Multi-Layer Workpieces and Multiple-Wire Electrochemical Micromachining with Horizontal Electrolyte Flushing
Abstract
1. Introduction
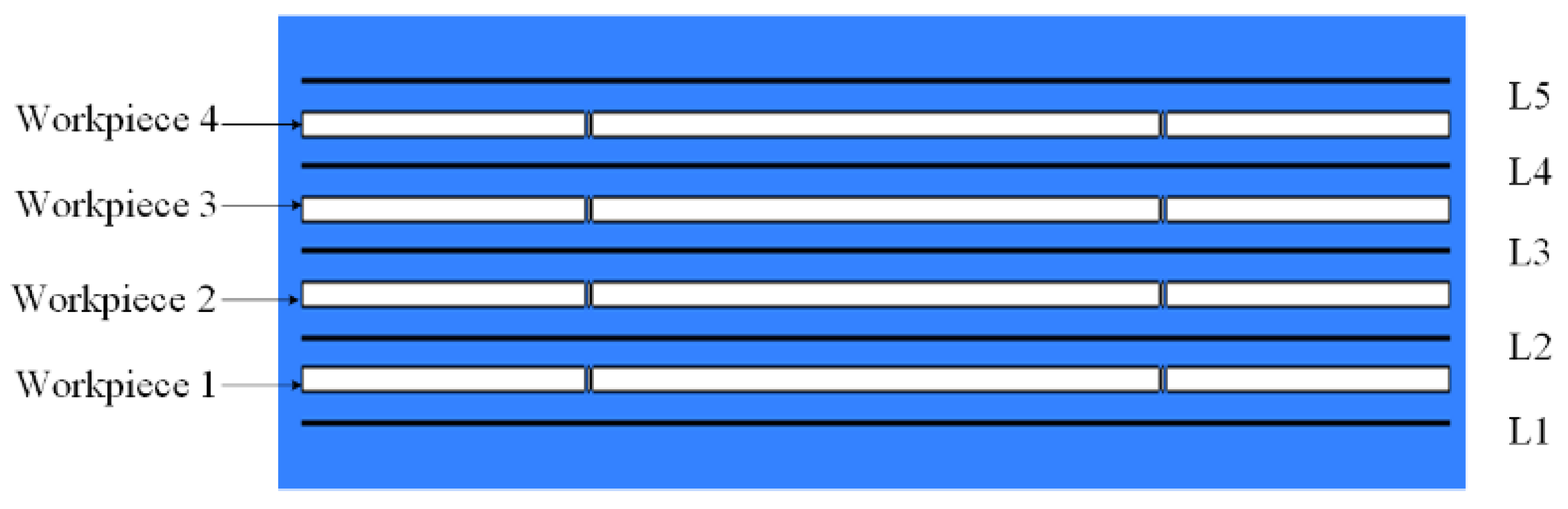
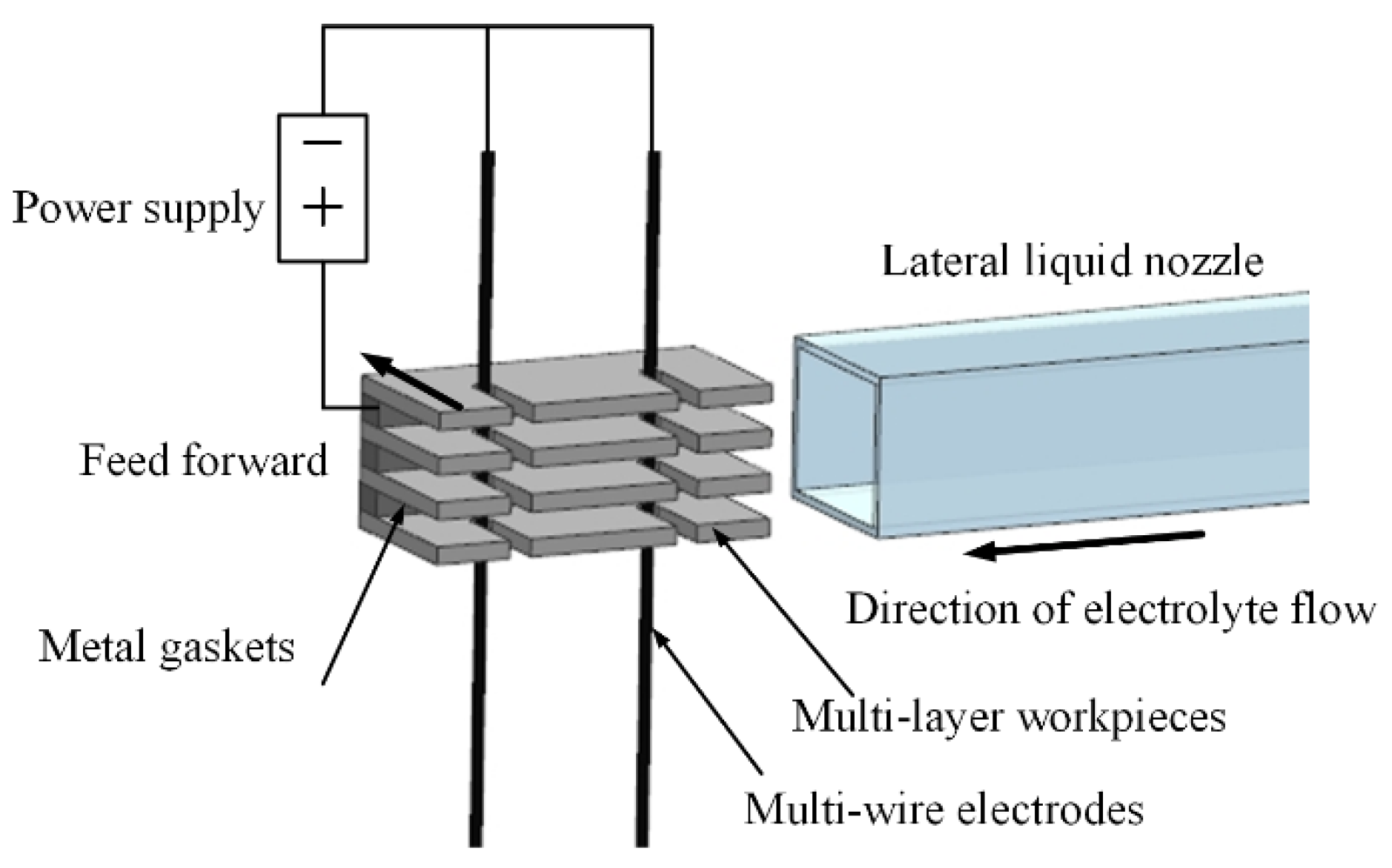
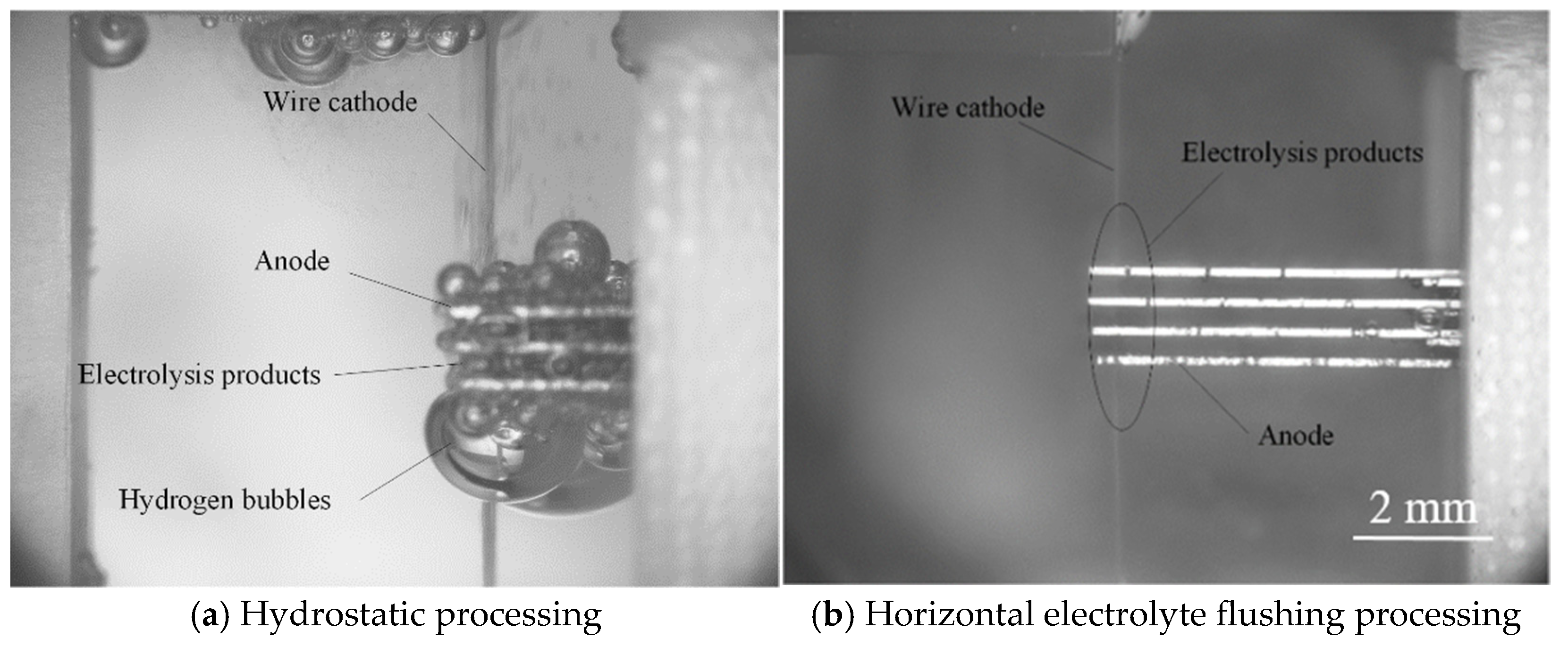
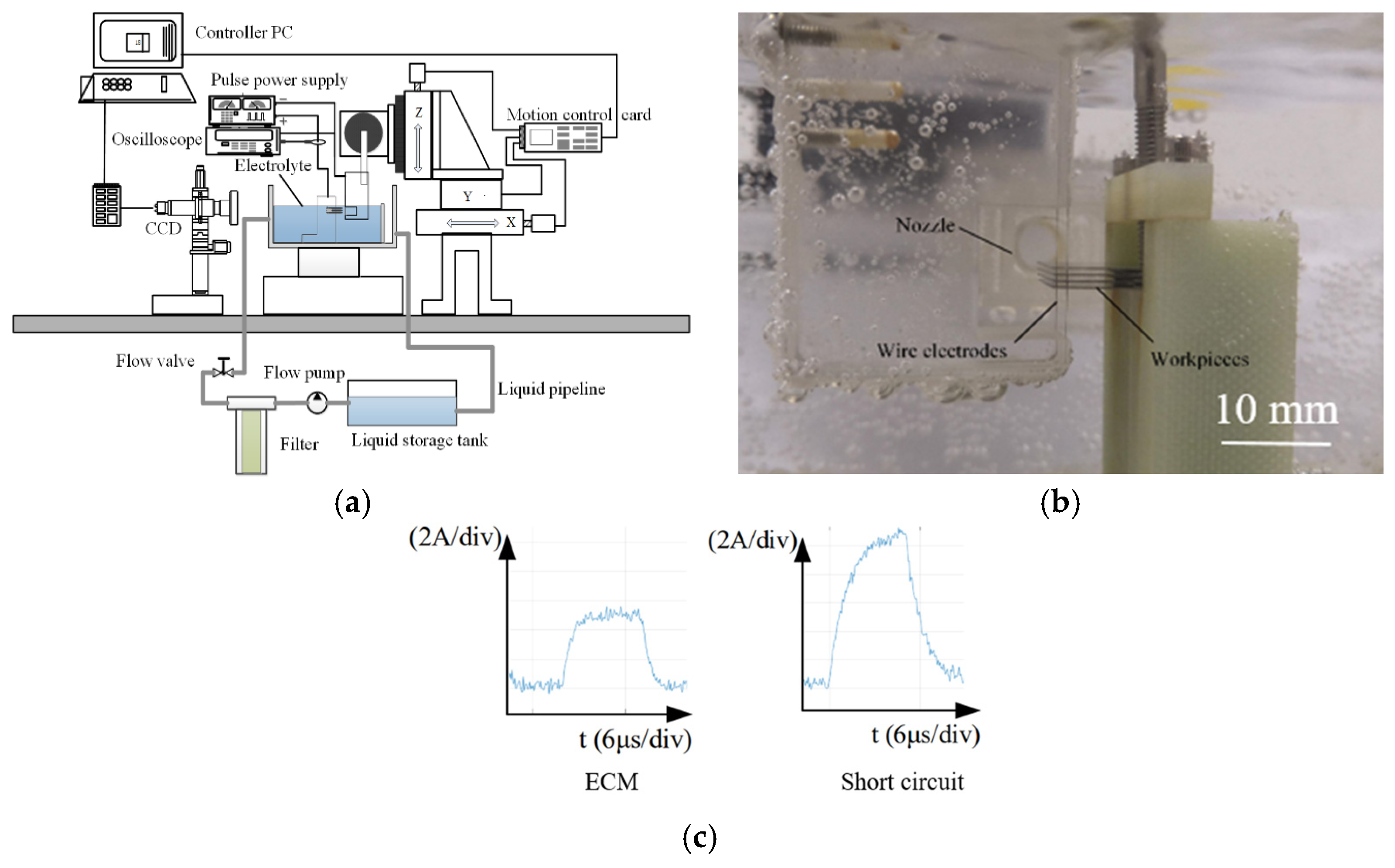
2. Principle of MWECMF and Experimental System
3. Results
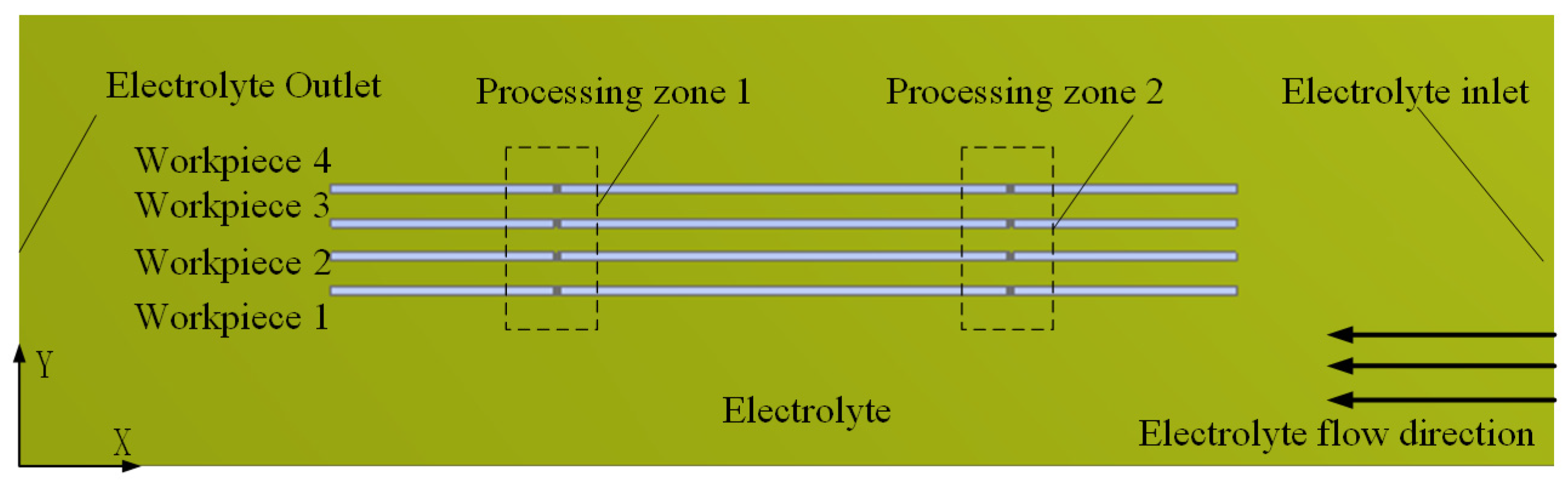
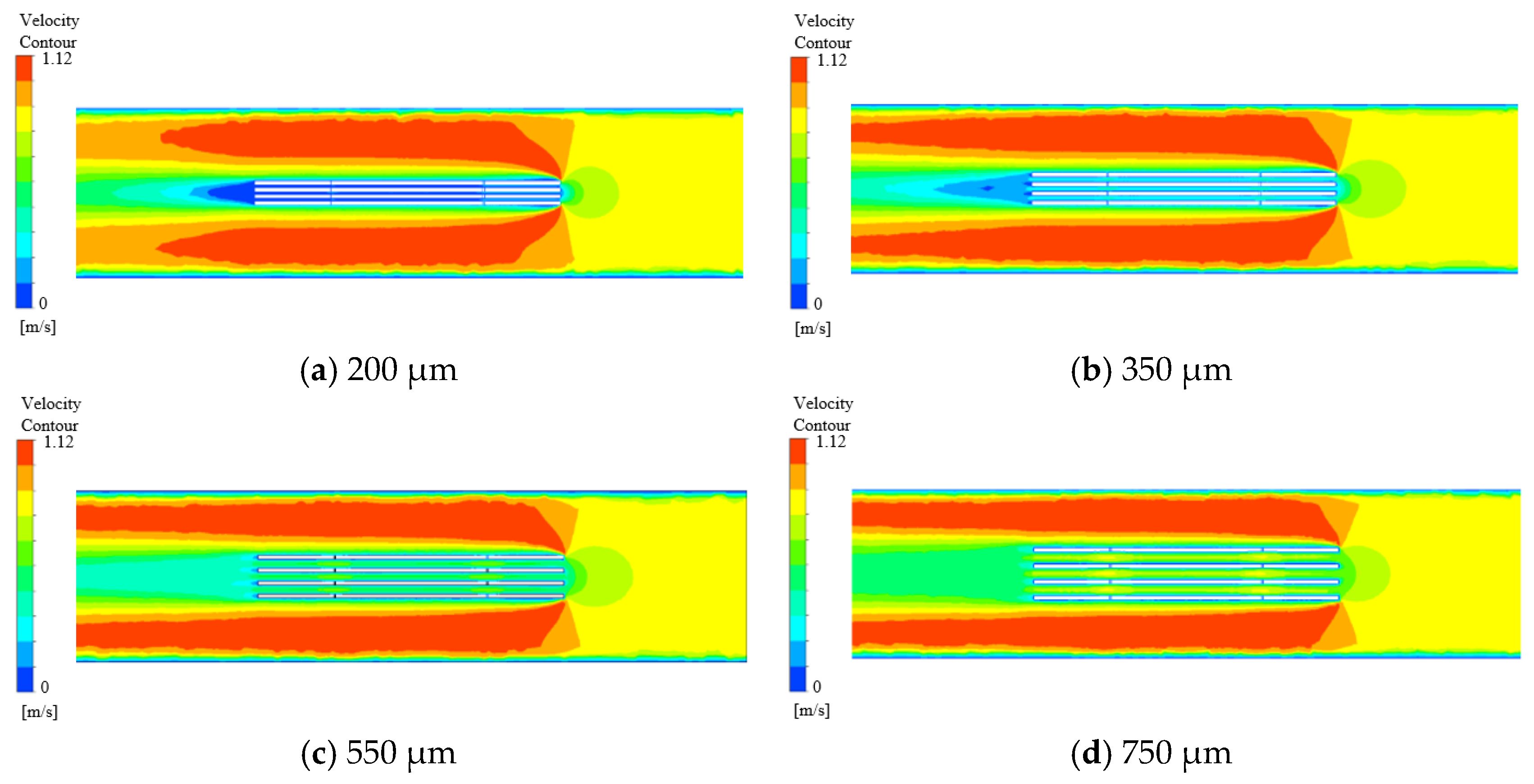
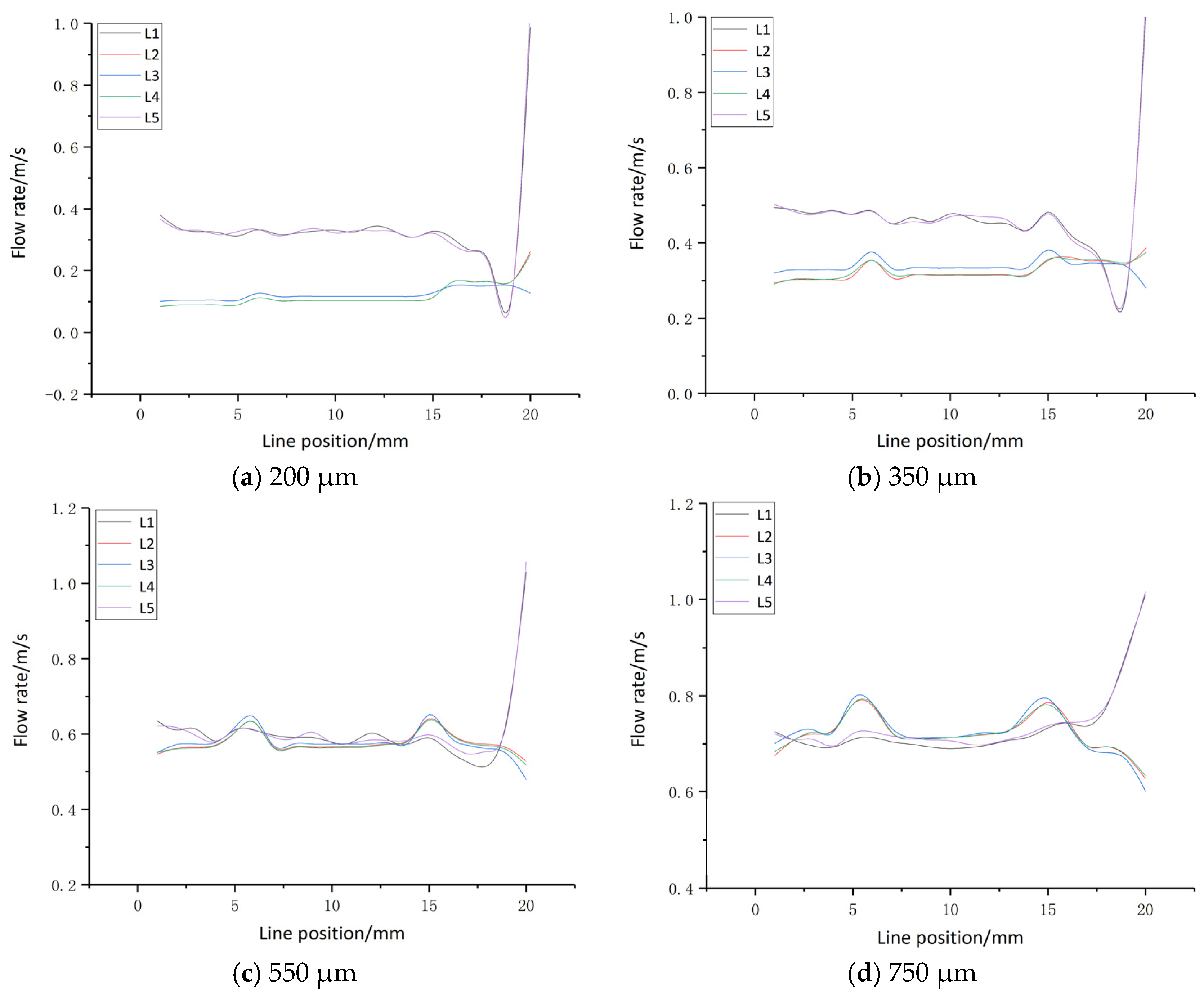
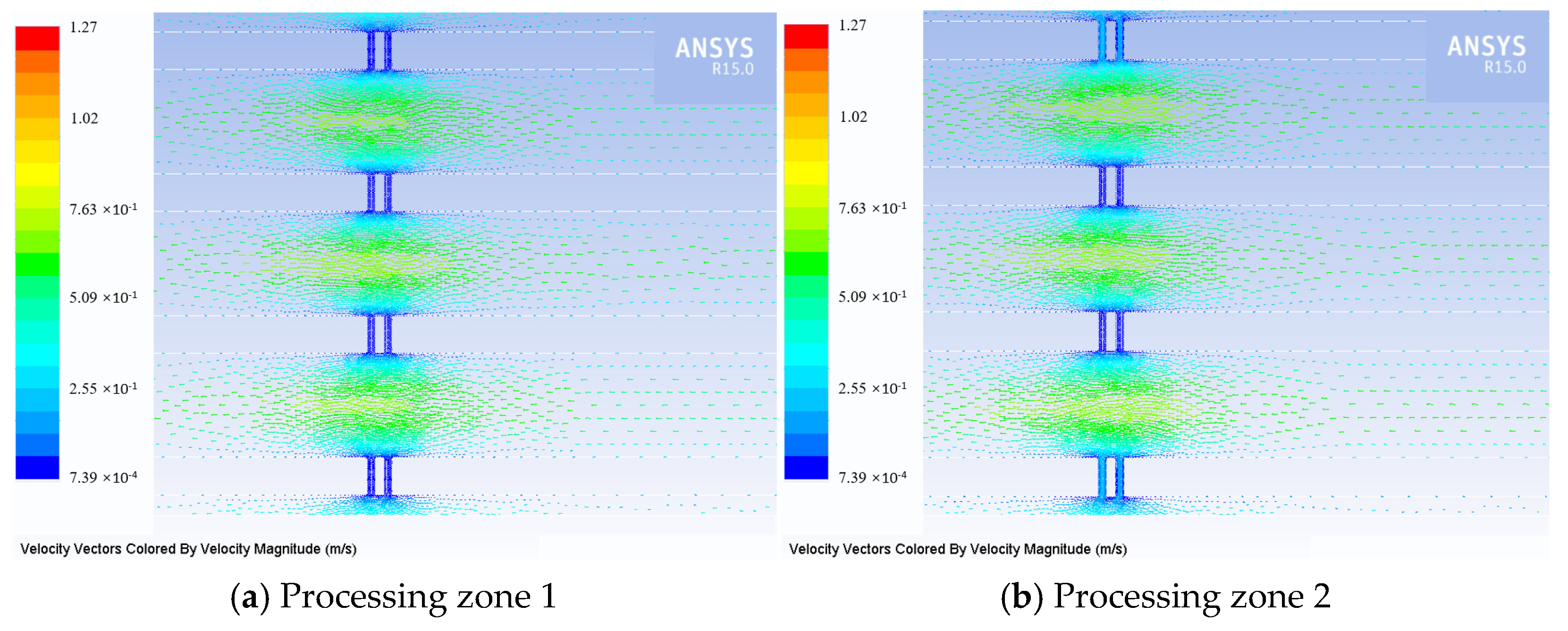
3.1. Flow Field Simulation Research
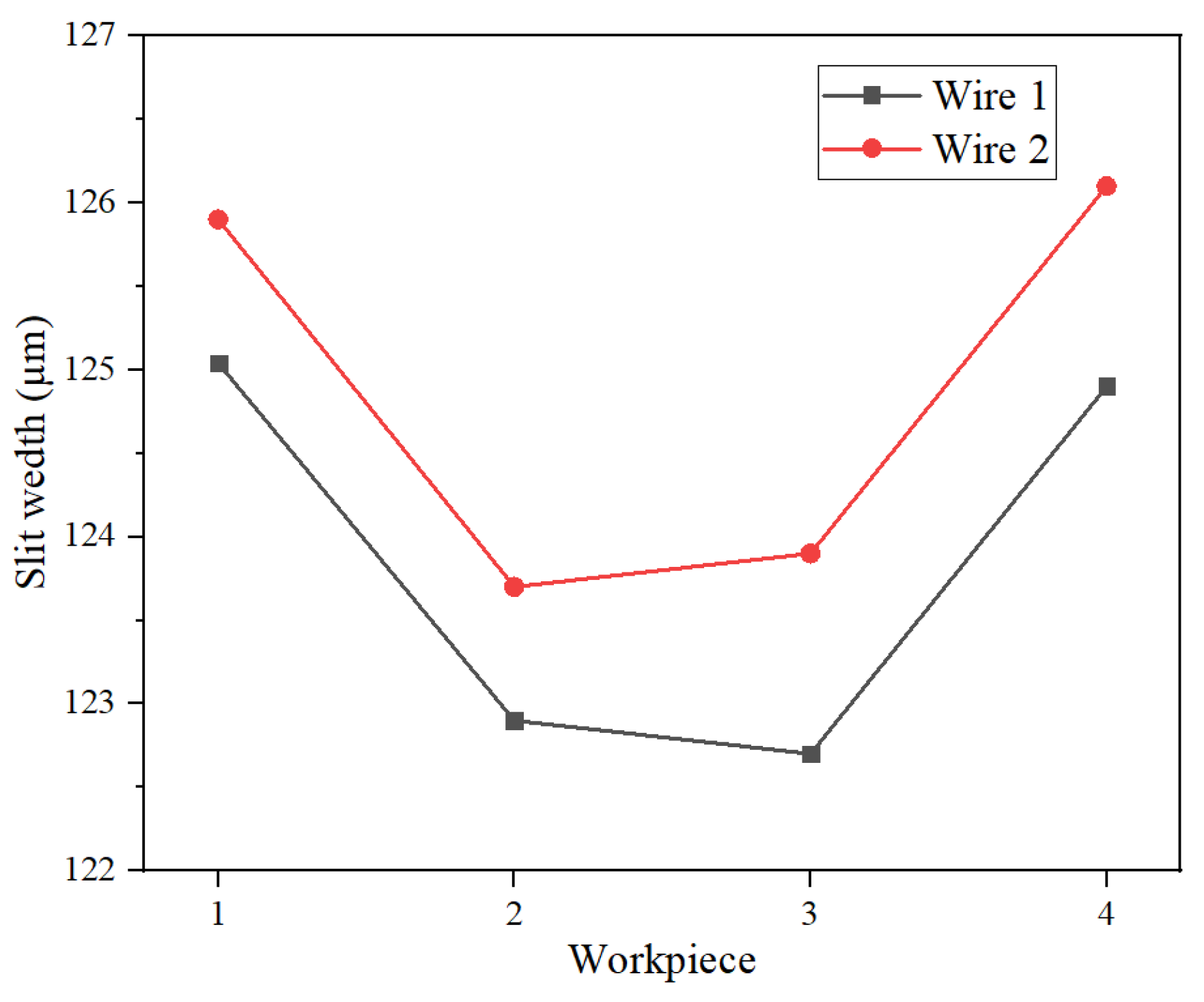
3.2. Micro Slit Processing Experiment
4. Discussion
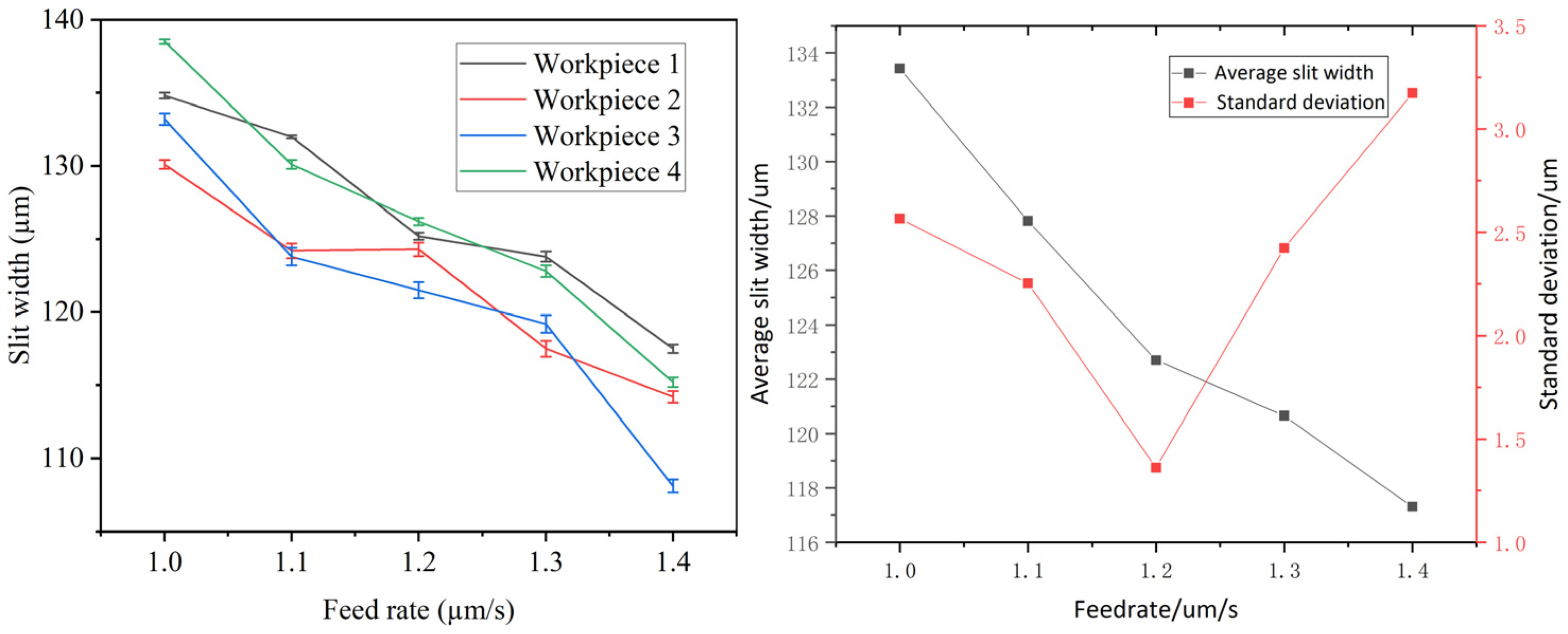
4.1. Effects of Feed Rate
4.2. Effects of Applied Voltage
4.3. Effects of Pulse Frequency
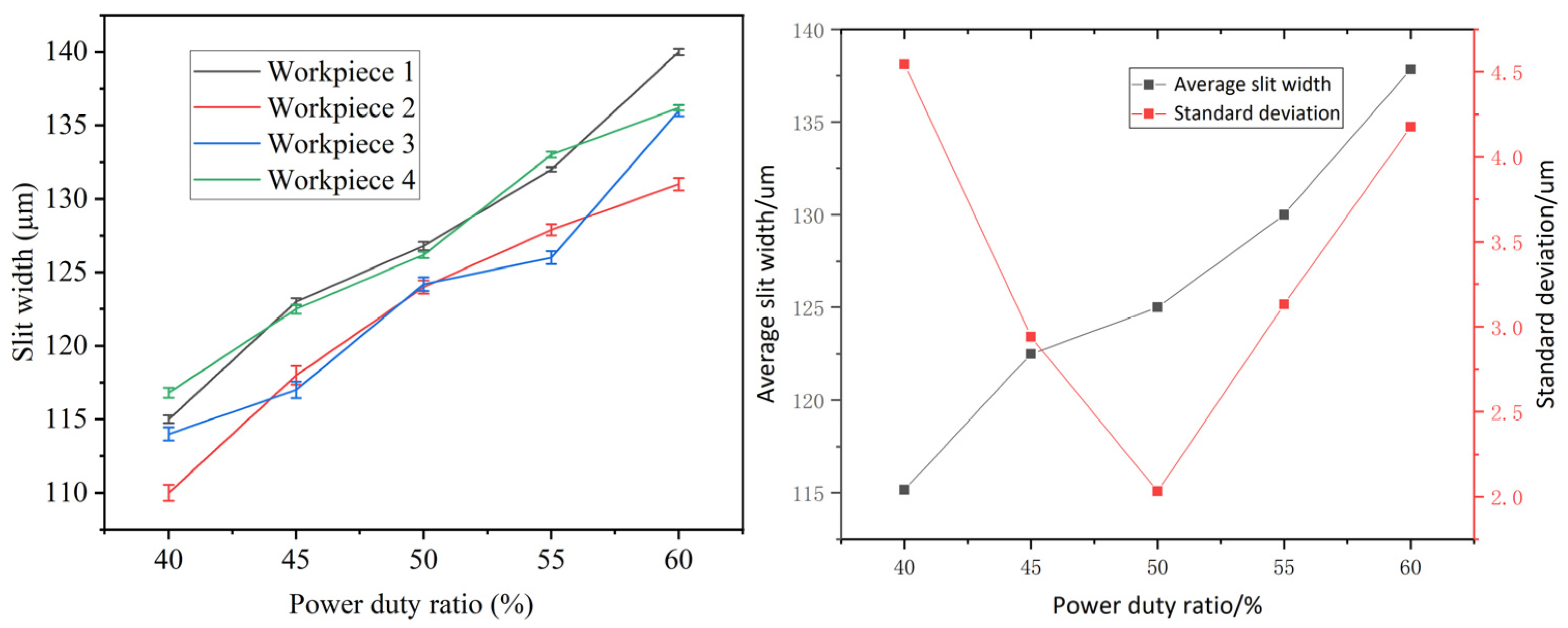
4.4. Effects of Duty Cycle
4.5. Effects of Electrolyte Concentration
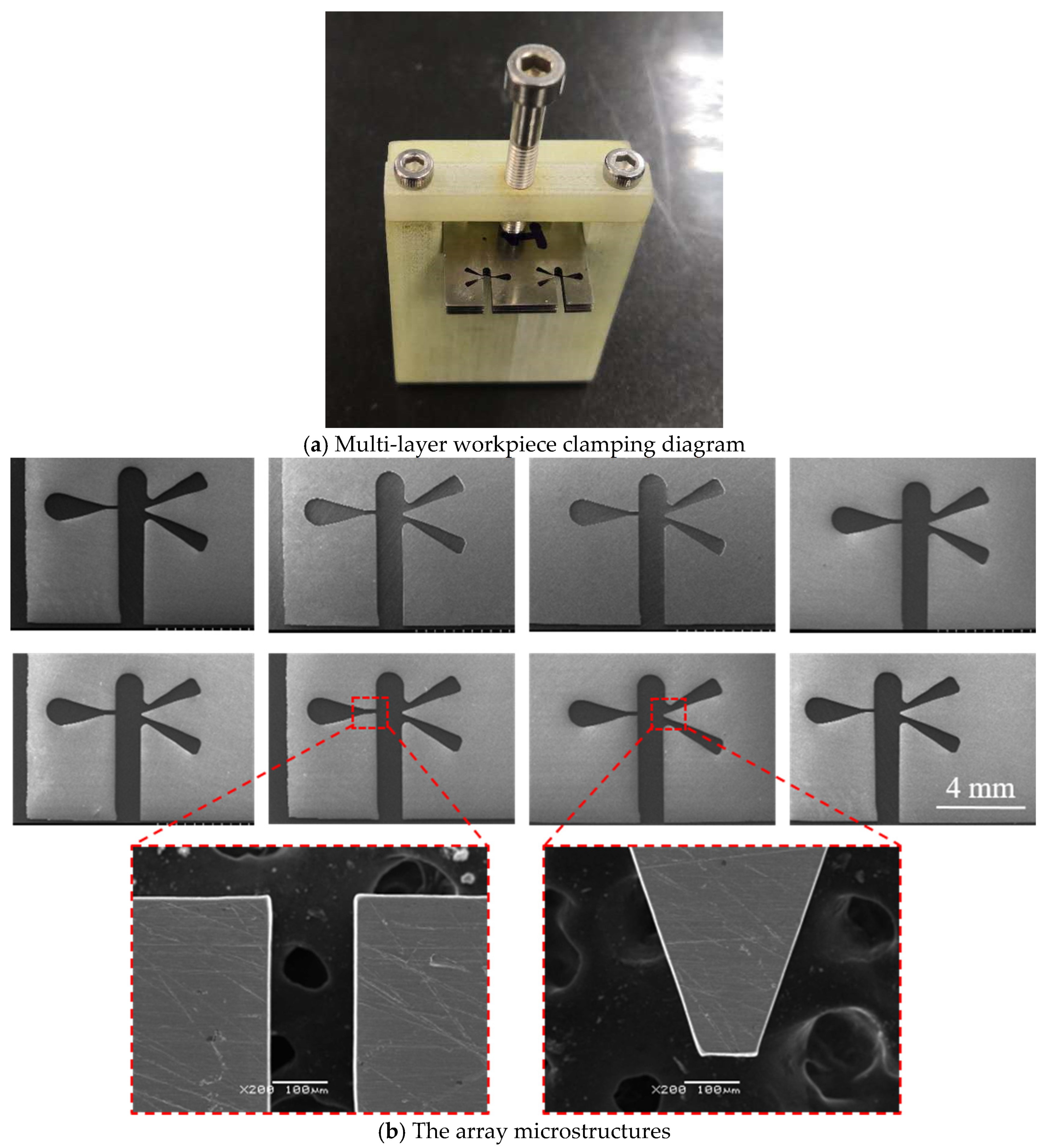
4.6. Microstructure Fabrication
5. Conclusions
- A multi-wire electrochemical microfabrication method under horizontal electrolytic flushing was proposed. The spacing between workpieces was optimized through fluid simulation based on ANSYS, and the optimal value was determined to be 550 µm.
- Using the lateral flushing method, the influence of main process parameters on the consistency of slit width was studied. The variables tested include feed rate, voltage, frequency, duty cycle, and electrolyte concentration. Finally, the optimal processing parameters were determined.
- Utilizing the optimized parameters, specifically a feed rate of 1.2 µm/s, arrayed microstructures were successfully fabricated, achieving an overall processing rate of 9.6 µm/s. The results demonstrate that MWECM significantly enhances machining efficiency compared to conventional wire electrochemical micromachining (WECM).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MWECM | Multi-layer workpieces and multiple wires electrochemical micromachining |
| MWECMF | Multi-layer workpieces and multiple wires electrochemical micromachining with horizontal electrolyte flushing |
| WECM | Wire electrochemical micromachining |
References
- El-Taweel, T.A.; Gouda, S.A. Study on the wire electrochemical groove turning process. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajurkar, K.P.; Levy, G.; Malshe, A.; Sundaram, M.M.; McGeough, J.; Hu, X.; Resnick, R.; DeSilva, A. Micro and Nano machining by electro-physical and chemical processes. CIRP Ann. 2006, 55, 643–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, B.; Mitra, S.; Boro, A.K. Electrochemical machining: New possibilities for micromachining. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2002, 18, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethapriyan, T.K.; Kalaichelvan, T. Muthuramalingam, Influence of coated tool electrode on drilling inconel alloy 718 in electrochemical micro machining. Procedia CIRP 2016, 46, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Kim, B.H.; Chu, C.N. Analysis of the side gap resulting from micro electrochemical machining with a tungsten wire and ultrashort voltage pulses. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 075009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, H. Microwave plasma-assisted polishing of polycrystalline diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 152, 111907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, K.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; An, P.; Ma, Y.; Hei, H.; Qu, S.; Yu, S. Synergistic Multi-Mechanism Enhancement in Chemomechanical Abrasive Polishing of Polycrystalline Diamond via a New SiO2–Diamond Slurry in High-Concentration H2O2 Solution. Materials 2025, 18, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Cheung, C.F.; Shokrani, A.; Zhan, Z.J.; Wang, C.J. Atomic-level flat polishing of polycrystalline diamond by combining plasma modification and chemical mechanical polishing. CIRP Ann. 2025, 74, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.H. Eco-friendly ECM in citric acid electrolyte with microwire and microfoil electrodes. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Wu, X.; Lei, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, W.; Diao, D. Vibration-assisted wire electro-chemical micromachining with a suspension of B4C particles in the electrolyte. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 3565–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, B.; Bhattacharyya, B. Vibration assisted electrochemical micromachining of high aspect ratio micro features. Precis. Eng. 2015, 42, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Patel, D.S.; Jain, V.K.; Ramkumar, J. Wire electrochemical micromachining: An overview. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 2020, 155, 103579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Patel, D.S.; Agrawal, V.; Jain, V.K.; Ramkumar, J. Investigations into machining accuracy and quality in wire electrochemical micromachining under sinusoidal and triangular voltage pulse condition. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 62, 348–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taweel, T.A.; Gouda, S.A. Performance analysis of wire electrochemical turning process-RSM approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 53, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.S.; Fang, X.L.; Li, W.; Zeng, Y.B.; Zhu, D. Wire electrochemical machining with axial electrolyte flushing for titanium alloy. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Sharma, V.; Jain, V.K.; Ramkumar, J. Investigations into side gap in wire electrochemical micromachining (wire-ECMM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 4469–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Lal, G.; Kanetkar, Y. Stray current attack stagnation zones in electrochemical drilling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2005, 26, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Masanta, M.; Bhattacharyya, B. Wire Electrochemical Machining employing newly developed tungsten micro wire with repeatedly similar cross sectional variations. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 74, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.C.; Zeng, Y.B.; Fang, X.L.; Zhu, D. Micro-shaping of metallic glass by wire electrochemical micro-machining with a reciprocating traveling workpiece. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 739, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.D.; Ge, S.H.; Zeng, Y.B. Control of corner arc radius in wire electrochemical micromachining. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 106, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.S.; Gao, C.P. Improving surface processing quality in wire electrochemical micromachining by gas bubble chain. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 294, 117136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Thickness of the gasket (µm) | 200, 350, 550, 750 |
| Thickness of the workpiece (µm) | 200 |
| Length of the workpiece (mm) | 20 |
| Wire electrode diameter (µm) | 50 |
| Slit width (µm) | 130 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Inlet velocity (m/s) | 0.8 |
| Electrolyte density (Kg/m3) | 1000 |
| Electrolyte viscosity (Pa×s) | 10−3 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Workpiece spacing | 550 µm |
| Workpiece | 200 µm thickness, 3J53 constant elastic alloy |
| Electrolyte | 12 g/L, NaNO3 aqueous solution |
| Wire electrode diameter | 50 µm |
| The inlet velocity of electrolyte nozzle | 0.8 m/s |
| Amplitude | 0.6 mm |
| Vibration frequency | 2 Hz |
| Voltage amplitude | 10 V |
| Duty cycle | 50% |
| Pulse frequency | 50 KHz |
| Feed rate | 1.2 µm/s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Zeng, Y. Multi-Layer Workpieces and Multiple-Wire Electrochemical Micromachining with Horizontal Electrolyte Flushing. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111236
Tang X, Zeng Y. Multi-Layer Workpieces and Multiple-Wire Electrochemical Micromachining with Horizontal Electrolyte Flushing. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111236
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xiaocong, and Yongbin Zeng. 2025. "Multi-Layer Workpieces and Multiple-Wire Electrochemical Micromachining with Horizontal Electrolyte Flushing" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111236
APA StyleTang, X., & Zeng, Y. (2025). Multi-Layer Workpieces and Multiple-Wire Electrochemical Micromachining with Horizontal Electrolyte Flushing. Micromachines, 16(11), 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111236






