The Pore-Forming α-Toxin from Clostridium septicum Activates the MAPK Pathway in a Ras-c-Raf-Dependent and Independent Manner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. α-Toxin Results in the Activation of the Three Canonical Arms of the MAPK Pathway
2.2. Activation of the MAPK Pathway is Dependent on Efficient Receptor Binding, Pore Formation and Extracellular Calcium Influx
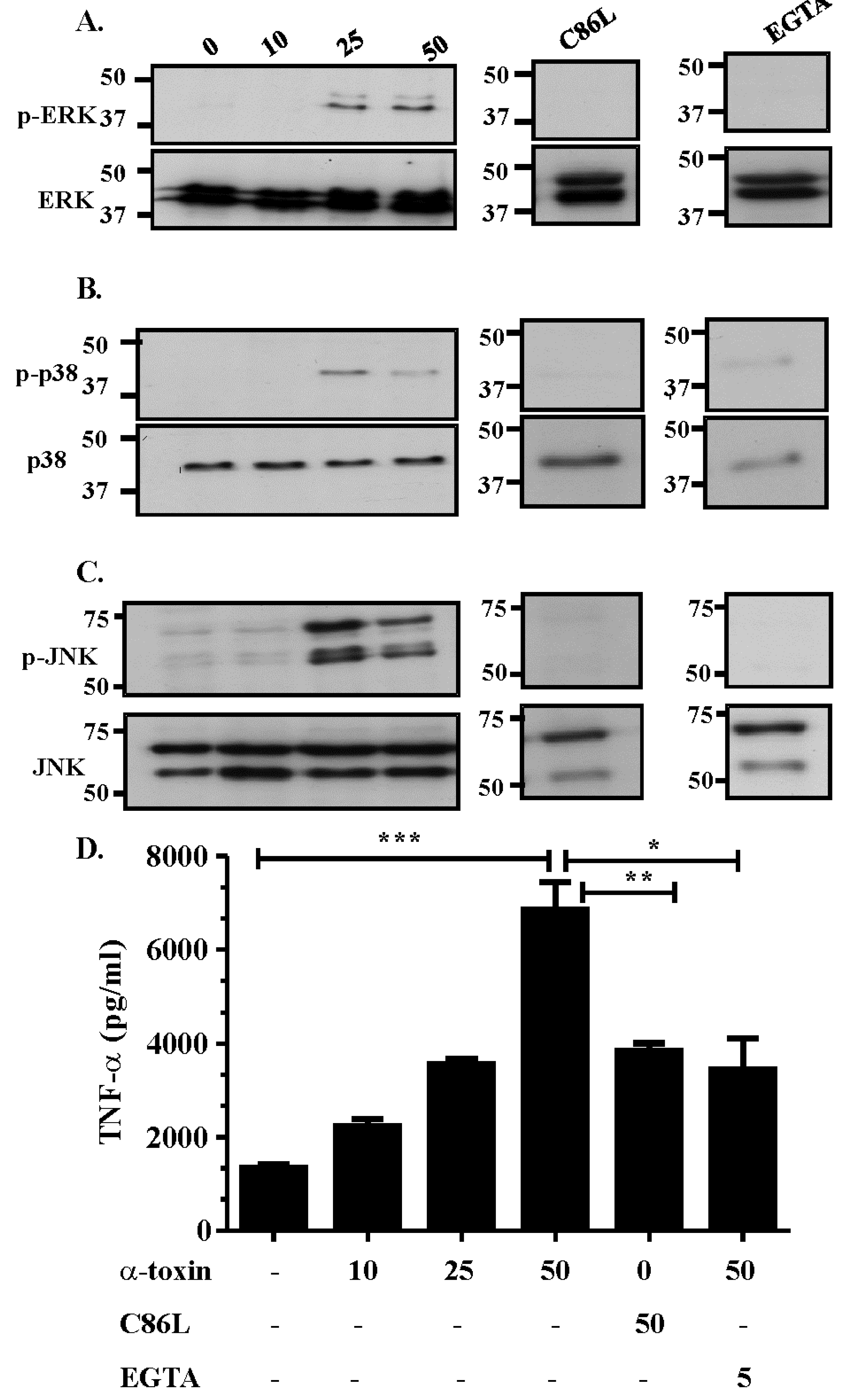
2.3. The Role of Extracellular Ca2+ in Activation of the MAPK Pathway
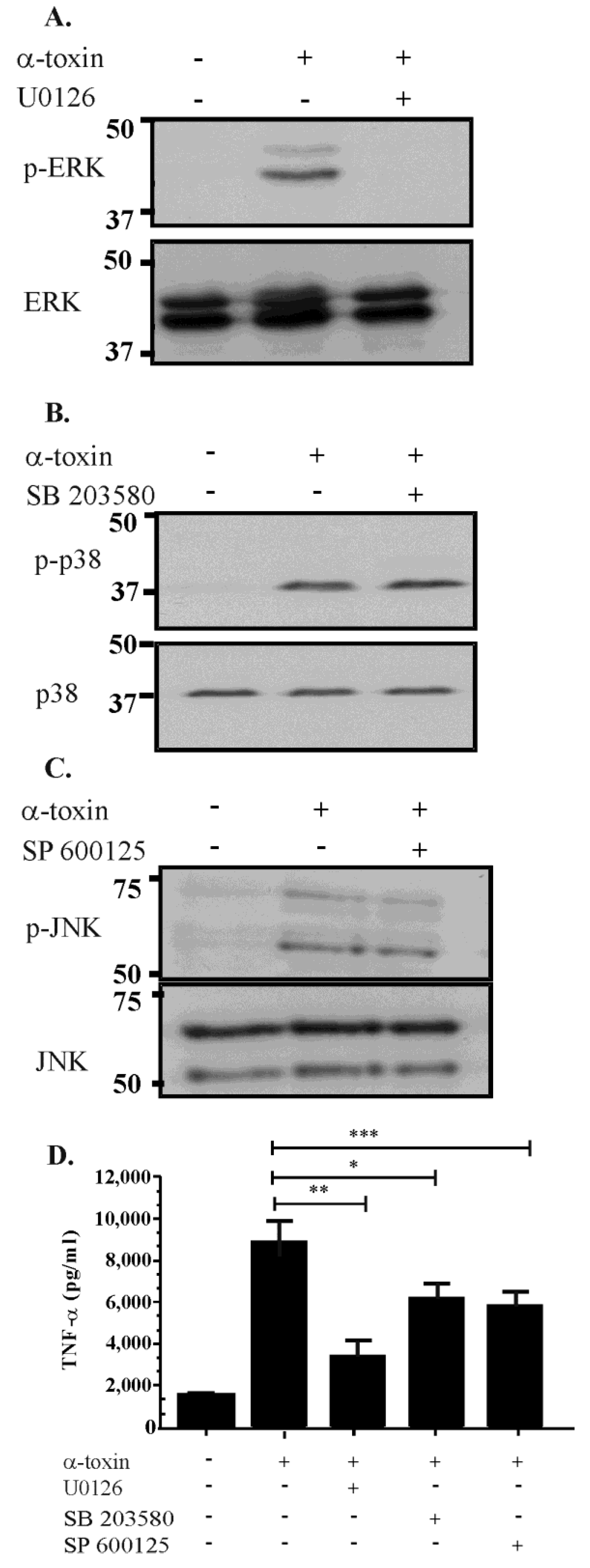
2.4. Inhibitor Studies Suggest that There Is Cross Talk between the ERK, JNK and p38 Pathways Following α-Toxin Intoxication
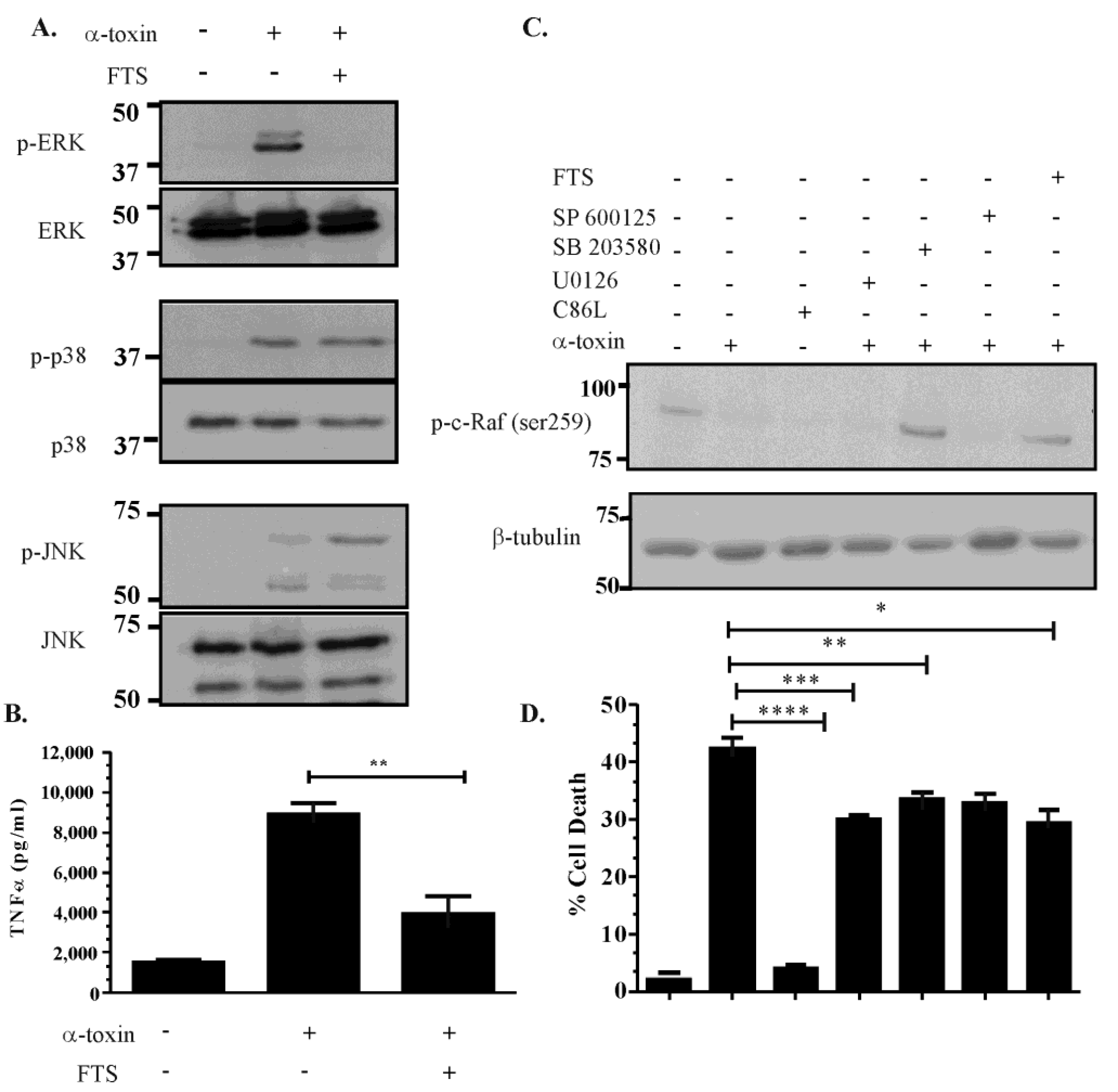
2.5. Activation of the ERK Pathway Is Ras-c-Raf Dependent
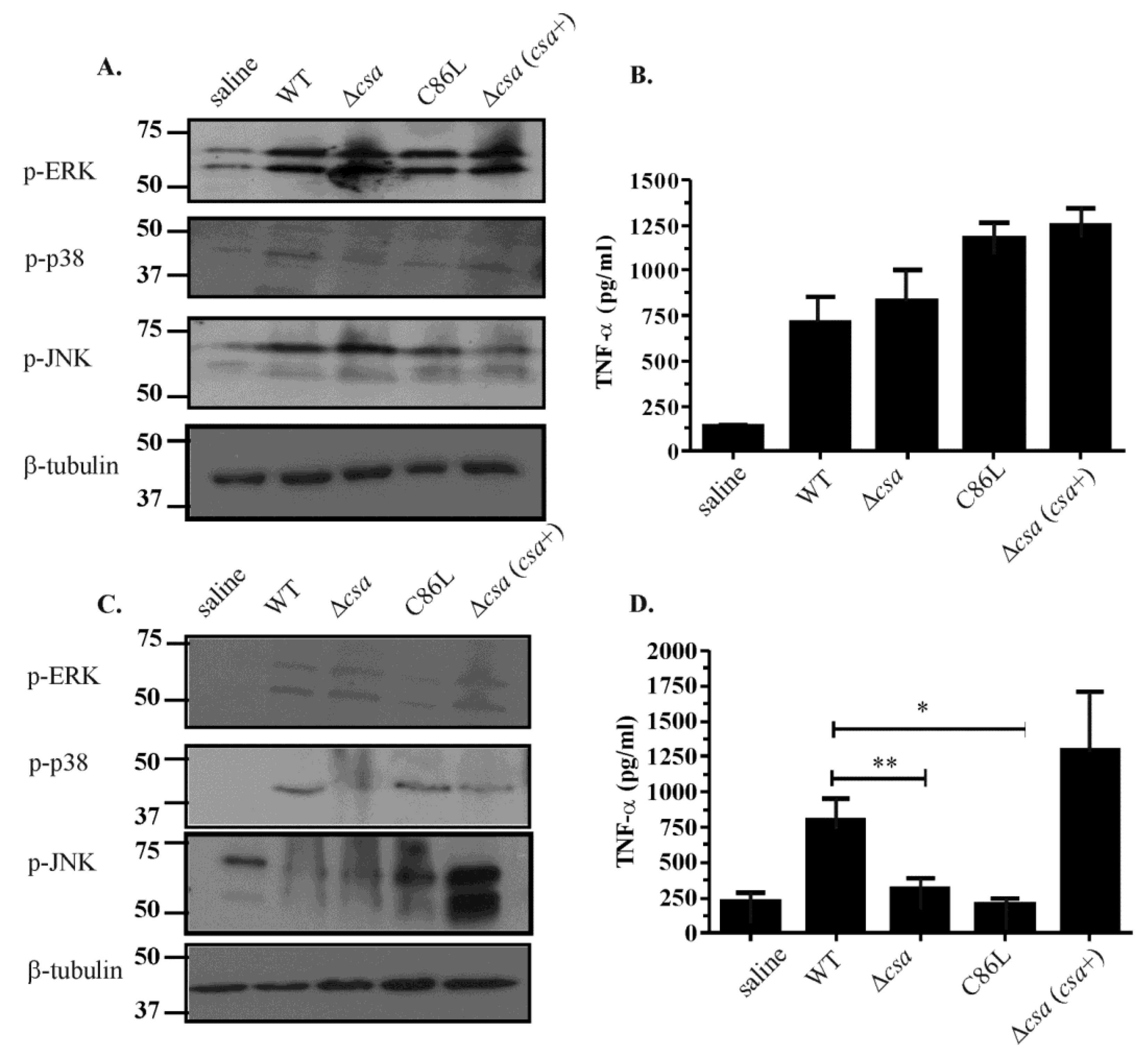
2.6. The Role of α-Toxin in Vivo Is Multifactorial
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Protein Purification
4.3. Toxin Stimulation of Vero Cells
4.4. Cell Cytotoxicity Assays
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Virulence Trials
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rood, J.I. Virulence genes of Clostridium perfringens. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1998, 52, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.L.; Aldape, M.J.; Bryant, A.E. Life-threatening clostridial infections. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, S.S.; Lubowski, D.Z. Clostridium septicum and malignancy. ANZ J. Surg. 2001, 71, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.; Gerstle, J.T.; Freedman, M.H.; Carcao, M.D. Clostridium septicum myonecrosis in congenital neutropenia. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e757–e760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, J.; Bryant, A.; Stevens, D.; Tweten, R.K. Purification and characterization of the lethal toxin (α-toxin) of Clostridium septicum. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tweten, R.K. Clostridium perfringens beta toxin and Clostridium septicum α toxin: Their mechanisms and possible role in pathogenesis. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 82, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C.L.; Krejany, E.O.; Young, L.F.; O’Connor, J.R.; Awad, M.M.; Boyd, R.L.; Emmins, J.J.; Lyras, D.; Rood, J.I. The α-toxin of Clostridium septicum is essential for virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, D.B.; Nelson, K.L.; Lawrence, T.S.; Sellman, B.R.; Tweten, R.K.; Buckley, J.T. Expression and properties of an aerolysin-Clostridium septicum α toxin hybrid protein. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, D.B.; Nelson, K.L.; Raja, S.M.; Pleshak, E.N.; Buckley, J.T. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors of membrane glycoproteins are binding determinants for the channel-forming toxin aerolysin. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2355–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türkcan, S.; Masson, J.B.; Casanova, D.; Mialon, G.; Gacoin, T.; Boilot, J.P.; Popoff, M.R.; Alexandrou, A. Observing the confinement potential of bacterial pore-forming toxin receptors inside rafts with nonblinking Eu3+-doped oxide nanoparticles. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukamoto, M.; Kimura, R.; Hang’ombe, M.B.; Kohda, T.; Kozaki, S. Analysis of tryptophan-rich region in Clostridium septicum α-toxin involved with binding to glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton-Witt, J.A.; Bentsen, L.M.; Tweten, R.K. Identification of functional domains of Clostridium septicum α toxin. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 14347–14354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, D.B.; Lawrence, T.S.; Ausio, J.; Howard, S.P.; Buckley, J.T. Secretion and properties of the large and small lobes of the channel-forming toxin aerolysin. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C.L.; Lyras, D.; Cheung, J.K.; Hiscox, T.J.; Emmins, J.J.; Rood, J.I. Cross-complementation of Clostridium perfringens PLC and Clostridium septicum α-toxin mutants reveals PLC is sufficient to mediate gas gangrene. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, O.; Maier, E.; Mkaddem, S.B.; Benz, R.; Bens, M.; Chenal, A.; Geny, B.; Vandewalle, A.; Popoff, M.R. Clostridium septicum α-toxin forms pores and induces rapid cell necrosis. Toxicon 2010, 55, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Davis, R.J.; Flavell, R.A. MAP kinases in the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Dong, C. Map kinases in immune responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 2, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.C. Erk and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J. 2009, 277, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellbrock, C.; Karasarides, M.; Marais, R. The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romashko, J., 3rd; Horowitz, S.; Franek, W.R.; Palaia, T.; Miller, E.J.; Lin, A.; Birrer, M.J.; Scott, W.; Mantell, L.L. MAPK pathways mediate hyperoxia-induced oncotic cell death in lung epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, A.J.; Hippe, K.R.; Aguilar, J.L.; Bender, M.H.; Nelson, A.L.; Weiser, J.N. Epithelial cells are sensitive detectors of bacterial pore-forming toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12994–12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, M.; Kihara, A.; Yoshioka, H.; Saito, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Uoo, K.; Higashihara, M.; Nagahama, M.; Koide, N.; Yokochi, T.; et al. Effect of erythromycin on biological activities induced by Clostridium perfringens α-toxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, H.; Cancino-Rodezno, A.; Soberon, M.; Bravo, A. Role of MAPK p38 in the cellular responses to pore-forming toxins. Peptides 2011, 32, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Ng, V.H.; Maeda, S.; Rest, R.F.; Karin, M. Anthrolysin O and other gram-positive cytolysins are toll-like receptor 4 agonists. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton, J.A.; Parker, M.W.; Rossjohn, J.; Buckley, J.T.; Tweten, R.K. The identification and structure of the membrane-spanning domain of the Clostridium septicum α toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14315–14322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Gunji, Y.; Yamasaki, S.; Takeda, Y. Shiga toxin activates p38 MAP kinase through cellular Ca2+ increase in Vero cells. FEBS Lett. 2000, 485, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C.L.; Smith, D.J.; Lyras, D.; Chakravorty, A.; Rood, J.I. Programmed cellular necrosis mediated by the pore-forming α-toxin from Clostridium septicum. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenda, A.; Rouse, J.; Doza, Y.N.; Meier, R.; Cohen, P.; Gallagher, T.F.; Young, P.R.; Lee, J.C. Sb 203580 is a specific inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 1995, 364, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, R.; Baccarini, M. Partner exchange: Protein-protein interactions in the Raf pathway. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Raf protein-serine/threonine kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Bryant, A.E.; Stevens, D.L.; Rood, J.I. Virulence studies on chromosomal α-toxin and theta-toxin mutants constructed by allelic exchange provide genetic evidence for the essential role of α-toxin in Clostridium perfringens-mediated gas gangrene. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 15, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Ellemor, D.M.; Bryant, A.E.; Matsushita, O.; Boyd, R.L.; Stevens, D.L.; Emmins, J.J.; Rood, J.I. Construction and virulence testing of a collagenase mutant of Clostridium perfringens. Microb. Pathog. 2000, 28, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, A.E. Biology and pathogenesis of thrombosis and procoagulant activity in invasive infections caused by group a streptococci and Clostridium perfringens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, A.E.; Bayer, C.R.; Aldape, M.J.; Wallace, R.J.; Titball, R.W.; Stevens, D.L. Clostridium perfringens phospholipase c-induced platelet/leukocyte interactions impede neutrophil diapedesis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, A.E.; Bayer, C.R.; Hayes-Schroer, S.M.; Stevens, D.L. Activation of platelet gpiibiiia by phospholipase C from Clostridium perfringens involves store-operated calcium entry. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, A.E.; Chen, R.Y.; Nagata, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Finegold, S.; Guth, P.H.; Stevens, D.L. Clostridial gas gangrene. I. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of microvascular dysfunction induced by exotoxins of Clostridium perfringens. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bryant, A.E. Pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringens infection: Mechanisms and mediators of shock. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25 (Suppl. 2), S160–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monturiol-Gross, L.; Flores-Diaz, M.; Araya-Castillo, C.; Pineda-Padilla, M.J.; Clark, G.C.; Titball, R.W.; Alape-Giron, A. Reactive oxygen species and the mek/erk pathway are involved in the toxicity of Clostridium perfringens α-toxin, a prototype bacterial phospholipase c. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, M.; Shiihara, R.; Ohmae, Y.; Kabura, M.; Takagishi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nagahama, M.; Inoue, M.; Abe, T.; Setsu, K.; et al. Clostridium perfringens α-toxin induces the release of IL-8 through a dual pathway via TrkA in A549 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012, 1822, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Monturiol-Gross, L.; Flores-Diaz, M.; Campos-Rodriguez, D.; Mora, R.; Rodriguez-Vega, M.; Marks, D.L.; Alape-Giron, A. Internalization of Clostridium perfringens α-toxin leads to ERK activation and is involved on its cytotoxic effect. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.R.; Bischofberger, M.; Freche, B.; Ho, S.; Parton, R.G.; van der Goot, F.G. Pore-forming toxins induce multiple cellular responses promoting survival. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1026–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahama, M.; Shibutani, M.; Seike, S.; Yonezaki, M.; Takagishi, T.; Oda, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Sakurai, J. The p38 MAPK and JNK pathways protect host cells against Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3703–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Jackson, C.A.; Goedert, M.; Hedge, P.; Cohen, P. Effect of SB 203580 on the activity of c-Raf in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, M.J.; Kwan, R.Y.; Awad, M.M.; Kennedy, C.L.; Young, L.F.; Hall, P.; Cordner, L.M.; Lyras, D.; Emmins, J.J.; Rood, J.I. Molecular and cellular basis of microvascular perfusion deficits induced by Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium septicum. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinfeld, H.; Seger, R. The ERK cascade: A prototype of MAPKsignaling. Mol. Biotechnol. 2005, 31, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seger, R.; Krebs, E.G. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C., Jr. Innate immunity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C., Jr. Innate immune recognition: Mechanisms and pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 173, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adib-Conquy, M.; Moine, P.; Asehnoune, K.; Edouard, A.; Espevik, T.; Miyake, K.; Werts, C.; Cavaillon, J.M. Toll-like receptor-mediated tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-10 production differ during systemic inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellman, B.R.; Kagan, B.L.; Tweten, R.K. Generation of a membrane-bound, oligomerized pre-pore complex is necessary for pore formation by Clostridium septicum α toxin. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, G.P.; Douce, G.R.; Govind, R.; Howarth, P.M.; Mackin, K.E.; Spencer, J.; Buckley, A.M.; Antunes, A.; Kotsanas, D.; Jenkin, G.A.; et al. The anti-sigma factor TcdC modulates hypervirulence in an epidemic BI/NAP1/027 clinical isolate of Clostridium difficile. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakravorty, A.; Awad, M.M.; Cheung, J.K.; Hiscox, T.J.; Lyras, D.; Rood, J.I. The Pore-Forming α-Toxin from Clostridium septicum Activates the MAPK Pathway in a Ras-c-Raf-Dependent and Independent Manner. Toxins 2015, 7, 516-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020516
Chakravorty A, Awad MM, Cheung JK, Hiscox TJ, Lyras D, Rood JI. The Pore-Forming α-Toxin from Clostridium septicum Activates the MAPK Pathway in a Ras-c-Raf-Dependent and Independent Manner. Toxins. 2015; 7(2):516-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020516
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakravorty, Anjana, Milena M. Awad, Jackie K. Cheung, Thomas J. Hiscox, Dena Lyras, and Julian I. Rood. 2015. "The Pore-Forming α-Toxin from Clostridium septicum Activates the MAPK Pathway in a Ras-c-Raf-Dependent and Independent Manner" Toxins 7, no. 2: 516-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020516
APA StyleChakravorty, A., Awad, M. M., Cheung, J. K., Hiscox, T. J., Lyras, D., & Rood, J. I. (2015). The Pore-Forming α-Toxin from Clostridium septicum Activates the MAPK Pathway in a Ras-c-Raf-Dependent and Independent Manner. Toxins, 7(2), 516-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7020516




