Mixed Convection Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Induced by an Inclined Cylinder with Lorentz Forces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of the Mathematical Model
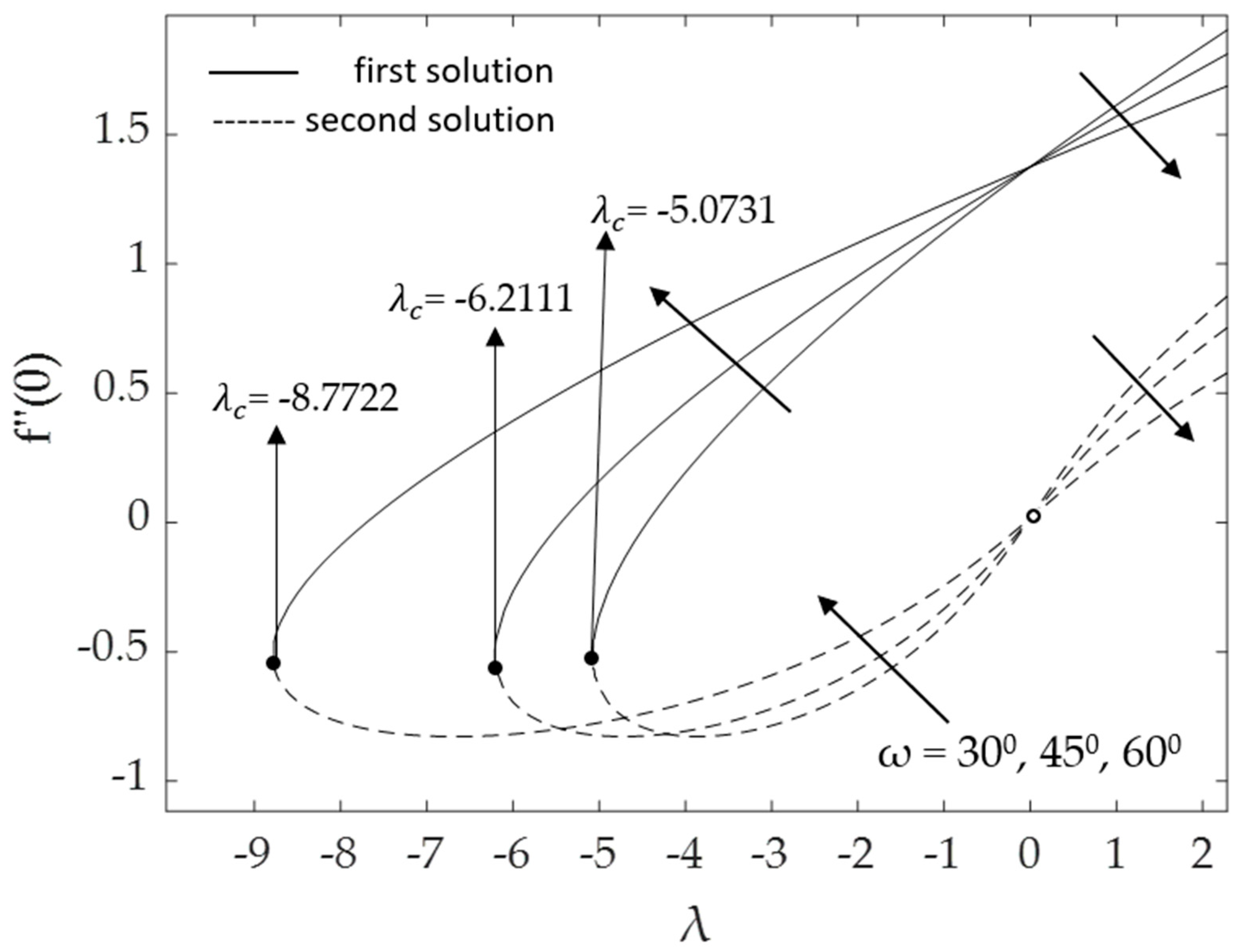
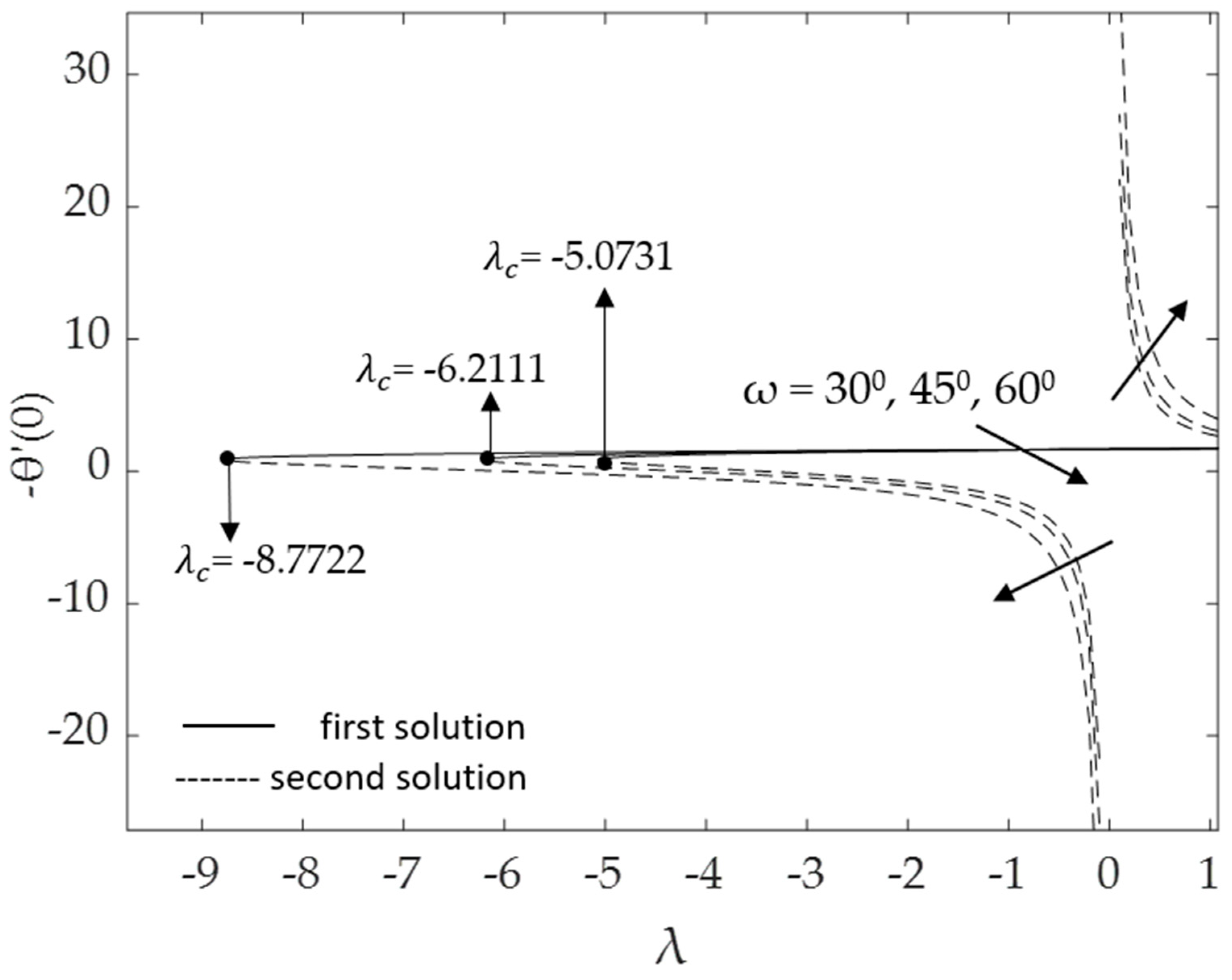
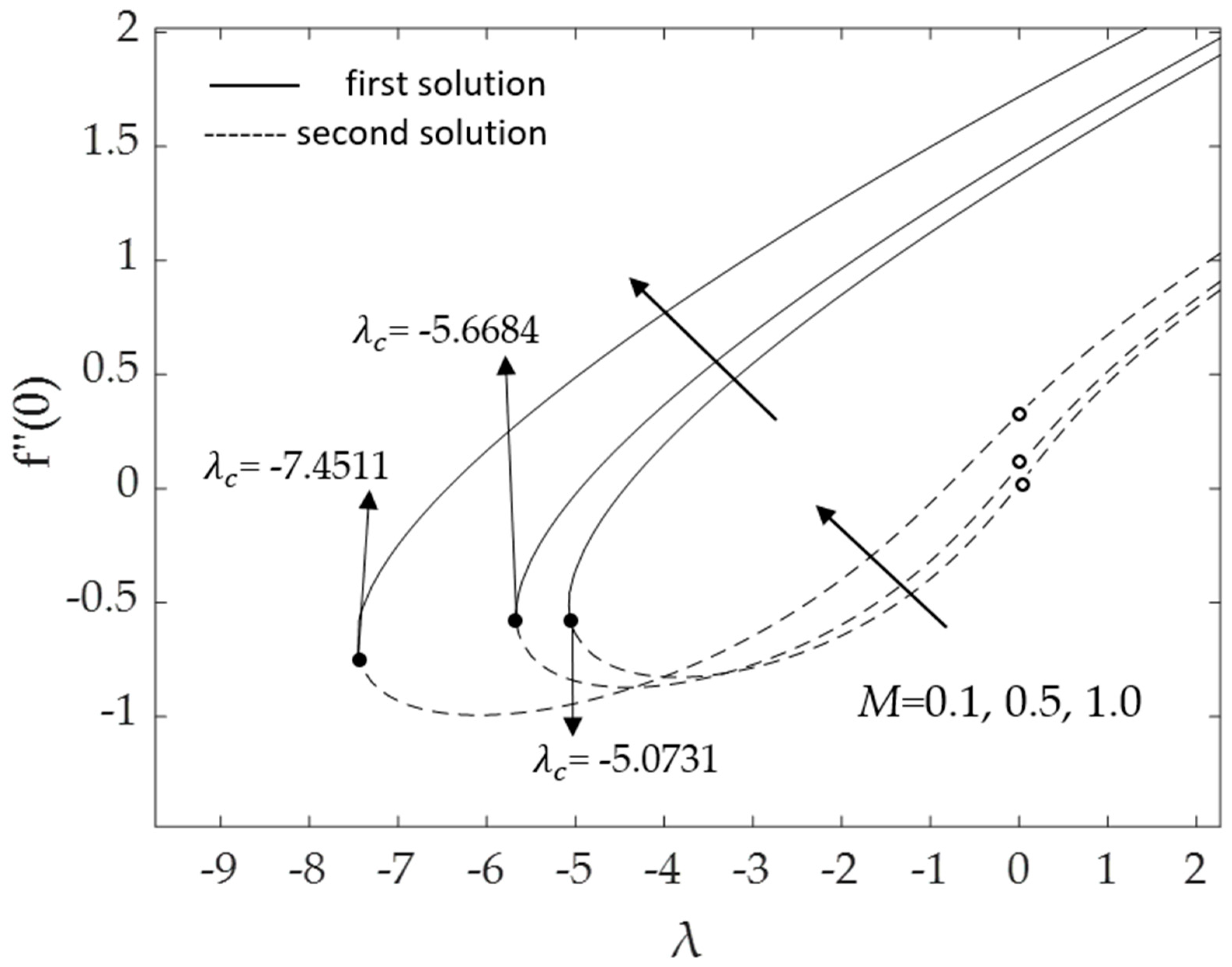
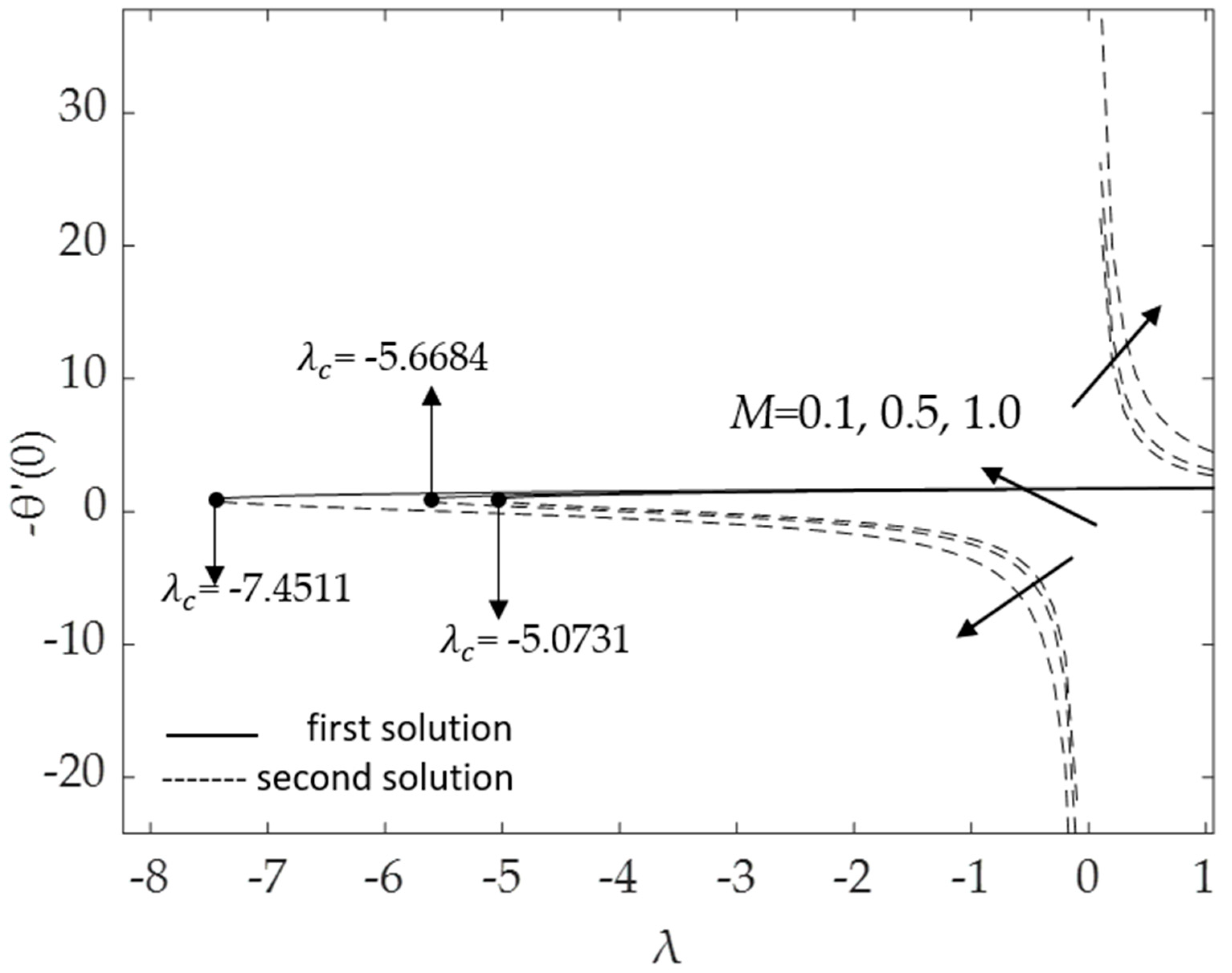
3. Stability Analysis
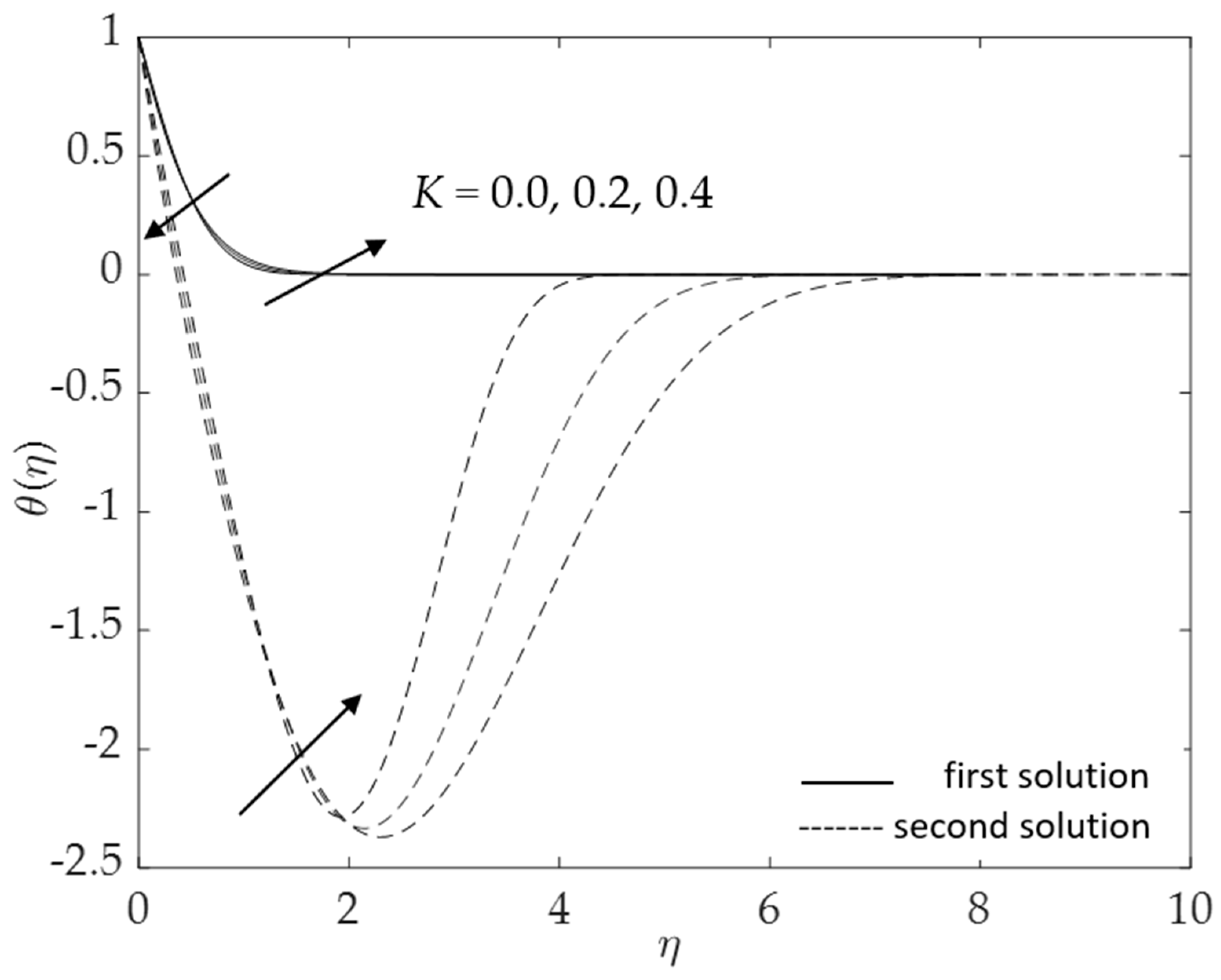
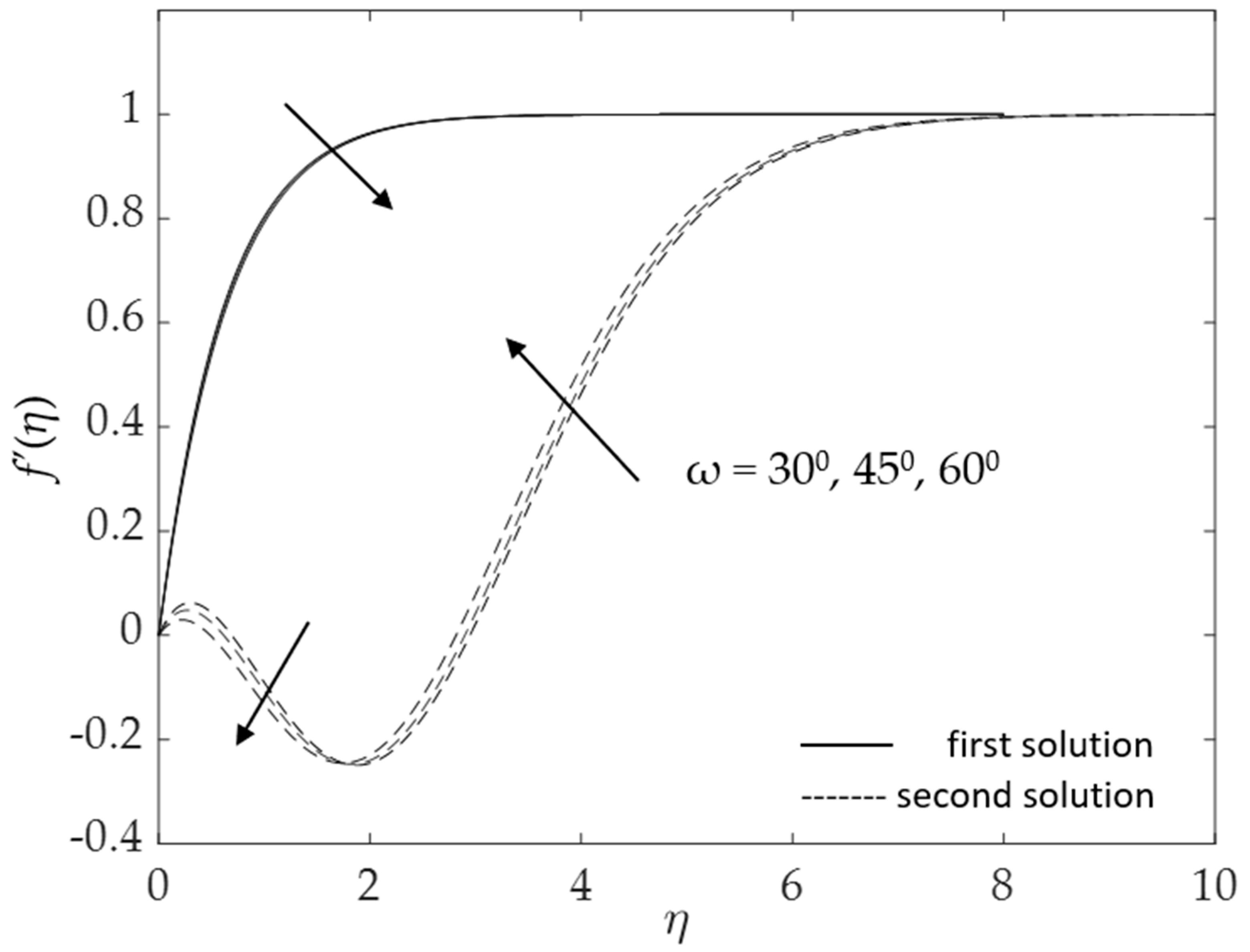
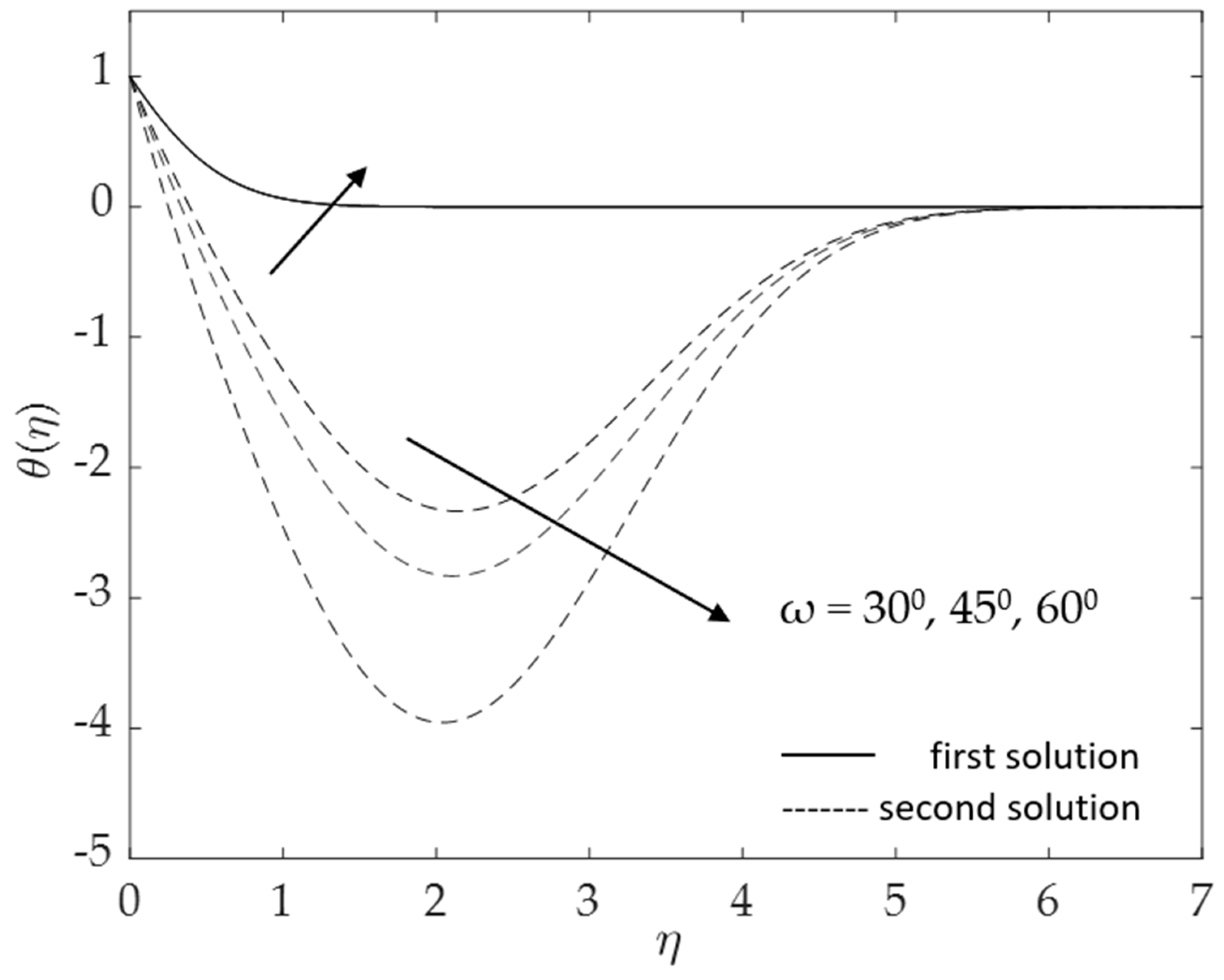
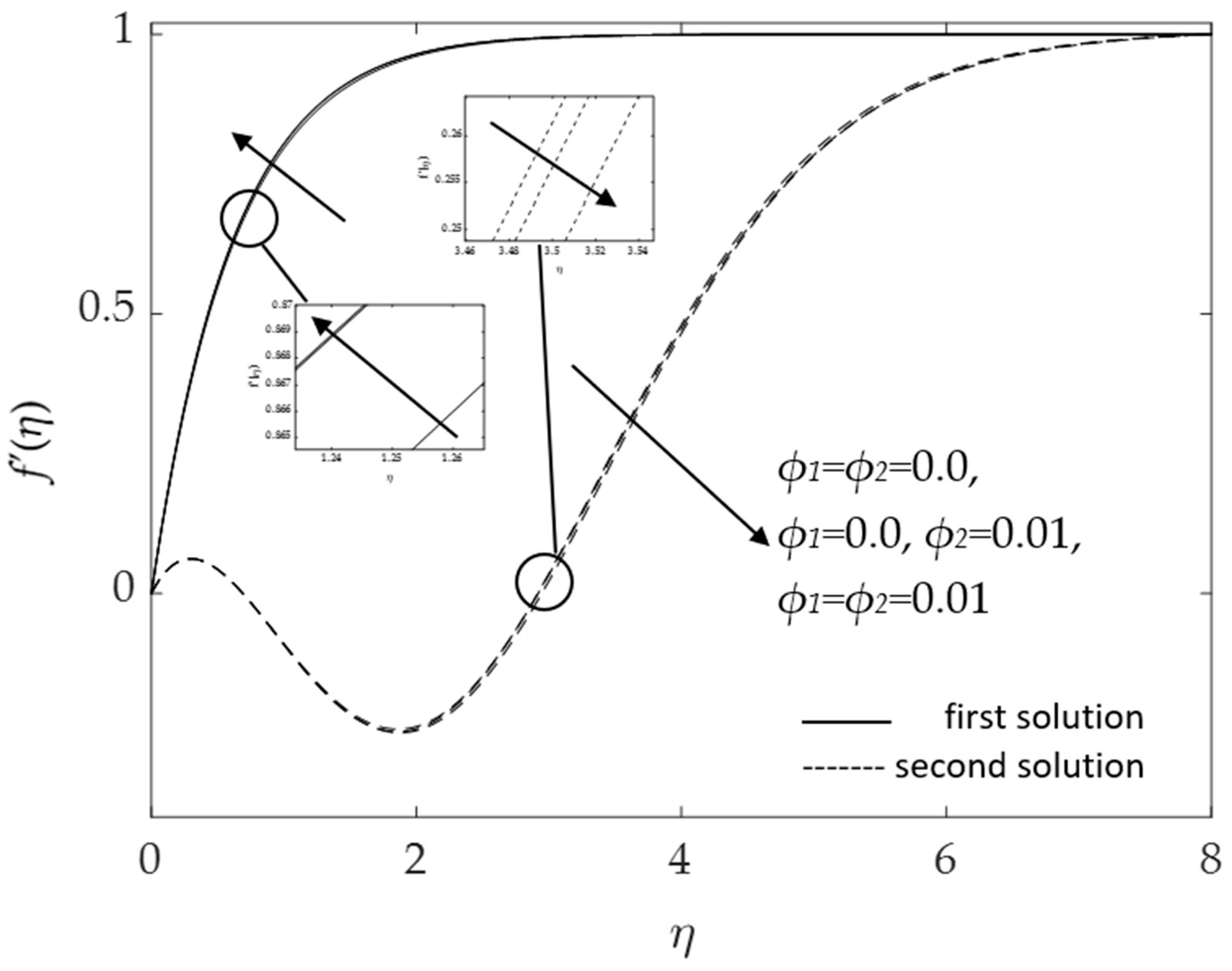
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
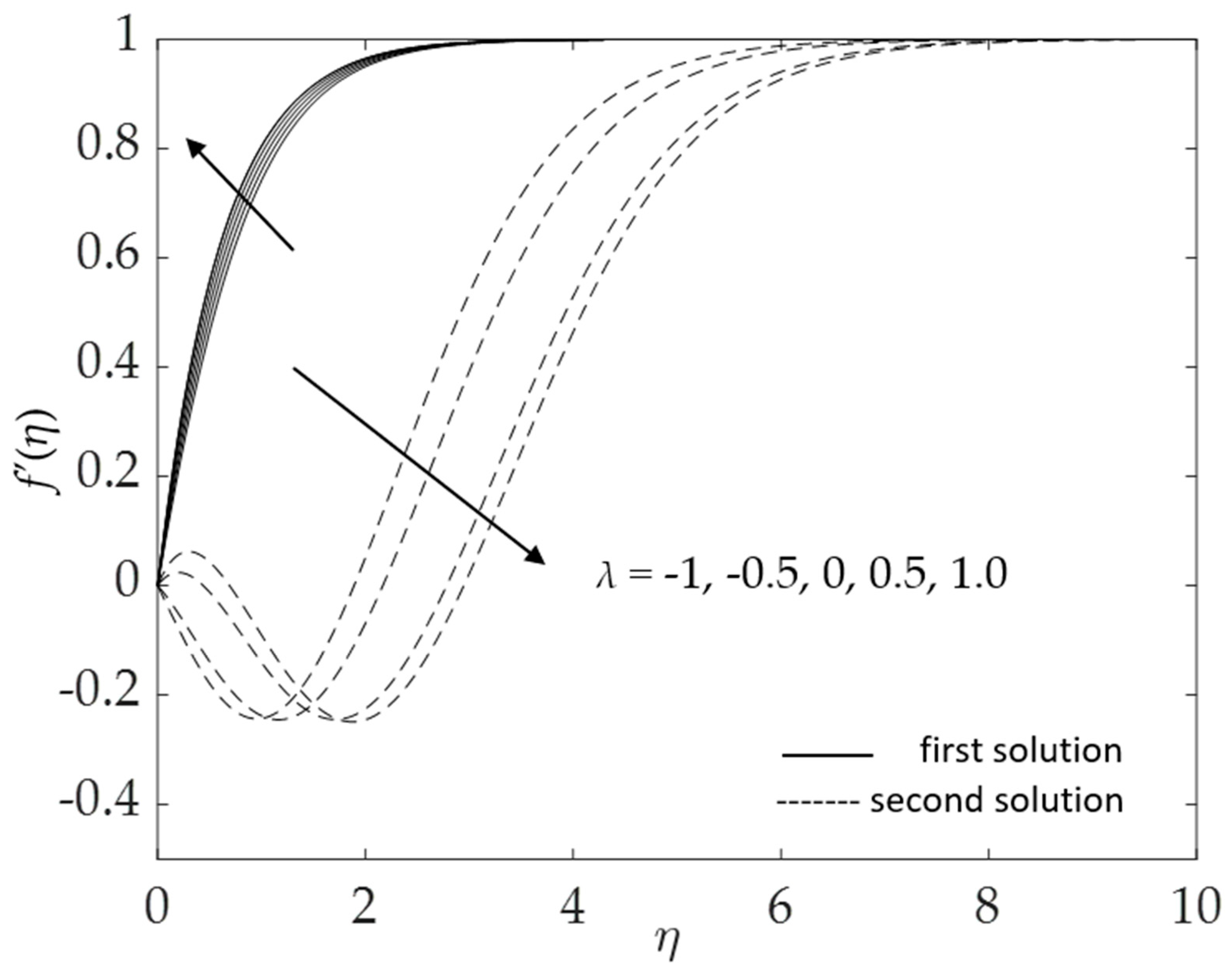
- Two solutions were obtained for both buoyancy assisting and opposing flows, whereas a unique solution was found in the absence of buoyancy force (λ = 0);
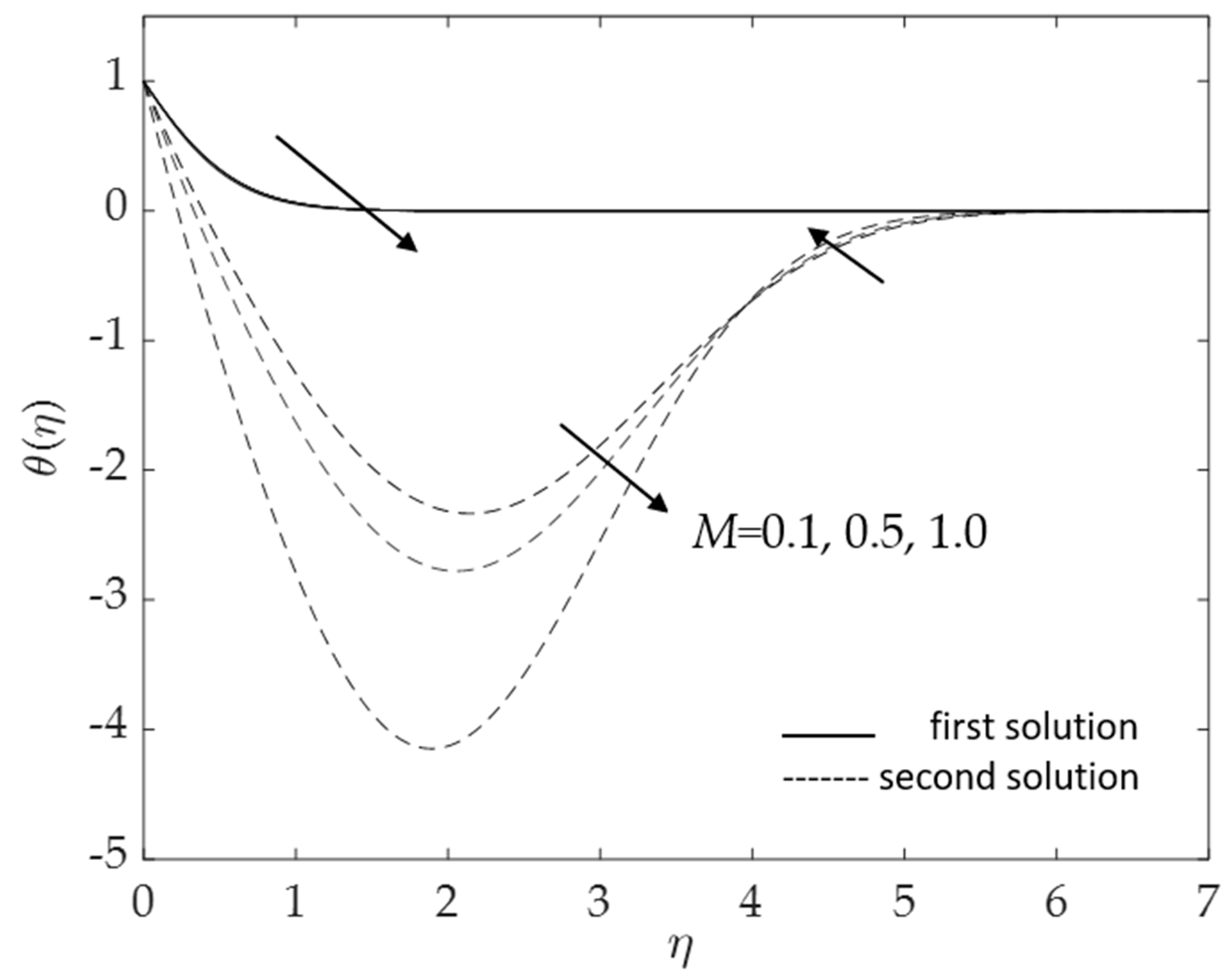
- Larger inclination angles ω lead to a lower gravitational force, increasing the friction factor but decreasing the heat transfer ;
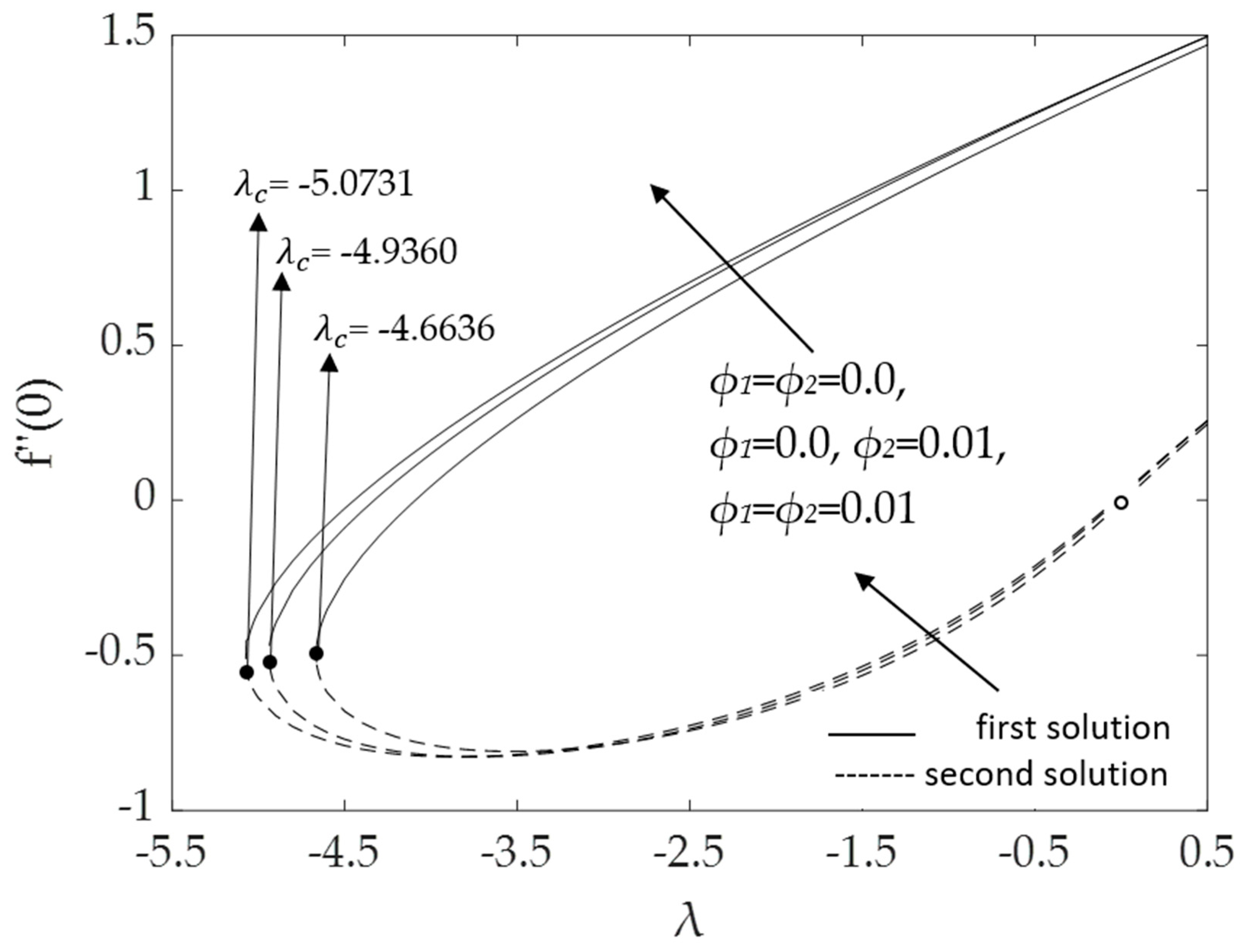
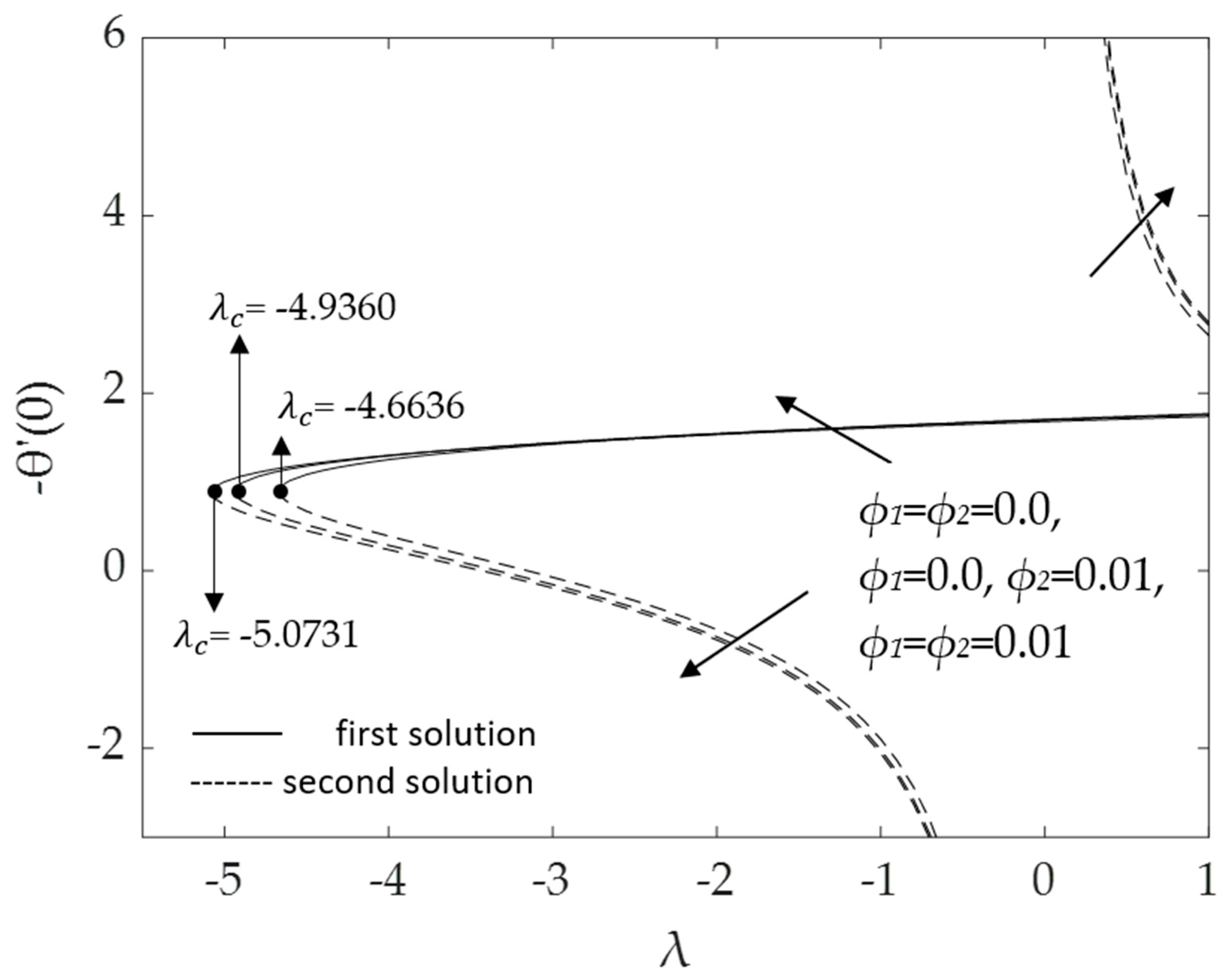
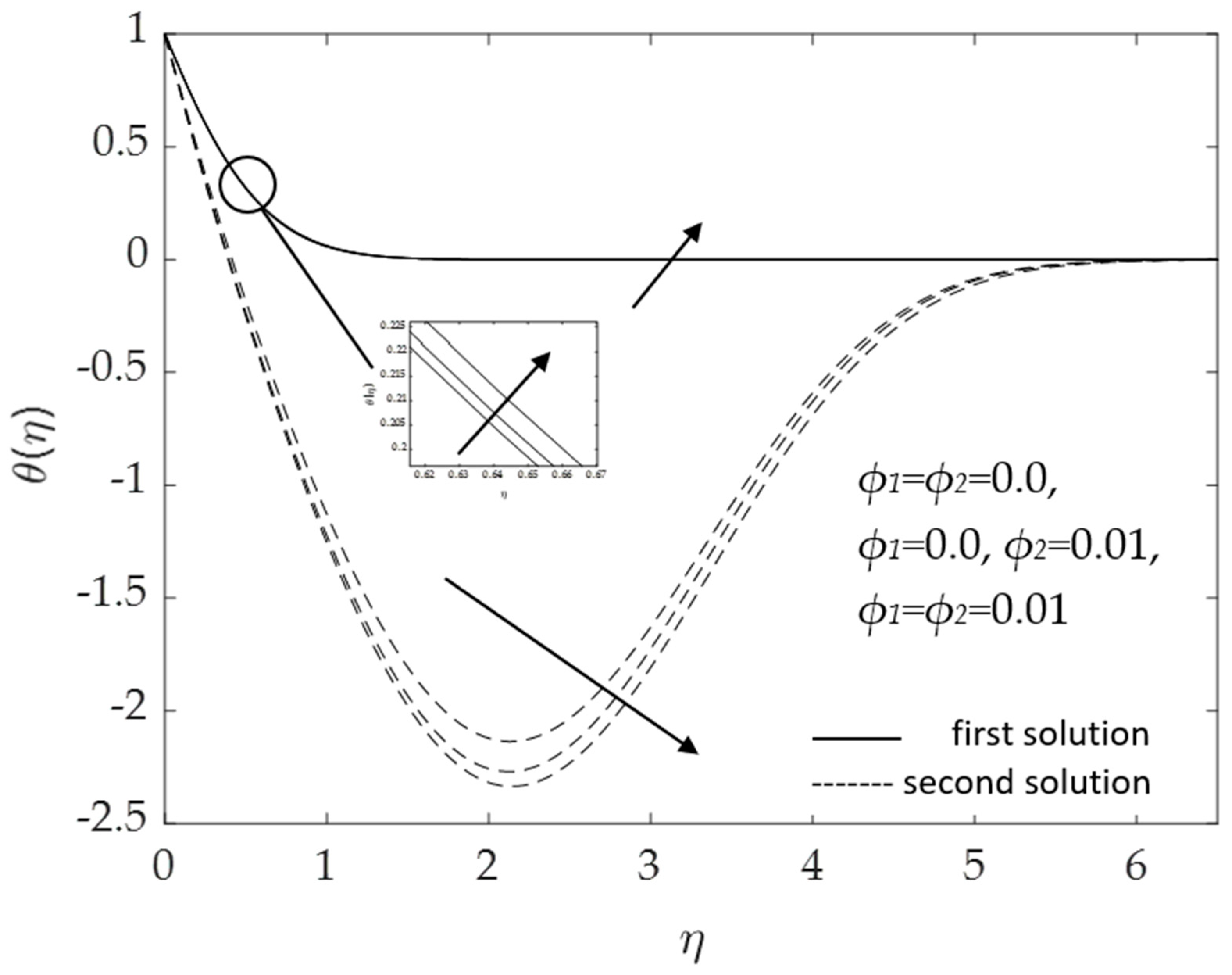
- The skin friction coefficient and the heat transfer rate of the Al2O3-Cu/H2O hybrid nanofluid (ϕ1 = ϕ2 = 0.01) is higher than that of the nanofluid (ϕ1 = 0%, ϕ2 = 1%) and water (ϕ1 = ϕ2 = 0.0);
- Larger values of the curvature parameter K and mixed convection parameter λ result in a slower detachment of the boundary layer;
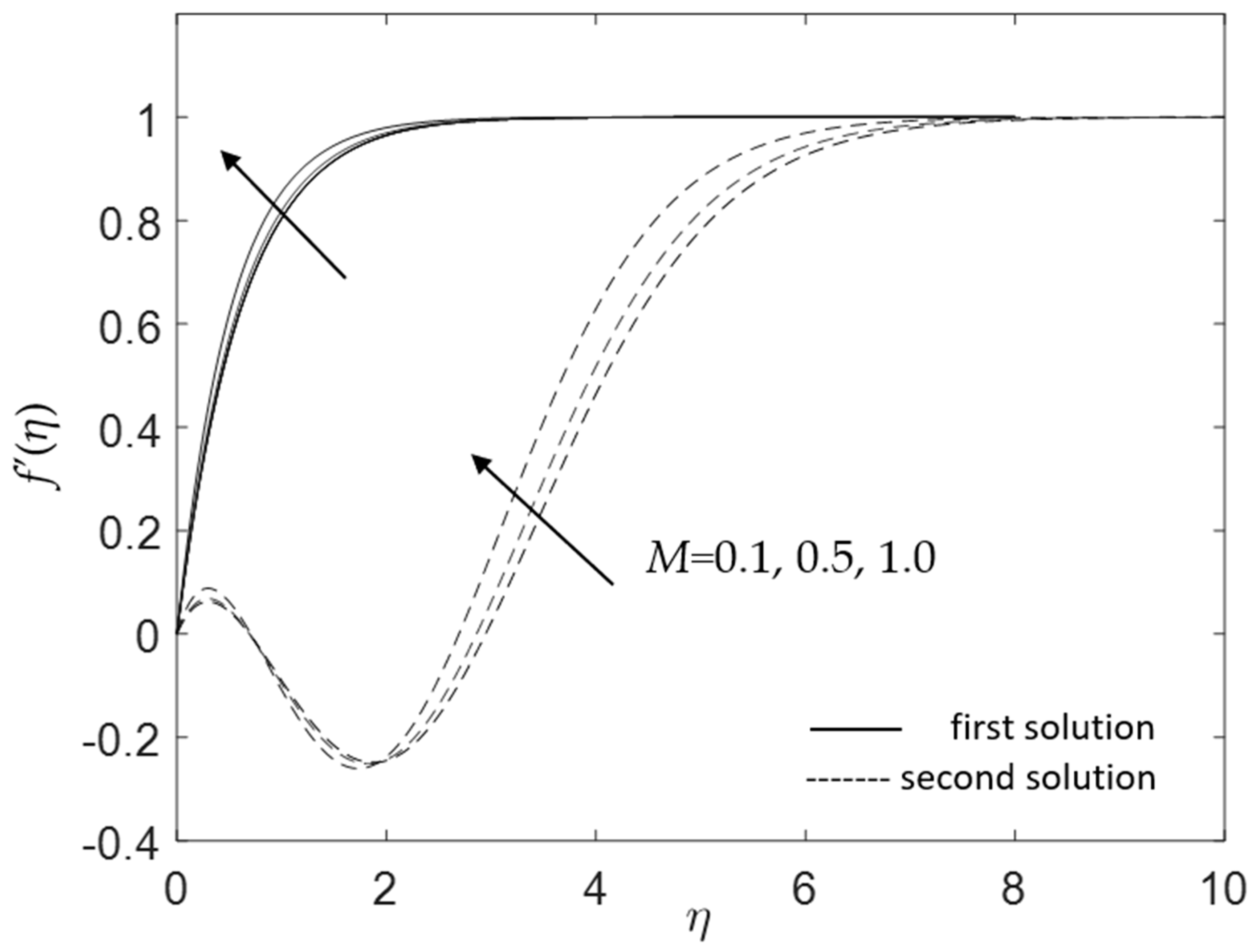
- Velocity increases with increasing values of the buoyancy parameter λ, magnetic parameter M, and hybrid nanofluid nanoparticle volume fraction ϕ1, ϕ2, whereas it declines for curvature parameter K and the inclined angle ω;
- The velocity and temperature gradients upsurge with a higher impact of the magnetic parameter;
- According to the temporal stability analysis, the first solution is physically stable as time evolves, whereas the second solution is not reliable in the long run.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daungthongsuk, W.; Wongwises, S. A critical review of convective heat transfer of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 797–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Yuan, W. Analysis and optimization of a microchannel heat sink with V-ribs using nanofluids for micro solar cells. Micromachines 2019, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Chen, T.; Qi, J.; Du, J.; Pan, G.; Huang, L. Investigation on the heat transfer enhancement by nanofluid under electric field considering electrophorestic and thermophoretic effect. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Synthesis of Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluids using two step method and its thermo physical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 388, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Su, Q.; Wang, R.; Huang, L.; Shao, C.; Zhu, Z. Why can hybrid nanofluid improve thermal conductivity more? A molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 372, 121178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Mixed convection flow over an exponentially stretching/shrinking vertical surface in a hybrid nanofluid. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.S.U.; Devi, S.P.A. Heat transfer enhancement of Cu−Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet. J. Niger. Math. Soc. 2017, 36, 419–433. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.R.; Pan, K.; Khan, A.U.; Nadeem, S. Dual solutions for mixed convection flow of SiO2−Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid near the stagnation point over a curved surface. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 547, 123959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Effect of Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluid in heat transfer. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 38, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshuhail, L.A.; Shaik, F.; Sundar, L.S. Thermal efficiency enhancement of mono and hybrid nanofluids in solar thermal applications–A review. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 68, 365–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga Babu, J.A.; Kiran Kumar, K.; Srinivasa Rao, S. Thermodynamic analysis of hybrid nanofluid based solar flat plate collector. World J. Eng. 2018, 15, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, E.; Movahed, S.; Hosseini, R. Experimental and numerical investigations on the effect of Al2O3/TiO2H2O nanofluids on thermal efficiency of the flat plate solar collector. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinheuer, J. Die lösungen der Blasiusschen grenzschichtdifferentialgleichung. Proc. Wiss. Ges. Braunschw. 1968, 20, 96–125. [Google Scholar]
- Klemp, J.B.; Acrivos, A. A moving-wall boundary layer with reverse flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1976, 76, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, G. On similarity solutions of boundary layer problems with upstream moving wall in non-Newtonian power-law fluids. IMA J. Appl. Math. Inst. Math. Its Appl. 2012, 77, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, M.Y.; Lakin, W.D. Existence and non-uniqueness of similarity solutions of a boundary-layer problem. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1986, 39, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.; Bachok, N. Power-law fluid flow on a moving wall. Eur. J. Sci. Res. ISSN 2009, 1450, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Khashi’ie, N.S.; Arifin, N.M.; Pop, I. Mixed convective stagnation point flow towards a vertical riga plate in hybrid Cu-Al2O3/water nanofluid. Mathematics 2020, 8, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer past a vertical thin needle with prescribed surface heat flux. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 29, 4875–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohut, F.H.; Ishak, A. MHD Stagnation Point of Blasius Flow for Micropolar Hybrid Nanofluid toward a Vertical Surface with Stability Analysis. Symmetry 2023, 15, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemenz, K. Die Grenzschicht an einem inden gleichförmigen Flüssigkeitsstrom eingetauchten geraden Kreiszylinder. Dinglers Polytech. J. 1911, 326, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Chiam, T.C. Stagnation-point flow towards a stretching plate. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 63, 2443–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y. Stagnation flow towards a shrinking sheet. Int. J. Non. Linear Mech. 2008, 43, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, Y.Y.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. MHD stagnation-point flow towards a shrinking sheet. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2011, 21, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaludin, I.S.; Weidman, P.D.; Ishak, A. Stability analysis of stagnation-point flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 045308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.; Nazar, R.; Bachok, N.; Pop, I. MHD mixed convection flow near the stagnation-point on a vertical permeable surface. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2010, 389, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, F.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary layer flow near stagnation-point on vertical surface with slip. Appl. Math. Mech. 2011, 32, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Mehdi, I.; Hasnain, J.; Alzahrani, A.K.; Asma, M. Homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in MHD mixed convection fluid flow between concentric cylinders with heat generation and heat absorption. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 42, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Ehsan, M.; Ahmad, H.; Ilyas, A. Combined effects of MHD and slip velocity on oscillatory mixed convective flow around a non-conducting circular cylinder embedded in a porous medium. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 38, 102341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N.A.; Nazar, R.; Naganthran, K.; Pop, I. MHD mixed convection stagnation point flow of a hybrid nanofluid past a vertical flat plate with convective boundary condition. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 66, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhu, Z. A review on heat transfer of nanofluids by applied electric field or magnetic field. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, H.B.M.; Isa, S.S.P.M.; Arifin, N.M. The boundary layer flow, heat and mass transfer beyond an exponentially stretching/shrinking inclined sheet. CFD Lett. 2020, 12, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Farooq, M.; Alsaedi, A. Inclined magnetic field effect in stratified stagnation point flow over an inclined cylinder. Z. Fur Naturforsch.–Sect. A J. Phys. Sci. 2015, 70, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Khan, I.; Gul, T.; Tassaddiq, A.; Alghamdi, W.; Mukhtar, S.; Kumam, P. Darcy-forchheimer hybrid nano fluid flow with mixed convection past an inclined cylinder. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 66, 2025–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil-Ur-Rehman; Malik, M.Y.; Bilal, S.; Bibi, M.; Ali, U. Logarithmic and parabolic curve fitting analysis of dual stratified stagnation point MHD mixed convection flow of Eyring-Powell fluid induced by an inclined cylindrical stretching surface. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanai, R.; Rana, P.; Kumar, L. MHD mixed convection nanofluid flow and heat transfer over an inclined cylinder due to velocity and thermal slip effects: Buongiorno’s model. Powder Technol. 2016, 288, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sharma, K. Mixed convective MHD flow and heat transfer of uniformly conducting nanofluid past an inclined cylinder in presence of thermal radiation. J. Nanofluids 2017, 6, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabi, B.; Salehi, S. Augmentation of the heat transfer performance of a sinusoidal corrugated enclosure by employing hybrid nanofluid. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 2014, 147059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Sikdar, S.; Basu, S. Experimental investigation of the effective electrical conductivity of aluminum oxide nanofluids. Powder Technol. 2009, 196, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Hybrid nanofluid flow over a permeable non-isothermal shrinking surface. Mathematics 2021, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A. Mixed convection boundary layer flow over a vertical cylinder with prescribed surface heat flux. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2009, 42, 195501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzulkifli, N.F.; Bachok, N.; Yacob, N.A.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H. Unsteady stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over a permeable exponential stretching/shrinking sheet in nanofluid with slip velocity effect: A stability analysis. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Sherif, E.-S.M. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of a Hybrid Nanofluid over a Stretching/Shrinking Sheet Executing MHD Flow. Symmetry 2020, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N. Double solutions and stability analysis of micropolar hybrid nanofluid with thermal radiation impact on unsteady stagnation point flow. Mathematics 2021, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. J. Eng. Math. 1986, 20, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidman, P.D.; Kubitschek, D.G.; Davis, A.M.J. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, Y.Y.; Amin, N.; Campean, D.; Pop, I. Steady mixed convection flow of a micropolar fluid near the stagnation point on a vertical surface. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2005, 15, 654–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Hybrid nanofluid flow towards a stagnation point on a stretching/shrinking cylinder. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaludin, A.; Naganthran, K.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I. MHD mixed convection stagnation-point flow of Cu-Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid over a permeable stretching/shrinking surface with heat source/sink. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2020, 84, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.U.; Malik, M.Y.; Salahuddin, T.; Naseer, M. Dual stratified mixed convection flow of Eyring-Powell fluid over an inclined stretching cylinder with heat generation/absorption effect. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 075112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Properties | Hybrid Nanofluid |
|---|---|
| Density | |
| Dynamic viscosity | |
| Thermal conductivity | |
| Electrical conductivity | |
| Heat capacity | |
| Thermal expansion |
| Physical Properties | Water | Cu | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4179 | 385 | 765 | |
| 21 | 1.67 | 0.85 | |
| 0.613 | 400 | 40 | |
| 0.05 | |||
| 997.1 | 8933 | 3970 | |
| Pr | 6.2 |
| Pr | Lok et al. [51] (Keller-Box) | Ishak et al. [28] (Keller-Box) | Current Study (bvp4c) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Solution | First Solution | Second Solution | First Solution | Second Solution | |
| 0.7 | 1.706376 | 1.7063 | 1.2387 | 1.706323 | 1.238728 |
| 1.0 | - | 1.6755 | 1.1332 | 1.675437 | 1.133192 |
| 7.0 | 1.517952 | 1.5179 | 0.5824 | 1.517913 | 0.582401 |
| 10.0 | - | 1.4928 | 0.4958 | 1.492839 | 0.495779 |
| 20.0 | 1.448520 | 1.4485 | 0.3436 | 1.448483 | 0.343640 |
| 40.0 | 1.410094 | 1.4101 | 0.2111 | 1.410058 | 0.211101 |
| 50.0 | - | 1.3989 | 0.1720 | 1.398930 | 0.172048 |
| 60.0 | 1.390311 | 1.3903 | 0.1413 | 1.390274 | 0.141292 |
| Pr | Lok et al. [51] (Keller-Box) | Ishak et al. [28] (Keller-Box) | Current Study (bvp4c) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Solution | First Solution | Second Solution | First Solution | Second Solution | |
| 0.7 | 0.764087 | 0.7641 | 1.0226 | 0.764063 | 1.022631 |
| 1.0 | - | 0.8708 | 1.1691 | 0.870779 | 1.169126 |
| 7.0 | 1.722775 | 1.7224 | 2.2191 | 1.722382 | 2.219194 |
| 10.0 | - | 1.9446 | 2.4940 | 1.944617 | 2.494029 |
| 20.0 | 2.458836 | 2.4576 | 3.1646 | 2.457590 | 3.164608 |
| 40.0 | 3.103703 | 3.1011 | 4.1080 | 3.101093 | 4.108024 |
| 50.0 | - | 3.3415 | 4.4976 | 3.341458 | 4.497588 |
| 60.0 | 3.555404 | 3.5514 | 4.8572 | 3.551406 | 4.857187 |
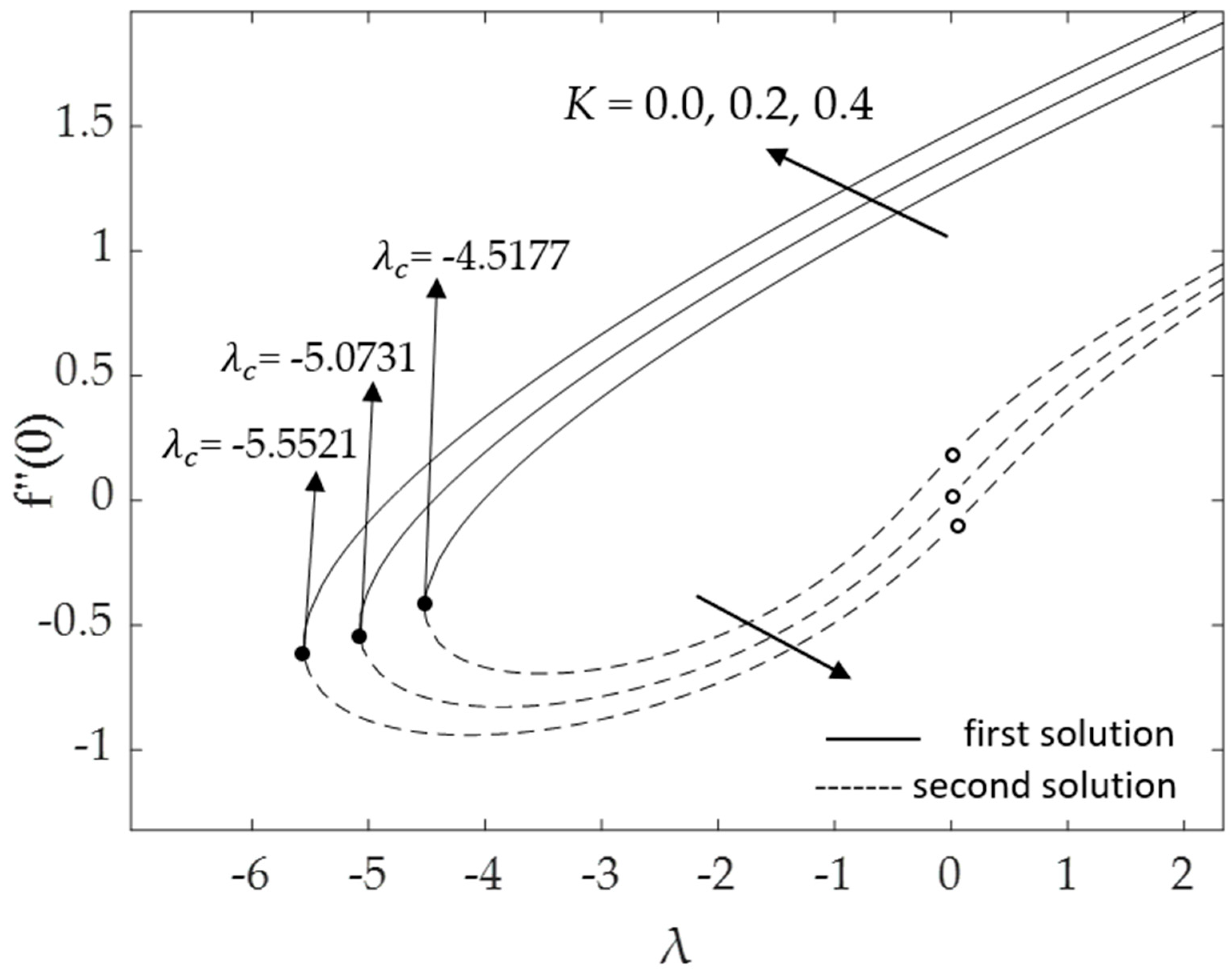
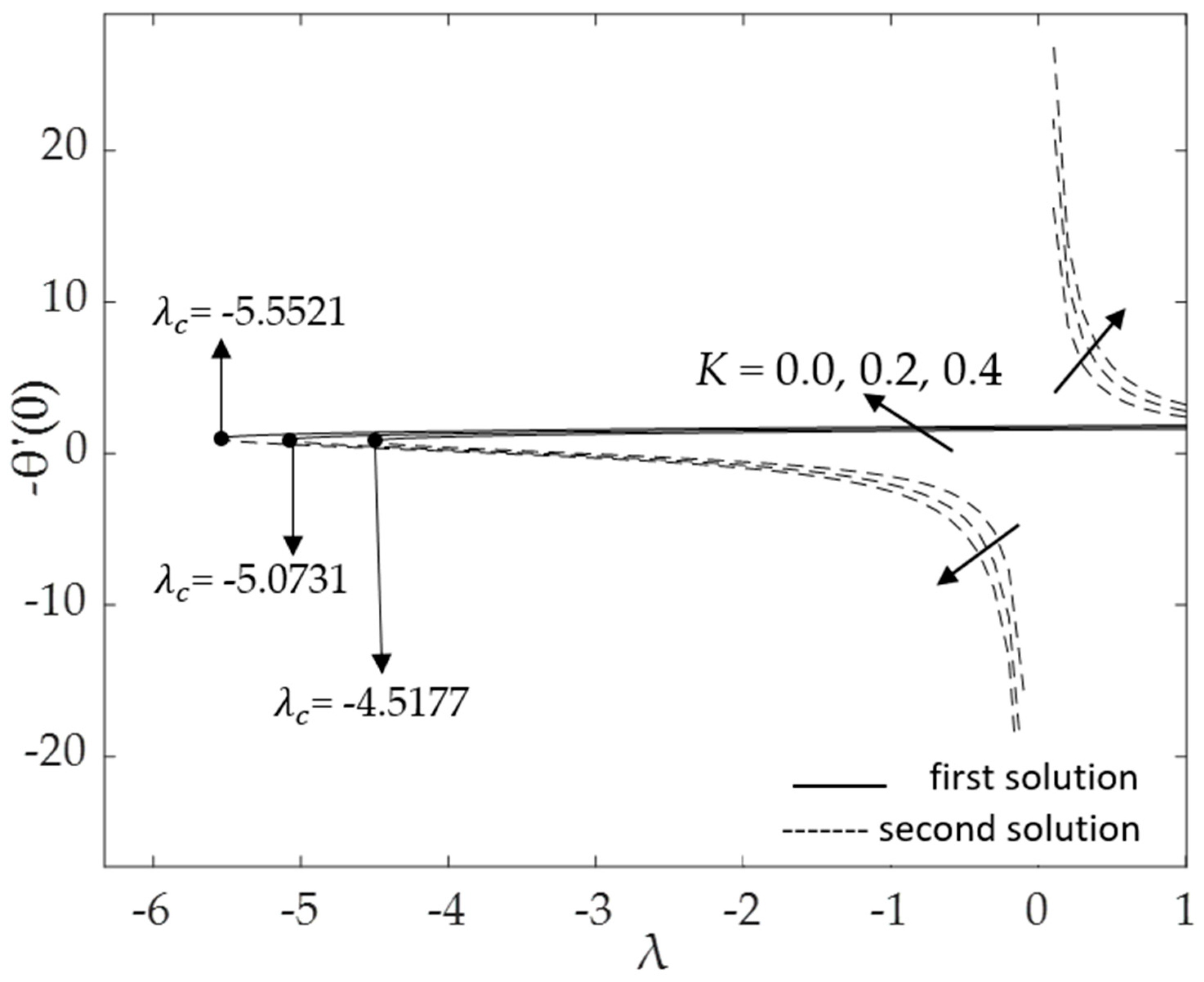
| K | Smallest Eigenvalue | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First Solution | Second Solution | ||
| 0.0 | −4.5 | 0.0972 | −0.0963 |
| −4.51 | 0.0641 | −0.0641 | |
| −4.517 | 0.0199 | −0.0218 | |
| −4.5177 | 0.0104 | −0.0103 | |
| 0.2 | −4.5 | 0.5486 | −0.5091 |
| −5.0 | 0.1996 | −0.1943 | |
| −5.07 | 0.0709 | −0.0703 | |
| −5.073 | 0.0597 | −0.0592 | |
| −5.0731 | 0.0593 | −0.0588 | |
| −4.5 | 0.7357 | −0.6675 | |
| 0.4 | −5.0 | 0.5353 | −0.4991 |
| −5.5 | 0.2065 | −0.2010 | |
| −5.55 | 0.1385 | −0.1361 | |
| −5.552 | 0.1351 | −0.1328 | |
| −5.5521 | 0.1350 | −0.1326 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohut, F.H.; Khan, U.; Ishak, A.; Soid, S.K.; Waini, I. Mixed Convection Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Induced by an Inclined Cylinder with Lorentz Forces. Micromachines 2023, 14, 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14050982
Sohut FH, Khan U, Ishak A, Soid SK, Waini I. Mixed Convection Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Induced by an Inclined Cylinder with Lorentz Forces. Micromachines. 2023; 14(5):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14050982
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohut, Farizza Haniem, Umair Khan, Anuar Ishak, Siti Khuzaimah Soid, and Iskandar Waini. 2023. "Mixed Convection Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Induced by an Inclined Cylinder with Lorentz Forces" Micromachines 14, no. 5: 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14050982
APA StyleSohut, F. H., Khan, U., Ishak, A., Soid, S. K., & Waini, I. (2023). Mixed Convection Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Induced by an Inclined Cylinder with Lorentz Forces. Micromachines, 14(5), 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14050982








