Stimulus-Evoked Activity Modulation of In Vitro Engineered Cortical and Hippocampal Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
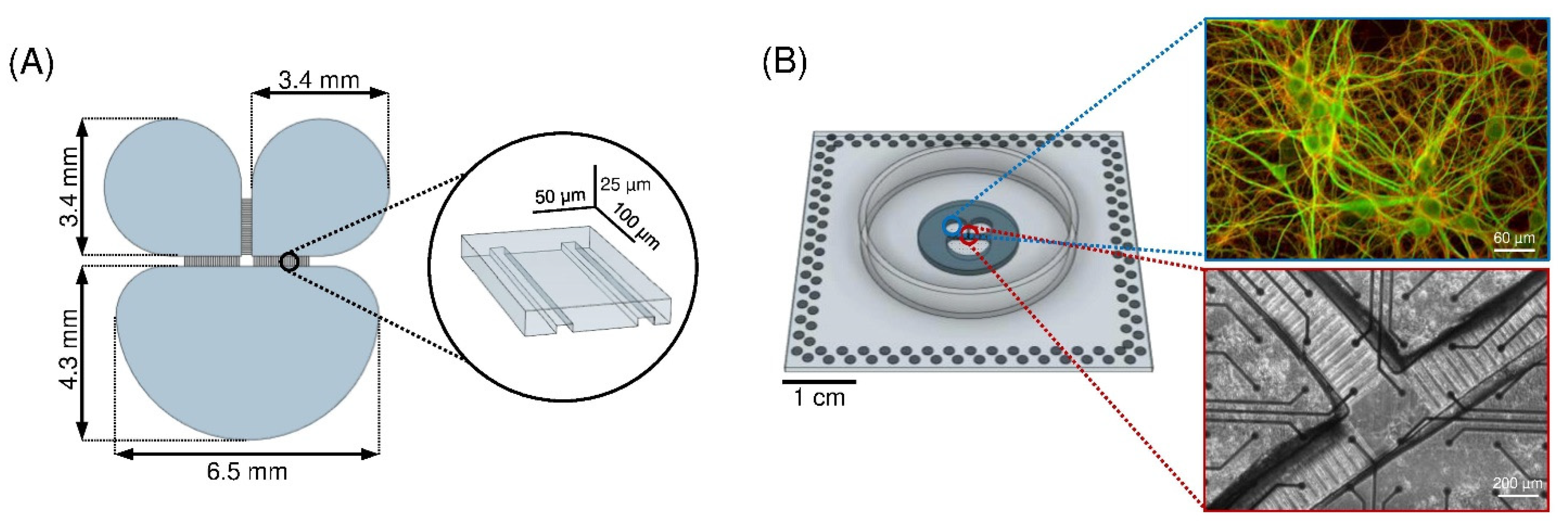
2.1. Polymeric Device
2.2. Cell Culture Preparation
2.3. Ethical Approval
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.5. Dataset
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
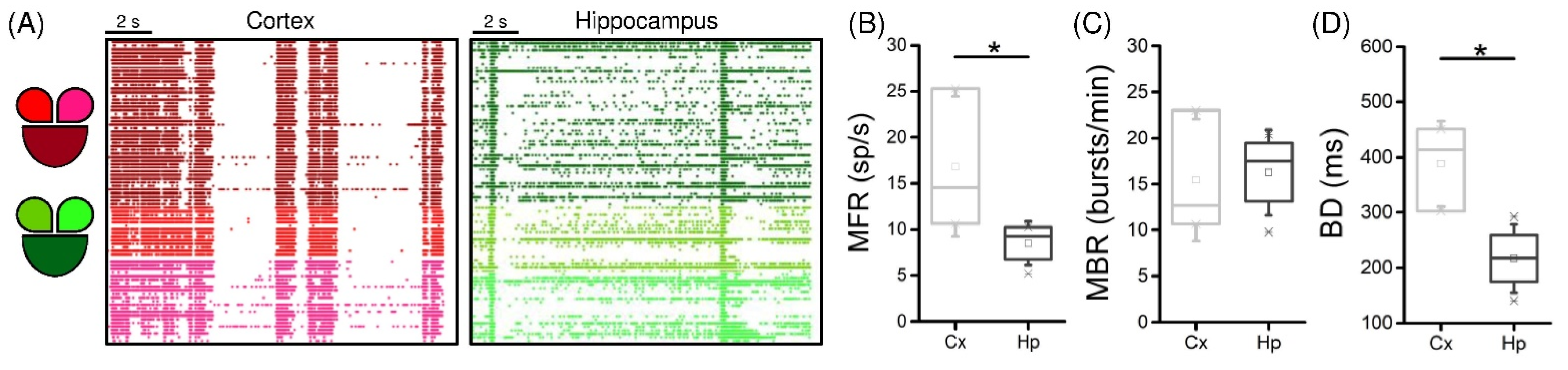
3.1. Interconnected Cortical and Hippocampal Assemblies Display Spontaneous Activity
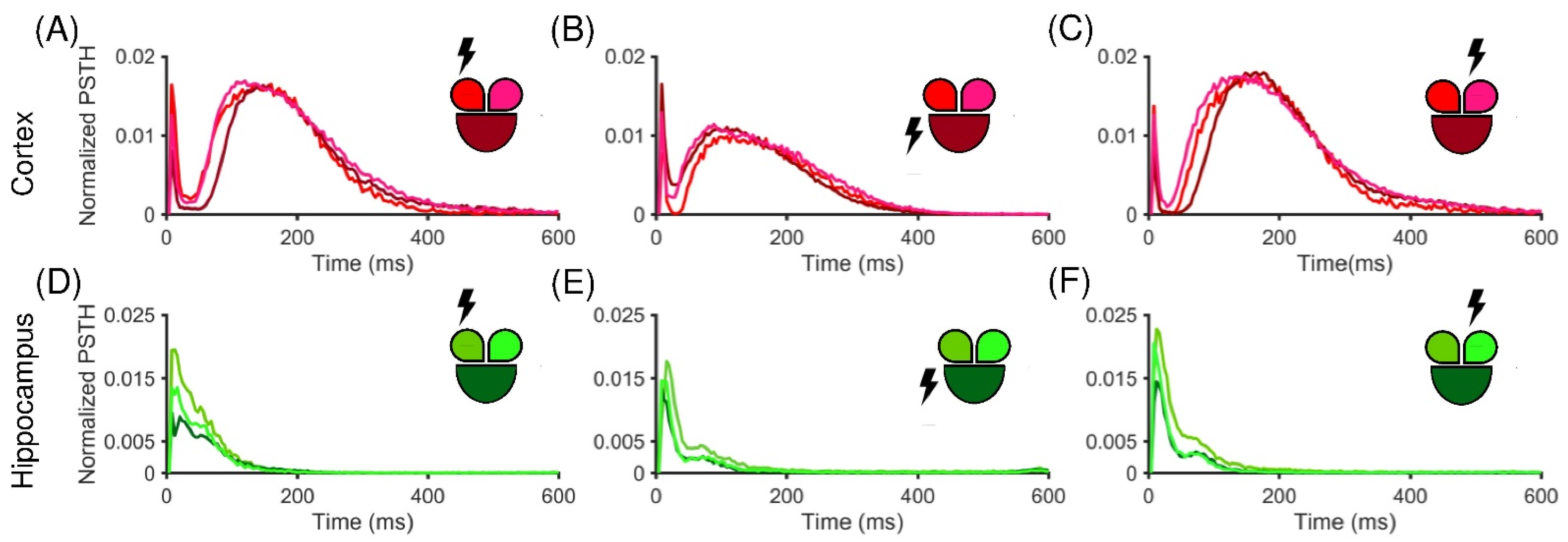
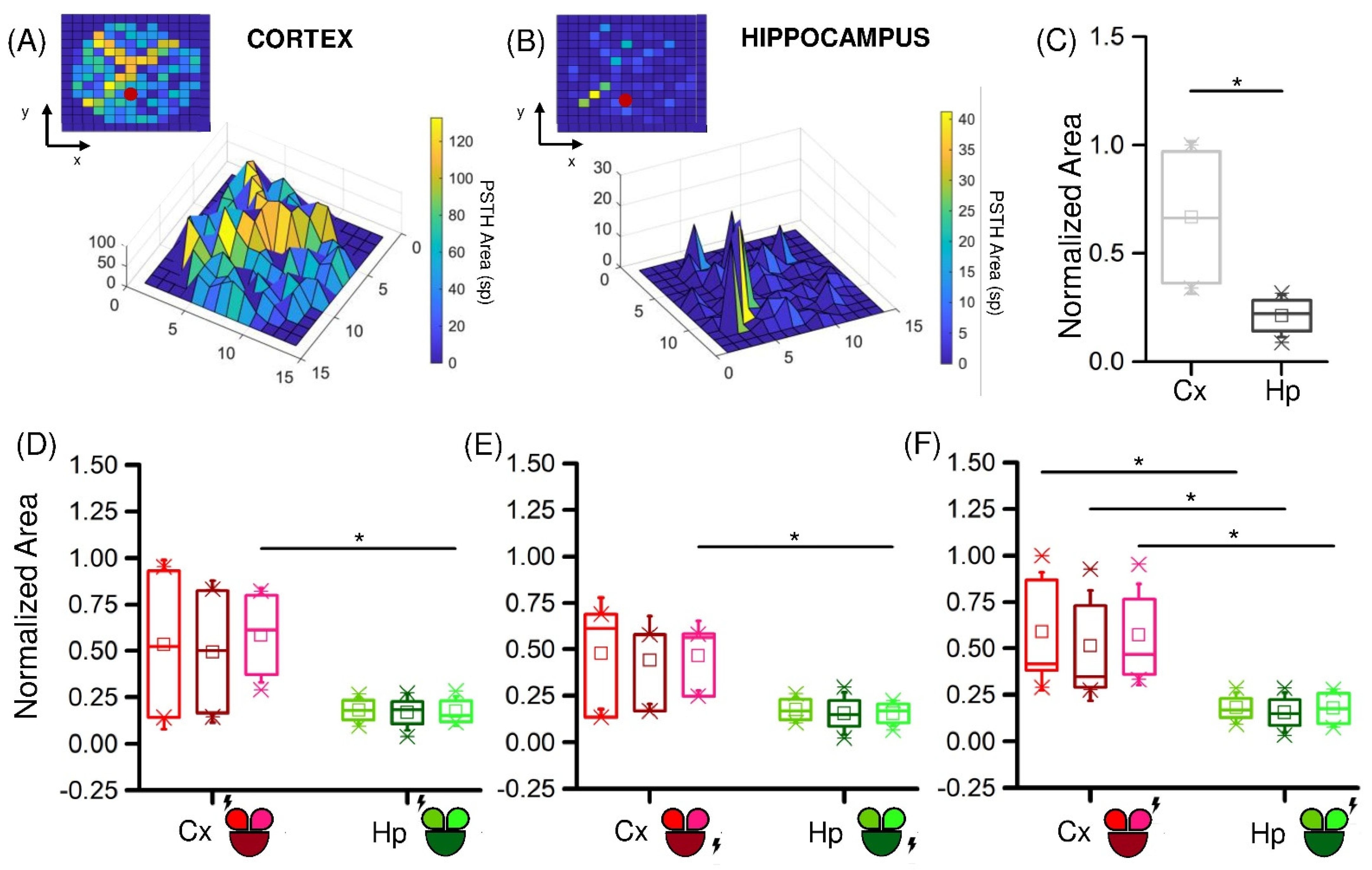
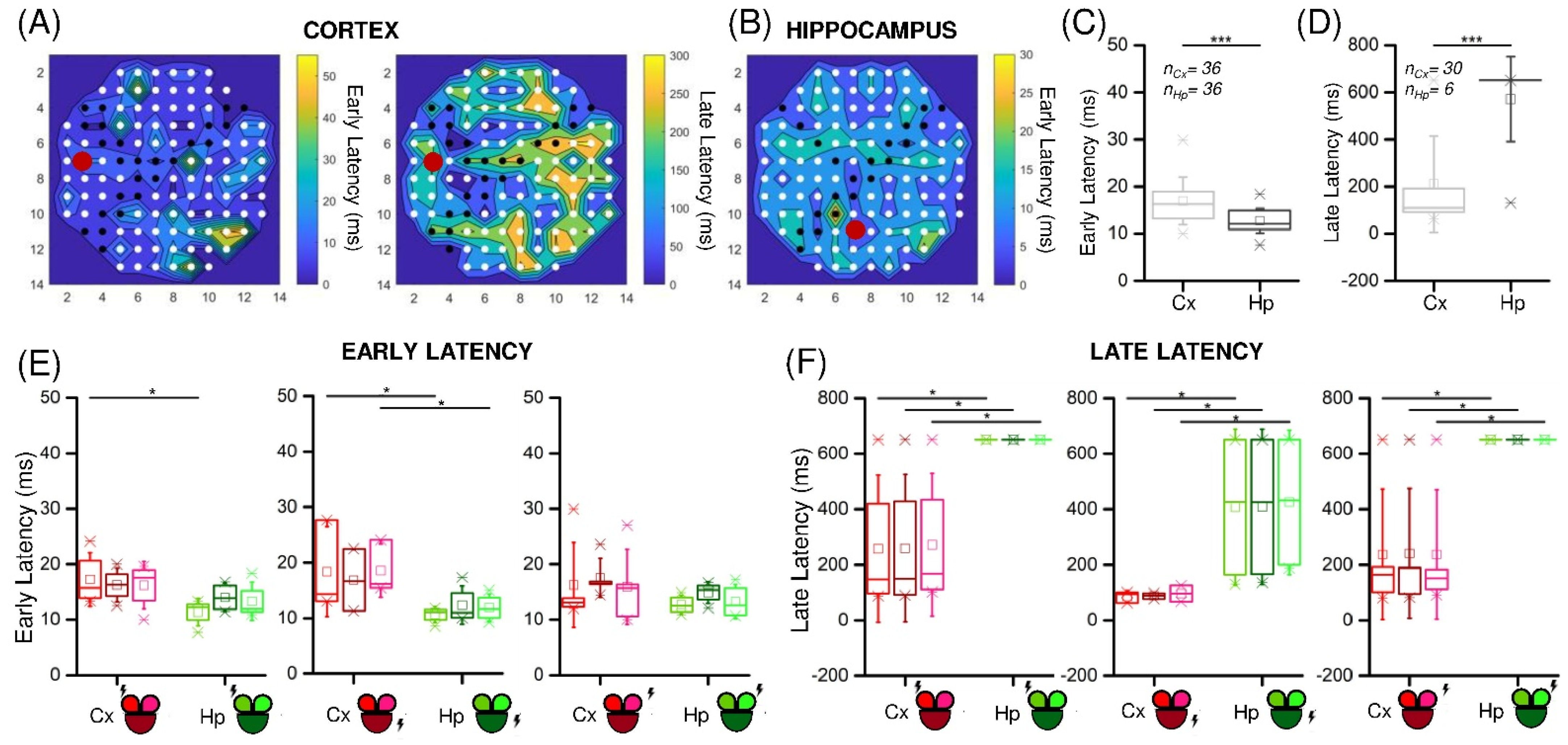
3.2. Low-Frequency Electrical Stimulation Produces Different Response Patterns in Cortical and Hippocampal Populations
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arieli, A.; Sterkin, A.; Grinvald, A.; Aertsen, A. Dynamics of Ongoing Activity: Explanation of the Large Variability in Evoked Cortical Responses. Science 1996, 273, 1868–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, D.A.; Pine, J.; Potter, S.M. An extremely rich repertoire of bursting patterns during the development of cortical cultures. BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, M.J. The origin of spontaneous activity in developing networks of the vertebrate nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1999, 9, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsáki, G.; Draguhn, A. Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 2004, 304, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, O. Structure and function of complex brain networks. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, D.; Pastore, V.P.; Massobrio, P. Functional connectivity in in vitro neuronal assemblies. Front. Neural Circuits 2015, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, A.D.; Madhavan, R.; Pine, J.; Potter, S.M. Controlling Bursting in Cortical Cultures with Closed-Loop Multi-Electrode Stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massobrio, P.; Baijon, P.L.; Maccione, A.; Chiappalone, M.; Martinoia, S. Activity modulation elicited by electrical stimulation in networks of dissociated cortical neurons. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 3008–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, M.S.; Charlesworth, P.; Kitzbichler, M.G.; Paulsen, O.; Bullmore, E.T. Emergence of rich-club topology and coordinated dynamics in development of hippocampal functional networks in vitro. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5459–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, V.P.; Massobrio, P.; Godjoski, A.; Martinoia, S. Identification of excitatory-inhibitory links and network topology in large-scale neuronal assemblies from multi-electrode recordings. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shein-Idelson, M.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Hanein, Y. Engineered neuronal circuits: A new platform for studying the role of modular topology. Front. Neuroeng. 2011, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, E.; Nieus, T.; Maccione, A.; Valente, P.; Simi, A.; Messa, M.; Dante, S.; Baldelli, P.; Berdondini, L.; Benfenati, F. Emergent Functional Properties of Neuronal Networks with Controlled Topology. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Alagapan, S.; Franca, E.; Leondopulos, S.S.; DeMarse, T.B.; Brewer, G.J.; Wheeler, B.C. An in vitro method to manipulate the direction and functional strength between neural populations. Front. Neural Circuits 2015, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Moriya, S.; Ide, K.; Hayakawa, T.; Akima, H.; Sato, S.; Kubota, S.; Tanii, T.; Niwano, M.; Teller, S.; et al. Impact of modular organization on dynamical richness in cortical networks. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauth, S.; Maoz, B.M.; Sheehy, S.P.; Hemphill, M.A.; Murty, T.; Macedonia, M.K.; Greer, A.M.; Budnik, B.; Parker, K.K. Neurons derived from different brain regions are inherently different in vitro: A novel multiregional brain-on-a-chip. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 1320–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimbo, Y.; Tateno, T.; Robinson, H.P.C. Simultaneous Induction of Pathway-Specific Potentiation and Depression in Networks of Cortical Neurons. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, M.E.; Bonifazi, P.; Torre, V. Toward the neurocomputer: Image processing and pattern recognition with neuronal cultures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappalone, M.; Massobrio, P.; Martinoia, S. Network plasticity in cortical assemblies. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Massobrio, P. High-frequency electrical stimulation promotes reshaping of the functional connections and synaptic plasticity in in vitro cortical networks. Phys. Biol. 2018, 15, 06LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eytan, D.; Marom, S. Dynamics and effective topology underlying synchronization in networks of cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 8465–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajda, I.; Van Pelt, J.; Wolters, P.; Chiappalone, M.; Martinoia, S.; Van Someren, E.; Van Ooyen, A. Low-frequency stimulation induces stable transitions in stereotypical activity in cortical networks. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 5028–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Feber, J.; Stegenga, J.; Rutten, W.L.C. The Effect of Slow Electrical Stimuli to Achieve Learning in Cultured Networks of Rat Cortical Neurons. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brofiga, M.; Massobrio, P. Brain-on-a-Chip: Dream or Reality? Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 837623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brofiga, M.; Pisano, M.; Tedesco, M.; Boccaccio, A.; Massobrio, P. Functional Inhibitory Connections Modulate the Electrophysiological Activity Patterns of Cortical-Hippocampal Ensembles. Cereb. Cortex 2022, 32, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.M.; Rhee, S.W.; Tu, C.H.; Cribbs, D.H.; Cotman, C.W.; Jeon, N.L. Microfluidic Multicompartment Device for Neuroscience Research. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrieger, F.W.; Barres, B.A. Synaptic efficacy enhanced by glial cells in vitro. Science 1997, 277, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Parpura, V.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Haydon, P.G. Tripartite synapses: Glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccione, A.; Gandolfo, M.; Massobrio, P.; Novellino, A.; Martinoia, S.; Chiappalone, M. A novel algorithm for precise identification of spikes in extracellularly recorded neuronal signals. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 177, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappalone, M.; Novellino, A.; Vajda, I.; Vato, A.; Martinoia, S.; van Pelt, J. Burst detection algorithms for the analysis of spatio-temporal patterns in cortical networks of neurons. Neurocomputing 2005, 65–66, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahaf, G.; Eytan, D.; Gal, A.; Kermany, E.; Lyakhov, V.; Zrenner, C.; Marom, S. Order-Based Representation in Random Networks of Cortical Neurons. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pasquale, V.; Martinoia, S.; Chiappalone, M. Stimulation triggers endogenous activity patterns in cultured cortical networks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonomano, D.V.; Maass, W. State-dependent computations: Spatiotemporal processing in cortical networks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, M.; la Camera, G.; Fusi, S.; Senn, W. The response of cortical neurons to in vivo-like input current: Theory and experiment: II. Time-varying and spatially distributed inputs. Biol. Cybern. 2008, 99, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkai, O.; Butterman, R.; Katz, B.; Lev, S.; Binshtok, A.M. The input-output relation of primary nociceptive neurons is determined by the morphology of the peripheral nociceptive terminals. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 9346–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieus, T.; D’Andrea, V.; Amin, H.; Di Marco, S.; Safaai, H.; Maccione, A.; Berdondini, L.; Panzeri, S. State-dependent representation of stimulus-evoked activity in high-density recordings of neural cultures. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Camera, G.; Giugliano, M.; Senn, W.; Fusi, S. The response of cortical neurons to in vivo-like input current: Theory and experiment. Biol. Cybern. 2008, 99, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrin, J.M.; Deleglise, B.; Saias, L.; Vignes, M.; Gougis, P.; Magnifico, S.; Betuing, S.; Pietri, M.; Caboche, J.; Vanhoutte, P.; et al. Axon diodes for the reconstruction of oriented neuronal networks in microfluidic chambers. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3663–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.I.; Choe, Y.; Li, J.; Han, A. A microchip for quantitative analysis of CNS axon growth under localized biomolecular treatments. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 221, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Pastore, V.P.; Martinoia, S.; Massobrio, P. From functional to structural connectivity using partial correlation in neuronal assemblies. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 026023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarse, T.B.; Pan, L.; Alagapan, S.; Brewer, G.J.; Wheeler, B.C. Feed-Forward Propagation of Temporal and Rate Information between Cortical Populations during Coherent Activation in Engineered In Vitro Networks. Front. Neural Circuits 2016, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brofiga, M.; Pisano, M.; Callegari, F.; Massobrio, P. Exploring the contribution of thalamic and hippocampal input on cortical dynamics in a brain-on-a-chip model. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2021, 3, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Furukawa, T.; Asahina, T.; Shimba, K.; Kotani, K.; Jimbo, Y. Coupling of in vitro Neocortical-Hippocampal Coculture Bursts Induces Different Spike Rhythms in Individual Networks. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 873664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenmos, D.J.; Azin, M.; Barbay, S.; Mahnken, J.D.; Dunham, C.; Mohseni, P.; Nudo, R.J. Restoration of function after brain damage using a neural prosthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 21177–21182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, L.J.; Rehme, A.K.; Michely, J.; Nettekoven, C.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Fink, G.R.; Grefkes, C. Shaping Early Reorganization of Neural Networks Promotes Motor Function after Stroke. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 2882–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, M.D.; Meira, B.; Fernandes, M.; Barbosa, R.; Bugalho, P. Deep brain stimulation for lesion-related tremors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 47, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebner, H.R.; Funke, K.; Aberra, A.S.; Antal, A.; Bestmann, S.; Chen, R.; Classen, J.; Davare, M.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Fox, P.T.; et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain: What is stimulated?—A consensus and critical position paper. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 140, 59–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brofiga, M.; Pisano, M.; Raiteri, R.; Massobrio, P. On the road to the brain-on-a-chip: A review on strategies, methods, and applications. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 41005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brofiga, M.; Pisano, M.; Tedesco, M.; Raiteri, R.; Massobrio, P. Three-dimensionality shapes the dynamics of cortical interconnected to hippocampal networks. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 56044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Callegari, F.; Brofiga, M.; Poggio, F.; Massobrio, P. Stimulus-Evoked Activity Modulation of In Vitro Engineered Cortical and Hippocampal Networks. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13081212
Callegari F, Brofiga M, Poggio F, Massobrio P. Stimulus-Evoked Activity Modulation of In Vitro Engineered Cortical and Hippocampal Networks. Micromachines. 2022; 13(8):1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13081212
Chicago/Turabian StyleCallegari, Francesca, Martina Brofiga, Fabio Poggio, and Paolo Massobrio. 2022. "Stimulus-Evoked Activity Modulation of In Vitro Engineered Cortical and Hippocampal Networks" Micromachines 13, no. 8: 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13081212
APA StyleCallegari, F., Brofiga, M., Poggio, F., & Massobrio, P. (2022). Stimulus-Evoked Activity Modulation of In Vitro Engineered Cortical and Hippocampal Networks. Micromachines, 13(8), 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13081212






