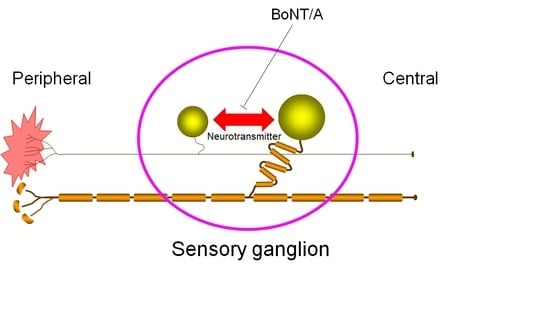
Cross-Excitation in Peripheral Sensory Ganglia Associated with Pain Transmission
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hindpaw Withdrawal Thresholds after Sciatic Nerve Entrapment (SNE) Surgery and BoNT/A Application
2.2. Motor Function after BoNT/A Application
2.3. Localization of Directly Administered BoNT/A-HC in the L4 DRG
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. BoNT/A and Fluorescent Labeling of Recombinant BoNT/A-HC
4.2. Cannula Implantation in L4 DRG
4.3. Sciatic Nerve Entrapment
4.4. Behavioral Testing
4.5. Histology Sample Preparation
4.6. Histological Assessment
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, C.; Shu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yao, H.; Greenquist, K.W.; White, F.A.; LaMotte, R.H. Similar electrophysiological changes in axotomized and neighboring intact dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 89, 1588–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, M.M.; Lieberman, A.R. Microtubule fascicles in the stem processes of cultured sensory ganglion cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1976, 169, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunge, R.; Glaser, L.; Lieberman, M.; Raben, D.; Salzer, J.; Whittenberger, B.; Woolsey, T. Growth control by cell to cell contact. J. Supramol. Struct. 1979, 11, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, R.; Devor, M. Functional cross-excitation between afferent A- and C-neurons in dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience 1999, 95, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devor, M.; Wall, P.D. Cross-excitation in dorsal root ganglia of nerve-injured and intact rats. J. Neurophysiol. 1990, 64, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amir, R.; Devor, M. Chemically Mediated Cross-Excitation in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 4733–4741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.Y.M.; Neher, E. Ca2+-Dependent Exocytosis in the Somata of Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons. Neuron 1996, 17, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, J.K.; Maidment, N.T.; Matsuka, Y.; Adelson, D.W.; Kruger, L.; Spigelman, I. Inflammation-induced changes in primary afferent-evoked release of substance P within trigeminal ganglia in vivo. Brain Res. 2000, 871, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuka, Y.; Neubert, J.K.; Maidment, N.T.; Spigelman, I. Concurrent release of ATP and substance P within guinea pig trigeminal ganglia in vivo. Brain Res. 2001, 915, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Flores, C.M.; Harding-Rose, C.A.; Goodis, H.E.; Hargreaves, K.M. Capsaicin-evoked release of immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide from rat trigeminal ganglion: Evidence for intraganglionic neurotransmission. Pain 2001, 91, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuka, Y.; Edmonds, B.; Mitrirattanakul, S.; Schweizer, F.E.; Spigelman, I. Two types of neurotransmitter release patterns in isolectin B4-positive and negative trigeminal ganglion neurons. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigelman, I.; Puil, E. Ionic mechanism of substance P actions on neurons in trigeminal root ganglia. J. Neurophysiol. 1990, 64, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishtal, O.A.; Marchenko, S.M.; Pidoplichko, V.I. Receptor for ATP in the membrane of mammalian sensory neurones. Neurosci. Lett. 1983, 35, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuka, Y.; Ono, T.; Iwase, H.; Mitrirattanakul, S.; Omoto, K.S.; Cho, T.; Lam, Y.Y.N.; Snyder, B.; Spigelman, I. Altered ATP release and metabolism in dorsal root ganglia of neuropathic rats. Mol. Pain 2008, 4, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, H.; Blasi, J.; Jahn, R. Clostridial neurotoxins: new tools for dissecting exocytosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1994, 4, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Matteoli, M.; Montecucco, C. Neurotoxins affecting neuroexocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 717–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.J.; Purkiss, J.R.; Foster, K.A. Sensitivity of embryonic rat dorsal root ganglia neurons to Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2000, 38, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, P.L.; Cady, R.; Cady, R. Regulation of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Secretion From Trigeminal Nerve Cells by Botulinum Toxin Type A: Implications for Migraine Therapy. Headache 2004, 44, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderre, T.J.; Kumar, N.; Lefebvre, C.D.; Yu, J.S.C. Evidence that gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Wang, J.; Lawrence, G.; Dolly, J.O. Synaptobrevin I mediates exocytosis of CGRP from sensory neurons and inhibition by botulinum toxins reflects their anti-nociceptive potential. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Mitsui, Y.; Yoshitomi, T.; Mashimo, K.; Aoki, S.; Mukuno, K.; Shimizu, K. Presynaptic effects of botulinum toxin type A on the neuronally evoked response of albino and pigmented rabbit iris sphincter and dilator muscles. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 44, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Khanijou, S.; Rubino, J.; Aoki, K.R. Subcutaneous administration of botulinum toxin A reduces formalin-induced pain. Pain 2004, 107, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosconi, T.; Kruger, L. Fixed-diameter polyethylene cuffs applied to the rat sciatic nerve induce a painful neuropathy: Ultrastructural morphometric analysis of axonal alterations. Pain 1996, 64, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Bautista, D.M.; Scherrer, G.; Julius, D. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 2009, 139, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. Can we conquer pain? Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5 Suppl, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skilling, S.R.; Harkness, D.H.; Larson, A.A. Experimental peripheral neuropathy decreases the dose of substance P required to increase excitatory amino acid release in the CSF of the rat spinal cord. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 139, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardell, L.R.; Vanderah, T.W.; Gardell, S.E.; Wang, R.; Ossipov, M.H.; Lai, J.; Porreca, F. Enhanced evoked excitatory transmitter release in experimental neuropathy requires descending facilitation. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 8370–8379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mark, M.A.; Colvin, L.A.; Duggan, A.W. Spontaneous release of immunoreactive neuropeptide Y from the central terminals of large diameter primary afferents of rats with peripheral nerve injury. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Quirion, R. Increased calcitonin gene-related peptide in neuroma and invading macrophages is involved in the up-regulation of interleukin-6 and thermal hyperalgesia in a rat model of mononeuropathy. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.P.; Khan, I.; Suhail, M.S.; Malkmus, S.; Yaksh, T.L. Spinal botulinum neurotoxin B: effects on afferent transmitter release and nociceptive processing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, A.; Oliveira, R.; Rossetto, O.; Cruz, C.D.; Cruz, F.; Avelino, A. Intrathecal administration of botulinum toxin type A improves urinary bladder function and reduces pain in rats with cystitis. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S.; Vacca, V.; Ricordy, R.; Uggenti, C.; Tata, A.M.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F. The analgesic effect on neuropathic pain of retrogradely transported botulinum neurotoxin A involves Schwann cells and astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47977. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, K.R. Evidence for antinociceptive activity of botulinum toxin type A in pain management. Headache 2003, 43, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y.; Matsuka, Y.; Spigelman, I.; Ishihara, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sonoyama, W.; Kuboki, T.; Oguma, K. Botulinum toxin type a (150 kDa) decreases exaggerated neurotransmitter release from trigeminal ganglion neurons and relieves neuropathy behaviors induced by infraorbital nerve constriction. Neuroscience 2009, 159, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Long-Distance Retrograde Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Tanimoto, T.; Nasu, M.; Ikeda, M.; Kadoi, J.; Matsumoto, S. Activation of NK1 receptor of trigeminal root ganglion via substance P paracrine mechanism contributes to the mechanical allodynia in the temporomandibular joint inflammation in rats. Pain 2005, 116, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Yokoyama, T.; Hwang, H.J.; Arimitsu, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawasaki, M.; Takigawa, T.; Takeshi, K.; Nishikawa, A.; Kumon, H.; Oguma, K. Clinical application of Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin purified by a simple procedure for patients with urinary incontinence caused by refractory destrusor overactivity. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalli, G.; Gschmeissner, S.; Schiavo, G. Myosin Va and microtubule-based motors are required for fast axonal retrograde transport of tetanus toxin in motor neurons. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 4639–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-M.; Li, H.; Brull, S.J. Perfusion of the Mechanically Compressed Lumbar Ganglion With Lidocaine Reduces Mechanical Hyperalgesia and Allodynia in the Rat. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 84, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omoto, K.; Maruhama, K.; Terayama, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; Matsushita, O.; Sugimoto, T.; Oguma, K.; Matsuka, Y. Cross-Excitation in Peripheral Sensory Ganglia Associated with Pain Transmission. Toxins 2015, 7, 2906-2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082906
Omoto K, Maruhama K, Terayama R, Yamamoto Y, Matsushita O, Sugimoto T, Oguma K, Matsuka Y. Cross-Excitation in Peripheral Sensory Ganglia Associated with Pain Transmission. Toxins. 2015; 7(8):2906-2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082906
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmoto, Katsuhiro, Kotaro Maruhama, Ryuji Terayama, Yumiko Yamamoto, Osamu Matsushita, Tomosada Sugimoto, Keiji Oguma, and Yoshizo Matsuka. 2015. "Cross-Excitation in Peripheral Sensory Ganglia Associated with Pain Transmission" Toxins 7, no. 8: 2906-2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082906
APA StyleOmoto, K., Maruhama, K., Terayama, R., Yamamoto, Y., Matsushita, O., Sugimoto, T., Oguma, K., & Matsuka, Y. (2015). Cross-Excitation in Peripheral Sensory Ganglia Associated with Pain Transmission. Toxins, 7(8), 2906-2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082906