Toxins and Secretion Systems of Photorhabdus luminescens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Toxins of Photorhabdus luminescens
2.1. Toxin Complexes (Tcs)
2.2. Photorhabdus Insect Related (Pir) Toxins
2.3. “Makes Caterpillars Floppy” Toxins
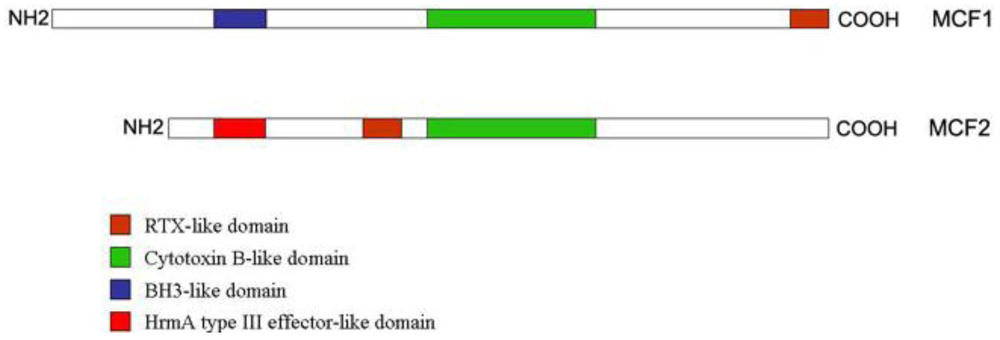
2.4. Photorhabdus Virulence Cassettes (PVC)
3. Secretion Systems and Photorhabdus luminescens
3.1. One Step Secretion Systems
3.1.1. Type I Secretion System
3.1.2. Type III Secretion System
| Components | NCBI Accession Number | Number of amino acids | Gene locus on P. luminescens chromosome | Identity (%) | Function/Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC 1 | NP_927979 | 711 aa | 726,383–728,518 | 57% (Bordetella pertussis CyaB) | Hypothetical protein similar to toxin secretion ATP-binding protein |
| MFP 1 | NP_927980 | 471 aa | 728,660–730,075 | 36% (Bordetella pertussis CyaD) | Hypothetical protein similar to hemolysin export system MFP HlyD of E. coli |
| ABC 2 | NP_930357 | 706 aa | 3,664,486–3,666,606 | 46.4% (Bordetella pertussis CyaB) | Hypothetical protein similar to toxin secretion transporter |
| NP_930359 | 719 aa | 3,667,994–3,670,153 | 44.4% (Bordetella pertussis CyaB) | Hypothetical protein similar to toxin secretion transporter | |
| MFP 2 | NP_93058 | 462 aa | 3,666,606–3,667,994 | 36% (Bordetella pertussis CyaD) | Hypothetical protein similar to toxin secretion transporter (MFP) |
| ABC 3 | NP_928641 | 716 aa | 1,546,913–1,549,063 | 42.3% (Escherichia coli HlyB) | Hypothetical protein similar to unknown protein VC1446 of V. cholerae, probable RTX toxin ABC transporter protein |
| NP_928643 | 701 aa | 1,550,414–1,552,519 | 41.8% (Escherichia coli HlyB) | RtxB (ABC transporter) | |
| MFP 3 | NP_928642 | 451 aa | 1,549,066–1,550,421 | 32.8% (Escherichia coli HlyD) | RTX toxin ABC transporter protein (MFP) RtxD |
| ABC 4 | NP_928002 | 576 aa | 754,786–756,516 | 70.4% (Serratia marcescens LipB) | ATP-binding protein PrtB |
| MFP 4 | NP_928003 | 444 aa | 756,577–757,911 | 62.7% (Serratia marcescens LipC) | MFP PrtC |
| TolC 1 | NP_931154 | 457 aa | 4,641,003–4,642,376 | 64.7% (Escherichia coli TolC) | Outer mebrane channel protein |
| TolC 2 | NP_928004 | 458 aa | 757,911–759,287 | 50.4% (Serratia marcescens LipD) | Outer membrane protein |
| TolC 3 | NP_929881 | 492 aa | 3,099,833–3,101,311 | 18.9% (Serratia marcescens LipD) | Hypothetical protein similar to outer membrane factor of ABC transport system |
3.1.3. Type IV Secretion System
3.1.4. Type VI Secretion System
3.2. Two Step Secretion Systems
3.2.1. IM Translocation
3.2.2. OM Translocation
3.2.2.1. Type II Secretion System
3.2.2.2. Type V Secretion System (Autotransporter Secretion System)
3.2.2.3. Two-Partner Secretion (TPS)
3.2.2.4. Chaperone-Usher Secretion (CU)
4. Conclusions
| Secretion System | # of putative systems identified |
|---|---|
| Type I | 6 |
| Type III | 2 |
| Type IV | 0 |
| Type VI | 4 |
| Secretion System | # of putative systems identified |
|---|---|
| Type II | 1 |
| Type V | 1 |
| TPS | 6 |
| Chaperone-Usher | 8 |
References
- Joyce, S.A.; Watson, R.J.; Clarke, D.J. The regulation of pathogenicity and mutualism in Photorhabdus. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ffrench-Constant, R.; Waterfield, N.; Daborn, P.; Joyce, S.; Bennett, H.; Au, C.; Dowling, A.; Boundy, S.; Reynolds, S.; Clarke, D. Photorhabdus: Towards a functional genomic analysis of a symbiont and pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 26, 433–456. [Google Scholar]
- Forst, S.; Dowds, B.; Boemare, N.; Stackebrandt, E. Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus spp.: Bugs That Kill Bugs. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Bowen, D.J.; Fetherston, J.D.; Perry, R.D.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. The tc genes of Photorhabdus: A growing family. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, M.B.; Domek, J.M.; Gelman, D.B.; Hu, J.S. The broadly insecticidal Photorhabdus luminescens toxin complex a (Tca): Activity against the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, and sweet potato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. J. Insect. Sci. 2005, 5, 11. [Google Scholar]
- ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Dowling, A.; Waterfield, N.R. Insecticidal toxins from Photorhabdus bacteria and their potential use in agriculture. Toxicon 2007, 49, 436–451. [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard, J.; Waterfield, N.; Vohra, R.; ffrench-Constant, R. Human infection with Photorhabdus asymbiotica: An emerging bacterial pathogen. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrard, J.G.; McNevin, S.; Alfredson, D.; Forgan-Smith, R.; Fraser, N. Photorhabdus Species: Bioluminescent Bacteria as Emerging Human Pathogens? Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parkhill, J.; Wren, B.W.; Thomson, N.R.; Titball, R.W.; Holden, M.T.G.; Prentice, M.B.; Sebaihia, M.; James, K.D.; Churcher, C.; Mungall, K.L.; Baker, S.; Basham, D.; Bentley, S.D.; Brooks, K.; Cerdeno-Tarraga, A.M.; Chillingworth, T.; Cronin, A.; Davies, R.M.; Davis, P.; Dougank, G.; Feltwell, T.; Hamlin, N.; Holroyd, S.; Jagels, K.; Karlyshev, A.V.; Leather, S.; Moule, S.; Oyston, P.C.F.; Quail, M.; Rutherford, K.; Simmonds, M.; Skelton, J.; Stevens, K.; Whitehead, S.; Barrell, B.G. Genome sequence of Yersinia pestis, the causative agent of plague. Nature 2001, 413, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- Duchaud, E.; Rusniok, C.; Frangeul, L.; Buchrieser, C.; Givaudan, A.; Taourit, S.; Bocs, S.; Boursaux-Eude, C.; Chandler, M.; Charles, J.-F.; Dassa, E.; Derose, R.; Derzelle, S.; Freyssinet, G.; Gaudriault, S.; Medigue, C.; Lanois, A.; Powell, K.; Siguier, P.; Vincent, R.; Wingate, V.; Zouine, M.; Glasier, P.; Boemare, N.; Danchin, A.; Kunst, F. The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Daborn, P.J.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Genomic islands in Photorhabdus. Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Daborn, P.J.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Insect pathogenicity islands in the insect pathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus. Physiol. Entomol. 2004, 29, 240–250. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Dowling, J.; Gerike, U.; ffrench-Contant, R.H.; Waterfield, N.R. Photorhabdus virulence cassettes confer injectable insecticidal activity against the wax moth. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2254–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Bowen, D.J. Novel insecticidal toxins from nematode-symbiotic bacteria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.; Rocheleau, T.A.; Blackburn, M.; Andreev, O.; Golubeva, E.; Bhartia, R.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Insecticidal Toxins from the Bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Science 1998, 280, 2129–2132. [Google Scholar]
- ffrench-Constant, R.; Bowen, D. Photorhabdus toxins: Novel biological insecticides. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.J.; Ensign, J.C. Purification and characterization of a high-molecular-weight insecticidal protein complex produced by the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3029–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, V.B.; Ellar, D.J. Expression and insecticidal activity of Yersinia pseudotubeculosis and Photorhabdus luminescens toxin complex proteins. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar]
- ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Waterfield, N.; Burland, V.; Perna, N.T.; Daborn, P.J.; Bowen, D.J.; Blattner, F.R. A Genomic sample sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens W14: Potential implications for virulence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3310–3329. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, M.; Golubeva, E.; Bowen, D.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. A novel insecticidal toxin from Photorhabdus luminescens, Toxin complex a (Tca), and its histopathological effects on the midgut of Manduca sexta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3036–3041. [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield, N.; Dowling, A.; Sharma, S.; Daborn, P.J.; Potter, U.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Oral toxicity of Photorhabdus luminescens W14 toxin complexes in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5017–5024. [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield, N.; Hares, M.; Yang, G.; Dowling, A.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Potentiation and cellular phenotypes of the insecticidal toxin complexes of Photorhabdus bacteria. Cell Microbiol. 2005, 7, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, P.; Waterfield, N.R.; Crossman, L.; Corton, G.; Sanchez-Contreras, M.; Vlisidou, I.; Barron, A.; Bignell, A.; Clark, L.; Ormond, D.; Mayho, M.; Bason, N.; Smith, F.; Simmonds, M.; Churcher, C.; Harris, D.; Thompson, N.R.; Quail, M.; Parkhill, J.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Comparative genomics of the emerging human pathogen Photorhabdus asymbiotica with the insect pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 302. [Google Scholar]
- Ahantarig, A.; Chantawat, N.; Waterfield, N.R.; ffrench-Contant, R.; Kittayapond, P. PirAB toxin from Photorhabdus asymbiotica as a larvicide against dengue vectors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4627–4629. [Google Scholar]
- Daborn, P.J.; Waterfield, N.; Silva, C.P.; Au, C.P.Y.; Sharma, S.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. A single Photorhabdus gene, makes caterpillars floppy (mcf), allows Escherichia coli to persist within and kill insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10742–10747. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, A.J.; Daborn, P.J.; Waterfield, N.R.; Wang, P.; Streuli, C.H.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. The insecticidal toxin Makes caterpillars floppy (Mcf) promotes apoptosis in mammalian cells. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Daborn, P.J.; Dowling, A.J.; Yang, G.; Hares, M.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. The insecticidal toxin Makes caterpillars floppy 2 (Mcf2) shows similarity to HrmA, an avirulence protein from a plant pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 229, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, M.R.H.; Glare, T.R.; Jackson, T.A. Cloning Serratia entomophila antifeeding genes—A putative defective prophage against the grass grub Costelytra zealandica. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5116–5128. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, M.R.H.; Glare, T.R.; Jackson, T.A.; Ronson, C.W. Plasmid-located pathogenicity determinants of Serratia entomophila, the causal agent of amber disease of grass grub, show similarity to the insecticidal toxins of Photorhabdus luminescens. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5127–5138. [Google Scholar]
- Kostakioti, M.; Newman, C.L.; Thanassi, D.G.; Stathopoulos, C. Mechanisms of protein export across the bacterial outer membrane. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4306–4314. [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos, C.; Yen, Y.; Tsang, C.; Cameron, T. Protein Secretion in Bacterial Cells. In Bacterial Physiology: A Molecular Approach; Charoud, W.E., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 129–154. [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire, P. Type I in gram-negative bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1694, 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, I.B.; Schmitt, L.; Young, J. Type 1 protein secretion in bacteria, the ABC-transporter dependent pathway. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2005, 22, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis, V.; Eswaran, J.; Hughes, C. The Type I export system. In Bacterial Protein Toxins; Burns, D.L., Barbier, J.T., Iglewski, B.H., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington DC, USA, 2003; pp. 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitseva, J.; Jenewein, S.; Oswald, S.; Jumpertz, I.; Holland, I.B.; Schmitt, L. A molecular understanding of the catalytic cycle of the nucleotide-binding domain of the ABC transporter HlyB. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 990–995. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P. Process of protein transport by the type III secretion system. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 771–795. [Google Scholar]
- Hueck, C. Type III secretion systems in bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 379–433. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis, G.R. Type III secretion: a bacterial device for close combat with cells of their eukaryotic host. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 681–693. [Google Scholar]
- Troisfontaines, P.; Cornelis, G.R. Type III secretion: more systems than you think. Physiology (Bethesda) 2005, 20, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christie, P.J.; Atmakuri, K.; Krishnamoorthy, V.; Jakubowski, S.; Cascales, E. Biogenesis, architecture and function of bacterial type IV secretion systems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 59, 451–485. [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne, J.-P.; Botella, E.; O' Callaghan, D. Type IV secretion system and their effectors: An update. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 2006, 54, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christie, P.J. Type IV secretion: The Agrobacterium VirB/D4 and related conjugation systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1694, 219–234. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, P.J.; Vogel, J.P. Bacterial type IV secretion: Conjugation systems adapted to deliver effector molecules to host cells. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, D.L. Type IV transporters of pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bingle, L.E.H.; Bailey, C.M.; Pallen, M.J. Type VI secretion: A beginner's guide. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Filloux, A.; Hachani, A.; Bleves, S. The bacterial type VI secretion machine: Yet another player for protein transport across membranes. Microbiology 2008, 154, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Mougous, J.D.; Cuff, M.E.; Raunser, S.; Shen, A.; Zhou, M.; Gifford, C.A.; Goodman, A.L.; Joachimiak, G.; Ordonez, C.L.; Lory, S.; Walz, T.; Joachimiak, A.; Mekalanos, J.J. A virulence locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a protein secretion apparatus. Science 2006, 312, 1526–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Pukatzki, S.; Ma, A.T.; Sturtevant, D.; Krastins, B.; Sarracino, D.; Nelson, W.C.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Mekalanos, J.J. Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2006, 103, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Leung, K.Y. Dissection of a type VI secretion system in Edwardsiella tarda. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Economou, A. Bacterial protein translocase: A unique molecular machine with an army of substrates. FEBS Lett. 2000, 476, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, T.; Berks, B.C. Moving folded proteins across the bacterial cell membrane. Microbiology 2003, 149, 547–556. [Google Scholar]
- Berks, B.C.; Sargent, F.; Palmer, T. The Tat protein export pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 35, 260–274. [Google Scholar]
- Berks, B.C.; Palmer, T.; Sargent, F. The Tat protein translocation pathway and its role in microbial physiology. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2003, 47, 187–254. [Google Scholar]
- Sandkvist, M. Biology of type II secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 271–283. [Google Scholar]
- Sandkvist, M. Type II secretion and pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3523–3535. [Google Scholar]
- Filloux, A. The underlying mechanisms of type II protein secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1694, 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos, C.; Hendrixson, D.R.; Thanassi, D.G.; Hultgren, S.J.; St.Geme, J.W., III; Curtiss, R., III. Secretion of virulence determinants by general secretory pathway in gram-negative bacteria: An evolving story. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, G.F.; Remaut, S.J.; Hultgren, S.J.; Waksman, G. Fiber assembly by the chaperone-usher pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1694, 259–267. [Google Scholar]
Supplementary Files
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodou, A.; Ankrah, D.O.; Stathopoulos, C. Toxins and Secretion Systems of Photorhabdus luminescens. Toxins 2010, 2, 1250-1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061250
Rodou A, Ankrah DO, Stathopoulos C. Toxins and Secretion Systems of Photorhabdus luminescens. Toxins. 2010; 2(6):1250-1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061250
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodou, Athina, Dennis O. Ankrah, and Christos Stathopoulos. 2010. "Toxins and Secretion Systems of Photorhabdus luminescens" Toxins 2, no. 6: 1250-1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061250
APA StyleRodou, A., Ankrah, D. O., & Stathopoulos, C. (2010). Toxins and Secretion Systems of Photorhabdus luminescens. Toxins, 2(6), 1250-1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2061250