Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin: A Powerful Tool with Capacity to Cause Imbalance in the Host Inflammatory Response
Abstract
:1. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
2. Leukotoxin Production

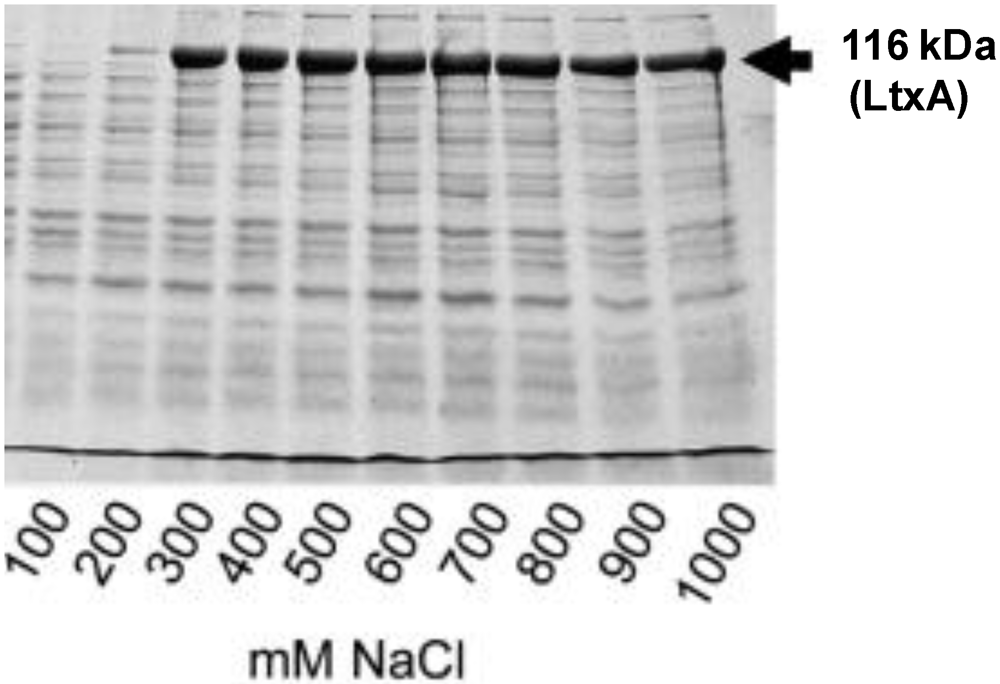
3. Leukotoxin Secretion

4. Molecular Structure of the Leukotoxin
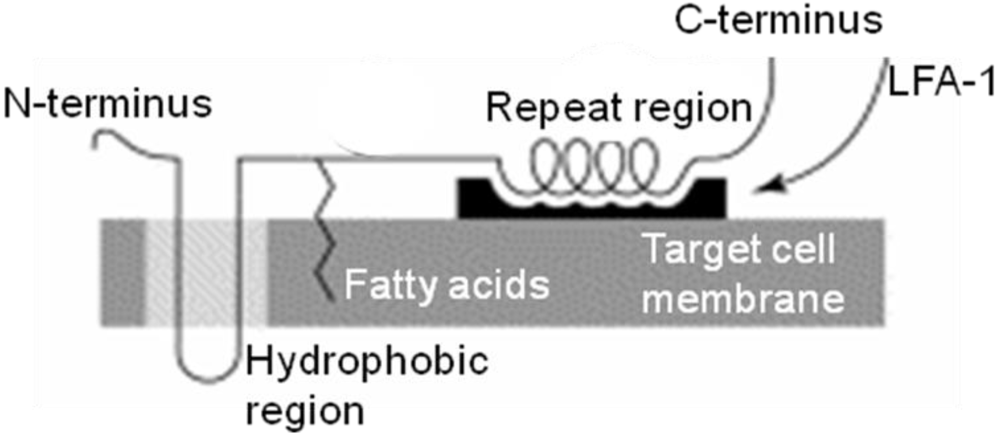
5. Interaction of LtxA with the Target Cell Membrane
6. Virulence Mechanisms of the Leukotoxin (LtxA)
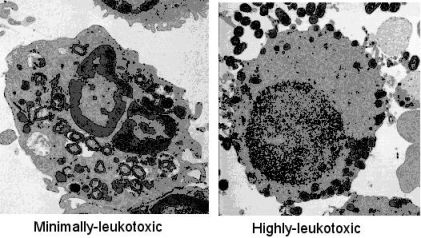
6.1. Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
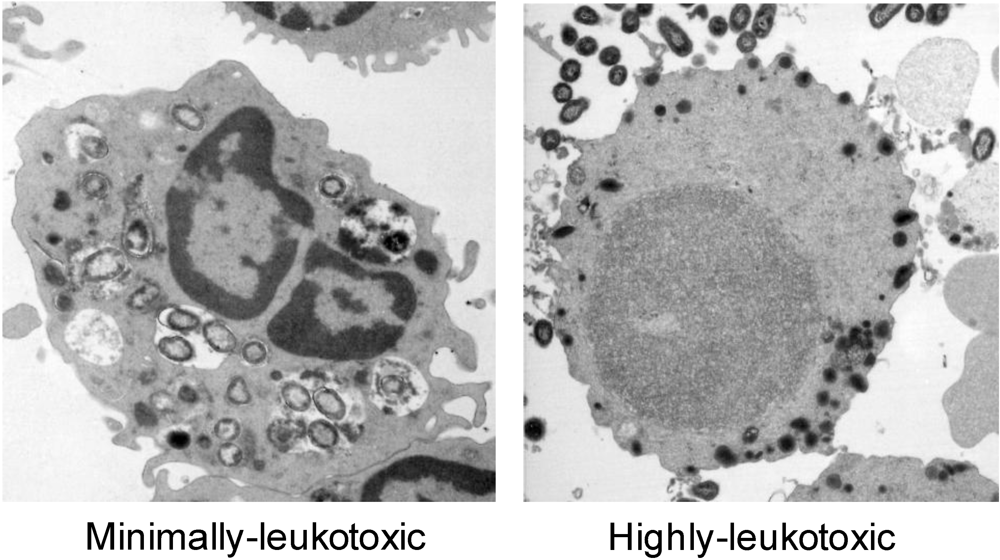
6.2. Lymphocytes
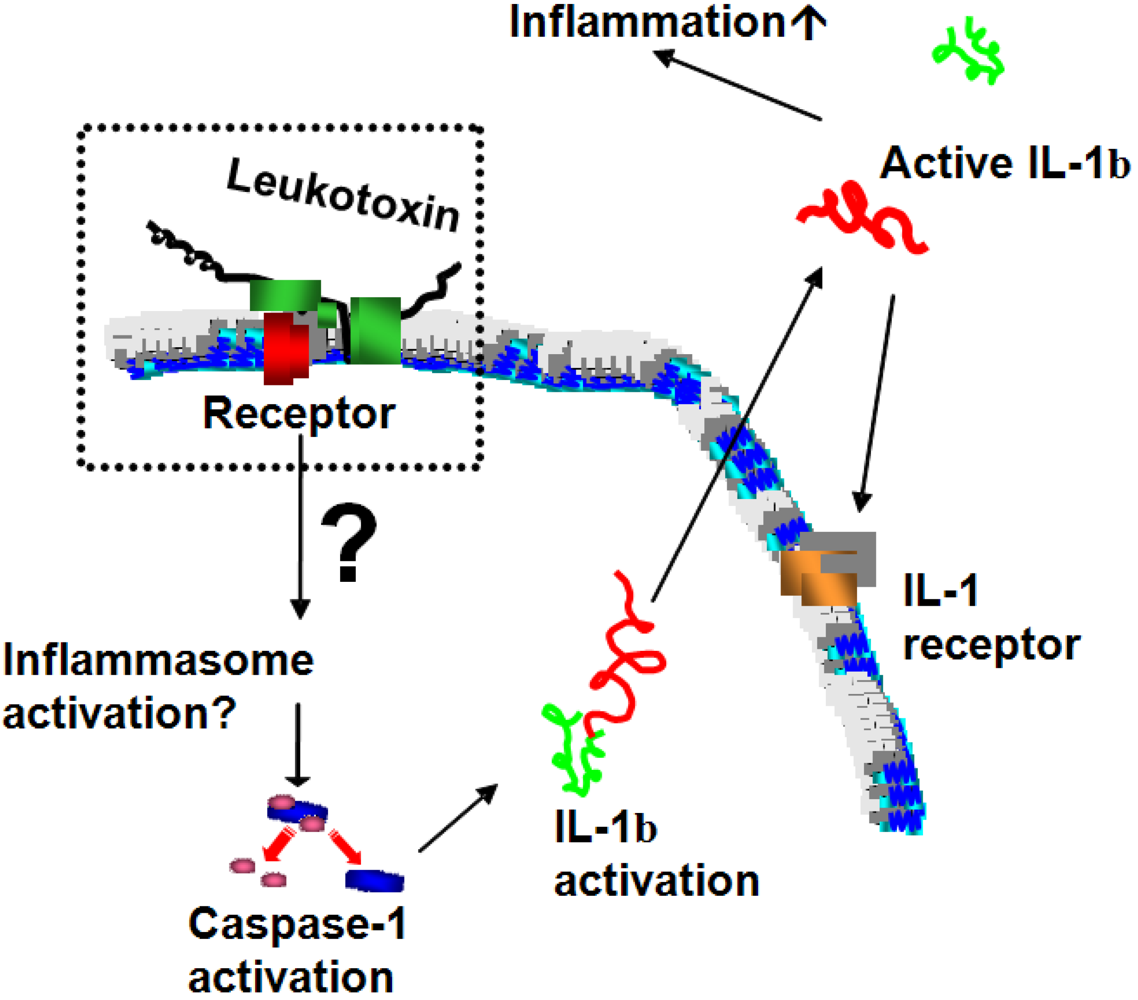
6.3. Monocytes/Macrophages
6.4. Erythrocytes
7. Acquired Humoral Immune Response to LtxA
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Henderson, B.; Ward, J.M.; Ready, D. Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans: a triple A* periodontopathogen? Periodontol. 2000 2010, 54, 78–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinane, D.; Bouchard, P. Group E of the European Workshop on Periodontology, Periodontal diseases and health: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Haubek, D. The highly leukotoxic JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: evolutionary aspects, epidemiology and etiological role in aggressive periodontitis. APMIS 2010, 118, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, D.H.; Kaplan, J.B.; Kachlany, S.C.; Schreiner, H.C. How we got attached to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: a model for infectious diseases. Periodontol. 2000 2006, 42, 114–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darveau, R.P. Periodontitis: a polymicrobial disruption of host homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 481–490. [Google Scholar]
- Pihlstrom, B.C.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Johnson, D.W. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005, 366, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Berezow, A.B.; Darveau, R.P. Microbial shift and periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000 2011, 55, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Mattsson, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Johansson, A. Cell cycle arrest of human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: involvement of the cytolethal distending toxin. Acta Physiol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2004, 112, 674–685. [Google Scholar]
- Lally, E.T.; Hill, R.B.; Kieba, I.R.; Korostoff, J. The interaction between RTX toxins and target cells. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhartová, I.; Bumba, L.; Mašín, J.; Basler, M.; Osička, R.; Kamanová, J.; Procházková, K.; Adkins, I.; Hejnová-Holubová, J.; Sadílková, L.; Morová, J.; Šebo, P. RTX proteins: a highly diverse family secreted by a common mechanism. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 1076–1112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kachlany, S.C. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin: from threat to therapy. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambon, J.J.; Slots, J.; Genco, R.J. Serology of oral Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and serotype distribution in human periodontal disease. Infect. Immun. 1983, 41, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brogan, J.M.; Lally, E.T.; Poulsen, K.; Kilian, M.; Demuth, D.R. Regulation of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin expression: Analysis of the promoter regions of leukotoxic and minimally leukotoxic strains. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Nishihara, T.; Demuth, D.R.; Ishikawa, I. A novel insertion sequence increases the expression of leukotoxicity in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans clinical isolates. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Hänström, L.; Kalfas, S. Inhibition of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxicity by bacteria from the subgingival flora. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 15, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubek, D.; Ennibi, O.K.; Poulsen, K.; Vaeth, M.; Poulsen, S.; Kilian, M. Risk of aggressive periodontitis in adolescent carriers of the JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans in Morocco: a perspective longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2008, 371, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, R.; Lagervall, M.; Höglund-Aberg, C.; Johansson, A.; Haubek, D. Detection of the highly leucotoxic JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in members of a Caucasian family living in Sweden. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haubek, D.; Poulsen, K.; Kilian, M. Microevolution and patterns of dissemination of the JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3080–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasteurellaceae: Biology, Genomics and Molecular Aspects; Kuhnert, P.; Christensen, H. (Eds.) Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2008.
- Crosby, J.A.; Kachlany, S.C. TdeA, a TolC-like protein required for toxin and drug export in Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans. Gene 2007, 388, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallant, C.V.; Sedic, M.; Chicoine, E.A.; Ruiz, T.; Mintz, K.P. Membrane morphology and leukotoxin secretion are associated with a novel membrane protein of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 5972–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthold, P.; Forti, D.; Kieba, I.R.; Rosenbloom, J.; Taichman, N.S.; Lally, E.T. Electron immunocytochemical localization of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1992, 7, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Kowashi, Y.; Demuth, D.R. Outer membrane-like vesicles secreted by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans are enriched in leukotoxin. Microb. Pathog. 2002, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lally, E.T.; Golub, E.E.; Kieba, I.R.; Taichman, N.S.; Rosenbloom, J.; Rosenbloom, J.C.; Gibson, C.W.; Demuth, D.R. Analysis of the Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin gene. Delineation of unique features and comparison to homologous toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 15451–15456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohta, H.; Kato, K.; Kokeguchi, S.; Hara, H.; Fukui, K.; Murayama, Y. Nuclease-sensitive binding of an Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin to the bacterial cell surface. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 4599–4605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohta, H.; Hara, H.; Fukui, K.; Kurihara, H.; Murayama, Y.; Kato, K. Association of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin with nucleic acids on the bacterial cell surface. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4878–4884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Claesson, R.; Hänström, L.; Kalfas, S. Serum-mediated release of leukotoxin from the cell surface of the periodontal pathogen Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2003, 111, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachlany, S.C.; Fine, D.H.; Figurski, D.H. Secretion of RTX leukotoxin by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6094–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brage, M.; Holmlund, A.; Johansson, A. Humoral immune response to Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. J. Periodontal Res. 2011, 46, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Claesson, R.; Hänström, L.; Sandström, G.; Kalfas, S. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte degranulation induced by leukotoxin from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J. Periodontal Res. 2000, 35, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Claesson, R.; Belibasakis, G.; Makoveichuk, E.; Hänström, L.; Olivecrona, G.; Sandström, G.; Kalfas, S. Protease inhibitors, the responsible components for the serum-dependent enhancement of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxicity. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2001, 109, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balashova, N.V.; Park, D.H.; Patel, J.K.; Figurski, D.H.; Kachlany, S.C. Interaction between leukotoxin and Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase in Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4490–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haar, S.F.; Hiemstra, P.S.; van Steenbergen, M.T.; Everts, V.; Beertsen, W. Role of polymorphonuclear leukocyte-derived serine proteinases in defense against Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5284–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, W.P.; Tsai, C.C.; Baehni, P.C.; Genco, R.J.; Taichman, N.S. Leukotoxic effects of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Modulation by serum components. J. Periodontal Res. 1981, 16, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraig, E.; Dailey, T.; Kolodrubetz, D. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: homology to the alpha-hemolysin/leukotoxin gene family. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lally, E.T.; Kieba, I.R; Golub, E.E.; Lear, J.D.; Tanaka, J.C. Structure/function Aspects of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. J. Periodontol. 1996, 67, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, R.A. RTX toxin structure and function: a story of numerous anomalies and few analogies in toxin biology. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 257, 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Balashova, N.V.; Shah, C.; Patel, J.K.; Megalla, S.; Kachlany, S.C. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans LtxC is required for leukotoxin activity and initial interaction between toxin and host cells. Gene 2009, 443, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, P.; Packman, L.C.; Koronakis, V.; Hughes, C. Fatty acylation of two internal lysine residues required for the toxic activity of Escherichia coli hemolysin. Science 1994, 266, 1992–1996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lally, E.T.; Golub, E.E.; Kieba, I.R. Identification and immunological characterization of the domain of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin that determines its specificity for human target cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 31289–31295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lally, E.T.; Kieba, I.R.; Sato, A.; Green, C.L.; Rosenbloom, J.; Korostoff, J.; Wang, J.F.; Shenker, B.J.; Ortlepp, S.; Robinson, M.K.; et al. RTX toxins recognize a beta2 integrin on the surface of human target cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30463–30469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Takahashi, K.; Ohta, H.; Kurihara, H.; Fukui, K.; Murayama, Y.; Taniguchi, S. Effect of Ca2+ on the binding of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin and the cytotoxicity to promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1993, 29, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lear, J.D.; Karakelian, D.; Furblur, U.; Lally, E.T.; Tanaka, J.C. Conformational studies of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin: partial denaturation enhances toxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1476, 350–362. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Kittichotirat, W.; Si, Y.; Bumgarner, R. Genome sequence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype c strain D11S-1. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 7378–7379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dileepan, T.; Kachlany, S.C.; Balashova, N.V.; Patel, J.; Maheswaran, S.K. Human CD18 is the functional receptor for Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4851–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieba, I.R.; Fong, K.P.; Tang, H.Y.; Hoffman, K.E.; Speicher, D.W.; Klickstein, L.B.; Lally, E.T. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin requires beta-sheets 1 and 2 of the human CD11a beta-propeller for cytotoxicity. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, K.P.; Pacheco, C.M.; Otis, L.L.; Baranwal, S.; Kieba, I.R.; Harrison, G.; Hersh, E.V.; Boesze-Battaglia, K.; Lally, E.T. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin requires lipid microdomains for target cell cytotoxicity. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dustin, M.L.; Bivona, T.G.; Philips, M.R. Membranes as messengers in T cell adhesion signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Shimaoka, M.; Xiao, T.; Liu, J.H.; Yang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Jun, C.D.; McCormack, A.; Zhang, R.; Joachimiak, A.; Takagi, J.; et al. Structures of the alpha L I domain and its complex with ICAM-1 reveal a shape-shifting pathway for integrin regulation. Cell 2003, 112, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baehni, P.; Tsai, C.C.; McArthur, W.P.; Hammond, B.F.; Taichman, N.S. Interaction of inflammatory cells and oral microorganisms. VIII. Detection of leukotoxic activity of a plaque-derived gram-negative microorganism. Infect. Immun. 1979, 24, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.C.; McArthur, W.P.; Baehni, P.C.; Hammond, B.F.; Taichman, N.S. Extraction and partial characterization of a leukotoxin from a plaque-derived Gram-negative microorganism. Infect. Immun. 1979, 25, 427–439. [Google Scholar]
- Taichman, N.S.; Dean, R.T.; Sanderson, C.J. Biochemical and morphological characterization of the killing of human monocytes by a leukotoxin derived from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 1980, 28, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mangan, D.F.; Taichman, N.S.; Lally, E.T.; Wahl, S.M. Lethal effects of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin on human T lymphocytes. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 3267–3272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balashova, N.V.; Crosby, J.A.; Al Ghofaily, L.; Kachlany, S.C. Leukotoxin confers beta-hemolytic activity to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kantarci, A.; van Dyke, T.E. Resolution of inflammation in periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Kantarci, A.M.; Oyaizu, K.; van Dyke, T.E. Neutrophil-mediated tissue injury in periodontal diseasepathogenesis: findings from localized aggressive periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lamster, I.B.; Novak, M.J. Host mediators in gingival crevicular fluid: implications for the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1992, 3, 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, A.; Sandström, G.; Claesson, R.; Hanström, L.; Kalfas, S. Anaerobic neutrophil-dependent killing of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in relation to the bacterial leukotoxicity. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2000, 108, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, G.; Wahlin, Y.B.; Johansson, A.; Olsson, A.; Eriksson, T.; Claesson, R.; Hänström, L.; Henter, J.I. Periodontal disease in patients from the original Kostmann family with severe congenital neutropenia. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 744–751. [Google Scholar]
- Claesson, R.; Johansson, A.; Belibasakis, G.; Hanström, L.; Kalfas, S. Release and activation of matrix metalloproteinase 8 from human neutrophils triggered by the leukotoxin of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J. Periodontal Res. 2002, 37, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pütsep, K.; Carlsson, G.; Boman, H.G.; Andersson, M. Deficiency of antibacterial peptides in patients with morbus Kostmann: an observation study. Lancet 2002, 360, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, D.L.; Berthold, P.; Taichman, N.S. Killing of human myelomonocytic leukemia and lymphocytic cell lines by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabie, G.; Lally, E.T.; Shenker, B.J. Immunosuppressive properties of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shenker, B.J.; Vitale, L.A.; Keiba, I.; Harrison, G.; Berthold, P.; Golub, E.; Lally, E.T. Flow cytometric analysis of the cytotoxic effects of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin on human natural killer cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 55, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelk, P.; Johansson, A.; Claesson, R.; Hanstrom, L.; Kalfas, S. Caspase 1 involvement in human monocyte lysis induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4448–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korostoff, J.; Wang, J.F.; Kieba, I.; Miller, M.; Shenker, B.J.; Lally, E.T. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin induces apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 4474–4483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kinane, D.F.; Lappin, D.F. Immune processes in periodontal disease: a review. Ann. Periodontol. 2002, 7, 62–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlrich, E.; Cullinan, M.; Seymour, G. The immunopathogenesis of periodontal disease. Aust. Dent. J. 2009, 54, S2–S10. [Google Scholar]
- Garlet, G.P. Destructive and protective roles of cytokines in periodontitis: a re-appraisal from host defense and tissue destruction viewpoints. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Califano, J.V.; Pace, B.E.; Gunsolley, J.C.; Schenkein, H.A.; Lally, E.T.; Tew, J.G. Antibody reactive with Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin in early-onset periodontitis patients. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1997, 12, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello, C.A. Anti-inflammatory Agents: Present and Future. Cell 2010, 140, 935–950. [Google Scholar]
- Latz, E. The inflammasomes: mechanisms of activation and function. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kelk, P.; Abd, H.; Claesson, R.; Sandström, G.; Sjöstedt, A.; Johansson, A. Cellular and molecular response of human macrophages exposed to Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, E.A.; Leaf, I.A.; Treuting, P.M.; Mao, D.P.; Dors, M.; Sarkar, A.; Warren, S.E.; Wewers, M.D.; Aderem, A. Caspase-1-induced pyroptosis is an innate immune effector mechanism against intracellular bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Kelk, P.; Claesson, R.; Hanstrom, L.; Lerner, U.H.; Kalfas, S.; Johansson, A. Abundant secretion ofbioactive interleukin-1beta by human macrophages induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelk, P.; Claesson, R.; Chen, C.; Sjostedt, A.; Johansson, A. IL-1beta secretion induced by Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans is mainly caused by the leukotoxin. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 298, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissmann, F.; Manz, M.G.; Jung, S.; Sieweke, M.H.; Merad, M.; Ley, K. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science 2010, 327, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1beta and the autoinflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2467–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Kimizuka, R.; Miura, T.; Okuda, K. Characterization of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans hemolysin. Microbiol. Immunol. 1996, 40, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haubek, D.; Dirienzo, J.M.; Tinoco, E.M.; Westergaard, J.; López, N.J.; Chung, C.P.; Poulsen, K.; Kilian, M. Racial tropism of a highly toxic clone of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans associated with juvenile periodontitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3037–3042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebersole, J.L. Humoral immune responses in gingival crevice fluid: local and systemic implications. Periodontol. 2000 2003, 31, 135–166. [Google Scholar]
- Taubman, M.A.; Valverde, P.; Han, X.; Kawai, T. Immune response: the key to bone resorption in periodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y.T. The role of acquired immunity and periodontal disease progression. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2003, 14, 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Källestål, C.; Matsson, L.; Persson, S. Proximal attachment loss in Swedish adolescents. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1991, 18, 760–765. [Google Scholar]
- Sjödin, B.; Arnrup, K.; Matsson, L.; Wranne, L.; Carlsson, J.; Hänström, L. Periodontal and systemic findings in children with marginal bone loss in the primary dentition. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 214–224. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, A.; Eriksson, M.; Åhrén, A.-M.; Boman, K.; Jansson, J.H.; Hallmans, G.; Johansson, I. Prevalence of systemic immunoreactivity to Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin in relation to the incidence of myocardial infarction. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Johansson, I.; Eriksson, M.; Ahrén, A.M.; Hallmans, G.; Stegmayr, B. Systemic antibodies to the leukotoxin of the oral pathogen Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans correlate negatively with stroke in women. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2005, 20, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deas, D.E.; Mealey, B.L. Response of chronic and aggressive periodontitis to treatment. Periodontol. 2000 2010, 53, 154–166. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Johansson, A. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin: A Powerful Tool with Capacity to Cause Imbalance in the Host Inflammatory Response. Toxins 2011, 3, 242-259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3030242
Johansson A. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin: A Powerful Tool with Capacity to Cause Imbalance in the Host Inflammatory Response. Toxins. 2011; 3(3):242-259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3030242
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohansson, Anders. 2011. "Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin: A Powerful Tool with Capacity to Cause Imbalance in the Host Inflammatory Response" Toxins 3, no. 3: 242-259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3030242
APA StyleJohansson, A. (2011). Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin: A Powerful Tool with Capacity to Cause Imbalance in the Host Inflammatory Response. Toxins, 3(3), 242-259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3030242