Integrated Control Strategies for a Precision Long-Travel Stage: Applications in Micro-Lens Fabrication
Abstract
1. Introduction
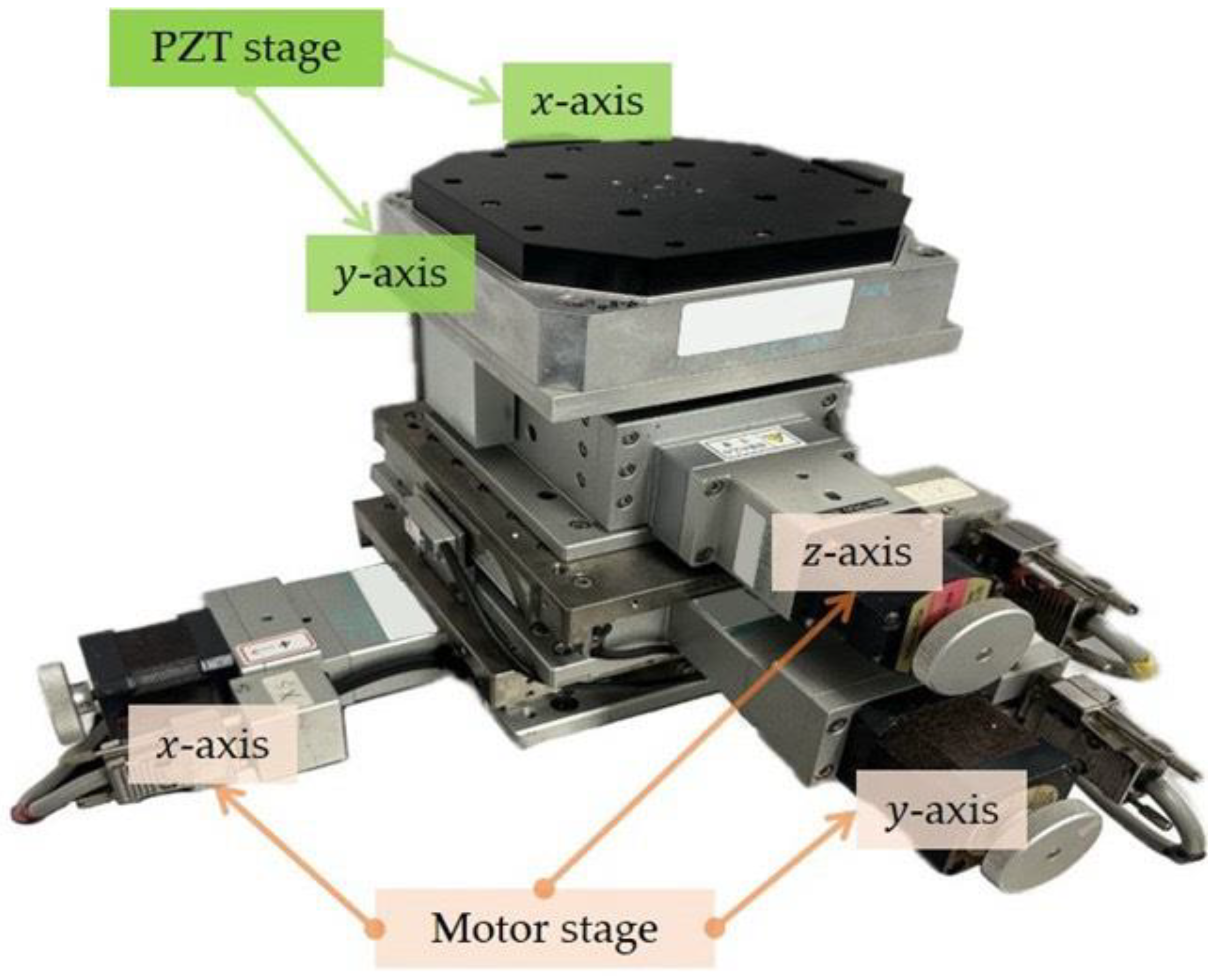
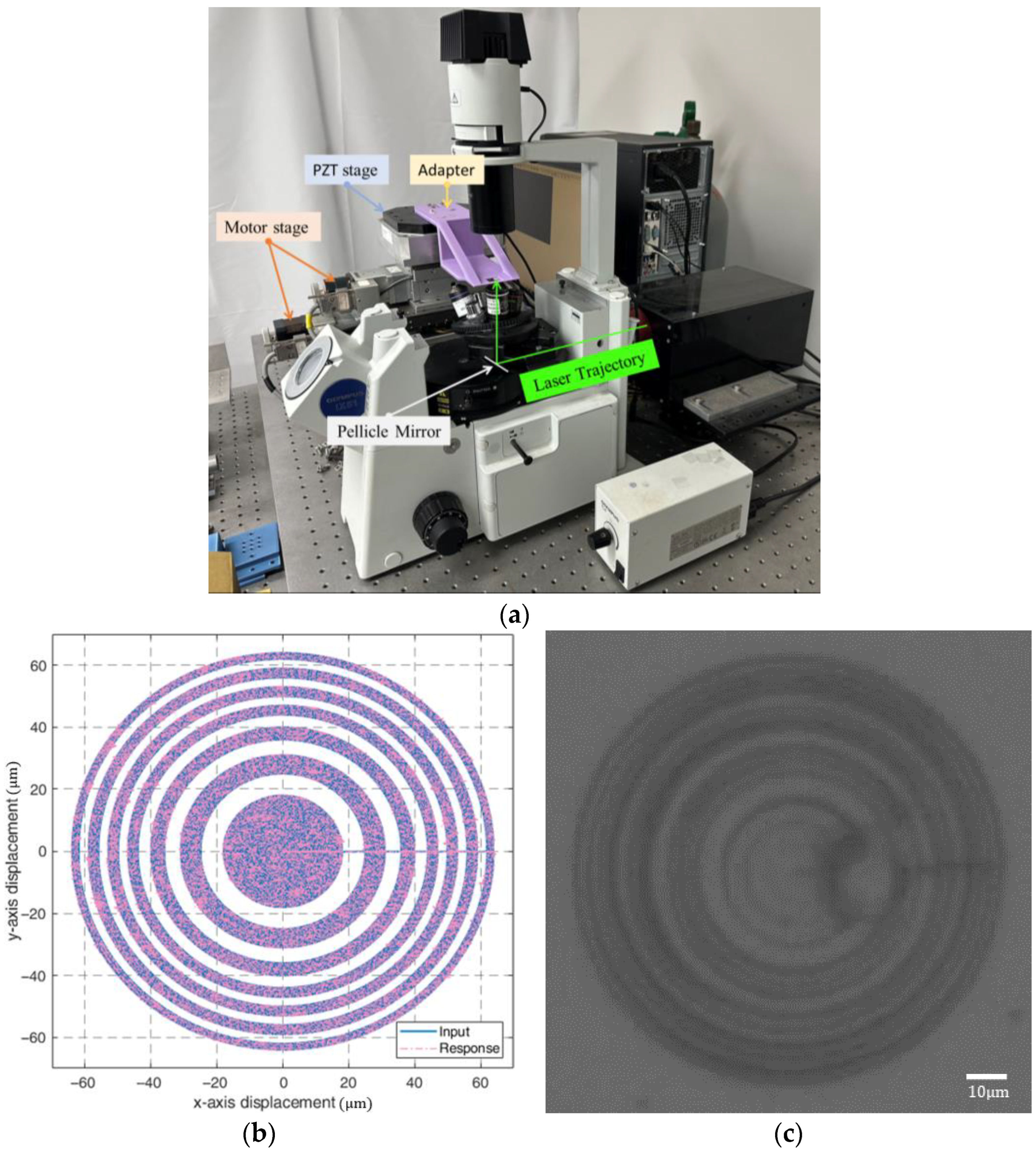
2. The Long-Travel Precision Stage
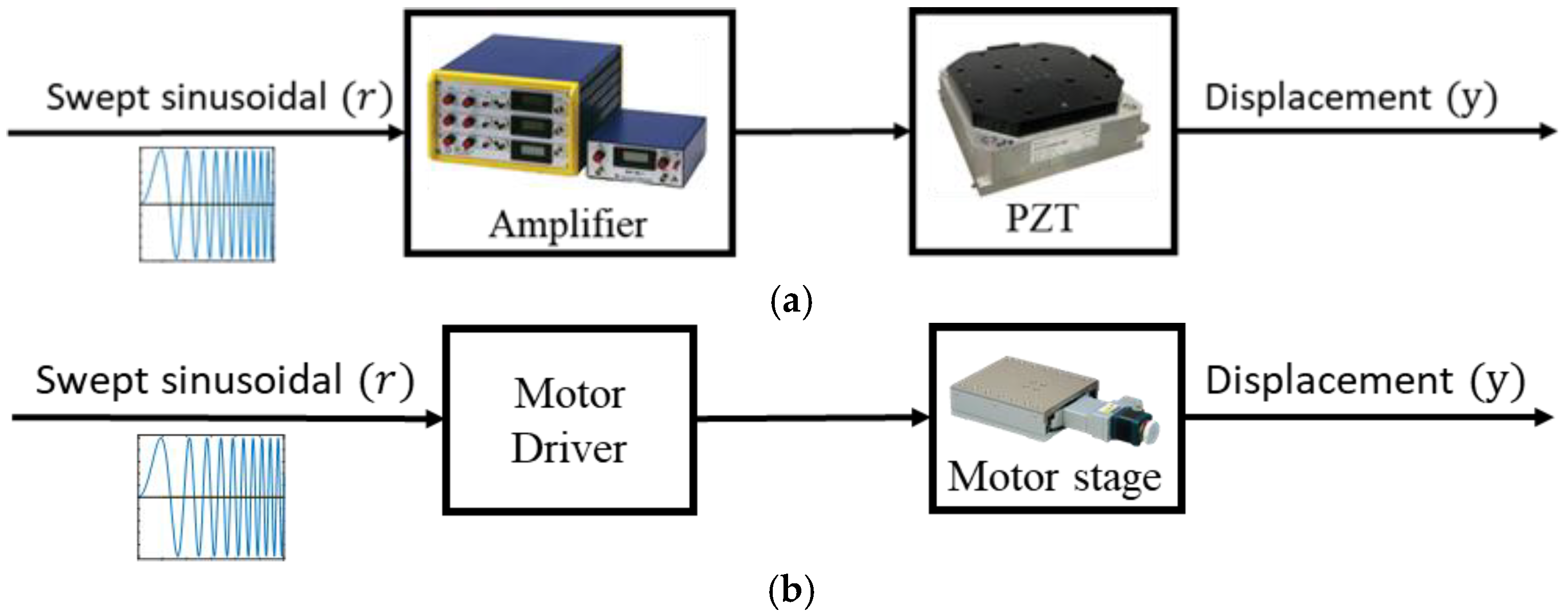
2.1. PZT Stage Models
2.2. Motor Stage Models
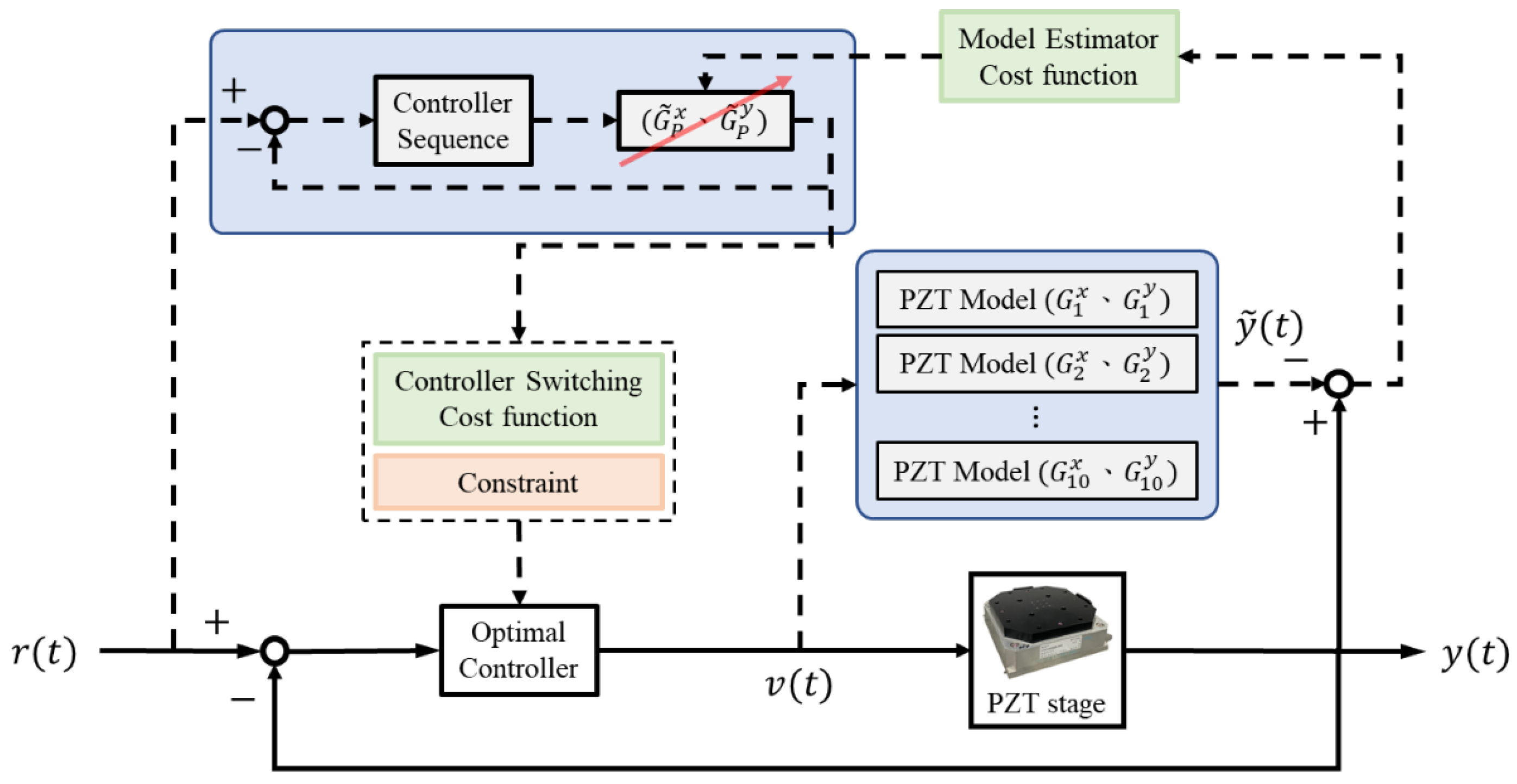
3. Control Switching and Model Estimation for the PZT Stage
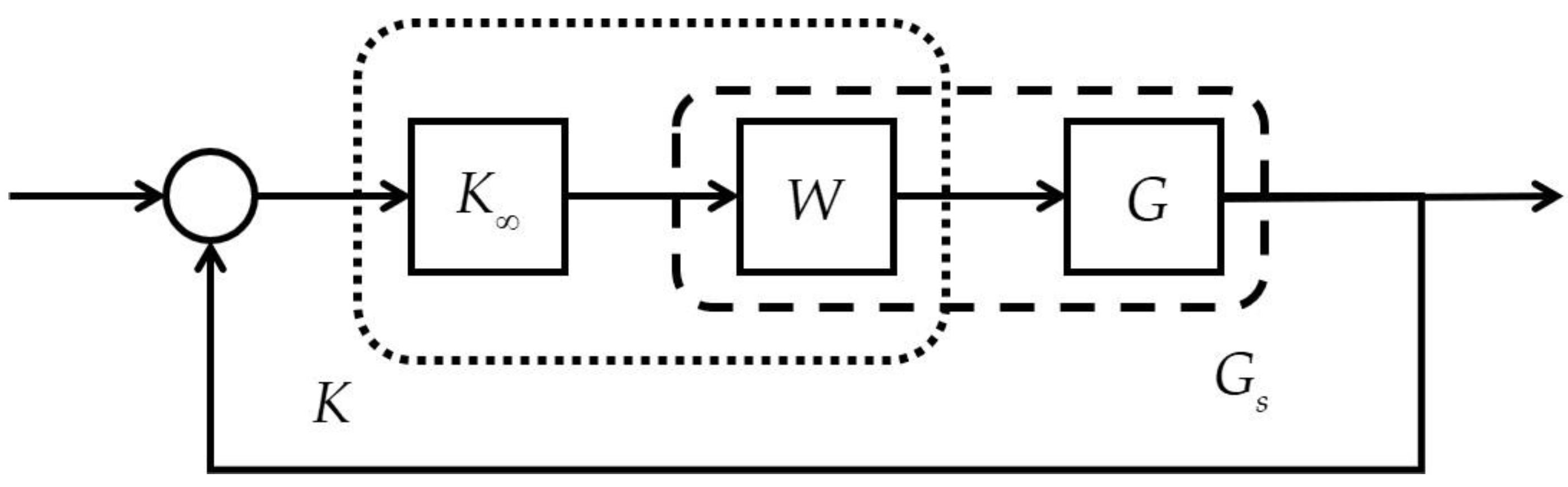
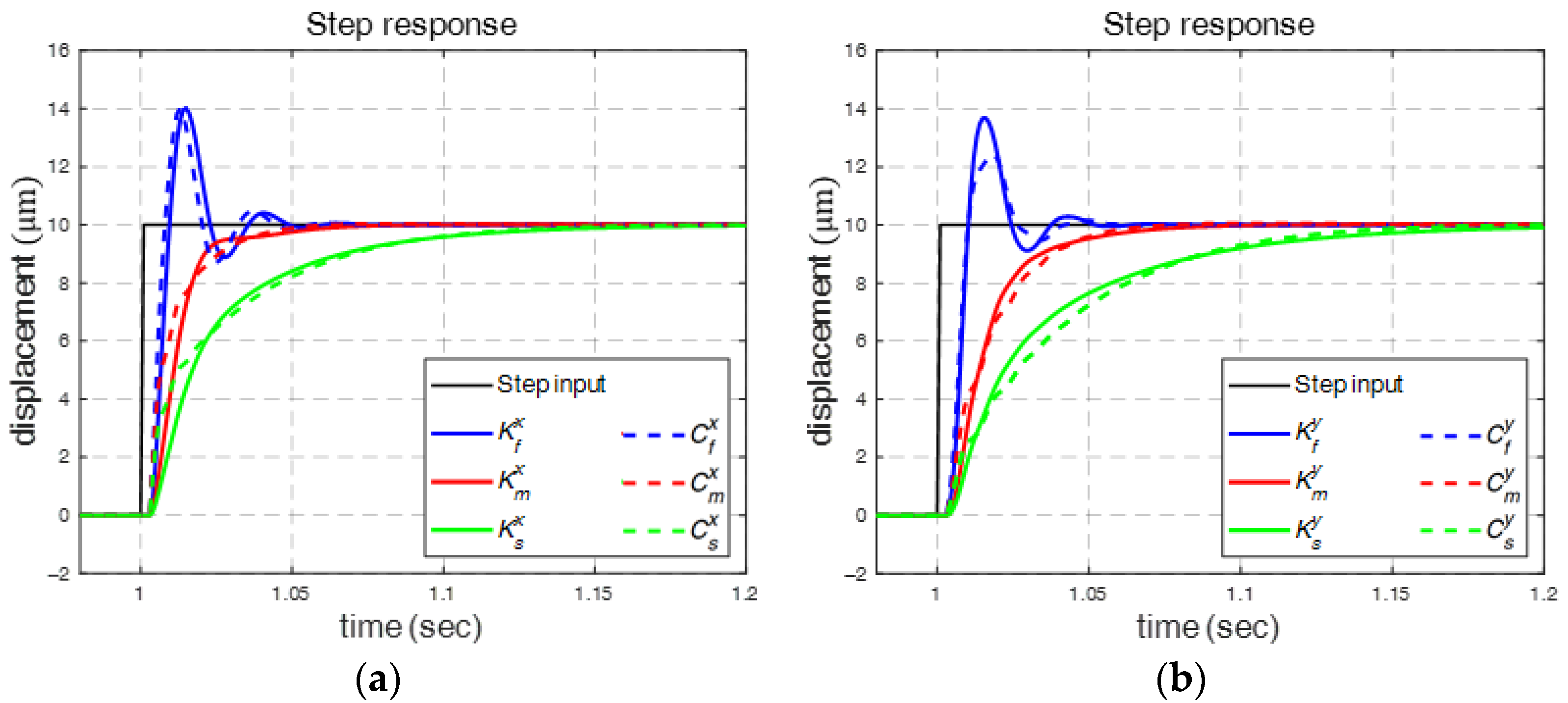
3.1. Robust Control Designs
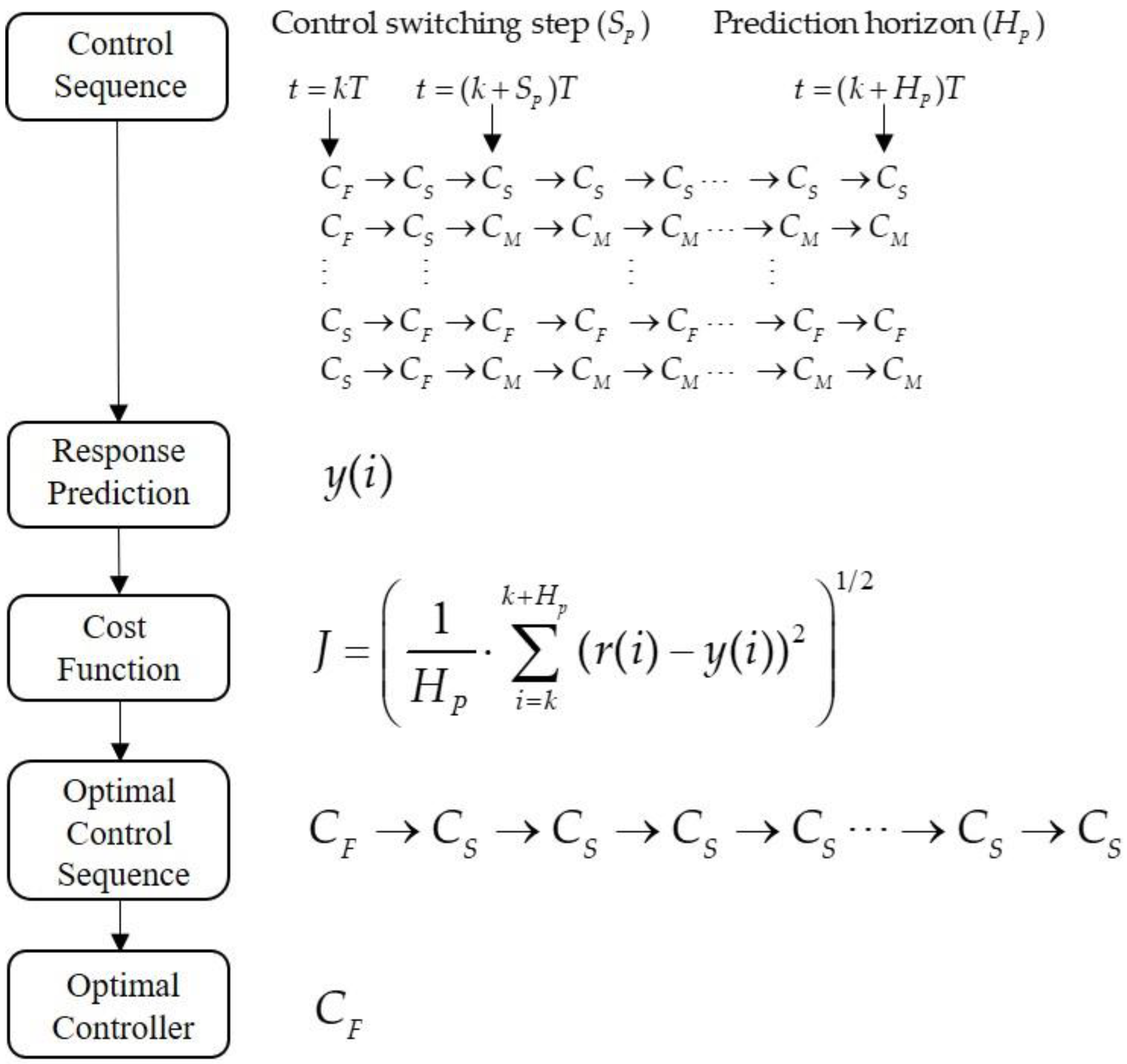
3.2. Multiple-Switching Control
3.3. Model Estimation
4. Gain Scheduling and Feedforward for the Motor Stage
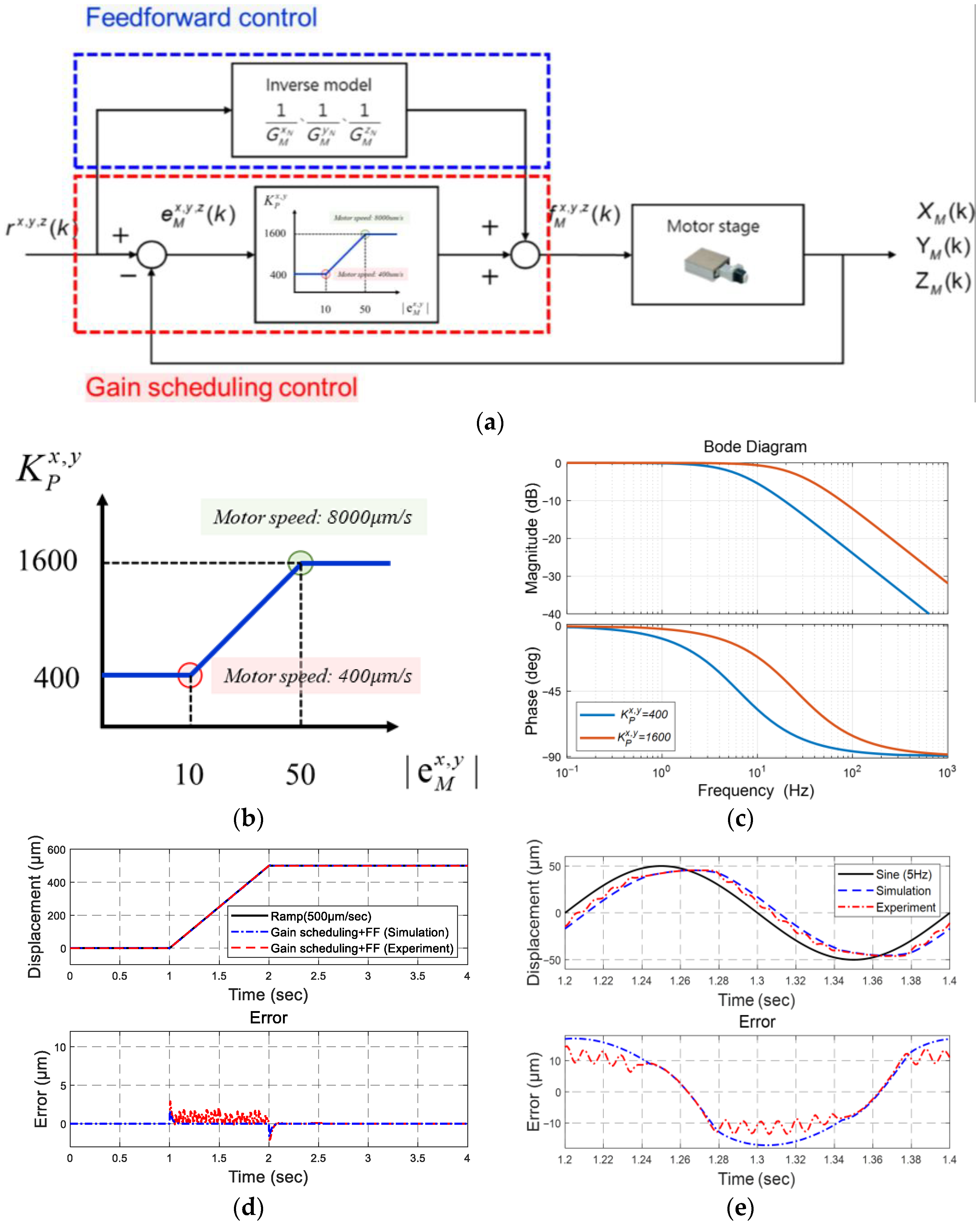
4.1. Gain Scheduling
4.2. Feedforward Compensation
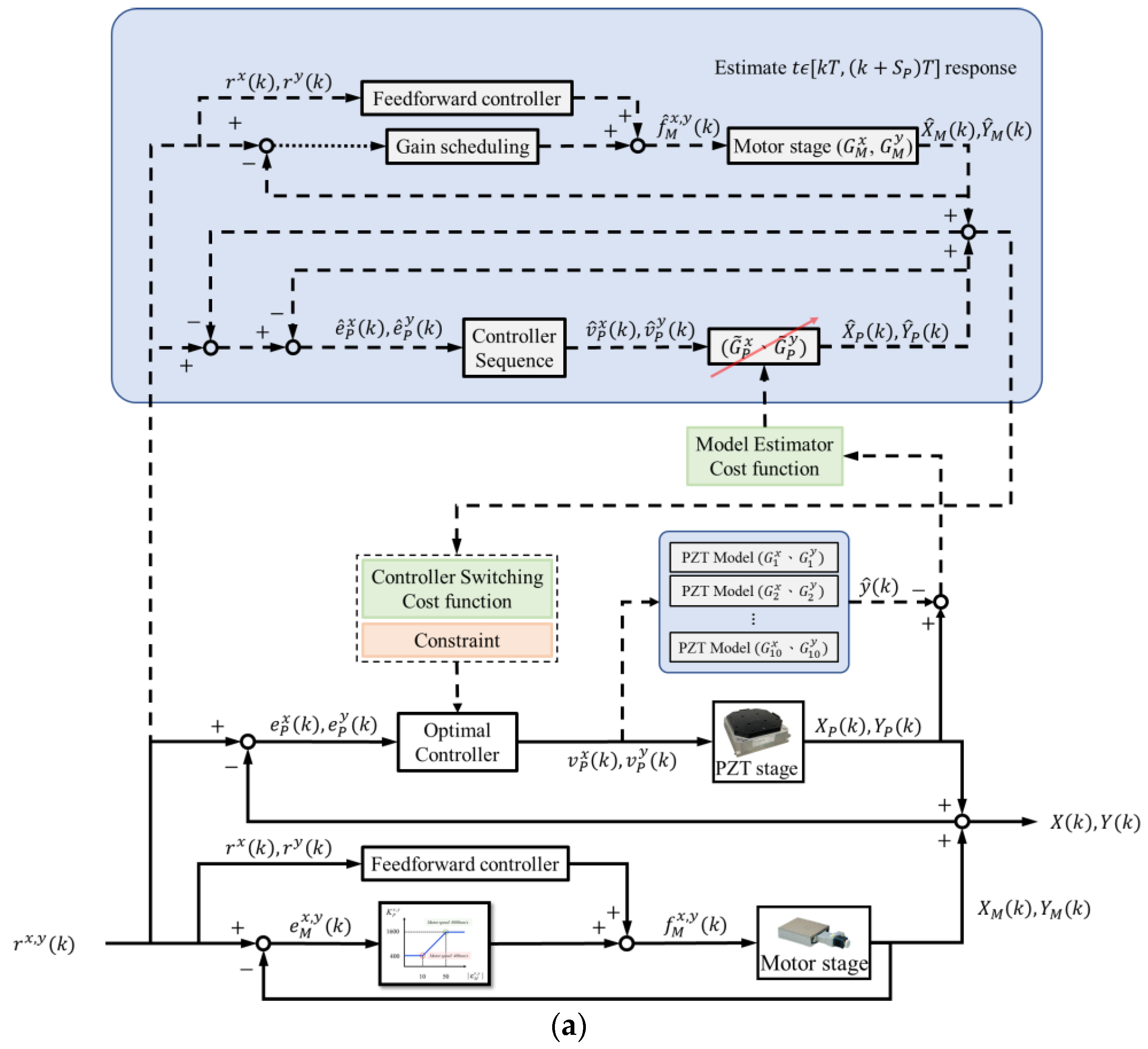
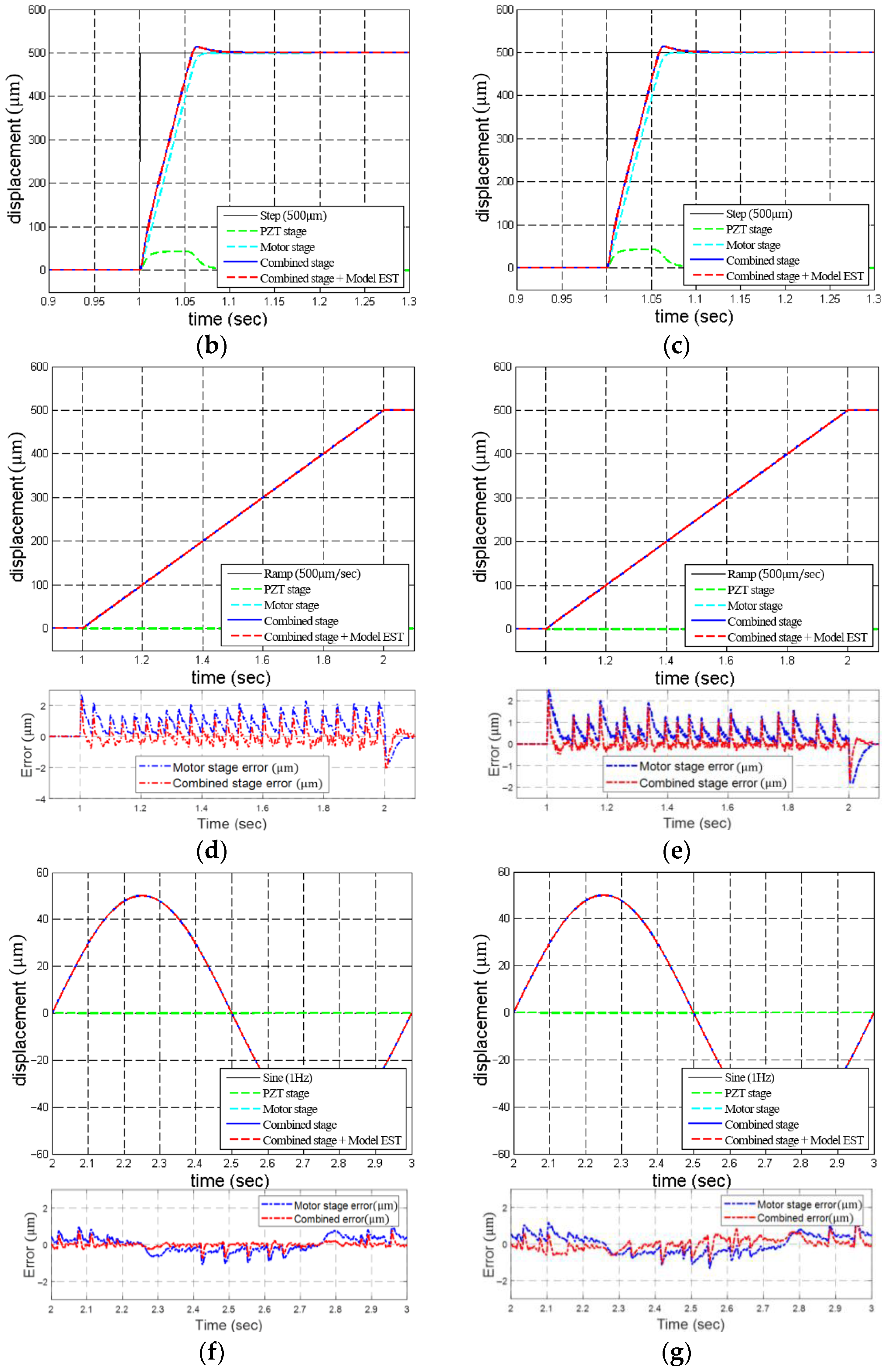
5. Integration of the Long-Travel Precision Stage
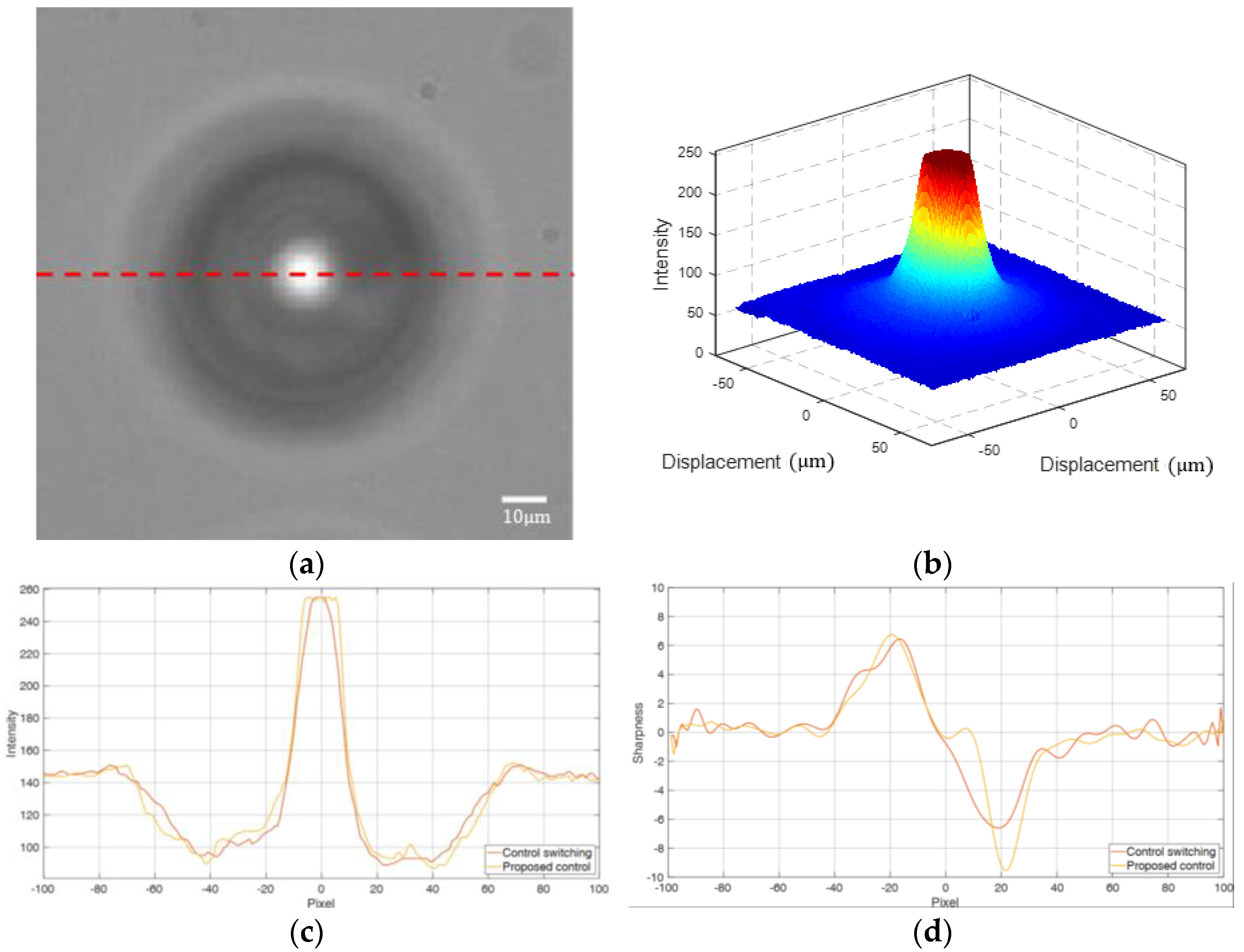
6. Micro-Lens Fabrication
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Stage Specifications
Appendix B. Stage Models
Appendix C. Modified Controllers
References
- Chen, J.; Peng, G.; Hu, H.; Ning, J. Dynamic hysteresis model and control methodology for force output using piezoelectric actuator driving. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 205136–205147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baziyad, A.G.; Ahmad, I.; Salamah, Y.B. Precision motion control of a piezoelectric actuator via a modified Preisach hysteresis model and two-degree-of-freedom H-Infinity robust control. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzpour, H.; Ghasemi, A. Hybrid fuzzy PID sound radiation control of a functionally graded porous GPL-reinforced plate with piezoelectric sensor and actuator layers. Appl. Math. Modell 2024, 127, 655–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, L.N.; Crocker, L.E.; Wright, L.; Rungger, I. A Compact Device Model for a Piezoelectric Nano-Transistor. Micromachines 2025, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Choi, Y.M.; Gweon, D.G. A novel mode switching control for fast settling and high precision positioning. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 17–20 October 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashash, S.; Saeidpourazar, R.; Jalili, N. Tracking control of time-varying discontinuous trajectories with application to probe-based imaging and nanopositioning. In Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–12 June 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J. A novel two-phase mode switching control strategy for PMSM position servo systems with fast-response and high-precision. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 38, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artetxe, E.; Barambones, O.; Calvo, I.; Del Rio, A.; Uralde, J. Combined control for a piezoelectric actuator using a feed-forward neural network and feedback integral fast terminal sliding mode control. Micromachines 2024, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, K.A.; Chung, T.T. The development of a long-stroke precision positioning stage for micro fabrication by two-photon polymerization. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2016, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, P. Enhanced robust nanopositioning control for an XY piezoelectric stage with sensor delays: An infinite dimensional H∞ optimization approach. Mechatronics 2021, 75, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarem, S.; Delibas, B.; Koc, B. Data-driven tuning of PID controlled piezoelectric ultrasonic motor. Actuators 2021, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Peng, Y.K.; Lu, J.F.; Chung, T.T.; Yen, J.Y. Micro-lens fabrication by a long-stroke precision stage with switching control based on model response prediction. Microsyst. Technol. 2022, 28, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Lu, J.F.; Su, W.J.; Yen, J.Y. Precision positioning control of a long-stroke stage employing multiple switching control. Microsyst. Technol. 2022, 28, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Lu, J.F.; Chung, T.T.; Yen, J.Y. Iterative parameter optimization for multiple switching control applied to a precision stage for microfabrication. Machines 2021, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Abdalmoaty, M.; Yin, M. Optimal data-driven prediction and predictive control using signal matrix models. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 63rd Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Milan, Italy, 16–19 December 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, K.; Koiwai, K.; Yamamoto, T. Design of a Database-Driven PID Controller Using Response Prediction for Unknown Time-delay Systems. IEEJ Trans. Electron. Inf. Syst. 2023, 143, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multi-Axis Piezo Scanner High Dynamics Nanopositioner/Scanner with Direct Position Measuring. Available online: https://reurl.cc/Om69QA (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- X Stage, ALS-510-HP, Chuo Precision Industrial Co. Ltd. Available online: https://reurl.cc/2Qapv4 (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- Z Lift Stage, ALV-104-HP, Chuo Precision Industrial Co. Ltd. Available online: https://reurl.cc/yAOzGE (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- Wang, F.C.; Wang, K.A.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Yen, J.Y. Impacts of sensor layouts on the performance of a long-stroke nano-positioning stage. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, K.; McFarlane, D. Robust stabilization of normalized coprime factor plant descriptions with H∞-bounded uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1989, 34, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, T.T.; Smith, M.C. Optimal robustness in the gap metric. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1990, 35, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Doyle, J.C. Essentials of Robust Control; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane, D.; Glover, K. A loop-shaping design procedure using H∞ synthesis. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1992, 37, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Chen, L.S.; Tsai, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Yen, J.Y. Robust loop-shaping control for a nano-positioning stage. J. Vib. Control 2014, 20, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.B.; Matsuo, S.; Misawa, H. Three-dimensional photonic crystal structures achieved with two-photon-absorption photopolymerization of resin. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrimgeour, J.; Sharp, D.N.; Blanford, C.F.; Roche, O.M.; Denning, R.G.; Turberfield, A.J. Three-Dimensional Optical Lithography for Photonic Microstructures. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1557–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.B.; Dong, X.Z.; Chen, W.Q.; Nakanishi, S.; Duan, X.M.; Kawata, S. Multicolor polymer nanocomposites: In situ synthesis and fabrication of 3D microstructures. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.K.; Sun, Z.B.; Zheng, M.L.; Dong, X.Z.; Zhao, Z.S.; Duan, X.M. Magnetic nickel–phosphorus/polymer composite and remotely driven three-dimensional micromachine fabricated by nanoplating and two-photon polymerization. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 11275–11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Wang, K.A.; Chung, T.T.; Yen, J.Y. Fabrication of large-scale micro-structures by two-photon polymerization with a long-stroke precision stage. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017695757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| C.S. [14] | Proposed Control | Imp. (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x-axis | Simulation | Overshoot (%) | 3.9786 | 1.8051 | 54.63 |
| RMSE (μm) | 1.6949 | 1.5126 | 1.08 | ||
| Settling time (s) | 1.0291 | 1.0114 | 1.72 | ||
| Rising time (s) | 0.0061 | 0.0064 | −4.92 | ||
| Experiment | Overshoot (%) | 8.9100 | 3.9200 | 56.00 | |
| RMSE (μm) | 1.4550 | 1.4092 | 3.15 | ||
| Settling time (s) | 1.0712 | 1.0503 | 1.96 | ||
| Rising time (s) | 0.0066 | 0.0069 | −4.55 | ||
| y-axis | Simulation | Overshoot (%) | 3.7525 | 1.7585 | 53.14 |
| RMSE (μm) | 1.4816 | 1.4681 | 0.91 | ||
| Settling time (s) | 1.0789 | 1.0117 | 6.23 | ||
| Rising time (s) | 0.0060 | 0.0065 | −8.33 | ||
| Experiment | Overshoot (%) | 2.2522 | 1.5104 | 32.90 | |
| RMSE (μm) | 1.4848 | 1.4672 | 1.20 | ||
| Settling time (s) | 1.0207 | 1.0115 | 0.90 | ||
| Rising time (s) | 0.0064 | 0.0066 | −3.13 |
| Ramp Input (500 μm/s) | Sinusoidal Input (5 Hz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation | Phase lag (deg) | - | 2.4000 |
| MAE (μm) | 1.6618 | 3.6400 | |
| RMSE (μm) | 0.1998 | 2.5352 | |
| Experiment | Phase lag (deg) | - | 3.6000 |
| MAE (μm) | 3.0000 | 4.7922 | |
| RMSE (μm) | 0.9122 | 4.1897 |
| x-Axis | y-Axis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Stage | Combined Stage | Motor Stage | Combined Stage | ||
| Step | Rising time (s) | 0.0487 | 0.0452 | 0.0501 | 0.0487 |
| Settling time (s) | 1.0674 | 1.0639 | 1.0852 | 1.0831 | |
| Overshoot (%) | 0 | 1.5200 | 0 | 1.4191 | |
| RMSE (μm) | 76.3951 | 76.3822 | 87.4249 | 87.4209 | |
| Ramp | MAE (μm) | 2.5000 | 2.4000 | 2.9000 | 2.9000 |
| RMSE (μm) | 0.7851 | 0.3958 | 0.9122 | 0.5301 | |
| Sinusoidal | Gain (dB) | 0.2229 | 0.0115 | 0.3072 | 0.0454 |
| MAE (μm) | 3.6000 | 0.7849 | 3.0000 | 0.9755 | |
| Phase lag (μm) | 4.7922 | 1.4390 | 5.5460 | 1.4162 | |
| RMSE (μm) | 4.1897 | 0.1687 | 4.0452 | 0.3321 | |
| C.S. [14] | Proposed Control | |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE (nm) | 94.2 | 92.5 |
| Maximum Intensity | 255 | 255 |
| Maximum Sharpness | 6.6 | 9.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chang, M.-H.; Zhong, B.-X.; Chung, T.-T.; Yen, J.-Y. Integrated Control Strategies for a Precision Long-Travel Stage: Applications in Micro-Lens Fabrication. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101105
Wang F-C, Chang Y-T, Chang M-H, Zhong B-X, Chung T-T, Yen J-Y. Integrated Control Strategies for a Precision Long-Travel Stage: Applications in Micro-Lens Fabrication. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101105
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fu-Cheng, Yan-Teng Chang, Ming-Hsiang Chang, Bo-Xuan Zhong, Tien-Tung Chung, and Jia-Yush Yen. 2025. "Integrated Control Strategies for a Precision Long-Travel Stage: Applications in Micro-Lens Fabrication" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101105
APA StyleWang, F.-C., Chang, Y.-T., Chang, M.-H., Zhong, B.-X., Chung, T.-T., & Yen, J.-Y. (2025). Integrated Control Strategies for a Precision Long-Travel Stage: Applications in Micro-Lens Fabrication. Micromachines, 16(10), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101105








