A Monoclonal–Monoclonal Antibody Based Capture ELISA for Abrin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Anti-Abrin Monoclonal Antibodies
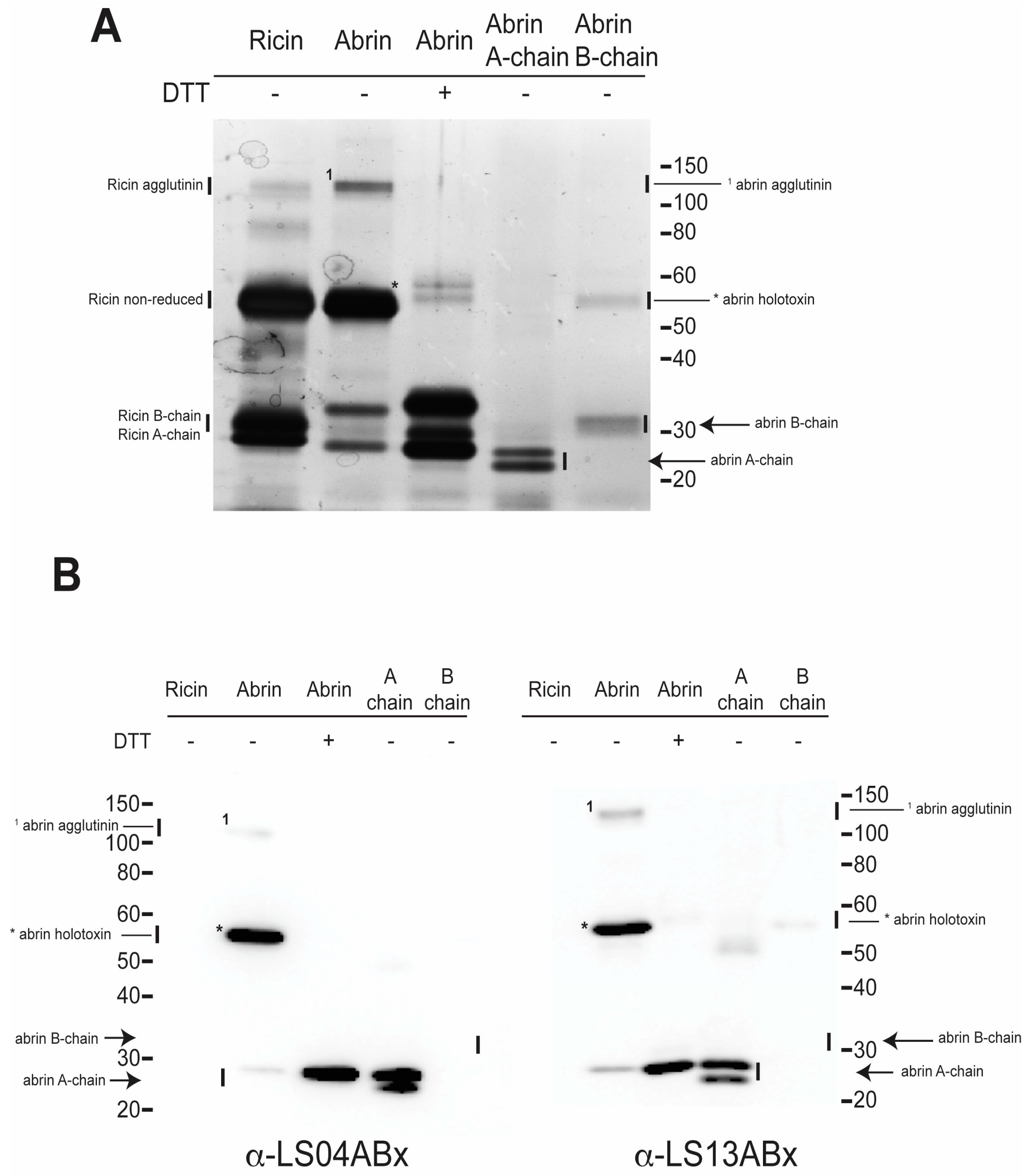
2.2. Silver Stain and Western Blots
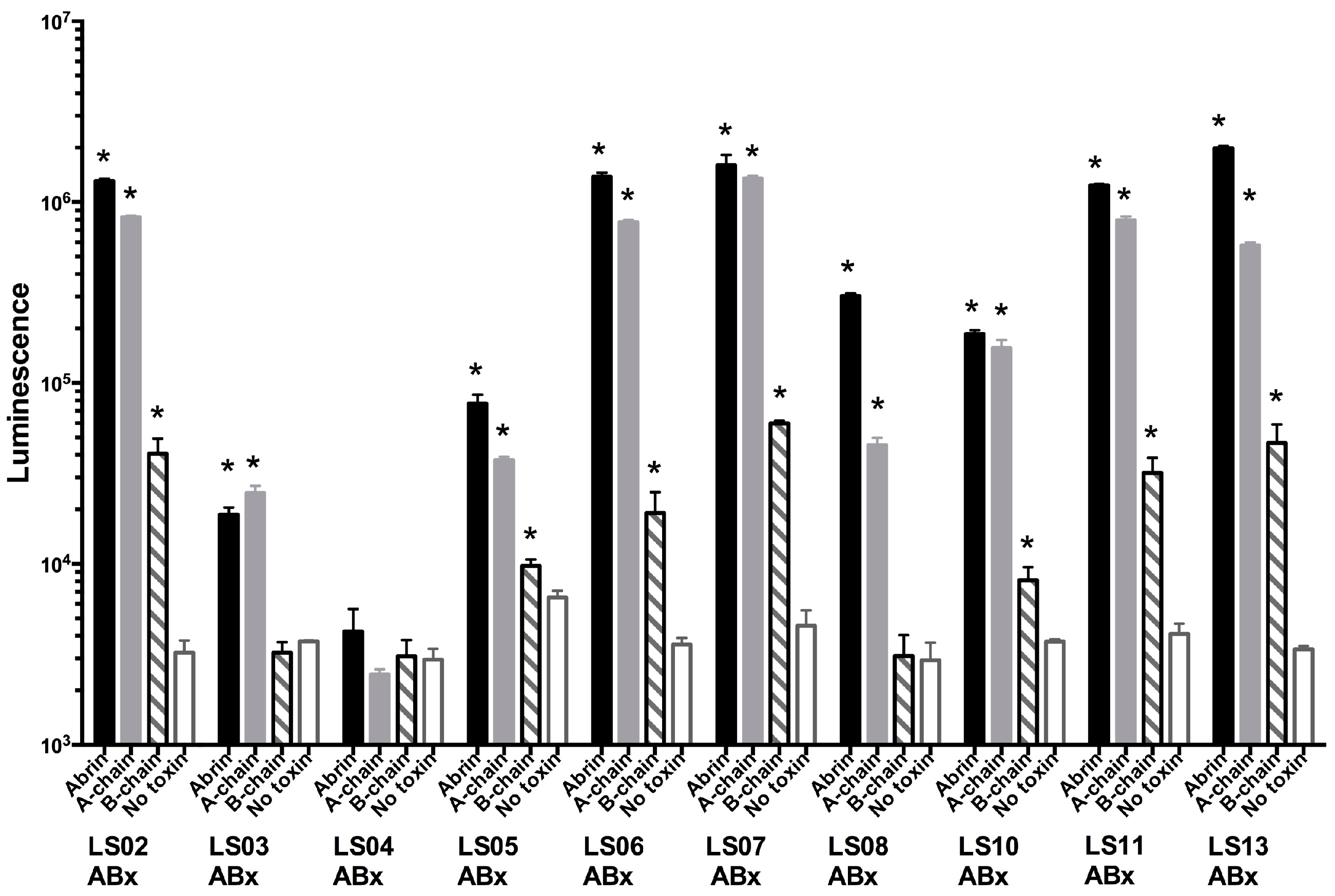
2.3. Monoclonal Antibody Binding to Abrin Toxin and Individual A and B-Chain Subunits
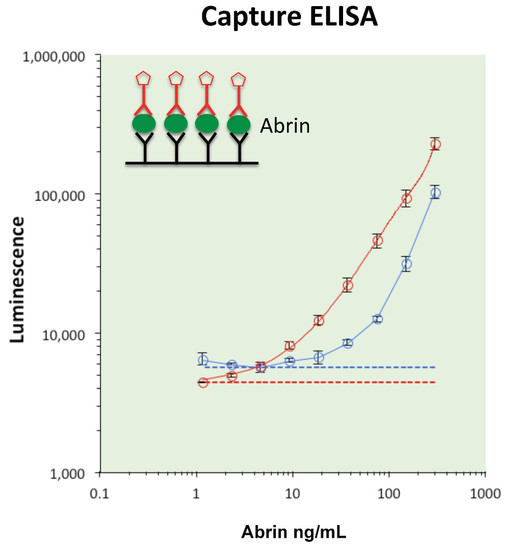
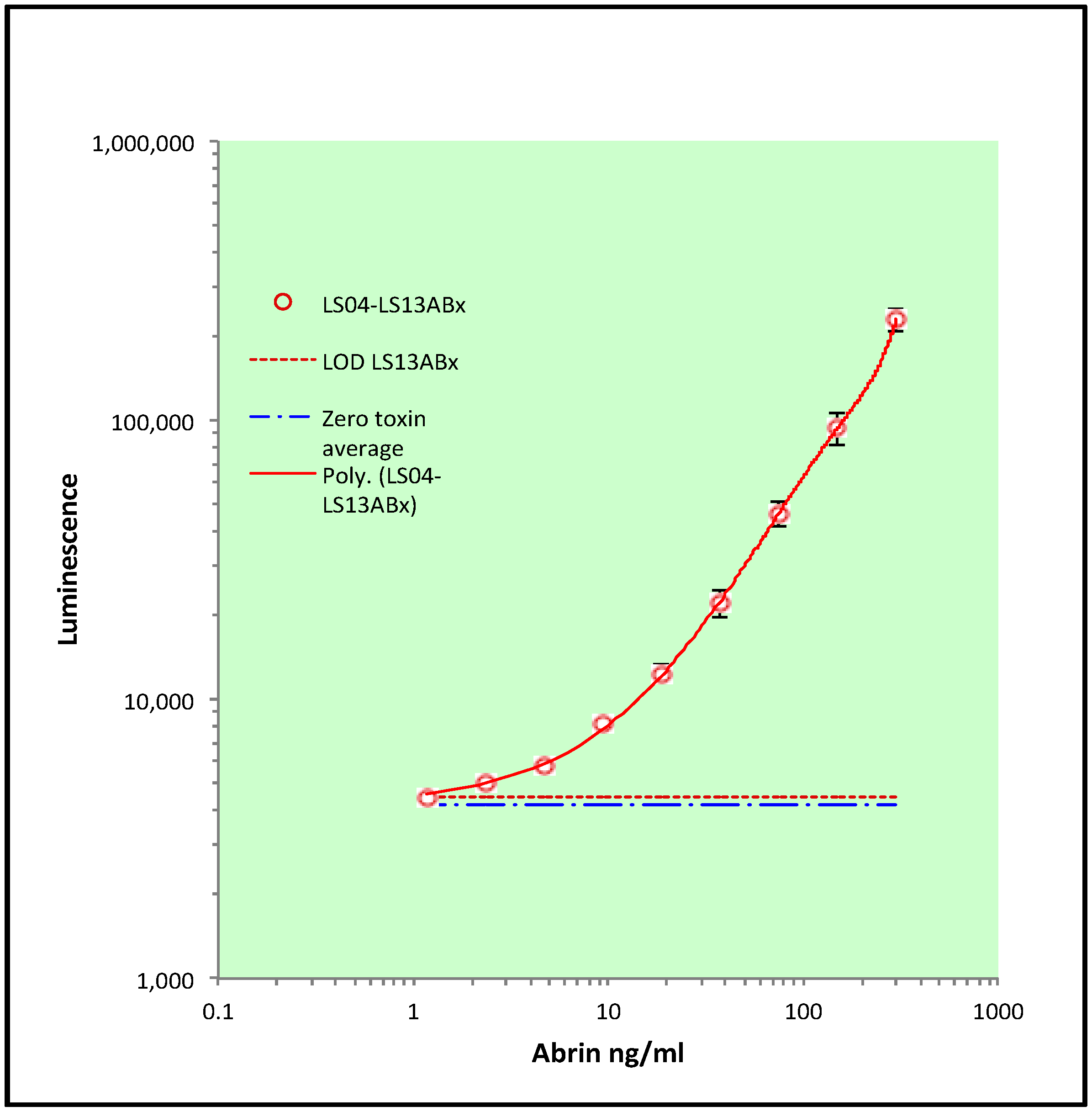
2.4. Monoclonal–Monoclonal Capture ELISA for Abrin
2.5. Specificity of Abrin Capture ELISA against Other Plant Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins (RIPs)
2.6. MAb Neutralization of Abrin Cytotoxicity in Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Monoclonal Antibody Procedure and Purification
4.3. ELISA Methods
4.4. SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis for Silver Stain and Western Blotting
4.5. Capture ELISA with Abrin/Ricin near Neighbor Extracts
4.6 Vero Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Endo, Y.; Tsurugi, K. Mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1986, 17, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Lu, T.H.; Liu, C.L.; Lin, J.Y. A biophysical elucidation for less toxicity of agglutinin than abrin-a from the seeds of abrus precatorius in consequence of crystal structure. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, B.; Ma, H.; Carney, C.; Janda, K.D. Selection and characterization of human monoclonal antibodies against abrin by phage display. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5690–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedman, L.; Shih, R.D.; Hung, O. Survival after an intentional ingestion of crushed abrus seeds. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 9, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, S.; Surolia, A.; Karande, A.A. Ribosome-inactivating protein and apoptosis: Abrin causes cell death via mitochondrial pathway in jurkat cells. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, S.; Surendranath, K.; Bora, N.; Surolia, A.; Karande, A.A. Ribosome inactivating proteins and apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, L.T.; Qu, X.L. Cloning, expression of the abrin-a a-chain in escherichia coli and measurement of the biological activities in vitro. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao 2002, 34, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hegde, R.; Maiti, T.K.; Podder, S.K. Purification and characterization of three toxins and two agglutinins from abrus precatorius seed by using lactamyl-sepharose affinity chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 194, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Lee, T.C.; Hu, S.T.; Tung, T.C. Isolation of four isotoxic proteins and one agglutinin from jequiriti bean (abrus precatorius). Toxicon 1981, 19, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olsnes, S.; Saltvedt, E.; Pihl, A. Isolation and comparison of galactose-binding lectins from abrus precatorius and ricinus communis. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.H.; Hartman, F.C.; Pfuderer, P.; Yang, W.K. Purification and characterization of two major toxic proteins from seeds of abrus precatorius. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, J.; Som, S.; Sen, A. Isolation, purification, and some properties of a lectin and abrin from abrus precatorius linn. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1976, 174, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Lee, T.C.; Tung, T.C. Isolation of antitumor proteins abrin-a and abrin-b from abrus precatorius. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1978, 12, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, M.S.; Behnke, W.D. A characterization of abrin a from the seeds of the abrus precatorius plant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 667, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, E.A. Toxicity and detection of ricin and abrin in beverages. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirpe, F.; Barbieri, L.; Battelli, M.G.; Soria, M.; Lappi, D.A. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: Present status and future prospects. Biotechnology 1992, 10, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.L.; Tsai, C.C.; Lin, S.C.; Wang, L.I.; Hsu, C.I.; Hwang, M.J.; Lin, J.Y. Primary structure and function analysis of the abrus precatorius agglutinin a chain by site-directed mutagenesis. Pro(199) of amphiphilic alpha-helix h impairs protein synthesis inhibitory activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1897–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.C.; Zhou, Y.; Jain, R.; Lemire, S.W.; Fox, S.; Sabourin, P.; Barr, J.R. Quantification of l-abrine in human and rat urine: A biomarker for the toxin abrin. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2009, 33, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, D.M. Bacterial toxins: A table of lethal amounts. Microbiol. Rev. 1982, 46, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wooten, J.V.; Pittman, C.T.; Blake, T.A.; Thomas, J.D.; Devlin, J.J.; Higgerson, R.A.; Johnson, R.C. A case of abrin toxin poisoning, confirmed via quantitation of l-abrine (n-methyl-l-tryptophan) biomarker. J. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Jaworski, J. A portable and chromogenic enzyme-based sensor for detection of abrin poisoning. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, E.A.; Venkateswaran, K.V.; O’Brien, T.W. Simultaneous multiplex detection and confirmation of the proteinaceous toxins abrin, ricin, botulinum toxins, and staphylococcus enterotoxins a, b, and c in food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6600–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Tian, X.L.; Li, Y.S.; Pan, F.G.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, X.R.; Ren, H.L.; Lu, S.Y.; Li, Z.H.; et al. Development of a monoclonal antibody-based sandwich-type enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (elisa) for detection of abrin in food samples. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2661–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanker, L.H.; Merrill, P.; Scotcher, M.C.; Cheng, L.W. Development and partial characterization of high-affinity monoclonal antibodies for botulinum toxin type a and their use in analysis of milk by sandwich elisa. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 336, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramage, J.G.; Prentice, K.W.; Morse, S.A.; Carter, A.J.; Datta, S.; Drumgoole, R.; Gargis, S.R.; Griffin-Thomas, L.; Hastings, R.; Masri, H.P.; et al. Comprehensive laboratory evaluation of a specific lateral flow assay for the presumptive identification of abrin in suspicious white powders and environmental samples. Biosecur. Bioterror. 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, C.; Xia, C.; Wu, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W. Development of elisa and colloidal gold-pab conjugate-based immunochromatographic assay for detection of abrin-a. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2015, 34, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Qiu, J.; Yang, R.; Zhou, L. Rapid detection of abrin in foods with an up-converting phosphor technology-based lateral flow assay. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.B.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Kong, T.; Li, D.N.; Tang, J.J.; Liu, L.; Liu, G.W.; Wang, Z. Preparation and identification of monoclonal antibody against abrin-a. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9796–9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Ni, P.; Dai, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, Z. Aptamer-based colorimetric biosensing of abrin using catalytic gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2015, 140, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotcher, M.C.; Cheng, L.W.; Stanker, L.H. Detection of botulinum neurotoxin serotype b at sub mouse ld(50) levels by a sandwich immunoassay and its application to toxin detection in milk. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, A.; Wang, C.; Powers, D.B.; Amersdorfer, P.; Smith, T.J.; Montgomery, V.A.; Sheridan, R.; Blake, R.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Potent neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin by recombinant oligoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11346–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.F.; Barash, J.R.; Lou, J.L.; Conrad, F.; Marks, J.D.; Arnon, S.S. Immunological characterization and neutralizing ability of monoclonal antibodies directed against botulinum neurotoxin type h. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Lou, J.; Wen, W.; Conrad, F.; Zhai, W.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. A three monoclonal antibody combination potently neutralizes multiple botulinum neurotoxin serotype f subtypes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Monoclonals | Isotype | Biotin/IgG |
|---|---|---|
| LS02ABx | IgG1, kappa | 4.0 ± 0.17 |
| LS03ABx | IgG1, kappa | 3.9 ± 0.10 |
| LS04ABx | IgG2a, kappa | 3.8 ± 0.20 |
| LS05ABx | IgG2b, kappa | 2.5 ± 0.50 |
| LS06ABx | IgG1, kappa | 1.5 ± 0.5 |
| LS07ABx | IgG1, kappa | 3.7 ± 0.3 |
| LS08ABx | IgG2a, lambda | 4.0 ± 0.16 |
| LS10ABx | IgG1, kappa | 2.5 ± 0.5 |
| LS11ABx | IgG1, kappa | 2.0 ± 0.01 |
| LS13ABx | IgG1, kappa | 1.8 ± 0.20 |
| Detectorm Abs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS02ABx | LS03ABx | LS04ABx | LS05ABx | LS06ABx | LS07ABx | LS08ABx | LS10ABx | LS11ABx | LS13ABx | |
| Capture mAbs | ||||||||||
| LS02ABx | - | 200 | 200 | - | - | - | 50 | - | - | - |
| LS03ABx | 100 | - | - | - | 200 | 200 | - | - | - | 200 |
| LS04ABx | - | - | - | 200 | - | - | - | - | 5 | 10 |
| LS05ABx | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LS06ABx | - | - | - | - | - | 75 | 10 | 100 | - | - |
| LS07ABx | - | - | - | - | - | 75 | 40 | - | - | - |
| LS08ABx | 100 | 40 | - | 100 | - | 100 | - | 75 | 5 | 50 |
| LS10ABx | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LS11ABx | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 | - | - | - |
| LS13ABx | 100 | 200 | 200 | - | - | - | 100 | - | - | - |
| Near Neighbours | Capture ELISA |
|---|---|
| Abrus laevigatus E. Mey. | - |
| Abrus precatorius L. + | + |
| Abrus schimperi subsp. Africanus (Vatke) Verdc. | - |
| Acalypha rhomboidea Raf. | - |
| Acalypha rhomboidea 11837 | - |
| Adriana quadripartite (Labill.) Gaudich. | - |
| Adriana quadripartita 76851 | - |
| Bryonia dioica Jacq. | - |
| Canavalia gladiate (Jacq.) DC. | - |
| Canavalia rosea (Sw.) DC | - |
| Canavalia madagascariensis J.D. Sauer | - |
| Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J.Presl. | - |
| Cucurbita moschata Duchesne | - |
| Dianthus caryophyllus Linnaeus | - |
| Fatsia japonica (Thunb.) Decne & Planch. | - |
| Fatsia japonica 39610 | - |
| Galactia striata (Jacq.) Urban | - |
| Galactia wrightii A. Gray | - |
| Iris hollandica Bf. | - |
| Jubernardia globifera (Benth.) Troupin | - |
| Jubernardia globifera 76851 | - |
| Luffa acutangula (L.) Roxb. | - |
| Luffa cylindrical (aegyptica) Bergquist, 1995 | - |
| Lychnis chalcedonica (L.) E.H.L. Krause | - |
| Macaranga grandifolia (Blanco) Merr. | - |
| Macaranga grandifolia 3403 | - |
| Mallotus nudiflorus (L.) Kulju & Welzen | - |
| Mallotus philippensis (Lam.) Müll. Arg. | - |
| Manihot escuelenta Crantz. | - |
| Manihot escuelenta 13562 | - |
| Mercurialis annua L. | - |
| Mercurialis annua 279720 | - |
| Momordica charantia L. | - |
| Phytolacca Americana L. | - |
| Phytolacca americana 39161 | - |
| Phytolacca dioica L. | - |
| Plukenetia volubilis 72130 | - |
| Plukenetia volubulis L. | - |
| Sambucus ebulus L. | - |
| Sambucus nigra L. | - |
| Saponaria officinalis L. | - |
| Saponaria officinalis 391915 | - |
| Senna occidentalis (L.) Link | - |
| Trewia nudiflora 85123 | - |
| Trichosanthes kirilowi Maxim. | - |
| Viscum album L. | - |
| Viscum album 22397 | - |
| Treatment | Relative Toxicity (%) |
|---|---|
| DMEM | 0 |
| Abrin | 100 |
| LS07ABx | 4 + 3 |
| LS13ABx | 4 ± 1 |
| LS02ABx | 4 ± 3 |
| LS02 + 07 + 13 | 4 ± 3 |
| LS04Abx + Abrin | 94 ± 1 |
| LS07Abx + Abrin | 69 ± 2 |
| LS08Abx + Abrin | 88 ± 1 |
| LS10Abx + Abrin | 94 ± 1 |
| LS13Abx + Abrin | 54 ± 1 |
| LS11Abx + Abrin | 77 ± 1 |
| LS03Abx + Abrin | 96 ± 0 |
| LS02Ax + Abrin | 66 ± 2 |
| LS02 + 07 + 13 + Abrin | 41 ± 2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tam, C.C.; Cheng, L.W.; He, X.; Merrill, P.; Hodge, D.; Stanker, L.H. A Monoclonal–Monoclonal Antibody Based Capture ELISA for Abrin. Toxins 2017, 9, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100328
Tam CC, Cheng LW, He X, Merrill P, Hodge D, Stanker LH. A Monoclonal–Monoclonal Antibody Based Capture ELISA for Abrin. Toxins. 2017; 9(10):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100328
Chicago/Turabian StyleTam, Christina C., Luisa W. Cheng, Xiaohua He, Paul Merrill, David Hodge, and Larry H. Stanker. 2017. "A Monoclonal–Monoclonal Antibody Based Capture ELISA for Abrin" Toxins 9, no. 10: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100328
APA StyleTam, C. C., Cheng, L. W., He, X., Merrill, P., Hodge, D., & Stanker, L. H. (2017). A Monoclonal–Monoclonal Antibody Based Capture ELISA for Abrin. Toxins, 9(10), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100328