Affinity-Bead-Mediated Enrichment of CD8+ Lymphocytes from Peripheral Blood Progenitor Cell Products Using Acoustophoresis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Labeling of CD8+ Cells with Affinity Beads
2.4. Magnetic Cell Separation
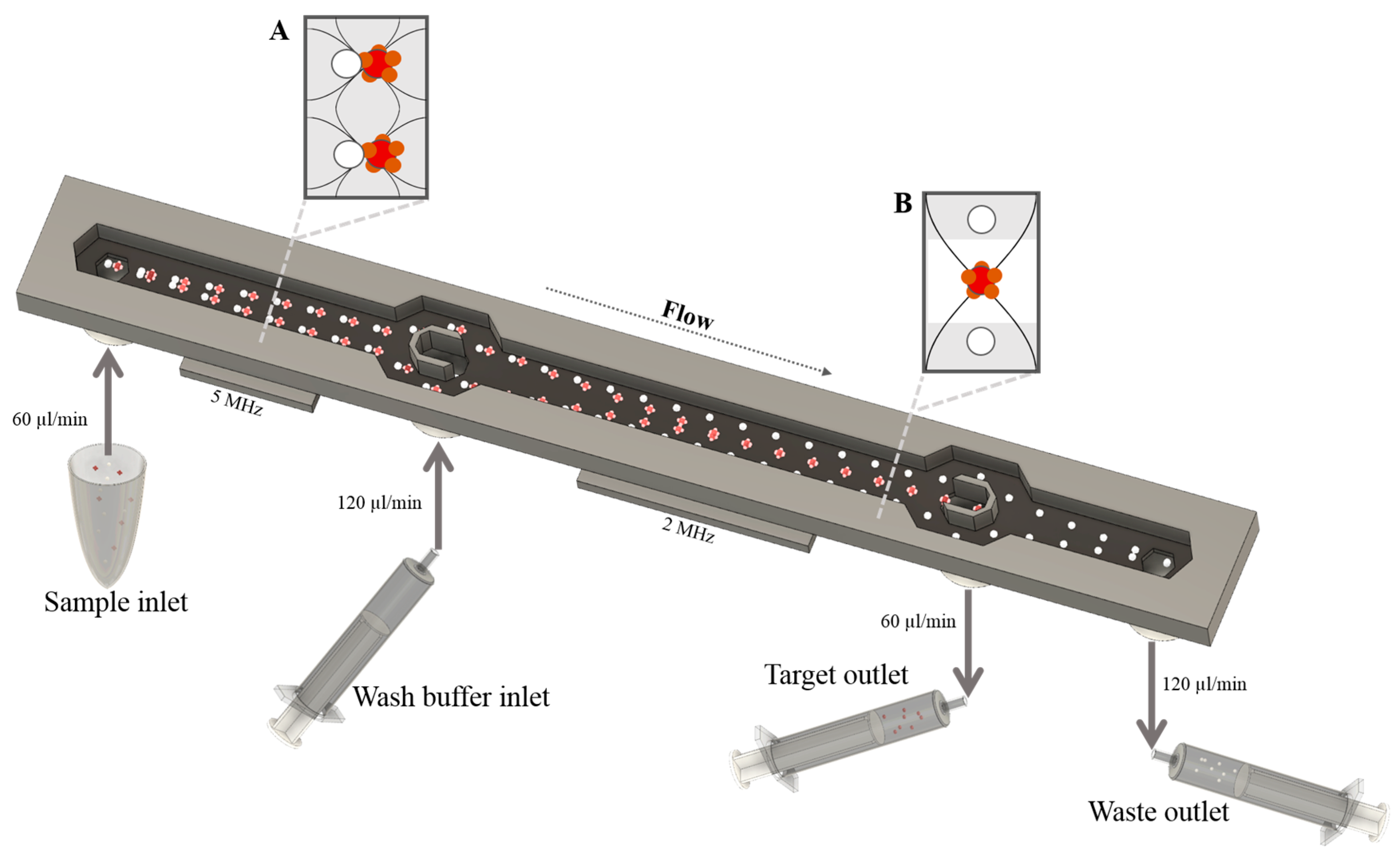
2.5. Acoustophoresis Chip
2.6. Fluidic Setup and Sample Procedure
2.7. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.8. In Vitro Cell Proliferation Assay
2.9. Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
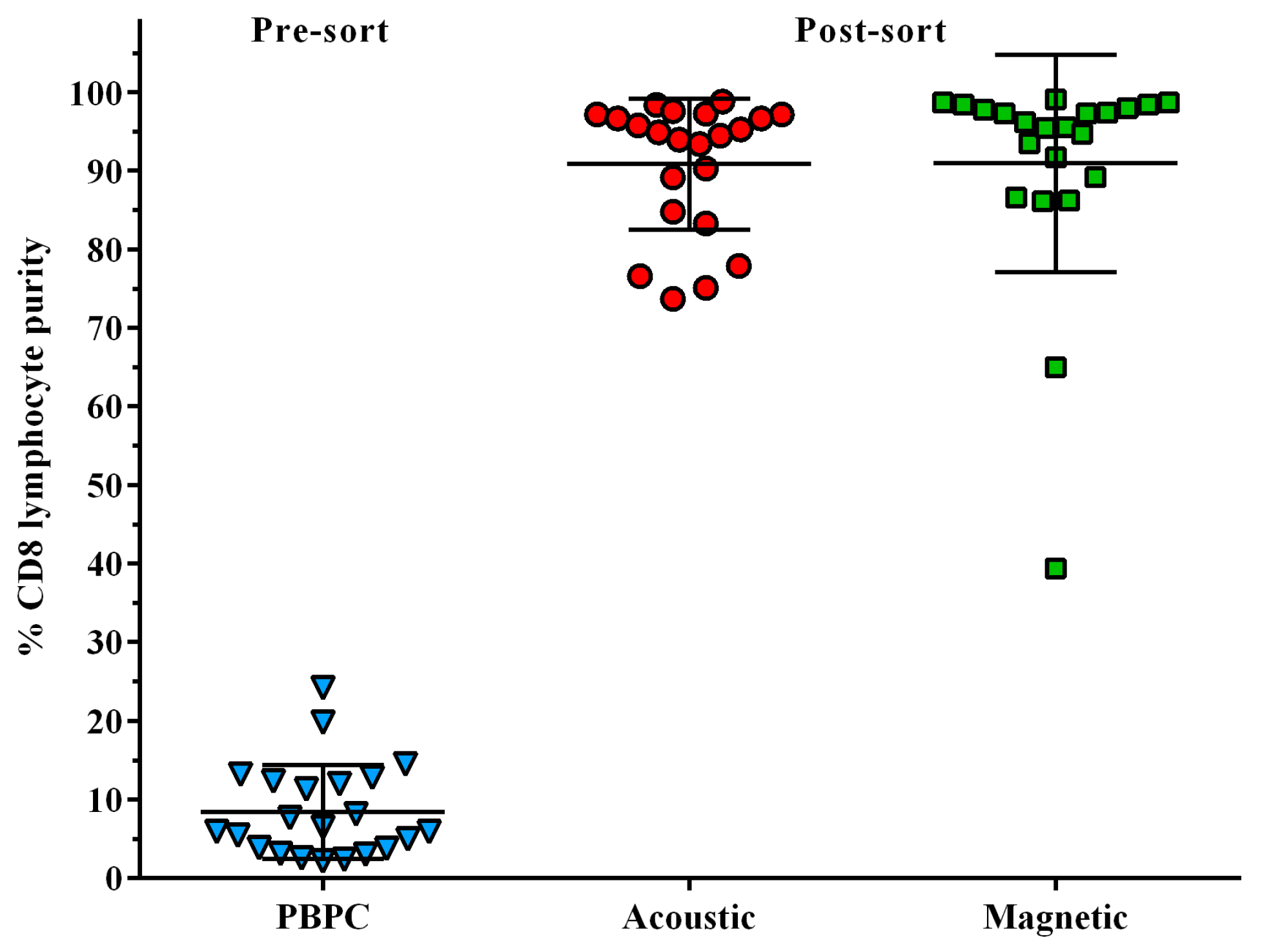
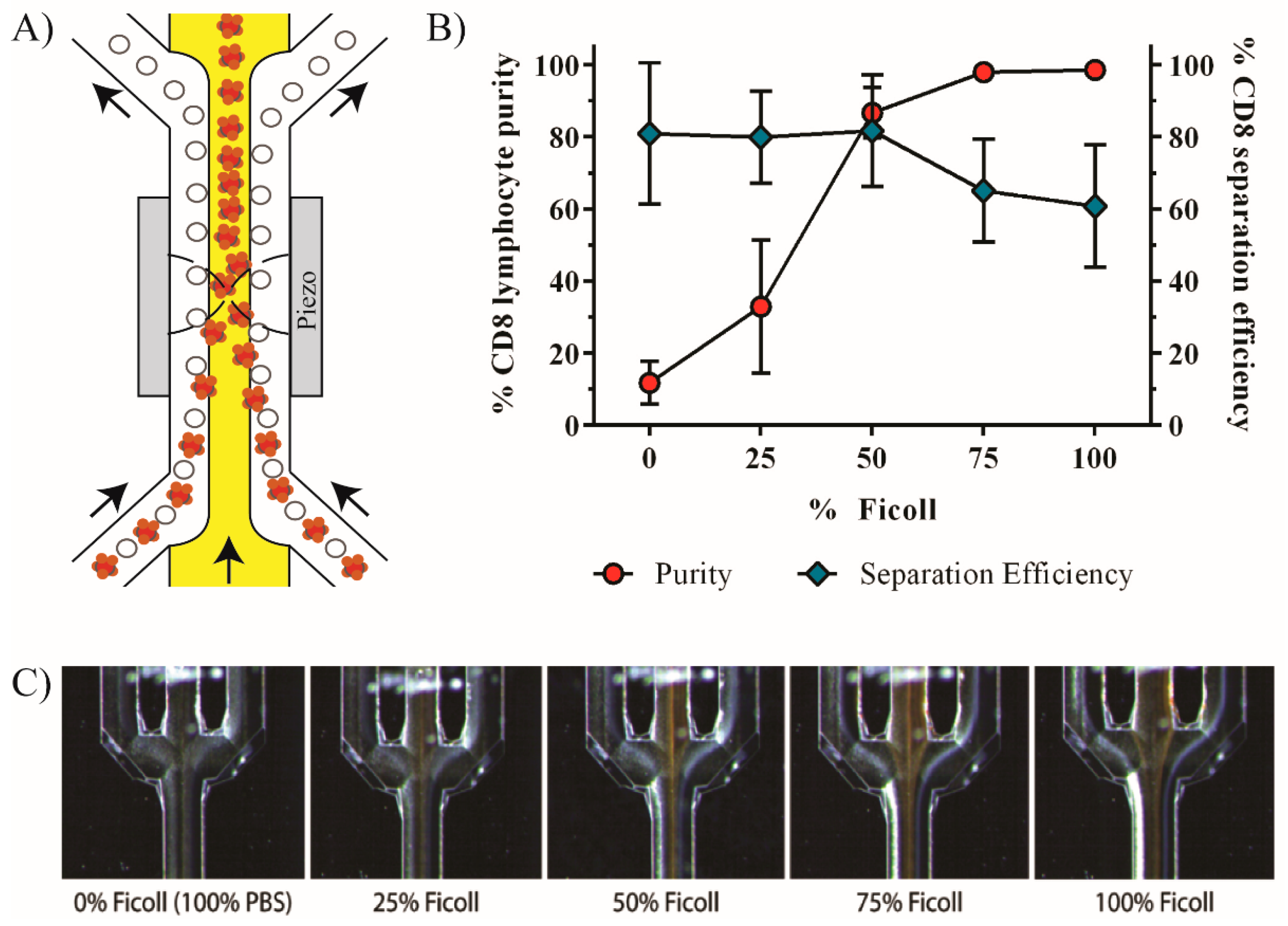
3.1. Enrichment of CD8+ Lymphocytes Using Affinity Bead Acoustophoresis
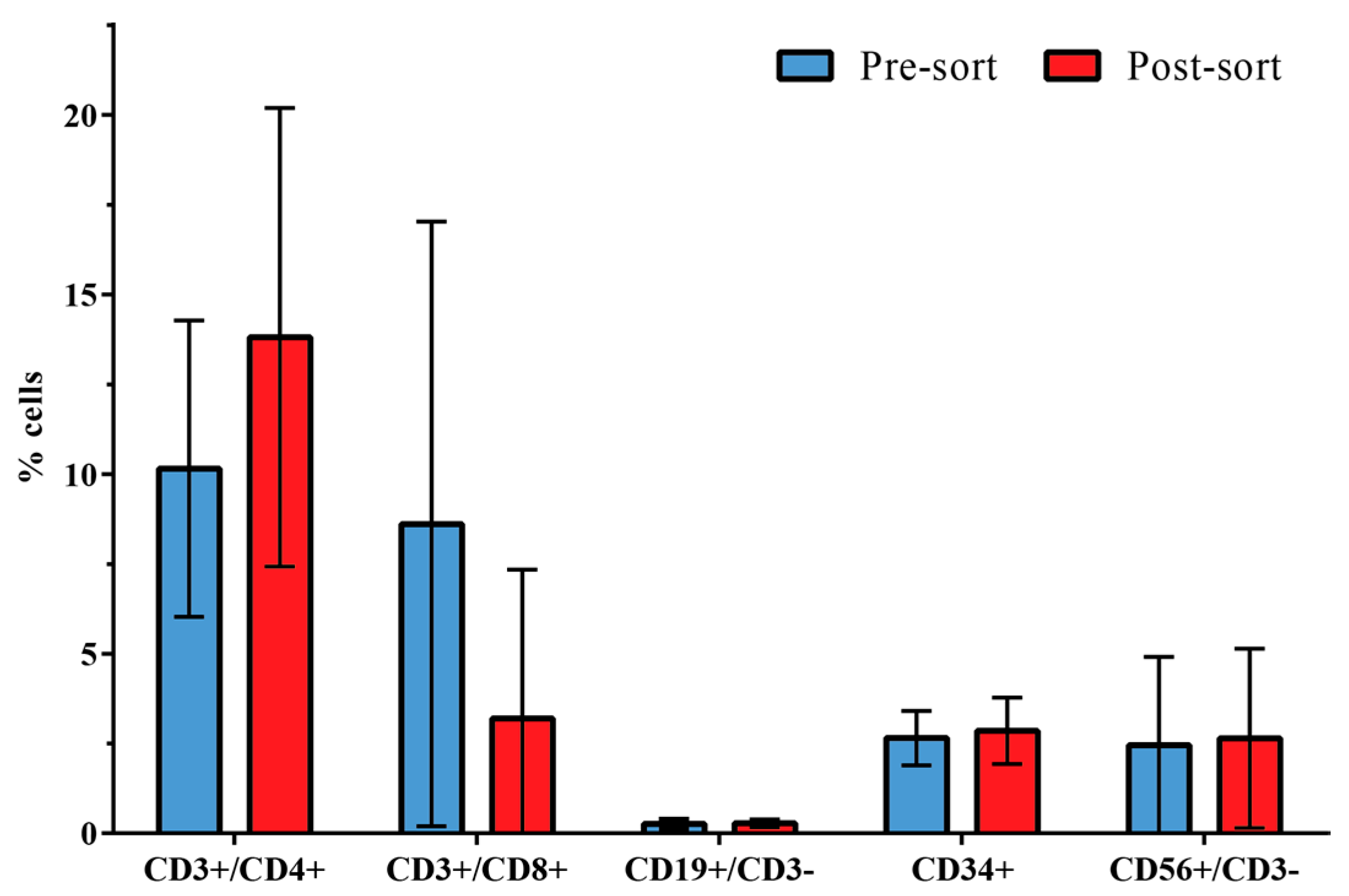
3.2. Distribution of Leukocyte Subpopulations
3.3. CD3/CD28-Mediated T Cell Proliferation Capacity of Acoustically Sorted Cells Is Unimpaired
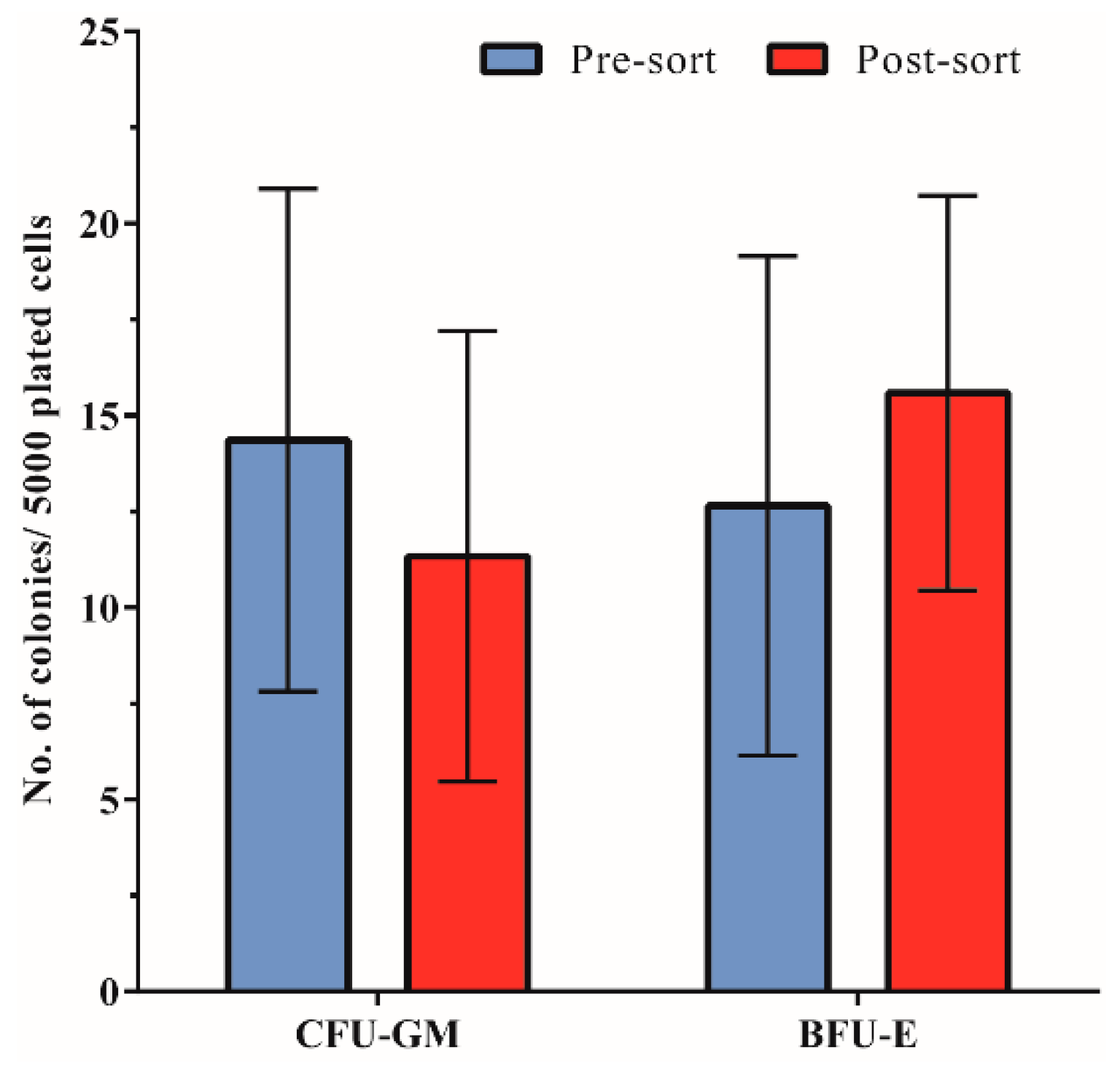
3.4. Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Colony-Forming Ability Is Unaffected by Acoustophoresis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gratwohl, A.; Baldomero, H.; Horisberger, B.; Schmid, C.; Passweg, J.; Urbano-Ispizua, A. Accreditation Committee of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) Current trends in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in Europe. Blood 2002, 100, 2374–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreger, P.; Haferlach, T.; Eckstein, V.; Jacobs, S.; Suttorp, M.; Löffler, H.; Müller-Ruchholtz, W.; Schmitz, N. G-CSF-mobilized peripheral blood progenitor cells for allogeneic transplantation: Safety, kinetics of mobilization, and composition of the graft. Br. J. Haematol. 1994, 87, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theilgaard-Mönch, K.; Raaschou-Jensen, K.; Palm, H.; Schjødt, K.; Heilmann, C.; Vindeløv, L.; Jacobsen, N.; Dickmeiss, E. Flow cytometric assessment of lymphocyte subsets, lymphoid progenitors, and hematopoietic stem cells in allogeneic stem cell grafts. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001, 28, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraceni, F.; Shem-Tov, N.; Olivieri, A.; Nagler, A. Mobilized peripheral blood grafts include more than hematopoietic stem cells: The immunological perspective. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015, 50, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, N.; Barrett, J. Optimizing engraftment—Source and dose of stem cells. Semin. Hematol. 2002, 39, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, F.; Baudoux, E.; Frère, P.; Tourqui, S.; Schaaf-Lafontaine, N.; Greimers, R.; Herens, C.; Fillet, G.; Beguin, Y. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation with CD8-depleted or CD34-selected peripheral blood stem cells. J. Hematother. Stem Cell Res. 2002, 11, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.M.; Shizuru, J.A.; Wong, R.M.; Sheehan, K.; Laport, G.G.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.E.; Johnston, L.J.; Stuart, M.J.; Grumet, F.C.; Negrin, R.S.; et al. Engraftment and survival following reduced-intensity allogeneic peripheral blood hematopoietic cell transplantation is affected by CD8+ T-cell dose. Blood 2005, 105, 2300–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Won, D.I.; Lee, N.Y.; Sohn, S.K.; Suh, J.S.; Lee, K.B. Non-CD34+ cells, especially CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and CD56+ natural killer cells, rather than CD34 cells, predict early engraftment and better transplantation outcomes in patients with hematologic malignancies after allogeneic peripheral stem cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006, 12, 719–728. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoef, M.E. Guidelines for efficient peripheral blood progenitor cell collection. Neth. J. Med. 1996, 48, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltenyi, S.; Müller, W.; Weichel, W.; Radbruch, A. High gradient magnetic cell separation with MACS. Cytometry 1990, 11, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinchmann, J. E.; Vartdal, F.; Gaudernack, G.; Markussen, G.; Funderud, S.; Ugelstad, J.; Thorsby, E. Direct immunomagnetic quantification of lymphocyte subsets in blood. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1988, 71, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial Focusing for Tumor Antigen–Dependent and –Independent Sorting of Rare Circulating Tumor Cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, W.A.; Hulett, H.R.; Sweet, R.G.; Herzenberg, L.A. Fluorescence activated cell sorting. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1972, 43, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, M.R.; Donahue, R.E. Rare event sorting of CD34+ hematopoietic cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 677, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenshof, A.; Laurell, T. Emerging clinical applications of microchip-based acoustophoresis. J. Lab. Autom. 2011, 16, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenje, M.; Lundgren, M.N.; Swärd-Nilsson, A.-M.; Kjeldsen-Kragh, J.; Lyxe, L.; Lenshof, A. Acoustophoretic removal of proteins from blood components. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurell, T.; Petersson, F.; Nilsson, A. Chip integrated strategies for acoustic separation and manipulation of cells and particles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersson, F.; Nilsson, A.; Holm, C.; Jonsson, H.; Laurell, T. Separation of lipids from blood utilizing ultrasonic standing waves in microfluidic channels. Analyst 2004, 129, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersson, F.; Aberg, L.; Swärd-Nilsson, A.-M.; Laurell, T. Free flow acoustophoresis: microfluidic-based mode of particle and cell separation. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5117–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, K.; Haupt, S. S.; Umemura, S.; Yagi, T.; Nishida, M.; Shibata, Y. Using acoustic radiation force as a concentration method for erythrocytes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultström, J.; Manneberg, O.; Dopf, K.; Hertz, H. M.; Brismar, H.; Wiklund, M. Proliferation and viability of adherent cells manipulated by standing-wave ultrasound in a microfluidic chip. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burguillos, M.A.; Magnusson, C.; Nordin, M.; Lenshof, A.; Augustsson, P.; Hansson, M.J.; Elmér, E.; Lilja, H.; Brundin, P.; Laurell, T.; Deierborg, T. Microchannel acoustophoresis does not impact survival or function of microglia, leukocytes or tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, H.; Holm, C.; Nilsson, A.; Petersson, F.; Johnsson, P.; Laurell, T. Particle separation using ultrasound can radically reduce embolic load to brain after cardiac surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 78, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenshof, A.; Ahmad-Tajudin, A.; Järås, K.; Swärd-Nilsson, A.-M.; Aberg, L.; Marko-Varga, G.; Malm, J.; Lilja, H.; Laurell, T. Acoustic whole blood plasmapheresis chip for prostate specific antigen microarray diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6030–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykes, J.; Lenshof, A.; Åstrand-Grundström, I.-B.; Laurell, T.; Scheding, S. Efficient removal of platelets from peripheral blood progenitor cell products using a novel micro-chip based acoustophoretic platform. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustsson, P.; Magnusson, C.; Nordin, M.; Lilja, H.; Laurell, T. Microfluidic, label-free enrichment of prostate cancer cells in blood based on acoustophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7954–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenvall, C.; Magnusson, C.; Lilja, H.; Laurell, T. Concurrent Isolation of Lymphocytes and Granulocytes Using Prefocused Free Flow Acoustophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenshof, A.; Jamal, A.; Dykes, J.; Urbansky, A.; Astrand-Grundström, I.; Laurell, T.; Scheding, S. Efficient purification of CD4+ lymphocytes from peripheral blood progenitor cell products using affinity bead acoustophoresis. Cytom. Part J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2014, 85, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Všianská, P.; Říhová, L.; Varmužová, T.; Suská, R.; Kryukov, F.; Mikulášová, A.; Kupská, R.; Penka, M.; Pour, L.; Adam, Z.; et al. Analysis of B-cell subpopulations in monoclonal gammopathies. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015, 15, e61–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrikson, R.C.; Mazurkiewicz, J.E. Histology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Turgeon, M.L. Clinical Hematology: Theory and Procedures; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- McClatchey, K.D. Clinical Laboratory Medicine; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sethu, P.; Sin, A.; Toner, M. Microfluidic diffusive filter for apheresis (leukapheresis). Lab. Chip 2006, 6, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustsson, P.; Persson, J.; Ekström, S.; Ohlin, M.; Laurell, T. Decomplexing biofluids using microchip based acoustophoresis. Lab. Chip 2009, 9, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, N.; Schuurhuis, G.J.; van der Pol, M.A.; Westra, G.; Weijers, G.W.D.; van Stijn, A.; Huijgens, P.C.; Ossenkoppele, G.J. High percentage of CD34-positive cells in autologous AML peripheral blood stem cell products reflects inadequate in vivo purging and low chemotherapeutic toxicity in a subgroup of patients with poor clinical outcome. Leukemia 2003, 17, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmaagacli, A.H.; Peceny, R.; Steckel, N.; Trenschel, R.; Ottinger, H.; Grosse-Wilde, H.; Schaefer, U.W.; Beelen, D.W. Outcome of transplantation of highly purified peripheral blood CD34+ cells with T-cell add-back compared with unmanipulated bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells from HLA-identical sibling donors in patients with first chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2003, 101, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Handgretinger, R.; Klingebiel, T.; Lang, P.; Gordon, P.; Niethammer, D. Megadose transplantation of highly purified haploidentical stem cells: Current results and future prospects. Pediatr. Transplant. 2003, 7, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Després, D.; Flohr, T.; Uppenkamp, M.; Baldus, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Huber, C.; Derigs, H. G. CD34+ cell enrichment for autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation by use of the CliniMACs device. J. Hematother. Stem Cell Res. 2000, 9, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perseghin, P.; Gaipa, G.; Dassi, M.; Belotti, D.; Pogliani, E.M.; Pioltelli, P.; Balduzzi, A.; Rovelli, A.; Uderzo, C.; Biondi, A. CD34+ stem cell recovery after positive selection of “overloaded” immunomagnetic columns. Stem Cells Dev. 2005, 14, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykes, J.H.; Toporski, J.; Juliusson, G.; Békássy, A.N.; Lenhoff, S.; Lindmark, A.; Scheding, S. Rapid and effective CD3 T-cell depletion with a magnetic cell sorting program to produce peripheral blood progenitor cell products for haploidentical transplantation in children and adults. Transfusion 2007, 47, 2134–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustsson, P.; Barnkob, R.; Wereley, S.T.; Bruus, H.; Laurell, T. Automated and temperature-controlled micro-PIV measurements enabling long-term-stable microchannel acoustophoresis characterization. Lab. Chip 2011, 11, 4152–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbansky, A.; Lenshof, A.; Dykes, J.; Laurell, T.; Scheding, S. Affinity-Bead-Mediated Enrichment of CD8+ Lymphocytes from Peripheral Blood Progenitor Cell Products Using Acoustophoresis. Micromachines 2016, 7, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060101
Urbansky A, Lenshof A, Dykes J, Laurell T, Scheding S. Affinity-Bead-Mediated Enrichment of CD8+ Lymphocytes from Peripheral Blood Progenitor Cell Products Using Acoustophoresis. Micromachines. 2016; 7(6):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060101
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbansky, Anke, Andreas Lenshof, Josefina Dykes, Thomas Laurell, and Stefan Scheding. 2016. "Affinity-Bead-Mediated Enrichment of CD8+ Lymphocytes from Peripheral Blood Progenitor Cell Products Using Acoustophoresis" Micromachines 7, no. 6: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060101
APA StyleUrbansky, A., Lenshof, A., Dykes, J., Laurell, T., & Scheding, S. (2016). Affinity-Bead-Mediated Enrichment of CD8+ Lymphocytes from Peripheral Blood Progenitor Cell Products Using Acoustophoresis. Micromachines, 7(6), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7060101






