Research Progress and Application Scenarios of Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing: From Process Control to Performance Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- WAAM has a high degree of freedom. The driving systems used in laser and electron beam additive manufacturing are primarily multi-axis machine tools, typically employing Cartesian three-axis translation to achieve bottom-up material deposition. In contrast, arc-based additive manufacturing commonly utilizes multi-axis robotic arms equipped with external axes. Positioning machines and gantry frames can realize the manufacturing of a high degree of freedom, high flexibility, and any complex spatial path.
- (2)
- (3)
- WAAM is also suitable for the repair of certain simple components.
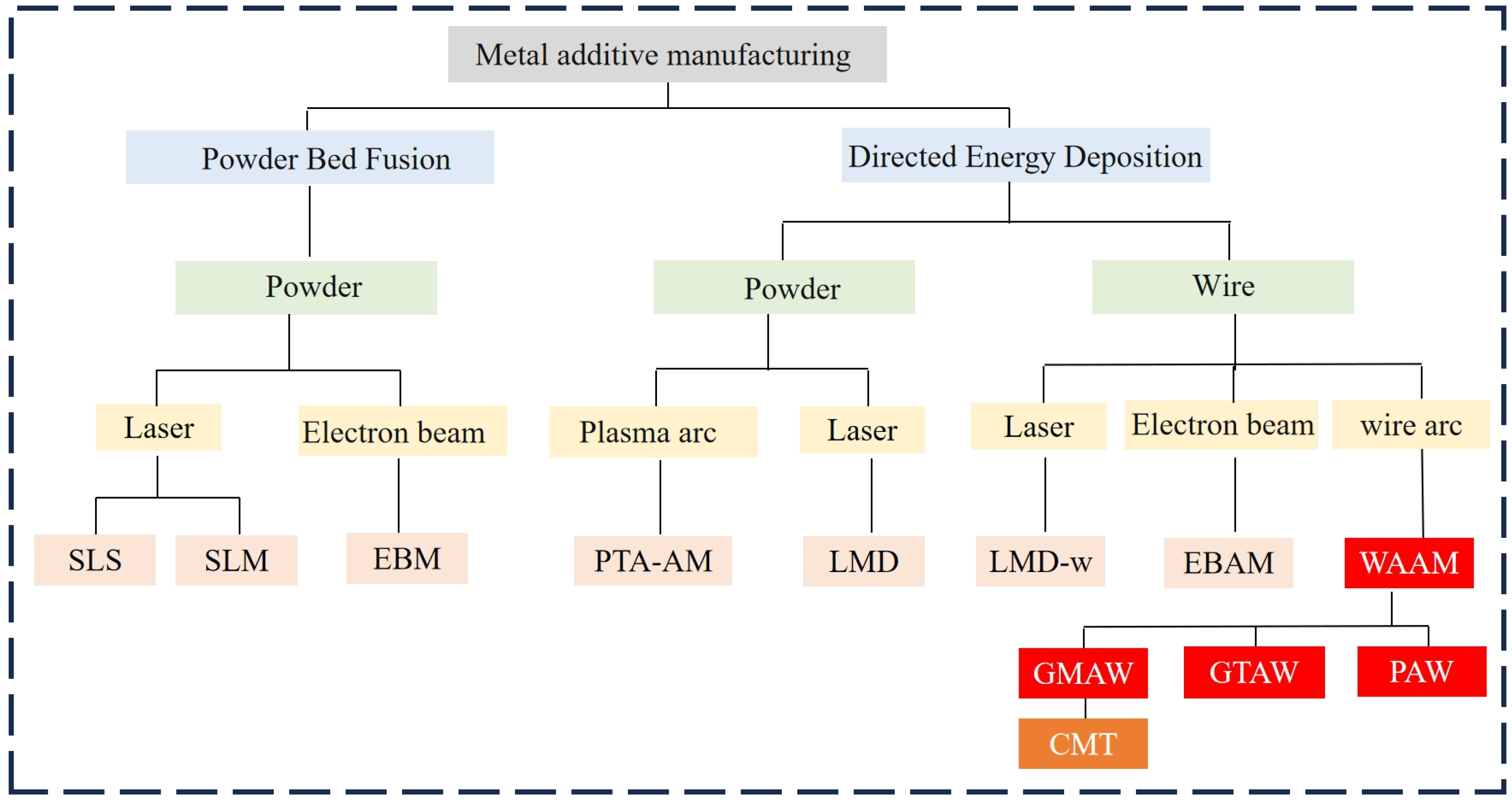
2. WAAM Technology
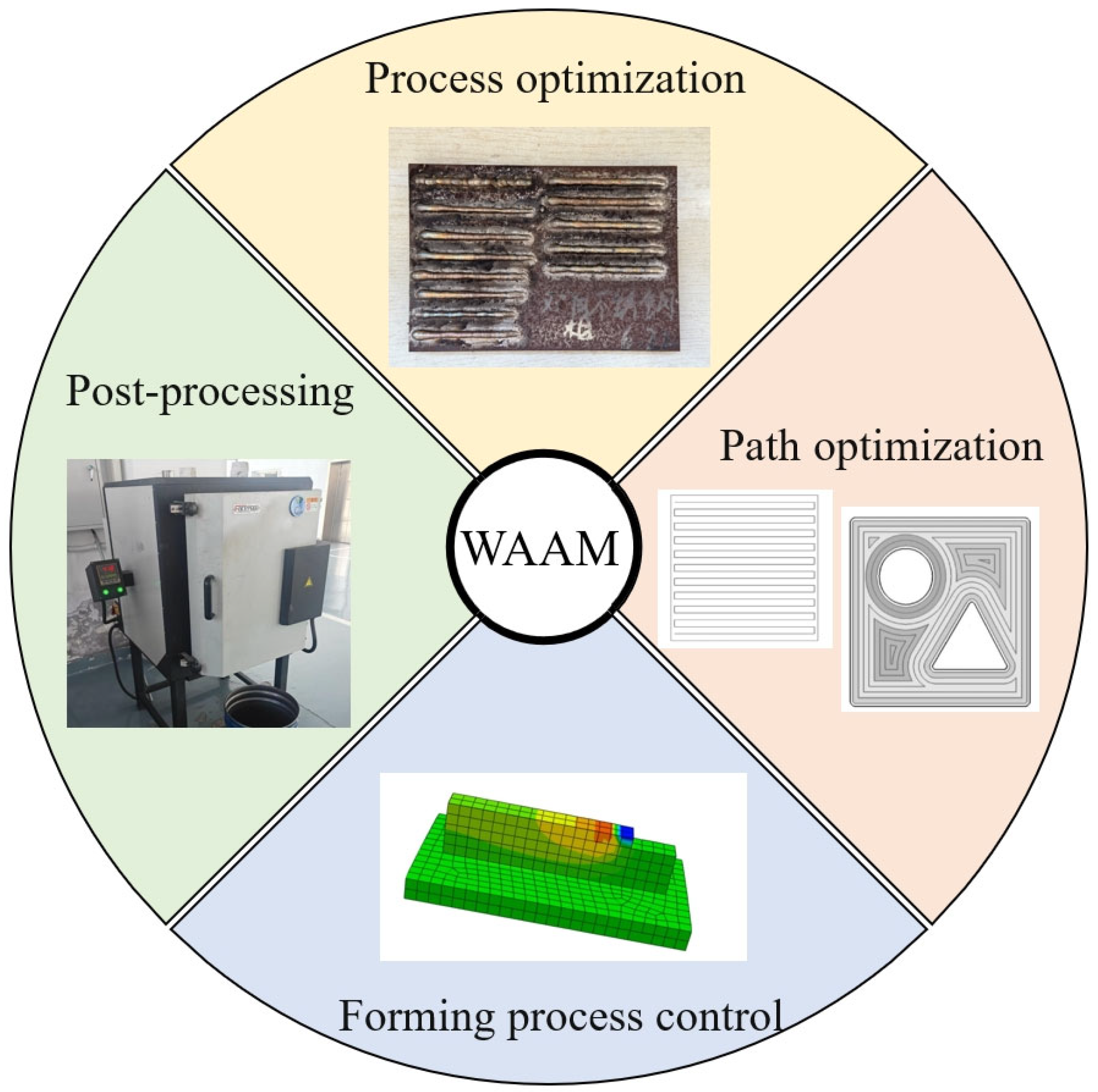
3. Research Status of WAAM Technology
3.1. Process Selection and Optimization of WAAM
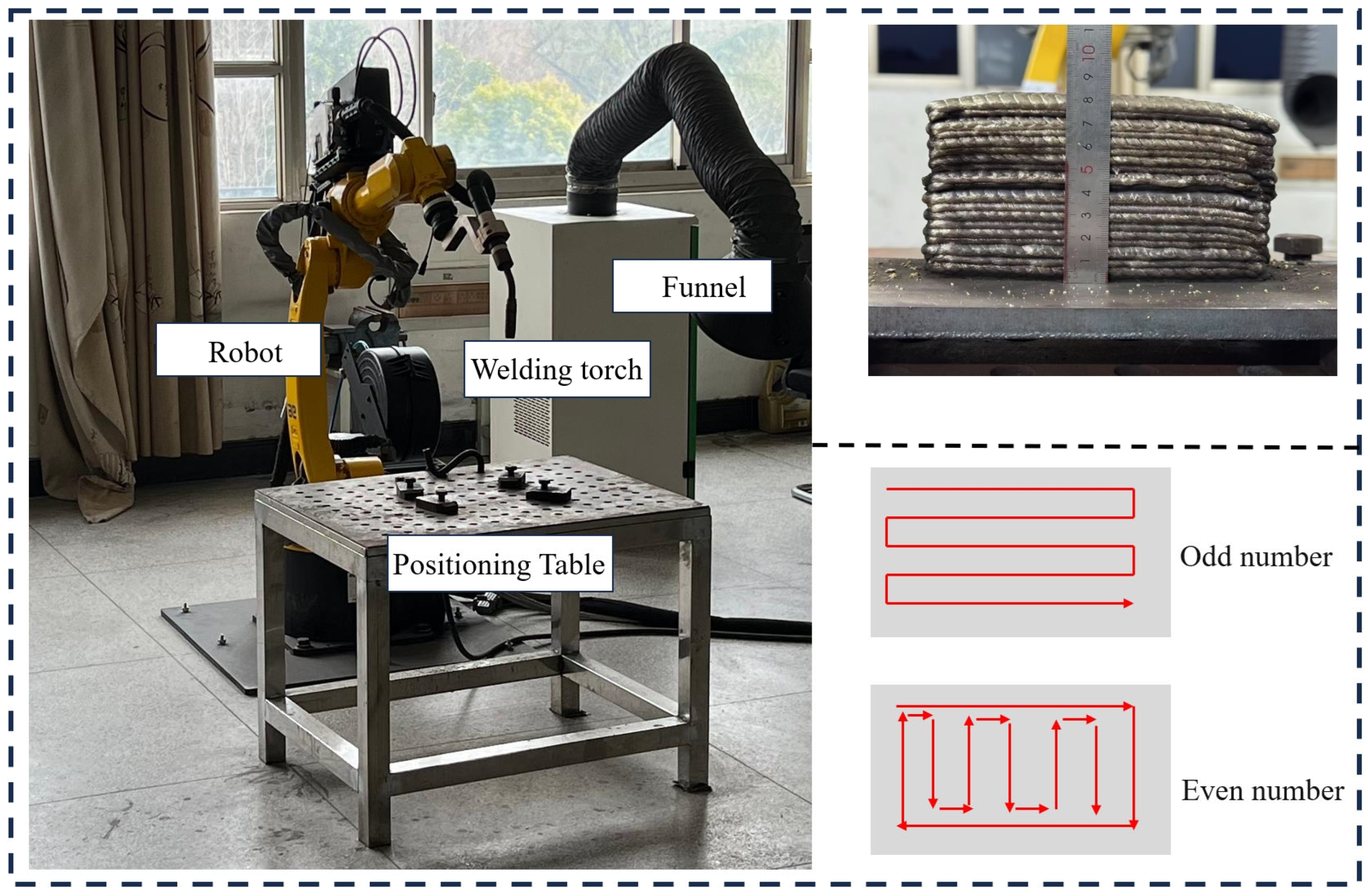
3.2. WAAM Technology Path Planning
3.3. Monitoring and Control Optimization of Forming Process in WAAM Technology
3.4. Wire Arc Additive Technology Performance Testing and Analysis
- (1)
- Micro-organizational analysis
- (2)
- Mechanical property testing and analysis
3.5. WAAM Technology Post-Processing
4. Common Defects and Improvement Methods of WAAM
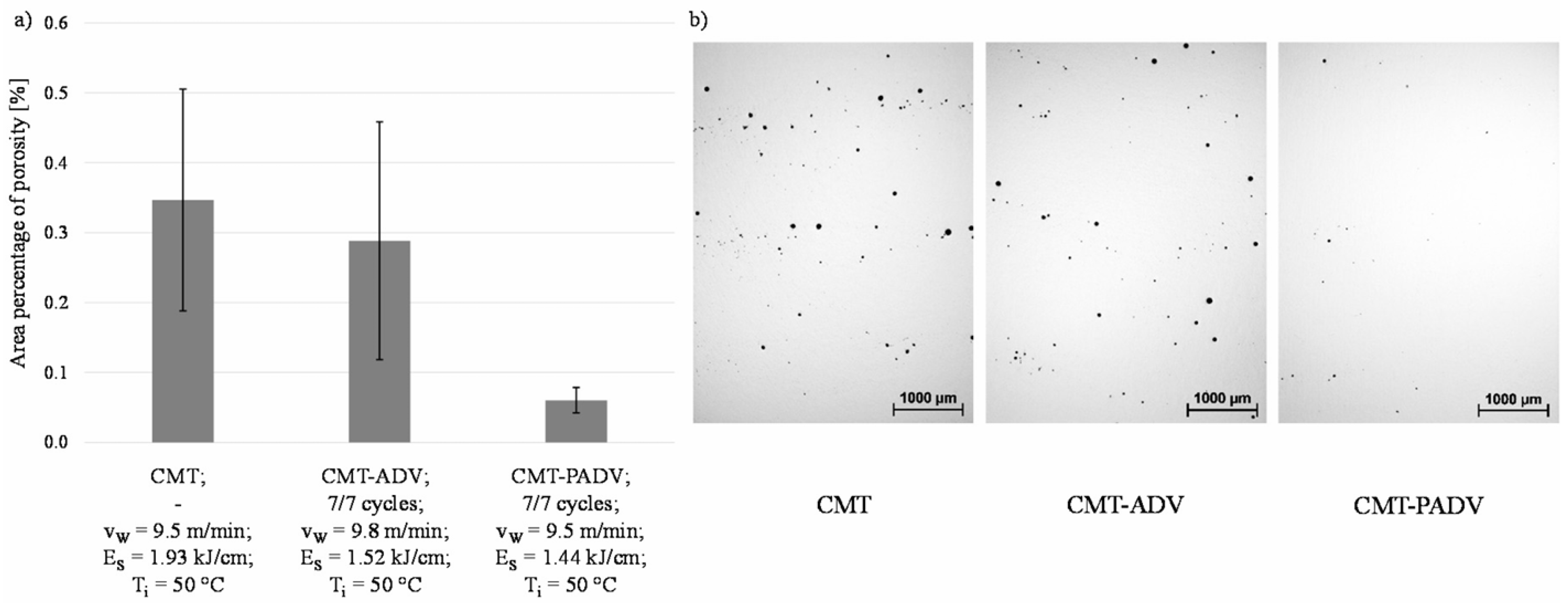
4.1. Porosity
4.2. Residual Stress and Strain
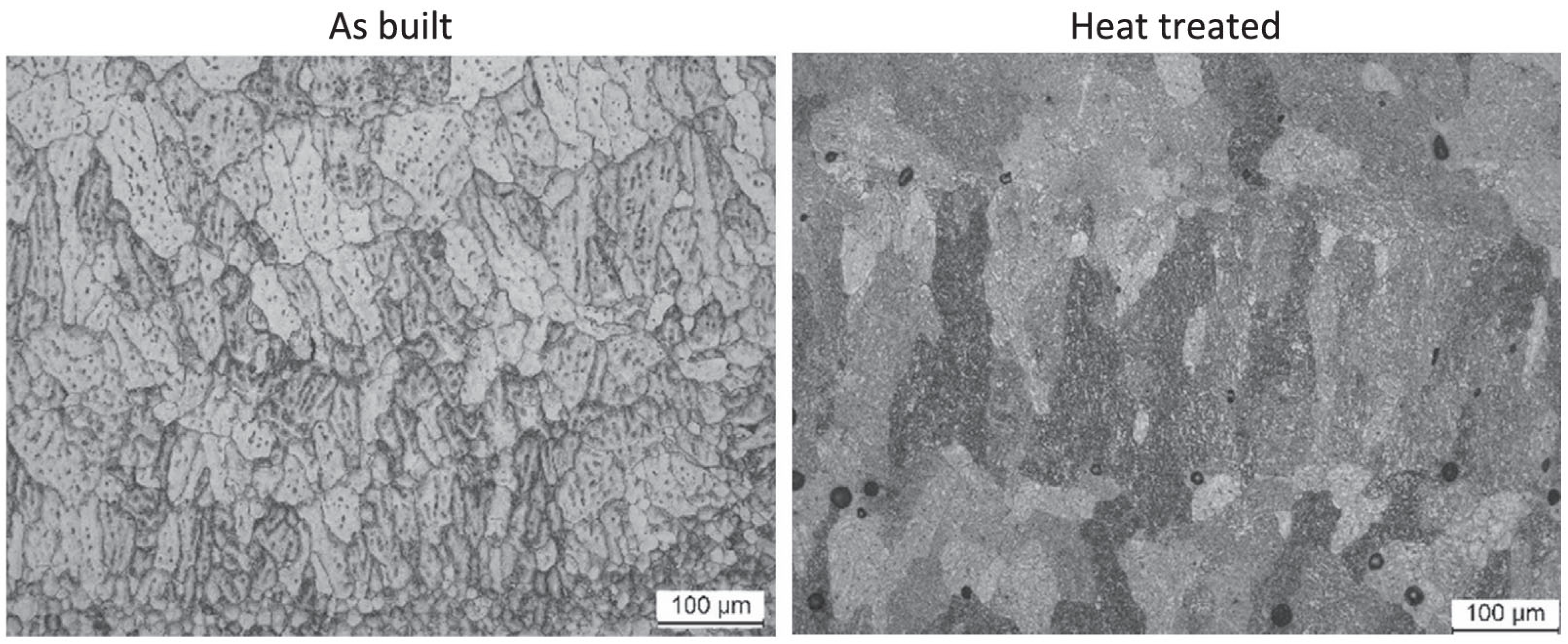
- (1)
- Heat treatment: Heat treatment is an effective method for reducing residual stress and enhancing the mechanical properties of components. As shown in Figure 10, Maider Arana et al. [92] found that neither grain size nor morphology of 2319 aluminum alloy annealing samples and heat treatment had any effect on the microstructure, but the coating grains were purer after heat treatment.
- (2)
- Interlayer rolling: Interlayer cold rolling not only reduces residual stress and deformation, but also significantly improves the anisotropy of components. It effectively refines grain structure, mitigates anisotropy and residual stress in additively manufactured components made from titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, and steels. However, the use of the interlayer rolling process is only suitable for simple-shaped components such as straight walls, not for curved surfaces or more complex and irregular components, and the efficiency is low, which has certain limitations [93].
5. Application of WAAM Technology
6. Conclusions and Outlook
- (1)
- Development of intelligent arc additive manufacturing equipment with software as the core
- (2)
- Forming process optimization and process library establishment
- (3)
- Materials and architecture innovation
- (4)
- Development of integrated system and technology of “additive-subtractive”
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ming, W.; He, W.; Ma, J. The metal additive-manufacturing technology of the ultrasonic-assisted wire-and-arc additive-manufacturing process. Metals 2023, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, J.; Zeng, L.; Tuo, Z.; Ren, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, H. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2/TiC Particle Modified Al-Mg-Si Alloys Fabricated by Wire-Arc Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2025, 18, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, F.; McLaughlin, E.; Ermakova, A.; Mehmanparast, A. Influence of overloading on residual stress distribution in surface-treated wire arc additive-manufactured steel specimens. Materials 2025, 18, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasegaram, D.R.; Steinbach, I. Modelling of microstructure formation in metal additive manufacturing: Recent progress, research gaps and perspectives. Metals 2021, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.A.; Alkahari, M.R.; bin Abdollah, M.F.; Maidin, S.; Ramli, F.R.; Herawan, S.G. Review on effect of heat input for wire arc additive manufacturing process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 2127–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Z.; He, J.; Guo, W.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H. Microstructure Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of High-Strength Invar Alloy by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Inconel 718 Alloy Fabricated Using Wire Feeding Oscillated Double-Pulsed GTA-AM. Metals 2025, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Lyu, F.; Wang, L.; Zhan, X. Investigation of Arc Stability in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of 2319 Aluminum Alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jin, X.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, L. Mechanical properties and interfacial characterization of additive-manufactured CuZrCr/CoCrMo multi-metals fabricated by powder bed fusion using pulsed wave laser. Micromachines 2024, 15, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhinakaran, V.; Ajith, J.; Fahmidha, A.F.Y.; Jagadeesha, T.; Sathish, T.; Stalin, B. Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) process of nickel based superalloys—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgar, A.; Fostervoll, H.; Nyhus, B.; Ren, X.; Eriksson, M.; Akselsen, O.M. Additive manufacturing using WAAM with AA5183 wire. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 259, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, V.R.; Rodrigues, T.A.; Schell, N.; Miranda, R.M.; Oliveira, J.P.; Santos, T.G. Hot forging wire and arc additive manufacturing (HF-WAAM). Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Konovalov, S.; Su, C.; Fan, P.; Wang, Y.; Panchenko, I. A review of challenges for wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2023, 76, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, S.; Al-Mufadi, F.A.; Soundararajan, R. Enhanced microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy joints using rare earth enriched filler produced by GTAW. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, L.; Chuanbao, J.; Peidun, C.; Jiakun, H.; Zhuo, W.; Qingye, Z.; Chuansong, W. Horizontal rotating arc narrow-gap GTAW of thick Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 369–381. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; You, W.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z. A novel controlled high-dynamic braking effect-driven droplet transition in GMAW. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 142, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.K.; Sheng, H.W.; Jasmin, J. Processing characteristics of Ni-WC MMC weld cladding by various types of GMAW. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2025, 40, 755–772. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Luo, S.; Cao, M.; Wang, X.; Nagaumi, H.; Hu, Z. Property enhancement in 6D10 aluminum alloy welds: A comparative study of CMT+P and oscillating laser welding techniques with novel Al-Si-Cu-Mg-Zn filler wire. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2025, 339, 118830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoo, Z.S.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, L.; Jing, B.; Jin, C.; Tang, C. Interface Hardness Analysis of between IN625 and CoCrMo Manufactured by Pulsed Wave Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Micromachines 2024, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantin, S.; Fiona, S.; Roland, H.; Anja, P. Investigation of Distribution of Mechanical Properties inside of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Parts. Defect Diffus. Forum 2025, 443, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Uyen, T.M.T.; Minh, P.S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Le, M.T.; Nguyen, V.T.T. Trajectory strategy effects on the material characteristics in the WAAM technique. Micromachines 2023, 14, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhao, W. Mechanical properties, microstructural characteristics and heat treatment effects of WAAM stainless-steel plate material. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 75, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankova, T.; Zhu, C.; Branco, R. Material Properties for Wire-and-arc Additively Manufactured Steel. ce/Papers 2022, 5, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; R, S.P.; Sajin Jose, S.S.; Upadhyay, R.K. Wire arc additive manufacturing: Materials, processes and its constraints. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2025, 40, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Miao, J.; Liu, H.; Babkin, A.; Chang, Y. Forming accuracy improvement in wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM): A review. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2023, 29, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, H.; Ding, D.; Li, H. A comprehensive review and future perspectives of simulation approaches in wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 7, 022016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, S.; Babu, N.; Santhosh, V. Effect of Post-Heat Treatment on Corrosion Resistance and Microstructural Characteristics of CMT-WAAM Inconel 718 in 3.5% NaCl Solution. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2025, 102, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Trodini, E.; Argumedo, J.L.G.; Richardson, I.M.; Hermans, M.J. Correlating geometry, microstructure and properties of high strength steel thin wall structures fabricated with WAAM. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2025, 11, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halisch, C.; Gaßmann, C.; Seefeld, T. Investigating the reproducibility of the wire arc additive manufacturing process. Adv. Mater. Res. 2021, 1161, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Kain, C.; Urbano, A.; Sarley, B. High throughput testing platform and application in wire arc additive manufactured superalloy: Anisotropy investigation and component qualification. Materialia 2021, 16, 101086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan Kumar, S.; Rajesh Kannan, A.; Pravin Kumar, N.; Pramod, R.; Siva Shanmugam, N.; Vishnu, A.S.; Channabasavanna, S.G. Microstructural features and mechanical integrity of wire arc additive manufactured SS321/Inconel 625 functionally gradient material. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 5692–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.T.; Zhang, T.; Gong, Z.; Zuo, W.; Wang, Z.; Zong, L.; Hu, L. Mechanical properties and microstructure characteristics of wire arc additively manufactured high-strength steels. Eng. Struct. 2024, 300, 117092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattera, G.; Polden, J.; Caggiano, A.; Nele, L.; Pan, Z.; Norrish, J. Semi-supervised learning for real-time anomaly detection in pulsed transfer wire arc additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 128, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, S.; Selin, R.; Voron, M. Welding materials for TIG welding, surfacing, and WAAM technology of titanium alloys. Weld. World 2023, 67, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Pan, Z.; Ding, D.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Norrish, J. A review of the wire arc additive manufacturing of metals: Properties, defects and quality improvement. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, F.; Roy, M.J.; Szost, B.A.; Terzi, S.; Colegrove, P.A.; Williams, S.W.; Hofmann, M. Residual stress of as-deposited and rolled wire+ arc additive manufacturing Ti–6Al–4V components. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.A.; Duarte, V.; Miranda, R.M.; Santos, T.G.; Oliveira, J.P. Current status and perspectives on wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Materials 2019, 12, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zheng, H.; Qi, B.; Yang, Z. Effect of arc behavior on Ti-6Al-4V welds during high frequency pulsed arc welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 243, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.; Thien, A.; Saleeby, D.K.; Saldana, D.C. A novel approach to path planning related to the intersections of aluminum WAAM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 137, 2579–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, R.F.; Silvello, A.; Albaladejo, V.; Sanchez, J.; Cano, I.G. Improving the wear and corrosion resistance of maraging part obtained by cold gas spray additive manufacturing. Metals 2021, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Hu, R.; Liu, C.; Chen, F. Microstructure and Properties of a 2.25 Cr1Mo0. 25V Heat-Resistant Steel Produced by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8470738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Pan, Z.; Polden, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. A review on wire arc additive manufacturing: Monitoring, control and a framework of automated system. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 57, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, G.; Murugana, N.; Arulmani, R. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel-625 slab component fabricated by wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.T.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zuo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, O.; Wang, Z. Mechanical behavior of austenitic stainless steels produced by wire arc additive manufacturing. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 196, 111455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, A.S.; Davut, K.; Koc, B.; Yilmaz, O. Wire arc additive manufacturing of high-strength low alloy steels: Study of process parameters and their influence on the bead geometry and mechanical characteristics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Han, Y.; Xu, T.; Fang, H. Fabricating pyramidal lattice structures of 304 L stainless steel by wire arc additive manufacturing. Materials 2020, 13, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, K. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of new Co-free maraging steel produced by wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 898, 146399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Quan, G.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ma, Y.Y.; Jiang, L.H.; Dai, W.W.; Jiang, Q. Influence of deposition path strategy on residual stress and deformation in weaving wire-arc additive manufacturing of disc parts. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 2242–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, S.; Zhao, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, E. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr Alloy Fabricated by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 928, 148060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Study on the role of chromium addition on sliding wear and corrosion resistance of high-manganese steel coating fabricated by wire arc additive manufacturing. Wear 2024, 540, 205242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Xue, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, X.; Ou, N. Effects of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMo0.2 high-entropy alloy prepared by wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Charact. 2024, 215, 114190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-J.; Feng, Y.; Peng, C.Q.; Cai, Z.Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.-M.; Kang, Z.-J.; Zhang, X.-D. Evolution of precipitates and mechanical properties of T6-treated and thermally exposed WAAM-ZL205A alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2025, 35, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Zabalza, A.; Veiga, F.; Suárez, A.; Uralde, V.; Sandua, X.; Alfaro, J.R. Application of Symmetric Neural Networks for Bead Geometry Determination in Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). Symmetry 2025, 17, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito Neto, F.M.; Ferreira, M.O.A.; dos Santos, S.A.C.; Pereira, J.N.; Meza, D.L.C.; Ahmed, W.; Arantes, V.L. Mechanical and corrosion behaviour of 316L stainless steel processed by wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.; Bidare, P.; Hassanin, H.; Tarlochan, F.; Dimov, S.; Essa, K. Powder-based laser hybrid additive manufacturing of metals: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 63–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, A.; Bras, G.; Bernard, H.; Michaud, P.; Balcaen, Y.; Alexis, J. Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V with wire laser metal deposition process. Mater. Sci. Forum 2021, 1016, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Hou, Z.; Chen, S. Wire and arc additive manufacturing of metal components: A review of recent research developments. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 111, 149–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W. Fabrication of corrosion-resistant ZL205A aluminum alloys thin-wall using WAAM: Exploring the synergistic effects of FSP and multidimensional nanomaterials. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1016, 178987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. Improved strength in nickel-aluminum bronze/steel bimetallic component fabricated using arcing-wire arc additive manufacturing with alternating deposition strategy. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 111, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Prajapati, A.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Upadhyay, C.; Satpathy, M.P. Adaptive control of filler wire speed in wire arc additive manufacturing: Impact of inter-layer dwell time on metallurgical and mechanical aspects of ER70S-6 deposits. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 136, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Schimmel, J.; Bosman, M.; Goulas, C.; Popovich, V.; Hermans, M.J. Fabrication of low thermal expansion Fe–Ni alloys by in-situ alloying using twin-wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2024, 240, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, R.F.; Arias, A.R.; Lima, E.J., II; Coelho, F.G.F. Pulsed GMAW-based WAAM–Influence of droplet detachment mode on the geometry and mechanical properties of 308 L stainless steel. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2025, 11, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, N.; Bermingham, M.J.; Colegrove, P.; Sales, A.; Soro, N.; Ng, C.H.; Dargusch, M.S. Effect of hot isostatic pressing and heat treatments on porosity of wire arc additive manufactured Al 2319. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 310, 117769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, K.; Oguzhan, Y. Radially graded porous structure design for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 296, 117186. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; He, B.; Lyu, T.; Zou, Y. A review on additive manufacturing of titanium alloys for aerospace applications: Directed energy deposition and beyond Ti-6Al-4V. JOM 2021, 73, 1804–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shen, J.; Hu, S.; Geng, H.; Wang, S. Numerical simulation of thermal and stress fields for multilayer and multi-pass weaving WAAM of magnesium alloy. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2025, 31, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanani, M.I.; Saputra, R.C.; Putra, A.K.; Triyono, T. Characterization Study of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Layer in Metal Inert Gas Welding Process. Eng. Innov. 2025, 12, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Dhiman, R.; Ambekar, A.; Thajudeen, T.; Kore, S.D. Investigating the effect of varying powder size range on particulate matter emission and mechanical properties of in situ micropowder alloyed WAAM depositions. Weld. World 2025, 69, 1171–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omiyale, B.O.; Ogedengbe, I.I.; Olugbade, T.O.; Rasheed, A.A.; Ogbeyemi, A.; Farayibi, P.K. Cold metal transfer WAAM of aluminum alloys: Influence of processing parameters. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 1967–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Balla, V.K.; Atre, S.V.; German, R.M.; Kate, K.H. Factors affecting properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy additive manufactured by metal fused filament fabrication. Powder Technol. 2021, 386, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattera, G.; Nele, L.; Paolella, D. Monitoring and control the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing process using artificial intelligence techniques: A review. J. Intell. Manuf. 2024, 35, 467–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.; Pardal, G.; Suder, W.; Ascari, A.; Fortunato, A.; Liverani, E.; Neto, L. Experimental investigations on solid and metal-cored creep-resistant wires deposited under GMA and PTA-based wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 1207–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albannai, A.I.; Ramirez, A.J. The effect of altering heat input & torch motion on the grain formation of SS316L material in WAAM. Discov. Mech. Eng. 2024, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Iturrioz, A.; Ukar, E.; Pereira, J.C. Influence of the manufacturing strategy on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Invar 36 alloy parts manufactured by CMT-WAAM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, Y. Fabrication and characterization of a new high-strength alloy via WAAM using GMAW+ cold wire feeding. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 328, 130038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanatha, H.M.; Rao, R.N.; Maiya, M.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, N.; Saxena, K.K.; Vijayan, V. Effects of arc current and travel speed on the processing of stainless steel via wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) process. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 2222–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Thirugnanasambandam, A.; Subramaniyan, M.K.; Elumalai, V. Fabrication of bimetallic structure (SS 316L/SS 308L) via wire+ arc additive manufacturing: A detailed characterization of interface. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, I.J.; Srinivas, J.; Leon, S.J.; Ramesh, A.; Rohith, I.J.; Senthil, T.S. Mechanical and microstructural investigation of multi-layered Inconel 825 wall fabricated using CMT-based WAAM. J. Alloys Metall. Syst. 2024, 8, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietala, M.; Keskitalo, M.; Jaskari, M.; Päkkilä, J.; Järvenpää, A. Assessment of the Influence of Surface Quality on the Bending Fatigue Strength of WAAM Ultra-High-Strength Steel. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 157, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Li, B.; Zhu, L.; Hou, X.; Li, Z.; Murr, L.E.; Pan, F. Optimizing microstructure and strength of CMT-wire arc additive manufactured WE43 Mg alloy through a novel active cooling technique. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 205, 112453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, T.S.; Babu, S.R.; Puviyarasan, M.; Balachandar, V.S. Experimental investigations on the multi-layered SS316L wall fabricated by CMT-based WAAM: Mechanical and microstructural studies. J. Alloys Metall. Syst. 2023, 2, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, J.; Parmar, H.; Chaudhari, R.; Khanna, S.; Doshi, M.; Patel, V. Experimental investigations on mechanical properties of multi-layered structure fabricated by GMAW-based WAAM of SS316L. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 20, 2748–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.P.; Tang, J.C.; Wang, D.W.; Wang, N.; He, Z.D.; Li, J.; Yan, M. Additive manufacturing of pure Ti with superior mechanical performance, low cost, and biocompatibility for potential replacement of Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pixner, F.; Warchomicka, F.; Peter, P.; Steuwer, A.; Colliander, M.H.; Pederson, R.; Enzinger, N. Wire-based additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V using electron beam technique. Materials 2020, 13, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, D.G. Influence of hot isostatic press on quasi-static and dynamic mechanical properties of SLM-printed Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. J. Korean Soc. Heat Treat. 2020, 33, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Leon, A.; Levy, G.K.; Ron, T.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. The effect of hot isostatic pressure on the corrosion performance of Ti-6Al-4 V produced by an electron-beam melting additive manufacturing process. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, W.; Dong, C.; Guo, C.; Deng, J.; Miao, S. Trailing rotating-extrusion-assisted wire arc additive manufacturing of duplex stainless steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2022, 27, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y.; Li, J. A real-time defect detection strategy for additive manufacturing processes based on deep learning and machine vision technologies. Micromachines 2024, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierth, M.; Henckell, P.; Ali, Y.; Scholl, J.; Bergmann, J.P. Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Aluminum Alloy AlMg5Mn with Energy-Reduced Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW). Materials 2020, 13, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wang, Z.; Chi, P.; Zhang, B.; Ding, T.; Zhang, Q. Evolutions of microstructure and mechanical property of 308L stainless steel repaired by the local dry underwater wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 898, 146365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Liu, F.; Xia, Y.; Dong, B.; Cai, X.; Lin, S. Wire arc additive manufacturing of the Al-5.55 Cu alloy: Insight the effect of intrinsic heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Charact. 2024, 211, 113859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana, M.; Ukar, E.; Rodriguez, I.; Aguilar, D.; Alvarez, P. Influence of deposition strategy and heat treatment on mechanical properties and microstructure of 2319 aluminium WAAM components. Mater. Des. 2022, 221, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, Y.F.; Gromov, V.E.; Konovalov, S.V.; Shliarova, Y.A.; Osintsev, K.A.; Panchenko, I.A. Study of the structure and properties of a high-entropy AlCoCrFeNi alloy after electron-beam processing. Phys. Solid State 2022, 64, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, F.; Gao, X.; Cao, S.; Liu, Z.; Han, Y. Enhancing the geometry accuracy and mechanical properties of wire arc additive manufacturing of an Al-5% Mg alloy through longitudinal magnetic field influence. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 118, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakeem, M.M.; Mollamahmutoglu, M.; Yilmaz, O.; Bol, N.; Kara, O.E. A deposition strategy for Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing based on temperature variance analysis to minimize overflow and distortion. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 85, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankong, B.D.; Abioye, T.E.; Olugbade, T.O.; Zuhailawati, H.; Gbadeyan, O.O.; Ogedengbe, T.I. Review of post-processing methods for high-quality wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
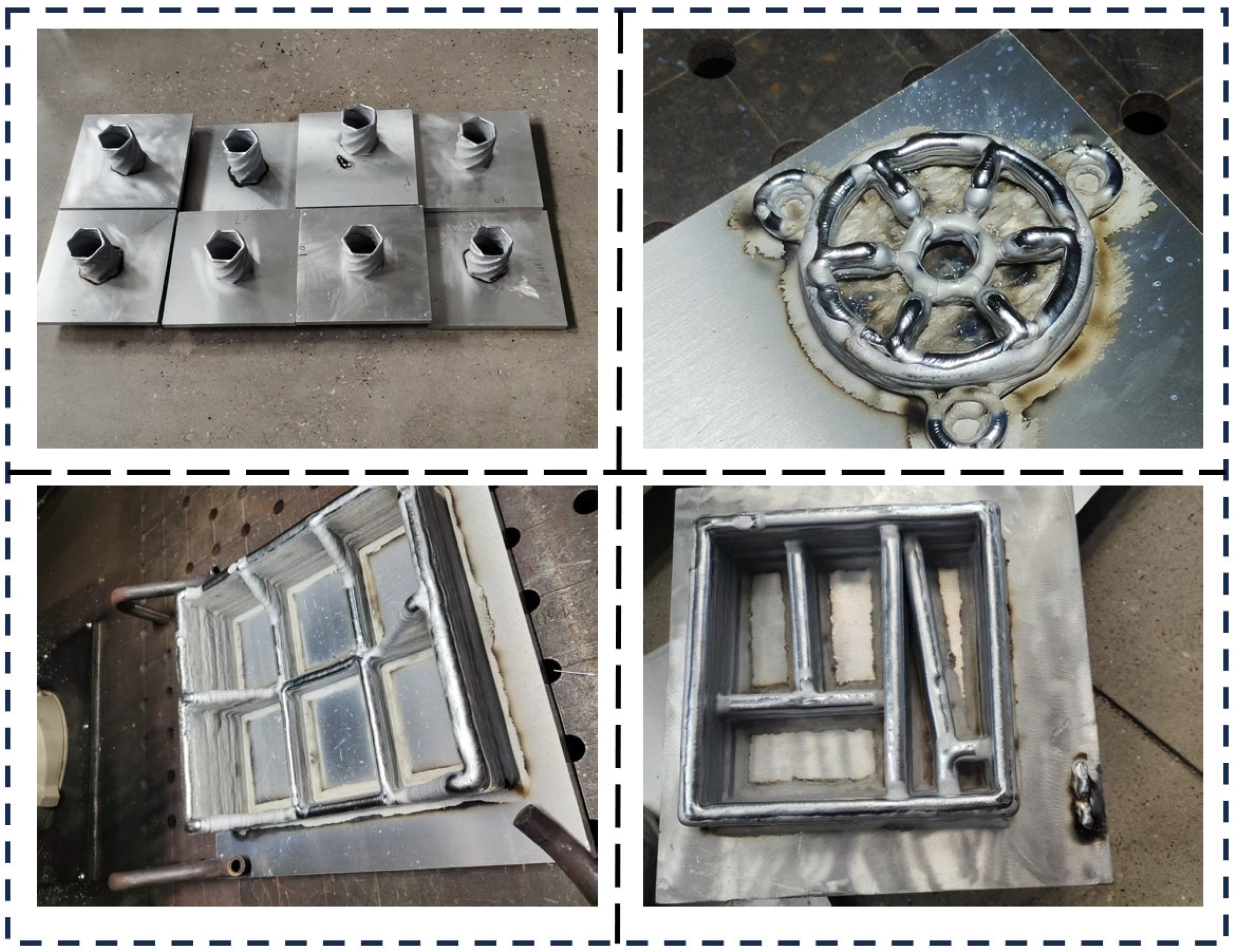





| WAAM | Energy Source | Features |
|---|---|---|
| GTAW-based | Gas Tungsten Arc Welding |
|
| GMAW-based | Gas Metal Arc Welding |
|
| CMT-based | Cold Metal Transfer |
|
| PAW-based | Plasma Arc Welding |
|
| Microhardness (HV) | Impact Test (J) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top | Middle | Bottom | Top | Middle | Bottom | |
| CMT | 217.98 | 222.03 | 226.18 | 96 | 108 | 112 |
| GMAW | 177.45 | 180.82 | 184.25 | 25.8 | 27.8 | 26.2 |
| Tensile Property | UTS (MPa) | YS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Top | Middle | Bottom | Top | Middle | Bottom | Top | Middle | Bottom | |
| CMT | Observed Value | 504 | 507 | 512 | 197 | 201 | 205 | 49.5 | 52.1 | 56.5 |
| Mean Value | 507.66 | 201 | 52.7 | |||||||
| GMAW | Observed Value | 520.6 | 512.7 | 504.29 | 268.6 | 249.26 | 251.85 | 48.98 | 49.72 | 49.36 |
| Mean Value | 512.53 | 256.57 | 49.35 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.; Lin, Q.; Hu, R.; Wu, S. Research Progress and Application Scenarios of Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing: From Process Control to Performance Evaluation. Micromachines 2025, 16, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070749
Guo C, Lin Q, Hu R, Wu S. Research Progress and Application Scenarios of Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing: From Process Control to Performance Evaluation. Micromachines. 2025; 16(7):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070749
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chun, Qingcheng Lin, Ruizhang Hu, and Suisong Wu. 2025. "Research Progress and Application Scenarios of Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing: From Process Control to Performance Evaluation" Micromachines 16, no. 7: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070749
APA StyleGuo, C., Lin, Q., Hu, R., & Wu, S. (2025). Research Progress and Application Scenarios of Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing: From Process Control to Performance Evaluation. Micromachines, 16(7), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070749







