The Receptors that Mediate the Direct Lethality of Anthrax Toxin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
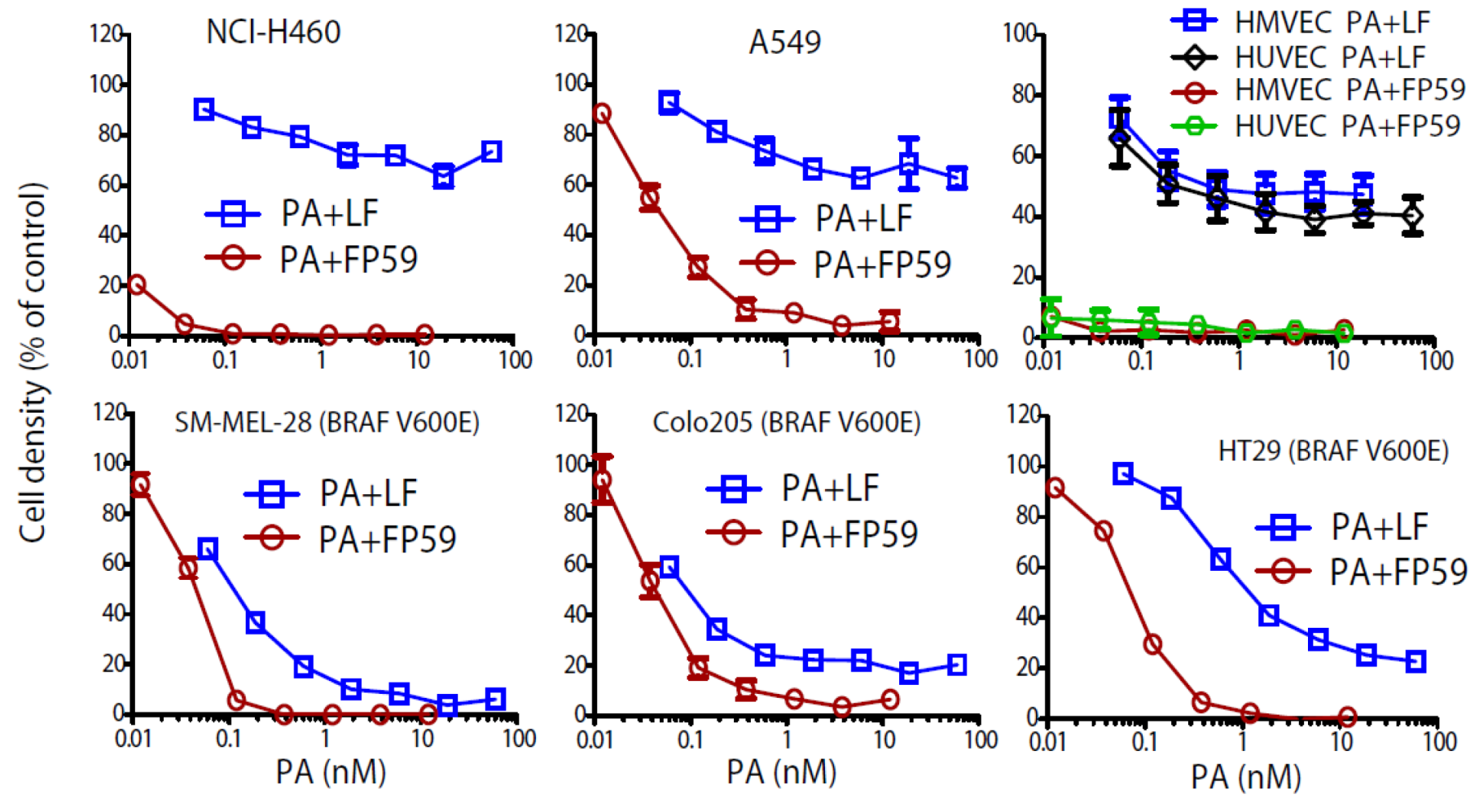
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Assay
3.2. Toxin Challenge Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Moayeri, M.; Leppla, S.H. Cellular and systemic effects of anthrax lethal toxin and edema toxin. Mol. Aspects Med. 2009, 30, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Schubert, R.L.; Bugge, T.H.; Leppla, S.H. Anthrax toxin: Structures, functions and tumour targeting. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2003, 3, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, K.A.; Mogridge, J.; Mourez, M.; Collier, R.J.; Young, J.A. Identification of the cellular receptor for anthrax toxin. Nature 2001, 414, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Scobie, H.M.; Rainey, G.J.; Bradley, K.A.; Young, J.A. Human capillary morphogenesis protein 2 functions as an anthrax toxin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5170–5174. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Crown, D.; Miller-Randolph, S.; Moayeri, M.; Wang, H.; Hu, H.; Morley, T.; Leppla, S.H. Capillary morphogenesis protein-2 is the major receptor mediating lethality of anthrax toxin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12424–12429. [Google Scholar]
- Martchenko, M.; Jeong, S.Y.; Cohen, S.N. Heterodimeric integrin complexes containing β1-integrin promote internalization and lethality of anthrax toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15583–15588. [Google Scholar]
- Mourez, M.; Lacy, D.B.; Cunningham, K.; Legmann, R.; Sellman, B.R.; Mogridge, J.; Collier, R.J. 2001: A year of major advances in anthrax toxin research. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 10, 287–293. [Google Scholar]
- Abrami, L.; Liu, S.; Cosson, P.; Leppla, S.H.; van der Goot, F.G. Anthrax toxin triggers endocytosis of its receptor via a lipid raft-mediated clathrin-dependent process. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Leppla, S.H. Cell surface tumor endothelium marker 8 cytoplasmic tail-independent anthrax toxin binding, proteolytic processing, oligomer formation, and internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5227–5234. [Google Scholar]
- Leppla, S.H. Anthrax toxin edema factor: A bacterial adenylate cyclase that increases cyclic AMP concentrations of eukaryotic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 3162–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoved, A.M.; Miller, G.F.; Moayeri, M.; Kakkar, R.; Shen, Y.; Wiggins, J.F.; McNally, E.M.; Tang, W.J.; Leppla, S.H. Bacillus anthracis edema toxin causes extensive tissue lesions and rapid lethality in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesbery, N.S.; Webb, C.P.; Leppla, S.H.; Gordon, V.M.; Klimpel, K.R.; Copeland, T.D.; Ahn, N.G.; Oskarsson, M.K.; Fukasawa, K.; Paull, K.D.; vande Woude, G.F. Proteolytic inactivation of MAP-kinase-kinase by anthrax lethal factor. Science 1998, 280, 734–737. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, G.; Pellizzari, R.; Recchi, C.; Napolitani, G.; Mock, M.; Montecucco, C. Anthrax lethal factor cleaves the N-terminus of MAPKKs and induces tyrosine/threonine phosphorylation of MAPKs in cultured macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 248, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, G.; Bernardi, L.; Napolitani, G.; Mock, M.; Montecucco, C. Susceptibility of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase family members to proteolysis by anthrax lethal factor. Biochem. J. 2000, 352, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayeri, M.; Haines, D.; Young, H.A.; Leppla, S.H. Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin induces TNF-α-independent hypoxia-mediated toxicity in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 670–682. [Google Scholar]
- Abrami, L.; Leppla, S.H.; van der Goot, F.G. Receptor palmitoylation and ubiquitination regulate anthrax toxin endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Leung, H.J.; Leppla, S.H. Characterization of the interaction between anthrax toxin and its cellular receptors. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, Z.L.; Printz, M.P.; Liu, S.; Crown, D.; Breen, L.; Miller-Randolph, S.; Flodman, P.; Leppla, S.H.; Moayeri, M. Susceptibility to anthrax lethal toxin-induced rat death is controlled by a single chromosome 10 locus that includes rNlrp1. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinsohn, J.L.; Newman, Z.L.; Hellmich, K.A.; Fattah, R.; Getz, M.A.; Liu, S.; Sastalla, I.; Leppla, S.H.; Moayeri, M. Anthrax lethal factor cleavage of Nlrp1 is required for activation of the inflammasome. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002638. [Google Scholar]
- Abi-Habib, R.J.; Singh, R.; Leppla, S.H.; Greene, J.J.; Ding, Y.; Berghuis, B.; Duesbery, N.S.; Frankel, A.E. Systemic anthrax lethal toxin therapy produces regressions of subcutaneous human melanoma tumors in athymic nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7437–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Currie, B.M.; Molinolo, A.; Leung, H.J.; Moayeri, M.; Basile, J.R.; Alfano, R.W.; Gutkind, J.S.; Frankel, A.E.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-activated anthrax lethal toxin demonstrates high potency in targeting tumor vasculature. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 529–540. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, N.; Klimpel, K.R.; Singh, Y.; Leppla, S.H. Fusions of anthrax toxin lethal factor to the ADP-ribosylation domain of Pseudomonas exotoxin A are potent cytotoxins which are translocated to the cytosol of mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 15542–15548. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Leppla, S.H. Retroviral insertional mutagenesis identifies a small protein required for synthesis of diphthamide, the target of bacterial ADP-ribosylating toxins. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bachran, C.; Gupta, P.; Miller-Randolph, S.; Wang, H.; Crown, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wein, A.N.; Singh, R.; Fattah, R.; Leppla, S.H. Diphthamide modification on eukaryotic elongation factor 2 is needed to assure fidelity of mRNA translation and mouse development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13817–13822. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Miller-Randolph, S.; Crown, D.; Moayeri, M.; Sastalla, I.; Okugawa, S.; Leppla, S.H. Anthrax toxin targeting of myeloid cells through the CMG2 receptor is essential for establishment of Bacillus anthracis infections in mice. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantsev, A.P.; Pomerantseva, O.M.; Moayeri, M.; Fattah, R.; Tallant, C.; Leppla, S.H. A Bacillus anthracis strain deleted for six proteases serves as an effective host for production of recombinant proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 80, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Moayeri, M.; Crown, D.; Fattah, R.J.; Leppla, S.H. Role of N-terminal amino acids in the potency of anthrax lethal factor. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3130. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hoover, B.; Leppla, S.H. The Receptors that Mediate the Direct Lethality of Anthrax Toxin. Toxins 2013, 5, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010001
Liu S, Zhang Y, Hoover B, Leppla SH. The Receptors that Mediate the Direct Lethality of Anthrax Toxin. Toxins. 2013; 5(1):1-8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shihui, Yi Zhang, Benjamin Hoover, and Stephen H. Leppla. 2013. "The Receptors that Mediate the Direct Lethality of Anthrax Toxin" Toxins 5, no. 1: 1-8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010001
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhang, Y., Hoover, B., & Leppla, S. H. (2013). The Receptors that Mediate the Direct Lethality of Anthrax Toxin. Toxins, 5(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5010001




