Macula Densa Alleviates Shiga Toxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via CCN1-Mediated Renal Tubular Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
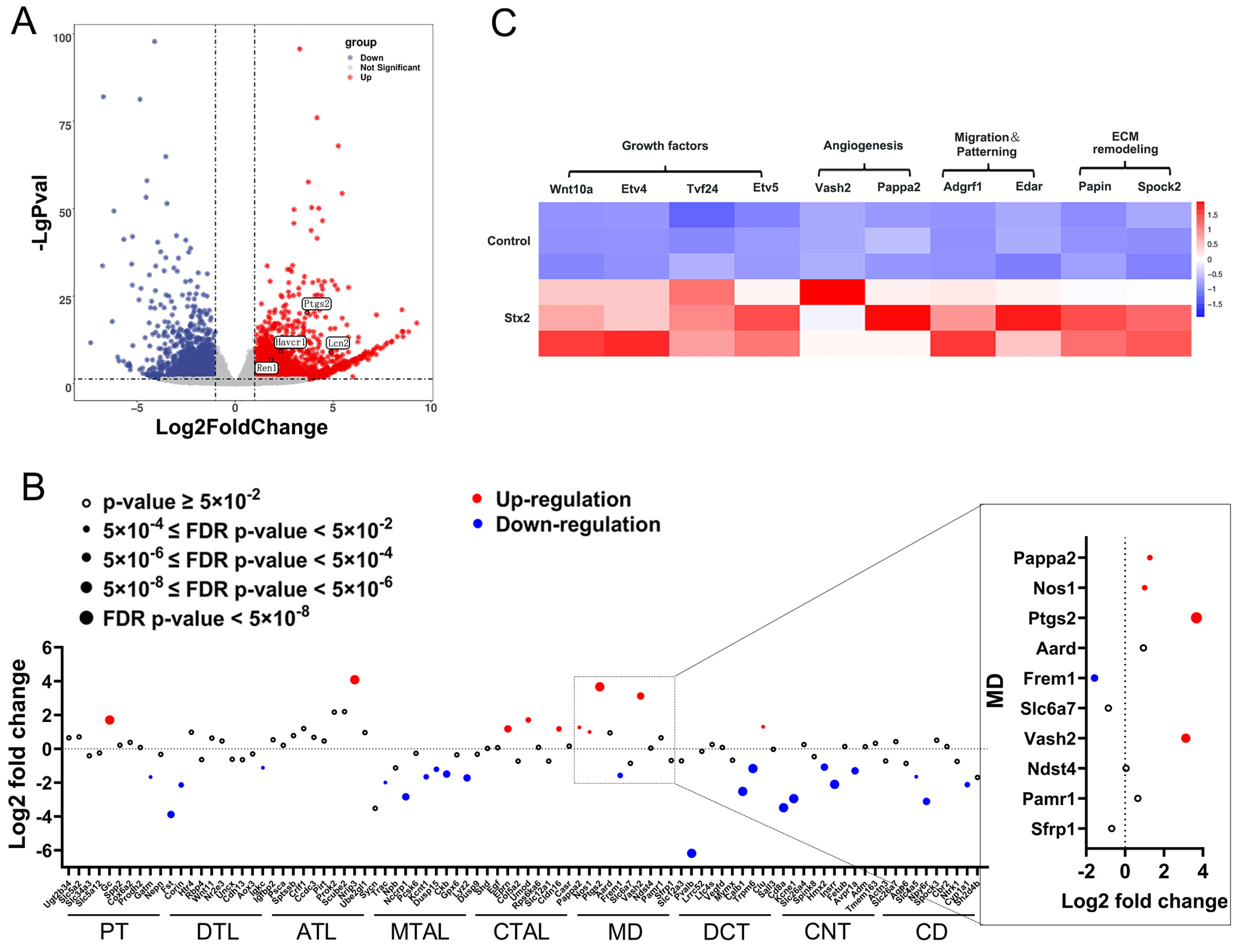
2.1. Macula Densa Apparatus Displays Transcriptional Signatures Associated with Renal Repair and Remodeling in Stx-Induced Renal Injury
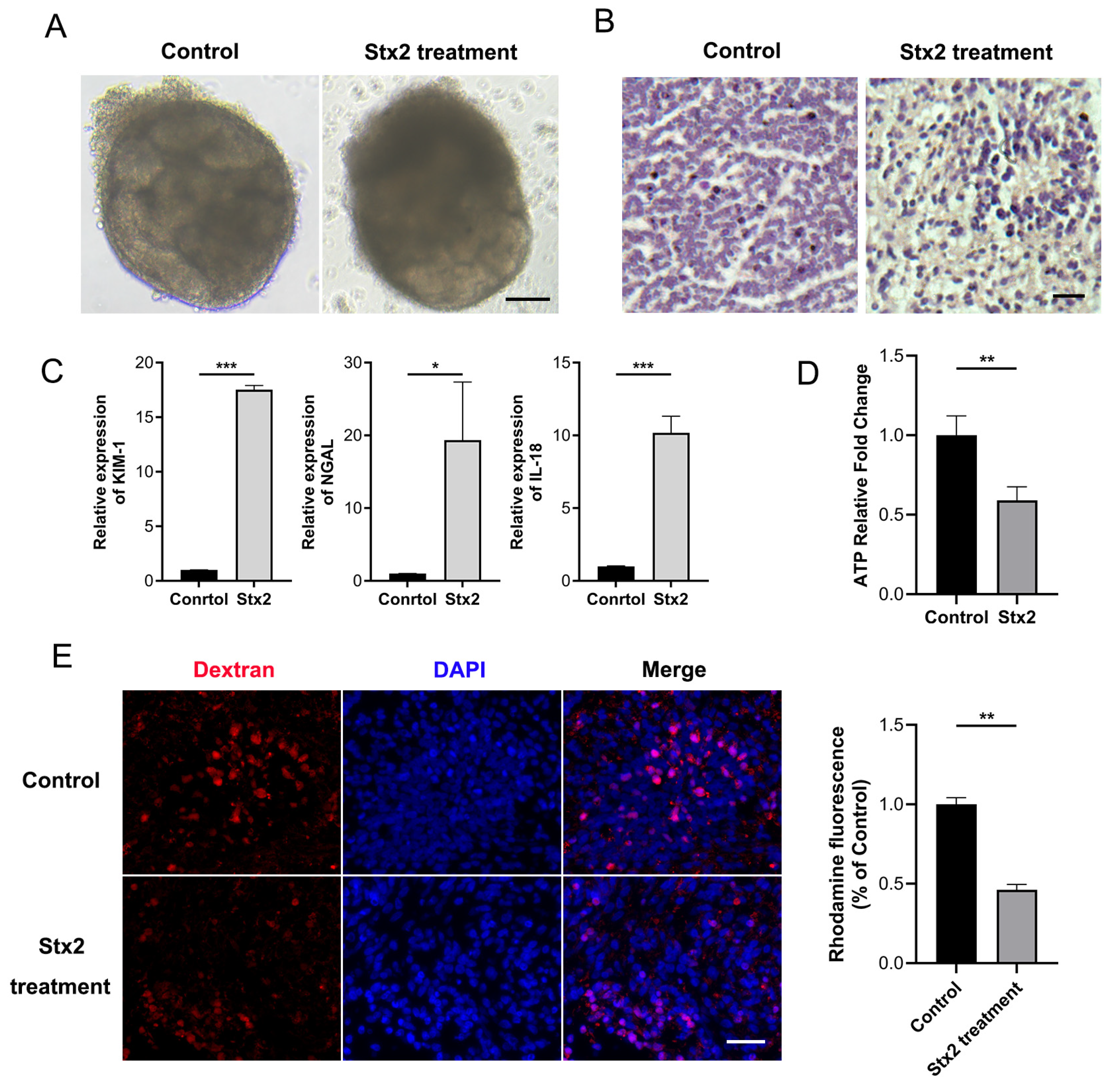
2.2. Stx Infection Induces Transcriptional Activation of Macula Densa-Derived Repair Factors in Human Renal Organoids
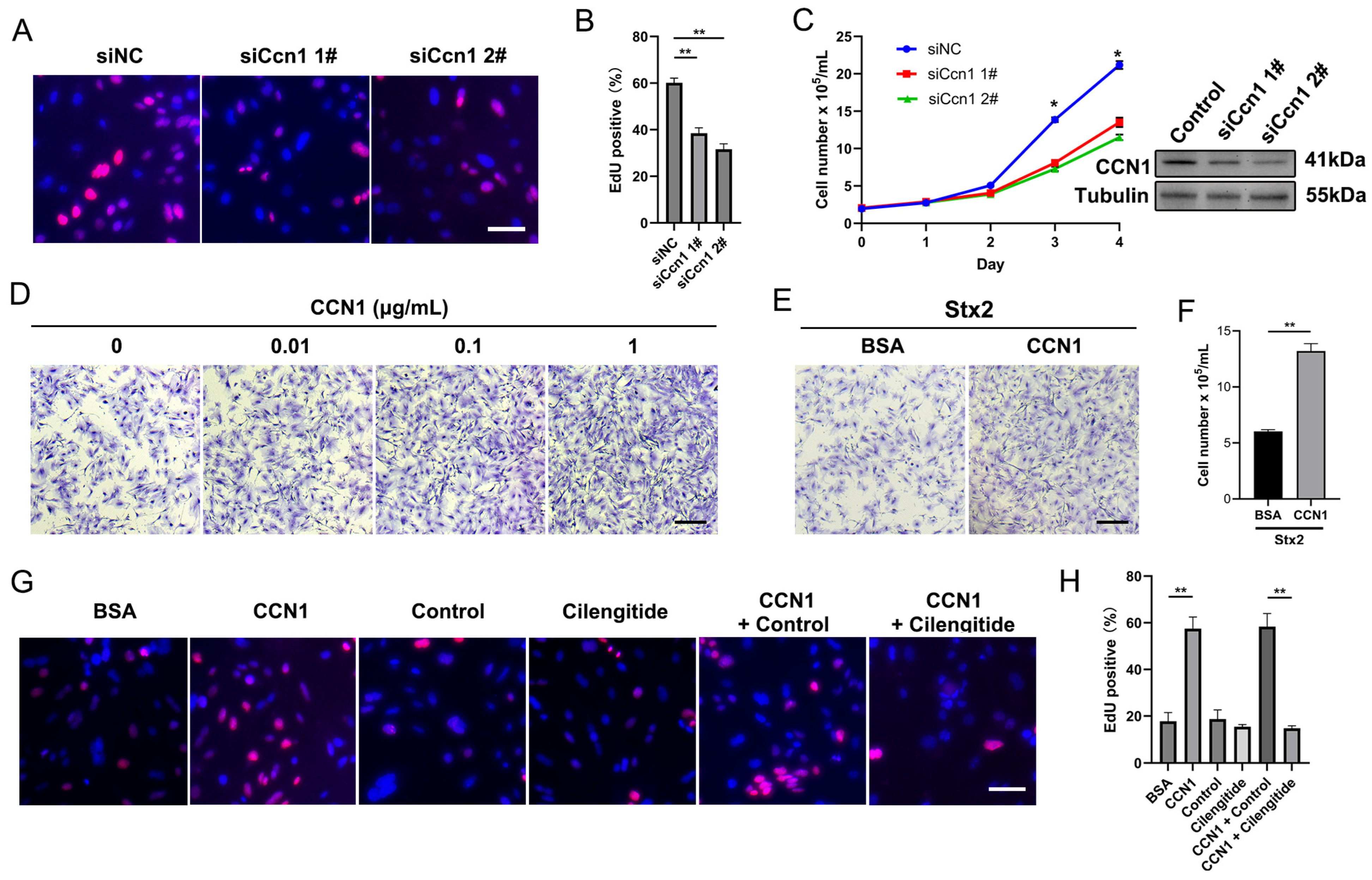
2.3. Macula Densa-Derived Niche Factor CCN1 Promotes the Proliferation and Regeneration of Stx-Injured RTECs
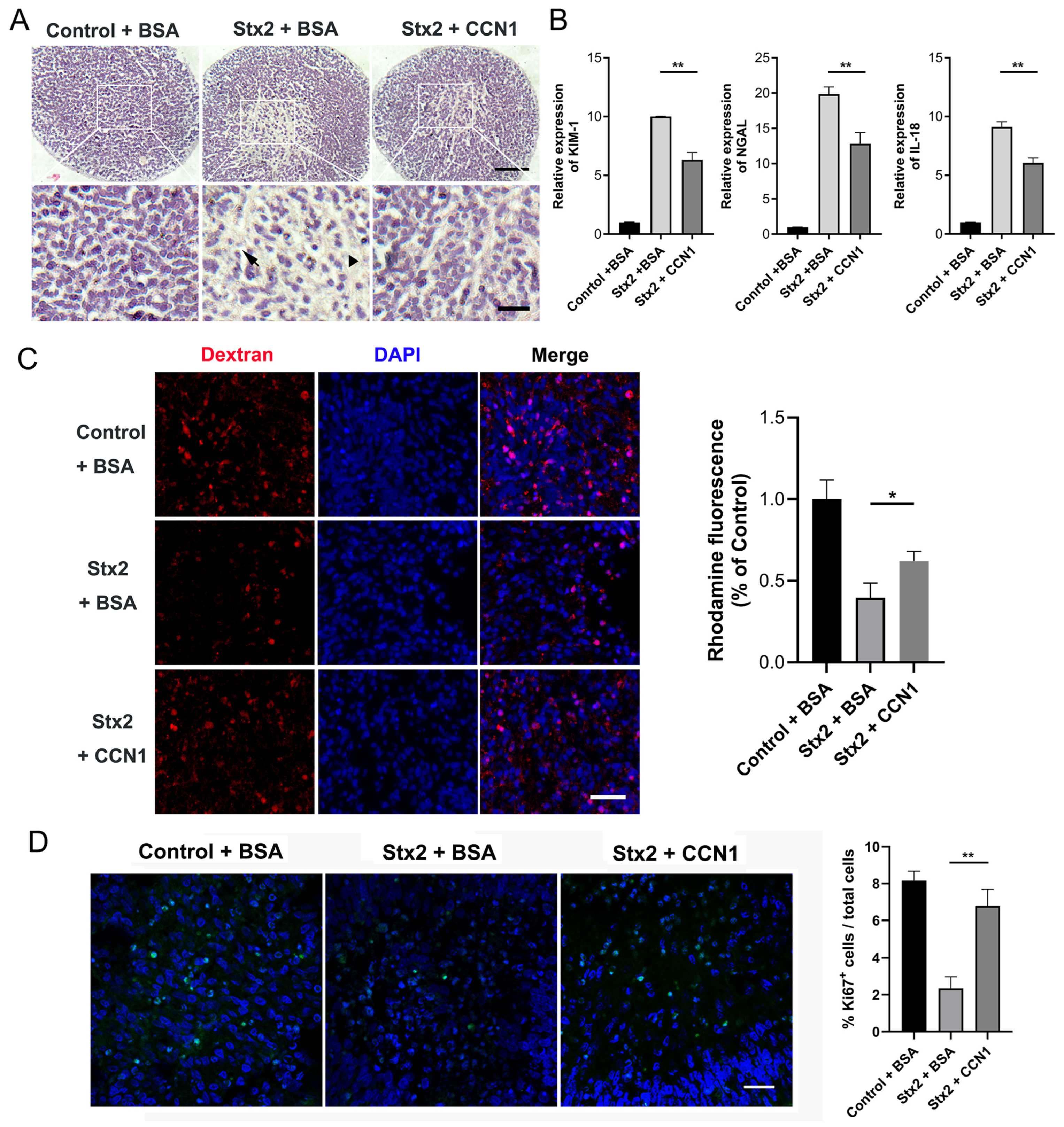
2.4. CCN1 Alleviates Stx2-Induced Renal Injury in Human Kidney Organoids
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Experimental Animal Group Design and Sample Collection
5.2. Human Kidney Organoids Culture
5.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR Assay)
5.4. Western Blot Analysis
5.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
5.6. Histological Analysis
5.7. Reabsorption Assay
5.8. ATP Quantification
5.9. Culture of Mouse Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
5.10. Transient Transfection
5.11. 5-Ethynyl-2′-Deoxyuridine (EdU) Assay
5.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Stx | Shiga toxin |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| STEC | Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli |
| HUS | Hemolytic uremic syndrome |
| Gb3 | Globotrihexosylceramide |
| RTEC | Renal tubular epithelial cell |
| MD | Macula densa |
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| hiPSCs | Human induced pluripotent stem cells |
| JGA | Juxtaglomerular apparatus |
References
- Alhadlaq, M.A.; Aljurayyad, O.I.; Almansour, A.; Al-Akeel, S.I.; Alzahrani, K.O.; Alsalman, S.A.; Yahya, R.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Hakami, M.A.; Alshahrani, S.D.; et al. Overview of pathogenic Escherichia coli, with a focus on Shiga toxin-producing serotypes, global outbreaks (1982–2024) and food safety criteria. Gut Pathog. 2024, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, M.; Bagga, A.; Sartain, S.E.; Smith, R.J.H. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2022, 400, 1722–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlen, S.; Dersch, P. Treatment Strategies for Infections with Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitz, W.J.C.; Bouwmeester, R.; van der Velden, T.; Goorden, S.; Licht, C.; van den Heuvel, L.; van de Kar, N. The Shiga Toxin Receptor Globotriaosylceramide as Therapeutic Target in Shiga Toxin E. coli Mediated HUS. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detzner, J.; Pohlentz, G.; Müthing, J. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and a Fresh View on Shiga Toxin-Binding Glycosphingolipids of Primary Human Kidney and Colon Epithelial Cells and Their Toxin Susceptibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porubsky, S.; Federico, G.; Müthing, J.; Jennemann, R.; Gretz, N.; Büttner, S.; Obermüller, N.; Jung, O.; Hauser, I.A.; Gröne, E.; et al. Direct acute tubular damage contributes to Shigatoxin-mediated kidney failure. J. Pathol. 2014, 234, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Moran, A.; Igarashi, P. Intrarenal cells, not bone marrow-derived cells, are the major source for regeneration in postischemic kidney. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, B.D.; Valerius, M.T.; Kobayashi, A.; Mugford, J.W.; Soeung, S.; Duffield, J.S.; McMahon, A.P.; Bonventre, J.V. Intrinsic epithelial cells repair the kidney after injury. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, B.D.; Czerniak, S.; DiRocco, D.P.; Hasnain, W.; Cheema, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Repair of injured proximal tubule does not involve specialized progenitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9226–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Gusella, G.L.; He, J.C. Epithelial proliferation and cell cycle dysregulation in kidney injury and disease. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Schmitt, R.; Israilova, M.; Nishio, H.; Cantley, L.G. Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via an endocrine effect. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2007, 18, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, D.B. Thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2014, 9, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chou, C.L.; Knepper, M.A. A Comprehensive Map of mRNAs and Their Isoforms across All 14 Renal Tubule Segments of Mouse. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2021, 32, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyarmati, G.; Shroff, U.N.; Riquier-Brison, A.; Kriz, W.; Kaissling, B.; Neal, C.R.; Arkill, K.P.; Ahmadi, N.; Gill, I.S.; Moon, J.Y.; et al. A new view of macula densa cell microanatomy. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2021, 320, F492–F504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Gomez, R.A.; Sequeira-Lopez, M.L.S. Renin Cells, from Vascular Development to Blood Pressure Sensing. Hypertension 2023, 80, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przepiorski, A.; Sander, V.; Tran, T.; Hollywood, J.A.; Sorrenson, B.; Shih, J.H.; Wolvetang, E.J.; McMahon, A.P.; Holm, T.M.; Davidson, A.J. A Simple Bioreactor-Based Method to Generate Kidney Organoids from Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutunea-Fatan, E.; Arumugarajah, S.; Suri, R.S.; Edgar, C.R.; Hon, I.; Dikeakos, J.D.; Gunaratnam, L. Sensing Dying Cells in Health and Disease: The Importance of Kidney Injury Molecule-1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2024, 35, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauer, S.; Sichler, O.; Obermüller, N.; Holzmann, Y.; Kiss, E.; Sobkowiak, E.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Geiger, H.; Mühl, H.; Hauser, I.A. IL-18 is expressed in the intercalated cell of human kidney. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striz, I.; Krasna, E.; Honsova, E.; Lacha, J.; Petrickova, K.; Jaresova, M.; Lodererova, A.; Bohmova, R.; Valhova, S.; Slavcev, A.; et al. Interleukin 18 (IL-18) upregulation in acute rejection of kidney allograft. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 99, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragas, N.; Qiu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Samstein, B.; Deng, S.X.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Viltard, M.; Yu, W.; Forster, C.S.; Gong, G.; et al. The Ngal reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to injury in real time. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyarmati, G.; Shroff, U.N.; Riquier-Brison, A.; Desposito, D.; Ju, W.; Stocker, S.D.; Izuhara, A.; Deepak, S.; Becerra Calderon, A.; Burford, J.L.; et al. Neuronally differentiated macula densa cells regulate tissue remodeling and regeneration in the kidney. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e174558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Chen, C.C.; Alpini, G.; Lau, L.F. CCN1 induces hepatic ductular reaction through integrin αvβ5-mediated activation of NF-κB. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1886–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Zhou, Y.; Suo, Y.; Liang, X.; Chai, B.; Duan, R.; Huang, X.; Li, Q. CCN1 accelerates re-epithelialization by promoting keratinocyte migration and proliferation during cutaneous wound healing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivam, M.; Jie, C.; Hamad, A.R.A. Renal tubular epithelial cells are constitutive non-cognate stimulators of resident T cells. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latzer, P.; Zelba, H.; Battke, F.; Reinhardt, A.; Shao, B.; Bartsch, O.; Rabsteyn, A.; Harter, J.; Schulze, M.; Okech, T.; et al. A real-world observation of patients with glioblastoma treated with a personalized peptide vaccine. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroff, U.N.; Gyarmati, G.; Izuhara, A.; Deepak, S.; Peti-Peterdi, J. A new view of macula densa cell protein synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2021, 321, F689–F704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, J.C.; Jones, N.L.; Ceponis, P.J.; Karmali, M.A.; Sherman, P.M. Escherichia coli shiga-like toxins induce apoptosis and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase via in vitro activation of caspases. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4669–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matussek, A.; Lauber, J.; Bergau, A.; Hansen, W.; Rohde, M.; Dittmar, K.E.; Gunzer, M.; Mengel, M.; Gatzlaff, P.; Hartmann, M.; et al. Molecular and functional analysis of Shiga toxin-induced response patterns in human vascular endothelial cells. Blood 2003, 102, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matise, I.; Sirinarumitr, T.; Bosworth, B.T.; Moon, H.W. Vascular ultrastructure and DNA fragmentation in swine infected with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Vet. Pathol. 2000, 37, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Lu, Z.; Li, F.; Shi, F.; Zhan, F.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Qin, Z. Escherichia coli induced ferroptosis in red blood cells of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Liu, Y.; Barkema, H.W.; Deng, Z.; Gao, J.; Kastelic, J.P.; Han, B.; Zhang, J. Escherichia coli infection induces ferroptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway-mediated mitophagy. Mitochondrion 2024, 78, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Roumeliotis, T.I.; Kozik, Z.; Cepeda-Molero, M.; Fernández, L.; Shenoy, A.R.; Bakal, C.; Frankel, G.; Choudhary, J.S. Clustering of Tir during enteropathogenic E. coli infection triggers calcium influx-dependent pyroptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Chatterjee, S.; Choudhary, J.S.; Frankel, G. EPEC-induced activation of the Ca2+ transporter TRPV2 leads to pyroptotic cell death. Mol. Microbiol. 2022, 117, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnich, J.M.; Chung, H.; Lau, A.; Sandall, C.F.; Bondzi-Simpson, A.; Chen, H.M.; Komada, T.; Trotman-Grant, A.C.; Brandelli, J.R.; Chun, J.; et al. Shiga Toxin/Lipopolysaccharide Activates Caspase-4 and Gasdermin D to Trigger Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Upstream of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1525–1536.e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Qin, R. Selenomethionine protects against Escherichia coli-induced endometritis by inhibiting inflammation and necroptosis via regulating the PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 379, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, K.A.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Larkin, K.; Troxell, M.L.; O’Brien, A.D.; Magun, B.E. Mouse model of hemolytic-uremic syndrome caused by endotoxin-free Shiga toxin 2 (Stx2) and protection from lethal outcome by anti-Stx2 antibody. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4469–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, F.; Tohyama, K.; Bonev, A.D.; Kolling, G.L.; Keepers, T.R.; Gross, L.K.; Nelson, M.T.; Sato, S.; Obrig, T.G. Shiga toxin 2 affects the central nervous system through receptor globotriaosylceramide localized to neurons. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.S.; Davis, R.; Stanley, E.G.; Elefanty, A.G. A protocol describing the use of a recombinant protein-based, animal product-free medium (APEL) for human embryonic stem cell differentiation as spin embryoid bodies. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova, V.V.; van den Hil, F.E.; Petrus-Reurer, S.; Drabsch, Y.; Ten Dijke, P.; Mummery, C.L. Generation, expansion and functional analysis of endothelial cells and pericytes derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1514–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breggia, A.C.; Himmelfarb, J. Primary mouse renal tubular epithelial cells have variable injury tolerance to ischemic and chemical mediators of oxidative stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2008, 1, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| KIM-1 | TGGCAGATTCTGTAGCTGGTT | AGAGAACATGAGCCTCTATTCCA |
| NGAL | ATCACTCTCAGGGTCTGCAC | GGCAGGGGAATGTGAGAACT |
| IL-18 | TTGTTGCGAGAGGAAGCGAT | GGAAAGAGCCTGTTTGAAGGC |
| CCN1 | CTCGCCTTAGTCGTCACCC | CGCCGAAGTTGCATTCCAG |
| PAPPA2 | AGAATAAGCCTGGCGATTTTGG | GGCCTTAGGTAGTTCCCAGC |
| GDF15 | GACCCTCAGAGTTGCACTCC | GCCTGGTTAGCAGGTCCTC |
| SEMA3F | AACACAACCGACTACCGAATC | GGCTGCCCAGTGTATAATGAG |
| Sense (5′ → 3′) | Antisense (5′ → 3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| siNC | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT |
| siCcn1 1# | CCCAGAACCAGUCAGAUUUTT | AAAUCUGACUGGUUCUGGGTT |
| siCcn1 2# | CCAGUGCACAUGUAUUGAUTT | AUCAAUACAUGUGCACUGGTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Su, Q.; Peng, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, B. Macula Densa Alleviates Shiga Toxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via CCN1-Mediated Renal Tubular Repair. Toxins 2025, 17, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090470
Wan H, Wang Y, Chen J, Liu H, Li J, Su Q, Peng H, Duan X, Wang B. Macula Densa Alleviates Shiga Toxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via CCN1-Mediated Renal Tubular Repair. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090470
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Hongzhi, Yuhui Wang, Jiahui Chen, Hongqi Liu, Jiamei Li, Qisheng Su, Hui Peng, Xiaotao Duan, and Bo Wang. 2025. "Macula Densa Alleviates Shiga Toxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via CCN1-Mediated Renal Tubular Repair" Toxins 17, no. 9: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090470
APA StyleWan, H., Wang, Y., Chen, J., Liu, H., Li, J., Su, Q., Peng, H., Duan, X., & Wang, B. (2025). Macula Densa Alleviates Shiga Toxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via CCN1-Mediated Renal Tubular Repair. Toxins, 17(9), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090470





