Effect of pH and Nanoparticle Capping Agents on Cr (III) Monitoring in Water: A Kinetic Way to Control the Parameters of Ultrasensitive Environmental Detectors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Preparation of Citrate or Oxalate Capped Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
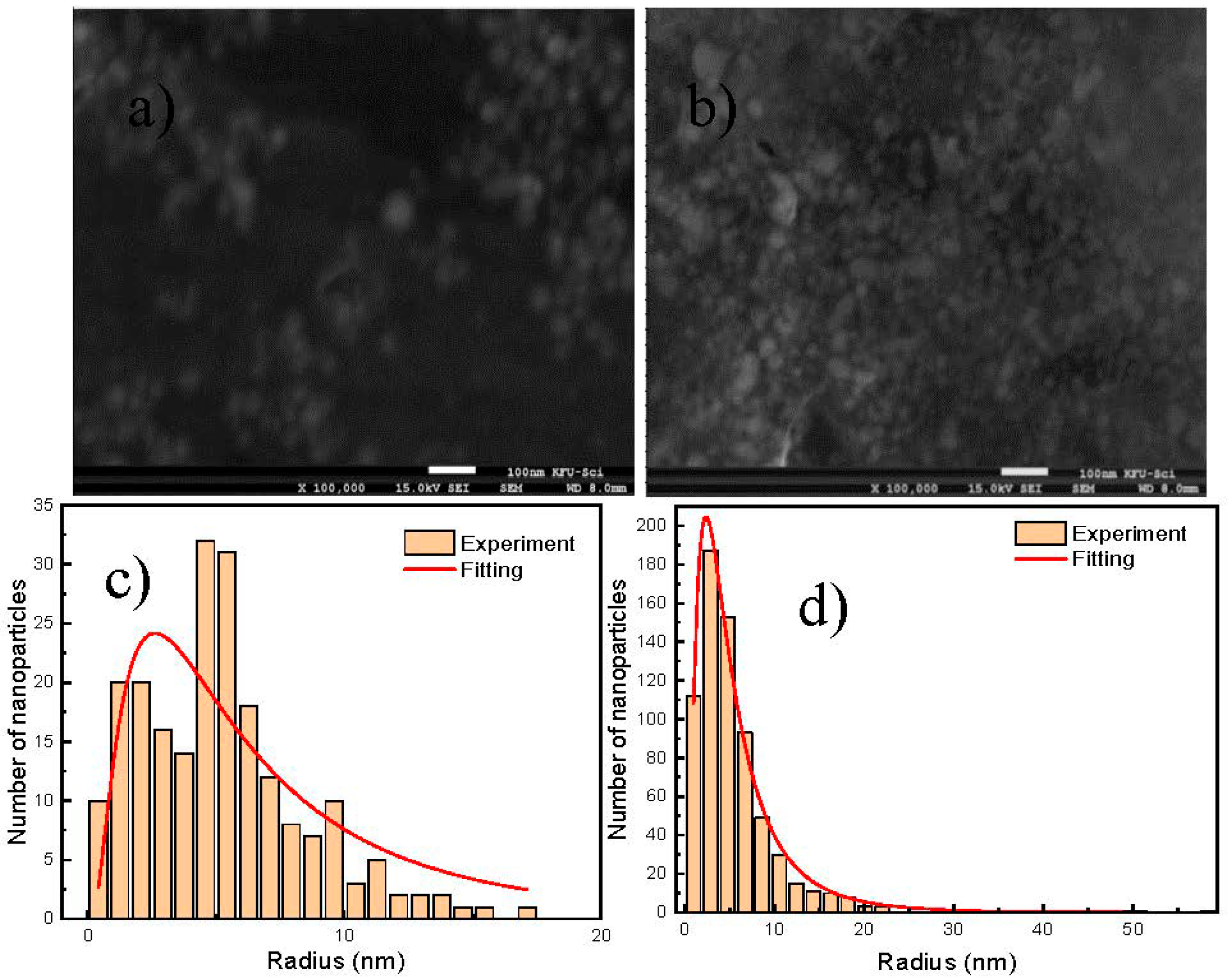
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
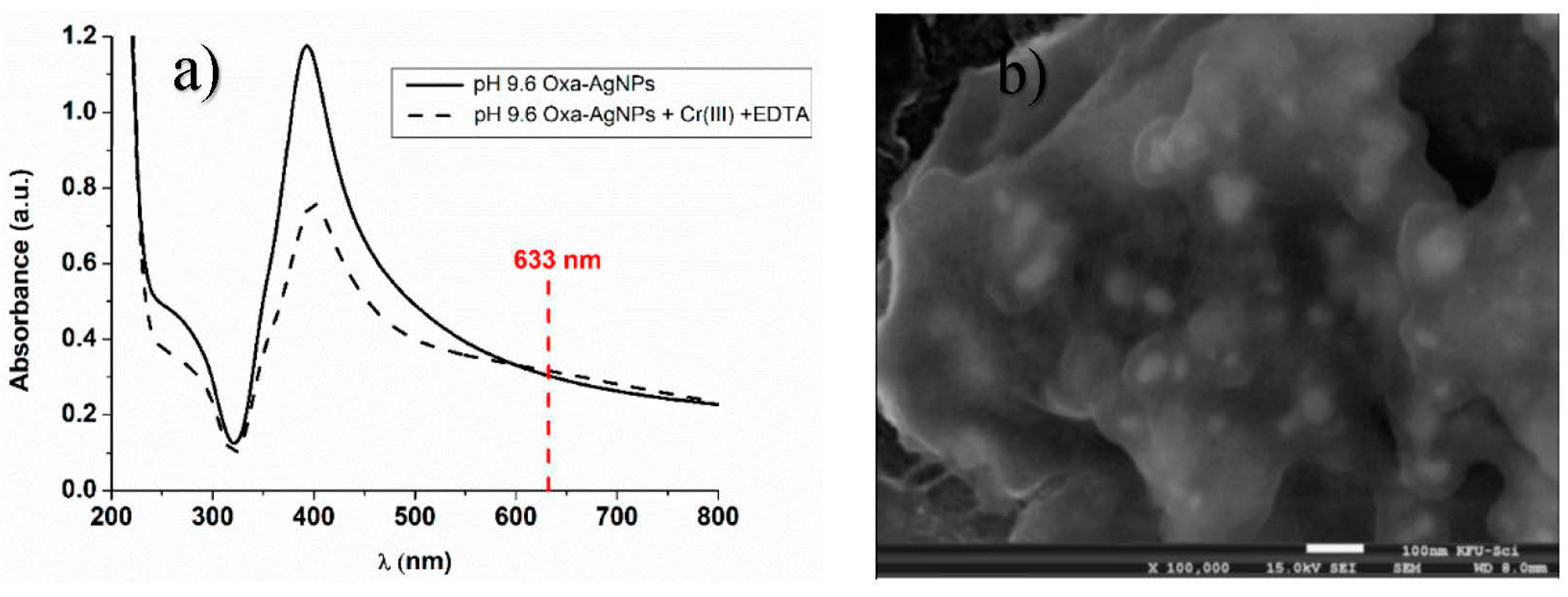
2.4. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
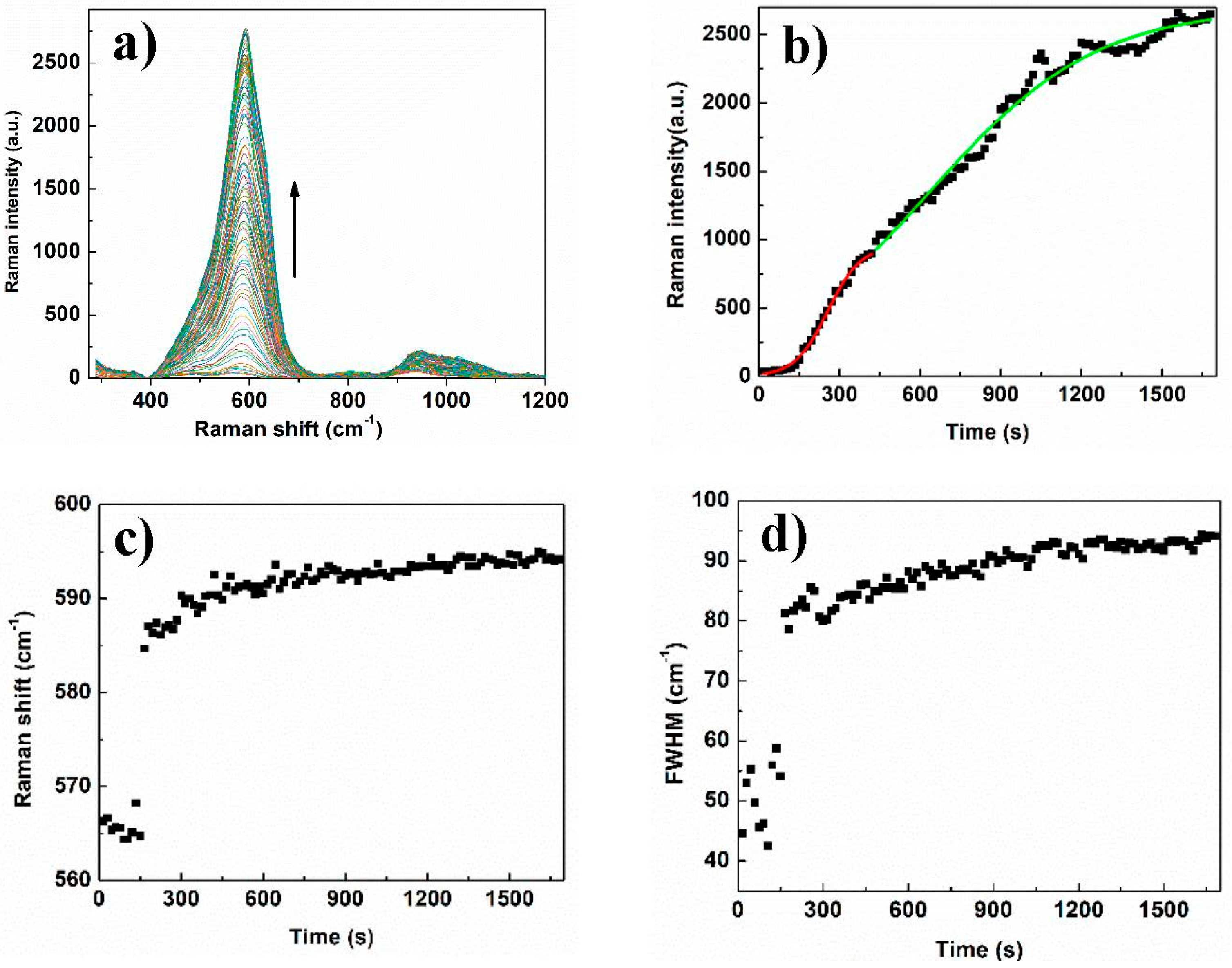
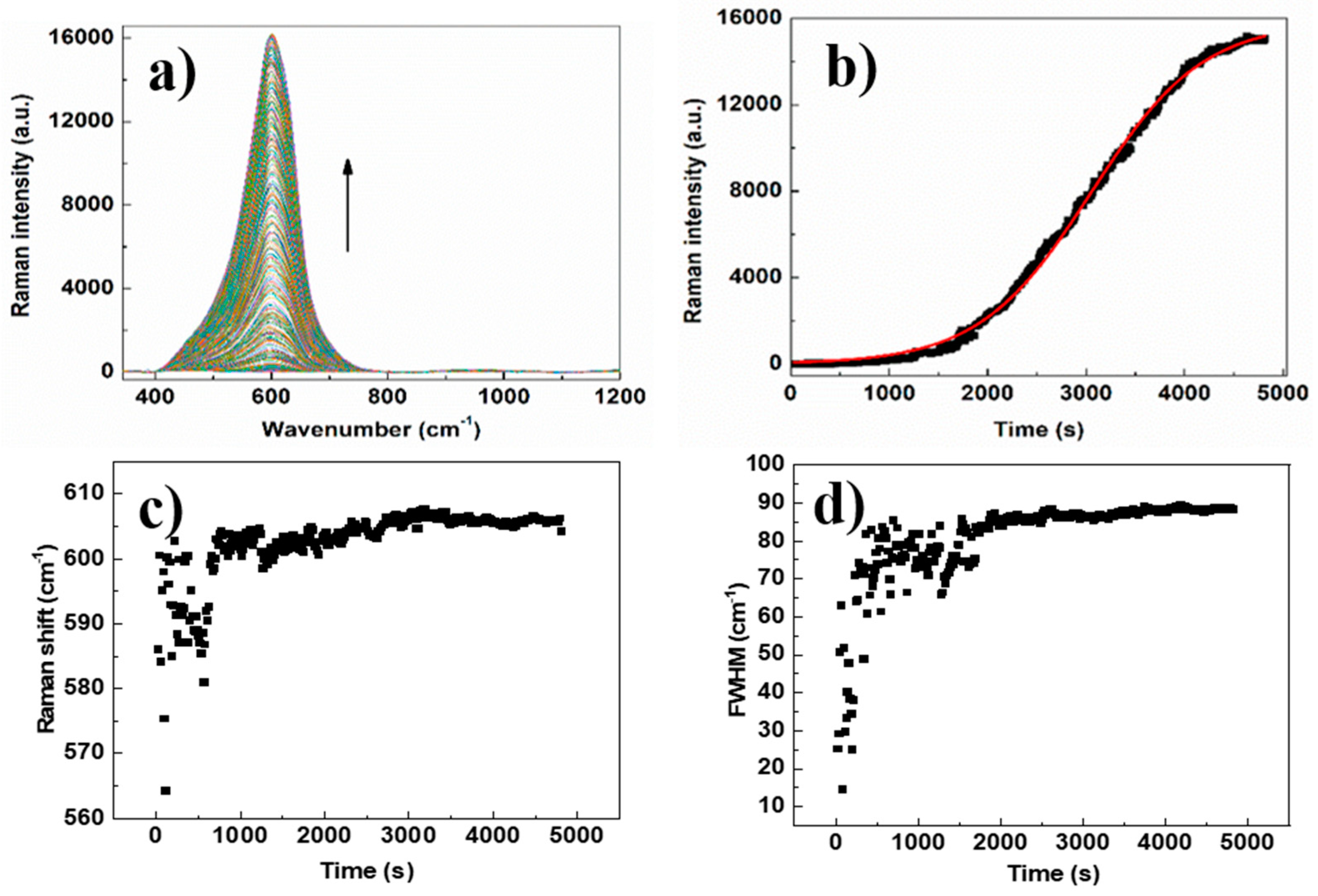
2.5. SERS Measurements
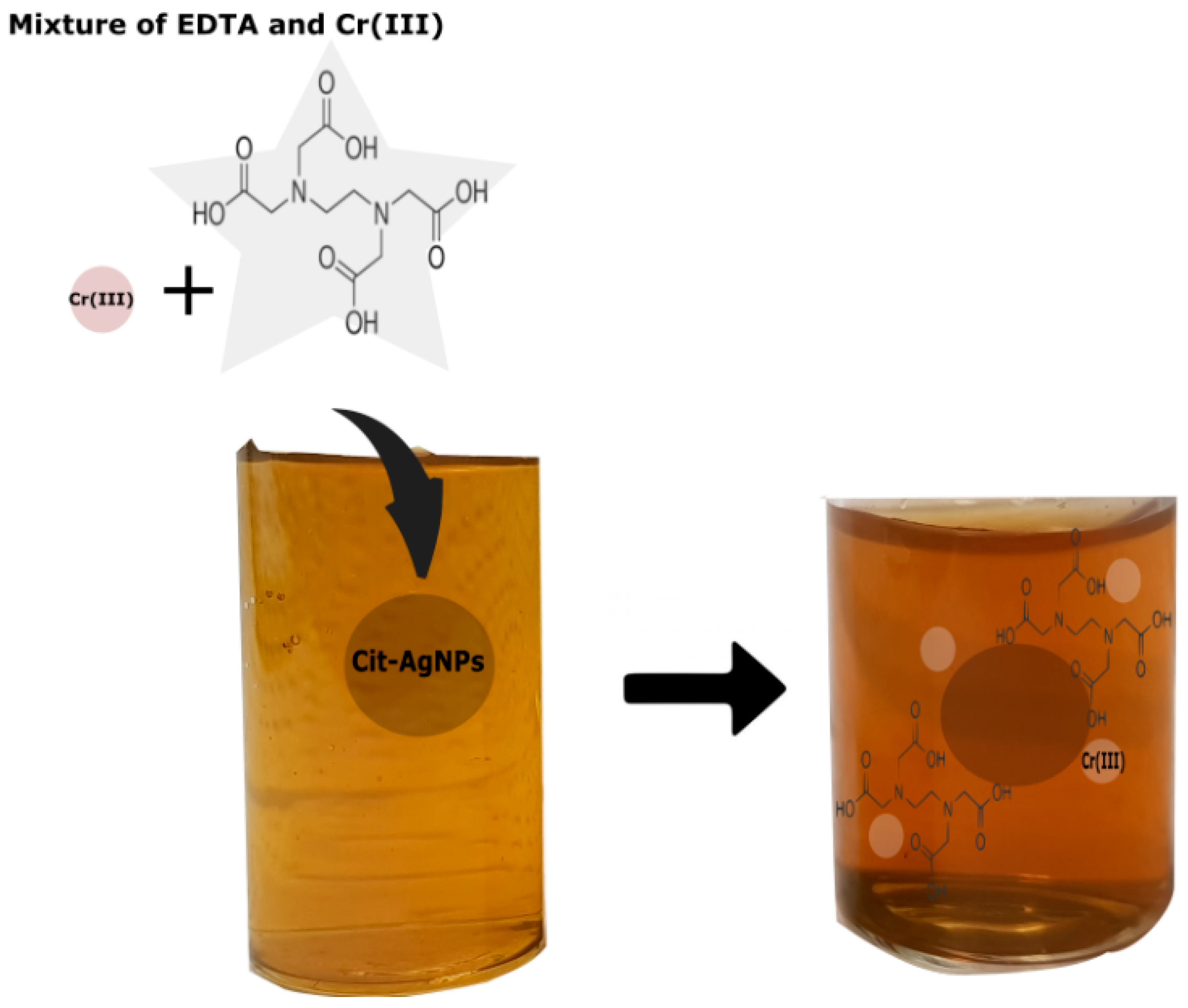
3. Results and Discussion
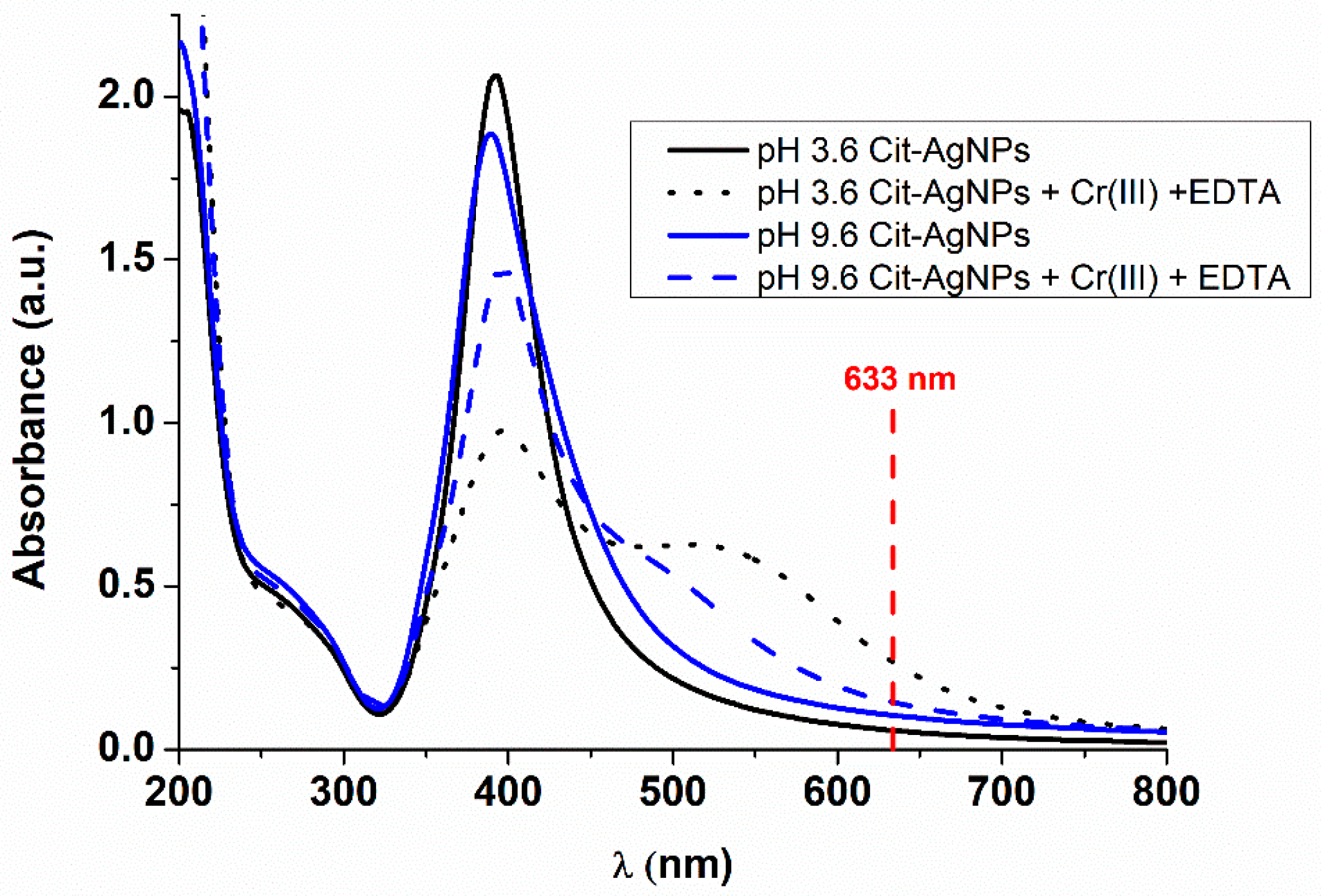
3.1. Effect of pH
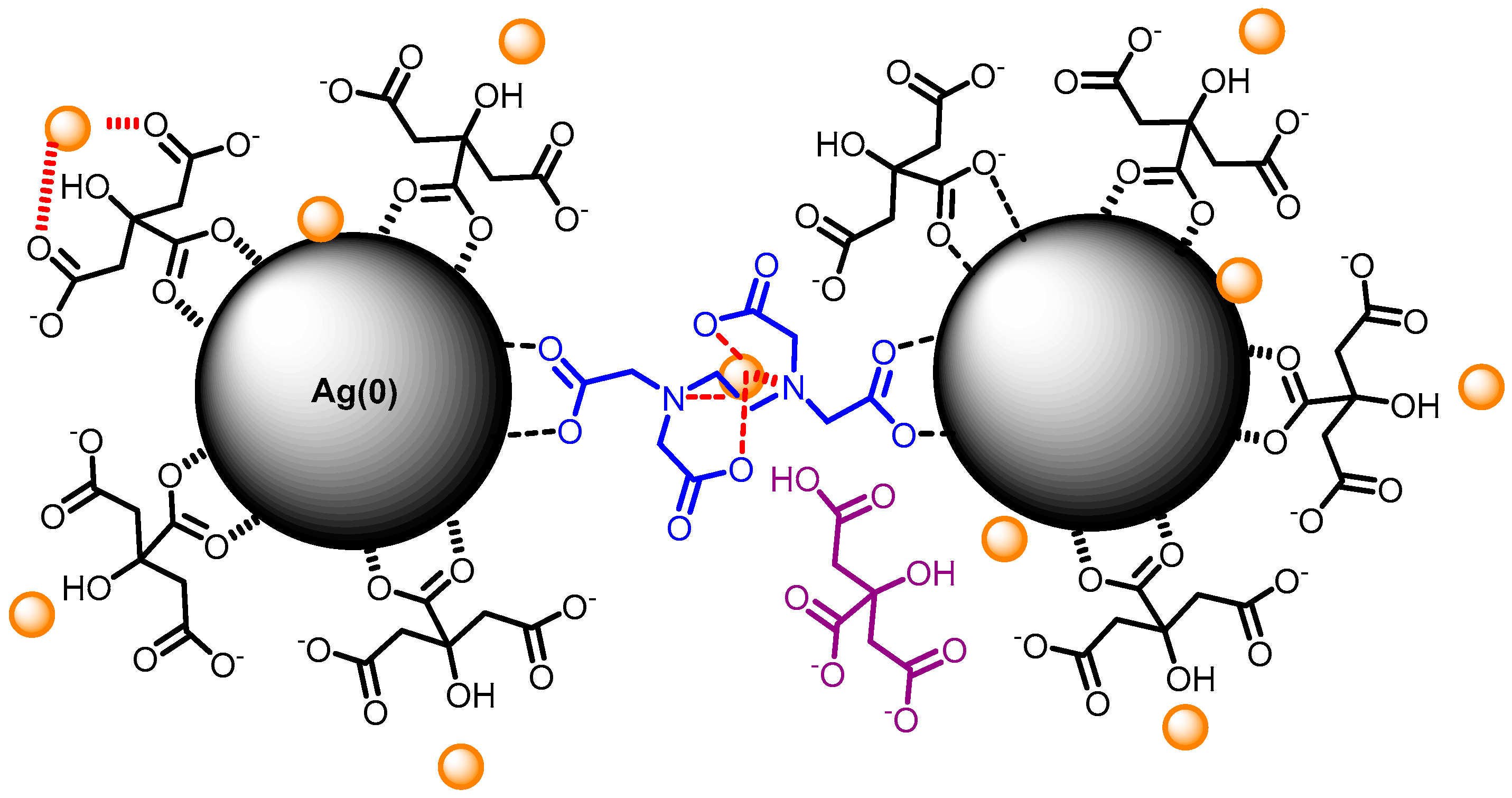
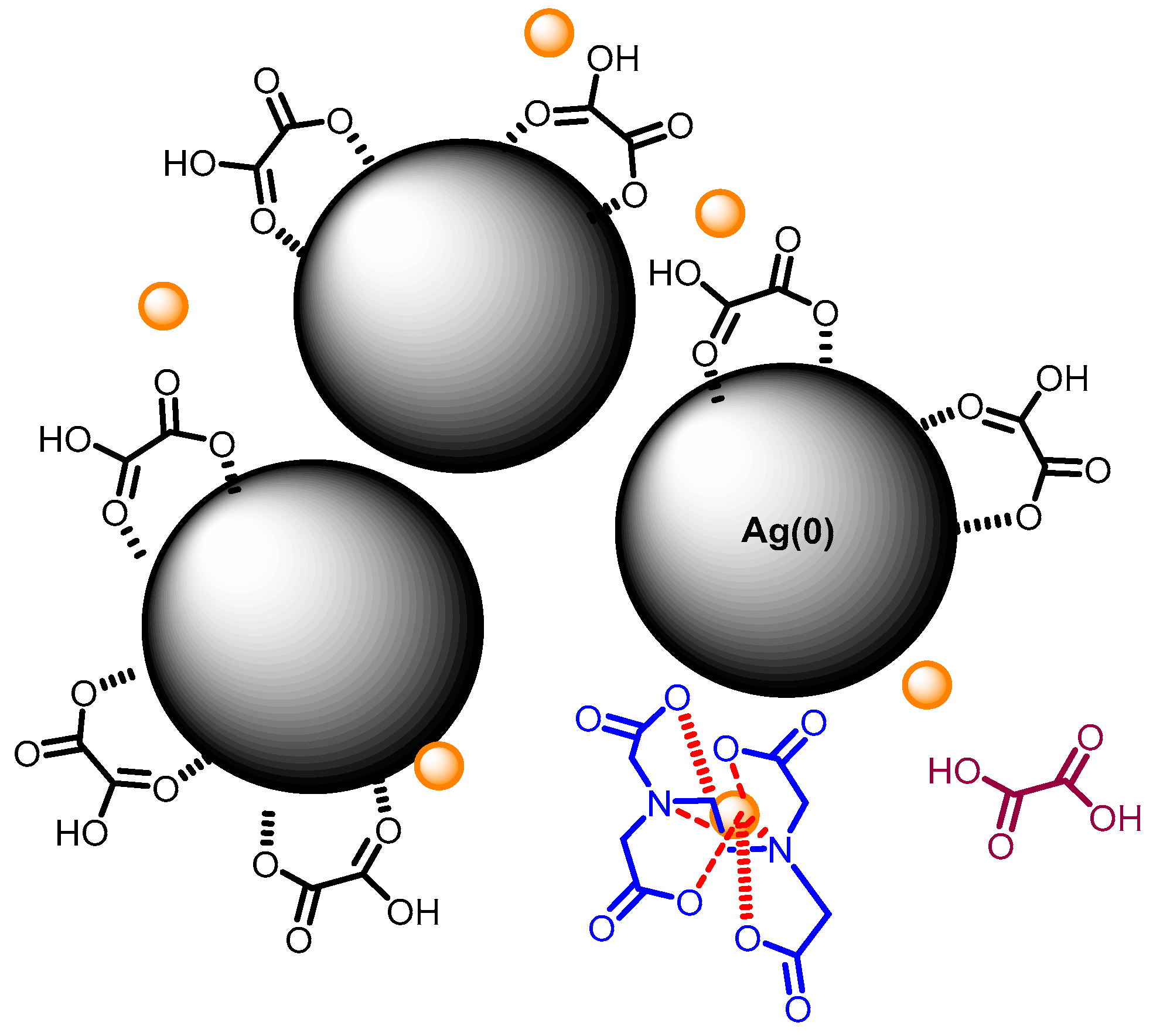
3.2. Effect of Capping
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Creedon, N.; Lovera, P.; Moreno, J.G.; Nolan, M.; O’Riordan, A. Highly Sensitive SERS Detection of Neonicotinoid Pesticides. Complete Raman Spectral Assignment of Clothianidin and Imidacloprid. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 7238–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Trau, M.; Koo, K.M. Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy for cancer immunotherapy applications: Opportunities, challenges, and current progress in nanomaterial strategies. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lai, K.; Fan, Y.; Rasco, B.A. Trace analysis of organic compounds in foods with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Methodology, progress, and challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 622–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; Cong, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.; Pan, L. Facile synthesis of hybrid silver/porous carbon black substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Chen, X.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Hu, S.; Li, J.F.; Wu, D.Y.; Moskovits, M.; Tian, Z.Q. Interfacial Construction of Plasmonic Nanostructures for the Utilization of the Plasmon-Excited Electrons and Holes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8053–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; He, L. Understanding the competitive interactions in aptamer-gold nanoparticle based colorimetric assays using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.B.; Zijlstra, P. Single-Molecule Plasmon Sensing: Current Status and Future Prospects. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1103–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilot, R.; Signorini, R.; Durante, C.; Orian, L.; Bhamidipati, M.; Fabris, L. A review on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Biosensors 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, C.; Weiss-Lopez, B.E.; Campos Vallette, M.M. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering activity of negatively charged bio-analytes from a modified silver colloid. Spectrosc. Lett. 2016, 49, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haes, H.T.P.A.J. Impacts of pH and Intermolecular Interactions on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Chemical Enhancements. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 14846–14856. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Traps and cages for universal SERS detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.; Contreras-Ciceres, R.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Perez-Juste, J.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Au@pNIPAM colloids as molecular traps for surface-enhanced, spectroscopic, ultra-sensitive analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furini, L.N.; Costa, G.; Leopoldo Constantino, C.J.; Alessio, P. pH-responsive Ag@PAH nanoparticles applied in SERS. Mater. Lett. 2020, 277, 128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Link, S.; Halas, N.J. Nano-optics from sensing to waveguiding. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Luo, J.; Jiang, L.; Song, Y. Mixed DNA-functionalized nanoparticle probes for surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based multiplex DNA detection. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7407–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z. Ethanol-Induced Formation of Silver Nanoparticle Aggregates for Highly Active SERS Substrates and Application in DNA Detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A.; Norton, S.J.; Gerhold, M.D.; Vo-Dinh, T. Comparison of FDTD numerical computations and analytical multipole expansion method for plasmonics-active nanosphere dimers. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 9688–9703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Badawy, A.M.; Luxton, T.P.; Silva, R.G.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Impact of Environmental Conditions (pH, Ionic Strength, and Electrolyte Type) on the Surface Charge and Aggregation of Silver Nanoparticles Suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, C.; Plathier, J.; Dab, C.; Charra, F.; Douillard, L.; Ruediger, A. High resolution scanning near field mapping of enhancement on SERS substrates: Comparison with photoemission electron microscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, R.N.; Graham, D.; Larmour, I.; Wark, A.W.; Faulds, K. Synthesis of size tunable monodispersed silver nanoparticles and the effect of size on SERS enhancement. Vib. Spectrosc. 2014, 71, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traboulsi, H.; Awada, C. Toward the Development of Ultrasensitive Detectors for Environmental Applications: A kinetic Study of Cr(III) monitoring in water Using EDTA and SERS Technique. ACS Omega 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.C.; Meisel, D. Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 3391–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Leskauskas, D.; Liu, G.; Matson, J.B. Molecular-Level Control over Plasmonic Properties in Silver Nanoparticle/Self-Assembling Peptide Hybrids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9158–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.; Zhou, Y. Impact of pH on the stability, dissolution and aggregation kinetics of silver nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, N. Colorimetric detection of trivalent chromium in aqueous solution using tartrate-capped silver nanoparticles as probe. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 6820–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Chen, L.B.; Zhang, Z.Y. Adsorption of cations onto the surfaces of silver nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 257, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, D.; Sass, B.M.; Moore, D.A. Chromium(III) hydrolysis constants and solubility of chromium(III) hydroxide. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Piao, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, E.; Sun, Z. Large-scale and facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles via a microwave method for a conductive pen. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 34041–34048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crea, F.; Stefano, C.; Millero, F.J.; Sharma, V.K. Dissociation Constants for Citric Acid in NaCl and KCl Solutions and their Mixtures at 25 °C. J. Solut. Chem. 2004, 33, 1349–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, G.C.; Young, M.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Electromagnetic mechanism of SERS. Top. Appl. Phys. 2006, 103, 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Valley, N.; Greeneltch, N.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Schatz, G.C. A Look at the Origin and Magnitude of the Chemical Contribution to the Enhancement Mechanism of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS): Theory and Experiment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E. The Prout-Tompkins rate equation in solid-state kinetics. Thermochim. Acta 1997, 300, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Emmons, E.D.; Christesen, S.D.; Fountain, A.W.; Guicheteau, J.A. Kinetics and Reaction Mechanisms of Thiophenol Adsorption on Gold Studied by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2013, 117, 22834–22842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhin, A.I.; Smetanin, I.V.; Mikhailov, S.I.; Bulychev, N.A. Spectral shifts of stimulated Rayleigh—Mie scattering in Ag nanoparticle colloids. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadi, M.K.; Abo Noqtah, O.A.; Alzoubi, F.Y.; Alzouby, J.; Aljarrah, K. pH effect on the aggregation of silver nanoparticles synthesized by chemical reduction. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2014, 32, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Awada, C.; Traboulsi, H. Effect of pH and Nanoparticle Capping Agents on Cr (III) Monitoring in Water: A Kinetic Way to Control the Parameters of Ultrasensitive Environmental Detectors. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121045
Awada C, Traboulsi H. Effect of pH and Nanoparticle Capping Agents on Cr (III) Monitoring in Water: A Kinetic Way to Control the Parameters of Ultrasensitive Environmental Detectors. Micromachines. 2020; 11(12):1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121045
Chicago/Turabian StyleAwada, Chawki, and Hassan Traboulsi. 2020. "Effect of pH and Nanoparticle Capping Agents on Cr (III) Monitoring in Water: A Kinetic Way to Control the Parameters of Ultrasensitive Environmental Detectors" Micromachines 11, no. 12: 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121045
APA StyleAwada, C., & Traboulsi, H. (2020). Effect of pH and Nanoparticle Capping Agents on Cr (III) Monitoring in Water: A Kinetic Way to Control the Parameters of Ultrasensitive Environmental Detectors. Micromachines, 11(12), 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11121045





