Continuous Flow Separation of Live and Dead Cells Using Gravity Sedimentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
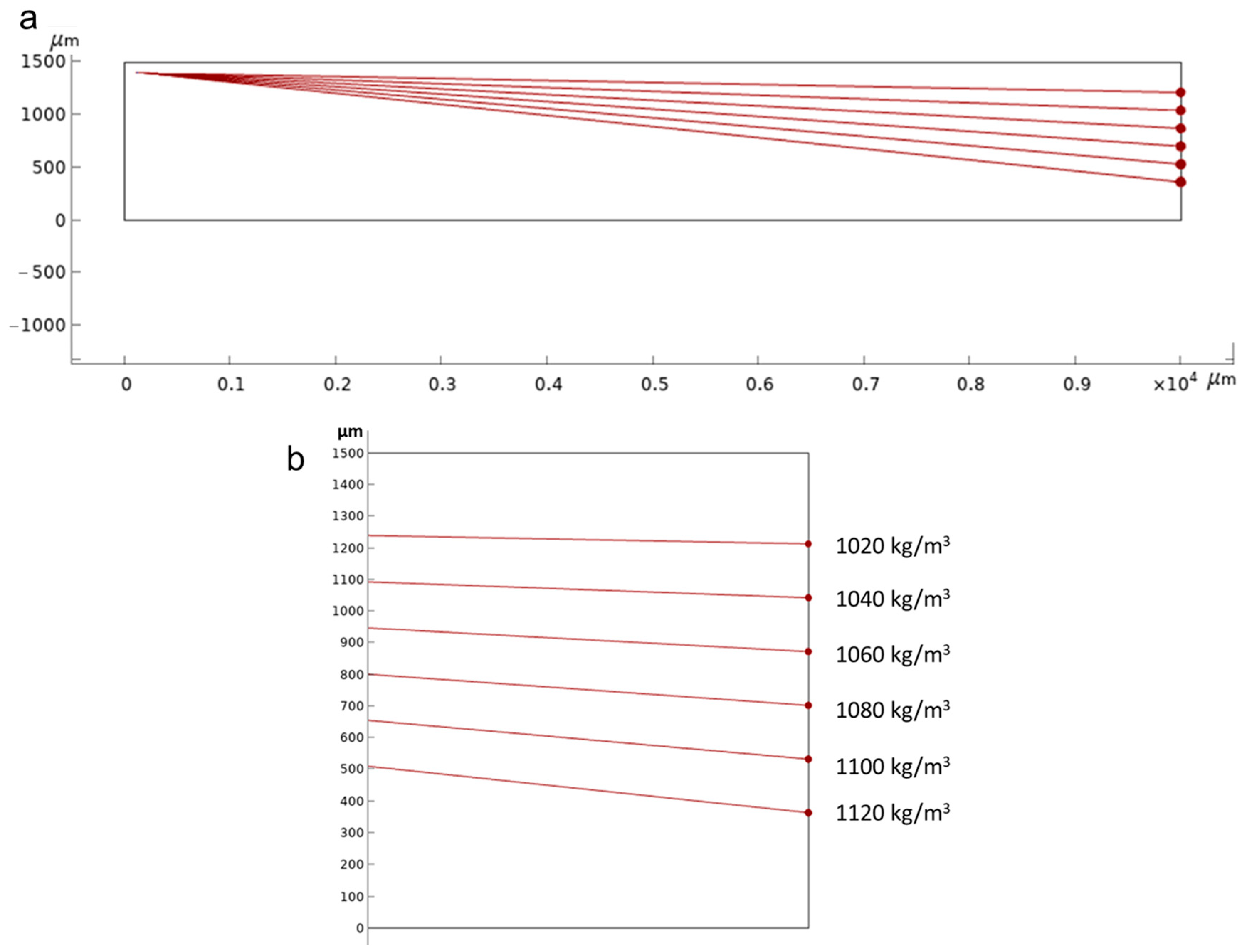
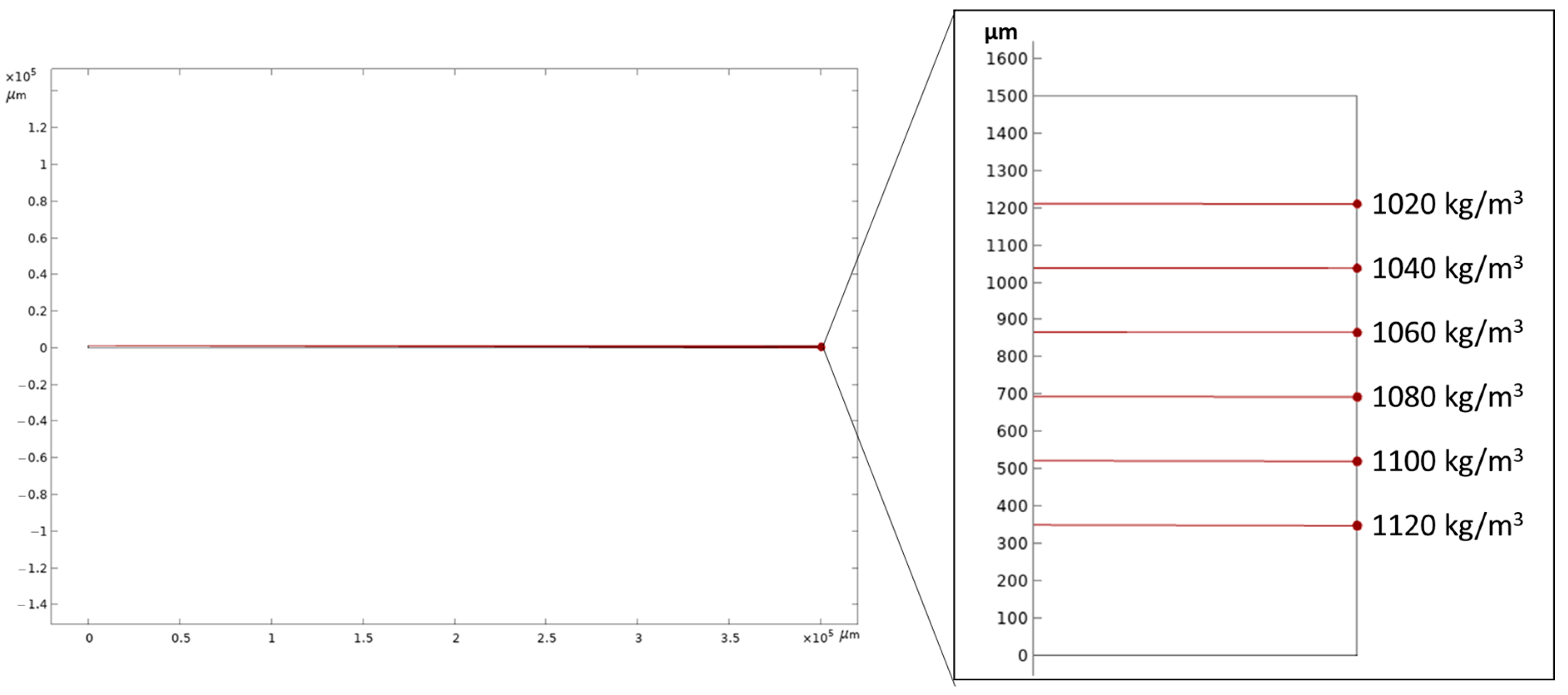
3.1. Numerical Simulation
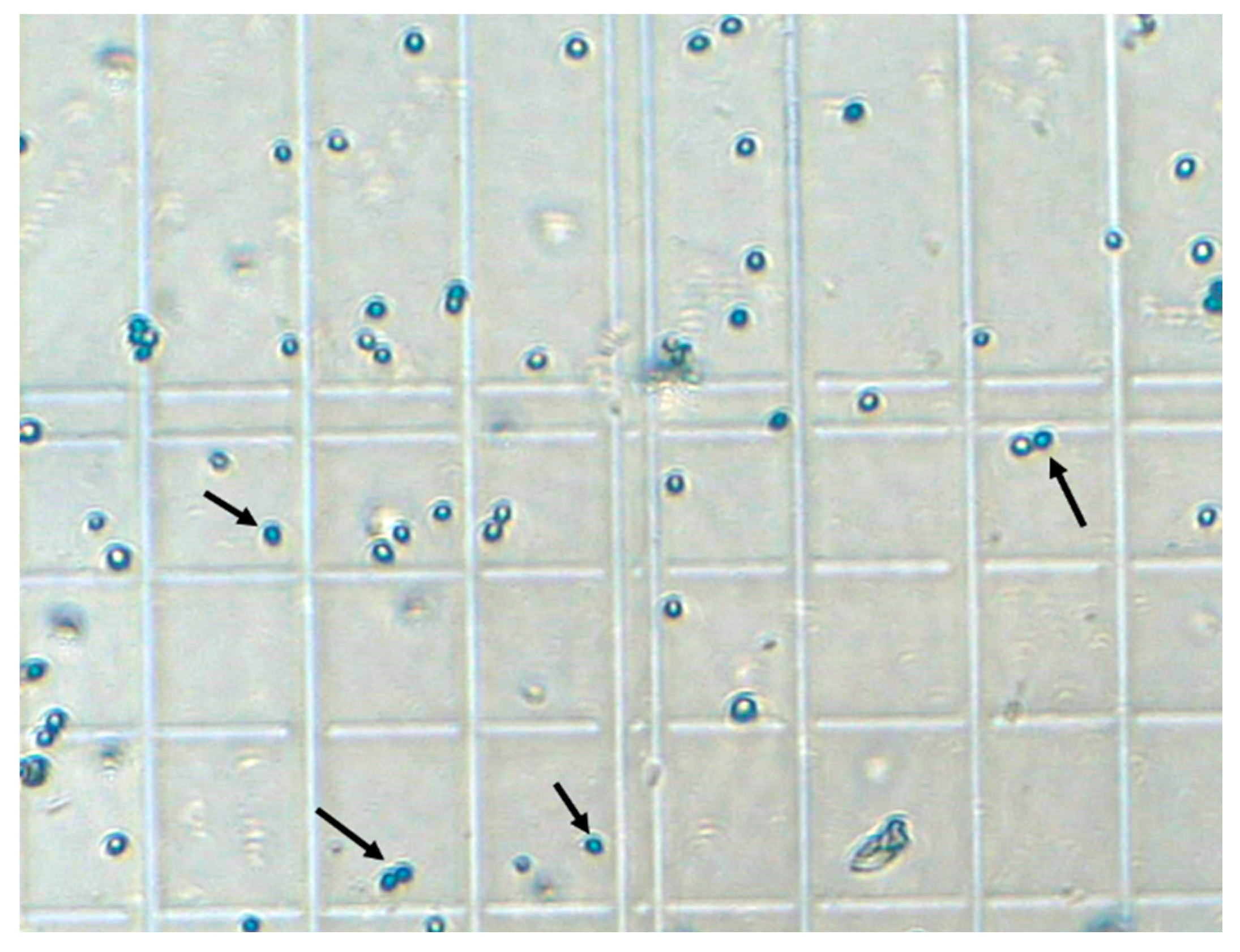
3.2. Experimental Characterization of Sedimentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Niess, H.; Conrad, C.; Schwarz, B.; Jauch, K.-W.; Huss, R.; Nelson, P.J.; Bruns, C.J. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Tumor-Targeted Gene Therapy in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T.-K.; Chou, W.-P.; Huang, S.-B.; Wang, H.-M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Wu, M.-H. Application of Optically-Induced-Dielectrophoresis in Microfluidic System for Purification of Circulating Tumour Cells for Gene Expression Analysis-Cancer Cell Line Model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H.; Huang, C. Nanotechnology-Assisted Isolation and Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells on Microfluidic Devices. Micromachines 2020, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.A.; Gran, M.L.; Peppas, N. a Targeted Nanodelivery of Drugs and Diagnostics. Nano Today 2010, 5, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Cai, F.; Jiang, P.; Deng, Z.; Li, F.; Niu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Zheng, H. On-Chip Targeted Single Cell Sonoporation with Microbubble Destruction Excited by Surface Acoustic Waves. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 073701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.Y.; Lam, P.Y.P. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Paracrine Factors for the Treatment of Brain Tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Mei, H.; Cai, Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, W. Patient-derived Renal Cell Carcinoma Organoids for Personalized Cancer Therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ozcelik, A.; Rufo, J.; Wang, Z.; Fang, R.; Jun Huang, T. Acoustofluidic Separation of Cells and Particles. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, A.; Cevik, O. Microfluidic Methods Used in Exosome Isolation. Biocell 2023, 47, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, M.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J. Acoustic Microfluidic Separation Techniques and Bioapplications: A Review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzenberg, L.A.; Parks, D.; Sahaf, B.; Perez, O.; Roederer, M.; Herzenberg, L.A. The History and Future of the Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorter and Flow Cytometry: A View from Stanford. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.A.; Chen, Y.; Nama, N.; Nissly, R.H.R.H.; Ren, L.; Ozcelik, A.; Wang, L.; McCoy, J.P.P.; Levine, S.J.S.J.; Huang, T.J.T.J. Acoustofluidic Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorter. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 12051–12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.Y.; Spence, C.; Scherer, A.; Arnold, F.H.; Quake, S.R. A Microfabricated Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorter. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, L.; Nikolajeff, F.; Johansson, S.; Thorslund, S. On-Chip Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting by an Integrated Miniaturized Ultrasonic Transducer. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5188–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Gao, C.; Gao, Y.; Wu, M.; Ahmadian Yazdi, A.; Xu, J. Acoustofluidic Micromixer on Lab-on-a-Foil Devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Gao, Y.; Ghaznavi, A.; Zhao, W.; Xu, J. AC Electroosmosis Micromixing on a Lab-on-a-Foil Electric Microfluidic Device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, J. Acoustic Bubble-Based Bidirectional Micropump. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2020, 24, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Ao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Song, S.; Mackie, K.; Guo, F. Intelligent Acoustofluidics Enabled Mini-Bioreactors for Human Brain Organoids. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Cai, H.; Wu, Z.; Ott, J.; Wang, H.; Mackie, K.; Guo, F. Controllable Fusion of Human Brain Organoids Using Acoustofluidics. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Cai, H.; Wu, Z.; Krzesniak, J.; Tian, C.; Lai, Y.Y.; Mackie, K.; Guo, F. Human Spinal Organoid-on-a-Chip to Model Nociceptive Circuitry for Pain Therapeutics Discovery. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ao, Z.; Chen, B.; Muhsen, M.; Bondesson, M.; Lu, X.; Guo, F. Acoustic Assembly of Cell Spheroids in Disposable Capillaries. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 504006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Qu, Z.; Mao, Z.; Huang, P.-H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; et al. Standing Surface Acoustic Wave (SSAW)-Based Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorter. Small 2018, 14, 1801996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, N.; Datta, A.; Ganguly, R. Cell Separation in a Microfluidic Channel Using Magnetic Microspheres. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2009, 6, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazian, M.; Li, W.; Nguyen, N.-T. Lab on a Chip for Continuous-Flow Magnetic Cell Separation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, M.A.; Freed, I.M.; Soper, S.A. Cell Separations and Sorting. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, A.A.S.; Bow, H.; Hou, H.W.; Tan, S.J.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Microfluidics for Cell Separation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menachery, A.; Kumawat, N.; Qasaimeh, M. Label-Free Microfluidic Stem Cell Isolation Technologies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Song, M.; Kang, T.; Kim, D.; Lee, L.P. Label-Free Density Difference Amplification-Based Cell Sorting. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 064108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Gao, Y.; Luan, Q.; Papautsky, I.; Chen, X.; Xu, J. Three-dimensional Lab-on-a-foil Device for Dielectrophoretic Separation of Cancer Cells. Electrophoresis 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, A.; Huang, T.J. Acoustic tweezers for single-cell manipulation. In Handbook of Single Cell Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Akkoyun, F.; Gucluer, S.; Ozcelik, A. Potential of the Acoustic Micromanipulation Technologies for Biomedical Research. Biomicrofluidics 2021, 15, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.G.; Shin, J.H.; Bae, C.Y.; Choi, S.; Park, J.-K. Label-Free Cancer Cell Separation from Human Whole Blood Using Inertial Microfluidics at Low Shear Stress. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6213–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, K.; Hammarström, B.; Wiklund, M. Acoustic Separation of Living and Dead Cells Using High Density Medium. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildizhan, Y.; Erdem, N.; Islam, M.; Martinez-Duarte, R.; Elitas, M. Dielectrophoretic Separation of Live and Dead Monocytes Using 3D Carbon-Electrodes. Sensors 2017, 17, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalis, M.C.; Reyes, J.F.; Augustsson, P.; Holmqvist, S.; Roybon, L.; Laurell, T.; Deierborg, T. Label-Free Concentration of Viable Neurons, HESCs and Cancer Cells by Means of Acoustophoresis. Integr. Biol. 2016, 8, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.; Brink, H.; Blanche, S.; DiPrete, C.; Bongiorno, T.; Stone, N.; Liu, A.; Philip, A.; Wang, G.; Lam, W.; et al. Microfluidic Sorting of Cells by Viability Based on Differences in Cell Stiffness. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, N.; Bhakta, H.C.; Grover, W.H. Sorting Cells by Their Density. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, D.; Bahng, J.H.; Ling, Y.; Wei, H.-H.; Kripfgans, O.D.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Grotberg, J.B.; Takayama, S. Gravity-Driven Microfluidic Particle Sorting Device with Hydrodynamic Separation Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benincasa, M.-A.; Moore, L.R.; Williams, P.S.; Poptic, E.; Carpino, F.; Zborowski, M. Cell Sorting by One Gravity SPLITT Fractionation. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5294–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, N.; Neubauer, P.; Birkholz, M. Spiral Microfluidic Devices for Cell Separation and Sorting in Bioprocesses. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 061501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Lee, J.; Ra, M.; Gwon, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Yoo, K.-C.; Sul, O.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, W.-Y.; et al. Continuous Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Whole Blood Using a Slanted Weir Microfluidic Device. Cancers 2019, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, S.O.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Pinho, D.; Miranda, J.M.; Minas, G.; Lima, R. Blood Cells Separation and Sorting Techniques of Passive Microfluidic Devices: From Fabrication to Applications. Micromachines 2019, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gucluer, S.; Guler, O. A Low-Cost Laser-Prototyped Microfluidic Device for Separating Cells and Bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javi, F.; Zaferani, M.; Lopez-Barbosa, N.; DeLisa, M.P.; Abbaspourrad, A. Sheathless Inertial Microfluidic Cell Separation via a Serpentine–Contraction–Expansion Device Coupled with a Combinatorial Extraction Regulator. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2022, 26, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyun, F.; Ozcelik, A. A Simple Approach for Controlling an Open-Source Syringe Pump. Eur. Mech. Sci. 2020, 4, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuß, M.; Josić, D.; Popović, M.; Bronn, W.K. Viscosity of Yeast Suspensions. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1979, 8, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
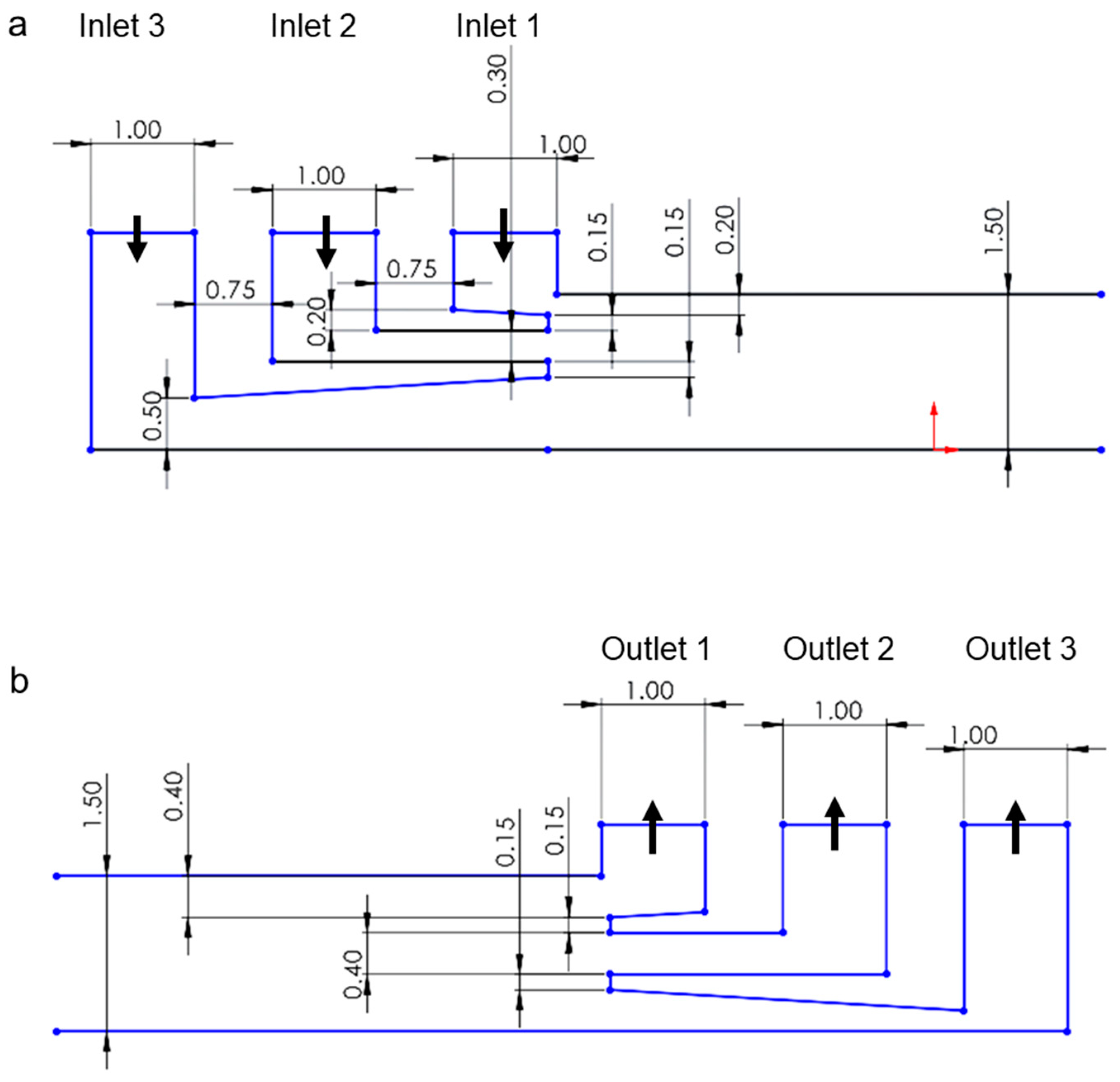
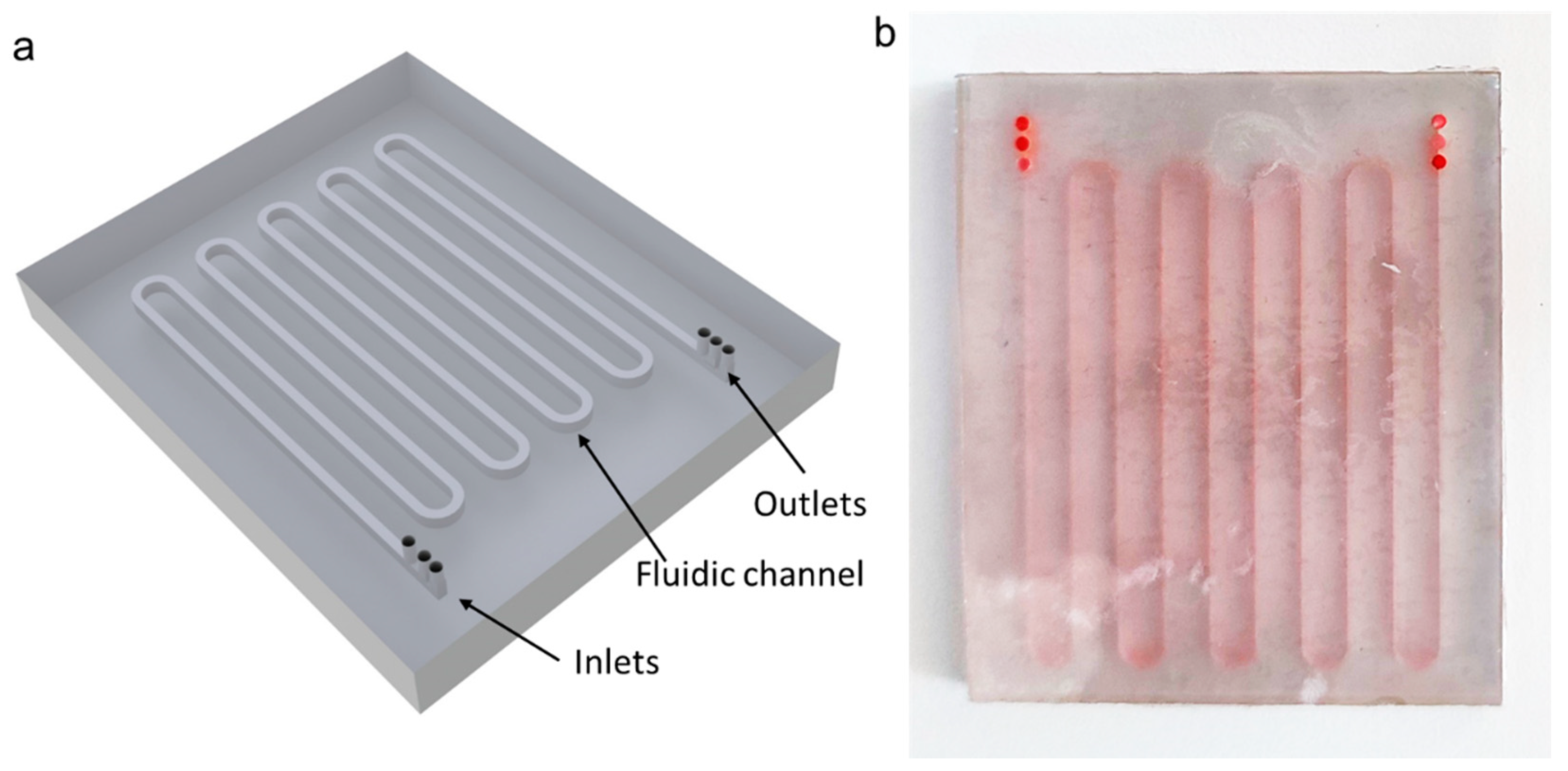
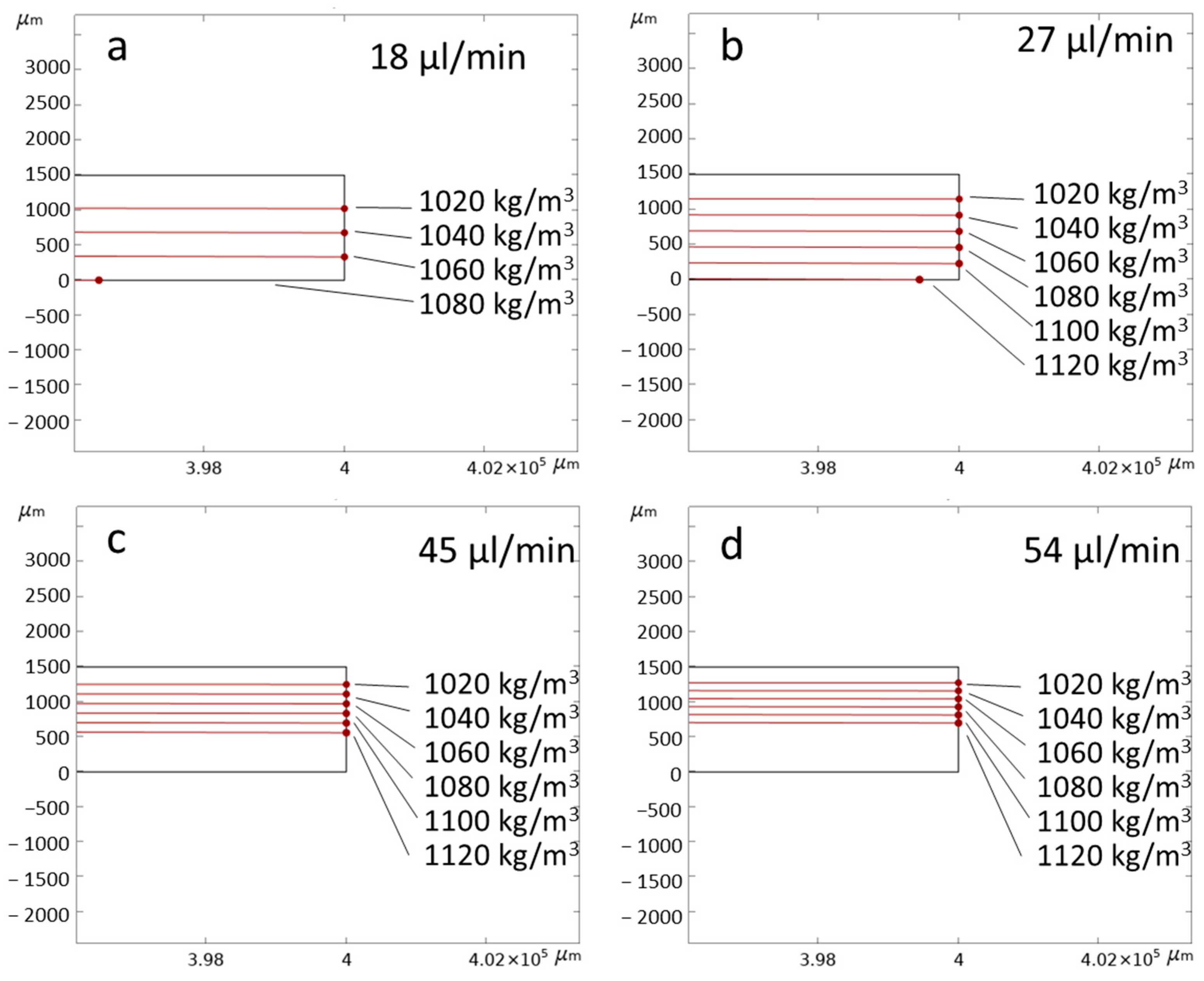
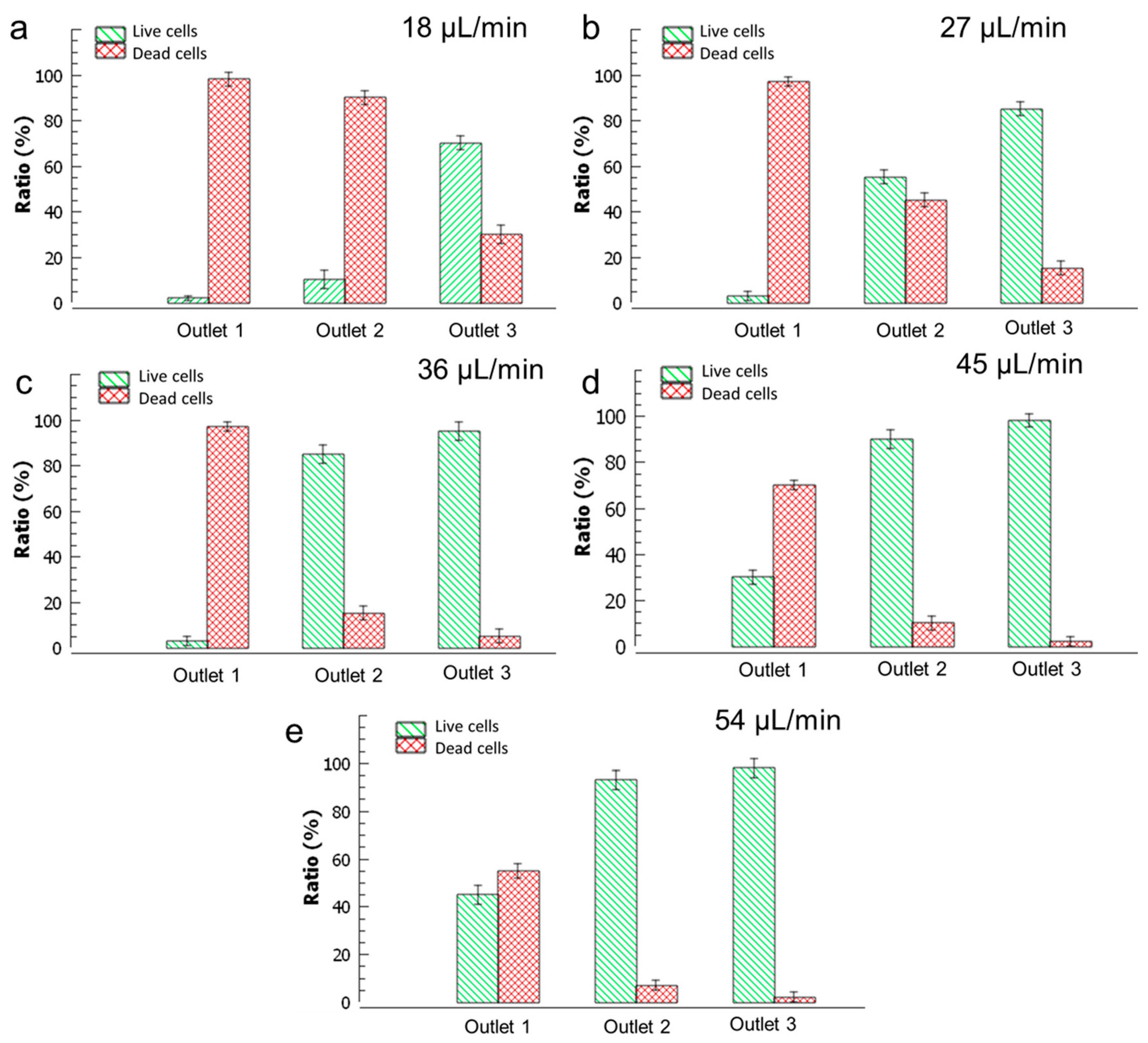
| Inlet 1 | Inlet 2 (Sample) | Inlet 3 | Total Flow Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 µL/min | 3 µL/min | 12 µL/min | 18 µL/min |
| 4.5 µL/min | 4.5 µL/min | 18 µL/min | 27 µL/min |
| 6 µL/min | 6 µL/min | 24 µL/min | 36 µL/min |
| 7.5 µL/min | 7.5 µL/min | 30 µL/min | 45 µL/min |
| 9 µL/min | 9 µL/min | 36 µL/min | 54 µL/min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozcelik, A.; Gucluer, S.; Keskin, T. Continuous Flow Separation of Live and Dead Cells Using Gravity Sedimentation. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081570
Ozcelik A, Gucluer S, Keskin T. Continuous Flow Separation of Live and Dead Cells Using Gravity Sedimentation. Micromachines. 2023; 14(8):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081570
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzcelik, Adem, Sinan Gucluer, and Tugce Keskin. 2023. "Continuous Flow Separation of Live and Dead Cells Using Gravity Sedimentation" Micromachines 14, no. 8: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081570
APA StyleOzcelik, A., Gucluer, S., & Keskin, T. (2023). Continuous Flow Separation of Live and Dead Cells Using Gravity Sedimentation. Micromachines, 14(8), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081570






