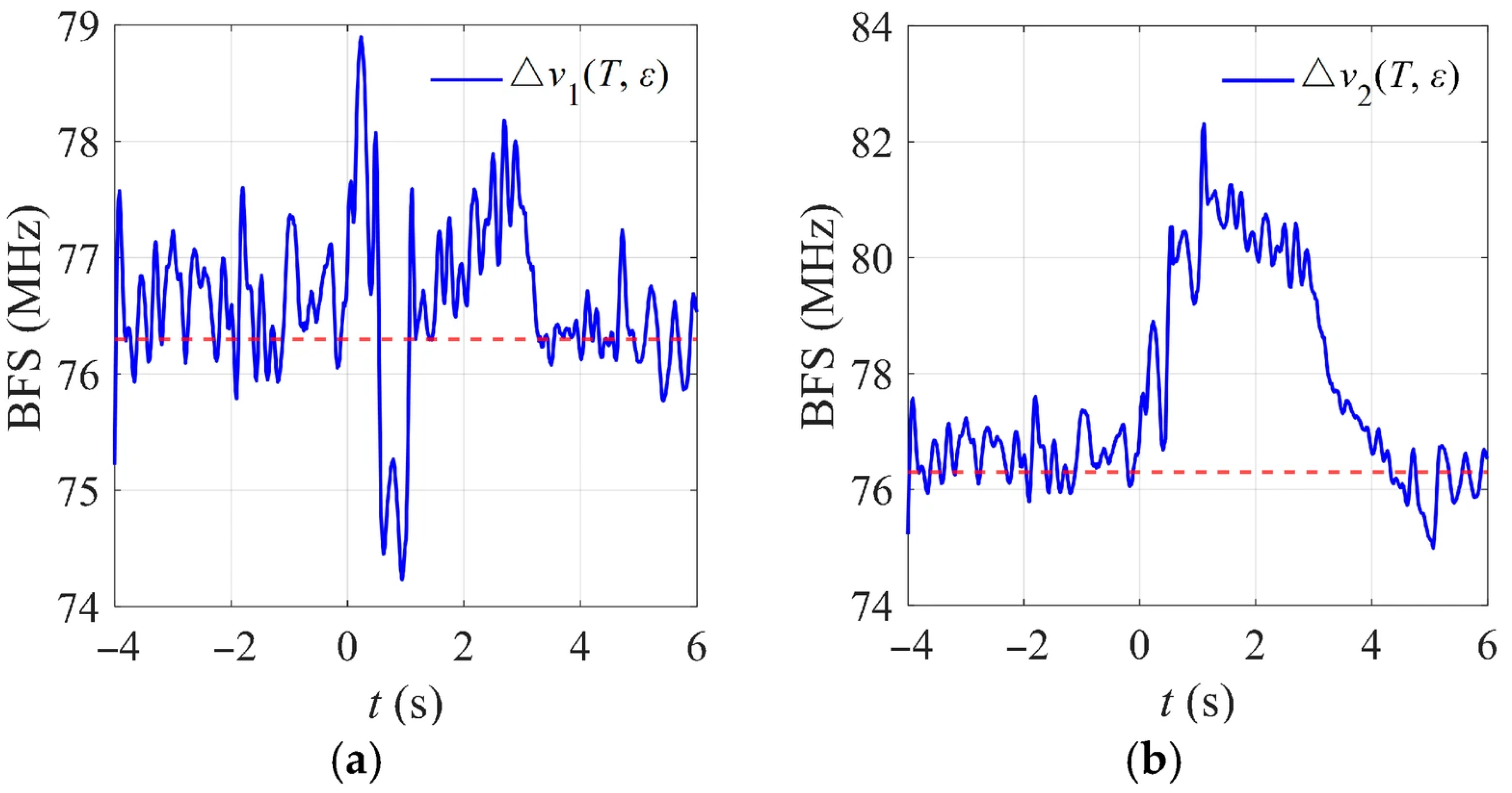
3.3. Decoupling Method for Temperature-Rise-Induced BFS
- (1)
- Ice-shedding group: Only the mechanical motion of ice-shedding was applied, without voltage. The resulting BFS variation was recorded as Δv1(T, ε).
- (2)
- Ice-shedding discharge group: Under identical mechanical motion conditions, the operating voltage was applied, causing breakdown across the gap. The resulting frequency-shift variation was recorded as Δv2(T, ε).
4. Results and Discussion
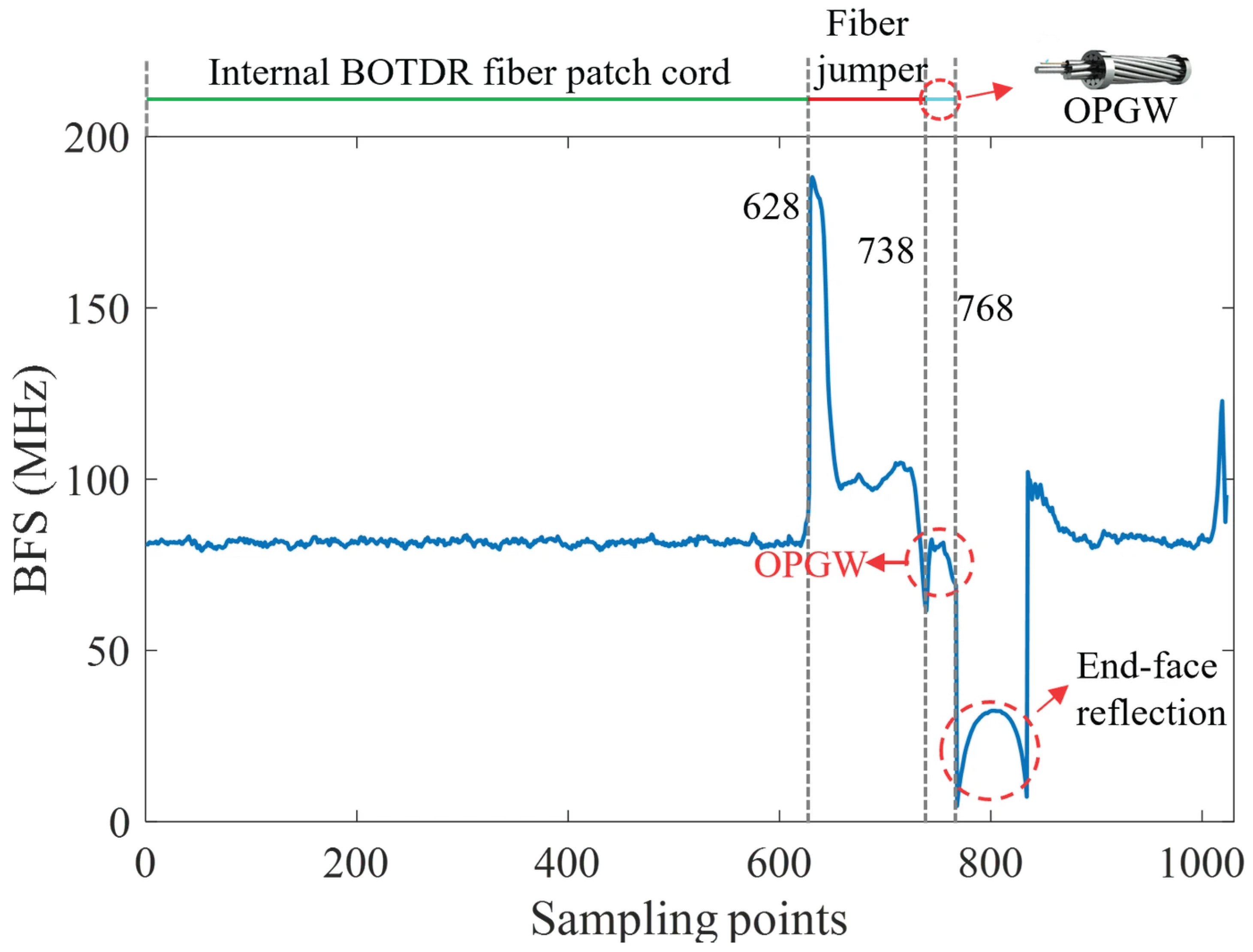
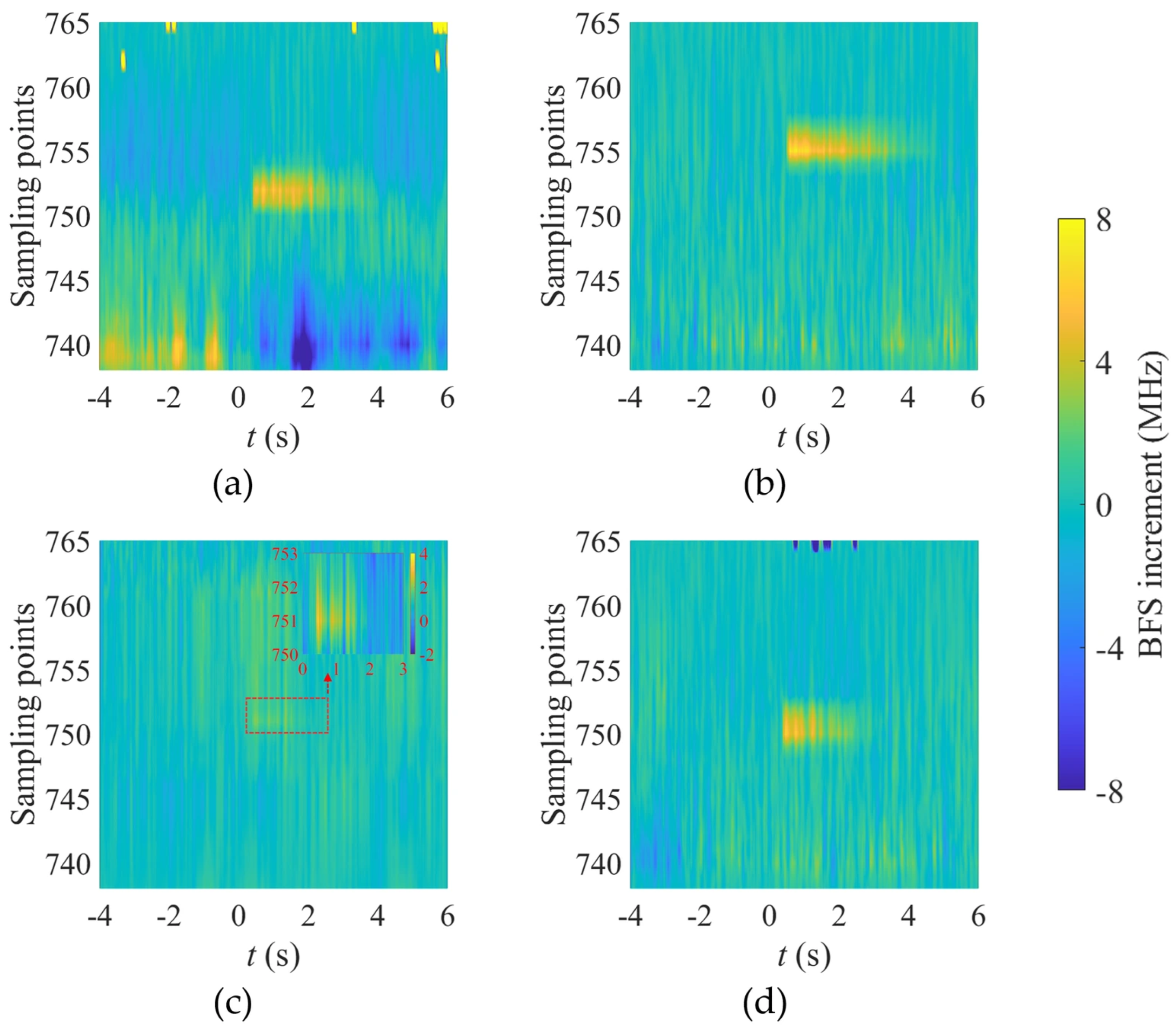
4.1. Characteristics of the BFS Along the Optical Fiber
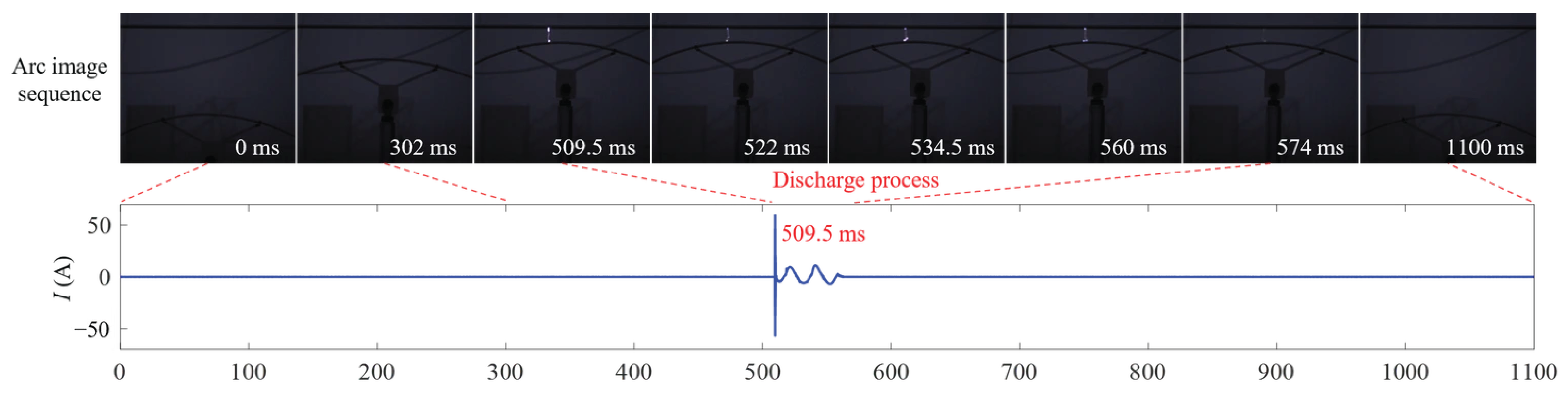
4.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution of BFS During Ice-Shedding Discharge
4.3. BFS Increment Induced by Temperature Rise During Ice-Shedding Discharge
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, K.; Yan, B.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Lu, J.; Liang, M. Characteristics of multi-span transmission lines following ice-shedding. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2024, 218, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xu, H.W.; Huang, M.F. Jump height of an iced transmission conductor considering joint action of ice-shedding and wind. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 199, 103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Wu, J.R.; Mao, X.; Huang, H.; Yang, L. Research on risk assessment and suppression measures for ice-shedding on 500 kV compact overhead lines. Energies 2022, 15, 8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Qi, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, X.; Liu, Z. Dynamic ice processes estimation model of transmission line based on micrometeorological monitoring. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2019, 47, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, V.T.; Swift, D.A. Jump height of overhead-line conductors after the sudden release of ice loads. Proc. IEEE 1964, 111, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, L.; Hou, L.; Fu, G.; Sun, B.; MacAlpine, M.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y. Dynamic characteristic of ice-shedding on UHV overhead transmission lines. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 66, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yan, B.; Wen, N.; Wu, C.; Li, Q. Study on jump height of transmission lines after ice-shedding by reduced-scale modeling test. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 165, 102781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yan, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, G. Experimental study on dynamic response characteristics of isolated-span transmission lines after ice-shedding. High Volt. 2023, 8, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekr, M.R.; McClure, G. Numerical modelling of the dynamic response of ice-shedding on electrical transmission lines. Atmos. Res. 1998, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q. Law of severe conditions of non-uniform ice-shedding jumping of transmission lines. High Volt. Eng. 2018, 44, 2442–2449. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, N.; Yan, B.; Mou, Z.; Huang, G.; Yang, H.; Lv, X. Prediction models for dynamic response parameters of transmission lines after ice-shedding based on machine learning method. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 202, 107580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lou, W.; Chen, S.; Gao, S.; Ma, Y. Dynamic response of a transmission conductor following delayed ice-shedding by reduced-scale model test. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2024, 226, 104288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, K.; Luo, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Conductor galloping monitoring system based on inertial sensors for transmission lines. High Volt. Eng. 2014, 40, 1312–1319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z. Research on Measurement of Conductor Jump Track After Ice-Shedding Based on Binocular Stereo Vision Technology. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z. Research on Dynamic Characteristics of Transmission Lines After Ice-Shedding and FBG Detection Technology. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M. Physics and applications of Raman distributed optical fiber sensing. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Jin, X.; Jiang, J.; Xu, T.; Ding, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xue, K.; Li, S.; Liu, T. Interferometer-based distributed optical fiber sensors in long-distance vibration detection: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 21428–21444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Mao, D.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zha, C.; Huang, H. Test method for minimum critical thickness of ice coating on OPGW based on BOTDR monitoring. High Volt. Eng. 2025, 51, 3191–3200. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Zha, C.; Mao, D.; Huang, L.; Huang, H. Icing monitoring method for isolated tension section OPGW based on micro-meteorological temperature demodulation BOTDR. High Volt. Eng. 2025, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Xiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X. Monitoring technology for ice-shedding and conductor galloping on optical fiber composite overhead ground wire based on distributed dynamic strain sensing. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2025, 1–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magunov, A.; Pylnev, M.; Lapshinov, B. Spectral pyrometry of objects with unknown emissivities in a temperature range of 400–1200 K. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2014, 57, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liang, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Experimental study on location of lightning stroke on OPGW by means of a distributed optical fiber temperature sensor. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 65, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Su, X.; Li, W.; Wu, B.; Feng, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, D.; Wu, G.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Lightning location method using orthogonal coded polarization optical time-domain reflectometer in optical fiber transmission. Photonics 2024, 11, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Song, P.; Lu, Y. Anti-icing technology for transmission lines based on new ground wire structures and operation modes. High Volt. Eng. 2024, 50, 4933–4941. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Pu, Z.; Huang, H. Effects of ice coating on the maximum discharge distance during ice-shedding of conductor–ground wire in 110 kV transmission lines. In Proceedings of the 2025 8th International Conference on Energy, Electrical and Power Engineering (CEEPE), Wuxi, China, 17–20 June 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. Communication in the Presence of Noise. Proc. IRE 2006, 37, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maximum measurement range | ≤2.5 km |
| 2 | Single-shot measurement time | 0.25 s @ 2.5 km |
| 3 | Spatial resolution | ≤1 m @ 2.5 km |
| 4 | Strain measurement accuracy | ±5 με |
| Icing Conditions | dm (cm) | Im (A) | ΔvTm (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No ice | 15 | 44.5 | 6.55 |
| 15 | 42.1 | 7.23 | |
| 15 | 43.2 | 5.43 | |
| 15 | 41.6 | 6.12 | |
| Light rime | 8 | 60.5 | 6.80 |
| 8 | 57.6 | 7.94 | |
| 9 | 53.0 | 5.77 | |
| 8 | 59.3 | — | |
| 8 | 56.1 | — | |
| Glaze ice | 17 | 38.3 | 3.76 |
| 17 | 38.0 | 2.91 | |
| 17 | 38.3 | 3.45 | |
| Glaze ice on conductor only | 19 | 34.4 | 6.43 |
| 18 | 37.6 | 6.12 | |
| 19 | 33.9 | 6.73 | |
| 19 | 32.8 | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Hao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, H. Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing of Temperature Rise During 110 kV Conductor–Ground Wire Ice-Shedding Discharge. Micromachines 2026, 17, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010032
Hao Y, Wu Z, Huang L, Zheng Y, Yang Q, Zhong Y, Huang H. Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing of Temperature Rise During 110 kV Conductor–Ground Wire Ice-Shedding Discharge. Micromachines. 2026; 17(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Yanpeng, Zijian Wu, Lei Huang, Yashuang Zheng, Qi Yang, Yao Zhong, and Huan Huang. 2026. "Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing of Temperature Rise During 110 kV Conductor–Ground Wire Ice-Shedding Discharge" Micromachines 17, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010032
APA StyleHao, Y., Wu, Z., Huang, L., Zheng, Y., Yang, Q., Zhong, Y., & Huang, H. (2026). Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing of Temperature Rise During 110 kV Conductor–Ground Wire Ice-Shedding Discharge. Micromachines, 17(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010032







