Ouabain Protects Human Renal Cells against the Cytotoxic Effects of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
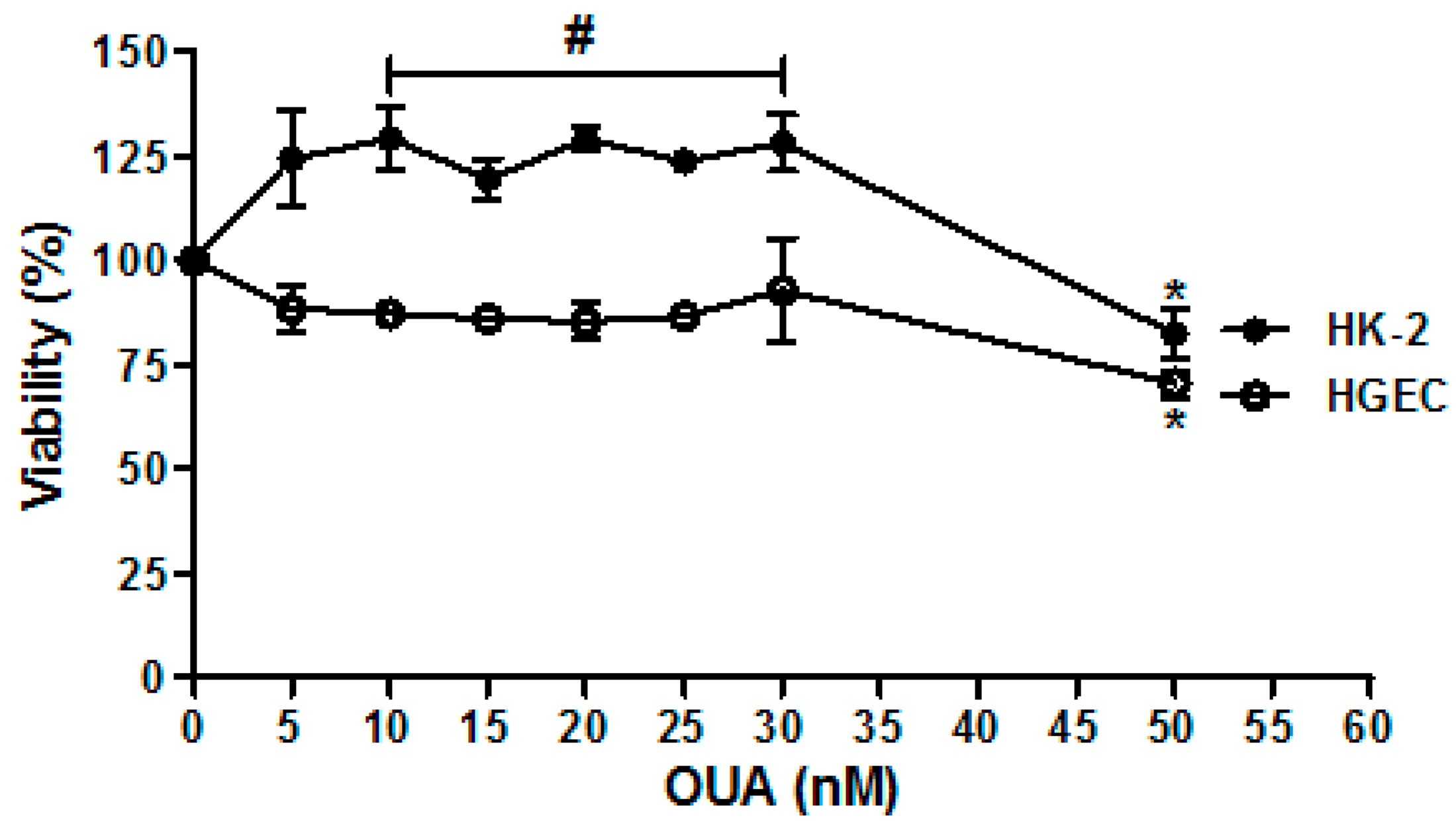
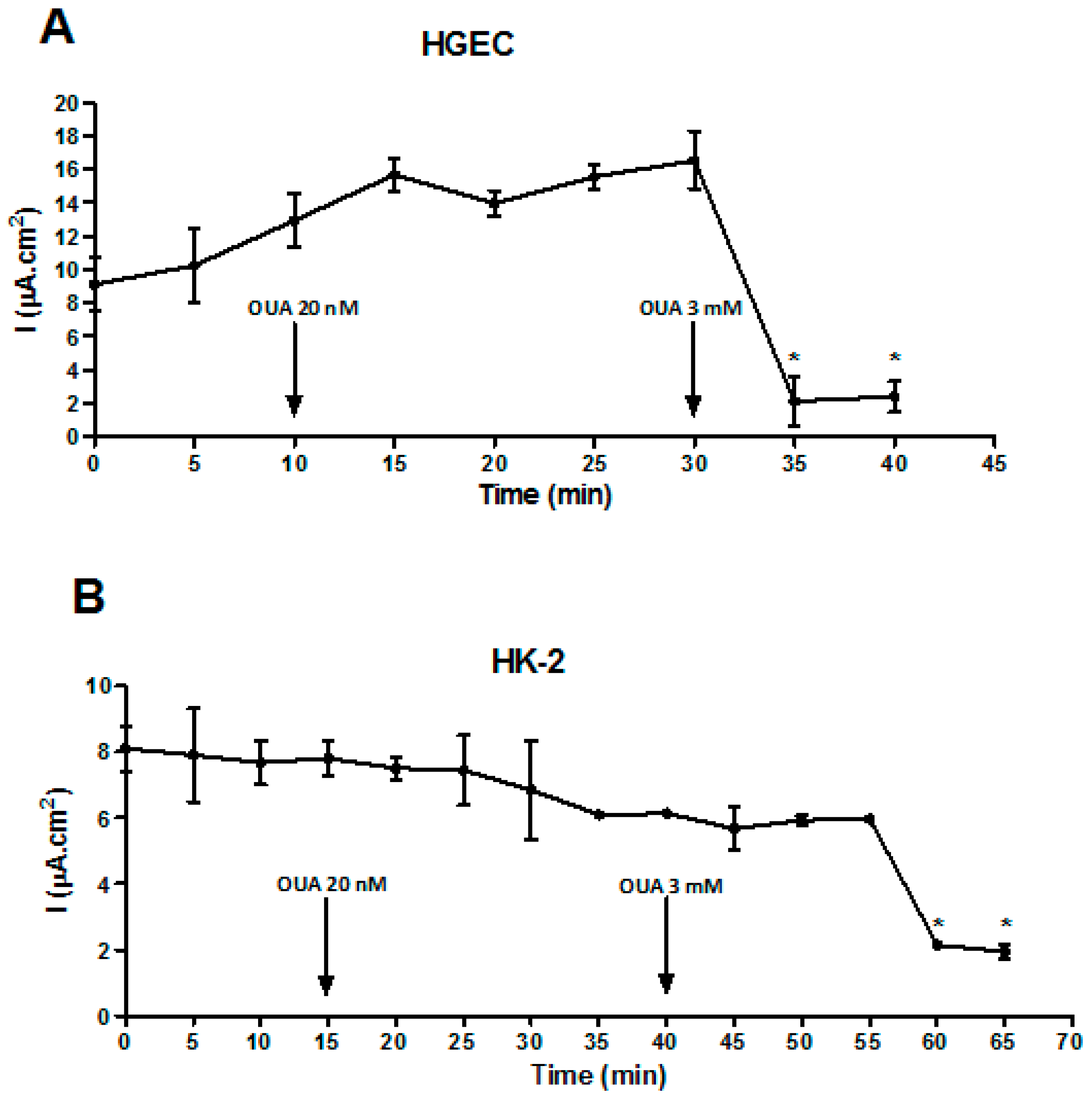
2.1. Establishment of OUA Non-Cytotoxic Concentrations for Renal Cells
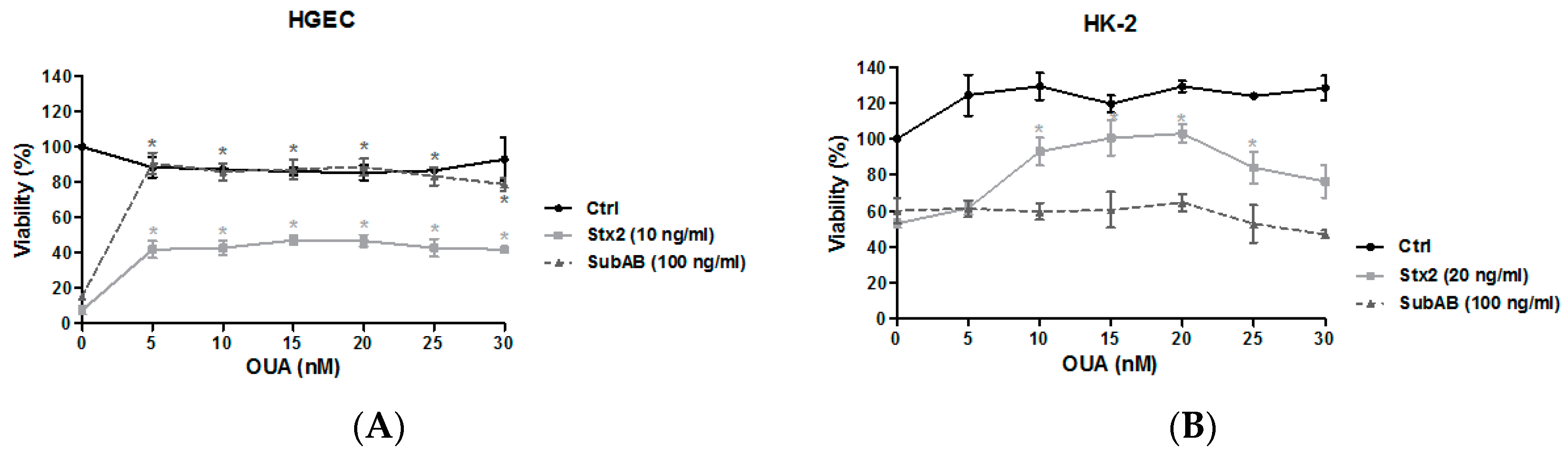
2.2. OUA Protected Human Renal Cell Viability from Cytotoxic Effects of Stx2 and SubAB
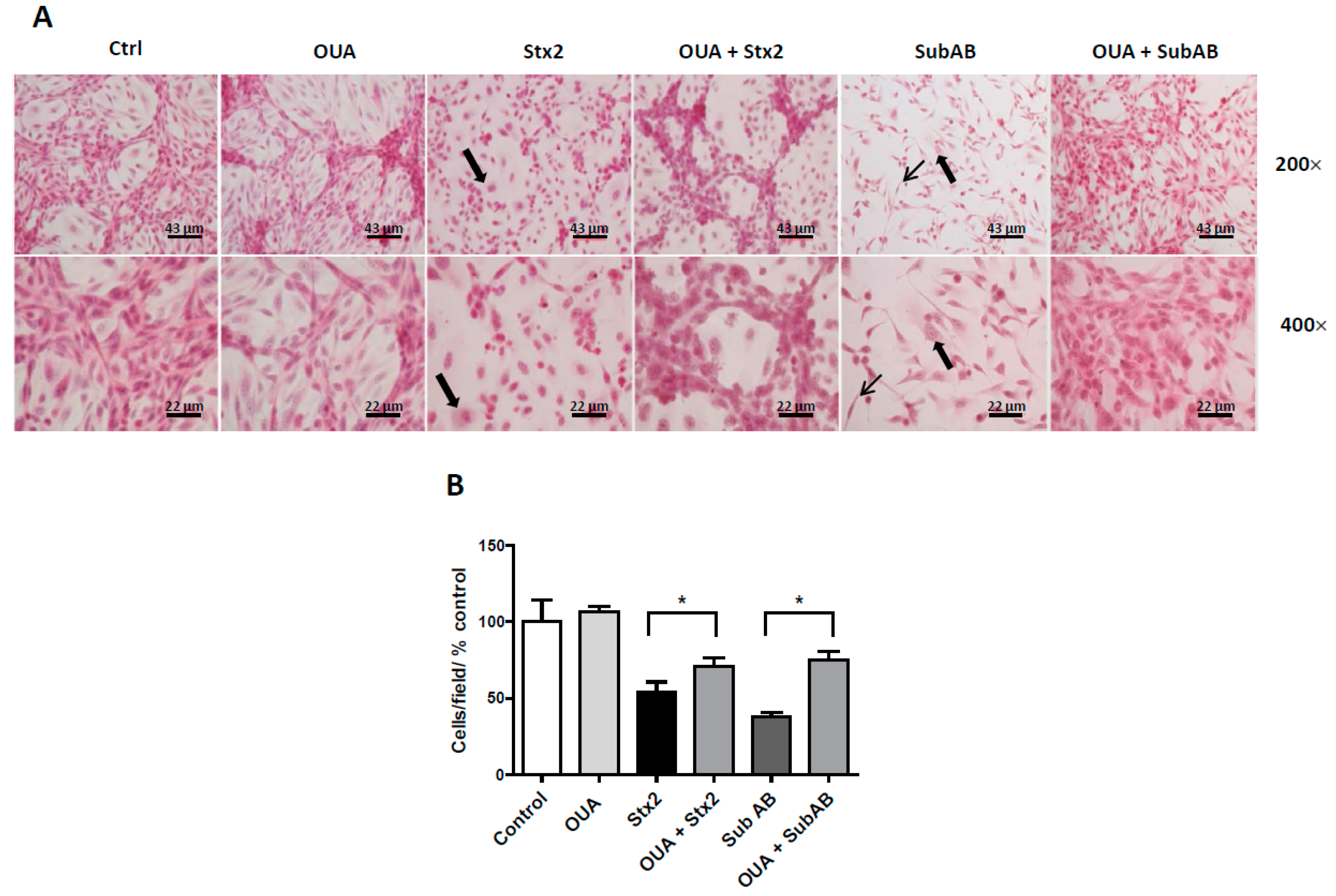
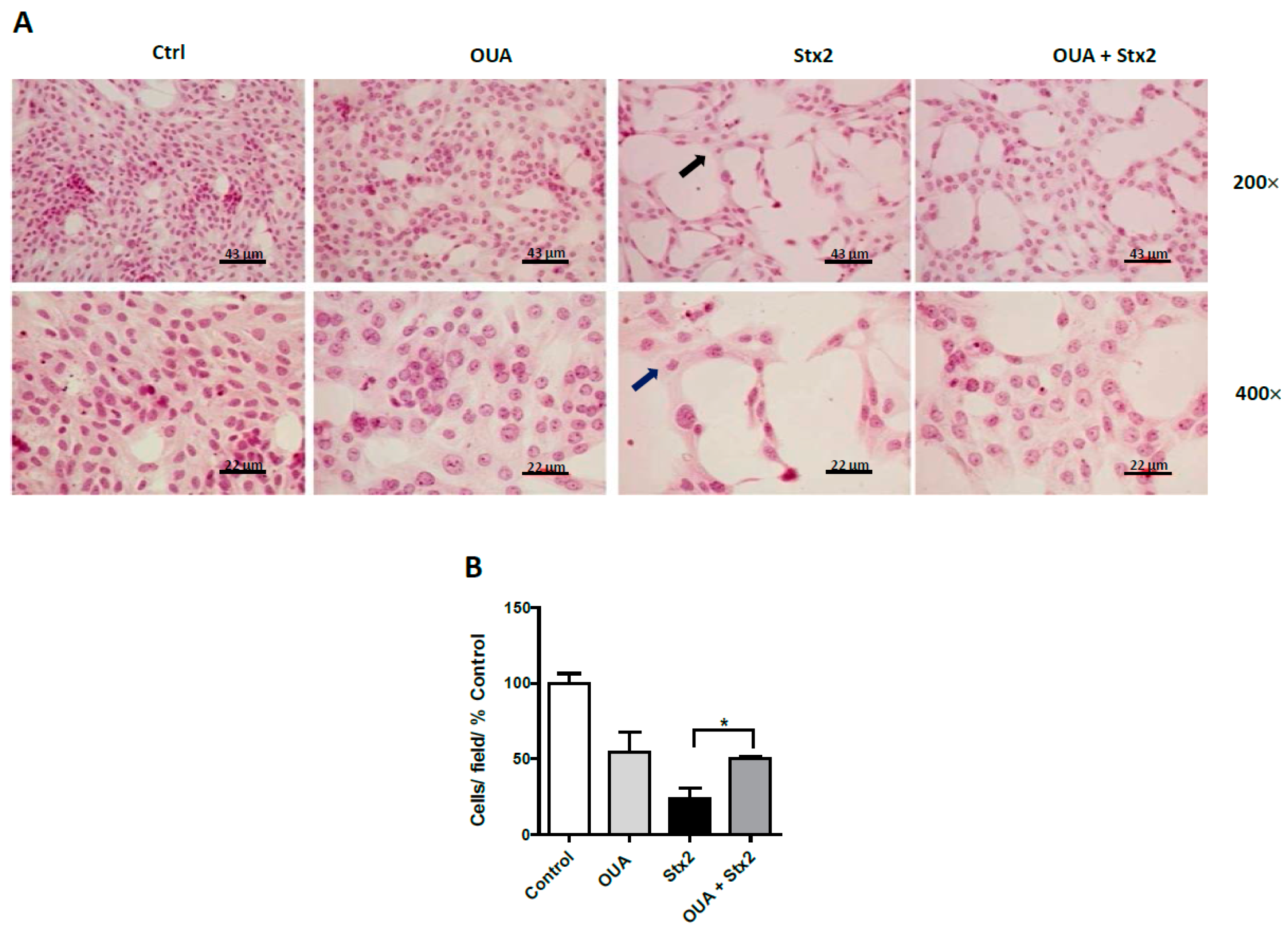
2.3. OUA Prevented Morphologic Alterations and Cell Detachment Induced by Stx2 and SubAB
2.4. OUA Did Not Affect Na/K-ATPase Function
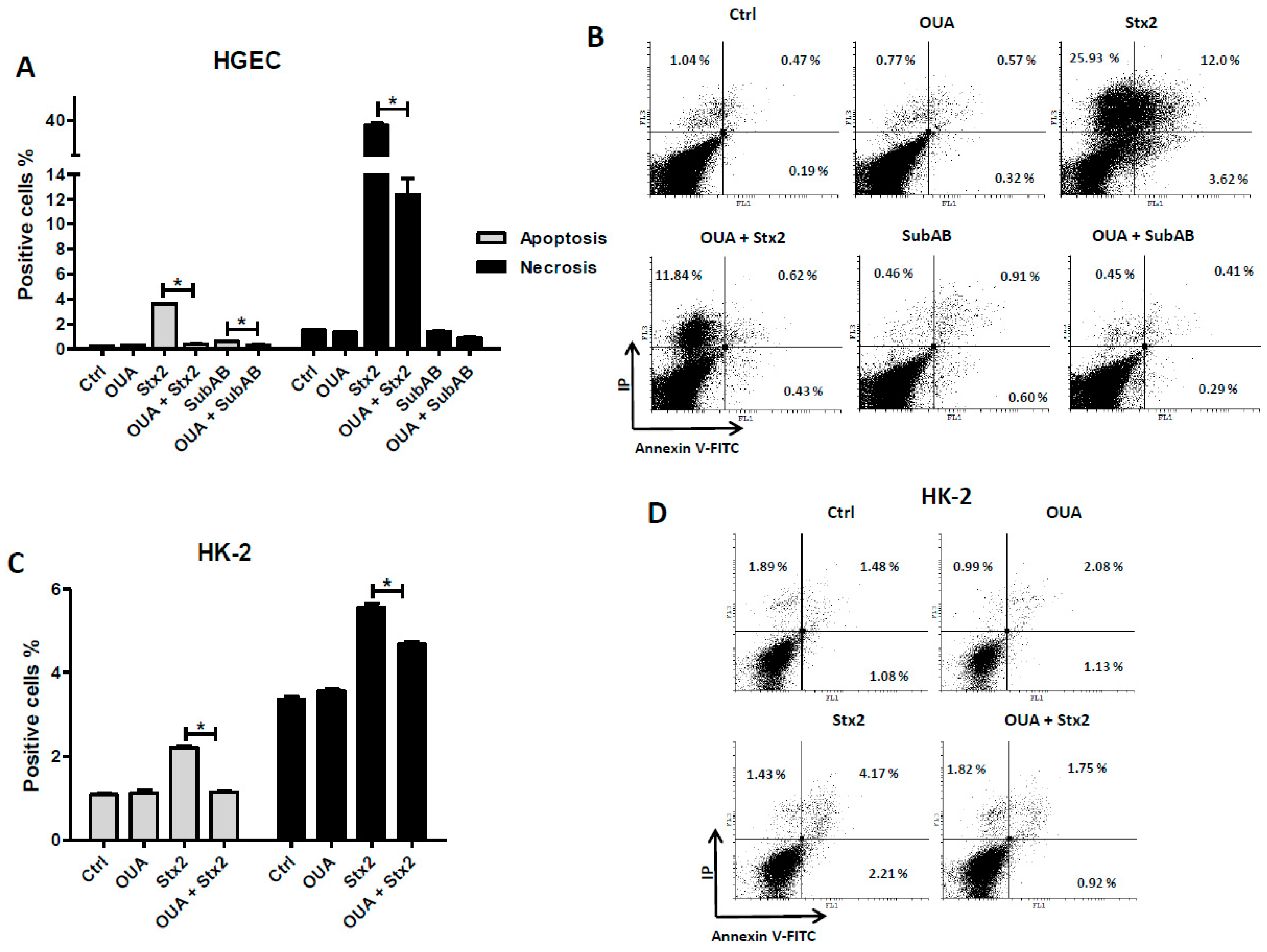
2.5. OUA Prevented Apoptosis and Necrosis Caused by Stx2 and SubAB
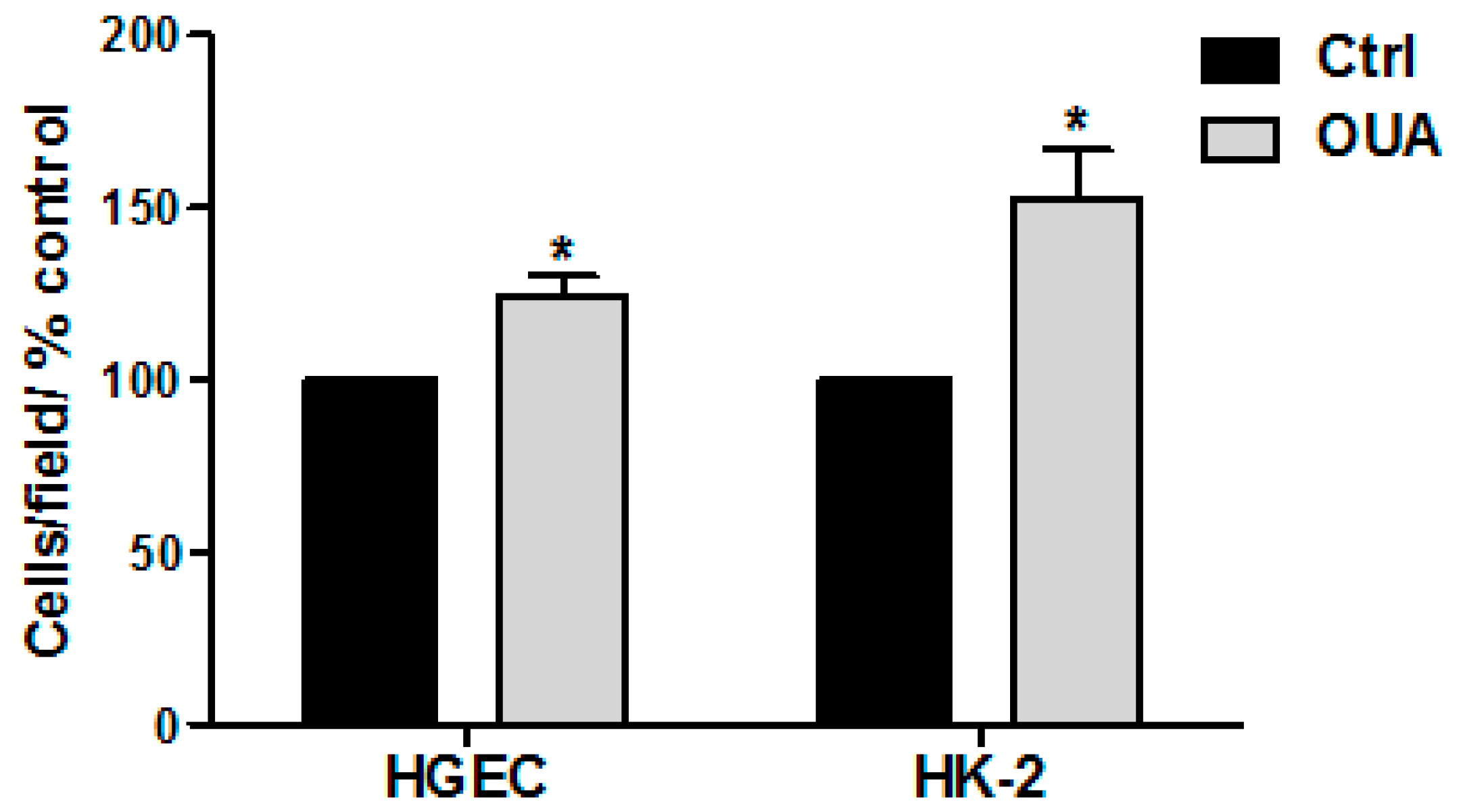
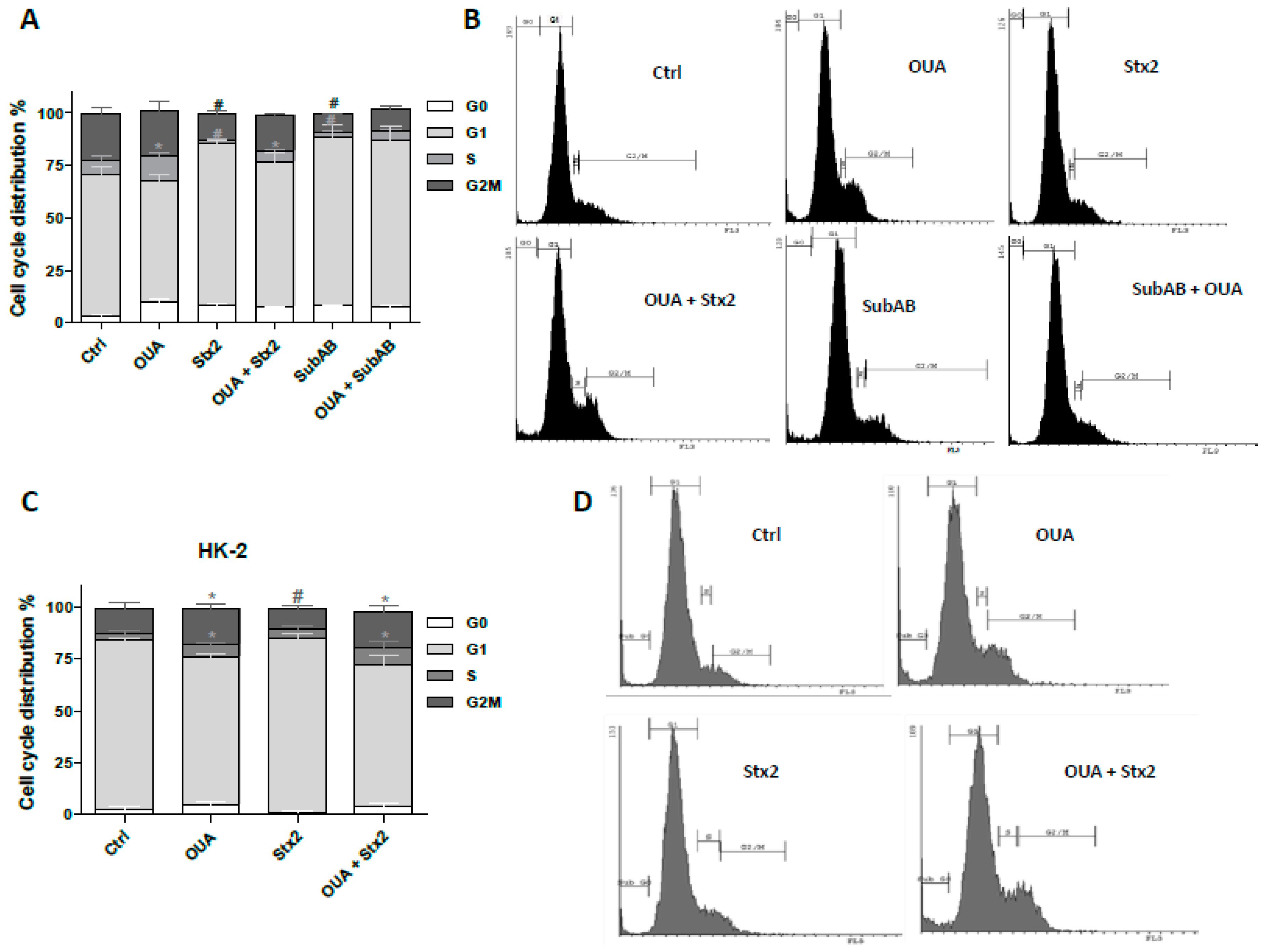
2.6. Cell Proliferation Was Stimulated by OUA
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Primary Culture
5.3. Cell Lines Culture
5.4. Neutral Red Cytotoxicity Assay
5.5. Cell Morphology Analysis
5.6. Na/K-ATPase Activity
5.7. Necrosis and Apoptosis
5.8. Cell Proliferation Studies
5.8.1. Trypan Blue Assay
5.8.2. Cell Cycle
5.9. Data Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gianantonio, C.A.; Vitacco, M.; Mendilaharzu, F.; Gallo, G.E.; Sojo, E.T. The hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Nephron 1973, 11, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmali, M.A.; Petric, M.; Lim, C.; Fleming, P.C.; Arbus, G.S.; Lior, H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, M.; Chinen, I.; Miliwebsky, E.; Masana, M. Risk factors for shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli-associated human diseases. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repetto, H.A. Microangiopatía trombótica y sindrome hemolítico urémico. Nefrología Clínica 3ra Edición 2009, 6, 286–297. [Google Scholar]
- Laing, C.R.; Zhang, Y.; Gilmour, M.W.; Allen, V.; Johnson, R.; Thomas, J.E.; Gannon, V.P. A comparison of shiga-toxin 2 bacteriophage from classical enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli serotypes and the german E. coli o104:H4 outbreak strain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37362. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, M.; Miliwebsky, E.; Chinen, I.; Deza, N.; Leotta, G.A. The epidemiology of hemolytic uremic syndrome in argentina. Diagnosis of the etiologic agent, reservoirs and routes of transmission. Medicina 2006, 66 (Suppl. 3), 27–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rivas, M.; Miliwebsky, E. Diagnóstico etiológico para establecer la asociación entre enfermedad humana e infección por escherichia coli productor de toxina shiga, cap 4. En síndrome urémico hemolítico post-entérico. Actualización en patogénesis, diagnóstico y tratamiento del síndrome urémico hemolítico asociado a la toxina shiga. Editorial Académica Española 2015, 4, 8–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz, M.; Clausen, H.; Nudelman, E.; Donohue-Rolfe, A.; Keusch, G.T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. Xi. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and hela cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 163, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesh, V.L. Activation of cell stress response pathways by shiga toxins. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, M.E.; Fujinaga, M.; Cherney, M.M.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Twiddy, E.M.; O’Brien, A.D.; James, M.N. Structure of shiga toxin type 2 (stx2) from Escherichia coli o157:H7. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27511–27517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velandia, C.V.; Mariel Sanso, A.; Kruger, A.; Suarez, L.V.; Lucchesi, P.M.; Parma, A.E. Occurrence of subtilase cytotoxin and relation with other virulence factors in verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from food and cattle in argentina. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, S.; Beristain, X.; Martinez, R.; Garcia, A.; Martin, C.; Vidal, D.; Diaz-Sanchez, S.; Rey, J.; Alonso, J.M.; Herrera-Leon, S. Subtilase cytotoxin encoding genes are present in human, sheep and deer intimin-negative, shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli o128:H2. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.C.; Reddy, S. Prevalences of shiga toxin subtypes and selected other virulence factors among shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from fresh produce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6917–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, A.W.; Srimanote, P.; Talbot, U.M.; Wang, H.; Paton, J.C. A new family of potent AB(5) cytotoxins produced by shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, L.; Miliwebsky, E.; Irino, K.; Leotta, G.; Rivas, M. Virulence profile comparison between LEE-negative shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) strains isolated from cattle and humans. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, A.W.; Beddoe, T.; Thorpe, C.M.; Whisstock, J.C.; Wilce, M.C.; Rossjohn, J.; Talbot, U.M.; Paton, J.C. AB5 subtilase cytotoxin inactivates the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP. Nature 2006, 443, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, G.; Morinaga, N.; Yahiro, K.; Komine, R.; Moss, J.; Yoshida, H.; Noda, M. Novel subtilase cytotoxin produced by shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli induces apoptosis in vero cells via mitochondrial membrane damage. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2919–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, K.L.; Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Escherichia coli subtilase cytotoxin induces apoptosis regulated by host bcl-2 family proteins bax/bak. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4691–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, J.J.; May, K.L.; Thorpe, C.M.; Jandhyala, D.M.; Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Subtilase cytotoxin activates PERK, IRE1 and ATF6 endoplasmic reticulum stress-signalling pathways. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byres, E.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Lofling, J.C.; Smith, D.F.; Wilce, M.C.; Talbot, U.M.; Chong, D.C.; Yu, H.; Huang, S.; et al. Incorporation of a non-human glycan mediates human susceptibility to a bacterial toxin. Nature 2008, 456, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiro, K.; Morinaga, N.; Satoh, M.; Matsuura, G.; Tomonaga, T.; Nomura, F.; Moss, J.; Noda, M. Identification and characterization of receptors for vacuolating activity of subtilase cytotoxin. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiro, K.; Morinaga, N.; Moss, J.; Noda, M. Subtilase cytotoxin induces apoptosis in hela cells by mitochondrial permeabilization via activation of bax/bak, independent of C/EBF-homologue protein (CHOP), ire1alpha or JNK signaling. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 49, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Pathologic changes in mice induced by subtilase cytotoxin, a potent new Escherichia coli AB5 toxin that targets the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.M.; Sacerdoti, F.; Jancic, C.; Repetto, H.A.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Ibarra, C. Action of shiga toxin type-2 and subtilase cytotoxin on human microvascular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.C.; Sacerdoti, F.; Rivera, F.P.; Repetto, H.A.; Ibarra, C.; Amaral, M.M. Prevention of renal damage caused by shiga toxin type 2: Action of miglustat on human endothelial and epithelial cells. Toxicon 2015, 105, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, L.B.; Velazquez, N.; Repetto, H.A.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Ibarra, C.; Silberstein, C. Effects of Escherichia coli subtilase cytotoxin and shiga toxin 2 on primary cultures of human renal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, R.S.; Sacerdoti, F.; Jancic, C.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Ibarra, C.; Amaral, M.M. Comparative characterization of shiga toxin type 2 and subtilase cytotoxin effects on human renal epithelial and endothelial cells grown in monolayer and bilayer conditions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.L.; Islur, A.; Haq, R.; Mascarenhas, M.; Karmali, M.A.; Perdue, M.H.; Zanke, B.W.; Sherman, P.M. Escherichia coli shiga toxins induce apoptosis in epithelial cells that is regulated by the bcl-2 family. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 278, G811–G819. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lapeyraque, A.L.; Malina, M.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Boppel, T.; Kirschfink, M.; Oualha, M.; Proulx, F.; Clermont, M.J.; Le Deist, F.; Niaudet, P.; et al. Eculizumab in severe shiga-toxin-associated hus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2561–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aperia, A. 2011 homer smith award: To serve and protect: Classic and novel roles for Na+, K+ -adenosine triphosphatase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizman, O.; Uhlen, P.; Lal, M.; Brismar, H.; Aperia, A. Ouabain, a steroid hormone that signals with slow calcium oscillations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13420–13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zelenin, S.; Aperia, A.; Aizman, O. Low doses of ouabain protect from serum deprivation-triggered apoptosis and stimulate kidney cell proliferation via activation of NF-kappaB. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakawa-Naito, A.; Uhlen, P.; Lal, M.; Aizman, O.; Mikoshiba, K.; Brismar, H.; Zelenin, S.; Aperia, A. Cell signaling microdomain with NA,K-ATPase and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor generates calcium oscillations. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50355–50361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlaka, I.; Liu, X.L.; Rebetz, J.; Arvidsson, I.; Yang, L.; Brismar, H.; Karpman, D.; Aperia, A. Ouabain protects against shiga toxin-triggered apoptosis by reversing the imbalance between Bax and Bcl-xL. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrig, T.G. Escherichia coli shiga toxin mechanisms of action in renal disease. Toxins 2010, 2, 2769–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoner, W. Sodium pump and steroid hormone receptor. Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, J.M.; Burlaka, I.; Khodus, G.; Brismar, H.; Aperia, A. Calcium oscillations triggered by cardiotonic steroids. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5450–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthouser, K.A.; Mandal, A.; Merchant, M.L.; Schelling, J.R.; Delamere, N.A.; Valdes, R.R., Jr.; Tyagi, S.C.; Lederer, E.D.; Khundmiri, S.J. Ouabain stimulates NA-K-ATPase through a sodium/hydrogen exchanger-1 (NHE-1)-dependent mechanism in human kidney proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2010, 299, F77–F90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijpers, A.H.; van Setten, P.A.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Assmann, K.J.; Dijkman, H.B.; Pennings, A.H.; Monnens, L.A.; van Hinsbergh, V.W. Verocytotoxin-induced apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khundmiri, S.J.; Amin, V.; Henson, J.; Lewis, J.; Ameen, M.; Rane, M.J.; Delamere, N.A. Ouabain stimulates protein kinase B (Akt) phosphorylation in opossum kidney proximal tubule cells through an ERK-dependent pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khundmiri, S.J.; Metzler, M.A.; Ameen, M.; Amin, V.; Rane, M.J.; Delamere, N.A. Ouabain induces cell proliferation through calcium-dependent phosphorylation of Akt (protein kinase B) in opossum kidney proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, P.I.; Gordon, C.A.; Chandler, W.L. Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creydt, V.P.; Silberstein, C.; Zotta, E.; Ibarra, C. Cytotoxic effect of shiga toxin-2 holotoxin and its b subunit on human renal tubular epithelial cells. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoner, W. Endogenous cardiac glycosides, a new class of steroid hormones. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment | Cytotoxicity |
|---|---|
| Stx2 (10 ng/mL) | 92.6 ± 2.3 |
| SubAB (100 ng/mL) | 84.9 ± 1.8 |
| Stx2 + OUA | 53.0 ± 3.3 * |
| SubAB + OUA | 11.4 ± 4.8 * |
| Treatment | Cytotoxicity |
|---|---|
| Stx2 (20 ng/mL) | 47.0 ± 2.2 |
| SubAB (100 ng/mL) | 40.0 ± 7.0 |
| Stx2 + OUA | 0 * |
| SubAB + OUA | 35.3 ± 4.6 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, M.M.; Girard, M.C.; Álvarez, R.S.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Repetto, H.A.; Sacerdoti, F.; Ibarra, C.A. Ouabain Protects Human Renal Cells against the Cytotoxic Effects of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin. Toxins 2017, 9, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9070226
Amaral MM, Girard MC, Álvarez RS, Paton AW, Paton JC, Repetto HA, Sacerdoti F, Ibarra CA. Ouabain Protects Human Renal Cells against the Cytotoxic Effects of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin. Toxins. 2017; 9(7):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9070226
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, María M., Magalí C. Girard, Romina S. Álvarez, Adrienne W. Paton, James C. Paton, Horacio A. Repetto, Flavia Sacerdoti, and Cristina A. Ibarra. 2017. "Ouabain Protects Human Renal Cells against the Cytotoxic Effects of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin" Toxins 9, no. 7: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9070226
APA StyleAmaral, M. M., Girard, M. C., Álvarez, R. S., Paton, A. W., Paton, J. C., Repetto, H. A., Sacerdoti, F., & Ibarra, C. A. (2017). Ouabain Protects Human Renal Cells against the Cytotoxic Effects of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin. Toxins, 9(7), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9070226






