High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Double-Side Patterned Surfaces Prepared by CO2 Laser for Human Motion Energy Harvesting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
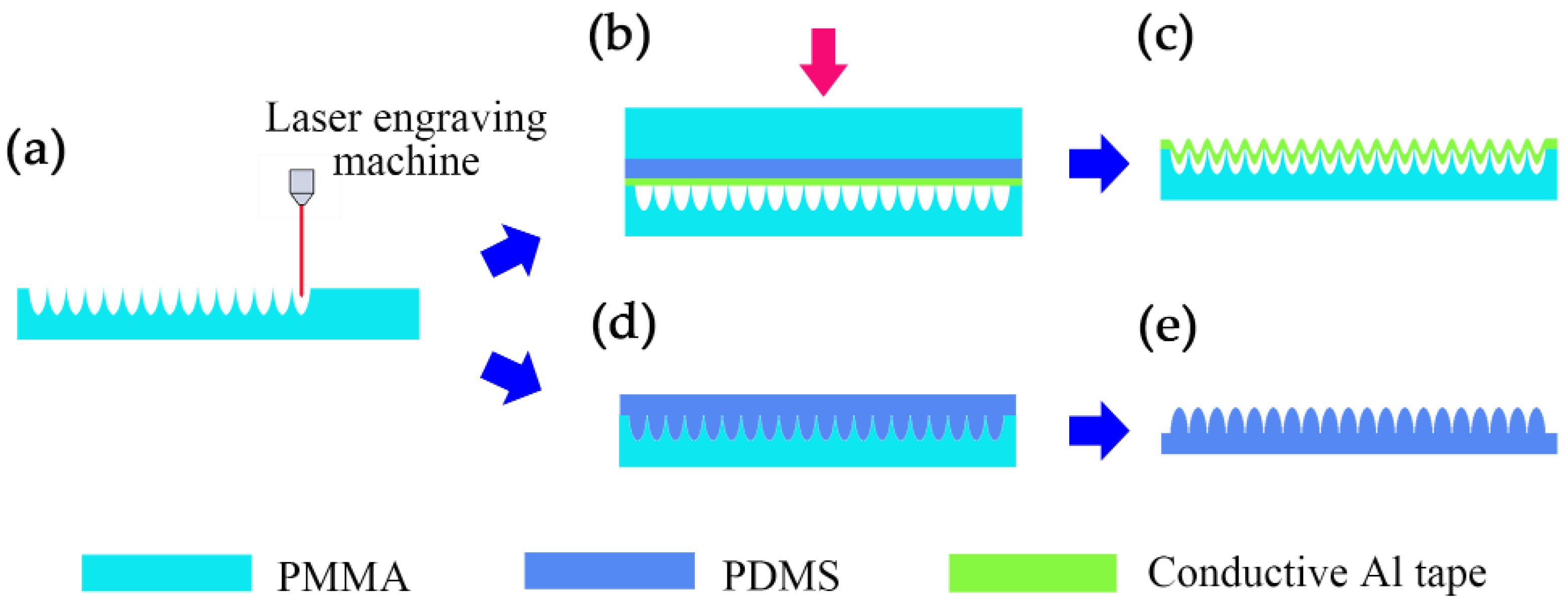
2.1. The Material Selection and Fabrication of Friction Pairs
2.2. The Measurement of MW-MC-TENG
3. Results
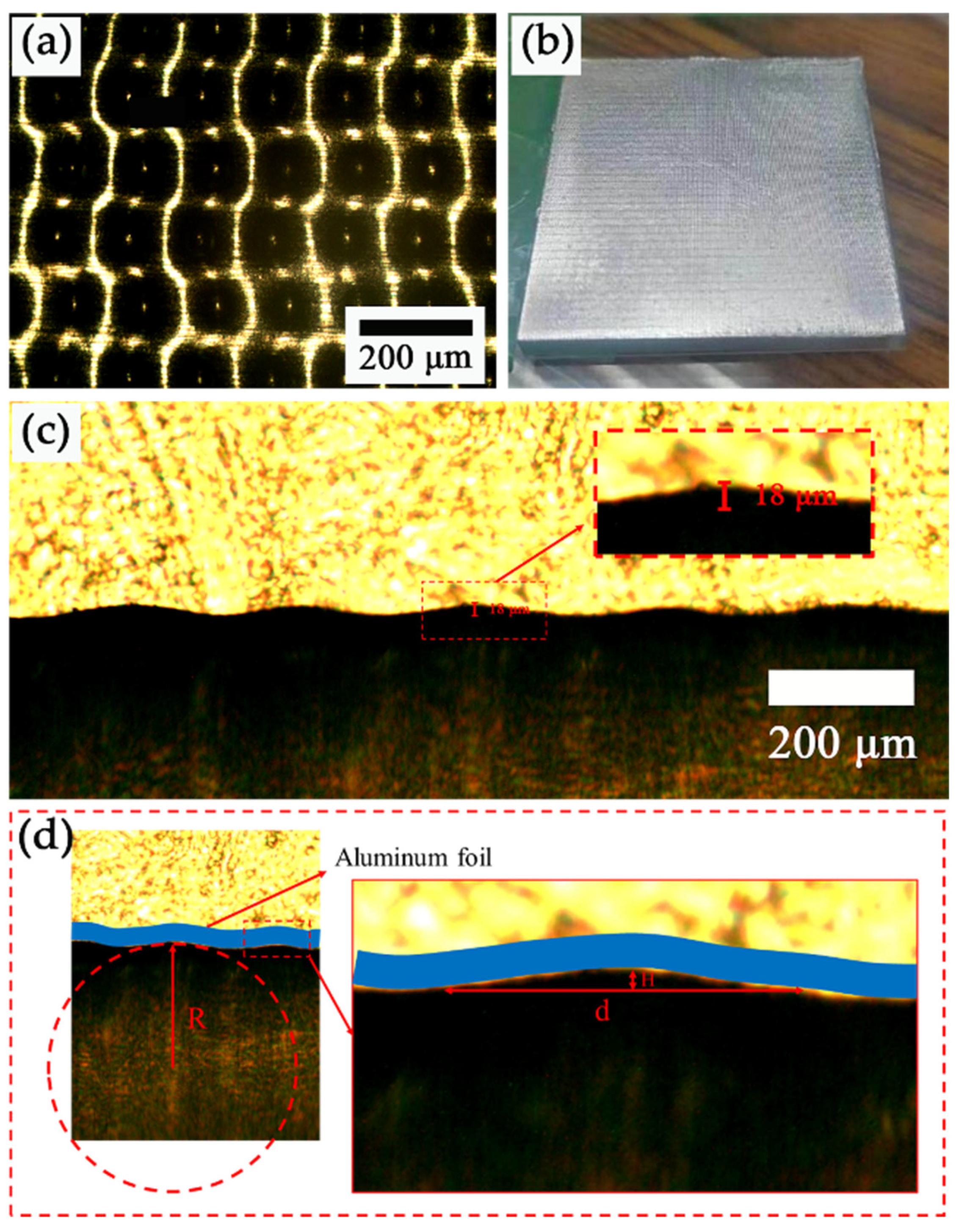
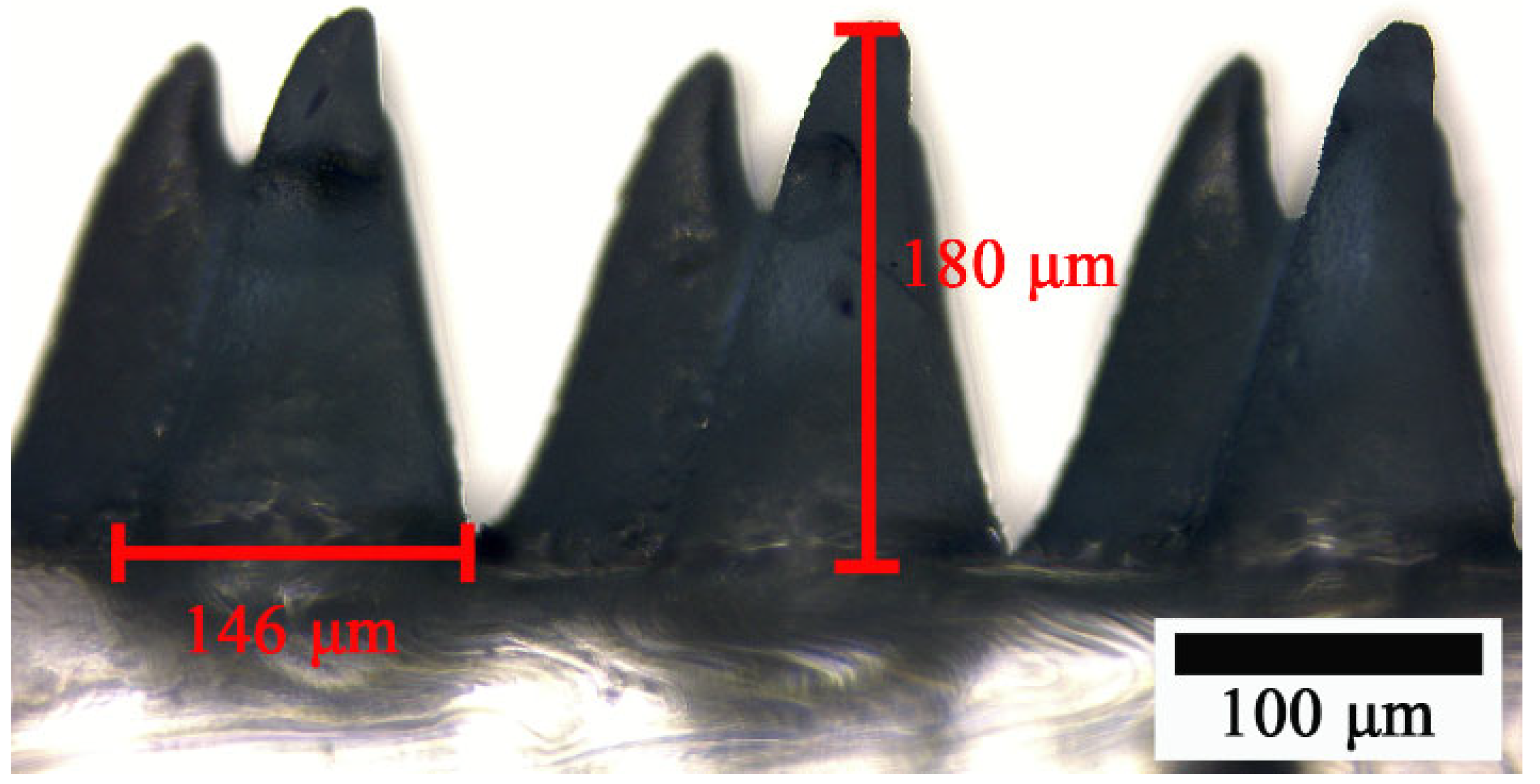
3.1. The Micromorphology Structure of the MW-Al and MC-PDMS
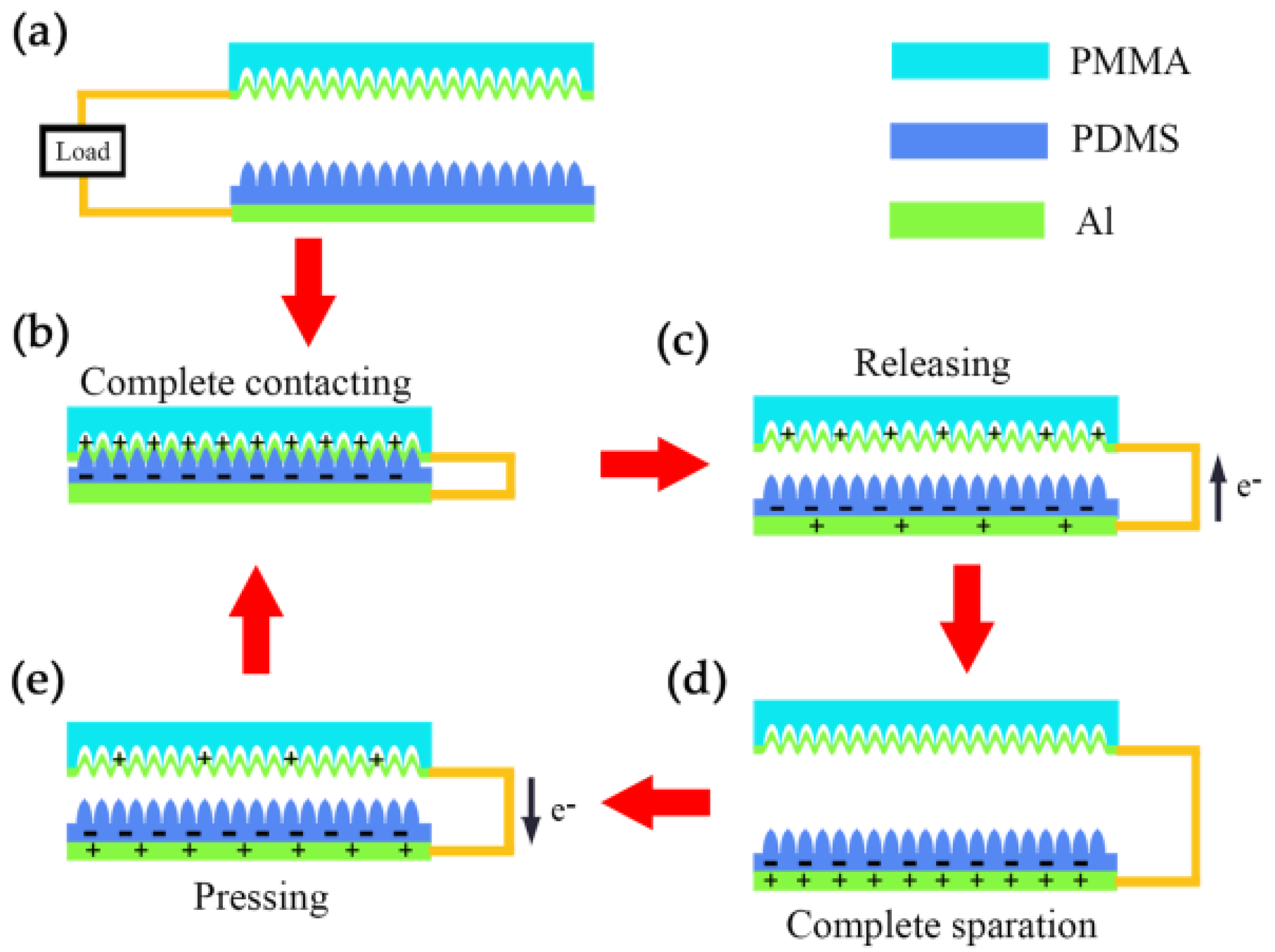
3.2. The Working Mechanism of the MW-MC-TENG
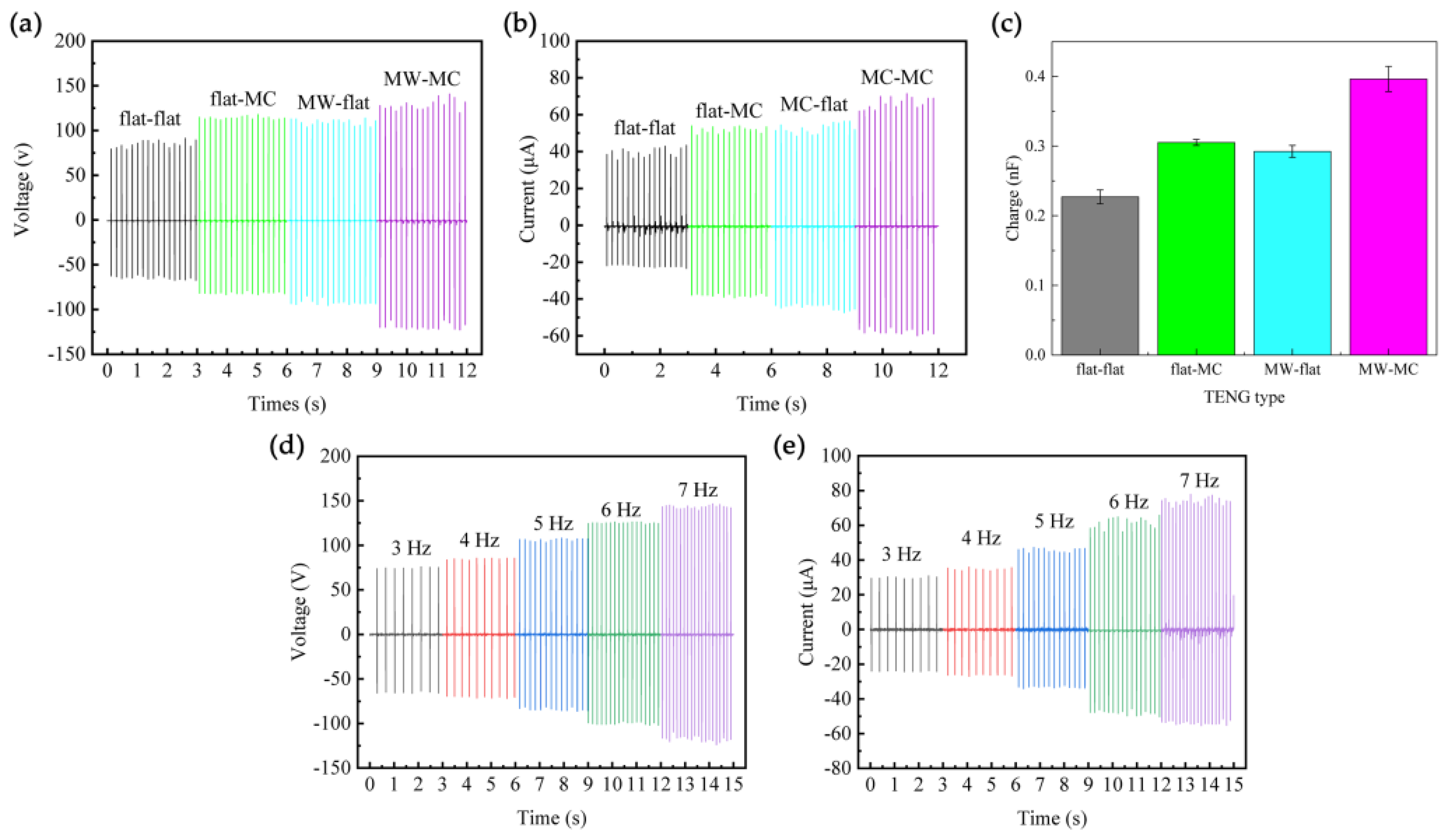
3.3. The Output Performance of the MW-MC-TENG
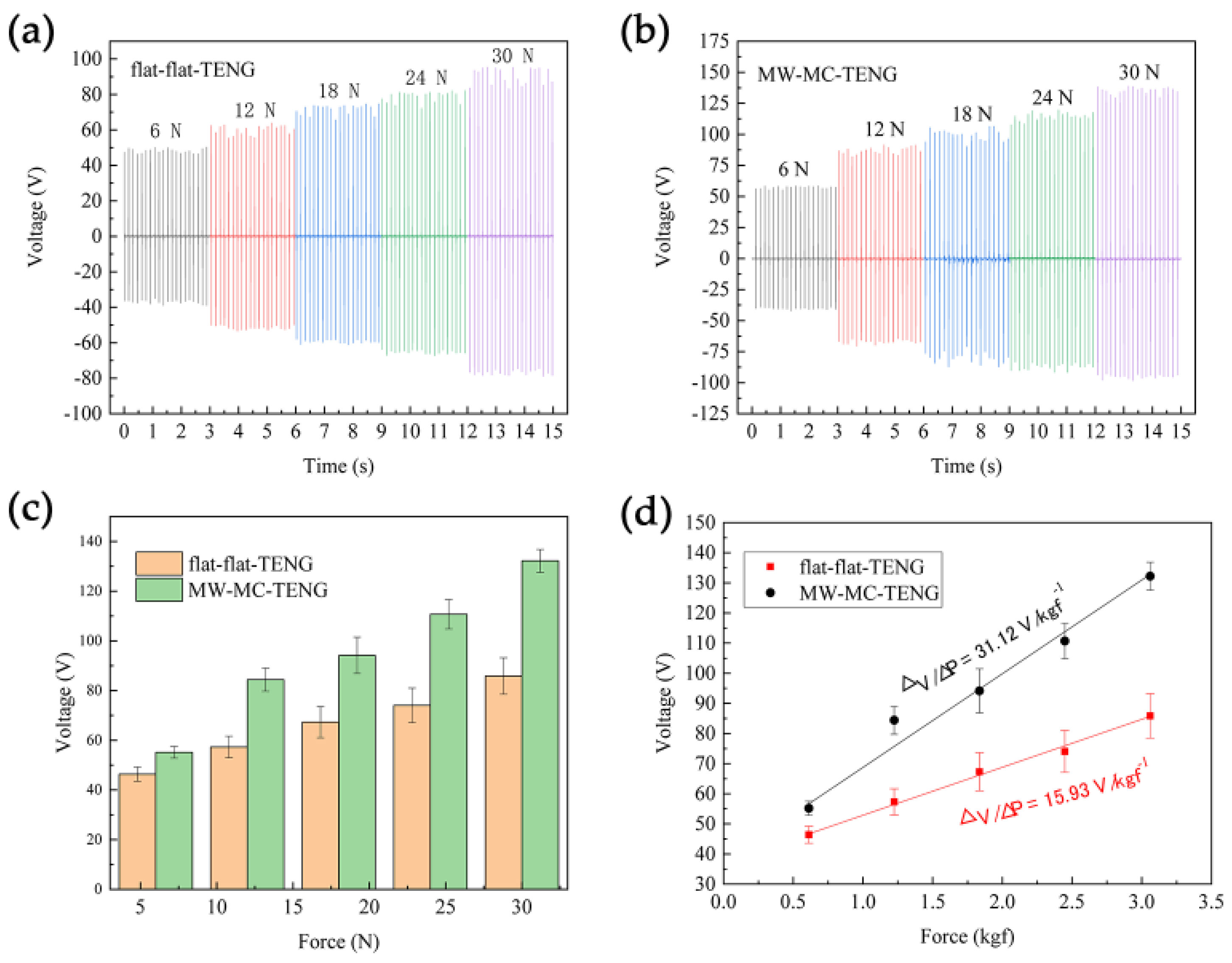
3.4. Enhancement Mechanism of the MW-MC-TENG
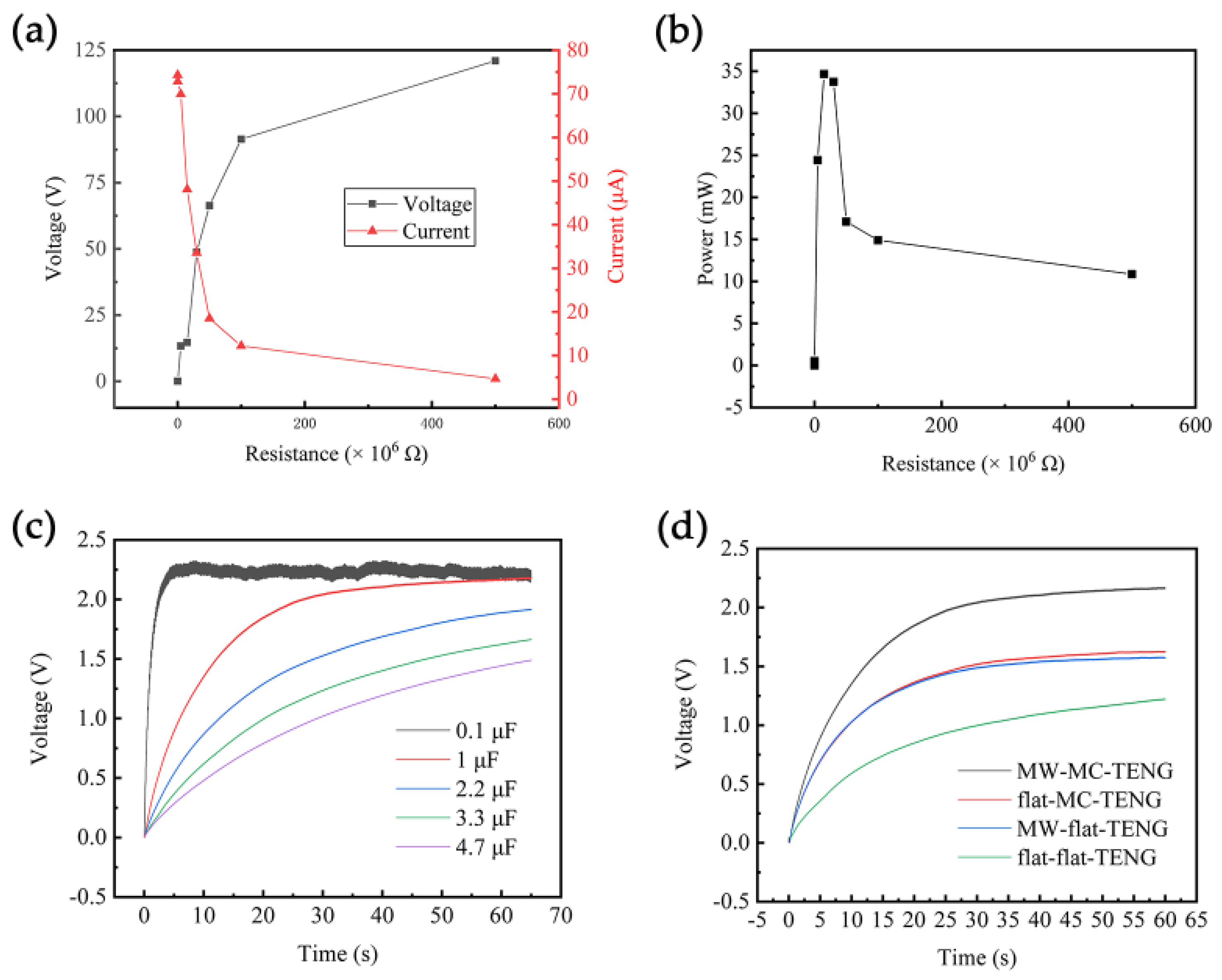
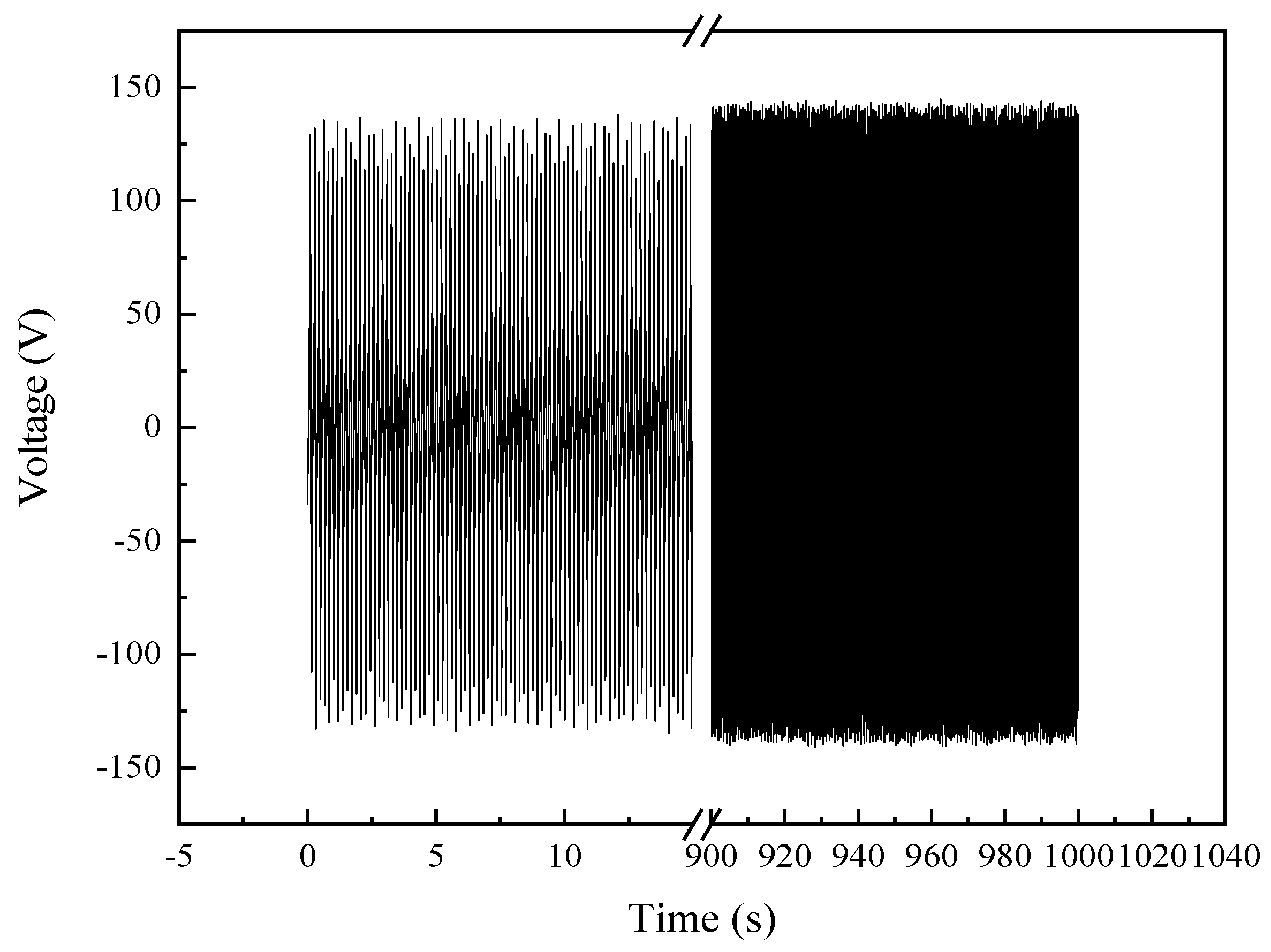
3.5. Power Generation, Energy Storage, and Durability
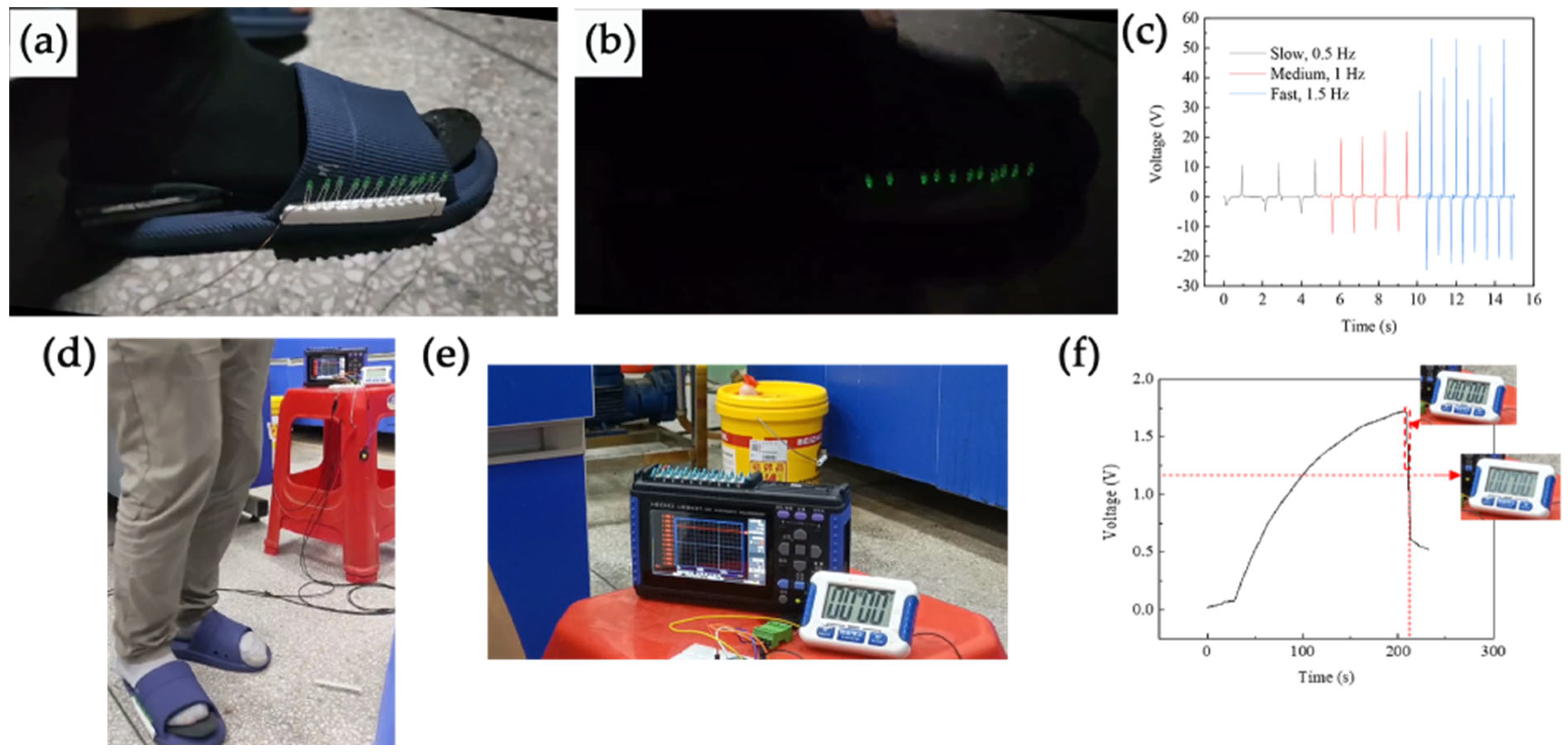
3.6. Demonstration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.H.; Yuan, H.Z.; Ji, X.P.; Yu, G.X.; Jia, X.D. Size effect of piezoelectric energy harvester for road with high efficiency electrical properties. Appl. Energy 2023, 330, 120379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Jiang, R.J.; Du, Y.; Shi, S.H.; Zhang, S.M.; Yan, Z.M.; Lin, Z.L.; Tan, T. Broadband omnidirectional piezoelectric-electromagnetic hybrid energy harvester for self-charged environmental and biometric sensing from human motion. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.M.; Cui, J.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Li, G.; Liu, T.S.; Liu, Y.B.; Hao, C.C.; Xue, C.Y. Electromagnetic-triboelectric energy harvester based on vibration-to-rotation conversion for human motion energy exploitation. Appl. Energy 2023, 329, 120292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wang, H.B.; Miao, L.M.; Chen, X.X.; Song, Y.; Guo, H.; Xu, C.; Ren, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.X. A flexible hybridized electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerator and its application for 3D trajectory sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 74, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Tian, T.; Xiao, T.X.; Yao, X.T.; Shen, S.C.; Wu, Y.S.; Liu, Y.L.; Bing, Z.S.; Huang, K.; Knoll, A.; et al. Humidity Stable Thermoelectric Hybrid Materials Toward a Self-Powered Triple Sensing System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2316088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, S.; Jia, S.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Jiang, S.; Yu, L.; Li, R.; Song, G.W.; Wang, A.B.; Martin, T.; et al. Scalable, washable and lightweight triboelectric-energy-generating fibers by the thermal drawing process for industrial loom weaving. Nano Energy 2020, 74, 104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S.W. Emerging Pyroelectric Nanogenerators to Convert Thermal Energy into Electrical Energy. Small 2021, 17, 201903469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Bowen, C.R.; Yang, Y. Phase transition enhanced pyroelectric nanogenerators for self-powered temperature sensors. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Cao, Z.Y.; Wu, Z.B.; Xing, H.T.; Ye, X.Y. All-in-One High Output Rotary Electrostatic Nanogenerators Based on Charge Pumping and Voltage Multiplying. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16861–16869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, P.S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.H. Super-Durable and Highly Efficient Electrostatic Induced Nanogenerator Circulation Network Initially Charged by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Environmental Energy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6949–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Li, Y.S.; Zou, Y.; Rao, W.; Gai, Y.S.; Xue, J.T.; Wu, L.; Qu, X.C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.D.; et al. A multi-mode triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and biomedical monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tian, J.; Peng, W.B.; Huang, D.Y.; Li, F.P.; He, Y.N. On the contact electrification mechanism in semiconductor–semiconductor case by vertical contact-separation triboelectric nanogenerator. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 295401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhao, D.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.L.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T.H. Contact-sliding-separation mode triboelectric nanogenerator. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 3932–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.H.; Yang, H.K.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, Q.Y.; Yang, Q.X.; Li, X.C.; Ji, P.Y.; Yu, P.; Xi, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Ultra-High DC and Low Impedance Output for Free-Standing Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Pan, C.F. Progress in nanogenerators for portable electronics. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jie, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators Driven Self-Powered Electrochemical Processes for Energy and Environmental Science. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Catch wave power in floating nets. Nature 2017, 542, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and self-powered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.R.; Zhao, Z.H.; Gao, Y.K.; Nan, Y.; Hu, Y.X.; Guo, Z.T.; Qiao, W.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.L.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Triboelectric nanogenerators exhibiting ultrahigh charge density and energy density. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 3819–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, J.Y.; Peng, Y.; Guo, H.Y. Standardized Volume Power Density Boost in Frequency-Up Converted Contact-Separation Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Research 2023, 6, 0237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guess, M.; Soltis, I.; Rigo, B.; Zavanelli, N.; Kapasi, S.; Kim, H.; Yeo, W.-H. Wireless batteryless soft sensors for ambulatory cardiovascular health monitoring. Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xie, Y.N.; Niu, S.M.; Wang, S.H.; Yang, P.K.; Wang, Z.L. Robust triboelectric nanogenerator based on rolling electrification and electrostatic induction at an instantaneous energy conversion efficiency of ~55%. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, H.M.; Choi, Y.K. Large-sized sandpaper coated with solution-processed aluminum for a triboelectric nanogenerator with reliable durability. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.L.; Niu, S.M.; Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Standards and figure-of-merits for quantifying the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Pressure Sensors Based on Micropatterned Plastic Films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.G.; Jiang, S.Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, N.Y.; Ding, J.N.; Zhang, W. Effect of argon plasma treatment on the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 412, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.L.; Zhang, B.B.; Jin, L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chu, W.J.; Zhang, H.T.; Zhu, M.H.; Yang, W.Q. Enhanced performance of ZnO microballoon arrays for a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 135401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, V.L.; Chung, C.K. A Facile Method and Novel Mechanism Using Microneedle-Structured PDMS for Triboelectric Generator Applications. Small 2017, 13, 1700373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Xu, L.; Cheng, X.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, H. Bioinspired Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Self-Powered Electronic Skin for Robotic Tactile Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Q.; Xu, B.A.; Li, Z.H.; Gao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Huang, X.X. Toward 3D double-electrode textile triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable biomechanical energy harvesting and sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasel, M.S.; Maharjan, P.; Salauddin, M.; Rahman, M.T.; Cho, H.O.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.Y. An impedance tunable and highly efficient triboelectric nanogenerator for large-scale, ultra-sensitive pressure sensing applications. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.S.; Ye, B.U.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, D.; Kang, C.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Baik, J.M. Boosted output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator via electric double layer effect. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Jeong, C.K.; Seo, M.H.; Joe, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Yoon, J.B.; Lee, K.J. Performance-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator enabled by wafer-scale nanogrates of multistep pattern downscaling. Nano Energy 2017, 35, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jun, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, H. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerators with artificially well-tailored interlocked interfaces. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, B.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.M.; Shen, G.Z. Surface Control and Electrical Tuning of MXene Electrode for Flexible Self-Powered Human–Machine Interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chung, C.K. PDMS Microfabrication and Design for Microfluidics and Sustainable Energy Application: Review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.L.; Xia, Y.F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, M.; Jia, C.Y.; Wang, X. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator powered flexible electroluminescence devices based on patterned laser-induced copper electrodes for visualized information interaction. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.H.; Lin, L.; Chung, C.K. Low-cost micro-graphite doped polydimethylsiloxane composite film for enhancement of mechanical-to-electrical energy conversion with aluminum and its application. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 135, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, V.L.; Chung, C.K. Harvesting mechanical energy, storage, and lighting using a novel PDMS based triboelectric generator with inclined wall arrays and micro-topping structure. Appl. Energ. 2018, 213, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Ke, K.H. High contact surface area enhanced Al/PDMS triboelectric nanogenerator using novel overlapped microneedle arrays and its application to lighting and self-powered devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, L.B.; Tao, X.M.; Li, L.X. Ultra-Flexible and Large-Area Textile-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators with a Sandpaper-Induced Surface Microstructure. Materials 2018, 11, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Lv, X.; Yang, L.P.; Niu, M.Y.; Liu, J.C. A High-Performance Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Double-Sided Patterned TiN/PDMS Composite Film for Human Energy Harvesting. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2100665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, G.; Graham, S.A.; Yu, J.S.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, D.W. Investigated a PLL surface-modified Nylon 11 electrospun as a highly tribo-positive frictional layer to enhance output performance of triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered wearable sensors. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajula, P.; Muhammad, F.M.; Reza, M.S.; Jaisankar, S.N.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, H.D. Fabrication of a silicon elastomer-based self-powered flexible triboelectric sensor for wearable energy harvesting and biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Morphology | Material | Fabrication Method | Operation Condition | Electrical Characteristics | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voc (V) | Isc (µA) | Power Density (mW/cm2) | |||||
| Microcone–microcone | PDMS@AgNWs-PDMS@ PTFE tiny burrs | Replication and molding, spray coating, evaporation and reactive ion etching | 25 kPa, 0.6 Hz | 3.14 | 0.0263 | - | [29] |
| Yarn–yarn | TPU-PDMS | Coating | 150 N, 6 Hz | 76 | 3 | ~0.02 | [30] |
| Nanogrit–nanogrit | PDMS@CNT-PDMS | Spin casting, dispersion and magnetic stirring | 450 kPa, 1 Hz | 92 | 55 | 0.007 | [31] |
| Micropore–nanoparticles | Al/porous PDMS-Al@Au NPs | Spin coating and curing | 50 N 10 Hz | ~120 | ~0.125 | - | [32] |
| Nano roughened structure–nanograting | PET-Au | Magnetron sputtering, inductively coupled plasma (ICP) | 10 Hz | ~125 | ~31.2 | ~0.32 | [33] |
| Nanopillar–Nanopillar | Ni-PDMS | Spin coating, electrodeposition | 10 kgf, 3 Hz | ~100 | ~23 | - | [34] |
| MW-Al and MC-PDMS | Al/PDMS/Al | CO2 laser ablation, cold imprinting | 30 N 6 Hz | 141 | 71.5 | 1.4 | ours |
| Combination | Patterning Type | Structure of Al | Structure of PDMS | Electrical Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voc (V) | Isc (µA) | J (µA/cm2) | ||||
| flat-flat | Nonpatterned | Flat | Flat | 91.5 | 43.5 | 1.74 |
| flat-MC | Single-Sided | Flat | Microcone | 118 | 54 | 2.16 |
| MW-flat | Single-Sided | Microwave | Flat | 114 | 56.5 | 2.26 |
| MW-MC | Double-Sided | Microwave | Microcone | 141 | 71.5 | 2.86 |
| Items | Symbol | MW-Al | Flat-Al |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size (cm2) | 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 | |
| The square sample length (mm) | L | 50 | 50 |
| Average MW center depth (μm) | H | 18 | - |
| Average MW bottom diameter (μm) | d | 201.6 | - |
| Average MW bottom radius (μm) | r | 100.8 | - |
| Average MW spherical radius (μm) | R | 365 | - |
| Average MW estimated surface area (μm2) | S | 41,259.6 | - |
| Number of MWs | N | 40,000 | - |
| Grain density (number of MWs/cm2) | 1600 | - | |
| Estimated surface area (Contact area) (mm2) | CS | 2874.2 | 2500 |
| Estimated voltage (V) | 128.9 | 85.0 | |
| Estimated current (μA) | 65.8 | 57.2 | |
| Measured voltage (V) | 141 | 91.5 | |
| Measured current (μA) | 71.5 | 43.5 |
| Device | Patterning Type | Area (mm2) | Frequency (Hz) | Voltage (V) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3000-T-TENG | Single-side | 50 × 60 | ~4 | ~4 | [41] |
| DSP-TiN/PDMS-based TENG | Single-side | 40 × 40 | ~5 | 6 | [42] |
| EC10S+PNy 11 TENG | Double-side | 20 × 20 | 2 | 2 | [43] |
| SF-TES | Double-side | 20 × 20 | ~1.5 | 4 | [44] |
| 3D-FTENG | Double-side | 28 × 30 | 1.5 | 40 | [30] |
| MW-MC-TENG | Double-side | 50 × 50 | 1.5 | 55 | Ours |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, D.-Y.; Chung, C.-K. High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Double-Side Patterned Surfaces Prepared by CO2 Laser for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111299
Lin D-Y, Chung C-K. High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Double-Side Patterned Surfaces Prepared by CO2 Laser for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines. 2024; 15(11):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111299
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Dong-Yi, and Chen-Kuei Chung. 2024. "High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Double-Side Patterned Surfaces Prepared by CO2 Laser for Human Motion Energy Harvesting" Micromachines 15, no. 11: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111299
APA StyleLin, D.-Y., & Chung, C.-K. (2024). High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Double-Side Patterned Surfaces Prepared by CO2 Laser for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines, 15(11), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111299







