Cytotoxic Proteins and Therapeutic Targets in Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Abstract
:1. Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
2. Granulysin
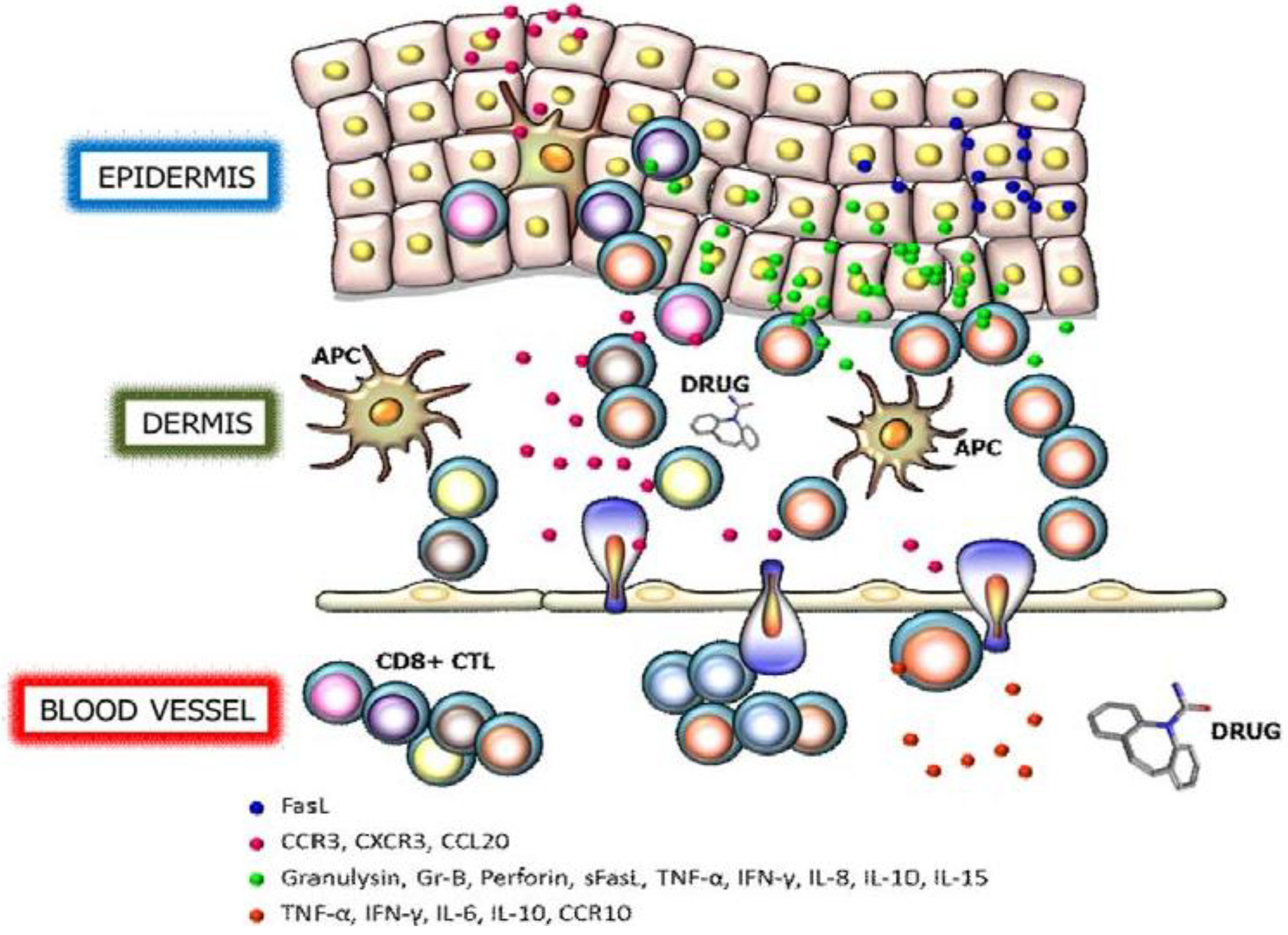
3. Perforin/Granzyme B
4. Fas/Fas Ligand
5. Cytokines and Chemokine Receptors
6. Therapeutic Interventions of SJS/TEN
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roujeau, J.C.; Stern, R.S. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet, P.; Pierard, G.E.; Quatresooz, P. Novel treatments for drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome). Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 136, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzany, B.; Correia, O.; Kelly, J.P.; Naldi, L.; Auquier, A.; Stern, R. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis during first weeks of antiepileptic therapy: A case-control study. Study group of the international case control study on severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Lancet 1999, 353, 2190–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, L.E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens Johnson syndrome: Our current understanding. Allergol. Int. 2006, 55, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzany, B.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Baur, S.; Schroder, W.; Stocker, U.; Mueller, J.; Hollander, N.; Bruppacher, R.; Schopf, E. Epidemiology of erythema exsudativum multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Germany (1990–1992): Structure and results of a population-based registry. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, E.; Papaliodis, D.N.; Papaliodis, G.N.; Daoud, Y.J.; Ahmed, A.R.; Foster, C.S. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: A review of the literature. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005, 94, 419–456, 419–436; quiz 436–438, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.E.; Archambault, R.; Mersfelder, T.L. Severe adverse skin reactions to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: A review of the literature. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.A.; Mudgil, A.V.; Rosmarin, D.M. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, A.T.; Lee, J.L.; Naguwa, S.M.; Cheema, G.S.; Gershwin, M.E. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 7, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastuji-Garin, S.; Fouchard, N.; Bertocchi, M.; Roujeau, J.C.; Revuz, J.; Wolkenstein, P. SCORTEN: A severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, V.N.; Srivastava, G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) Lyell’s syndrome. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2005, 16, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvey, J.M.; Padowitz, A.; Lindley-Jones, M.; Nickels, R. Mycoplasma pneumoniae associated with Stevens Johnson syndrome. Anaesth Intens. Care 2007, 35, 414–417. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, R.; Koren, G.; Shear, N.H. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in children: A review of 10 year’ experience. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockenhaupt, M.; Viboud, C.; Dunant, A.; Naldi, L.; Halevy, S.; Bouwes-Bavinck, J.N.; Sidoroff, A.; Schneck, J.; Roujeau, J.C.; Flahault, A. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Assessment of medication risks with emphasis on recently marketed drugs. The EuroSCAR-study. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujeau, J.C.; Kelly, J.P.; Naldi, L.; Rzany, B.; Stern, R.S.; Anderson, T.; Auquier, A.; Bastuji-Garin, S.; Correia, O.; Locati, F.; et al. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, M.; Illing, P.; Theodossis, A.; Purcell, A.W.; Rossjohn, J.; McCluskey, J. Drug hypersensitivity and human leukocyte antigens of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 401–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.M.; Uetrecht, J. Bioactivation of drugs in the skin: Relationship to cutaneous adverse drug reactions. Drug Metab. Rev. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Guo, S.; Hall, D.; Cammett, A.M.; Jayadev, S.; Distel, M.; Storfer, S.; Huang, Z.; Mootsikapun, P.; Ruxrungtham, K.; et al. Toxicogenomics of nevirapine-associated cutaneous and hepatic adverse events among populations of African, Asian, and European descent. Aids 2011, 25, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Acharjya, B. Adverse cutaneous drug reaction. Ind. J. Dermatol. 2008, 53, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.H.; Hung, S.I.; Yang, J.Y.; Su, S.C.; Huang, S.P.; Wei, C.Y.; Chin, S.W.; Chiou, C.C.; Chu, S.C.; Ho, H.C.; et al. Granulysin is a key mediator for disseminated keratinocyte death in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, S.V.; Hanson, D.A.; Carr, B.A.; Goralski, T.J.; Krensky, A.M. Processing, subcellular localization, and function of 519 (granulysin), a human late T cell activation molecule with homology to small, lytic, granule proteins. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 2680–2688. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, D.A.; Kaspar, A.A.; Poulain, F.R.; Krensky, A.M. Biosynthesis of granulysin, a novel cytolytic molecule. Mol. Immunol. 1999, 36, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.H.; Sawaya, M.R.; Cascio, D.; Ernst, W.; Modlin, R.; Krensky, A.; Eisenberg, D. Granulysin crystal structure and a structure-derived lytic mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, W.A.; Thoma-Uszynski, S.; Teitelbaum, R.; Ko, C.; Hanson, D.A.; Clayberger, C.; Krensky, A.M.; Leippe, M.; Bloom, B.R.; Ganz, T.; et al. Granulysin, a T cell product, kills bacteria by altering membrane permeability. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 7102–7108. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, S.; Li, Q.; Whitin, J.C.; Clayberger, C.; Krensky, A.M. Intracellular mediators of granulysin-induced cell death. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, J.; Perez-Galan, P.; Gamen, S.; Marzo, I.; Monleon, I.; Kaspar, A.A.; Susin, S.A.; Kroemer, G.; Krensky, A.M.; Naval, J.; et al. A role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in granulysin-induced apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar, A.A.; Okada, S.; Kumar, J.; Poulain, F.R.; Drouvalakis, K.A.; Kelekar, A.; Hanson, D.A.; Kluck, R.M.; Hitoshi, Y.; Johnson, D.E.; et al. A distinct pathway of cell-mediated apoptosis initiated by granulysin. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Tewary, P.; Yang, D.; de la Rosa, G.; Li, Y.; Finn, M.W.; Krensky, A.M.; Clayberger, C.; Oppenheim, J.J. Granulysin activates antigen-presenting cells through TLR4 and acts as an immune alarmin. Blood 2010, 116, 3465–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Lyu, S.C.; Clayberger, C.; Krensky, A.M. Granulysin, a cytolytic molecule, is also a chemoattractant and proinflammatory activator. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5243–5248. [Google Scholar]
- Clayberger, C.; Finn, M.W.; Wang, T.; Saini, R.; Wilson, C.; Barr, V.A.; Sabatino, M.; Castiello, L.; Stroncek, D.; Krensky, A.M. 15 kDa granulysin causes differentiation of monocytes to dendritic cells but lacks cytotoxic activity. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 6119–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krensky, A.M.; Clayberger, C. Biology and clinical relevance of granulysin. Tissue Antigens 2009, 73, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oono, T.; Morizane, S.; Yamasaki, O.; Shirafuji, Y.; Huh, W.K.; Akiyama, H.; Iwatsuki, K. Involvement of granulysin-producing T cells in the development of superficial microbial folliculitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 150, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Jiang, W.Y.; Raychaudhuri, S.K.; Krensky, A.M. Lesional T cells and dermal dendrocytes in psoriasis plaque express increased levels of granulysin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 1006–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInturff, J.E.; Wang, S.J.; Machleidt, T.; Lin, T.R.; Oren, A.; Hertz, C.J.; Krutzik, S.R.; Hart, S.; Zeh, K.; Anderson, D.H.; et al. Granulysin-derived peptides demonstrate antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects against Propionibacterium acnes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 256–263. [Google Scholar]
- Ammar, M.; Mokni, M.; Boubaker, S.; El Gaied, A.; Ben Osman, A.; Louzir, H. Involvement of granzyme B and granulysin in the cytotoxic response in lichen planus. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2008, 35, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, C.; Zawodniak, A.; Irla, N.; Adam, J.; Hunger, R.E.; Yerly, D.; Pichler, W.J.; Yawalkar, N. NKp46+ cells express granulysin in multiple cutaneous adverse drug reactions. Allergy 2011, 66, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Abe, R.; Yoshioka, N.; Murata, J.; Fujita, Y.; Shimizu, H. Prolonged elevation of serum granulysin in drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 452–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, M.; Isoda, T.; Itoh, S.; Kajiwara, M.; Morio, T.; Shimizu, N.; Ogawa, K.; Nagata, K.; Nakamura, M.; Mizutani, S. Analysis of serum granulysin in patients with hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: Its usefulness as a marker of graft-versus-host reaction. Am. J. Hematol. 2006, 81, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, S.J.; Padial, A.; Torres, M.J.; Mayorga, C.; Leyva, L.; Sanchez, E.; Alvarez, J.; Romano, A.; Juarez, C.; Blanca, M. Delayed reactions to drugs show levels of perforin, granzyme B, and Fas-L to be related to disease severity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.; Bensussan, A.; Dorothee, G.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Bachot, N.; Bagot, M.; Boumsell, L.; Roujeau, J.C. Drug specific cytotoxic T-cells in the skin lesions of a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, J.A.; Smyth, M.J. Functional significance of the perforin/granzyme cell death pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.H.; Lukoyanova, N.; Voskoboinik, I.; Caradoc-Davies, T.T.; Baran, K.; Dunstone, M.A.; D’Angelo, M.E.; Orlova, E.V.; Coulibaly, F.; Verschoor, S.; et al. The structural basis for membrane binding and pore formation by lymphocyte perforin. Nature 2010, 468, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskoboinik, I.; Thia, M.C.; Fletcher, J.; Ciccone, A.; Browne, K.; Smyth, M.J.; Trapani, J.A. Calcium-dependent plasma membrane binding and cell lysis by perforin are mediated through its C2 domain: A critical role for aspartate residues 429, 435, 483, and 485 but not 491. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8426–8434. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, S.J.; Rajotte, R.V.; Korbutt, G.S.; Bleackley, R.C. Granzyme B: A natural born killer. Immunol. Rev. 2003, 193, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, M.; Medema, J.P. Granzymes at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 5011–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veugelers, K.; Motyka, B.; Goping, I.S.; Shostak, I.; Sawchuk, T.; Bleackley, R.C. Granule-mediated killing by granzyme B and perforin requires a mannose 6-phosphate receptor and is augmented by cell surface heparan sulfate. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, C.H.; Sun, J.; Ung, K.; Karambalis, D.; Whisstock, J.C.; Trapani, J.A.; Bird, P.I. Cationic sites on granzyme B contribute to cytotoxicity by promoting its uptake into target cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7854–7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyka, B.; Korbutt, G.; Pinkoski, M.J.; Heibein, J.A.; Caputo, A.; Hobman, M.; Barry, M.; Shostak, I.; Sawchuk, T.; Holmes, C.F.; et al. Mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor is a death receptor for granzyme B during cytotoxic T cell-induced apoptosis. Cell 2000, 103, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, C.J.; Orth, K.; Turbov, J.; Seth, P.; Gottlieb, R.; Babior, B.; Shah, G.M.; Bleackley, R.C.; Dixit, V.M.; Hanna, W. New paradigm for lymphocyte granule-mediated cytotoxicity. Target cells bind and internalize granzyme B, but an endosomolytic agent is necessary for cytosolic delivery and subsequent apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 29073–29079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, D.; Shi, L.; Feske, S.; Massol, R.; Navarro, F.; Kirchhausen, T.; Lieberman, J. Perforin triggers a plasma membrane-repair response that facilitates CTL induction of apoptosis. Immunity 2005, 23, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.J.; Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Shi, L.; Chuang, T.H.; Casiano, C.A.; O’Brien, G.A.; Fitzgerald, P.; Tan, E.M.; Bokoch, G.M.; Greenberg, A.H.; et al. The cytotoxic cell protease granzyme B initiates apoptosis in a cell-free system by proteolytic processing and activation of the ICE/CED-3 family protease, CPP32, via a novel two-step mechanism. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar]
- Darmon, A.J.; Nicholson, D.W.; Bleackley, R.C. Activation of the apoptotic protease CPP32 by cytotoxic T-cell-derived granzyme B. Nature 1995, 377, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heibein, J.A.; Goping, I.S.; Barry, M.; Pinkoski, M.J.; Shore, G.C.; Green, D.R.; Bleackley, R.C. Granzyme B-mediated cytochrome c release is regulated by the Bcl-2 family members bid and Bax. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, V.R.; Davis, J.E.; Cancilla, M.; Johnstone, R.W.; Ruefli, A.A.; Sedelies, K.; Browne, K.A.; Trapani, J.A. Initiation of apoptosis by granzyme B requires direct cleavage of bid, but not direct granzyme B-mediated caspase activation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, V.R.; Wowk, M.E.; Cancilla, M.; Trapani, J.A. Caspase activation by granzyme B is indirect, and caspase autoprocessing requires the release of proapoptotic mitochondrial factors. Immunity 2003, 18, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goping, I.S.; Sawchuk, T.; Rieger, A.; Shostak, I.; Bleackley, R.C. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes overcome Bcl-2 inhibition: Target cells contribute to their own demise. Blood 2008, 111, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Beresford, P.J.; Greenberg, A.H.; Lieberman, J. Granzymes A and B directly cleave lamins and disrupt the nuclear lamina during granule-mediated cytolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5746–5751. [Google Scholar]
- Viard, I.; Wehrli, P.; Bullani, R.; Schneider, P.; Holler, N.; Salomon, D.; Hunziker, T.; Saurat, J.H.; Tschopp, J.; French, L.E. Inhibition of toxic epidermal necrolysis by blockade of CD95 with human intravenous immunoglobulin. Science 1998, 282, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viard-Leveugle, I.; Bullani, R.R.; Meda, P.; Micheau, O.; Limat, A.; Saurat, J.H.; Tschopp, J.; French, L.E. Intracellular localization of keratinocyte Fas ligand explains lack of cytolytic activity under physiological conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16183–16188. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, R.; Shimizu, T.; Shibaki, A.; Nakamura, H.; Watanabe, H.; Shimizu, H. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome are induced by soluble Fas ligand. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, P.H. CD95’s deadly mission in the immune system. Nature 2000, 407, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, P.H. CD95(APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis: Live and let die. Adv. Immunol. 1999, 71, 163–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kischkel, F.C.; Hellbardt, S.; Behrmann, I.; Germer, M.; Pawlita, M.; Krammer, P.H.; Peter, M.E. Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5579–5588. [Google Scholar]
- Strasser, A.; Jost, P.J.; Nagata, S. The many roles of FAS receptor signaling in the immune system. Immunity 2009, 30, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, C.J.; Yuan, J. Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 1998, 94, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Budihardjo, I.; Zou, H.; Slaughter, C.; Wang, X. Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 1998, 94, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Azad, N.; Kongkaneramit, L.; Chen, F.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, B.H.; Rojanasakul, Y. The Fas death signaling pathway connecting reactive oxygen species generation and FLICE inhibitory protein down-regulation. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3072–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.H.; Park, S.M.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, M.S.; Yoon, J.B.; Vilcek, J.; Lee, T.H. Non-apoptotic signaling pathways activated by soluble Fas ligand in serum-starved human fibroblasts. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47100–47106. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Jodo, S.; Sung, S.S.; Marshak-Rothstein, A.; Ju, S.T. A novel signaling mechanism for soluble CD95 ligand. Synergy with anti-CD95 monoclonal antibodies for apoptosis and NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50907–50913. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, M.E.; Budd, R.C.; Desbarats, J.; Hedrick, S.M.; Hueber, A.O.; Newell, M.K.; Owen, L.B.; Pope, R.M.; Tschopp, J.; Wajant, H.; et al. The CD95 receptor: Apoptosis revisited. Cell 2007, 129, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Nabel, G.J. Regulation of the proinflammatory effects of Fas ligand (CD95L). Science 1998, 282, 1714–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.S.; Dixit, V.; Ashkenazi, A. Death receptor signal transducers: Nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LA, O.R.; Tai, L.; Lee, L.; Kruse, E.A.; Grabow, S.; Fairlie, W.D.; Haynes, N.M.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Zhang, J.G.; Belz, G.T.; et al. Membrane-bound Fas ligand only is essential for Fas-induced apoptosis. Nature 2009, 461, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Suda, T.; Takahashi, T.; Nagata, S. Expression of the functional soluble form of human fas ligand in activated lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, P.G.; Milner, A.E.; Green, N.K.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Young, L.S. Inhibition of metalloproteinase cleavage enhances the cytotoxicity of Fas ligand. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 677–685. [Google Scholar]
- Paquet, P.; Nikkels, A.; Arrese, J.E.; Vanderkelen, A.; Pierard, G.E. Macrophages and tumor necrosis factor alpha in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch. Dermatol. 1994, 130, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G. Molecular mechanism of TNF signaling and beyond. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Galan, L.; Arenas-Del Angel, M.C.; Zenteno, E.; Chavez, R.; Lascurain, R. Cell death mechanisms induced by cytotoxic lymphocytes. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 6, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrick, J.W.; Wright, S.C. Cytotoxic mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. FASEB J. Off. Public. Feder. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1990, 4, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Royall, J.A.; Berkow, R.L.; Beckman, J.S.; Cunningham, M.K.; Matalon, S.; Freeman, B.A. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 alpha increase vascular endothelial permeability. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 257, L399–L410. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, M.U.; Lister, K.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Issekutz, A.; Hickey, M.J. TNF regulates leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions and microvascular dysfunction during immune complex-mediated inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 144, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hickey, M.J.; Reinhardt, P.H.; Ostrovsky, L.; Jones, W.M.; Jutila, M.A.; Payne, D.; Elliott, J.; Kubes, P. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces leukocyte recruitment by different mechanisms in vivo and in vitro. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Hwang, J.M.; Kubes, P. Modulating leukocyte recruitment in inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caproni, M.; Torchia, D.; Schincaglia, E.; Volpi, W.; Frezzolini, A.; Schena, D.; Marzano, A.; Quaglino, P.; de Simone, C.; Parodi, A.; et al. Expression of cytokines and chemokine receptors in the cutaneous lesions of erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Hertzog, P.J.; Ravasi, T.; Hume, D.A. Interferon-gamma: An overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 163–189. [Google Scholar]
- Viard-Leveugle, I.; Gaide, O.; Jankovic, D.; Feldmeyer, L.; Kerl, K.; Pickard, C.; Roques, S.; Friedmann, P.S.; Contassot, E.; French, L.E. TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma are potential inducers of Fas-mediated keratinocyte apoptosis through activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla-Sarkar, M.; Lindner, D.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Williams, B.R.; Sen, G.C.; Silverman, R.H.; Borden, E.C. Apoptosis and interferons: Role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of apoptosis. Apoptosis Int. J. Programmed. Cell Death 2003, 8, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fu, X.Y.; Plate, J.; Chong, A.S. IFN-gamma induces cell growth inhibition by Fas-mediated apoptosis: Requirement of STAT1 protein for up-regulation of Fas and FasL expression. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2832–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto, M.; Yip, Y.K.; Vilcek, J. Interferon-gamma enhances expression of cellular receptors for tumor necrosis factor. J. Immunol. 1986, 136, 2441–2444. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, T.; Ishihara, M.; Lamphier, M.S.; Tanaka, N.; Oishi, I.; Aizawa, S.; Matsuyama, T.; Mak, T.W.; Taki, S.; Taniguchi, T. DNA damage-induced apoptosis and Ice gene induction in mitogenically activated T lymphocytes require IRF-1. Leukemia 1997, 11, 439–440. [Google Scholar]
- Steimle, V.; Siegrist, C.A.; Mottet, A.; Lisowska-Grospierre, B.; Mach, B. Regulation of MHC class II expression by interferon-gamma mediated by the transactivator gene CIITA. Science 1994, 265, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Fruh, K.; Yang, Y. Antigen presentation by MHC class I and its regulation by interferon gamma. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1999, 11, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet, P.; Paquet, F.; Al Saleh, W.; Reper, P.; Vanderkelen, A.; Pierard, G.E. Immunoregulatory effector cells in drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2000, 22, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, O.; Delgado, L.; Barbosa, I.L.; Campilho, F.; Fleming-Torrinha, J. Increased interleukin 10, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin 6 levels in blister fluid of toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 47, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.; Moslehi, H.; le Gouvello, S.; Bagot, M.; Lyonnet, L.; Michel, L.; Boumsell, L.; Bensussan, A.; Roujeau, J.C. Evaluation of the potential role of cytokines in toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, B.; Padial, A.; Sanchez-Sabate, E.; Alvarez-Ferreira, J.; Morel, E.; Blanca, M.; Bellon, T. Involvement of CCL27-CCR10 interactions in drug-induced cutaneous reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.C.; Chung, W.H. Update on pathobiology in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Dermatol. Sin. 2013, 31, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Lin, J.J.; Lu, C.S.; Ong, C.T.; Hsieh, P.F.; Yang, C.C.; Tai, C.T.; Wu, S.L.; Lu, C.H.; Hsu, Y.C.; et al. Carbamazepine-induced toxic effects and HLA-B*1502 screening in Taiwan. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, T.A.; Mortimer, N.J.; Sladden, M.J.; Hall, A.P.; Hutchinson, P.E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Current evidence, practical management and future directions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerull, R.; Nelle, M.; Schaible, T. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A review. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Doval, I.; LeCleach, L.; Bocquet, H.; Otero, X.L.; Roujeau, J.C. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch. Dermatol. 2000, 136, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Sakellariou, G.; Koukoudis, P.; Karpouzas, J.; Alexopoulos, E.; Papadopoulou, D.; Chrisomalis, F.; Skenteris, N.; Tsakaris, D.; Papadimitriou, M. Plasma exchange (PE) treatment in drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Int. J. Artif. Organs 1991, 14, 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, C.A.; Grant, W.J.; Morris, S.E.; Saffle, J.R.; Zone, J.J. Plasmapheresis as an adjunct treatment in toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1999, 40, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, Y.M.; Hirahara, K.; Mizukawa, Y.; Kano, Y.; Shiohara, T. Efficacy of plasmapheresis for the treatment of severe toxic epidermal necrolysis: Is cytokine expression analysis useful in predicting its therapeutic efficacy? J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Takamori, K. Status of plasmapheresis for the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis in Japan. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2008, 12, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furubacke, A.; Berlin, G.; Anderson, C.; Sjoberg, F. Lack of significant treatment effect of plasma exchange in the treatment of drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis? Intens. Care Med. 1999, 25, 1307–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halebian, P.H.; Corder, V.J.; Madden, M.R.; Finklestein, J.L.; Shires, G.T. Improved burn center survival of patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis managed without corticosteroids. Ann. Surg. 1986, 204, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revuz, J.; Penso, D.; Roujeau, J.C.; Guillaume, J.C.; Payne, C.R.; Wechsler, J.; Touraine, R. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clinical findings and prognosis factors in 87 patients. Arch. Dermatol. 1987, 123, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Maldonado, R. Acute disseminated epidermal necrosis types 1, 2, and 3: Study of sixty cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1985, 13, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, M.C.; Allen, S.G. Efficacy of cyclophosphamide in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clinical and pathophysiologic aspects. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1991, 25, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G.; Boridy, I.; Mazhar, M.; Mathews, R.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Cate, T. Cyclophosphamide in the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis. South. Med. J. 1996, 89, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Wolkenstein, P.; Brochard, L.; Ortonne, N.; Maitre, B.; Revuz, J.; Bagot, M.; Roujeau, J.C. Open trial of ciclosporin treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, P.; Rademaker, M.; Havill, J.; Pullon, H. Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with cyclosporin and granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1997, 22, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, I.; Patel, S.; Reed, R.; Dalziel, K.L. Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with severe hypocalcaemia, and treated with cyclosporin. Br. J. Dermatol. 1995, 133, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, P.; de Felipe, I.; de la Pena, A.; Aramendia, J.M.; Vanaclocha, V. Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Treatment with N-acetylcysteine. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 136, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, A.; Moreno, J.C. Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with N-acetylcysteine. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanclemente, G.; de la Roche, C.A.; Escobar, C.E.; Falabella, R. Pentoxyfylline in toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Int. J. Dermatol. 1999, 38, 878–879. [Google Scholar]
- Wolkenstein, P.; Latarjet, J.; Roujeau, J.C.; Duguet, C.; Boudeau, S.; Vaillant, L.; Maignan, M.; Schuhmacher, M.H.; Milpied, B.; Pilorget, A.; et al. Randomised comparison of thalidomide versus placebo in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Lancet 1998, 352, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, M.; Cassano, P.; Bollero, D.; Clemente, A.; Giorio, G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with intravenous high-dose immunoglobulins: Our experience. Dermatology 2001, 203, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristani-Firouzi, P.; Petersen, M.J.; Saffle, J.R.; Morris, S.E.; Zone, J.J. Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with intravenous immunoglobulin in children. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 47, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, C.; Kerdel, F.A.; Padilla, R.S.; Hunziker, T.; Chimenti, S.; Viard, I.; Mauri, D.N.; Flynn, K.; Trent, J.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins: Multicenter retrospective analysis of 48 consecutive cases. Arch. Dermatol. 2003, 139, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.W.; Thong, B.Y.; Yip, L.W.; Chng, H.H.; Ng, S.K. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulins in the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis: An Asian series. J. Dermatol. 2005, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Trent, J.T.; Kirsner, R.S.; Romanelli, P.; Kerdel, F.A. Analysis of intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis using SCORTEN: The University of Miami Experience. Arch. Dermatol. 2003, 139, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bachot, N.; Revuz, J.; Roujeau, J.C. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: A prospective noncomparative study showing no benefit on mortality or progression. Arch. Dermatol. 2003, 139, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.C.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, T.J. The efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.M.; Silver, G.M.; Halerz, M.; Walaszek, P.; Sandroni, A.; Gamelli, R.L. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Does immunoglobulin make a difference? J. Burn Care Rehabil. 2004, 25, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortt, R.; Gomez, M.; Mittman, N.; Cartotto, R. Intravenous immunoglobulin does not improve outcome in toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Burn Care Rehabil. 2004, 25, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Fiedler, E.; Marsch, W.C.; Wohlrab, J. Antitumour necrosis factor-alpha antibodies (infliximab) in the treatment of a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 146, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, S.-C.; Chung, W.-H. Cytotoxic Proteins and Therapeutic Targets in Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions. Toxins 2014, 6, 194-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6010194
Su S-C, Chung W-H. Cytotoxic Proteins and Therapeutic Targets in Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions. Toxins. 2014; 6(1):194-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6010194
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Shih-Chi, and Wen-Hung Chung. 2014. "Cytotoxic Proteins and Therapeutic Targets in Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions" Toxins 6, no. 1: 194-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6010194
APA StyleSu, S.-C., & Chung, W.-H. (2014). Cytotoxic Proteins and Therapeutic Targets in Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions. Toxins, 6(1), 194-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6010194



