Acetone Sensor Based on FAIMS-MEMS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Basic Working Principle of FAIMS
2.1. Principle and Sensor Design
2.1.1. The Ionization Area
2.1.2. The Migration Zone
2.1.3. The Detection Area
2.2. Design of the Sensor
2.2.1. The Ionization Zone
2.2.2. The Migration Area and the Collection Area
2.2.3. Readout Circuit
2.3. Manufacturing of Sensors
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Test Systems
3.2. Testing of Sensors
3.2.1. Testing of Acetone Gas
3.2.2. Nitrogen Interference Test
3.2.3. Moisture Interference Test
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saasa, V.; Malwela, T.; Beukes, M.; Mokgotho, M.; Liu, C.P.; Mwakikunga, B. Sensing Technologies for Detection of Acetone in Human Breath for Diabetes Diagnosis and Monitoring. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A. Toward portable breath acetone analysis for diabetes detection. J. Breath Res. 2011, 5, 037109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, W.; Duan, Y. Current Status of Methods and Techniques for Breath Analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2007, 37, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. A portable real-time ringdown breath acetone analyzer: Toward potential diabetic screening and management. Sensors 2016, 16, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belluomo, I.; Boshier, P.R.; Myridakis, A.; Vadhwana, B.; Markar, S.R.; Spanel, P.; Hanna, G.B. Selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry for targeted analysis of volatile organic compounds in human breath. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3419–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsé, C.; Hagemeyer, O.; van Kampen, V.; Raulf, M.; Weiss, T.; Menne, E.; Jettkant, B.; Kendzia, B.; Merget, R.; Brüning, T.; et al. Human Inhalation Study with Zinc Oxide: Analysis of Zinc Levels and Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath Condensate. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maurin, N.; Rousseau, R.; Trzpil, W.; Aoust, G.; Hayot, M.; Mercier, J.; Bahriz, M.; Gouzi, F.; Vicet, A. First clinical evaluation of a quartz enhanced photo-acoustic CO sensor for human breath analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 319, 128247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; Lamm, W.J.; Hlastala, M.P. Measuring airway exchange of endogenous acetone using a single-exhalation breathing maneuver. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Salmi, H.; Al-Douh, M.H.; Al-Hmmadi, K.; Al-Alas, A. Determination of arsenic and cadmium as toxic metals in human blood samples collected from targeted people of Sana’a governorate. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1900, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoyama, M.; Nitta, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ueda, H. Acetone and Isoprene Concentrations in Exhaled Breath in Healthy Subjects. Eisei Kagaku 2008, 54, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Si:WO3 Sensors for Highly Selective Detection of Acetone for Easy Diagnosis of Diabetes by Breath Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3581–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Gass, S.; Schmid, A.; Amann, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Breath acetone monitoring by portable Si:WO3 gas sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 738, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Worrall, A.D.; Bernstein, J.A.; Angelopoulos, A.P. Portable method of measuring gaseous acetone concentrations. Talanta 2013, 112, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Nikan, E.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mortazavi, Y. Highly sensitive carbon nanotubes–SnO2 nanocomposite sensor for acetone detection in diabetes mellitus breath. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Choi, S.; Kim, S.; Jang, J. Exhaled breath sensors. In Smart Sensors for Health and Environment Monitoring; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 19–49. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, C.; Walton, C.; Hoashi, S.; Evans, M. Breath acetone concentration decreases with blood glucose concentration in type I diabetes mellitus patients during hypoglycaemic clamps. J. Breath Res. 2009, 3, 046004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, M.J.; BAKarge Wrenshall, G.A. Acetone in the breath; a study of acetone exhalation in diabetic and nondiabetic human subjects. Diabetes 1952, 1, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwoebel, H.; Schubert, R.; Sklorz, M.; Kischkel, S.; Zimmermann, R.; Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W. Phase-resolved real-time breath analysis during exercise by means of smart processing of PTR-MS data. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2079–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Shaw, M.D.; Gillot, S.; Lewis, A.C. The impacts of watervapour and co-pollutants on the performance of electrochemical gas sensor used for air quality monitoring. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 266, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.J.; Patil, A.V.; Dighavkar, C.G.; Thakare, K.S.; Borase, R.Y.; Nandre, S.J.; Deshpande, N.G.; Ahire, R.R. Semiconductor metal oxide compounds based gas sensors: A literature review. Front. Mater. Sci. 2015, 9, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoshiki, Y.; Nakamoto, T. Ternary Gas Mixture Quantification Using Field Asymmetric Ion Mobility Spectrometry (FAIMS). Sensors 2019, 19, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Covington, J.A.; van der Schee, M.P.; Edge AS, L.; Boyle, B.; Savage, R.S.; Arasaradnam, R.P. The application of FAIMS gas analysis in medical diagnostics. Analyst 2015, 140, 6775–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maenaka, K. MEMS inertial sensors and their applications. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Networked Sensing Systems 2008 (INSS 2008), IKanazawa, Japan, 17–19 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shaeffer, D.K. MEMS inertial sensors: A tutorial overview. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2013, 51, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, M.T.; Taylor, S. Recent advances and development trends in miniature mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 422, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z. Study on simulation and experiment of array micro Faraday cup ion detector for FAIMS. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 3225–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, K.K.M. Detection of Contaminants Using a MEMS FAIMS Sensor. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Li, K.; Chen, C. Rapid Identification and On-Site Detection of Different Labeled Gasoline by the Integrated MEMS-FAIMS. Micronanoelectron. Technol. 2019, 56(09), 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Sielemann, S.; Baumbach, J.I.; Schmidt, H.; Pilzecker, P. Quantitative Analysis of Benzene, Toluene, and m-Xylene with the Use of a UV-Ion Mobility Spectrometer. Field Anal. Chem. Technol. 2000, 4, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Nazarov, E.G.; Eiceman, G.A.; King, A.T. A MEMS radio-frequency ion mobility spectrometer for chemical vapor detection. Sens. Actuators A 2001, 91, 201–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomiero, A.; Bianchi, S.; Comini, E.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Sberveglieri, G. Controlled Growth and Sensing Properties of In2O3 Nanowires. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 7, 2500–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakati, N.; Jee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.S. Thickness dependency of sol-gel derived ZnO thin films on gas sensing behaviors. Thin Solid Films 2010, 519, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Wang, Y.; Jee, S.H.; Park, M.; Yoon, Y.S.; Kim, D.J. Enhanced UV activation of electrochemically doped Ni in ZnO nanorods for room temperature acetone sensing. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 511, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bo, R.; Shrestha, A.; Xin, B.; Nasiri, N.; Zhou, J.; di Bernardo, I.; Dodd, A.; Saunders, M.; Lipton-Duffin, J.; et al. NiO–ZnO Nanoheterojunction Networks for Room-Temperature Volatile Organic Compounds Sensing. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, K.W.; Hsu, M.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Gwo, S.; Yeh, J.A. A Sub-ppm Acetone Gas Sensor for Diabetes Detection Using 10 nm Thick Ultrathin InN FETs. Sensors 2012, 12, 7157–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.S.; Lin, K.H.; Chang, Y.M.; Yeh, J.A. Epitaxy of m-plane GaN on nanoscale patterned c-plane sapphire substrates. Surf. Sci. 2012, 606, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














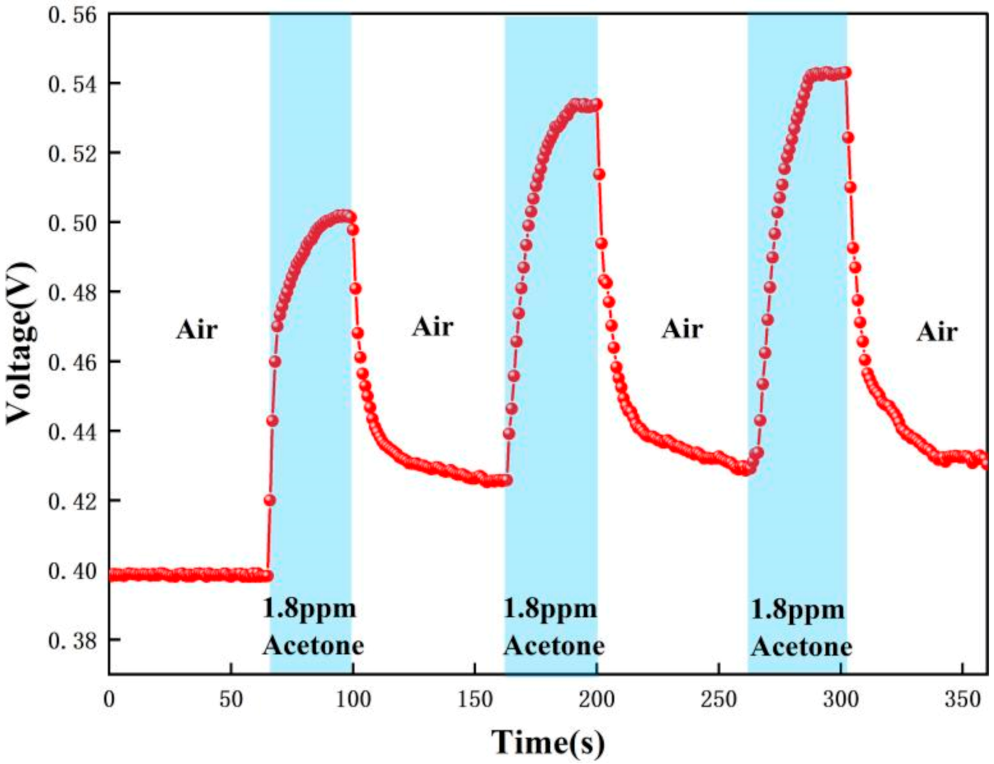

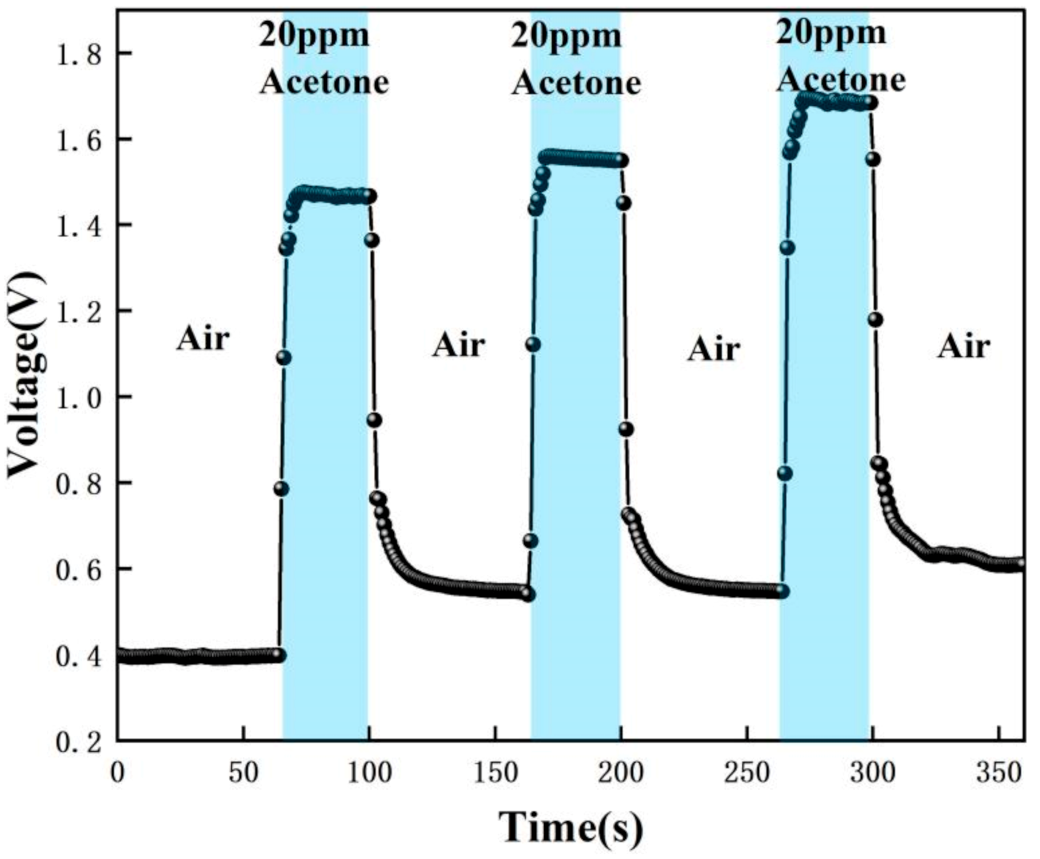





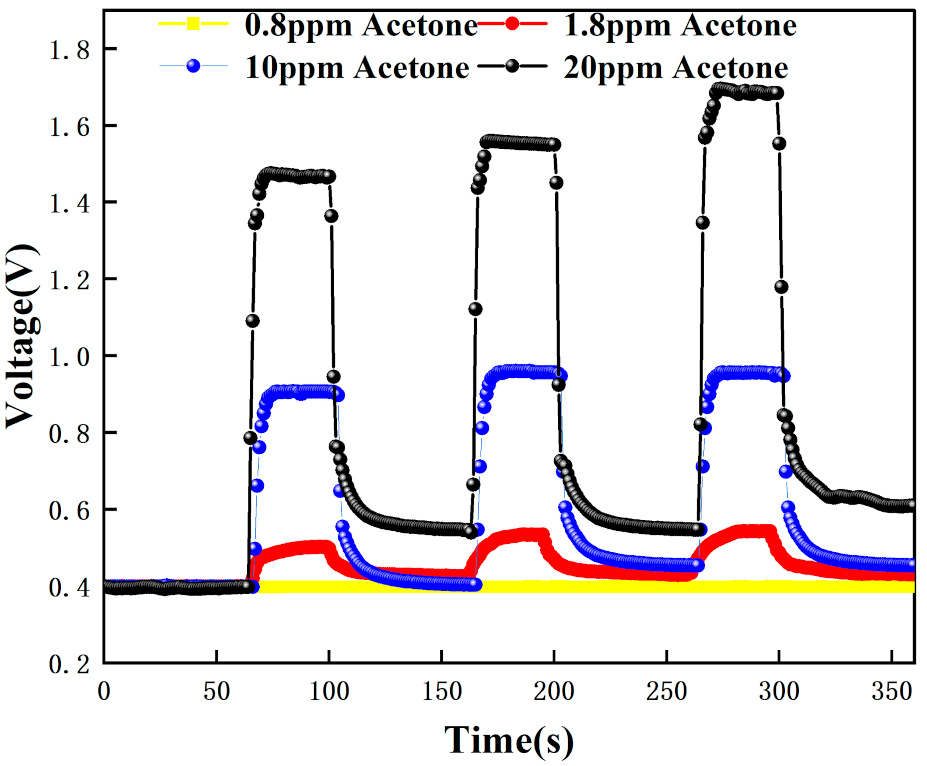






| 0–60 s | 61–100 s | 101–160 s | 161–200 s | 201–260 s | 261–300 s | 301–360 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | 0.8 ppm acetone | Air | 0.8 ppm acetone | Air | 0.8 ppm acetone | Air |
| Air | 1.8 ppm acetone | Air | 1.8 ppm acetone | Air | 1.8 ppm acetone | Air |
| Air | 10 ppm acetone | Air | 10 ppm acetone | Air | 10 ppm acetone | Air |
| Air | 20 ppm acetone | Air | 20 ppm acetone | Air | 20 ppm acetone | Air |
| Air | Nitrogen | Air | Nitrogen | Air | Nitrogen | Air |
| Air | Moisture | Air | Moisture | Air | Moisture | Air |
| Material | Type | Sensitivity | Detection Limit (ppm) | Operating Temperature (℃) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si: WO3 | Metal oxide gas sensors | 4.3(S = Rair/Racetone − 1) | 0.02 | 400 | [11] |
| In2O3 | Metal oxide gas sensors | 0.6% | 25 | 400 | [31] |
| ZnO | Metal oxide gas sensors | 5.71% | 100 | 200 | [32] |
| ZnO + Ni +UV light | Metal oxide gas sensors | 1.61% | 100 | RT | [33] |
| NiO-ZnO | Metal oxide gas sensors | −0.25(S = Iacetone/Iair − 1) | 0.11 | RT | [34] |
| InN | Metal nitride gas sensors | 28.7% | 0.4 | 200 | [35] |
| GaN | Metal nitride gas sensors | 23% | 500 | 350 | [36] |
| Si: BF33, Au | FAIMS-MEMS | 0.02 ppm/mV | 0.8 | RT | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Lei, C.; Liang, T.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Qi, L.; Ghaffar, A.; Xiong, J. Acetone Sensor Based on FAIMS-MEMS. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121531
Zhang J, Lei C, Liang T, Liu R, Zhao Z, Qi L, Ghaffar A, Xiong J. Acetone Sensor Based on FAIMS-MEMS. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121531
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junna, Cheng Lei, Ting Liang, Ruifang Liu, Zhujie Zhao, Lei Qi, Abdul Ghaffar, and Jijun Xiong. 2021. "Acetone Sensor Based on FAIMS-MEMS" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121531
APA StyleZhang, J., Lei, C., Liang, T., Liu, R., Zhao, Z., Qi, L., Ghaffar, A., & Xiong, J. (2021). Acetone Sensor Based on FAIMS-MEMS. Micromachines, 12(12), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121531







