Small and Smaller—sRNAs and MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Toxin Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: A Mini-Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Prokaryotic Small RNAs (sRNAs) in the Context of the Regulation of Toxin Gene Expression
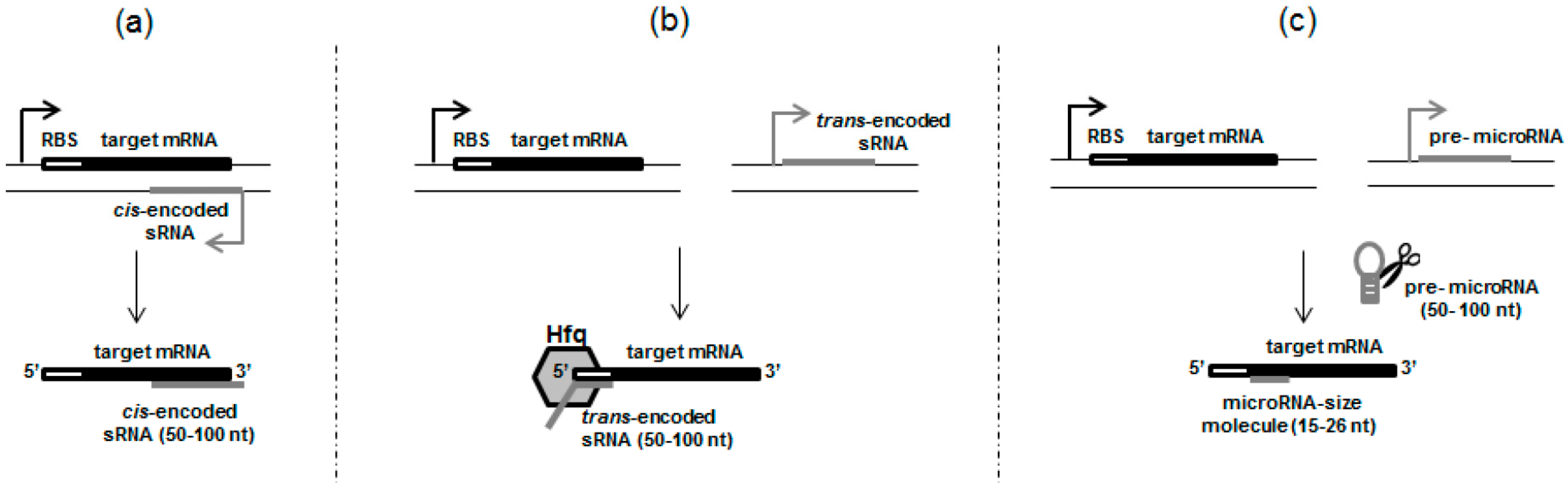
2.1. cis-Encoded sRNAs
2.2. trans-Encoded sRNAs, Resembling Eukaryotic Small RNAs
3. Something Smaller than sRNAs—True MicroRNAs in Prokaryotic Cells
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacob, F.; Monod, J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1961, 3, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaux, C.; Verneuil, N.; Hartke, A.; Giard, J.C. Physiological roles of small RNA molecules. Microbiology 2014, 160, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, S.; McCullen, C.A.; Guillier, M.; Vanderpool, C.K.; Majdalani, N.; Benhammou, J.; Thompson, K.M.; FitzGerald, P.C.; Sowa, N.A.; FitzGerald, D.J. Small RNA regulators and the bacterial response to stress. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 71, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, G.R.; Vanderpool, C.K. Molecular call and response: The physiology of bacterial small RNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1809, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderpool, C.K.; Balasubramanian, D.; Lloyd, C.R. Dual-function RNA regulators in bacteria. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, G.; Lee, J.; Suk, S.; Kim, D.; Young Lee, J.; Kim, K.S.; Choi, B.S.; Lee, Y. Identification of novel sRNAs involved in biofilm formation, motility, and fimbriae formation in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, S.; Storz, G. Bacterial small RNA regulators: Versatile roles and rapidly evolving variations. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fozo, E.M.; Hemm, M.R.; Storz, G. Small toxic proteins and the antisense RNAs that repress them. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 72, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenfort, K.; Said, N.; Welsink, T.; Lucchini, S.; Hinton, J.C.; Vogel, J. Specific and pleiotropic patterns of mRNA regulation by ArcZ, a conserved, Hfq-dependent small RNA. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 74, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.S.; Updegrove, T.B.; Gogol, E.B.; Shabalina, S.A.; Gross, C.A.; Storz, G. MicL, a new σE-dependent sRNA, combats envelope stress by repressing synthesis of Lpp, the major outer membrane lipoprotein. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1620–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, S.; Szybalski, W. Control of short leftward transcripts from the immunity and ori regions in induced coliphage lambda. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1973, 126, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejman-Faleńczyk, B.; Bloch, S.; Licznerska, K.; Felczykowska, A.; Dydecka, A.; Węgrzyn, A.; Węgrzyn, G. Small regulatory RNAs in lambdoid bacteriophages and phage-derived plasmids: Not only antisense. Plasmid 2015, 78, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, M. Divergently overlapping cis-encoded antisense RNA regulating toxin-antitoxin systems from E. coli: Hok/sok, ldr/rdl, symE/symR. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershko-Shalev, T.; Odenheimer-Bergman, A.; Elgrably-Weiss, M.; Ben-Zvi, T.; Govindarajan, S.; Seri, H.; Papenfort, K.; Vogel, J.; Altuvia, S. Gifsy-1 Prophage IsrK with dual function as small and messenger RNA modulates vital bacterial machineries. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfeldt, E.; Taylor, D.; von Gabain, A.; Arvidson, S. Activation of alpha-toxin translation in Staphylococcus aureus by the trans-encoded antisense RNA, RNAIII. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4569–4577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Le Rhun, A.; Charpentier, E. Small RNAs in streptococci. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, K.; Bhowmik, S.K.; Hayashi, H.; Shimizu, T. Identification of a novel locus that regulates expression of toxin genes in Clostridium perfringens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 209, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, S.; Cho, K.H. The Mechanisms of virulence regulation by small noncoding RNAs in low GC Gram-positive pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29797–29814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.G.; Unoson, C. The toxin-antitoxin system tisB-istR1: Expression, regulation, and biological role in persister phenotypes. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejman-Faleńczyk, B.; Bloch, S.; Licznerska, K.; Dydecka, A.; Felczykowska, A.; Topka, G.; Węgrzyn, A.; Węgrzyn, G. A small, microRNA-size, ribonucleic acid regulating gene expression and development of Shiga toxin-converting bacteriophage Φ24B. Sci. Rep. 2015, 11, 10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, Y.; Finethy, R.; Saka, H.A.; Xet-Mull, A.M.; Sisk, D.M.; Smith, K.L.; Lee, S.; Coers, J.; Valdivia, R.H.; Tobin, D.M.; et al. Search for microRNAs expressed by intracellular bacterial pathogens in infected mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, S.C.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, H.J. Secretable Small RNAs via outer membrane vesicles in periodontal pathogens. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K.; Wagner, E.G. RNA antitoxins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinke, L.; Wulff, D.L. OOP RNA, produced from multicopy plasmids, inhibits lambda cII gene expression through an RNase III-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev. 1987, 1, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinke, L.; Mahoney, M.; Wulff, D.L. The role of the OOP antisense RNA in coliphage lambda development. Mol. Microbiol. 1991, 5, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Węgrzyn, G.; Licznerska, K.; Węgrzyn, A. Phage λ—New insights into regulatory circuits. Adv. Virus Res. 2012, 82, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loś, J.M.; Loś, M.; Węgrzyn, G. Bacteriophages carrying Shiga toxin genes: Genomic variations, detection and potential treatment of pathogenic bacteria. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, P.L.; Livny, J.; Neely, M.N.; David, W.K.; Acheson, D.W.K.; Friedman, D.I.; Waldor, M.K. Bacteriophage control of Shiga toxin 1 production and release by E. coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, S.K.; Felczykowska, A.; Nejman-Faleńczyk, B. Escherichia coli O104:H4 outbreak—Have we learnt a lesson from it? Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chevallereau, A.; Blasdel, B.G.; De Smet, J.; Monot, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Kogadeeva, M.; Sauer, U.; Jorth, P.; Whiteley, M.; Debarbieux, L.; et al. Next-Generation “-omics” approaches reveal a massive alteration of host RNA metabolism during bacteriophage infection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskinen, K.; Blasdel, B.G.; Lavigne, R.; Skurnik, M. RNA-sequencing reveals the progression of phage-host interactions between φR1-37 and Yersinia enterocolitica. Viruses 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.G.; Romby, P. Small RNAs in bacteria and archaea: Who they are, what they do, and how they do it. Adv. Genet. 2015, 90, 133–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, S. Micros for microbes: Non-coding regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Trends Genet. 2005, 21, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternan, N.G. Small regulatory RNA molecules in bacteria. OA Microbiol. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.C.; Pertea, M.; Lee, S.; Salzberg, S.L.; Mendell, J.T. Genome-wide annotation of microRNA primary transcript structures reveals novel regulatory mechanisms. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in control of gene expression: An overview of nuclear functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repoila, F.; Majdalani, N.; Gottesman, S. Small non-coding RNAs, co-ordinators of adaptation processes in Escherichia coli: The RpoS paradigm. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zuo, X.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Yan, Y.; et al. MicroRNA directly enhances mitochondrial translation during muscle differentiation. Cell 2014, 158, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiya, A.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.C. Transition of a microRNA from repressing to activating translation depending on the extent of base pairing with the target. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Vogel, J. Multiple target regulation by small noncoding RNAs rewires gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tree, J.J.; Granneman, S.; McAteer, S.P.; Tollervey, D.; Gally, D.L. Identification of bacteriophage-encoded anti-sRNAs in pathogenic Escherichia coli. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, N.; Soma, A.; Muto, A.; Iyoda, S.; Suh, M.; Kurihara, N.; Abe, H.; Tobe, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; et al. A novel small regulatory RNA enhances cell motility in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedrick, R.M.; Marinelli, L.J.; Newton, G.L.; Pogliano, K.; Pogliano, J.; Hatfull, G.F. Functional requirements for bacteriophage growth: Gene essentiality and expression in mycobacteriophage Giles. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinezhad Orang, A.; Safaralizadeh, R.; Kazemzadeh-Bavili, M. Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated gene regulation from common downregulation to mRNA-specific upregulation. Int. J. Genom. 2014, 2014, 970607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Tang, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, J.; Xu, K. MicroRNA-derived fragment length polymorphism assay. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Analysis of microRNA-size, small RNAs in Streptococcus mutans by deep sequencing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 326, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.M.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, Y.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, H.J. Identification of microRNA-size, small RNAs in Escherichia coli. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Kwon, T.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, H.J. Isolation and Characterization of a microRNA-size secretable Small RNA in Streptococcus sanguinis. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, M.J.; Kesty, N.C. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles and the host-pathogen interaction. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starega-Roslan, J.; Krol, J.; Koscianska, E.; Kozlowski, P.; Szlachcic, W.J.; Sobczak, K.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Structural basis of microRNA length variety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, A.; Behlen, L.; Reynolds, A.; Wolfson, A.; Marshall, W.S.; Karpilow, J.; Khvorova, A. The contributions of dsRNA structure to Dicer specificity and efficiency. RNA 2005, 11, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Lai, E.C. Alternative miRNA biogenesis pathways and the interpretation of core miRNA pathway mutants. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöström, A.E.; Sandblad, L.; Uhlin, B.E.; Wai, S.N. Membrane vesicle-mediated release of bacterial RNA. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, E.F. Bacteriophage-encoded bacterial virulence factors and phage-pathogenicity island interactions. Adv. Virus Res. 2012, 82, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brüssow, H.; Canchaya, C.; Hardt, W.D. Phages and the evolution of bacterial pathogens: From genomic rearrangements to lysogenic conversion. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 560–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, M. MicroRNAs regulate immune system via multiple targets. Discov. Med. 2014, 18, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Yuasa, Y. Multiple-to-multiple relationships between microRNAs and target genes in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Feature | cis-Acting sRNAs | trans-Encoded sRNAs | MicroRNA-Sized Molecules |
|---|---|---|---|
| Action on the target gene Complementarity with targets One or multiple targets Accompanying proteins Structure Processing | cis-regulation extensive one usually not required broad secondary structures with very long stems does not occur | trans-regulation limited multiple usually required more loosely structures with shorter stems usually does not occur 2 | trans-regulation limited multiple 1 not determined usually single stem-loop precursor structure occur 3 |
| The most common size range of the mature sRNA molecule (nt) | 50–100 | 50–100 | 15–26 |
| sRNA Type | sRNA Name | sRNA Source | sRNA Function in the Context of the Regulation of Toxin Production and Secretion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cis-encoded sRNAs | OOP | Bacteriophage λ | Is predicted to repress the synthesis of the cII protein and thus indirectly regulate the production of Shiga toxins by Stx phages | [11,12] |
| Sok | Plasmid R1 & chromosome of E. coli | Indirectly inhibits the synthesis of the highly toxic protein Hok, responsible for cell membrane damage | [13] | |
| Rdl | Chromosome of E. coli | Regulates the synthesis of the Ldr toxin, whose over expression leads to rapid host cell killing | [13] | |
| SymR | Chromosome of E. coli | Regulates the endogenous level of the SymE toxin | [13] | |
| trans-encoded sRNAs | IsrK | Bacteriophage Gifsy-1 | Controls the production of the toxic AntQ protein which is responsible for bacterial growth arrest and cell death | [14] |
| RNAIII | Chromosome of Staphylococcus aureus | Induces the expression of genes encoding the staphylococcal alpha-toxin | [15] | |
| FasX | Chromosome of Streptococcus pyogenes | Positively controls the production of streptococcal haemolytic exotoxin streptolysin S (SLS) | [16] | |
| VR-RNA | Chromosome of Clostridium perfringens | Is responsible for the regulation of the expression of toxin genes, such as plc (α toxin phospholipase C) and colA, (κ toxin, collagenase) | [17] | |
| VirX | Chromosome of Clostridium perfringens | Regulates the expression of genes : plc, colA and pfoA coding for pore-forming toxin perfringolysin A; Controls the production of enterotoxin | [18] | |
| VirU | Chromosome of Clostridium perfringens | Has a positive effect on the production of pore-forming toxin perfringolysin A | [18] | |
| VirT | Chromosome of Clostridium perfringens | Negatively regulates pfoA and colA transcription | [18] | |
| IstR-1 | Chromosome of E. coli | Inhibits translation of the toxic protein TisB, which is responsible for cell growth arrest under stress conditions | [19] | |
| microRNA-size RNAs | 24B_1 | Bacteriophage Φ24B | Is predicted to regulate the phage d_ant gene, and thus indirectly stimulate the lysogenic state of the Stx phage during which Shiga toxins are not produced | [20] |
| MM-H | Chromosome of Mycobacterium marinum | Does not have a defined function | [21] | |
| AA_20050 PG_122 TD_16563 | Chromosome of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola | Do not have defined functions and are transmitted by outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) that enable bacteria to secrete a large, complex group of proteins, including toxins | [22] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bloch, S.; Węgrzyn, A.; Węgrzyn, G.; Nejman-Faleńczyk, B. Small and Smaller—sRNAs and MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Toxin Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: A Mini-Review. Toxins 2017, 9, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060181
Bloch S, Węgrzyn A, Węgrzyn G, Nejman-Faleńczyk B. Small and Smaller—sRNAs and MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Toxin Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: A Mini-Review. Toxins. 2017; 9(6):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060181
Chicago/Turabian StyleBloch, Sylwia, Alicja Węgrzyn, Grzegorz Węgrzyn, and Bożena Nejman-Faleńczyk. 2017. "Small and Smaller—sRNAs and MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Toxin Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: A Mini-Review" Toxins 9, no. 6: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060181
APA StyleBloch, S., Węgrzyn, A., Węgrzyn, G., & Nejman-Faleńczyk, B. (2017). Small and Smaller—sRNAs and MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Toxin Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: A Mini-Review. Toxins, 9(6), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060181








