A Vibrotactile Belt for Measuring Vibrotactile Acuities on the Human Torso Using Coin Motors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Measurement of Objective Parameters of the Coin Motor
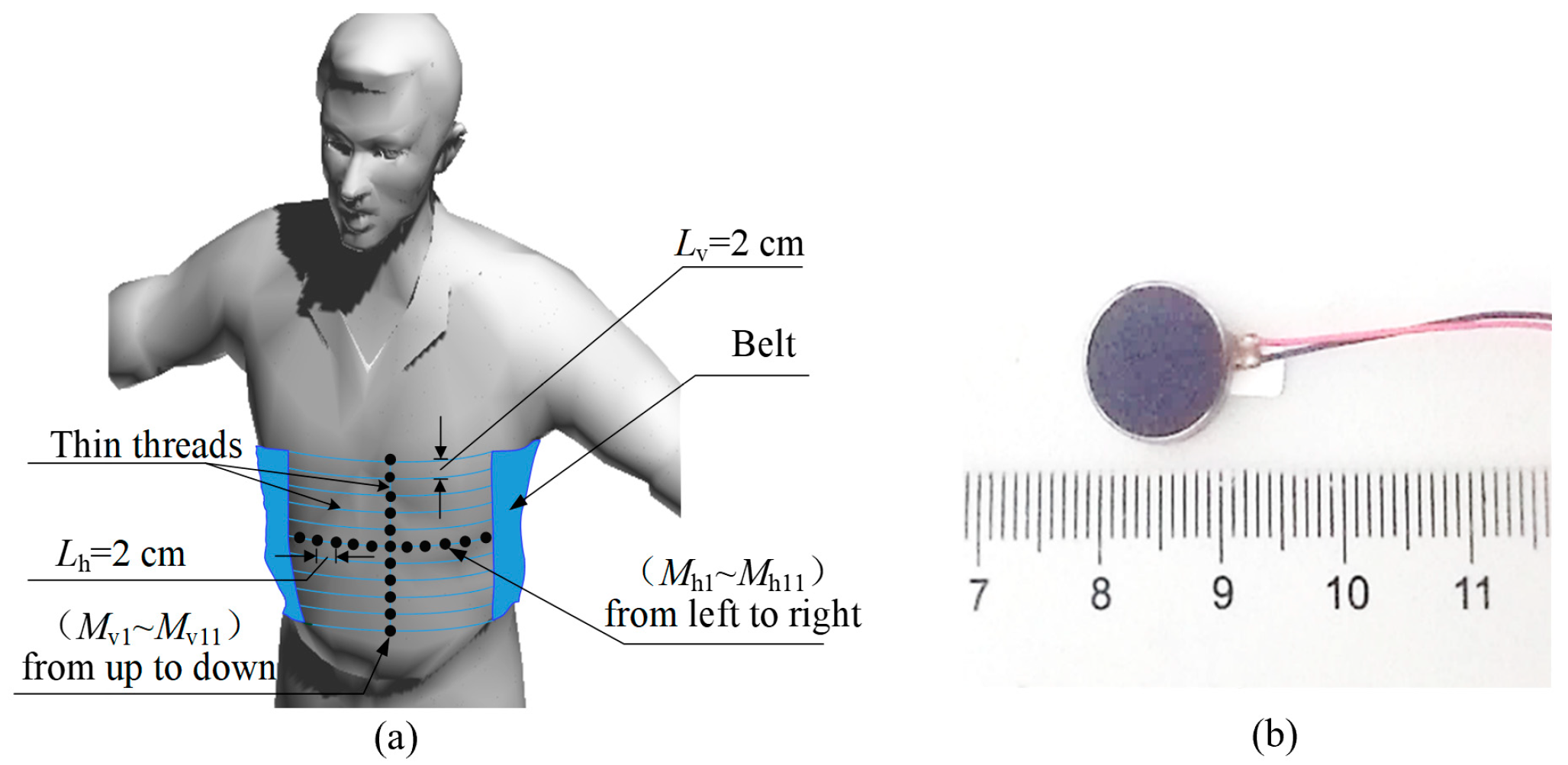
2.1. Testing Platform
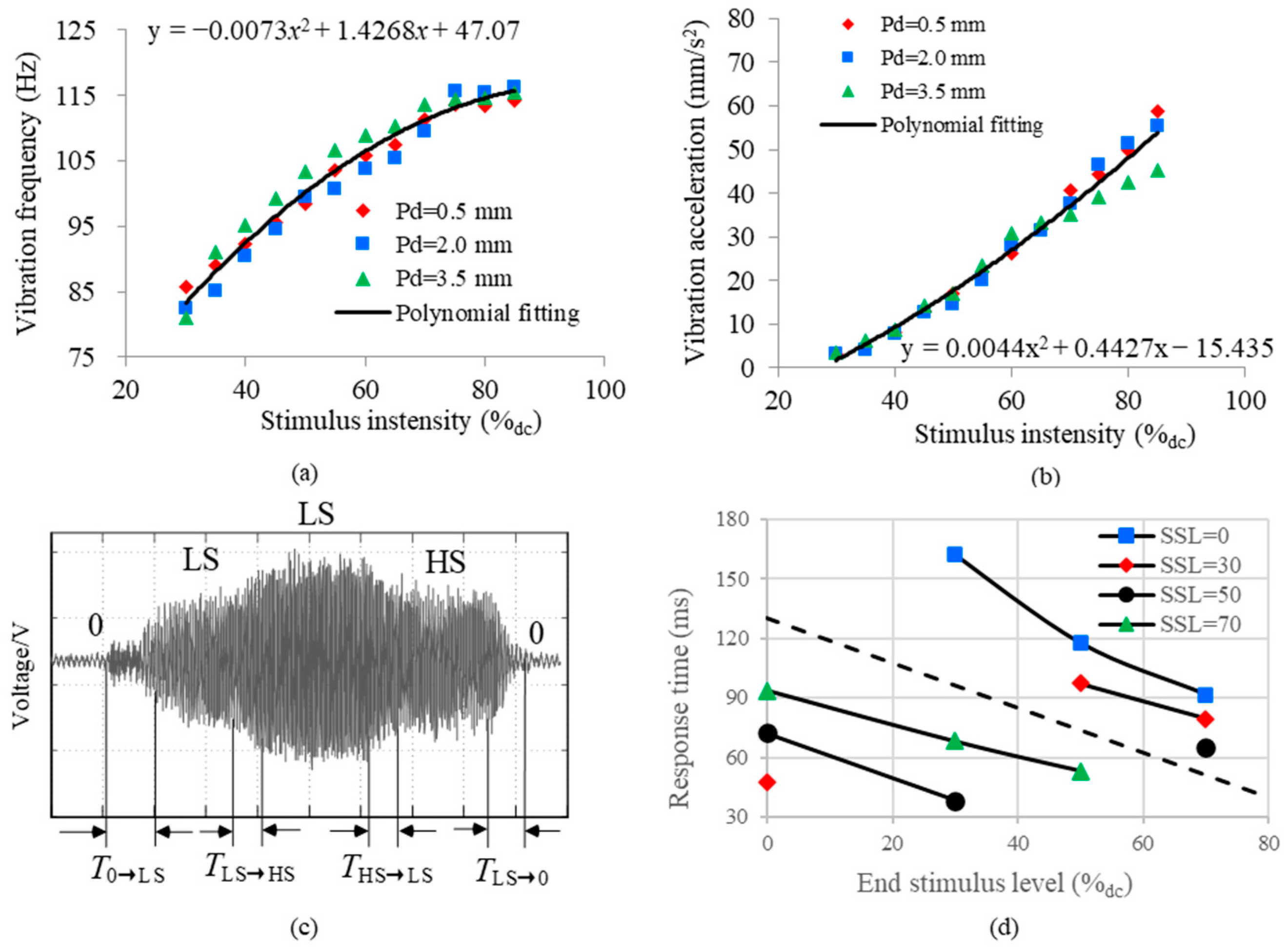
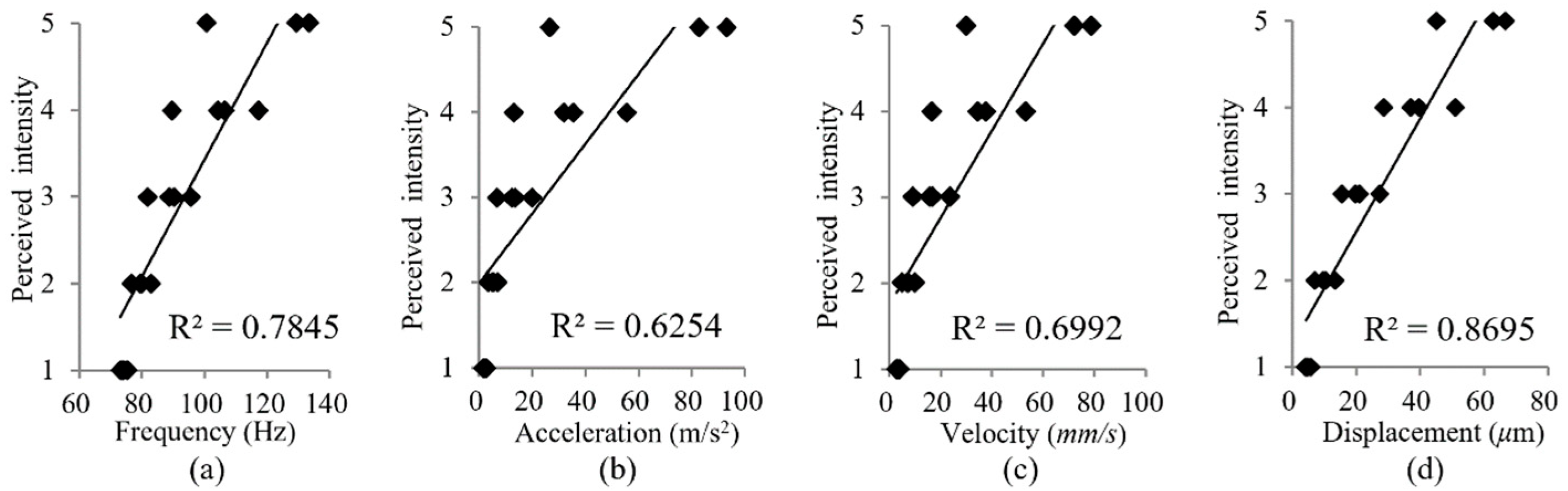
2.2. Results of Objective Testing
3. Psychophysical Study of Measuring Vibrotactile Acuities Using a Vibrotactile Belt
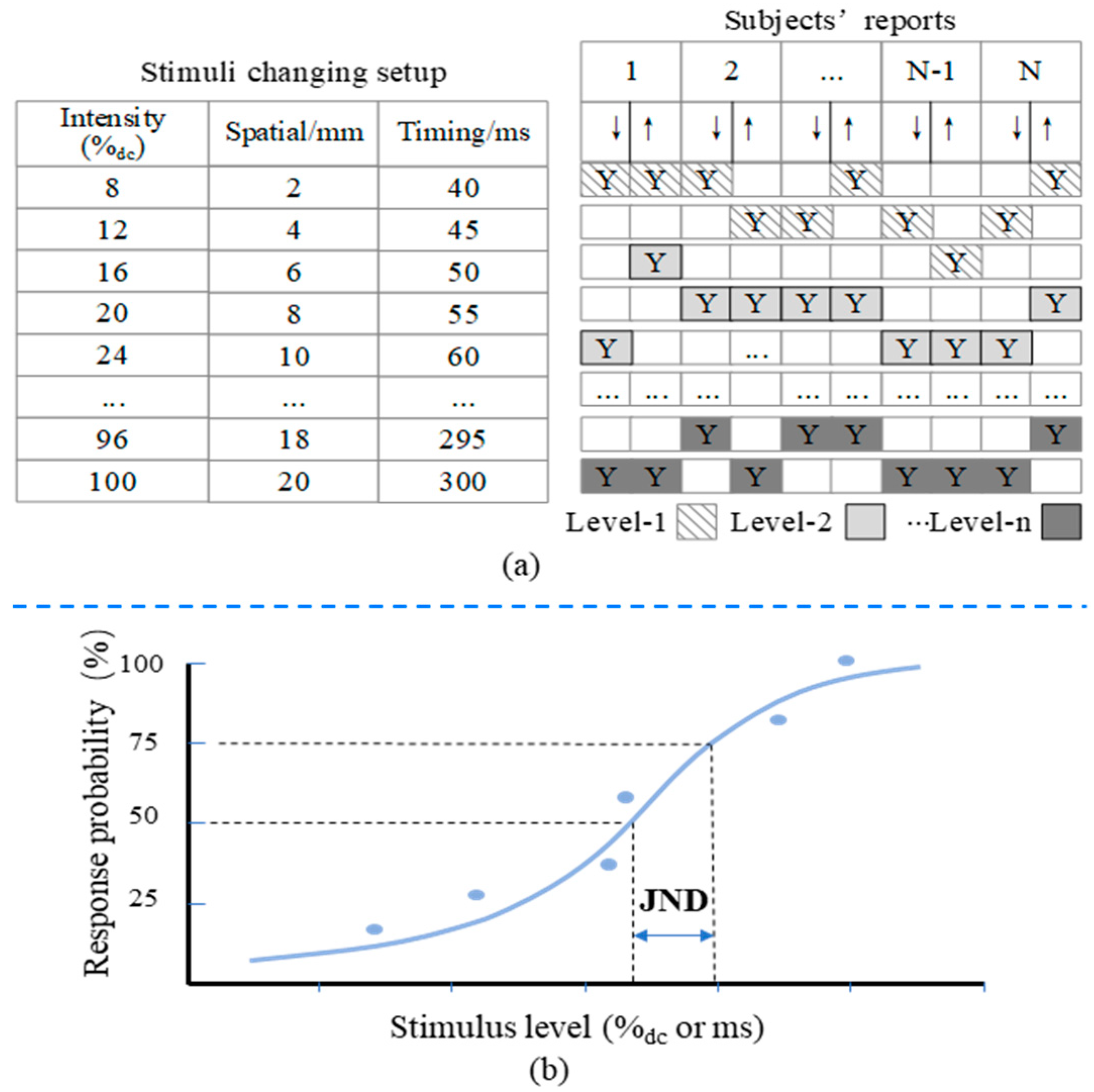
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Experimental Procedures
3.3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Relevant Studies
4.2. Application of Current Work
4.3. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cholewiak, R.W.; Brill, J.C.; Schwab, A. Vibrotactile localization on the abdomen: Effects of place and space. Percept. Psychophys. 2004, 66, 970–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, G.; Kurniawan, S.; Manduchi, R.; Martinson, E.; Morales, L.M.; Sisbot, E.A. Vibrotactile Guidance for Wayfinding of Blind Walkers. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2015, 8, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novich, S.D.; Eagleman, D.M. Using space and time to encode vibrotactile information: Toward an estimate of the skin’s achievable throughput. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 2777–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerdegari, H.; Kim, Y.; Prescott, T.J. Head-Mounted Sensory Augmentation Device: Designing a Tactile Language. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2016, 9, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Harders, M.; Gassert, R. Identification of Vibrotactile Patterns Encoding Obstacle Distance Information. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2015, 8, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Wu, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, D. A Vibrotactile Belt to Display Precise Directional Information for Visually Impaired. IEICE Electron. Express 2018, 15, 20180615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, M. Vibrotactile Display of Flight Attitude with Combination of Multiple Coding Parameters. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupert, A.H.; Lawson, B.D.; Basso, J.E. Tactile Situation Awareness System Recent Developments for Aviation. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 19–23 September 2016; SAGE Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 722–726. [Google Scholar]
- Morrell, J.; Wasilewski, K. Design and evaluation of a vibrotactile seat to improve spatial awareness while driving. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Haptics Symposium, Waltham, MA, USA, 25–26 March 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stronks, H.C.; Parker, D.J.; Barnes, N. Vibrotactile Spatial Acuity and Intensity Discrimination on the Lower Back Using Coin Motors. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2016, 9, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.A.; Lockyer, B.; Piateski, E. Tactile display and vibrotactile pattern recognition on the torso. Adv. Robot. 2006, 20, 1359–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Erp, J.B. Vibrotactile spatial acuity on the torso: Effects of location and timing parameters. In Proceedings of the First Joint Eurohaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems. World Haptics Conference, Pisa, Italy, 18–20 March 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Saddiki-Traki, F.; Tremblay, N.; Tremblay, R.W.; Derraz, S.; El-Khamlichi, A.; Harrisson, M. Differences between the tactile sensitivity on the anterior torso of normal individuals and those having suffered complete transection of the spinal cord. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 1999, 16, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Lee, H.; Choi, S. Real-Time Dual-Band Haptic Music Player for Mobile Devices. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2013, 6, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrick, C.E. A scale for rate of tactual vibration. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modarres, A.; Cruz-Hernandez, J.M.; Grant, D.A.; Ramstein, C. Haptic Feedback Using Composite Piezoelectric Actuator. US Patent 8390594B2, 5 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, L.A.; Nakamura, M.; Lockyer, B. Development of a Tactile Vest. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, 2004. HAPTICS ‘04, Chicago, IL, USA, 27–28 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Lee, W.; Kang, S. Development of Vibrotactile Pedestal With Multiple Actuators and Application of Haptic Illusions for Information Delivery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, J. Virtual reality: 5G headset coupled with full-body suit promises complete virtual immersion. Eng. Technol. 2017, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What if Skin Was the Interface to the Virtual World? Available online: http://www.charlottefuret.com/skinterface/ (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Chauvelin, C.; Sagi, T.; Coni, P.; André, J.; Jauze, C.; Lespinet-Najib, V. Haptics on a touch screen: Characterization of perceptual thresholds. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2014, 30, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, W.M.; Houtsma, A.; Durlach, N.I.; Delhorne, L.A. Multidimensional tactile displays: Identification of vibratory intensity, frequency, and contactor area. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gescheider, G.A.; Bolanowski, S.J.; Pope, J.V.; Verrillo, R.T. A four-channel analysis of the tactile sensitivity of the fingertip: Frequency selectivity, spatial summation, and temporal summation. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2009, 19, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzfeld, C.; Kern, T.A.; Werthschützky, R. Design and evaluation of a measuring system for human force perception parameters. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 162, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewiak, R.W.; Collins, A.A. Vibrotactile localization on the arm: Effects of place, space, and age. Percept. Psychophys. 2003, 65, 1058–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilska, A. On the vibrational sensitivity in different regions of the body surface. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1954, 31, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nau, A.; Bach, M.; Fisher, C. Clinical Tests of Ultra-Low Vision Used to Evaluate Rudimentary Visual Perceptions Enabled by the BrainPort Vision Device. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stronks, H.C.; Parker, D.J.; Walker, J.; Lieby, P.; Barnes, N. The Feasibility of Coin Motors for Use in a Vibrotactile Display for the Blind. Artif. Organs 2015, 39, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeno, T. Structure and function of finger pad and tactile receptors. J. Robot. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 18, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, H.T.; Darian-Smith, I.; Hans, H. The Sense of Flutter-Vibration: Comparison of the Human Capacity with Response Patterns of Mechanoreceptive Afferents From the Monkey Hand. J. Neurophysiol. 1968, 31, 301–334. [Google Scholar]
- Bikah, M.; Hallbeck, M.S.; Flowers, J.H. Supracutaneous vibrotactile perception threshold at various non-glabrous body loci. Ergonomics 2008, 51, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóhannesson, Ó.I.; Hoffmann, R.; Valgeirsdóttir, V.V.; Unnþórsson, R.; Moldoveanu, A.; Kristjánsson, Á. Relative vibrotactile spatial acuity of the torso. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 3505–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, I.R.; Cooper, P.G.; Wright, P.; Gratton, D.A.; Milnes, P.; Brown, B.H. Information from time-varying vibrotactile stimuli. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102, 3686–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.A.; Sarter, N.B. Tactile Displays: Guidance for Their Design and Application. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2008, 50, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, L.; Yan, R.; Ni, D.; Liu, W. Experimental study on virtual texture force perception using the JND Method. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2012, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, S.H. Introduction to Perception; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 883–884. [Google Scholar]
- Gescheider, G. Chapter 3: The Classical Psychophysical Methods. In Psychophysics: The Fundamentals, 3rd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.L.; Dosher, B. Adaptive Psychophysical Procedures. Vis. Res. 2013, 35, 2503–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, S.S. On the psychophysical law. Psychol. Rev. 1957, 64, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, H. The Bonferonni and Šidák corrections for multiple comparisons. Encycl. Meas. Stat. 2007, 3, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Munger, B.L.; Ide, C. The structure and function of cutaneous sensory receptors. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 1988, 51, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, R.S.; Vallbo, A.B. Tactile sensibility in the human hand: Relative and absolute densities of four types of mechanoreceptive units in glabrous skin. J. Physiol. 1979, 286, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laming, D.; Laming, D. Fechner’s Law—The normal model. In The Measurement of Sensation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cholewiak, R.W. The perception of tactile distance: Influences of body site, space, and time. Perception 1999, 28, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghout, A.; Cha, J.; El Saddik, A.; Kammerl, J.; Steinbach, E. Spatial resolution of vibrotactile perception on the human forearm when exploiting funneling illusion. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and Games, HAVE 2009, Lecco, Italy, 7–8 November 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Goldreich, D. A Bayesian perceptual model replicates the cutaneous rabbit and other tactile spatiotemporal illusions. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldreich, D.; Tong, J. Prediction, Postdiction, and Perceptual Length Contraction: A Bayesian Low-Speed Prior Captures the Cutaneous Rabbit and Related Illusions. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Ryu, J. The Haptic steering Wheel: Vibro-tactile based navigation for the driving environment. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PERCOM Workshops), Mannheim, Germany, 29 March–2 April 2010; pp. 660–665. [Google Scholar]
- Heuten, W.; Henze, N.; Boll, S.; Pielot, M. Tactile wayfinder: A non-visual support system for wayfinding. In Proceedings of the 5th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction: Building Bridges, Lund, Sweden, 20–22 October 2008; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Arasan, A.; Basdogan, C.; Sezgin, T.M. Haptic Stylus with Inertial and Vibro-Tactile Feedback. In Proceedings of the 2013 World Haptics Conference (WHC), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 14–17 April 2013; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Hayward, V. A brief taxonomy of tactile illusions and demonstrations that can be done in a hardware store. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 75, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederman, S.J.; Jones, L.A. Tactile and Haptic Illusions. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2011, 4, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Dai, W.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, R.; Hong, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, S.; Ruan, X.; et al. A Vibrotactile Belt for Measuring Vibrotactile Acuities on the Human Torso Using Coin Motors. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111341
Wang S, Dai W, Yu L, Liu Y, Yang Y, Guo R, Hong Y, Chen J, Lin S, Ruan X, et al. A Vibrotactile Belt for Measuring Vibrotactile Acuities on the Human Torso Using Coin Motors. Micromachines. 2024; 15(11):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111341
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shaoyi, Wei Dai, Lichao Yu, Yong Liu, Yidong Yang, Ruomi Guo, Yuemin Hong, Jianning Chen, Shangxiong Lin, Xingxing Ruan, and et al. 2024. "A Vibrotactile Belt for Measuring Vibrotactile Acuities on the Human Torso Using Coin Motors" Micromachines 15, no. 11: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111341
APA StyleWang, S., Dai, W., Yu, L., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Guo, R., Hong, Y., Chen, J., Lin, S., Ruan, X., Ouyang, Q., & Wang, X. (2024). A Vibrotactile Belt for Measuring Vibrotactile Acuities on the Human Torso Using Coin Motors. Micromachines, 15(11), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111341





