Jet Mode Recognition of Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Writing Based on Micro/Nano Current
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Detection and Measurement System of Micro/Nano Current
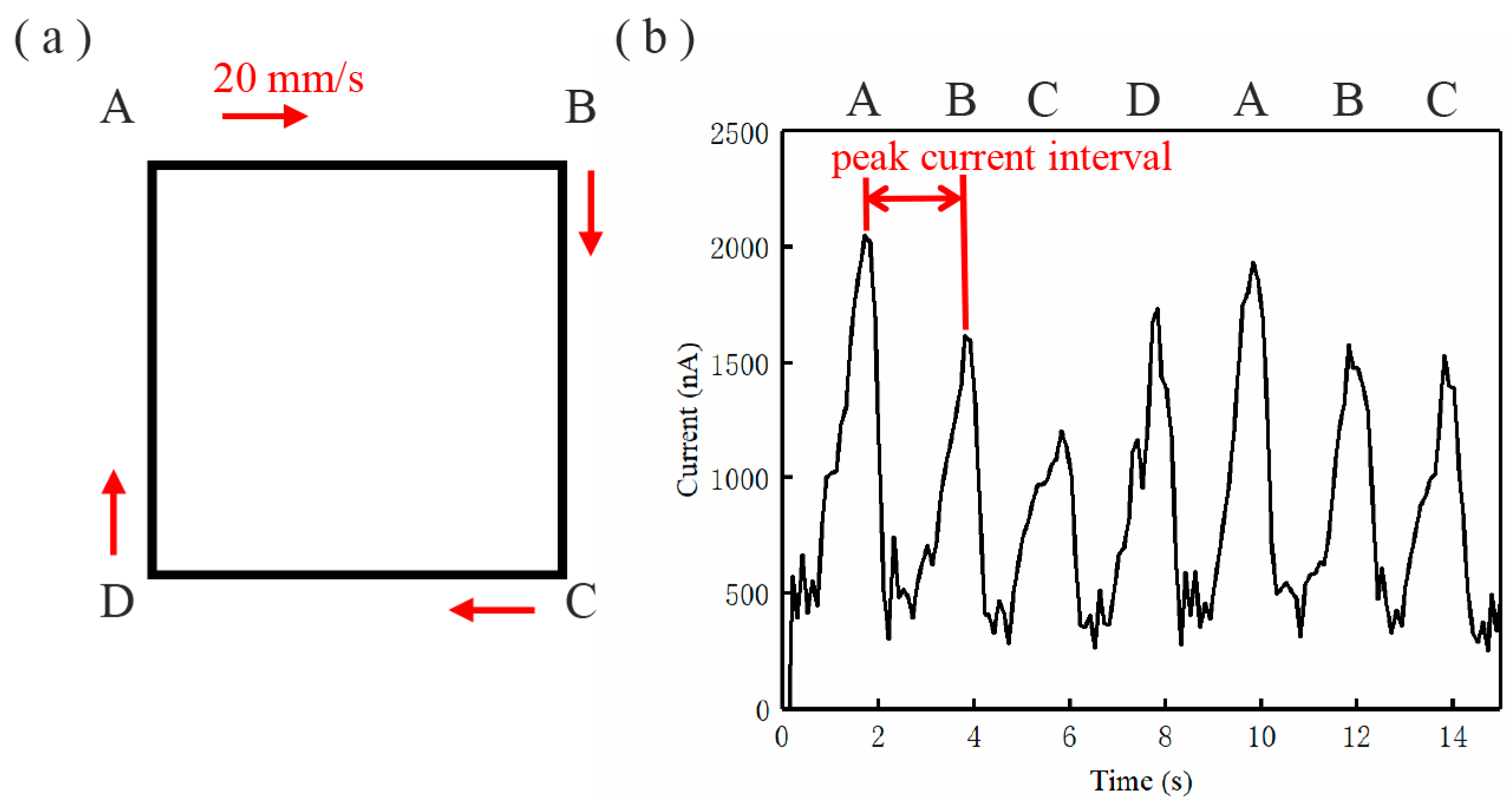
2.2. Micro/Nano Current in Printing Patterns
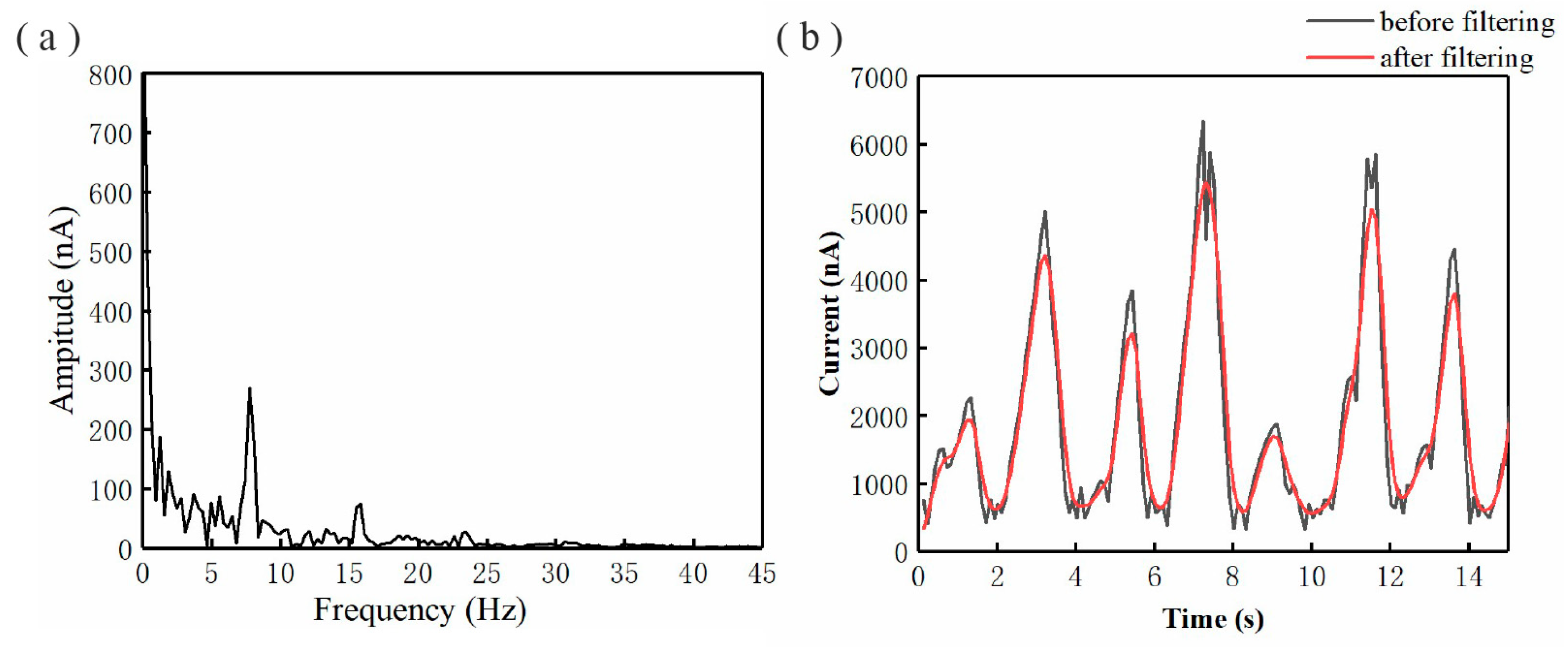
2.3. Data Processing of Micro/Nano Current
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, Z.; Han, Y.; Huang, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhu, Y. Electrohydrodynamic printing of silver nanowires for flexible and stretchable electronics. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6806–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.W.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Shim, Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Park, J.U. High-resolution printing of 3D structures using an electrohydrodynamic inkjet with multiple functional inks. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4322–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayavenkataraman, S.; Thaharah, S.; Zhang, S.; Lu, W.F.; Fuh, J.Y.H. Electrohydrodynamic jet 3D-printed PCL/PAA conductive scaffolds with tunable biodegradability as nerve guide conduits (NGCs) for peripheral nerve injury repair. Mater. Des. 2019, 162, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjairaj, V.; Kannan, S.; Cao, T.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Sriram, G.; Lu, W.F. 3D-Printed PCL/PPy Conductive Scaffolds as Three-Dimensional Porous Nerve Guide Conduits (NGCs) for Peripheral Nerve Injury Repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 266. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasinghe, S.N.; Qureshi, A.N.; Eagles, P.A. Electrohydrodynamic jet processing: An advanced electric-field-driven jetting phenomenon for processing living cells. Small 2006, 2, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Electrohydrodynamic printing: A potential tool for high-resolution hydrogel/cell patterning. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2016, 11, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. Precision deposition of a nanofibre by near-field electrospinning. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 415501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, G. Bead-on-string structure printed by electrohydrodynamic jet under alternating current electric field. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachewicz, U.; Yurteri, C.U.; Marijnissen, J.C.; Dijksman, J.F. Stability regime of pulse frequency for single event electrospraying. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 224105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, T.H.; Kim, S.; Kwon, K.S. A high speed electrohydrodynamic (EHD) jet printing method for line printing. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 095003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Duan, H.; Li, C.; Deng, W. Crossover of Varicose and Whipping Instabilities in Electrified Microjets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Chang, C.; Li, S.; Lin, L. Near-field electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Bu, N.; Duan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, Z.; Xiong, Y. Electrohydrodynamic direct-writing. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12007–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.X.; Wu, Y.K.; Fan, J.; Wang, L.; Su, Z.B.; Qin, L.M.; Liang, L.B.; Li, Y.T.; Cheng, J.H.; Liu, Y. Numerical approach to controlling a moving jet’s vibration in an electrospinning system: An auxiliary electrode and uniform electric field. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2019, 38, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A.; Krupa, A. Classification of the modes of ehd spraying. J. Aerosol Sci. 1999, 30, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druesedow, C.J.; Batur, C.; Cakmak, M.; Yalcin, B. Pressure control system for electrospinning process. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.K.; Schneider, T.M.; Brenner, M.P.; Mckinley, G.H.; Rutledge, G.C. On the measured current in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 2355–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.M.; Iskandar, F.; Khairurrijal; Okuyama, K. A constant-current electrospinning system for production of high quality nanofibers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2008, 79, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, D.B.; Chen, C.H. Pulsating electrohydrodynamic cone-jets: From choked jet to oscillating cone. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 689, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, G.; Luo, Z.; Li, W. Current characteristics of various ejection modes in electrohydrodynamic printing. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 127120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Jin, H.; Dang, H.W.; Choi, K.H.; Ahn, K.H. Optimization of experimental parameters to determine the jetting regimes in electrohydrodynamic printing. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13630–13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, K.; Mishra, S.; Alleyne, A.; Ferreira, P.; Rogers, J. Control of high-resolution electrohydrodynamic jet printing. Control Eng. Pract. 2011, 19, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.F.; Xue, W.D.; Chen, H.T.; Sun, L.L.; Jiang, J.X.; Wang, X.; Guo, S.M.; Li, W.W. Measurement and Time Response of Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Writing Current. Micromachines 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, J. Electrohydrodynamic direct-writing microfiber patterns under stretching. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, G. Electrohydrodynamic direct-writing micropatterns with assisted airflow. Micromachines 2018, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.Y.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, J.X.; Wang, X.; Li, W.W.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, G.F. Jet behaviors and ejection mode recognition of electrohydrodynamic direct-write. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

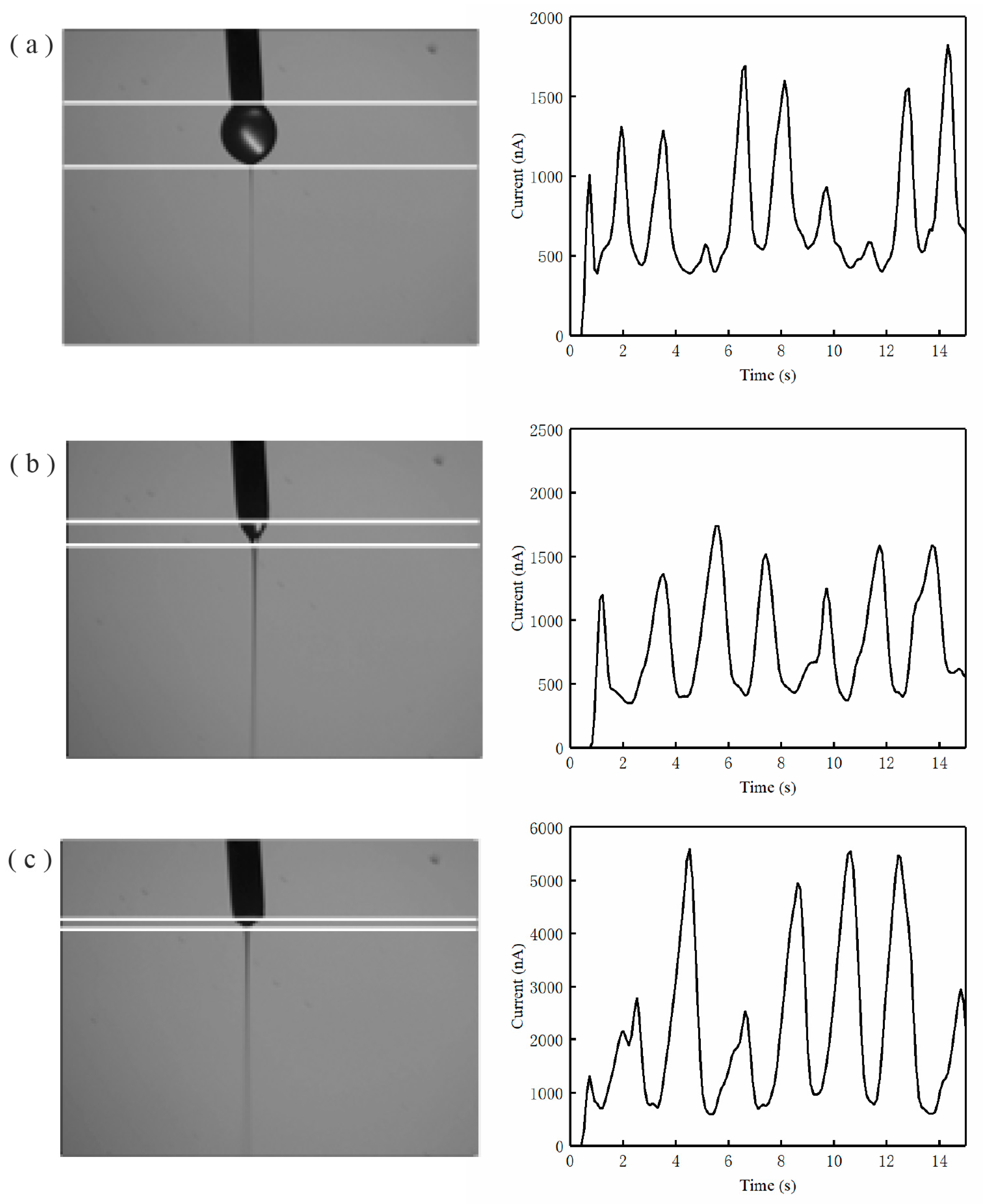
| Jet Mode | Imin (nA) | Imax (nA) | Imean (nA) | Imax/Imin | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Droplet ejection mode | 282.22 ± 42.88 | 1399.75 ± 161.52 | 684.54 ± 84.66 | 4.95 ± 0.44 | 0.83 ± 0.27 |
| Taylor cone ejection mode | 310.04 ± 40.36 | 1612.86 ± 107.95 | 828.01 ± 63.22 | 5.20 ± 0.48 | 0.32 ± 0.08 |
| Retractive ejection mode | 357.96 ± 72.65 | 3704.45 ± 122.02 | 1608.13 ± 529.59 | 10.34 ± 1.84 | 0.85 ± 0.23 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, G.; Zheng, G.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J. Jet Mode Recognition of Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Writing Based on Micro/Nano Current. Micromachines 2020, 11, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020128
Kang G, Zheng G, Chen Y, Jiang J, Chen H, Wang X, Li W, Huang Y, Zheng J. Jet Mode Recognition of Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Writing Based on Micro/Nano Current. Micromachines. 2020; 11(2):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020128
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Guoyi, Gaofeng Zheng, Yanping Chen, Jiaxin Jiang, Huatan Chen, Xiang Wang, Wenwang Li, Yuqing Huang, and Jianyi Zheng. 2020. "Jet Mode Recognition of Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Writing Based on Micro/Nano Current" Micromachines 11, no. 2: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020128
APA StyleKang, G., Zheng, G., Chen, Y., Jiang, J., Chen, H., Wang, X., Li, W., Huang, Y., & Zheng, J. (2020). Jet Mode Recognition of Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Writing Based on Micro/Nano Current. Micromachines, 11(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020128






