Inverted Red Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes with ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Zinc Acetate Dihydrate and Potassium Hydroxide in Open and Closed Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
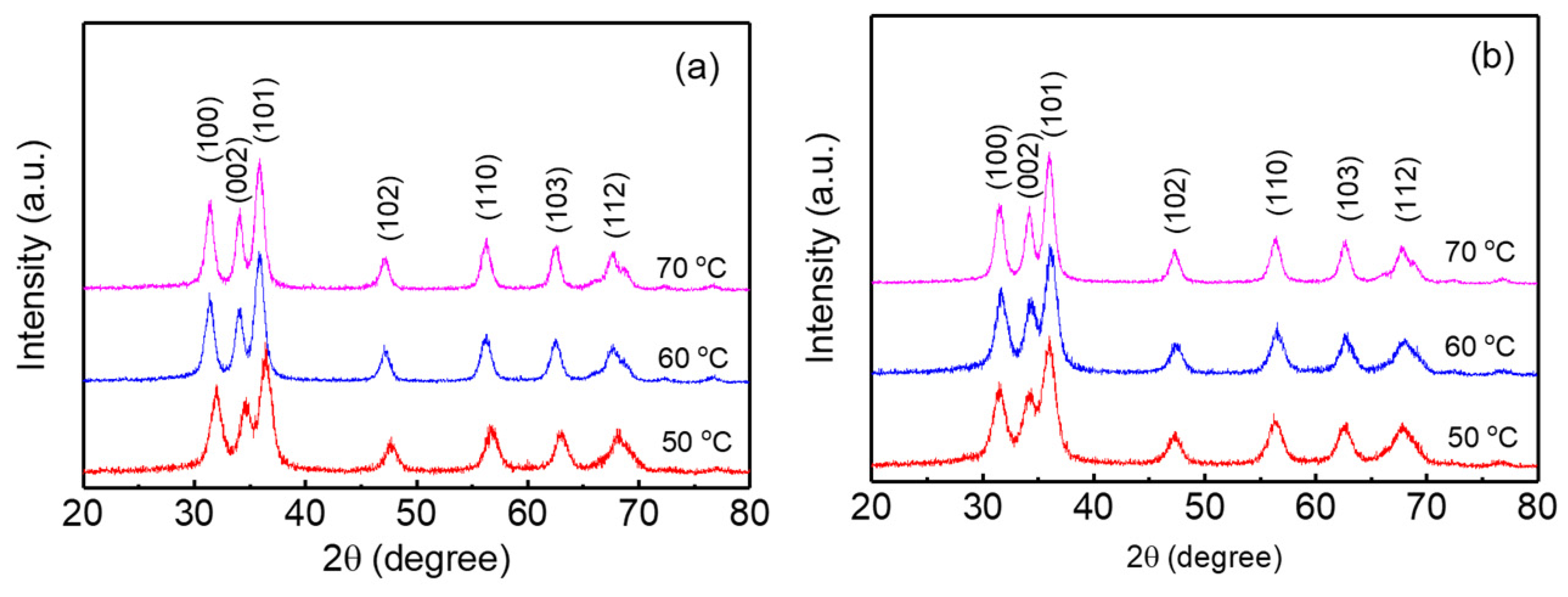
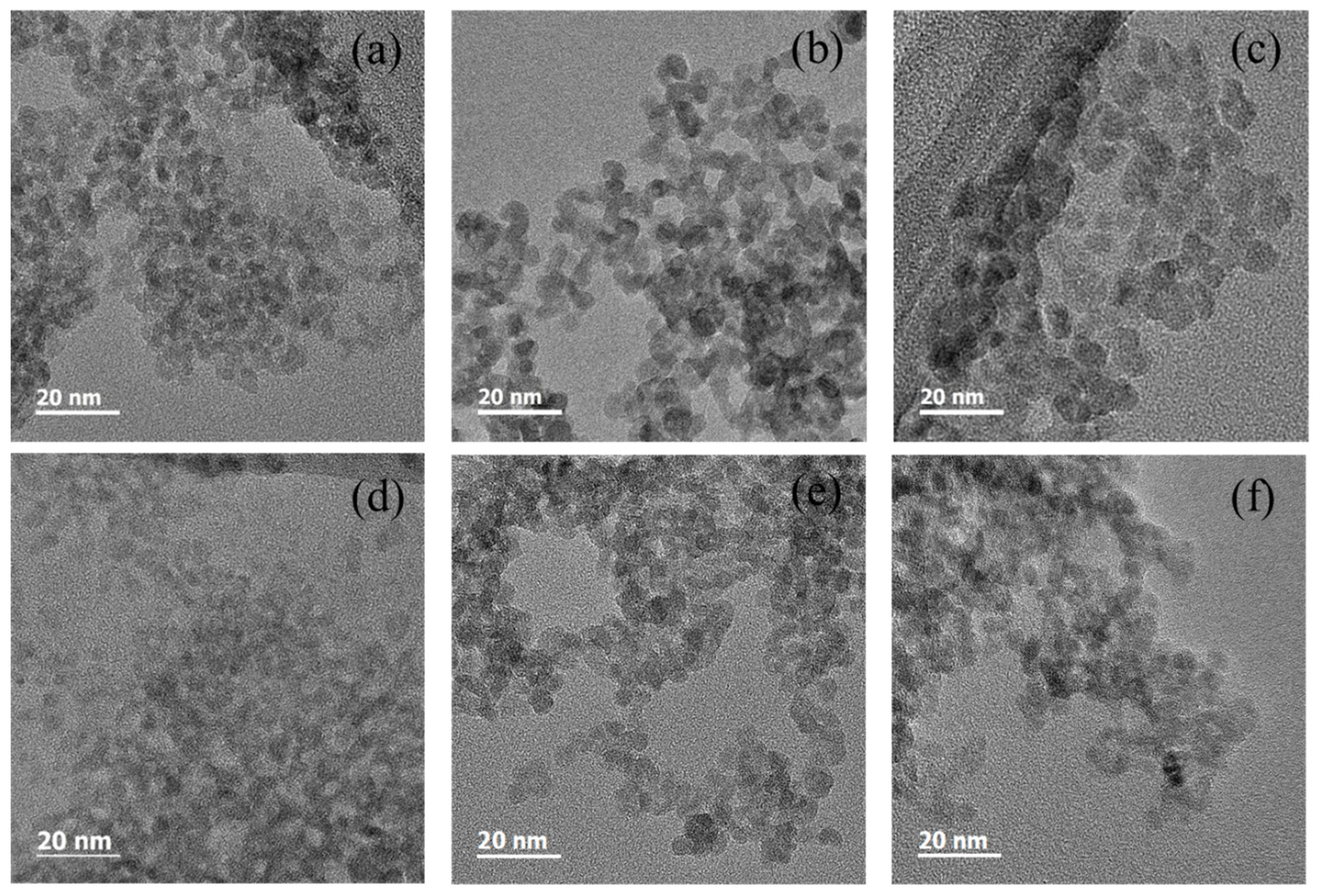
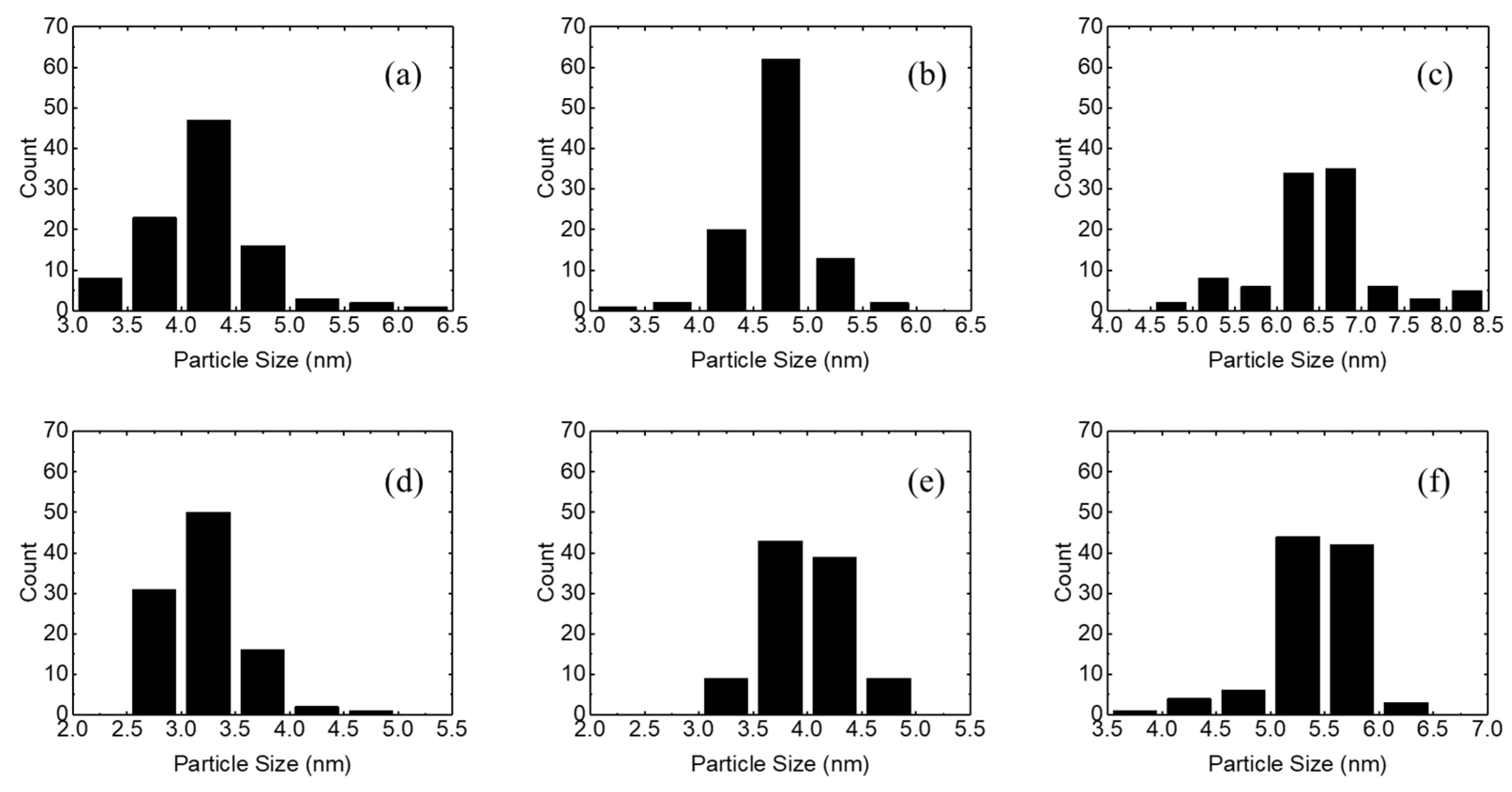
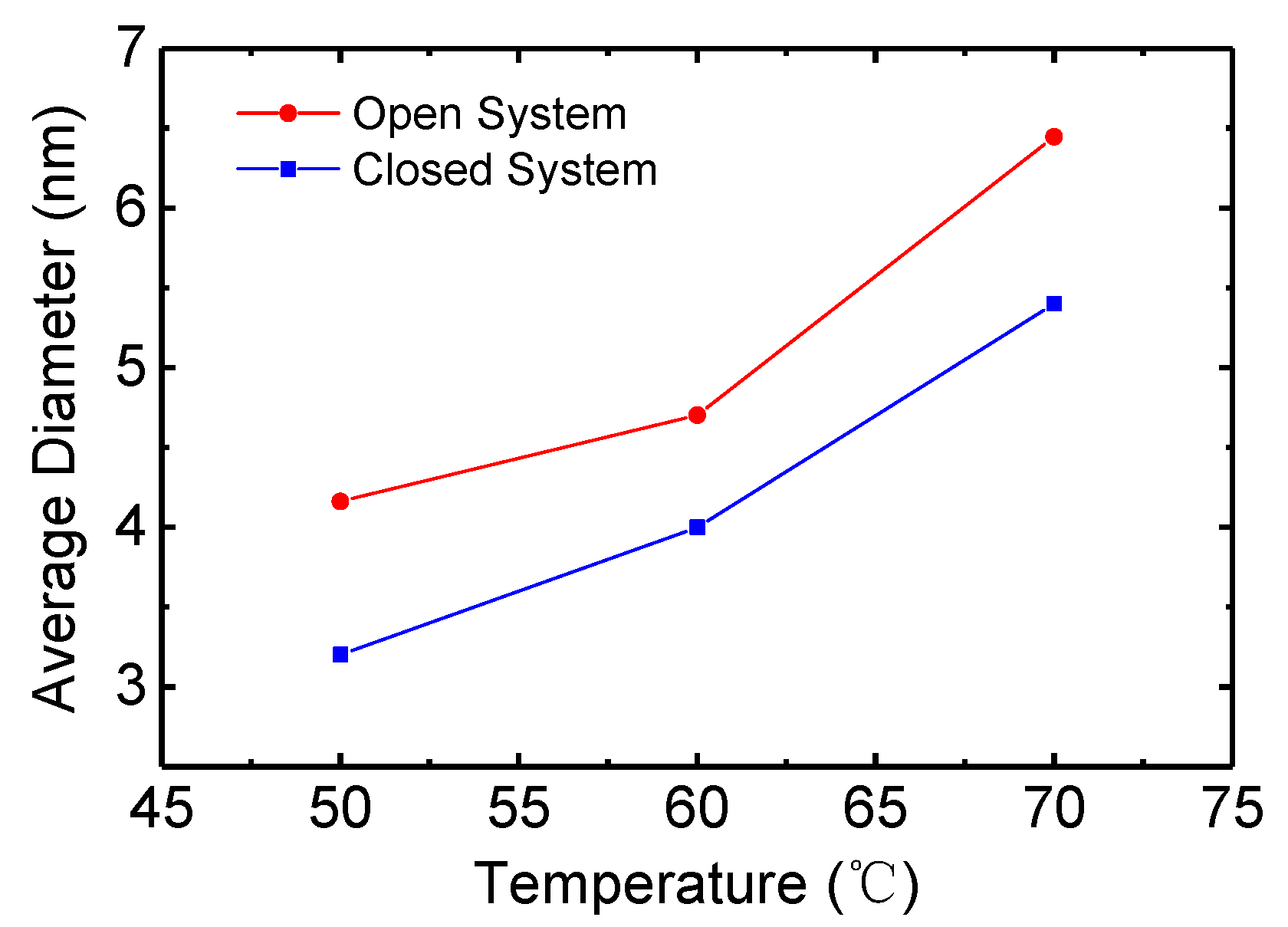
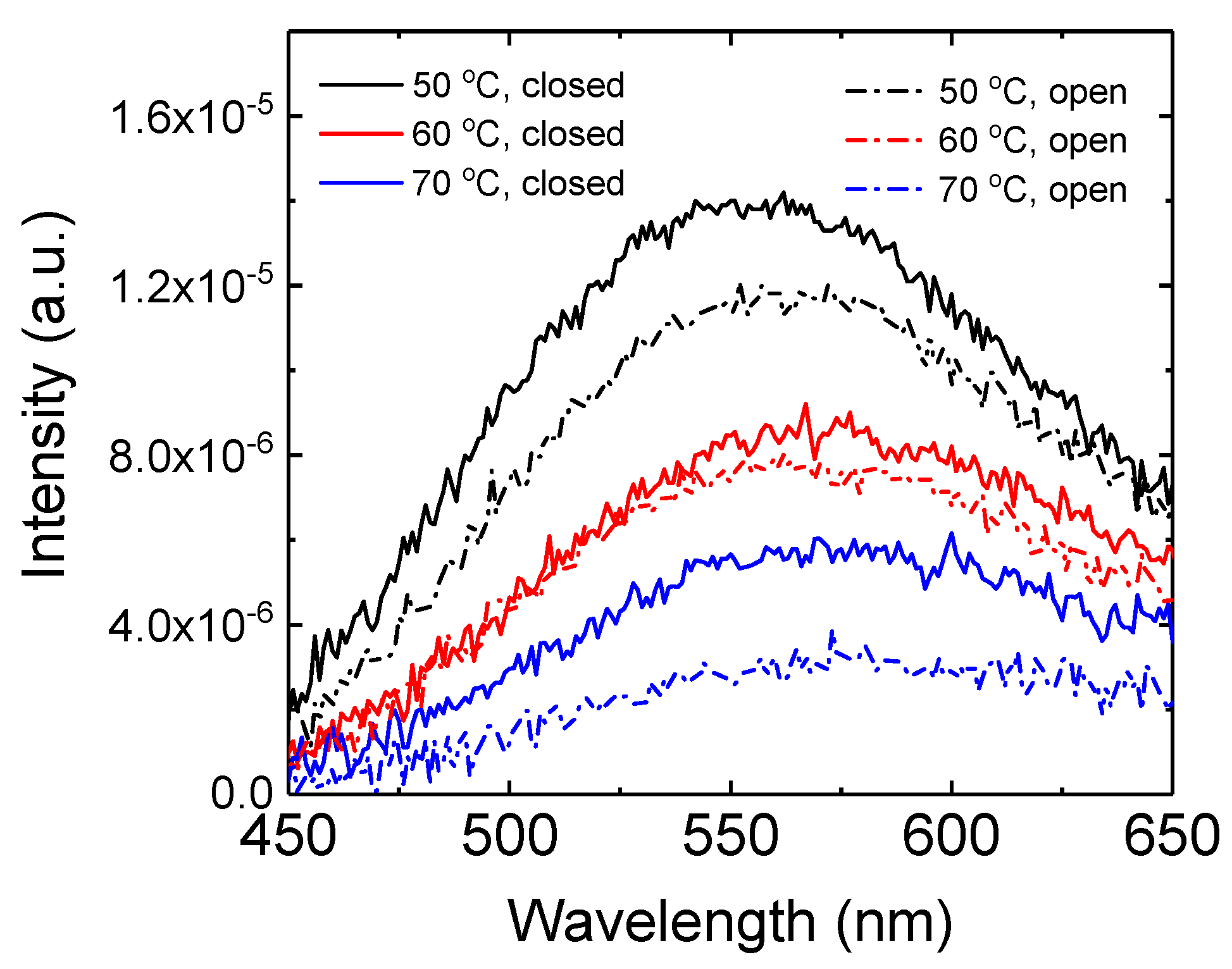
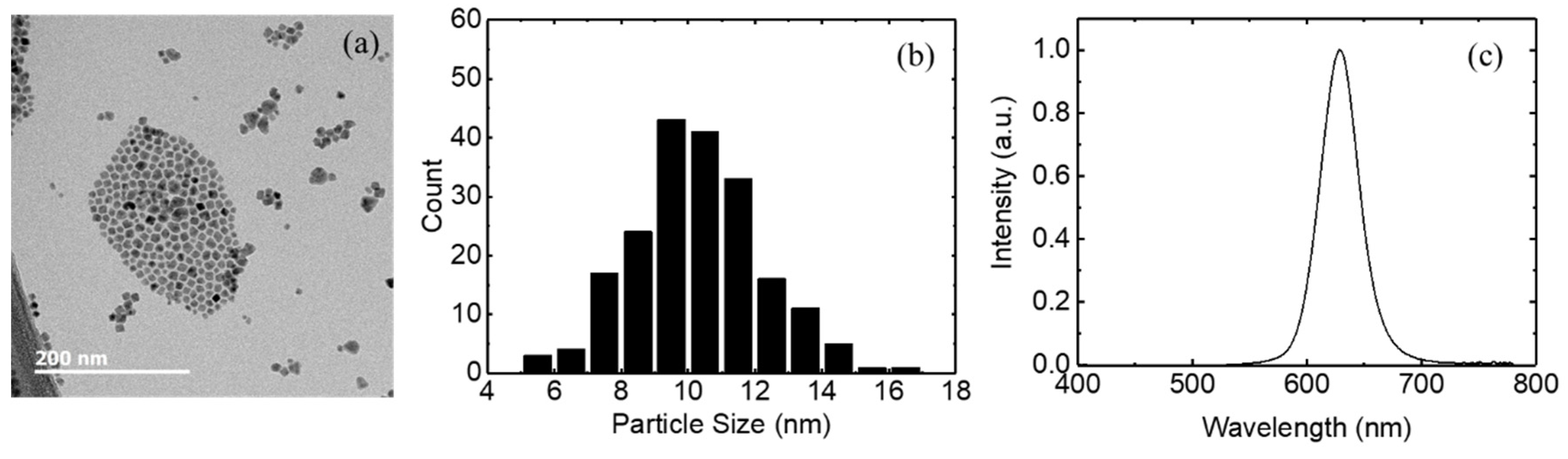
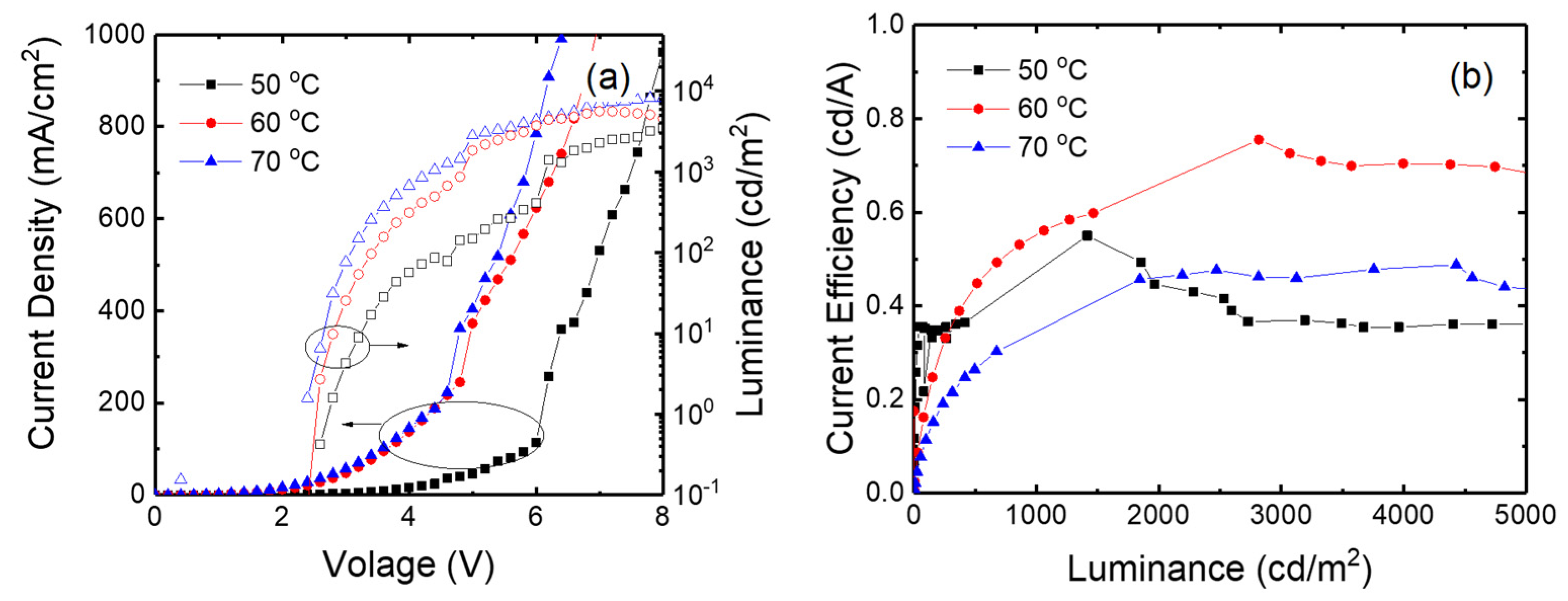
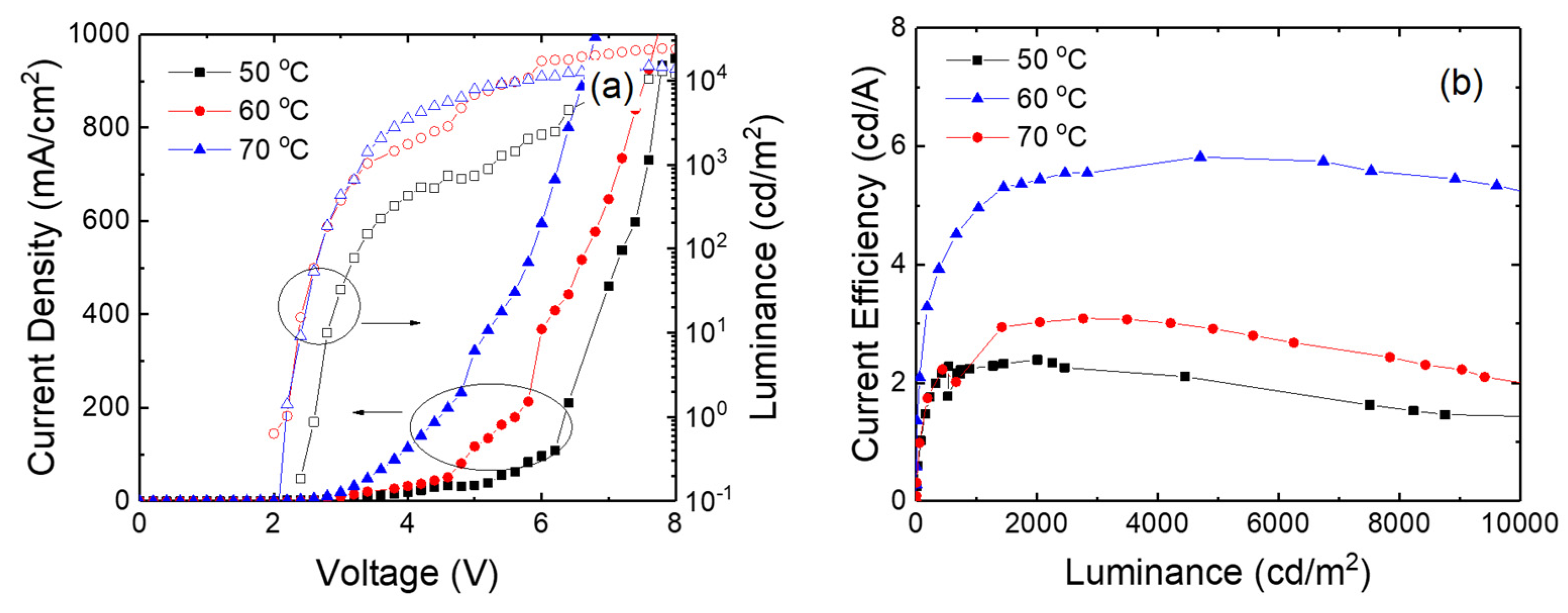
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colvin, V.L.; Schlamp, M.C.; Allvisatos, A.P. Light-emitting diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. Nature 1994, 370, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasaki, Y.; Supran, G.J.; Bawendi, M.G.; Bulovic, V. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies. Nature Photon. 2013, 7, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arquer, F.P.G.; Talapin, D.V.; Klimov, V.I.; Arakawa, Y.; Bayer, M.; Sargent, E.H. Semiconductor quantum dots: Technological progress and future challenges. Science 2021, 373, 640. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, T.; Yu, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W. A review on the electroluminescence properties of quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Org. Electron. 2021, 90, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, K.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Lei, W.; Xa, J. Highly-improved performance of TiO2 nanocrystals based quantum dot light emitting diodes. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12104–12108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, N.; Yang, J.H.; Han, C.W.; Kim, H.M.; Han, W.; Park, H.H.; Yang, H.; Kim, J. High-efficiency quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on Li-doped TiO2 nanoparticles as an alternative electron transport layer. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2838–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Song, J.; An, M.; Lim, J.; Lee, C.; Roh, J.; Lee, D. Colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes employing solution-processable thin dioxide nanoparticles in an electron transport layer. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 8261–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Ma, W.; Sun, X.; Wu, L.; Lin, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Shen, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. Highly stable SnO2-based quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with the conventional device structure. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9631–9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Han, C.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Greco, T.; Ippen, C.; Wedel, A.; Ju, B.K.; et al. Transparent InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes with ZrO2 electron transport layer and indium zinc oxide top electrode. Adv. Func. Mater. 2016, 26, 3454–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouwdam, J.W.; Janssen, R.A.J. Red, green, and blue quantum dot LEDs with solution processable ZnO nanocrystal electron injection layers. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, J.; Holloway, P.H. Stable and efficient quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed multilayer structures. Nature Photon. 2011, 5, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Khan, Q.; Liu, X.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, W.; Nathan, A. Size tunable ZnO nanoparticles to enhance electron injection in solution processed QLEDs. ACS Photonics 2016, 3, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.S.; Kang, B.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.W.; Cha, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.W. Efficient quantum dots light-emitting devices using polyvinyl pyrrolidone-capped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced charge transport. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, M.; Cao, S.; Li, Q.; Luo, H.; Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Improving performance of InP-based quantum dot light-emitting diodes by controlling defect states of the ZnO electron transport layer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Niu, Y.; Cao, H.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based quantum dots. Nature 2014, 515, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Kim, D.; Lee, W.; Chae, H. Highly efficient and fully solution-processed inverted light-emitting diodes with charge control interlayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17295–17300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, O.; Shen, H.; Lin, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.S. Over 30% external quantum efficiency light-emitting diodes by engineering quantum-dot-assisted energy level match for hole transport layer. Adv. Func. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, N.; Singh, B.; Mulvaney, P. Enhancing quantum dot LED efficiency by tuning electron mobility in the ZnO electron transport layer. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xie, L.; Guo, X.; Su, W.; Zhang, Q. Photocross-linkable hole transport materials for inkjet-printed high-efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 58369–58377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.Q.Q.; Su, W. Cross-linking strategies for hole transport/emissive layers in quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 6130–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.S.; Davidson-Hall, T.; Cotella, G.; Lyu, Q.; Chun, P.; Aziz, H. Significant lifetime enhancement in QLEDs by reducing interfacial charge accumulation via fluorine incorporation in the ZnO electron transport layer. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Ma, H.; Huang, G.; Gao, M.; Cai, F.; Fang, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, S.; et al. A review on quantum dot light-emitting diodes: From materials to applications. Adv. Optical Mater. 2023, 11, 2201965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Bae, W.K.; Lee, D.; Park, I.; Lim, J.; Park, M.; Cho, H.; Woo, H.; Yoon, D.Y.; Char, K.; et al. Bright and efficient full-color colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes using an inverted device structure. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2362–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castan, A.; Kim, H.M.; Jang, J. All-solution-processed inverted quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Mu, L.; He, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Cun, Y.; Mai, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Highly efficient all-solution processed inverted quantum dots based light emitting devices. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wei, C.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, J.; Huang, Q.; Su, W.; Cui, Z.; Nathan, A.; Lei, W.; Chen, J. Boosting the efficiency of inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes by balancing charge densities and suppressing exciton quenching through band alignment. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Lin, G.; Zhou, X.; Wu, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. All-solution processed inverted green quantum dot light-emitting diodes with concurrent high efficiency and long lifetime. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, H.; Wei, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S. Efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes with a Zn0.85Mg0.15O interfacial modification layer. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8962–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Hahm, D.; Kim, K.; Bae, W.K.; Lee, C.; Kwak, J. Highly efficient and bright inverted top-emitting InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes introducing a hole-suppressing interlayer. Small 2019, 15, 1905162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, S.M.; Tintori, F.; Sadeghi, S.; Linkov, P.; Dayneko, S.; Shahalizad, A.; Pahlevaninezhad, H.; Pahlevani, M. Tailored ZnO functional nanomaterials for solution-processed quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Adv. Photonics Res. 2022, 3, 2200159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, X.; Chen, D.; Ye, Y.; Gao, Y.; Peng, X.; Jin, Y. Inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes with conductive interlayers of zirconium acetylacetonate. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 3154–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mude, N.N.; Kim, S.J.; Lampande, R.; Kwon, J.H. An efficient organic and inorganic hybrid interlayer for high performance inverted red cadmium-free quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacholski, C.; Kornowski, A.; Weller, H. Self-assembly of ZnO: From nanodots to nanorods. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 41, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyen, E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Jang, J. ZnO nanoparticles for quantum-dot based light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater. 2020, 3, 5203–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yin, L.; Wang, C.; Lun, N.; Qi, Y.; Xiang, D. Origin of visible photoluminescence of ZnO quantum dots: Defect-dependent and size-dependent. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 9651–9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, S.-H.; Kim, G.-E.; Byun, S.-U.; Lee, K.-H.; Moon, D.-G. Inverted Red Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes with ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Zinc Acetate Dihydrate and Potassium Hydroxide in Open and Closed Systems. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111297
Jang S-H, Kim G-E, Byun S-U, Lee K-H, Moon D-G. Inverted Red Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes with ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Zinc Acetate Dihydrate and Potassium Hydroxide in Open and Closed Systems. Micromachines. 2024; 15(11):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111297
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Se-Hoon, Go-Eun Kim, Sang-Uk Byun, Kyoung-Ho Lee, and Dae-Gyu Moon. 2024. "Inverted Red Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes with ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Zinc Acetate Dihydrate and Potassium Hydroxide in Open and Closed Systems" Micromachines 15, no. 11: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111297
APA StyleJang, S.-H., Kim, G.-E., Byun, S.-U., Lee, K.-H., & Moon, D.-G. (2024). Inverted Red Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes with ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Zinc Acetate Dihydrate and Potassium Hydroxide in Open and Closed Systems. Micromachines, 15(11), 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111297





