Synthesis of Er3+:YAG Nanocrystals and Comparative Spectroscopic Analysis with Bulk Counterparts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
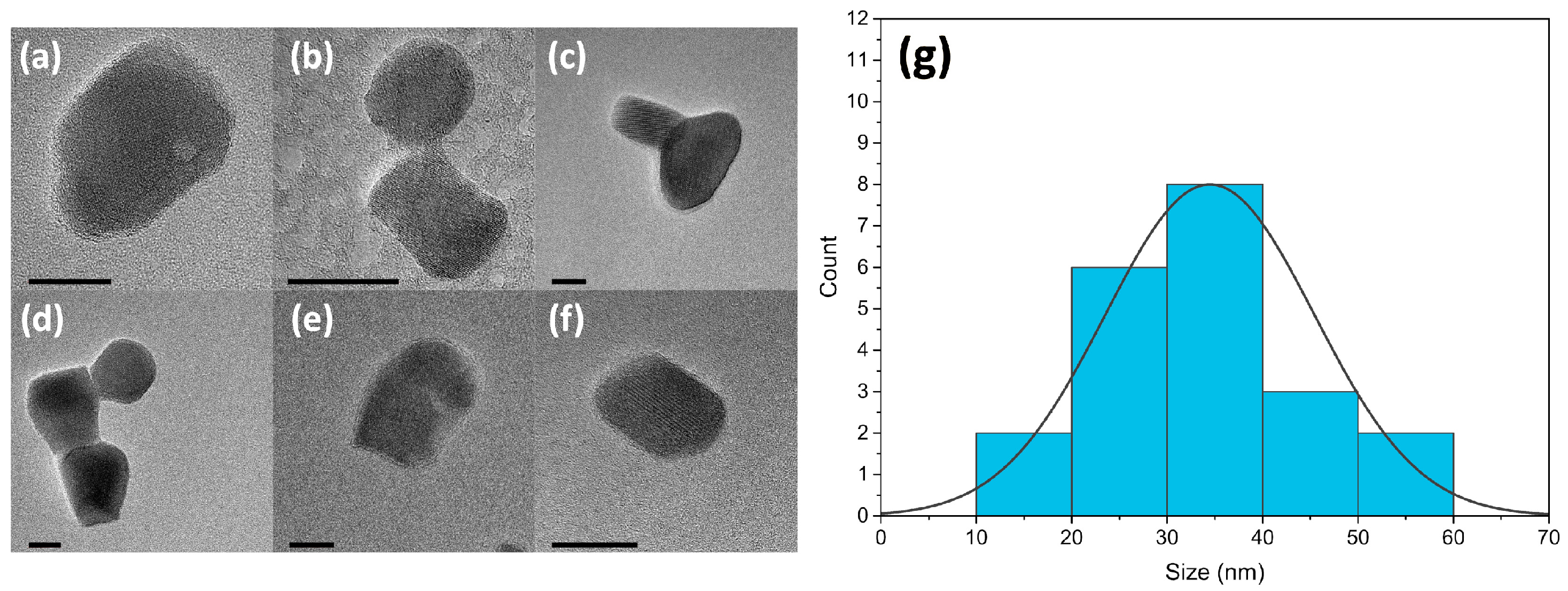
3.1. Morphology
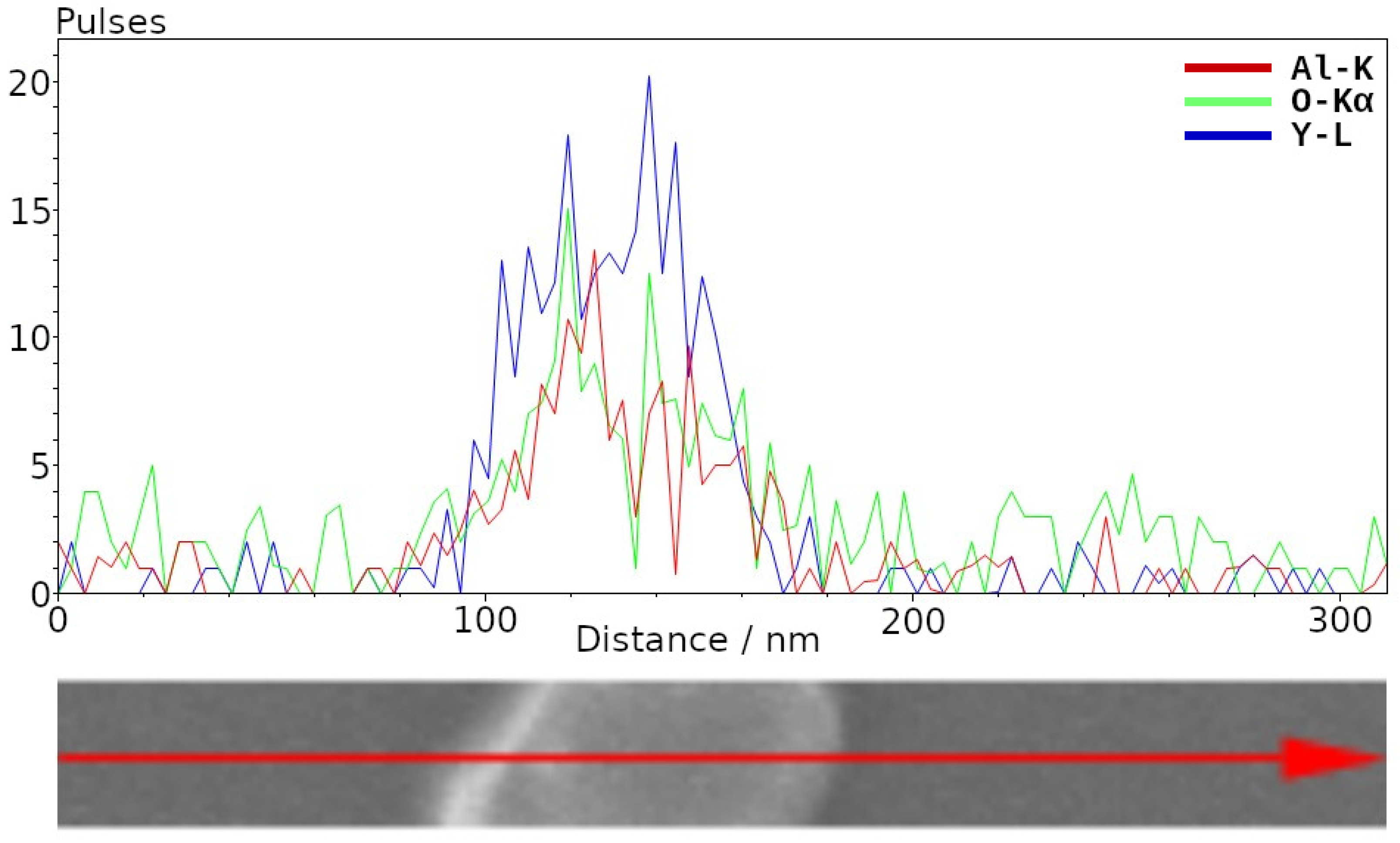
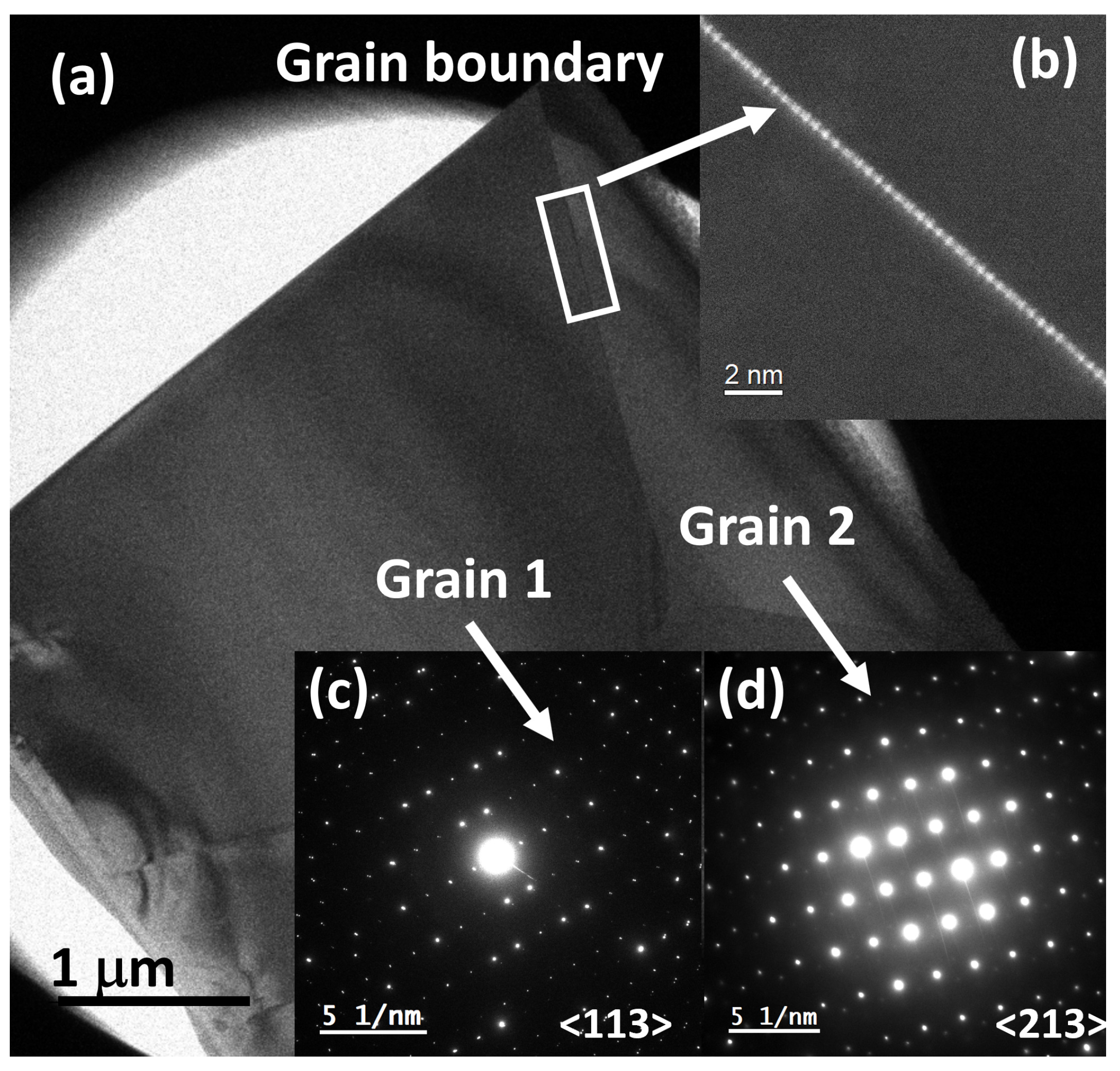
3.2. Microscopy
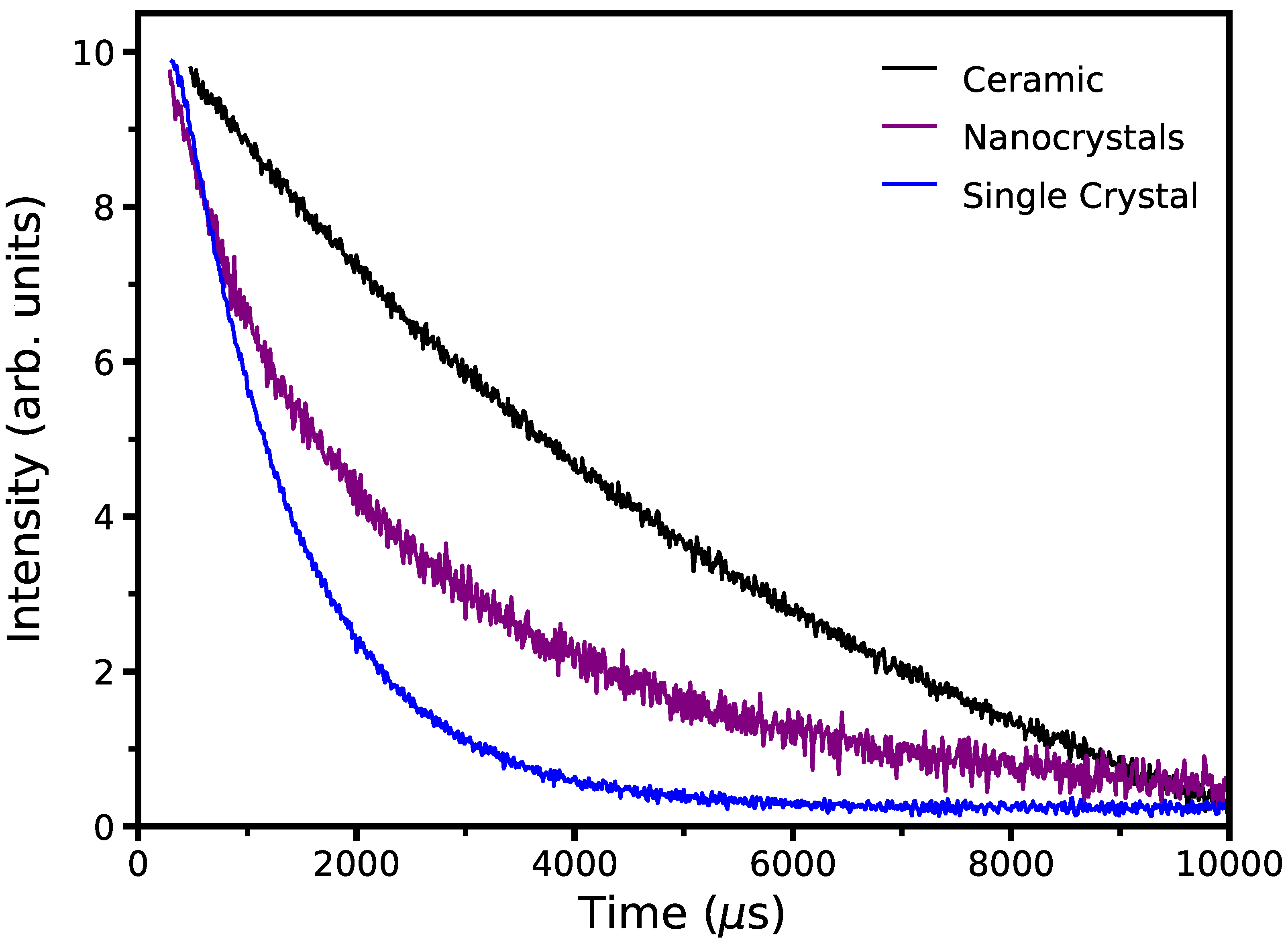
3.3. Spectroscopy
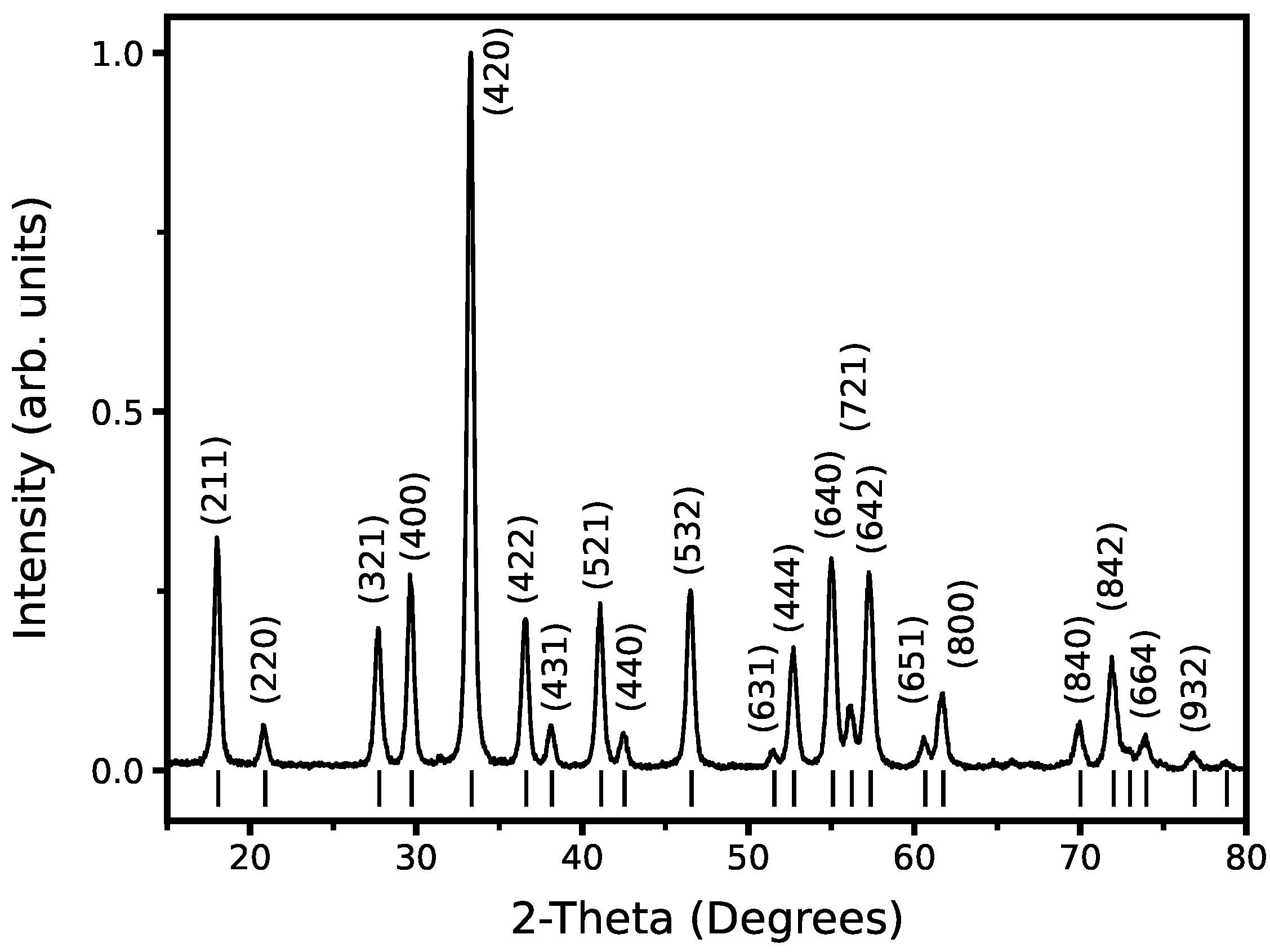
3.4. Crystal Structure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YAG | Yttrium aluminum garnet |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| RE | Rare-earth |
| XRD | X-Ray diffraction |
| FWHM | Full width at half maximum |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| STEM | Scanning transmission electron microscope |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| HRTEM | High-resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| PTI | Photon technology international |
| FIB | Focused ion beam |
| SAED | Selected area electron diffraction |
| PED | Precession electron diffraction |
| HAADF | High-angle annular dark field |
| Cs | Spherical aberration correction |
References
- Koechner, W. Solid-State Laser Engineering; Springer Series in Optical Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccheo, S.; Laporta, P.; Longhi, S.; Svelto, O.; Svelto, C. Diode-pumped bulk erbium-ytterbium lasers. Appl. Phys. B 1996, 63, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, T.; Jensen, T.; Heumann, E.; Huber, G. Spectroscopic properties and diode pumped 1.6 μm laser performance in Yb-codoped Er:Y3Al5O12 and Er:Y2SiO5. Opt. Commun. 1995, 118, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, H.; Shen, D.; Chen, H.; Zhou, G.; Luo, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Tang, D. Fabrication and Optical Properties of Highly Transparent Er:YAG Polycrystalline Ceramics for Eye-Safe Solid-State Lasers. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2013, 10, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dawes, J.M.; Burns, P.; Piper, J.A.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Meng, X. Diode-pumped cw tunable Er3+:Yb3+:YCOB laser at 1.5–1.6 μm. Opt. Mater. 2002, 19, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieke, G.H. Spectra and Energy Levels of Rare Earth Ions in Crystals. Am. J. Phys. 1970, 38, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greskovich, C.; Chernoch, J.P. Polycrystalline ceramic lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 1973, 44, 4599–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekita, M.; Haneda, H.; Shirasaki, S.; Yanagitani, T. Optical spectra of undoped and rare-earth-(=Pr, Nd, Eu, and Er) doped transparent ceramic Y3Al5O12. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 3709–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.A.; Jianren, L.; Kaminskii, A.A.; Ueda, K.I.; Yagi, H.; Yanagitani, T.; Unnikrishnan, N.V. Spectroscopic and stimulated emission Characteristics of Nd3+ in transparent YAG ceramics. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2004, 40, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupei, V.; Lupei, A.; Ikesue, A. Transparent polycrystalline ceramic laser materials. Opt. Mater. 2008, 30, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.B.; Nijjar, A.S.; Sardar, D.K.; Yow, R.M.; Russell, C.C.; Allik, T.H.; Zandi, B. Spectral analysis and energy-level structure of Er3+(4f11) in polycrystalline ceramic garnet Y3Al5O12. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 063519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikesue, A.; Kinoshita, T.; Kamata, K.; Yoshida, K. Fabrication and optical properties of high-performance polycrystalline Nd:YAG ceramics for solid-state lasers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 78, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Prabhu, M.; Xu, J.; Ueda, K.i.; Yagi, H.; Yanagitani, T.; Kaminskii, A.A. Highly efficient 2% Nd: Yttrium aluminum garnet ceramic laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 3707–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ueda, K.i.; Yagi, H.; Yanagitani, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Kaminskii, A.A. Neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Y3Al5O12) nanocrystalline ceramics—A new generation of solid state laser and optical materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 341, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Q.; Bass, M.; Birnbaum, M. Effects of energy transfer among Er3+ ions on the fluorescence decay and lasing properties of heavily doped Er:Y3Al5O12. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1990, 7, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhekov, V.I. Cooperative process in Y3Al5O12:Er3+ crystals. Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 1986, 16, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, D.K.; Russell, C.C.; Gruber, J.B.; Allik, T.H. Absorption intensities and emission cross sections of principal intermanifold and inter-Stark transitions of Er3+ (4f11) in polycrystalline ceramic garnet Y3Al5O12. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladino, M.L.; Caponetti, E.; Martino, D.C.; Enzo, S.; Ibba, G. Effect of the dopant selection (Er, Eu, Nd or Ce) and its quantity on the formation of yttrium aluminum garnet nanopowders. Opt. Mater. 2008, 31, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, M.; Tanabe, S.; Inoue, M.; Takahashi, M.; Fujita, K.; Hirao, K. Optical-telecommunication-band fluorescence properties of Er3+-doped YAG nanocrystals synthesized by glycothermal method. Opt. Mater. 2005, 27, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.A.; Tobar, E.H.; la Rosa, E.D.; Díaz-Torres, L.A.; Salas, P.; Torres, A.; Felix, M.V.; Castañeda-Contreras, J.; Yacaman, M.J. Structural and photoluminescence characterization of nanocrystalline YAG: Er3+ prepared with the addition of PVA and UREA. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6639, 66390K. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarles, G.J. (VLOC, 7826 Photonics Drive, New Port Richey, FL 34655, USA). Personal Communication, 2020.
- Kokta, M.R. (Bicron Crystal Products, 750 South 32nd Street, Washougal, WA 98671, USA). Personal Communication, 2020.
- Dai, P.; Ji, C.; Shen, L.; Qian, Q.; Guo, G.; Zhang, X.; Bao, N. Photoluminescence properties of YAG:Ce3+,Pr3+ nano-sized phosphors synthesized by a modified co-precipitation method. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, M.; Kumar, G.A.; Ma, C.G.; Brik, M.G.; Langloss, B.W.; Stanton, I.N.; Therien, M.J.; Sardar, D.K.; Mao, Y. Electronic and optical properties of Er-doped Y2O2S phosphors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 11486–11496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltmarsh, N.; Kumar, G.; Kailasnath, M.; Shenoy, V.; Santhosh, C.; Sardar, D. Spectroscopic characterizations of Er doped LaPO4 submicron phosphors prepared by homogeneous precipitation method. Opt. Mater. 2016, 53, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimun, L.C.; Ajithkumar, G.; Rightsell, C.; Langloss, B.W.; Therien, M.J.; Sardar, D.K. Synthesis and characterization of Na(Gd0.5Lu0.5)F4: Nd3+, a core-shell free multifunctional contrast agent. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathri, K.; Kumar, G.A.; Manrique, S.I.R.; Santhosh, C.; Sardar, D.K. Optical characterization of infrared emitting Nd3+ doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method. J. Lumin. 2017, 185, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, H.; Keith, M. Complete substitution of aluminum for silicon: The system 3MnO·Al2O3·3SiO2–3Y2O3·5Al2O3. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1951, 36, 519–533. [Google Scholar]
- Jüstel, T.; Nikol, H.; Ronda, C. New Developments in the Field of Luminescent Materials for Lighting and Displays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 3084–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.; Sanchez, D.; Sardar, D.; Arellano, J.; Ponce, A. Microstructural Analysis of Polycrystalline Er:YAG using Automated Crystal Orientation Mapping. Proc. Microsc. Microanal. 2018, 24, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennycook, S. Z-contrast stem for materials science. Ultramicroscopy 1989, 30, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, M.; Kumar, G.A.; Samuel, P.; Ueda, K.I.; Yanagitani, T.; Yagi, H.; Sardar, D.K. Infrared and upconversion spectroscopic studies of high Er3+ content transparent YAG ceramic. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, M.; Ray, N.; Kumar, G.A.; Sardar, D.K. Comparative studies of the spectroscopic properties of Nd3+: YAG nanocrystals, transparent ceramic and single-crystal. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rightsell, C.; Sanchez, D.; Escudero, J.; Ortega, E.; Ajithkumar, G.; Sardar, D.; Ponce, A. Synthesis of Er3+:YAG Nanocrystals and Comparative Spectroscopic Analysis with Bulk Counterparts. Micromachines 2023, 14, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020255
Rightsell C, Sanchez D, Escudero J, Ortega E, Ajithkumar G, Sardar D, Ponce A. Synthesis of Er3+:YAG Nanocrystals and Comparative Spectroscopic Analysis with Bulk Counterparts. Micromachines. 2023; 14(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleRightsell, Chris, David Sanchez, José Escudero, Eduardo Ortega, Gangadharan Ajithkumar, Dhiraj Sardar, and Arturo Ponce. 2023. "Synthesis of Er3+:YAG Nanocrystals and Comparative Spectroscopic Analysis with Bulk Counterparts" Micromachines 14, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020255
APA StyleRightsell, C., Sanchez, D., Escudero, J., Ortega, E., Ajithkumar, G., Sardar, D., & Ponce, A. (2023). Synthesis of Er3+:YAG Nanocrystals and Comparative Spectroscopic Analysis with Bulk Counterparts. Micromachines, 14(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020255






