Design and Analysis Method of Piezoelectric Liquid Driving Device with Elastic External Displacement
Abstract
1. Introduction
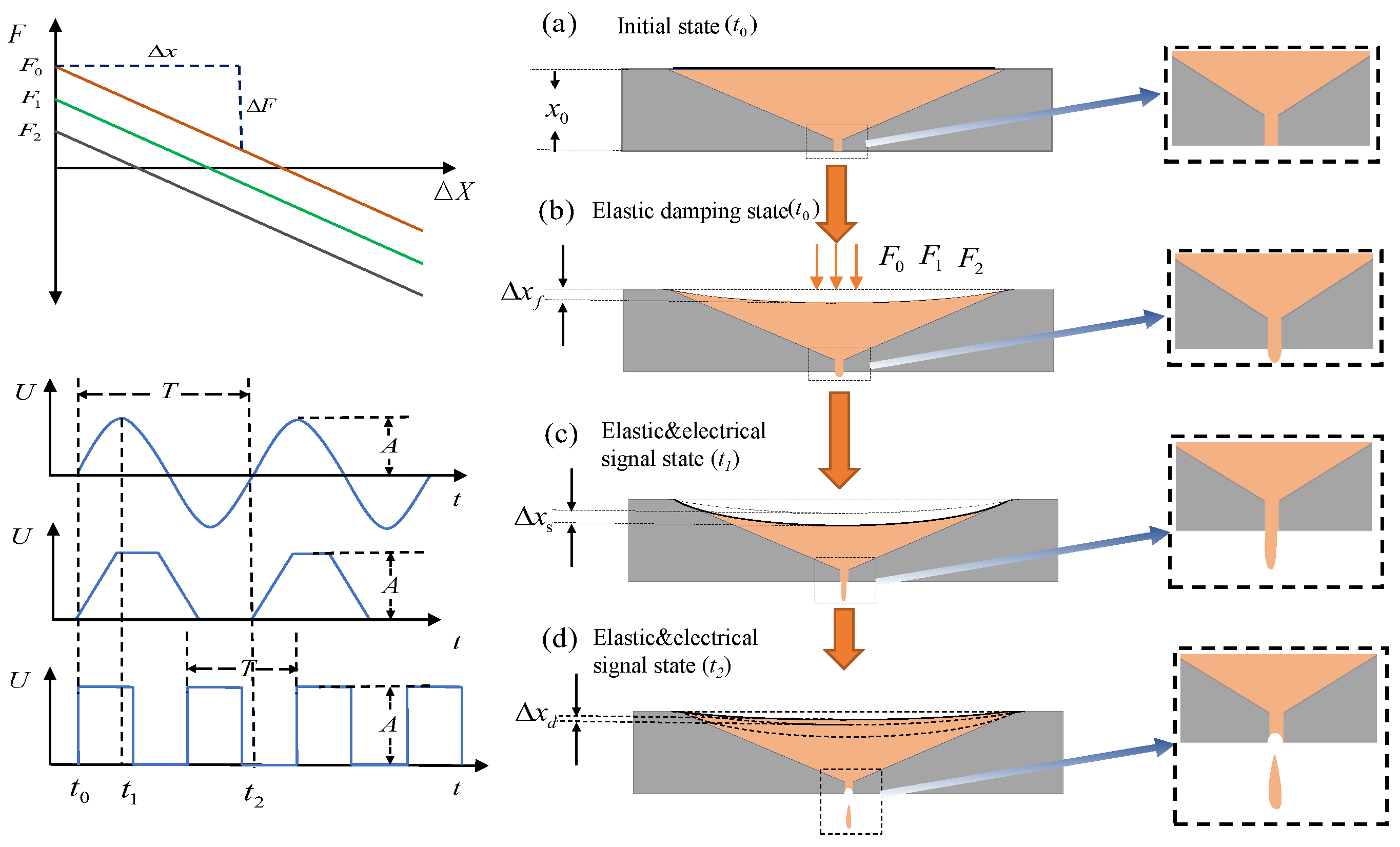
2. Model and Principle Structure Design
3. Numerical Simulation and Analysis
3.1. Principle of Numerical Analysis
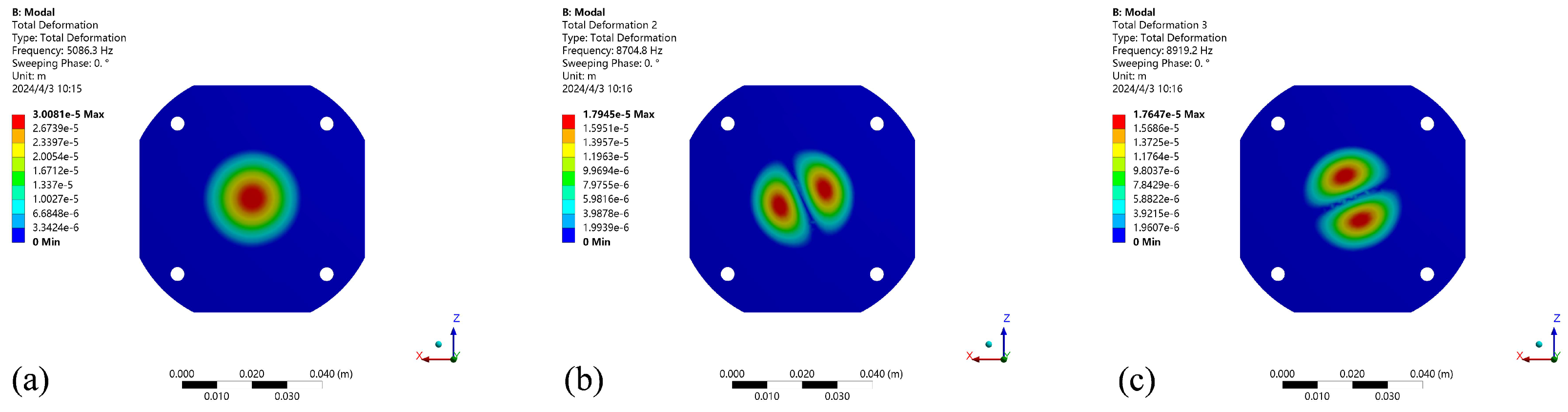
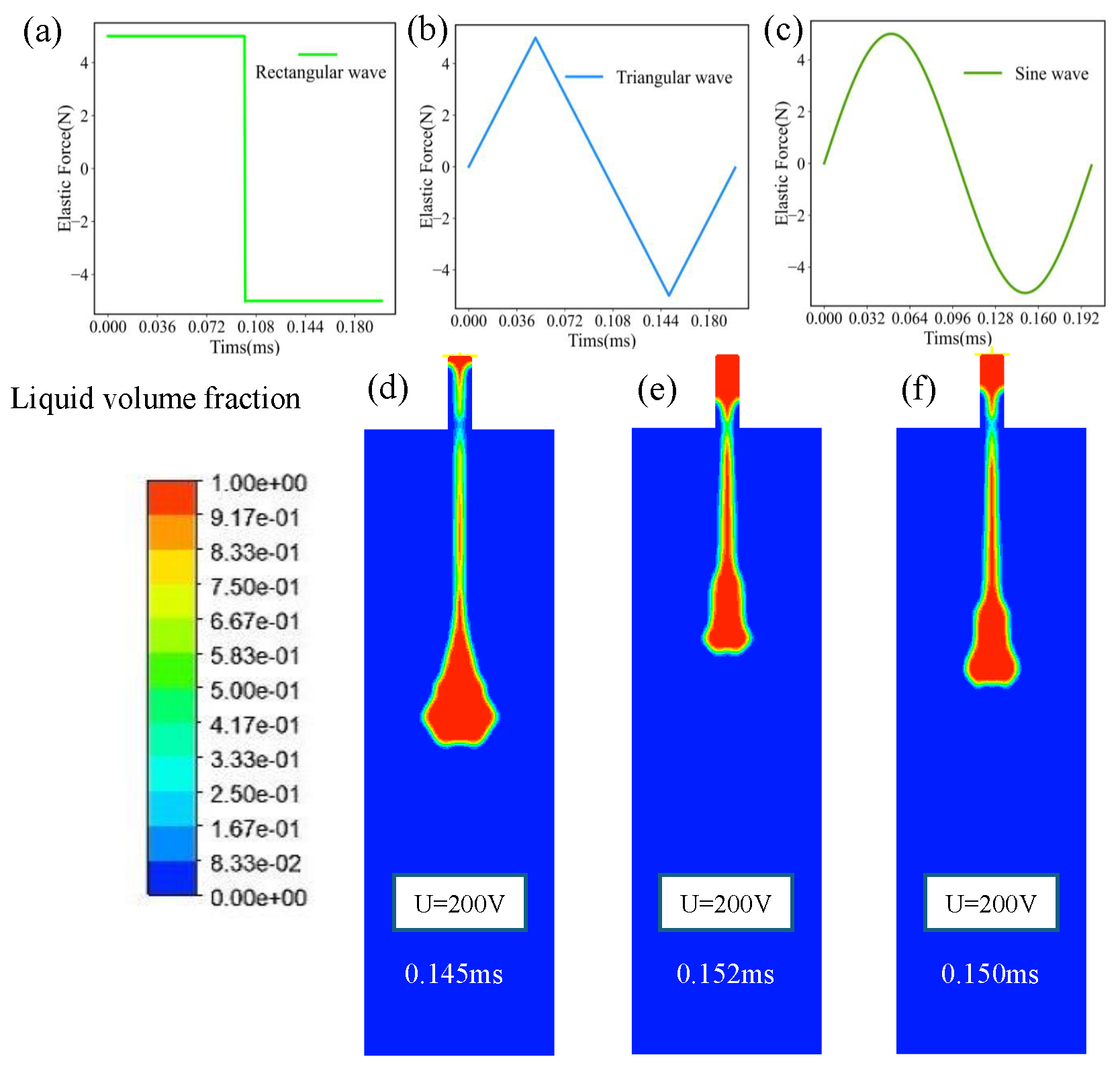
3.2. Numerical Analysis Calculation
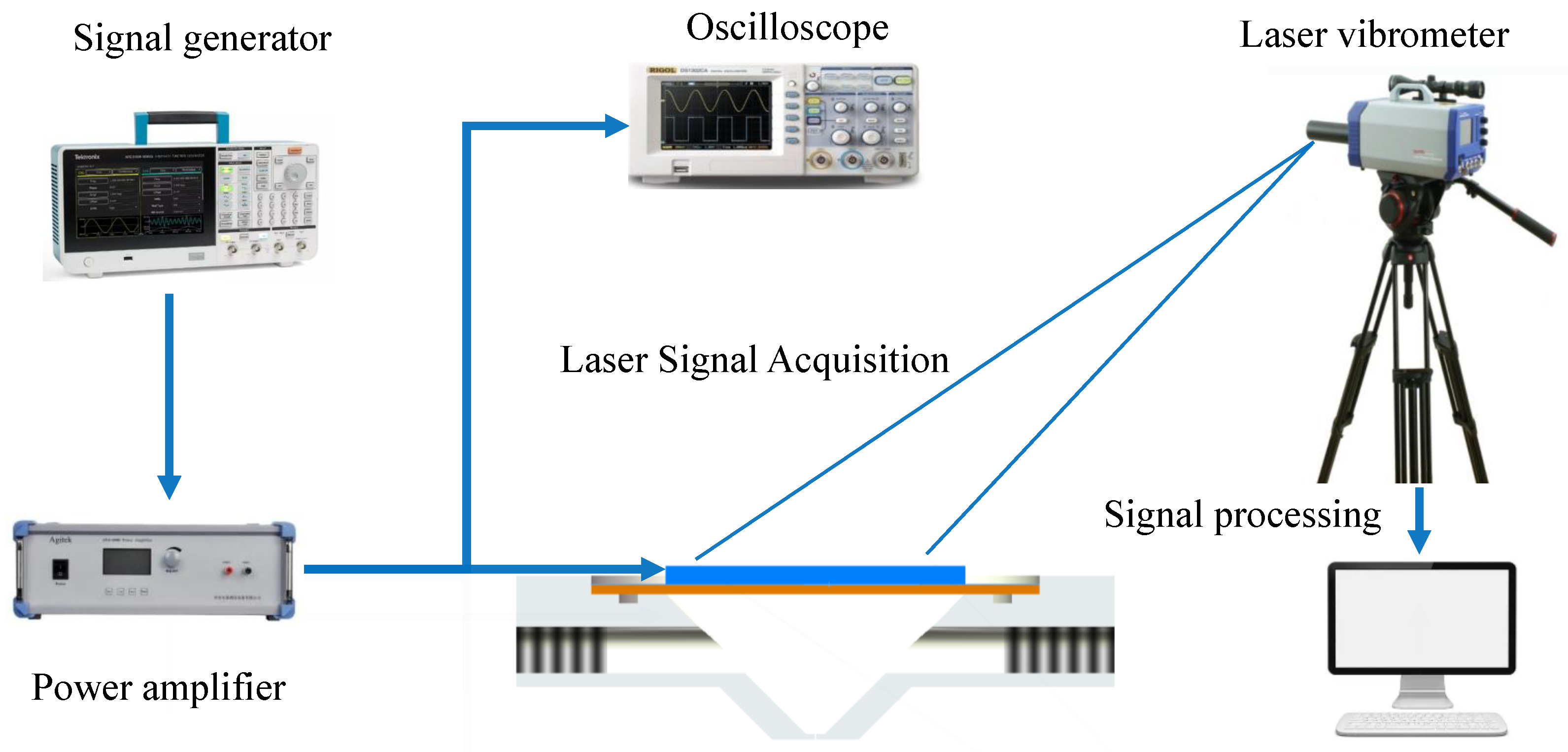
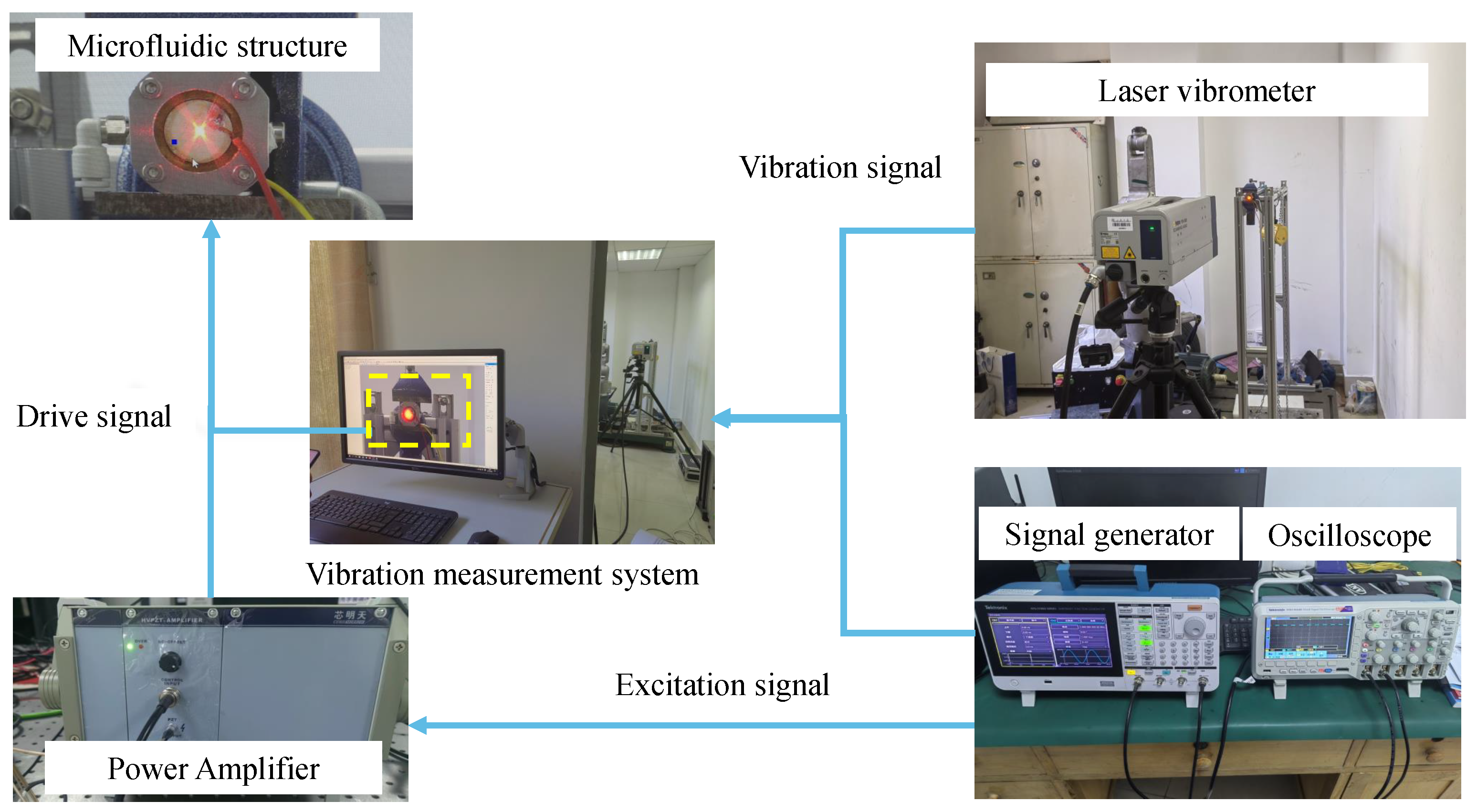
4. Experimental Device and Method
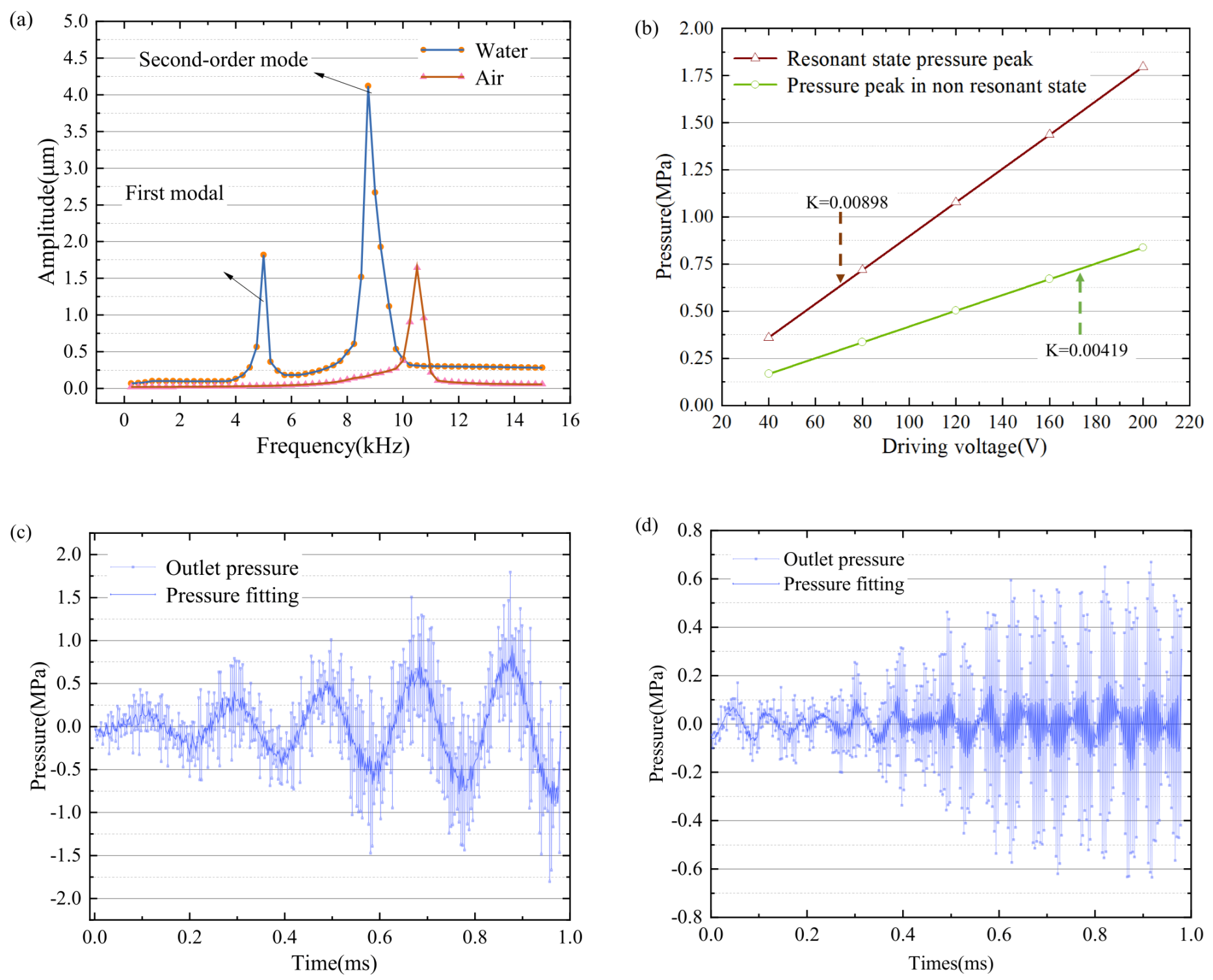
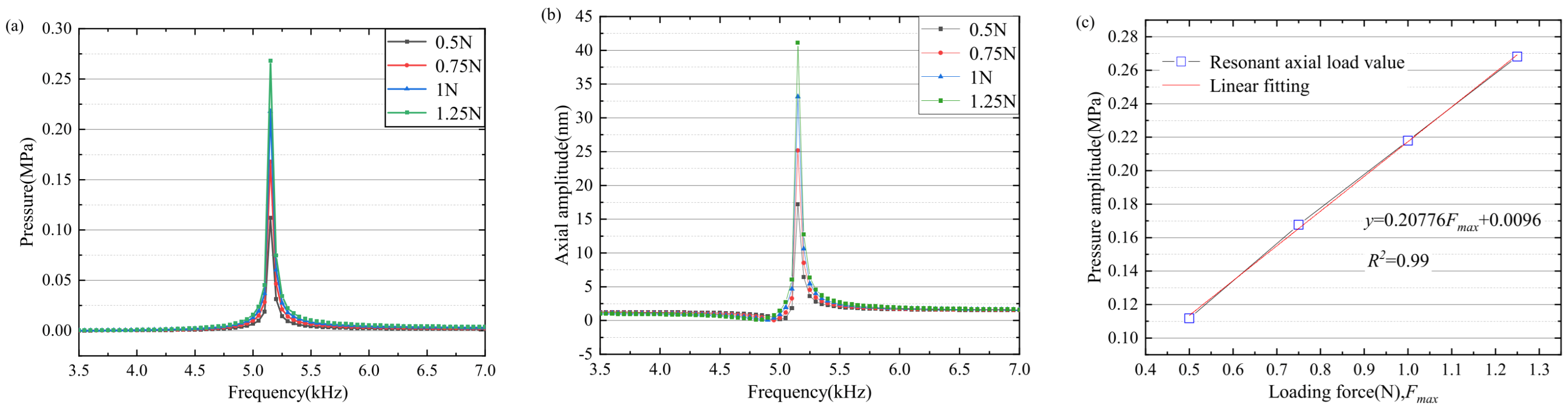
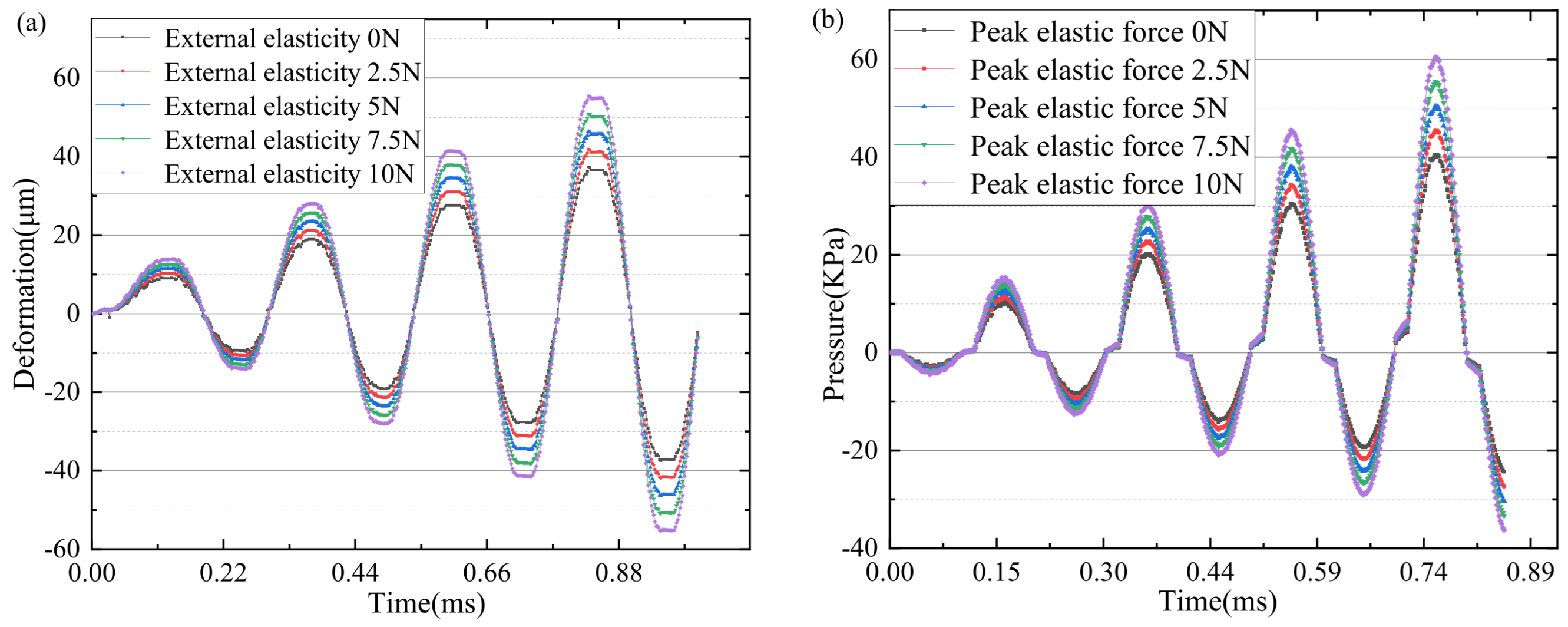
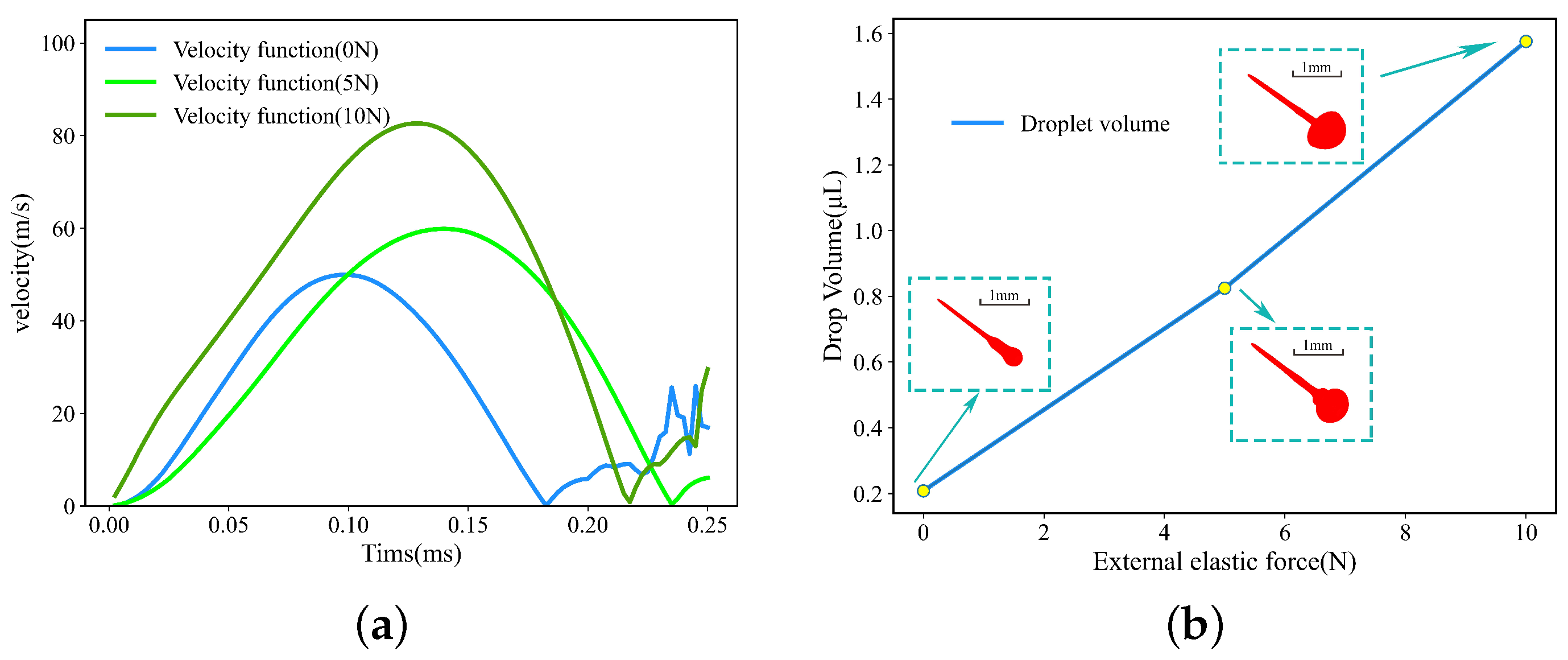
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric actuators 2008: Key factors for commercialization. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldkar, R.K.; Khalatkar, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Sheorey, T. New piezoelectric actuator design for enhance the micropump flow. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.R.; Prasad, M. Piezoelectric mems based acoustic sensors: A review. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2020, 301, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Li, M.-H.; Yang, Y.; Manzaneque, T.; Gong, S. Accurate extraction of large electromechanical coupling in piezoelectric mems resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2019, 28, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hake, A.E.; Zhao, C.; Sung, W.-K.; Grosh, K. Design and experimental assessment of low-noise piezoelectric microelectromechanical systems vibration sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 17703–17711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.; Kim, D.-I.; Duy, L.T.; Nguyen, M.T.; Muhammad, S.; Yoon, W.-S.; Lee, N.-E. High-performance flexible lead-free nanocomposite piezoelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting and storage. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naval, S.; Beigh, N.T.; Mukherjee, D.; Jain, A.; Mallick, D. Flexible v-shaped piezoelectric-triboelectric device for biomechanical energy harvesting and sensing. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 365501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liseli, J.B.; Agnus, J.; Lutz, P.; Rakotondrabe, M. An overview of piezoelectric self-sensing actuation for nanopositioning applications: Electrical circuits, displacement, and force estimation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y. A review of recent studies on non-resonant piezoelectric actuators. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 133, 106254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibas, B.; Koc, B. Single crystal piezoelectric motor operating with both inertia and ultrasonic resonance drives. Ultrasonics 2024, 136, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Behera, B.; Kumar, J. A brief review on the recent evolution in piezoelectric linear ultrasonic motors. Eng. Express 2021, 3, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, K. A 2-dof needle insertion device using inertial piezoelectric actuator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 3918–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Guo, Q.; Yang, J.; Xiao, J.; Wang, H.; Lou, Y.; Liang, X. A high-flow, self-filling piezoelectric pump driven by hybrid connected multiple chambers with umbrella-shaped valves. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 126961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y. Performance analysis of a microfluidic pump based on combined actuation of the piezoelectric effect and liquid crystal backflow effect. Micromachines 2019, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, F.D.; Brunelli, D.; Polonelli, T.; Benini, L. Structural health monitoring system with narrowband iot and mems sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16371–16380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, R.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. Effect of mechanical compliance of mounting clamp on electrical properties and vibration response of high-frequency piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer for microelectronic packaging and interconnection. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2022, 335, 113374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Xia, K.; Xu, Z. A self-supported structure hybrid triboelectric/piezoelectric nanogenerator for bio-mechanical energy harvesting and pressure sensing. Microelectron. Eng. 2022, 256, 111723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiao, F.; Song, D.; Qian, L.; Feng, Y.; Fu, B.; Dong, K.; Li, C.; Zhang, K. Research of micro area piezoelectric properties of aln films and fabrication of high frequency saw devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 199, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chen, R.; Yu, N.; Hsu, Y. A miniature circular pump with a piezoelectric bimorph and a disposable chamber for biomedical applications. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2016, 251, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Hamza, M.; Kumar, P.A.; Sravani, K.G. Design and optimization of mems based piezoelectric actuator for drug delivery systems. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Konishi, S. Small, soft and safe micro-machines for biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 Transducers-2015 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 863–866. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.-K.; Luo, W.-F.; Lin, J.-Y. Development of a piezoelectric micropump with novel separable design for medical applications. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2015, 236, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, P.; Sung, J.; Lee, M.H. Control of droplet formation for low viscosity fluid by double waveforms applied to a piezoelectric inkjet nozzle. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minov, S.V.; Cointault, F.; Vangeyte, J.; Pieters, J.G.; Nuyttens, D. Droplet generation and characterization using a piezoelectric droplet generator and high speed imaging techniques. Crop Prot. 2015, 69, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.-Y.; Wu, X.-S.; Hu, Y.-W.; Lin, X.-D.; Sun, D.-F. Injection of viscous micro-droplet via nozzle-driven piezoelectric micro-jet and its performance control method. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Sheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Han, W.; Wang, K. Squeeze-type piezoelectric inkjet printhead actuating waveform design method based on numerical simulation and experiment. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, J.H.; Sohn, D.K.; Ko, H.S. The effect of ink supply pressure on piezoelectric inkjet. Micromachines 2022, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, T.; Lian, Q.; Zhao, T.; Wang, H. Influence of ink properties and voltage parameters on piezoelectric inkjet droplet formation. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, R.; Brovelli, S.; Viviani, P.; Soldo, M.; Giusti, D.; Magagnin, L. Piezoelectric drop-on-demand inkjet printing of high-viscosity inks. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, K.; Li, H.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y. Waveform optimization of piezoelectric micro-jet for the control of metal micro-droplet ejection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, S.; Hwang, J.; Kim, Y.-J. Drop-on-demand hybrid printing using a piezoelectric mems printhead at various waveforms, high voltages and jetting frequencies. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 065011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

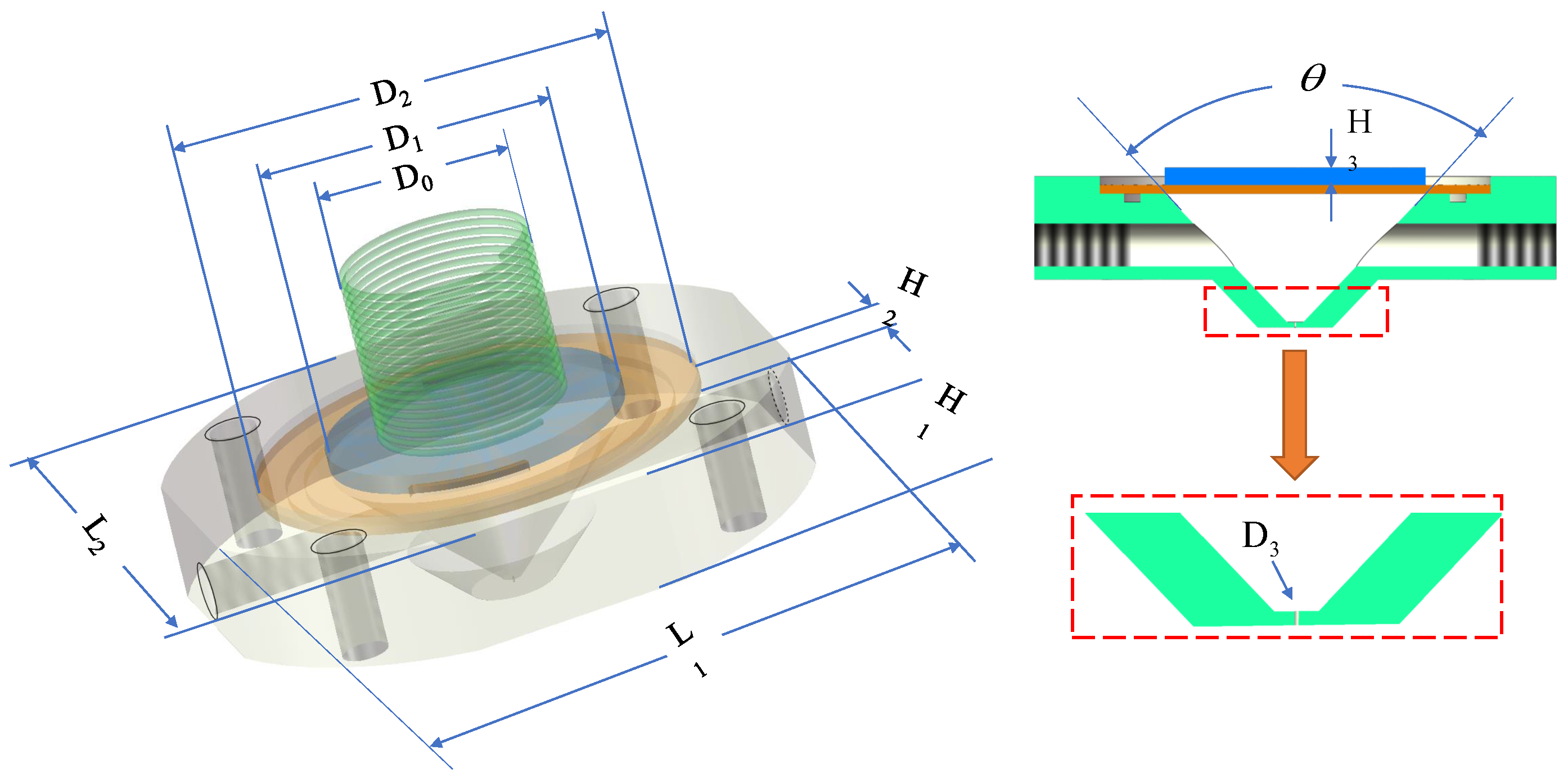



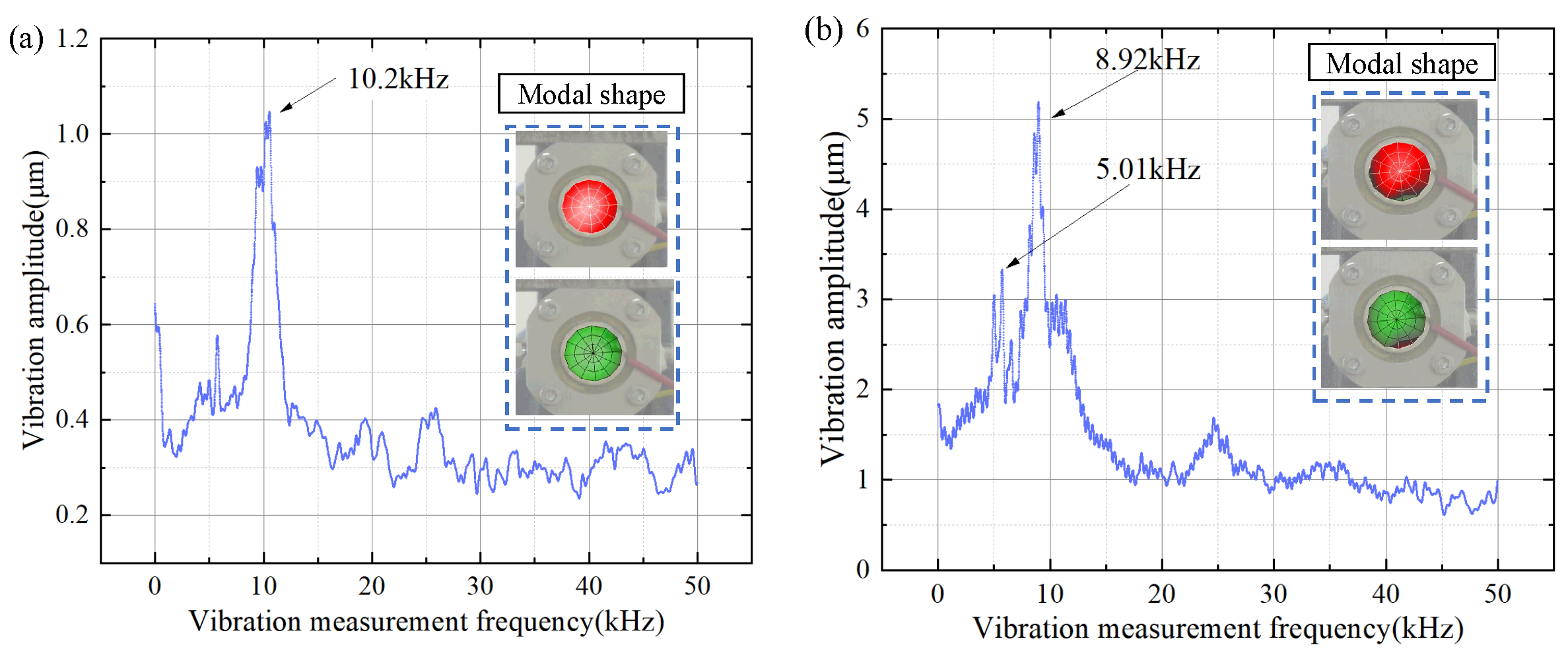
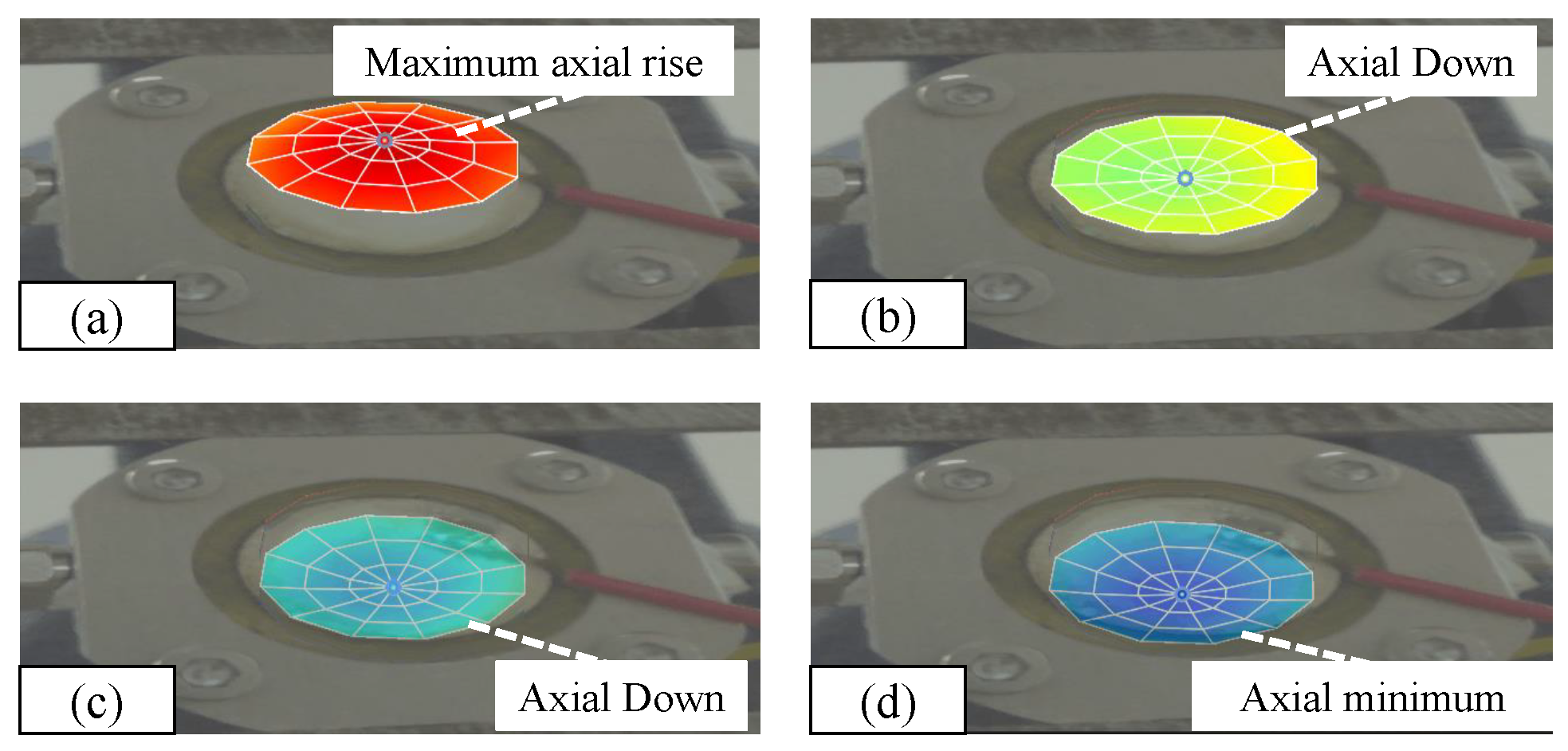
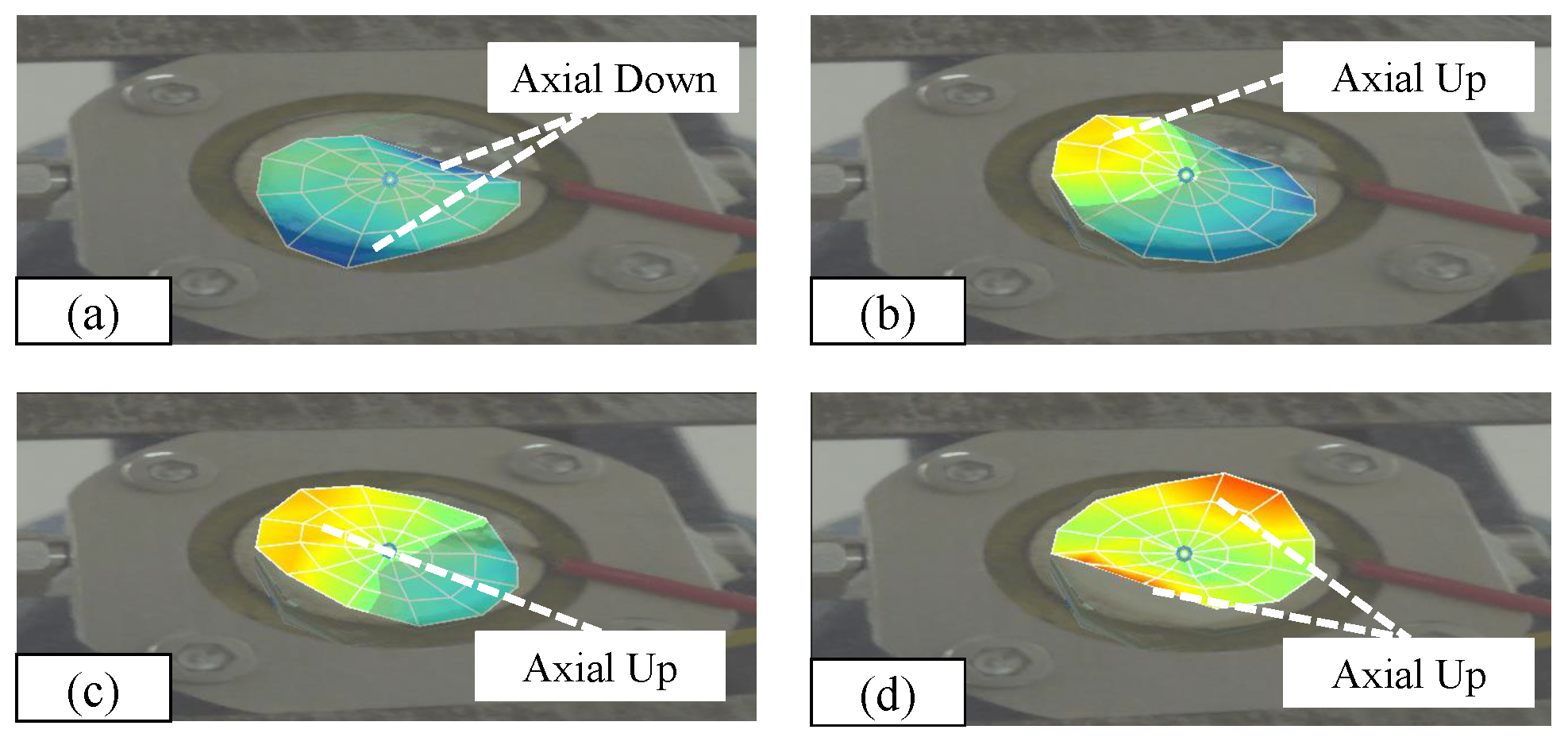
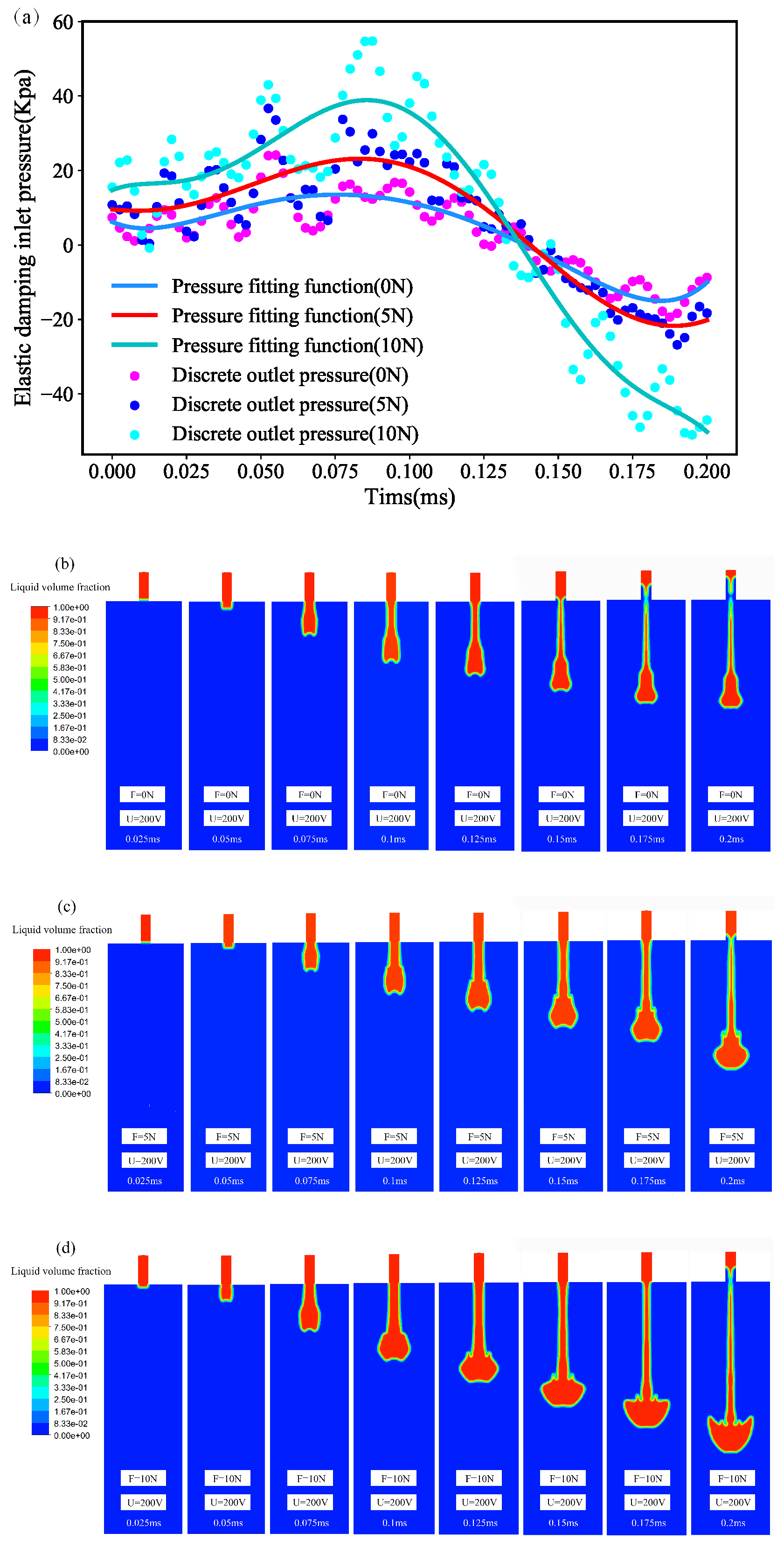
| Structural Parameters | Values | Structural Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 mm | 32 mm | ||
| 16 mm | 32 mm | ||
| 24 mm | 6 mm | ||
| 0.1 mm | 0.5 mm | ||
| 90° | 1.5 mm |
| Mode of Vibration | Mode 1 | Mode 2 | Mode 3 | Mode 4 | Mode 5 | Mode 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| water (kHz) | 5.086 | 7.704 | 7.919 | 15.092 | 15.316 | 16.224 |
| Air (kHz) | 10.632 | 27.242 | 33.507 | 36.631 | 41.016 | 43.372 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Ge, M.; Jia, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Dong, C. Design and Analysis Method of Piezoelectric Liquid Driving Device with Elastic External Displacement. Micromachines 2024, 15, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15040523
Li W, Ge M, Jia R, Zhao X, Zhao H, Dong C. Design and Analysis Method of Piezoelectric Liquid Driving Device with Elastic External Displacement. Micromachines. 2024; 15(4):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15040523
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wangxin, Mingfeng Ge, Ruihao Jia, Xin Zhao, Hailiang Zhao, and Chuanhe Dong. 2024. "Design and Analysis Method of Piezoelectric Liquid Driving Device with Elastic External Displacement" Micromachines 15, no. 4: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15040523
APA StyleLi, W., Ge, M., Jia, R., Zhao, X., Zhao, H., & Dong, C. (2024). Design and Analysis Method of Piezoelectric Liquid Driving Device with Elastic External Displacement. Micromachines, 15(4), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15040523






