Confirmation and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL for Aflatoxin Resistance in Maize Using a Combination of Linkage and Association Mapping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantitative Variation of the AA and RAI Score in Maize Populations
2.2. Phenotypic Correlations between the AA and RAI Score in Maize Populations
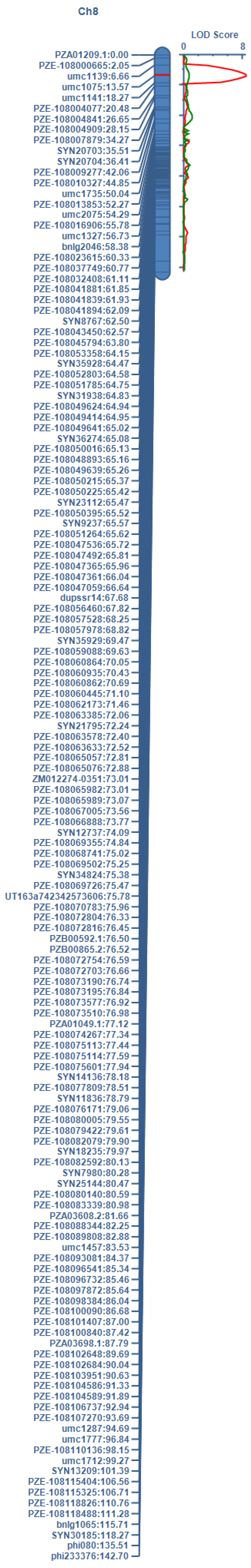
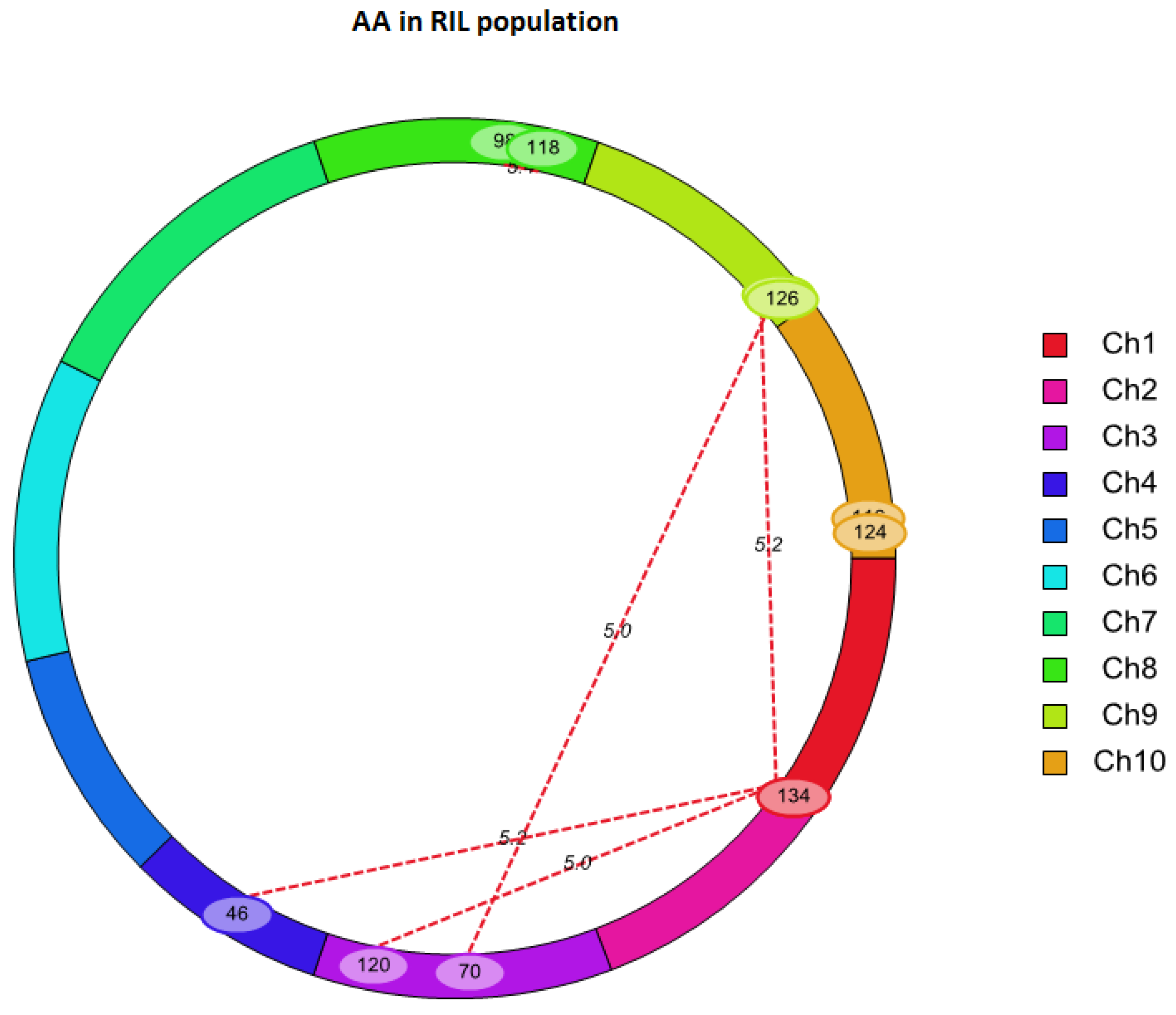
2.3. QTL Mapping for AA Using Linkage Analysis
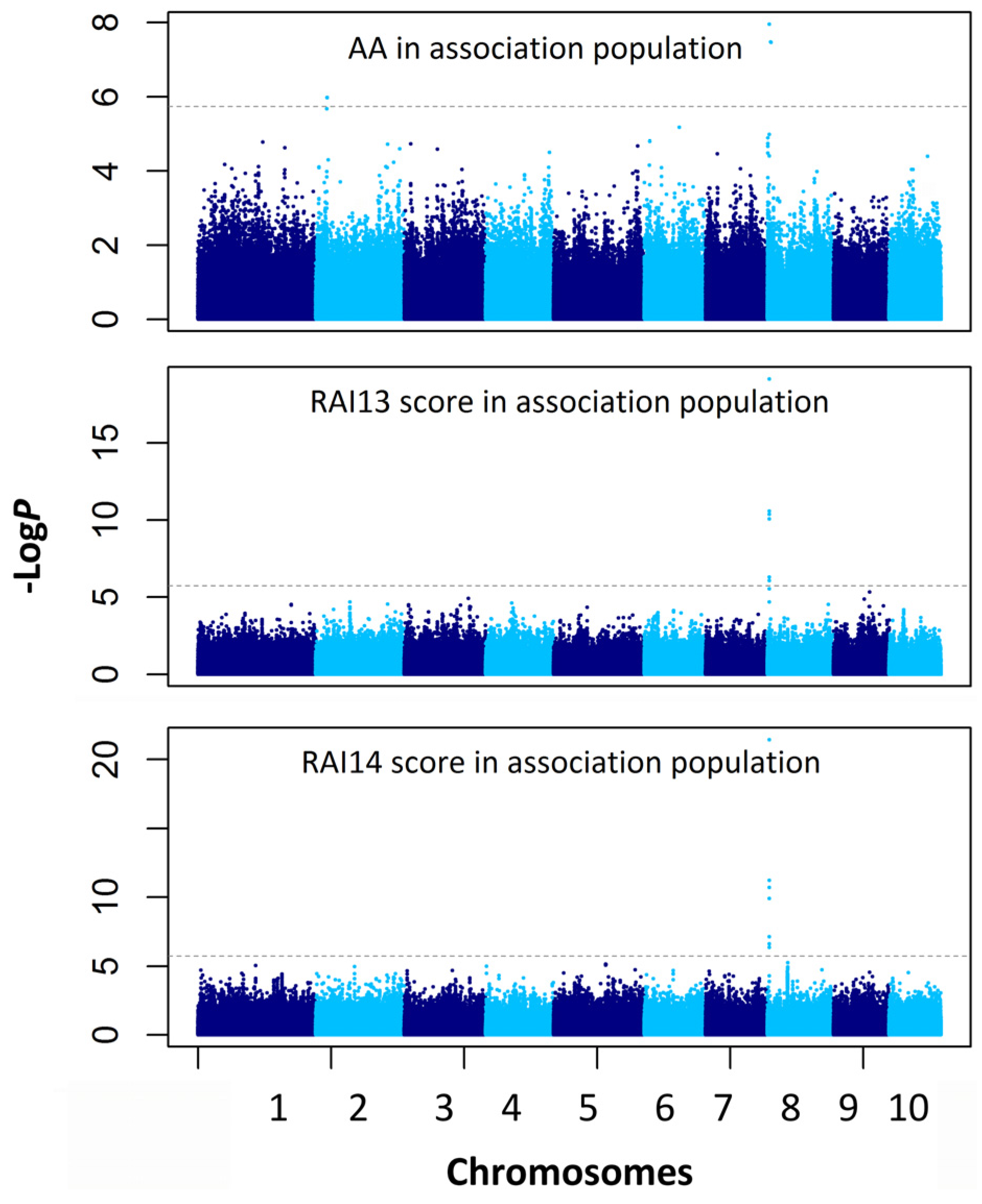
2.4. Association Mapping for the AA and RAI Score
3. Discussion
3.1. Direct Inoculation and Cultivation of A. flavus Fungi on Maize Kernels under Controlled Conditions Is an Accurate Method for Phenotypic Identification
3.2. Confirmation and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL for Maize A. flavus Resistance Breeding
3.3. Candidate Genes Predicted for Maize A. flavus Resistance
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Materials and Plant Growth Conditions
5.2. Phenotypic Evaluation
5.3. Statistical Analysis and QTL Mapping
5.4. Gene Prediction
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamblin, A.; White, D. Inheritance of resistance to Aspergillus ear rot and aflatoxin production of corn from Tex6. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.S.; Moreno, O.J.; Kang, M. Maize improvement for resistance to aflatoxins: Progress and challenges. In Crop Improvements: Challenges in the Twenty First Century; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Warburton, M.L.; Williams, W.P. Aflatoxin resistance in maize: What have we learned lately. Adv. Bot. 2014, 14, 2356–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.L.; Liang, B. Perspectives on aflatoxin control for human food and animal feed. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1993, 4, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haumann, F. Eradicating mycotoxins in food and feeds. Inform 1995, 6, 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Van Egmond, H.; Jonker, M. Worldwide Regulations for Mycotoxins in Food and Feed in 2003; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, K.; Hamblin, A.; White, D. Inheritance of resistance to aflatoxin production in the cross between corn inbreds B73 and LB31. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 1144–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.; Naidoo, G.; Forbes, A.; Mikkilineni, V.; White, D.; Rocheford, T. Quantitative trait loci for low aflatoxin production in two related maize populations. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widstrom, N.; Butron, A.; Guo, B.; Wilson, D.; Snook, M.; Cleveland, T.; Lynch, R. Control of preharvest aflatoxin contamination in maize by pyramiding QTL involved in resistance to ear-feeding insects and invasion by Aspergillus spp. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.D.; Williams, W.P.; Windham, G.L.; Willcox, M.C.; Abbas, H.K. Quantitative trait loci contributing resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in the maize inbred Mp313E. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Alwala, S.; Kimbeng, C.A.; Williams, W.; Kang, M.S. Molecular markers associated with resistance to Aspergillus flavus in maize grain: QTL and discriminant analyses. J. New Seeds 2008, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, M.L.; Brooks, T.D.; Krakowsky, M.D.; Shan, X.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P. Identification and mapping of new sources of resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in maize. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, M.L.; Brooks, T.D.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P. Identification of novel QTL contributing resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in maize. Mol. Breed. 2011, 27, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, K.L. Improving Maize by QTL Mapping. In Agronomic Performance and Breeding to Reduce Aflatoxin in Texas; Texas A&M University: Canyon, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Willcox, M.C.; Davis, G.L.; Warburton, M.L.; Windham, G.L.; Abbas, H.K.; Betrán, J.; Holland, J.B.; Williams, W.P. Confirming quantitative trait loci for aflatoxin resistance from Mp313E in different genetic backgrounds. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mideros, S.X.; Warburton, M.L.; Jamann, T.M.; Windham, G.L.; Williams, W.P.; Nelson, R.J. Quantitative trait loci influencing mycotoxin contamination of maize: Analysis by linkage mapping, characterization of near-isogenic lines, and meta-analysis. Crop. Sci. 2014, 54, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Gu, X.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, D. Quantitative trait locus mapping of resistance to Aspergillus flavus infection using a recombinant inbred line population in maize. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavis, W. The power and deceit of QTL experiments: Lessons from comparative QTL studies. In Proceedings of the Forty-Ninth Annual Corn and Sorghum Industry Research Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 8–9 December 1994.
- Yan, J.; Warburton, M.; Crouch, J. Association mapping for enhancing maize (Zea mays L.) genetic improvement. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfan, I.D.B.; Gerald, N.; Murray, S.C.; Isakeit, T.; Huang, P.-C.; Warburton, M.; Williams, P.; Windham, G.L.; Kolomiets, M. Genome wide association study for drought, aflatoxin resistance, and important agronomic traits of maize hybrids in the sub-tropics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, M.L.; Tang, J.D.; Windham, G.L.; Hawkins, L.K.; Murray, S.C.; Xu, W.; Boykin, D.; Perkins, A.; Williams, W.P. Genome-Wide Association Mapping of and Aflatoxin Accumulation Resistance in Maize. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.J.; Lipka, A.E.; Buckler, E.S. Lessons from Dwarf8 on the strengths and weaknesses of structured association mapping. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Song, H.; Cheng, H.; Hao, D.; Wang, H.; Kan, G.; Jin, H.; Yu, D. The acid phosphatase-encoding gene GmACP1 contributes to soybean tolerance to low-phosphorus stress. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Gao, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Prasanna, B.M.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Yan, J. Characterization of a global germplasm collection and its potential utilization for analysis of complex quantitative traits in maize. Mol. Breed. 2011, 28, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Jiang, S.-X.; Wang, Y.-J.; Bian, Y.-L.; Chen, J.-J.; Bo, J. Genetic analysis of the resistance to Aspergillus flavus infection in maize (Zea mays L.). Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Gai, J.; Bian, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Identification of maize germplasm resistant to Aspergillus flavus. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2002, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D.; Jiang, S.; Bian, Y. Selection of germplasm resources contributing resistance to Aspergillus flavus of corn. China Seeds 1999, 2, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Brown, R.; Damann, K.; Cleveland, T. Identification of unique or elevated levels of kernel proteins in aflatoxin-resistant maize genotypes through proteome analysis. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, G.A.; Widstrom, N.W. Aflatoxin in maize. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1992, 10, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.; Klich, M. Chotoxins C lin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.Z.; Andorf, C.M.; Schaeffer, M.L.; Harper, L.C.; Sparks, M.E.; Duvick, J.; Brendel, V.P.; Cannon, E.; Campbell, D.A.; Lawrence, C.J. MaizeGDB becomes ‘sequence-centric’. Database 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dat, J.; Vandenabeele, S.; Vranová, E.; van Montagu, M.; Inzé, D.; van Breusegem, F. Dual action of the active oxygen species during plant stress responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, R.; Cao, A.; Butrón, A. Genetic factors involved in fumonisin accumulation in maize kernels and their implications in maize agronomic management and breeding. Toxins 2015, 7, 3267–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Peng, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Chai, Y.; Guo, T.; Yang, N. Genome-wide association study dissects the genetic architecture of oil biosynthesis in maize kernels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windham, G.; Williams, W. Aspergillus flavus infection and aflatoxin accumulation in resistant and susceptible maize hybrids. Plant Dis. 1998, 82, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.E.; Zummo, N. Sources of resistance in maize to kernel infection by Aspergillus flavus in the field. Crop Sci. 1988, 28, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squizzato, S.; Park, Y.M.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Cowley, A.; Li, W.; Uludag, M.; Pundir, S.; Cham, J.A.; McWilliam, H.; et al. The EBI Search engine: Providing search and retrieval functionality for biological data from EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
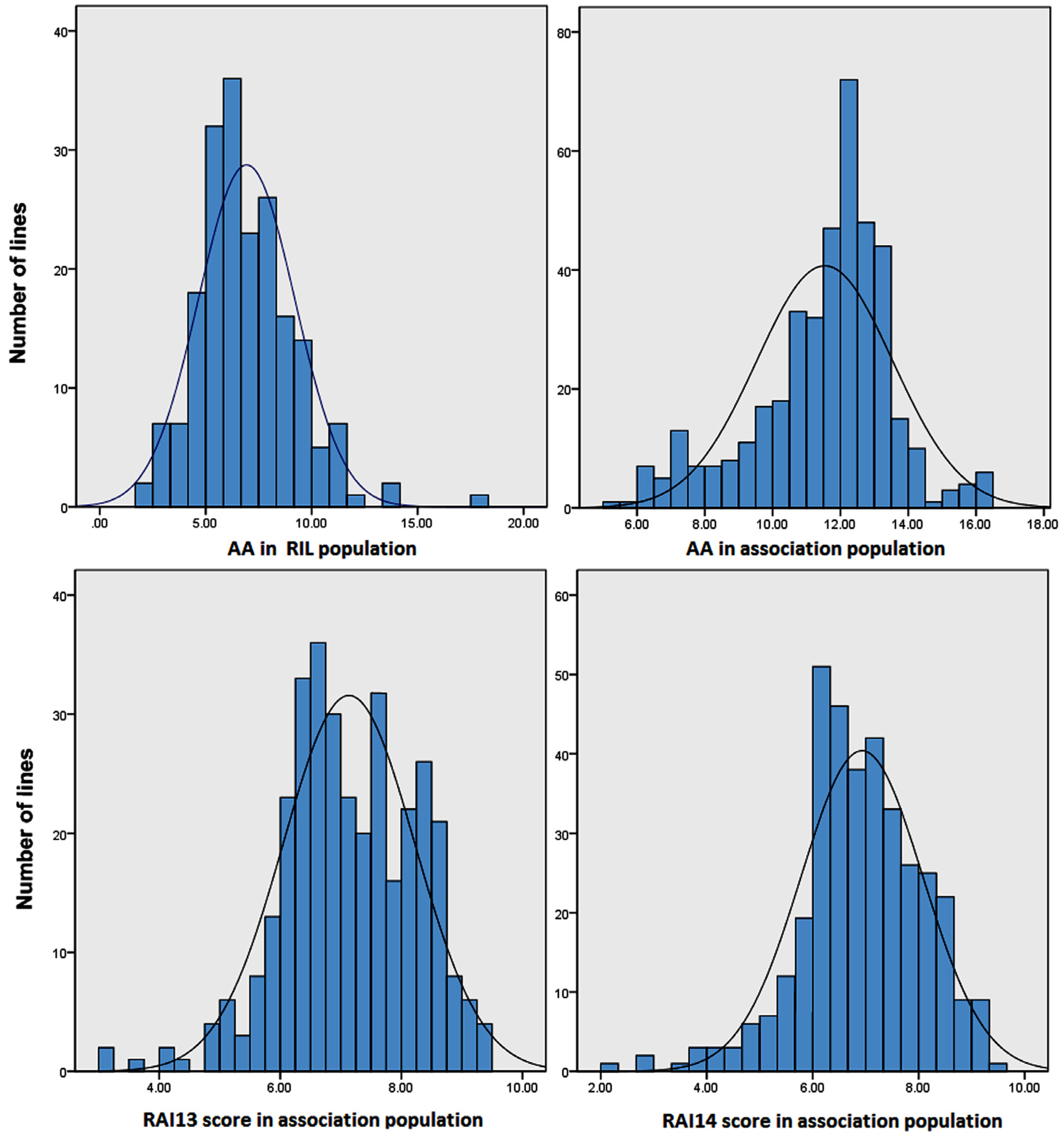
| Plant Material | Traits a | Mean ± SD b | Range c | Skew | Kurt | Replicate d | Genotype e | h2 (%) f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIL male parent M53 | AA | 10.70 ± 1.10 | 9.63–11.84 | |||||
| RIL female parent RA | AA | 9.07 ± 1.02 | 8.21–10.21 | |||||
| RIL population | AA | 6.93 ± 3.54 | 2.46–18.23 | 0.98 | 0.81 | ** | ** | 79.4% |
| Association population | AA | 11.55 ± 2.10 | 4.72–16.20 | −0.68 | 0.52 | ns | ** | 78.2% |
| RAI13 score | 7.20 ± 1.23 | 2.92–9.67 | −0.33 | −0.07 | ** | ** | 83.5% | |
| RAI14 score | 6.99 ± 1.30 | 2.08–9.67 | −0.46 | 0.46 | ** | ** | 85.1% |
| Traits | AA in RIL Population | AA in Association Population | RAI13 Score in Association Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAI score in RIL population | 0.33 ** | ||
| RAI13 score in association population | 0.40 ** | ||
| RAI14 score in association population | 0.34 ** | 0.72 ** |
| QTL | Chr. | Marker Interval | Position | LOD | ADD | PVE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qAA8 | 8 | umc1139–umc1075 | 42.31 | 8.42 | 0.99 | 18.23 |
| Chr. | Left Marker | Right Marker | Chr. | Left Marker | Right Marker | LOD | PVE (%) | Add × Add |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SYN7055 | PZE-101199598 | 3 | PZE-103164358 | PZE-103175779 | 5.02 | 19.38 | 1.55 |
| 1 | SYN7055 | PZE-101199598 | 4 | SYN32516 | PZE-104016174 | 5.21 | 17.04 | 1.88 |
| 1 | SYN7055 | PZE-101199598 | 9 | PZE-109104633 | umc1982 | 5.17 | 17.15 | 1.75 |
| 3 | PZE-103112971 | umc1399 | 9 | umc1982 | umc1657 | 5.05 | 16.63 | 1.83 |
| 8 | umc1777 | PZE-108110136 | 8 | bnlg1065 | SYN30185 | 5.42 | 14.05 | -1.51 |
| 10 | SYN19288 | PZE-110111130 | 10 | PZE-110111130 | PZE-110110920 | 5.01 | 22.6 | -1.75 |
| Traits | Chr. | Marker Position (Mb) | P a | −logP | R2 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | 8 | chr8.S_3662578 | 1.1 × 10−8 | 7.96 | 0.104 |
| AA | 8 | chr8.S_3353245 | 1.3 × 10−8 | 7.88 | 0.067 |
| AA | 2 | chr2.S_9361865 | 2.1 × 10−7 | 6.68 | 0.079 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662578 | 7.4 × 10−20 | 19.13 | 0.266 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662694 | 2.7 × 10−11 | 10.57 | 0.148 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662804 | 2.7 × 10−11 | 10.57 | 0.148 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662702 | 4.3 × 10−11 | 10.37 | 0.154 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | SYNGENTA16977 | 8.5 × 10−11 | 10.07 | 0.145 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662186 | 4.9 × 10−7 | 6.31 | 0.091 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662564 | 8.3 × 10−7 | 6.08 | 0.089 |
| RAI13 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662567 | 8.3 × 10−7 | 6.08 | 0.089 |
| RAI13 score | 9 | chr9.S_136479765 | 1.6 × 10-6 | 5.78 | 0.074 |
| RAI13 score | 9 | chr9.S_136479840 | 1.6 × 10−6 | 5.78 | 0.074 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662578 | 3.7 × 10−22 | 21.43 | 0.268 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662694 | 5.9 × 10−12 | 11.23 | 0.144 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662804 | 5.9 × 10−12 | 11.23 | 0.144 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662702 | 2.0 × 10−11 | 10.70 | 0.144 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | SYNGENTA16977 | 1.2 × 10−10 | 9.91 | 0.130 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662564 | 7.4 × 10−8 | 7.13 | 0.096 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662567 | 7.4 × 10−8 | 7.13 | 0.096 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662186 | 2.4 × 10−7 | 6.61 | 0.087 |
| RAI14 score | 8 | chr8.S_3662642 | 4.4 × 10−7 | 6.36 | 0.082 |
| RAI14 score | 5 | chr5.S_159454183 | 7.2×10−6 | 5.92 | 0.065 |
| RAI14 score | 5 | chr5.S_159758011 | 7.4 × 10−6 | 5.86 | 0.065 |
| RAI14 score | 5 | chr5.S_159454148 | 8.7 × 10−6 | 5.78 | 0.064 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Kan, X.; Sun, Q.; Deng, D.; Yin, Z. Confirmation and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL for Aflatoxin Resistance in Maize Using a Combination of Linkage and Association Mapping. Toxins 2016, 8, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090258
Zhang Y, Cui M, Zhang J, Zhang L, Li C, Kan X, Sun Q, Deng D, Yin Z. Confirmation and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL for Aflatoxin Resistance in Maize Using a Combination of Linkage and Association Mapping. Toxins. 2016; 8(9):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090258
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Min Cui, Jimin Zhang, Lei Zhang, Chenliu Li, Xin Kan, Qian Sun, Dexiang Deng, and Zhitong Yin. 2016. "Confirmation and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL for Aflatoxin Resistance in Maize Using a Combination of Linkage and Association Mapping" Toxins 8, no. 9: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090258
APA StyleZhang, Y., Cui, M., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Li, C., Kan, X., Sun, Q., Deng, D., & Yin, Z. (2016). Confirmation and Fine Mapping of a Major QTL for Aflatoxin Resistance in Maize Using a Combination of Linkage and Association Mapping. Toxins, 8(9), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090258






