Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study on Picosecond Laser Polishing of 4H-SiC Wafer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Model
2.1. Two-Temperature Model
2.2. Material Removal Simulation
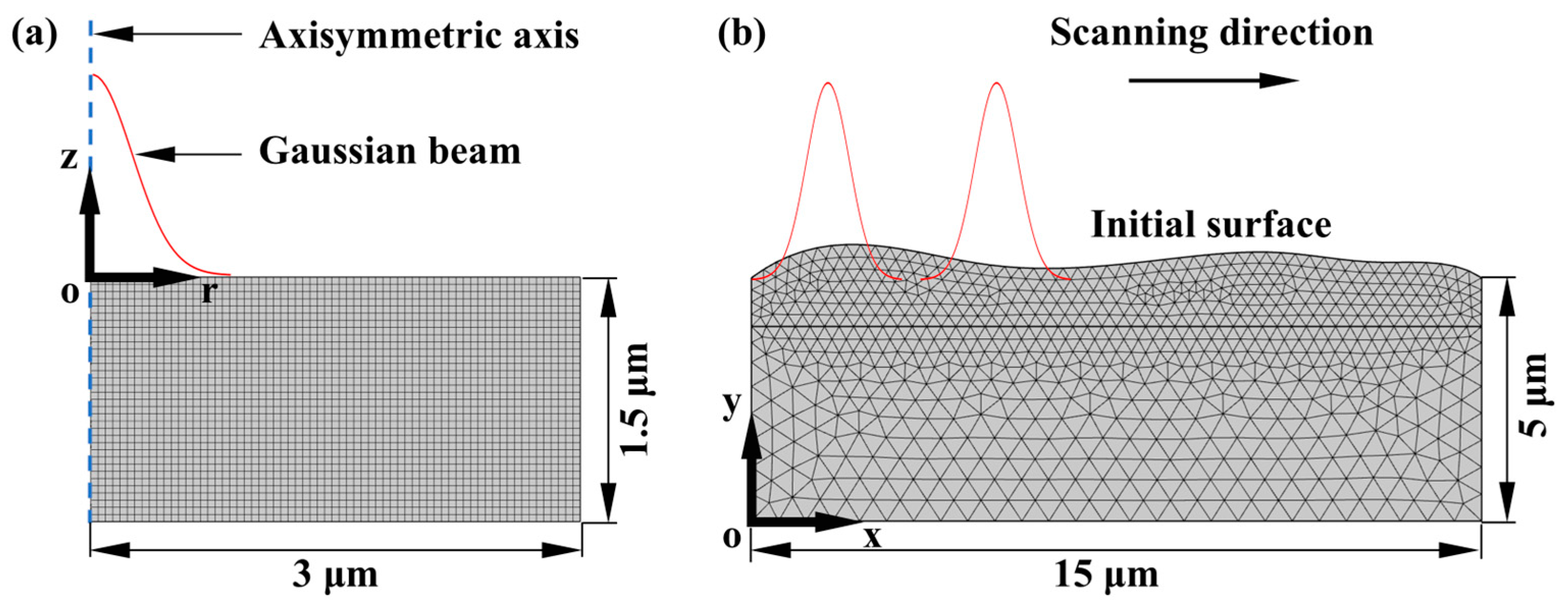
2.3. Axisymmetric Model of Laser Ablation
2.4. Two-Dimensional Model of Laser Polishing
2.5. Properties and Parameters
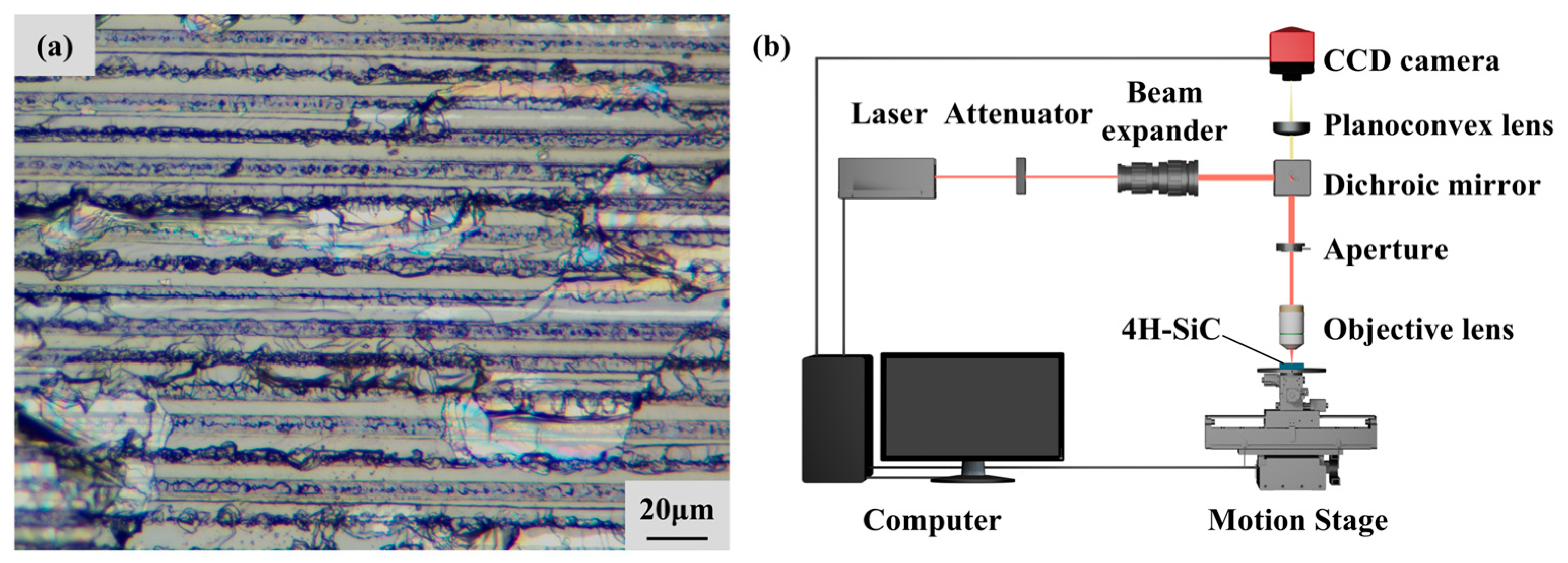
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussion
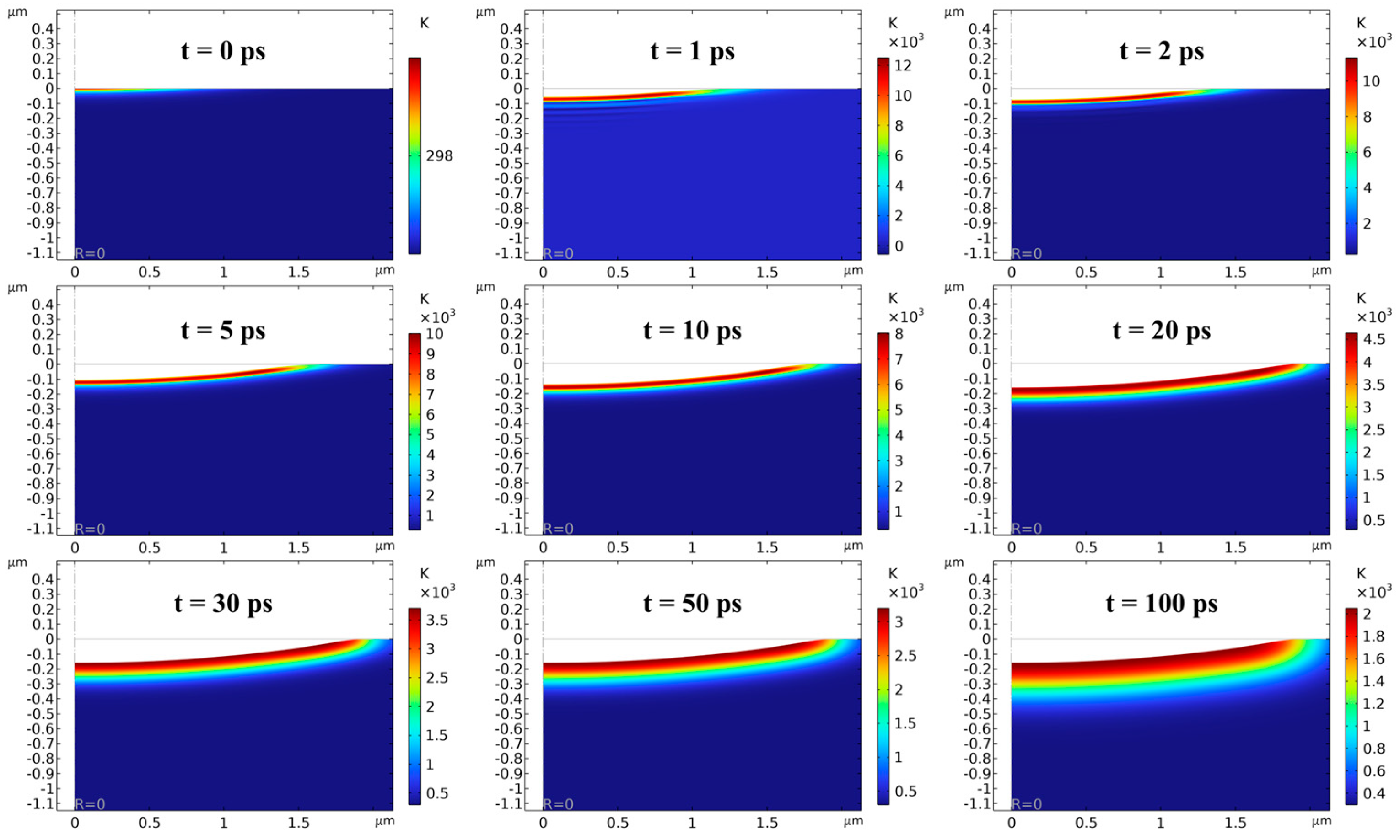
4.1. Simulation Results
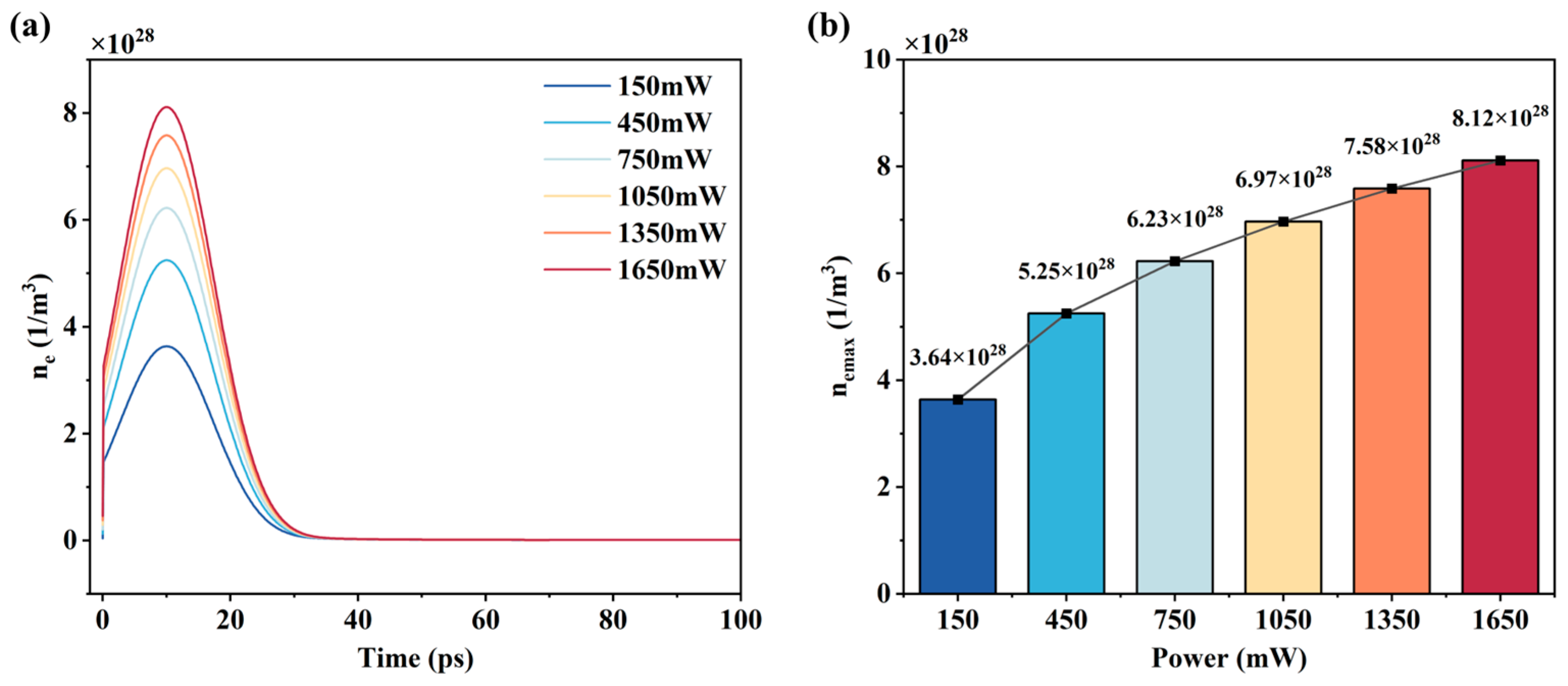
4.1.1. Free Electron Density Evolution
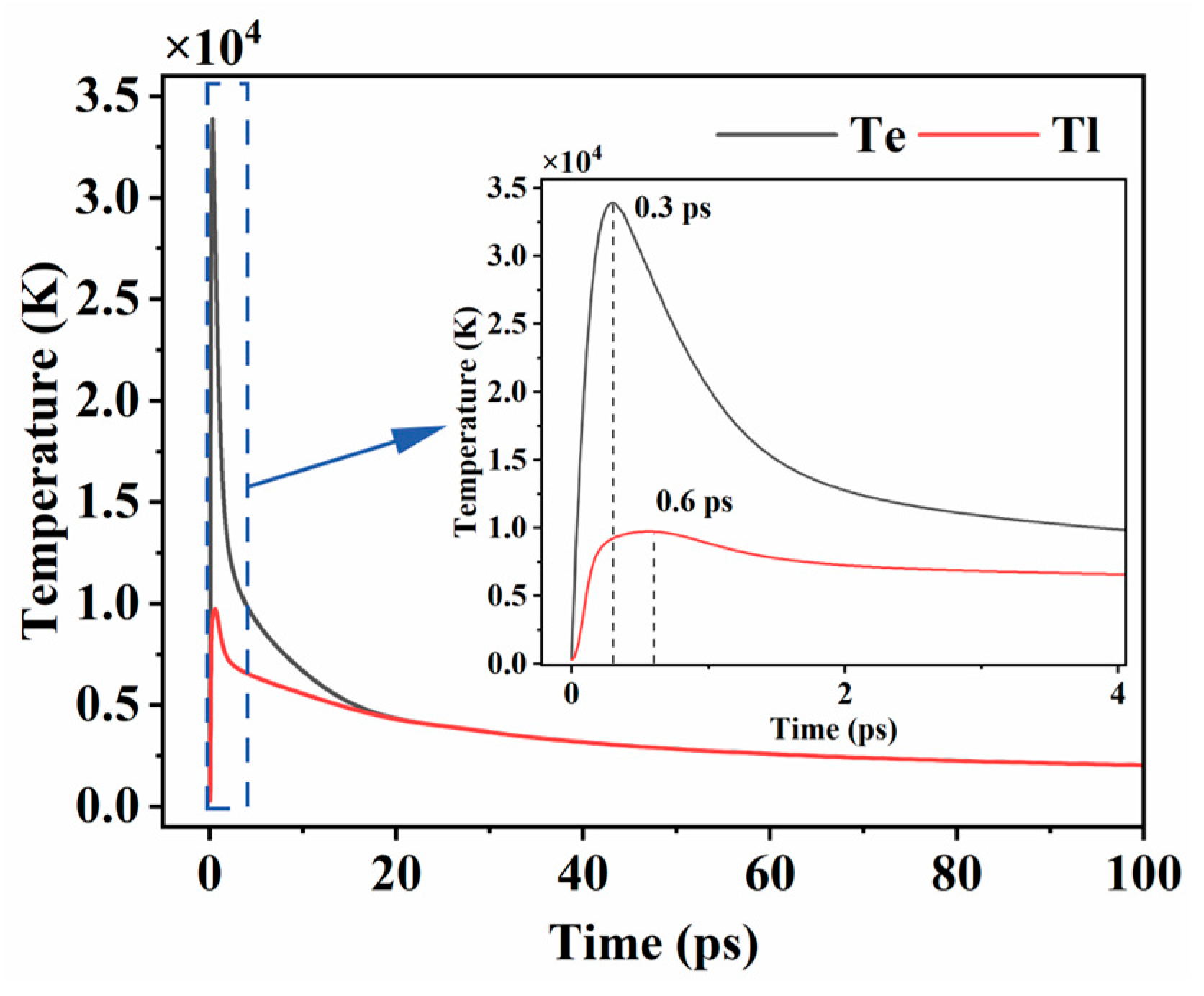
4.1.2. Electron and Lattice Temperature Evolutions
4.1.3. Single-Pulse Ablation
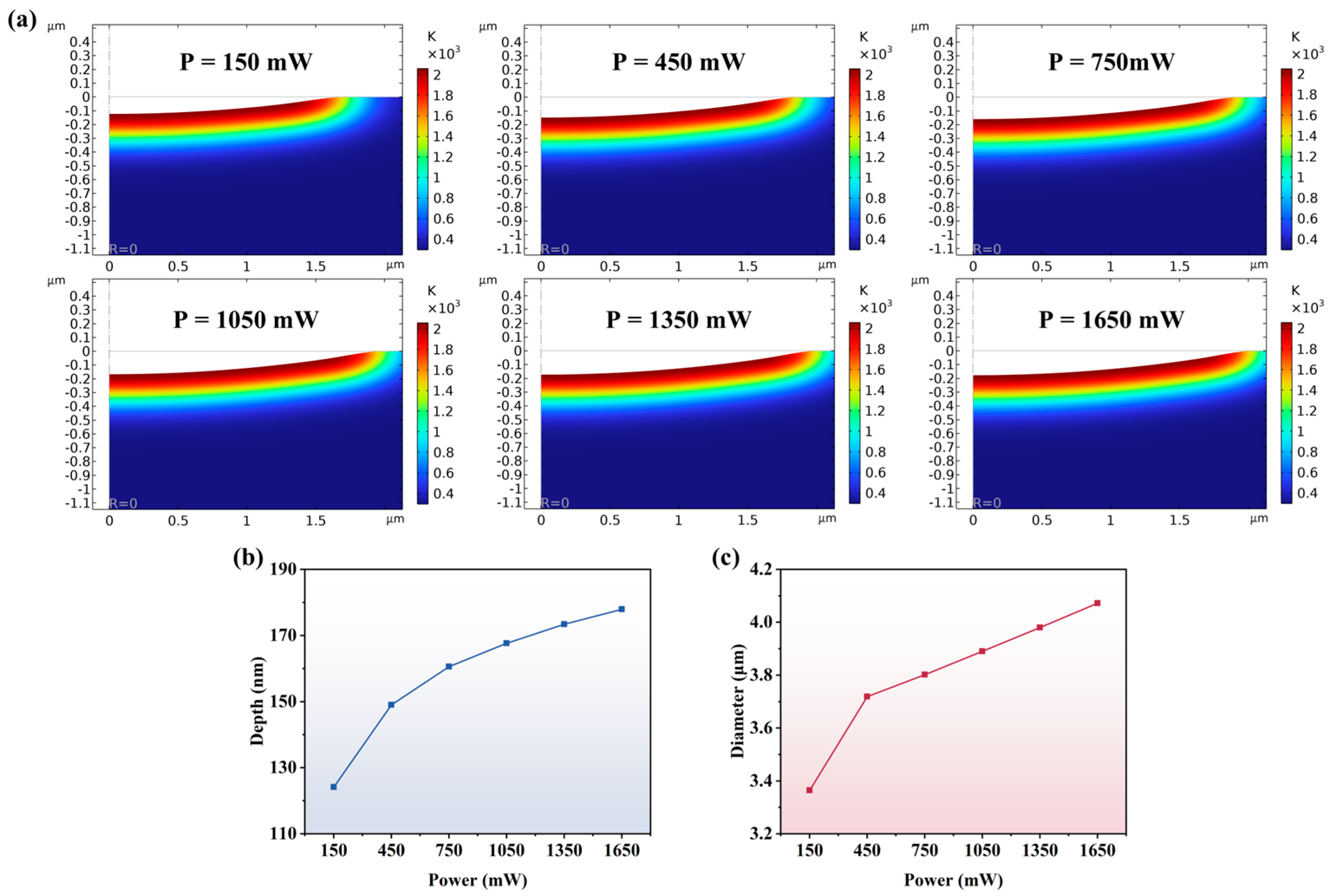
4.1.4. Multi-Pulse Polishing
4.2. Experimental Results
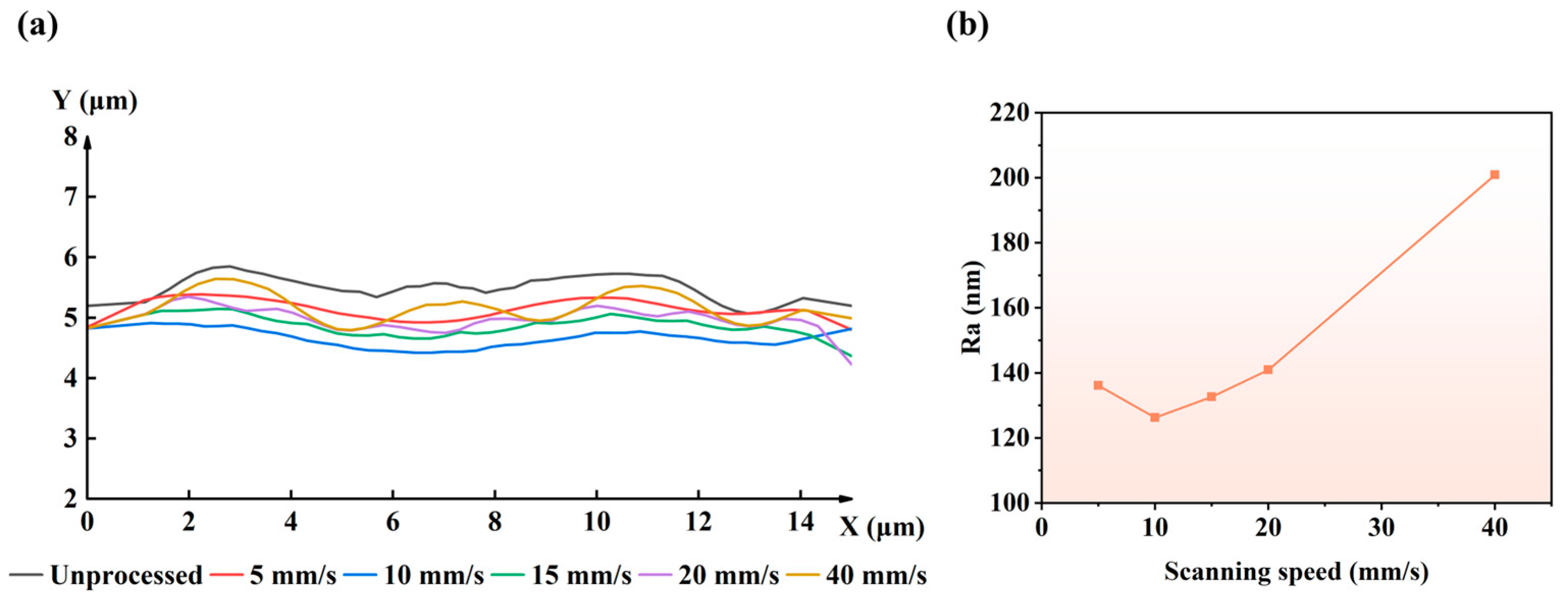
4.2.1. Influence of Laser Power on Surface Roughness
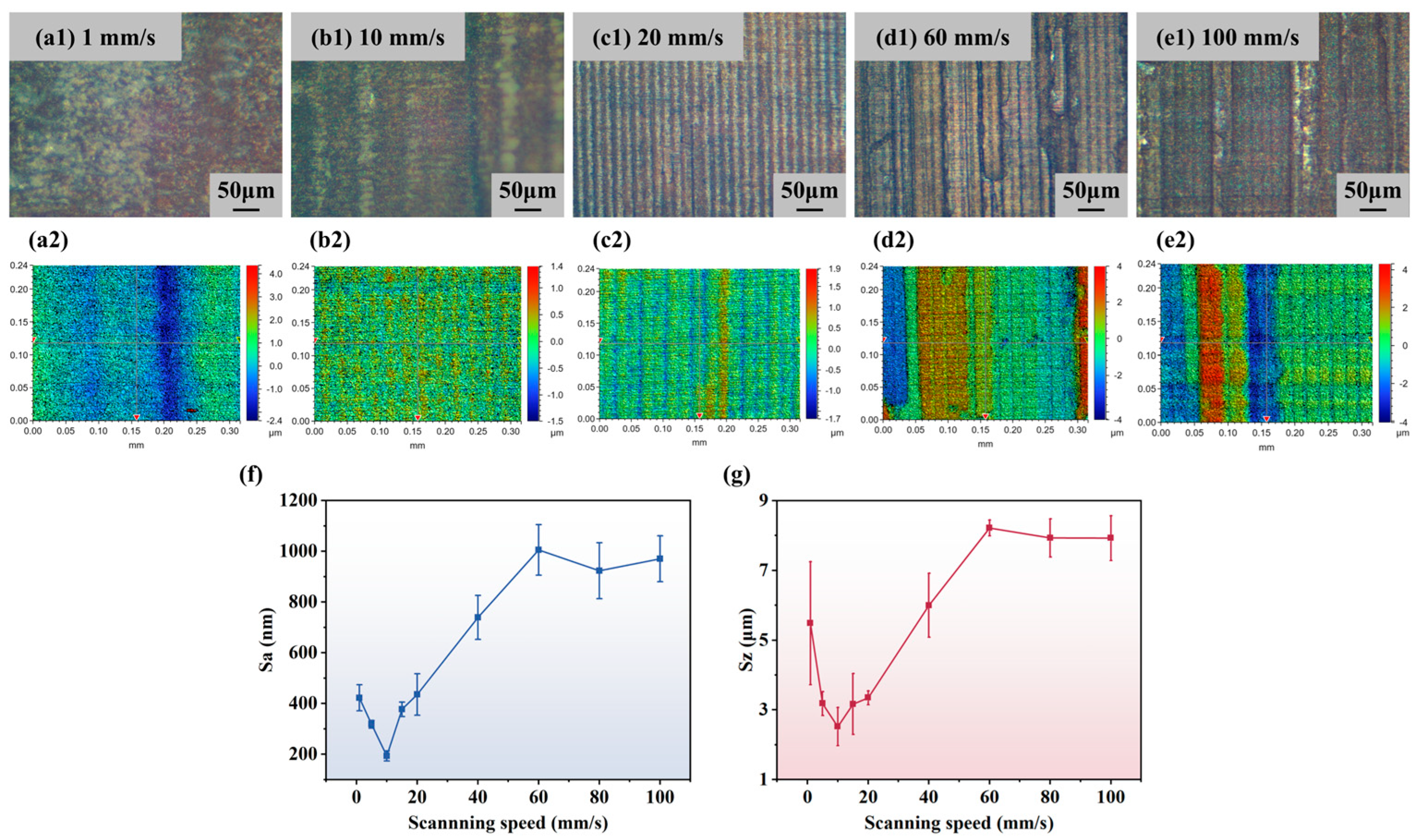
4.2.2. Influence of Scanning Speed on Surface Roughness
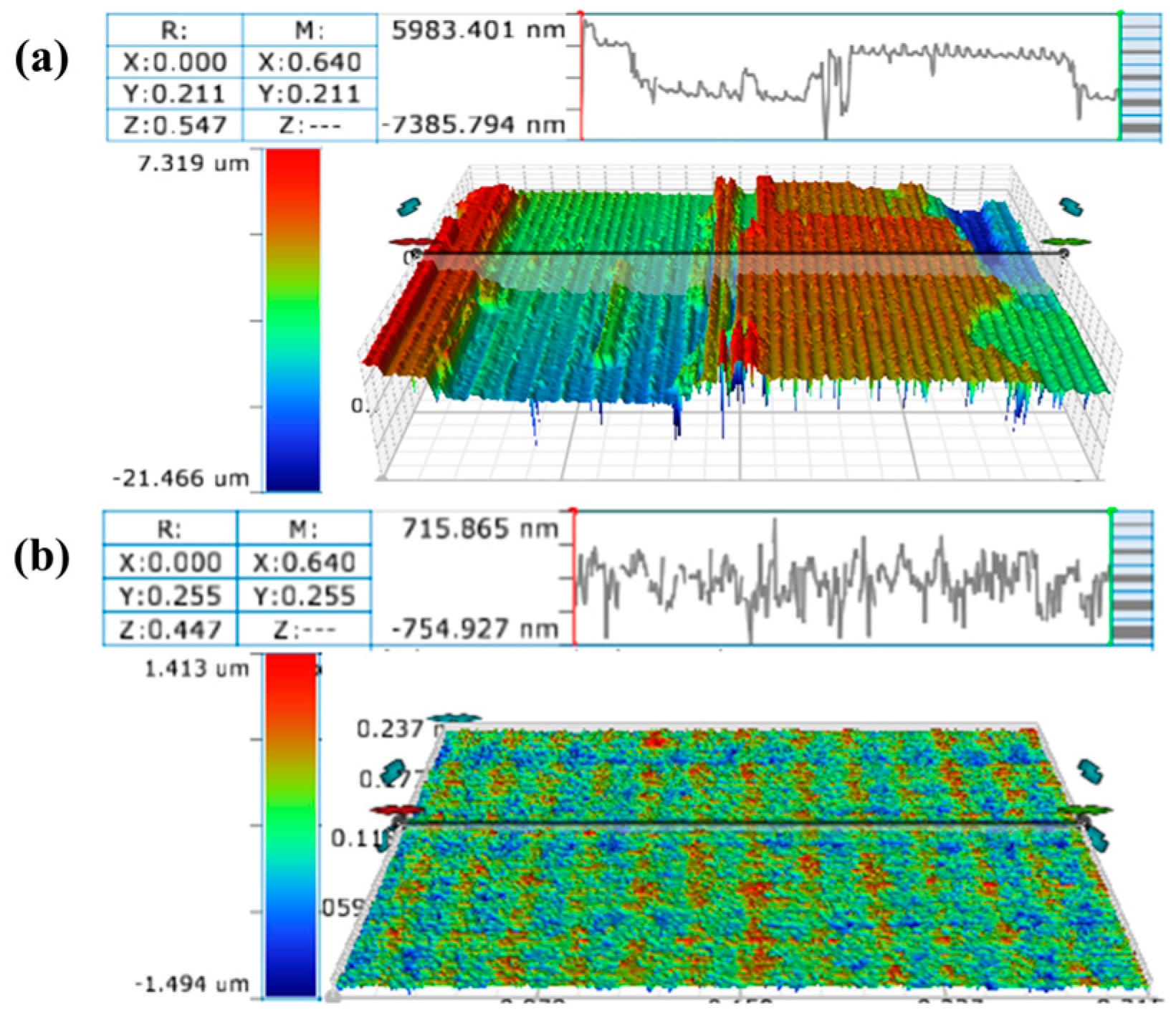
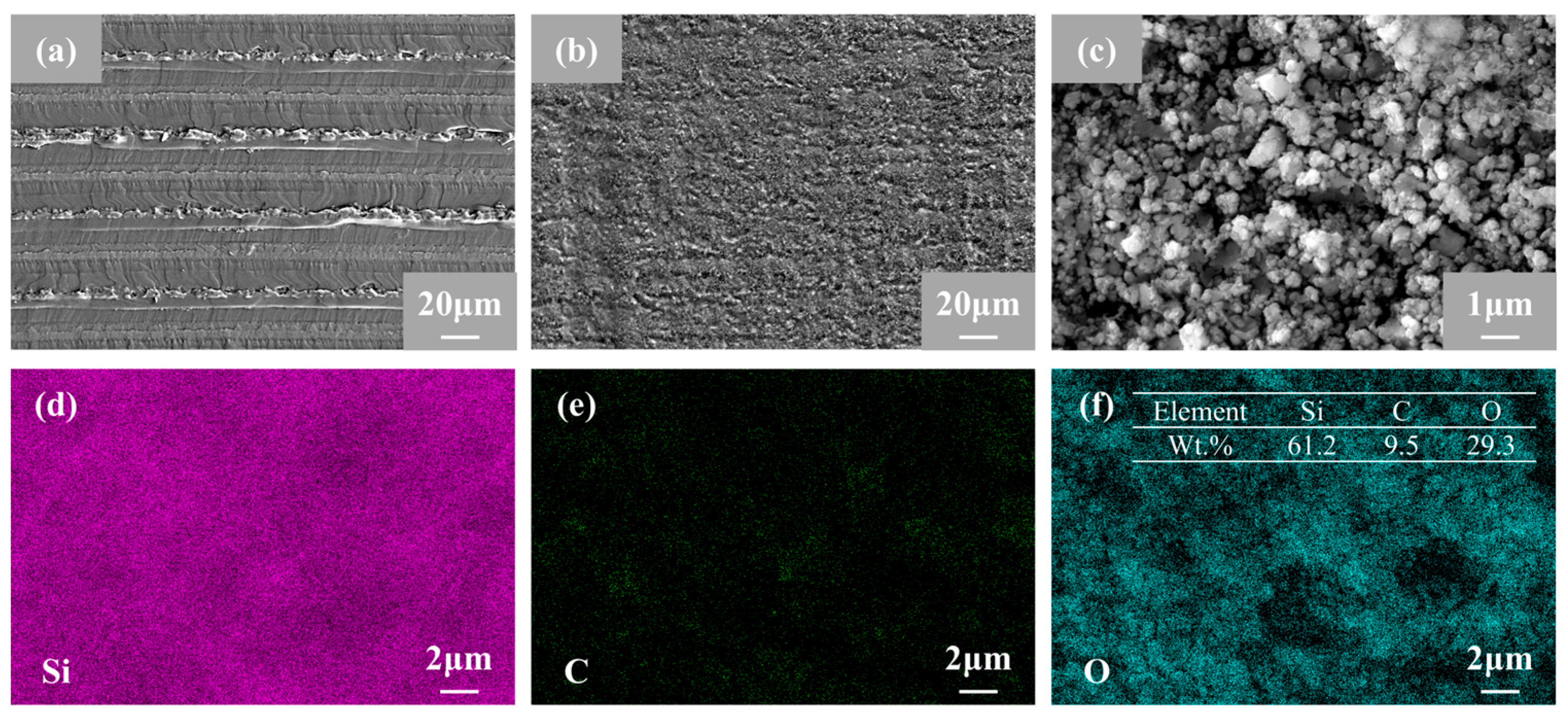
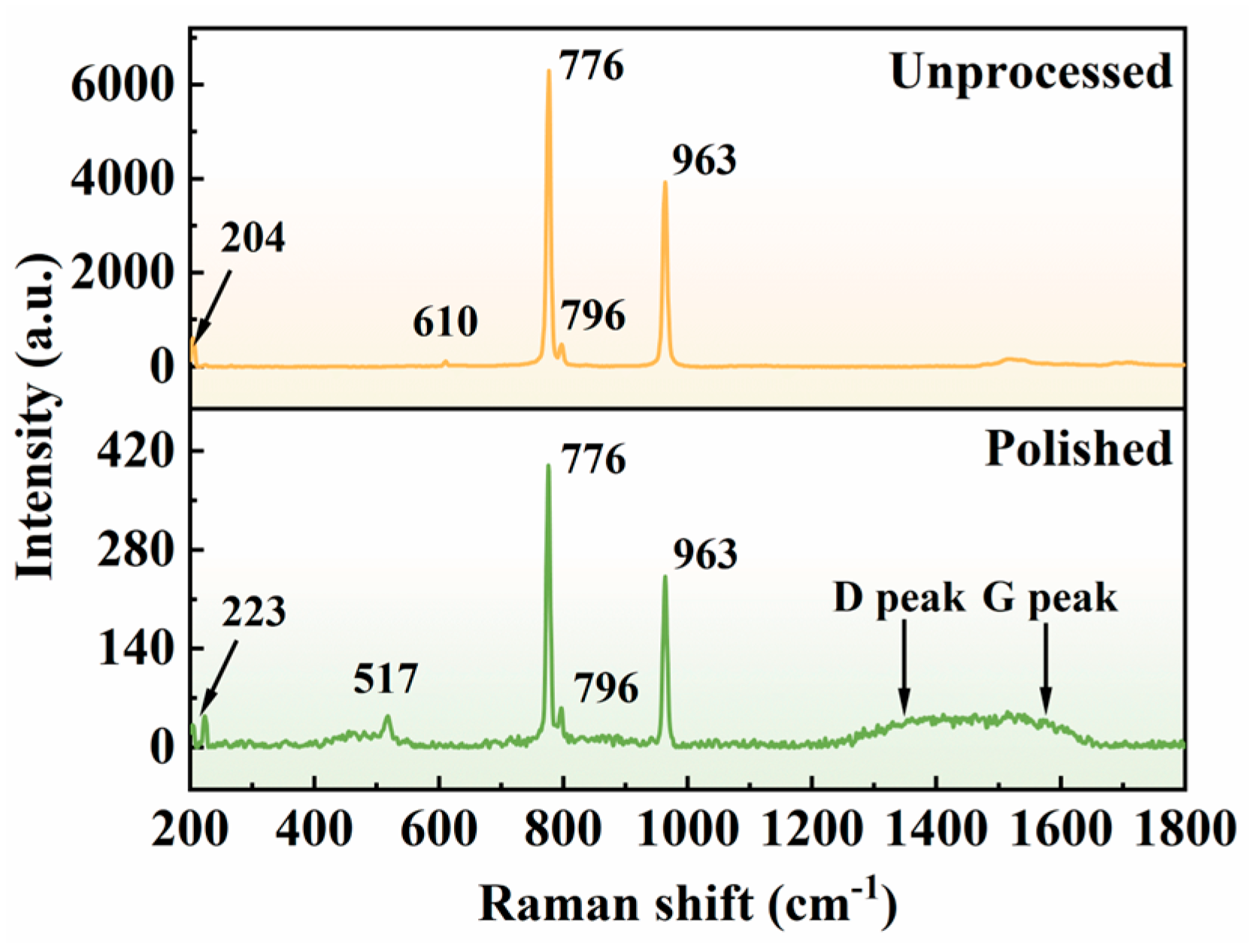
4.2.3. Micro-Morphology Analysis
4.2.4. Component Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The two-temperature model reveals the dynamic process of the interaction between the picosecond laser and 4H-SiC. The evolution of free electron density is jointly regulated by multiphoton absorption and plasma-shielding effects, and the electron and lattice temperatures exhibit significant spatiotemporal non-equilibrium characteristics.
- (2)
- The synergistic regulation of laser power and scanning speed is the key to determining the quality of 4H-SiC surface polishing. Excessive laser power will induce thermal damage and deteriorate the material surface, while insufficient power cannot effectively remove the material. The scanning speed significantly affects the polishing effect by regulating the energy density. Low speed induces thermal accumulation, leading to recast layer defects, while high speed reduces the material removal efficiency due to insufficient energy input.
- (3)
- 4H-SiC underwent thermal decomposition, oxidation, and amorphization phase transition during picosecond laser polishing, and finally formed a multiphase hybrid system. The rapid cooling process after laser action resulted in the formation of the nanoparticle cluster/pore composite structure on the polished surface.
- (4)
- This study has certain limitations, such as insufficient exploration of the process of suppressing material phase transition and the inability to achieve industrial grade surface quality on the surface at present. However, this study verified the technical feasibility of efficient planarization of rough surfaces of 4H-SiC using ultrafast lasers from both theoretical and experimental perspectives, providing a theoretical basis for its potential application as a pre-polishing process after slicing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choyke, W.J.; Pensl, G. Physical Properties of SiC. MRS Bull. 1997, 22, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Xie, X.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Shao, C.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Xu, X. Research Progress of Large Size SiC Single Crystal Materials and Devices. LIGHT-Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Pi, X.; Yang, D.; Huang, Y. Advances and Challenges in 4H Silicon Carbide: Defects and Impurities. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 092001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaforte, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Greco, G.; Lo Nigro, R.; Giannazzo, F.; Iucolano, F.; Saggio, M. Emerging Trends in Wide Band Gap Semiconductors (SiC and GaN) Technology for Power Devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 187, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, M.S.; Priya, R.; Rajakumari, R.F.; Valsalan, P.; Chakravarthi, M.K.; Latha, G.C.P.; Mathupriya, S.; Rajan, K. Review and Evaluation of Power Devices and Semiconductor Materials Based on Si, SiC, and Ga-N. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 8648284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. Wire Sawing Technology: A State-of-the-Art Review. Precis. Eng.-J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2016, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ge, P.; Zhang, L.; Bi, W. Study on the Subsurface Microcrack Damage Depth in Electroplated Diamond Wire Saw Slicing SiC Crystal. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 22927–22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H. An Investigation on Barrier Inhomogeneities of 4H-SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes Induced by Surface Morphology and Traps. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2012, 59, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, F. Combination of Plasma Electrolytic Processing and Mechanical Polishing for Single-Crystal 4H-SiC. Micromachines 2021, 12, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, D.; Pi, X. Oxidation Anisotropy of 4H-SiC Wafers during Chemical-Mechanical Polishing. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2025, 185, 109014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, H.; Wang, C. Cavitation-Driven Nanosecond Laser Irradiation Assisted Chemical–Mechanical-Polishing (CMP) for Atomic-Scale Material Removal of 4H-SiC. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 191, 113328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-K.; Chen, C.-C.A.; Tu, C.-C.; Kuo, H.-C. Recent Advances In Silicon Carbide Chemical Mechanical Polishing Technologies. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Hu, B.; Song, X.; Dong, Z.; Kang, R. Dispersal Mechanism of Different Dispersants and Its Effect on Performance of 4H-SiC Polishing Slurry. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 3943–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, D.; Pi, X. Chemical–Mechanical Polishing of 4H Silicon Carbide Wafers. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2202369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, W.; Hong, M. Hybrid Laser Precision Engineering of Transparent Hard Materials: Challenges, Solutions and Applications. LIGHT-Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, P.; Song, S.; Sun, T.; Chen, Y.; Shi, H.; Yan, H.; Lu, Q.; Chen, G. A Review of Ultra-Short Pulse Laser Micromachining of Wide Bandgap Semiconductor Materials: SiC and GaN. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2024, 180, 108559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Huang, K.-C.; Lee, C.-J.; Yeh, J.A.; Yang, Y.; Ding, C.-F. Precision Material Removal and Hardness Reduction in Silicon Carbide Using Ultraviolet Nanosecond Pulse Laser. Appl. Phys. A 2025, 131, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidys, M.; Žemaitis, A.; Gečys, P.; Gedvilas, M. Efficient Surface Polishing Using Burst and Biburst Mode Ultrafast Laser Irradiation. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 3586–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-D.; Tsai, W.-J.; Liu, S.-H.; Horng, J.-B. Picosecond Laser Pulse Polishing of ASP23 Steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 107, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Lei, W.; Wang, C. Surface Morphology Evolution Mechanisms of Pulse Laser Polishing Mold Steel. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 269, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.-V.; Nguyen, H.-D.; Vu, T.-T.; Tran, N.-H.; Nguyen, T.-T.-H.; Tran, V.-T.; Trinh, Q.-H. Modelling and Analysis of Nanosecond Laser Polishing for Skd11 Steel with Surface Roughness Prediction and Optimization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 138, 3517–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, B.; Li, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Study on Surface Quality of Ultrasonic Assisted Underwater Laser Polishing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 5761–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Yan, T. Polishing of Alumina Ceramic to Submicrometer Surface Roughness by Picosecond Laser. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 397, 125962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, C.; Chen, T.; Shao, M.; Jiang, C.; Lu, C.; Song, S. Parameter Optimization of RB-SiC Polishing by Femtosecond Laser. Materials 2023, 16, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Ma, G.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L. Influence of Pulse Energy and Defocus Amount on the Mechanism and Surface Characteristics of Femtosecond Laser Polishing of SiC Ceramics. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu Kang, K.; Hyuk Lee, S.; Ki Choi, Y.; Ryou, H.-S.; Sik Lee, J.; Park, S. Fokker-Planck Approach to Laser-Induced Damage in Dielectrics with Subpicosecond Pulses. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 2006, 10, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethfeld, B.; Ivanov, D.S.; Garcia, M.E.; Anisimov, S.I. Modelling Ultrafast Laser Ablation. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 193001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Han, X.; Dong, F.; Liu, S. Innovative Multiscale Simulation with Experimental Validation of Ultrafast Laser Processing in Silicon Carbide (4H-SiC). J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 137, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Atomic-Scale Insights into the Abrasive Concentration Effects on 6H-SiC Removal in CMP. Tribol. Int. 2026, 214, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. A Unique Insight into the Atomic-Scale Removal on 6H-SiC. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 143, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Al-amin, M.; Grøndahl, L.; Lu, M.; Cheung, C.F.; Huang, H. MD Simulation of Chemically Enhanced Polishing of 6H-SiC in Aqueous H2O2. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 107, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.-K.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C. Investigation of Polishing Pads Impregnated with Fe and Al2O3 Particles for Single-Crystal Silicon Carbide Wafers. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Zeng, N. Improved Chemical Mechanical Polishing Performance in 4H-SiC Substrate by Combining Novel Mixed Abrasive Slurry and Photocatalytic Effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 575, 151676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, X.; Pan, G. Surface Modulation to Enhance Chemical Mechanical Polishing Performance of Sliced Silicon Carbide Si-Face. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 536, 147963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter Type | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Laser parameters | Laser wavelength (λ) | 1064 nm |
| Laser frequency (ƒ) | 100 kHz | |
| Beam waist radius (ω0) | 1 μm | |
| Pulse width (tp) | 10 ps | |
| Reflectivity (R) | 0.5 | |
| Thermophysical parameters | Ambipolar diffusion coefficient (D) | 2.5 cm2/s |
| Single-photon absorption coefficient (α) | 4.464 × 105 1/cm | |
| Two-photon absorption coefficient (β) | 0.4 × 10−11 m/W | |
| Reduced Planck constant (ℏ) | 1.055 × 10−34 J·s | |
| Single photon recombination coefficient (A) | 3.846 × 106 1/s | |
| Two-photon recombination coefficient (B) | 3 × 10−11 cm3/s | |
| Auger recombination coefficient (C) | 7 × 10−31 cm6/s | |
| Initial electron concentration (ne0) | 5 × 1017 1/cm3 | |
| Electron heat capacity (Ce) | 311.53 J/kg/K | |
| Electron thermal conductivity (ke) | 2 × 10−4 W/m/K | |
| Electron/phonon coupling constant (G) | 9.8 × 1018 W/m3/K | |
| Lattice heat capacity (Cl) | 690 J/kg/K | |
| Lattice thermal conductivity (kl) | 370 W/m/K | |
| Material density (ρ) | 3210 kg/m3 | |
| Vaporization temperature (Tv) | 3840 K | |
| Latent heat of vaporization (Lv) | 4 × 105 J/mol | |
| Molar mass (M) | 4 × 10−2 kg/mol |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gao, P. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study on Picosecond Laser Polishing of 4H-SiC Wafer. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101163
Yan Y, Cheng Y, Chen S, Tang Y, Zhang F, Gao P. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study on Picosecond Laser Polishing of 4H-SiC Wafer. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101163
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yixiong, Yuxuan Cheng, Sijia Chen, Yu Tang, Fan Zhang, and Piaopiao Gao. 2025. "Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study on Picosecond Laser Polishing of 4H-SiC Wafer" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101163
APA StyleYan, Y., Cheng, Y., Chen, S., Tang, Y., Zhang, F., & Gao, P. (2025). Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study on Picosecond Laser Polishing of 4H-SiC Wafer. Micromachines, 16(10), 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101163







