Treatment of Chronic Migraine with OnabotulinumtoxinA: Mode of Action, Efficacy and Safety
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
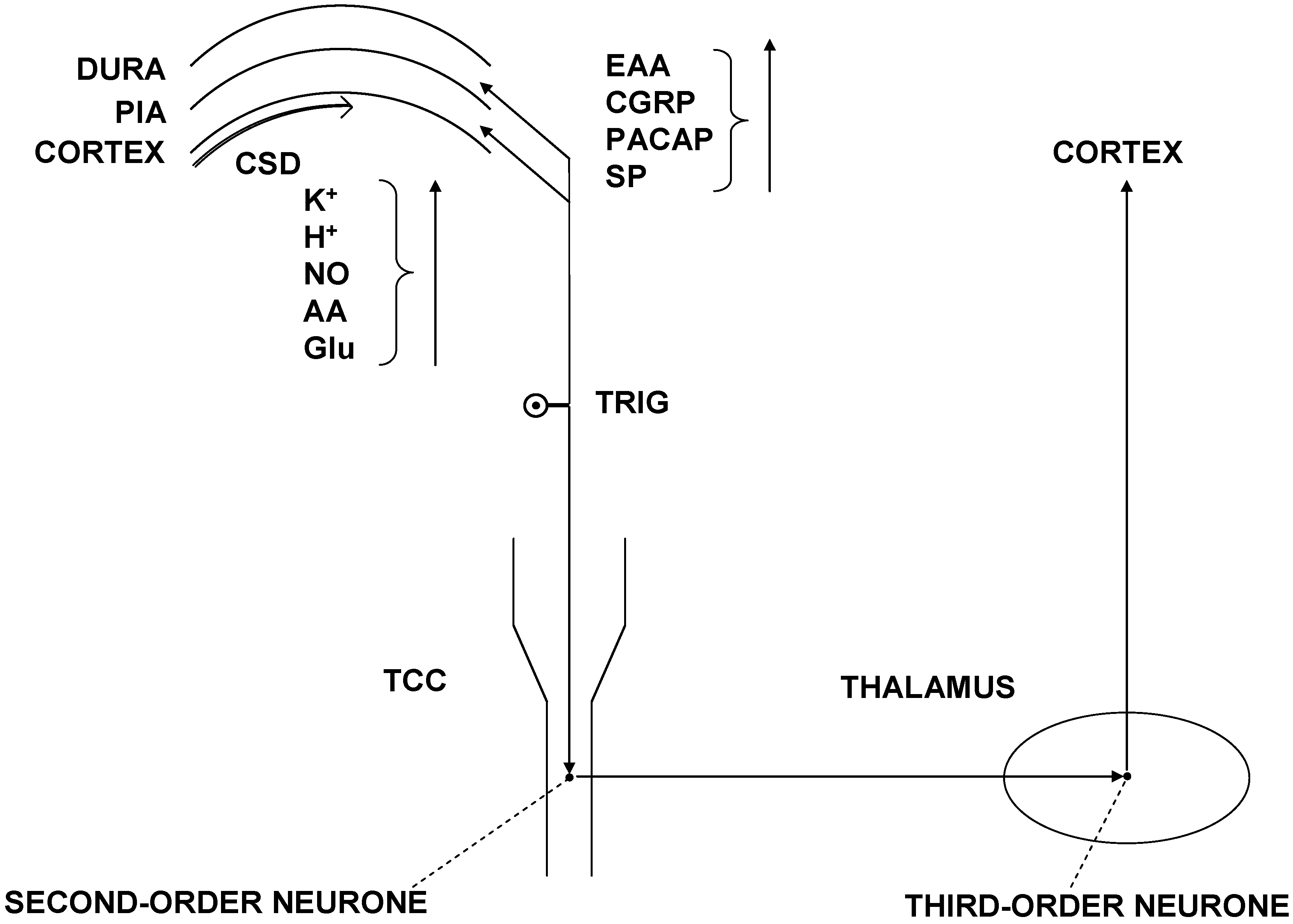
3.1. Pathomechanism of CM
3.2. Supposed Mode of Action of OBOT-A in Chronic Migraine Therapy
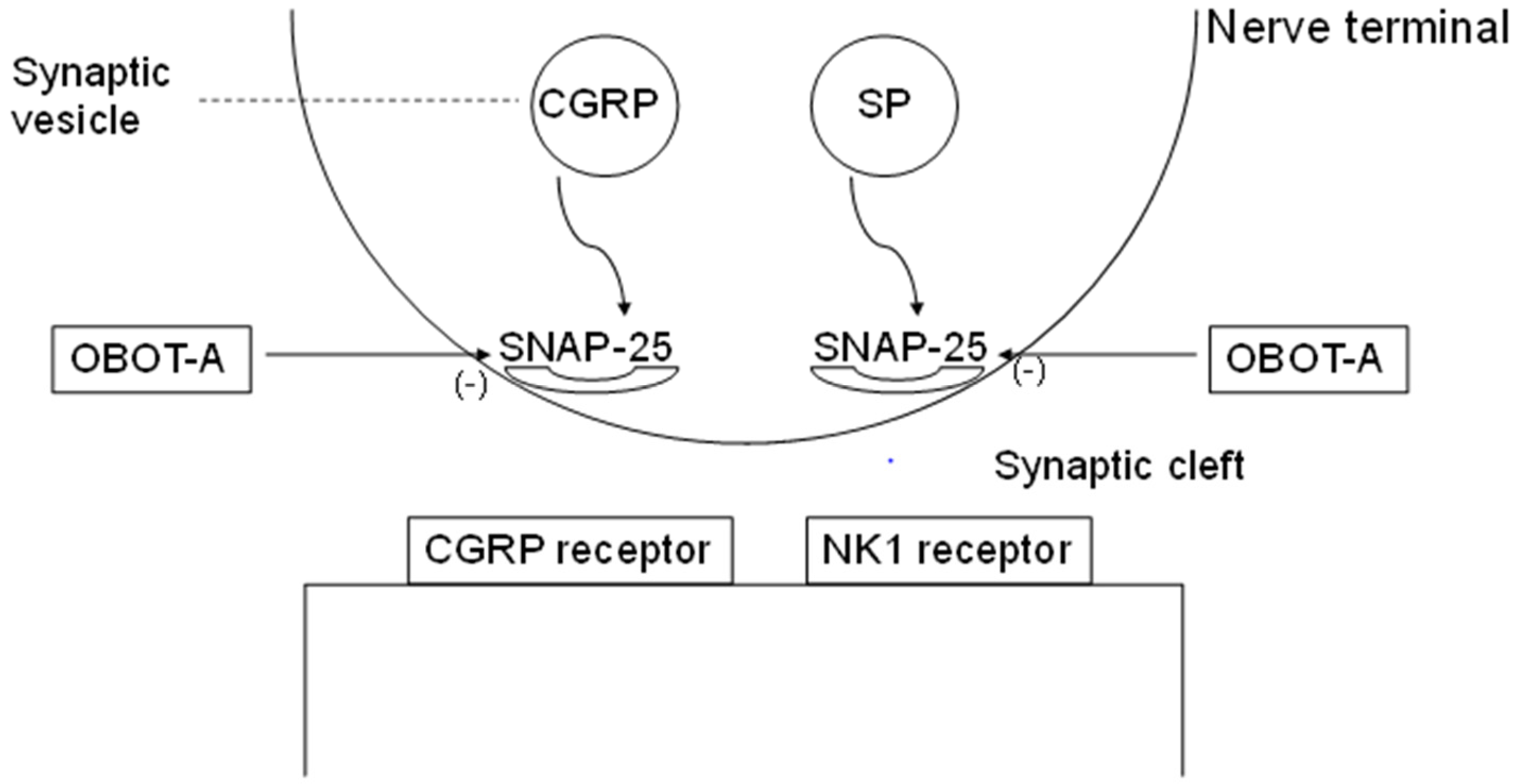
3.3. Therapeutic Indications of OBOT-A in Primary Headaches
3.4. Technique of Injection of OBOT-A in CM
3.5. Efficacy of OBOT-A in Treatment of CM
3.6. Tolerability and Safety of OBOT-A in Treatment of CM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of interest
References
- Lipton, R.B.; Stewart, W.F.; Diamond, S.; Diamond, M.L.; Reed, M. Prevalence and burden of migraine in the United States: Data from the American Migraine Study II. Headache 2001, 41, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smitherman, T.A.; Burch, R.; Sheikh, H.; Loder, E. The prevalence, impact, and treatment of migraine and severe headaches in the United States: A review of statistics from national surveillance studies. Headache 2013, 53, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, T.W.; Hu, X.; Campbell, J.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine prevalence by age and sex in the United States: A life-span study. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.J.; Stovner, L.J.; Katsarava, Z.; Lainez, J.M.; Lampl, C.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Rastenyte, D.; Ruiz de la Torre, E.; Tassorelli, C.; Barre, J.; et al. The impact of headache in Europe: Principal results of the Eurolight project. J. Headache Pain 2014, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar]
- Lanteri-Minet, M. Economic burden and costs of chronic migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2014, 18, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecsei, L.; Majlath, Z.; Szok, D.; Csati, A.; Tajti, J. Drug safety and tolerability in prophylactic migraine treatment. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2015, 14, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcup, S.M.; Turkel, C.C.; DeGryse, R.E.; Brin, M.F. Development of onabotulinumtoxinA for chronic migraine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1329, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, D.C.; Manack, A.; Serrano, D.; Turkel, C.; Lipton, R.B. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 2010, 81, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurora, S.K.; Dodick, D.W.; Diener, H.C.; DeGryse, R.E.; Turkel, C.C.; Lipton, R.B.; Silberstein, S.D. OnabotulinumtoxinA for chronic migraine: Efficacy, safety, and tolerability in patients who received all five treatment cycles in the PREEMPT clinical program. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, D.C.; Loder, E.W.; Gorman, J.A.; Stewart, W.F.; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B. Sex differences in the prevalence, symptoms, and associated features of migraine, probable migraine and other severe headache: Results of the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study. Headache 2013, 53, 1278–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natoli, J.L.; Manack, A.; Dean, B.; Butler, Q.; Turkel, C.C.; Stovner, L.; Lipton, R.B. Global prevalence of chronic migraine: A systematic review. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, N.T. Pathophysiology of chronic migraine and mode of action of preventive medications. Headache 2011, 51, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couch, J.R. Amitriptyline in the prophylactic treatment of migraine and chronic daily headache. Headache 2011, 51, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, H.C.; Bussone, G.; van Oene, J.C.; Lahaye, M.; Schwalen, S.; Goadsby, P.J.; TOPMAT-MIG-201(TOP-CHROME). Study Group. Topiramate reduces headache days in chronic migraine: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurekli, V.A.; Akhan, G.; Kutluhan, S.; Uzar, E.; Koyuncuoglu, H.R.; Gultekin, F. The effect of sodium valproate on chronic daily headache and its subgroups. J. Headache Pain 2008, 9, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, G.P.; Grosberg, B.M.; McAllister, P.J.; Lipton, R.B.; Buse, D.C. Prophylactic onabotulinumtoxinA in patients with chronic migraine and comorbid depression: An open-label, multicenter, pilot study of efficacy, safety and effect on headache-related disability, depression, and anxiety. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2015, 9, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Blumenfeld, A. OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of headache. Headache 2013, 53, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodick, D.W.; Turkel, C.C.; DeGryse, R.E.; Aurora, S.K.; Silberstein, S.D.; Lipton, R.B.; Diener, H.C.; Brin, M.F.; PREEMPT Chronic Migraine Study Group. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phases of the PREEMPT clinical program. Headache 2010, 50, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, J.; Szok, D.; Tuka, B.; Csati, A.; Kuris, A.; Majlath, Z.; Lukacs, M.; Vecsei, L. Botulinum neurotoxin—A therapy in migraine. Ideggyogy. Szle. 2012, 65, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi, M.G.; Moskowitz, M.A. The trigemino-vascular system and migraine. Pathol. Biol. 1992, 40, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tajti, J.; Pardutz, A.; Vamos, E.; Tuka, B.; Kuris, A.; Bohar, Z.; Fejes, A.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. Migraine is a neuronal disease. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, J.; Szok, D.; Pardutz, A.; Tuka, B.; Csati, A.; Kuris, A.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. Where does a migraine attack originate? In the brainstem. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvinsson, L.; Villalon, C.M.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Basic mechanisms of migraine and its acute treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvinsson, L. CGRP receptor antagonists and antibodies against CGRP and its receptor in migraine treatment. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrobon, D.; Moskowitz, M.A. Pathophysiology of migraine. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 365–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuka, B.; Helyes, Z.; Markovics, A.; Bagoly, T.; Nemeth, J.; Mark, L.; Brubel, R.; Reglodi, D.; Pardutz, A.; Szolcsanyi, J.; et al. Peripheral and central alterations of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the rat in response to activation of the trigeminovascular system. Peptides 2012, 33, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuka, B.; Helyes, Z.; Markovics, A.; Bagoly, T.; Szolcsanyi, J.; Szabo, N.; Toth, E.; Kincses, Z.T.; Vecsei, L.; Tajti, J. Alterations in PACAP-38-like immunoreactivity in the plasma during ictal and interictal periods of migraine patients. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecsei, L.; Tuka, B.; Tajti, J. Role of PACAP in migraine headaches. Brain 2014, 137, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goadsby, P.J. Migraine, allodynia, sensitisation and all of that. Eur. Neurol 2005, 53, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J.; Burstein, R.; Ashina, M.; Tfelt-Hansen, P. Origin of pain in migraine: Evidence for peripheral sensitisation. Lancet Neurol 2009, 8, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, T.; Goadsby, P.J. Stimulation of the greater occipital nerve induces increased central excitability of dural afferent input. Brain 2002, 125, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, T.; Goadsby, P.J. Increased responses in trigeminocervical nociceptive neurons to cervical input after stimulation of the dura mater. Brain 2003, 126, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, R.; Yarnitsky, D.; Goor-Aryeh, I.; Ransil, B.J.; Bajwa, Z.H. An association between migraine and cutaneous allodynia. Ann. Neurol 2000, 47, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.; Silberstein, S. Central sensitization theory of migraine: Clinical implications. Headache 2006, 46, S182–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, N.T.; Kailasam, J.; Seifert, T. Clinical recognition of allodynia in migraine. Neurology 2004, 63, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigal, M.E.; Ashina, S.; Burstein, R.; Reed, M.L.; Buse, D.; Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B.; AMPP Group. Prevalence and characteristics of allodynia in headache sufferers: A population study. Neurology 2008, 70, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louter, M.A.; Bosker, J.E.; van Oosterhout, W.P.; van Zwet, E.W.; Zitman, F.G.; Ferrari, M.D.; Terwindt, G.M. Cutaneous allodynia as a predictor of migraine chronification. Brain 2013, 136, 3489–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarava, Z.; Schneeweiss, S.; Kurth, T.; Kroener, U.; Fritsche, G.; Eikermann, A.; Diener, H.C.; Limmroth, V. Incidence and predictors for chronicity of headache in patients with episodic migraine. Neurology 2004, 62, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carod-Artal, F.J. Tackling chronic migraine: Current perspectives. J. Pain Res. 2014, 7, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashina, S.; Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B.; Maizels, M.; Manack, A.N.; Turkel, C.C.; Reed, M.L.; Buse, D.C. Depression and risk of transformation of episodic to chronic migraine. J. Headache Pain 2012, 13, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, D.C.; Silberstein, S.D.; Manack, A.N.; Papapetropoulos, S.; Lipton, R.B. Psychiatric comorbidities of episodic and chronic migraine. J. Neurol 2013, 260, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiller, C.; May, A.; Limmroth, V.; Juptner, M.; Kaube, H.; Schayck, R.V.; Coenen, H.H.; Diener, H.C. Brain stem activation in spontaneous human migraine attacks. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, K.M.; Nagesh, V.; Aurora, S.K.; Gelman, N. Periaqueductal gray matter dysfunction in migraine: Cause or the burden of illness? Headache 2001, 41, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, K.; Chaddock, J.A.; Acharya, K.R. Botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins: Structure, function and therapeutic utility. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.E. OnabotulinumtoxinA (BOTOX(R)): A review of its use in the prophylaxis of headaches in adults with chronic migraine. Drugs 2012, 72, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Kang, W.H.; Saga, K.; Sato, K.T. Biology of sweat glands and their disorders. I Normal sweat gland function. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1989, 20, 537–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartling, C.; Naver, H.; Pihl-Lundin, I.; Hagforsen, E.; Vahlquist, A. Sweat gland morphology and periglandular innervation in essential palmar hyperhidrosis before and after treatment with intradermal botulinum toxin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazawa, K.; Sobue, G.; Mitsuma, T.; Ogawa, T. Modulatory effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P on human cholinergic sweat secretion. Clin. Auton. Res. 1994, 4, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazawa, K.; Sobue, G.; Mitsuma, T.; Sugenoya, J.; Ogawa, T. Impairment of calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced potentiation of cholinergic sweat secretion in patients with multiple system atrophy. Clin. Auton. Res. 1997, 7, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naver, H.; Swartling, C.; Aquilonius, S.M. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin: One-year clinical follow-up. Eur. J. Neurol 2000, 7, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danigo, A.; Magy, L.; Richard, L.; Sturtz, F.; Funalot, B.; Demiot, C. A reversible functional sensory neuropathy model. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 571, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, J.; Uddman, R.; Moller, S.; Sundler, F.; Edvinsson, L. Messenger molecules and receptor mRNA in the human trigeminal ganglion. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1999, 76, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, S.; Salvatore, C.A.; Calamari, A.; Kane, S.A.; Tajti, J.; Edvinsson, L. Differential distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide and its receptor components in the human trigeminal ganglion. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.L.; Zheng, C.X.; Sui, B.D.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.L. A closer look to botulinum neurotoxin type A-induced analgesia. Toxicon 2013, 71, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, P.L.; Cady, R. Regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide secretion from trigeminal nerve cells by botulinum toxin type A: Implications for migraine therapy. Headache 2004, 44, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, P.L.; Masterson, C.G. Two mechanisms involved in trigeminal CGRP release: Implications for migraine treatment. Headache 2013, 53, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.J.; Purkiss, J.R.; Foster, K.A. Sensitivity of embryonic rat dorsal root ganglia neurons to Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2000, 38, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, R.; Zhang, X.; Levy, D.; Aoki, K.R.; Brin, M.F. Selective inhibition of meningeal nociceptors by botulinum neurotoxin type A: Therapeutic implications for migraine and other pains. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.W.; Edvinsson, L.; Goadsby, P.J. CGRP and its receptors provide new insights into migraine pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2010, 6, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsan, N.; Goadsby, P.J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and migraine. Curr. Opin. Neurol 2015, 28, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalakoti, S.; Patil, V.V.; Damodaram, S.; Vause, C.V.; Langford, L.E.; Freeman, S.E.; Durham, P.L. Neuron-glia signaling in trigeminal ganglion: Implications for migraine pathology. Headache 2007, 47, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollbracht, S.; Rapoport, A.M. The pipeline in headache therapy. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigal, M.E.; Walter, S.; Rapoport, A.M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and migraine current understanding and state of development. Headache 2013, 53, 1230–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecsei, L.; Szok, D.; Csati, A.; Tajti, J. CGRP antagonists and antibodies for the treatment of migraine. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2015, 24, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, J.; Kuris, A.; Vecsei, L.; Xu, C.B.; Edvinsson, L. Organ culture of the trigeminal ganglion induces enhanced expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide via activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.L.; Yu, L.C. The colocalization of CGRP receptor and AMPA receptor in the spinal dorsal horn neuron of rat: A morphological and electrophysiological study. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 414, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Lundeberg, T.; Yu, L.C. Role of calcitonin gene-related peptide and its antagonist on the evoked discharge frequency of wide dynamic range neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord in rats. Regul. Pept. 2002, 103, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernuda-Morollon, E.; Ramon, C.; Martinez-Camblor, P.; Serrano-Pertierra, E.; Larrosa, D.; Pascual, J. OnabotulinumtoxinA decreases interictal CGRP plasma levels in patients with chronic migraine. Pain 2015, 156, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Silberstein, S.D. Episodic and chronic migraine headache: Breaking down barriers to optimal treatment and prevention. Headache 2015, 55, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenfeld, A.; Silberstein, S.D.; Dodick, D.W.; Aurora, S.K.; Turkel, C.C.; Binder, W.J. Method of injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for chronic migraine: A safe, well-tolerated, and effective treatment paradigm based on the PREEMPT clinical program. Headache 2010, 50, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Blumenfeld, A.M.; Cady, R.K.; Turner, I.M.; Lipton, R.B.; Diener, H.C.; Aurora, S.K.; Sirimanne, M.; DeGryse, R.E.; Turkel, C.C.; et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: PREEMPT 24-week pooled subgroup analysis of patients who had acute headache medication overuse at baseline. J. Neurol Sci. 2013, 331, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, S.; Afra, J.; Frese, A.; Goadsby, P.J.; Linde, M.; May, A.; Sandor, P.S.; European Federation of Neurological Societies. EFNS guideline on the drug treatment of migraine—Revised report of an EFNS task force. Eur. J. Neurol 2009, 16, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, N.T.; Jaffri, S.F. A double-blind comparison of onabotulinumtoxina (BOTOX) and topiramate (TOPAMAX) for the prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine: A pilot study. Headache 2009, 49, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Dodick, D.W.; Lindblad, A.S.; Holroyd, K.; Harrington, M.; Mathew, N.T.; Hirtz, D. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of propranolol added to topiramate in chronic migraine. Neurology 2012, 78, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, R.K.; Schreiber, C.P.; Porter, J.A.; Blumenfeld, A.M.; Farmer, K.U. A multi-center double-blind pilot comparison of onabotulinumtoxinA and topiramate for the prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine. Headache 2011, 51, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernuda-Morollon, E.; Ramon, C.; Larrosa, D.; Alvarez, R.; Riesco, N.; Pascual, J. Long-term experience with onabotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of chronic migraine: What happens after one year? Cephalalgia 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grazzi, L. Onabotulinum toxin A for treatment of chronic migraine with medication overuse. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, S27–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grazzi, L.; Usai, S. Botulinum toxin A: A new option for treatment of chronic migraine with medication overuse. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Zafar, H.W.; Quarshie, V.; Ahmed, F. Prospective analysis of the use of OnabotulinumtoxinA (BOTOX) in the treatment of chronic migraine; real-life data in 254 patients from Hull, U.K. J. Headache Pain 2014, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, H.C.; Dodick, D.W.; Turkel, C.C.; Demos, G.; Degryse, R.E.; Earl, N.L.; Brin, M.F. Pooled analysis of the safety and tolerability of onabotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of chronic migraine. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innamorati, M.; Pompili, M.; Fiorillo, M.; Lala, N.; Negro, A.; Del Bono, S.D.; Lester, D.; Girardi, P.; Martelletti, P. Overattachment and perceived disability in chronic migraineurs. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, G.; Pompili, M.; Innamorati, M.; Gentile, G.; Borro, M.; Lamis, D.A.; Lala, N.; Negro, A.; Simmaco, M.; Girardi, P.; et al. Gene variants with suicidal risk in a sample of subjects with chronic migraine and affective temperamental dysregulation. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manzoni, G.C.; Camarda, C.; Torelli, P. Chronification of migraine: What clinical strategies to combat it? Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, S57–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berra, E.; Sances, G.; de Icco, R.; Avenali, M.; Berlangieri, M.; de Paoli, I.; Bolla, M.; Allena, M.; Ghiotto, N.; Guaschino, E.; et al. Cost of Chronic and Episodic Migraine. A pilot study from a tertiary headache centre in northern Italy. J. Headache Pain 2015, 16, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloudek, L.M.; Stokes, M.; Buse, D.C.; Wilcox, T.K.; Lipton, R.B.; Goadsby, P.J.; Varon, S.F.; Blumenfeld, A.M.; Katsarava, Z.; Pascual, J.; et al. Cost of healthcare for patients with migraine in five European countries: Results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS). J. Headache Pain 2012, 13, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batty, A.J.; Hansen, R.N.; Bloudek, L.M.; Varon, S.F.; Hayward, E.J.; Pennington, B.W.; Lipton, R.B.; Sullivan, S.D. The cost-effectiveness of onabotulinumtoxinA for the prophylaxis of headache in adults with chronic migraine in the UK. J. Med. Econ. 2013, 16, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodick, D.W.; Turkel, C.C.; de Gryse, R.E.; Diener, H.C.; Lipton, R.B.; Aurora, S.K.; Nolan, M.E.; Silberstein, S.D. Assessing clinically meaningful treatment effects in controlled trials: Chronic migraine as an example. J. Pain 2015, 16, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szok, D.; Csáti, A.; Vécsei, L.; Tajti, J. Treatment of Chronic Migraine with OnabotulinumtoxinA: Mode of Action, Efficacy and Safety. Toxins 2015, 7, 2659-2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072659
Szok D, Csáti A, Vécsei L, Tajti J. Treatment of Chronic Migraine with OnabotulinumtoxinA: Mode of Action, Efficacy and Safety. Toxins. 2015; 7(7):2659-2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072659
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzok, Délia, Anett Csáti, László Vécsei, and János Tajti. 2015. "Treatment of Chronic Migraine with OnabotulinumtoxinA: Mode of Action, Efficacy and Safety" Toxins 7, no. 7: 2659-2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072659
APA StyleSzok, D., Csáti, A., Vécsei, L., & Tajti, J. (2015). Treatment of Chronic Migraine with OnabotulinumtoxinA: Mode of Action, Efficacy and Safety. Toxins, 7(7), 2659-2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072659





