A Novel Anti-BoNT/A Neutralizing Antibody Possessed Overlapped Epitope with SV2 and Had Prolonged Half-Life In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
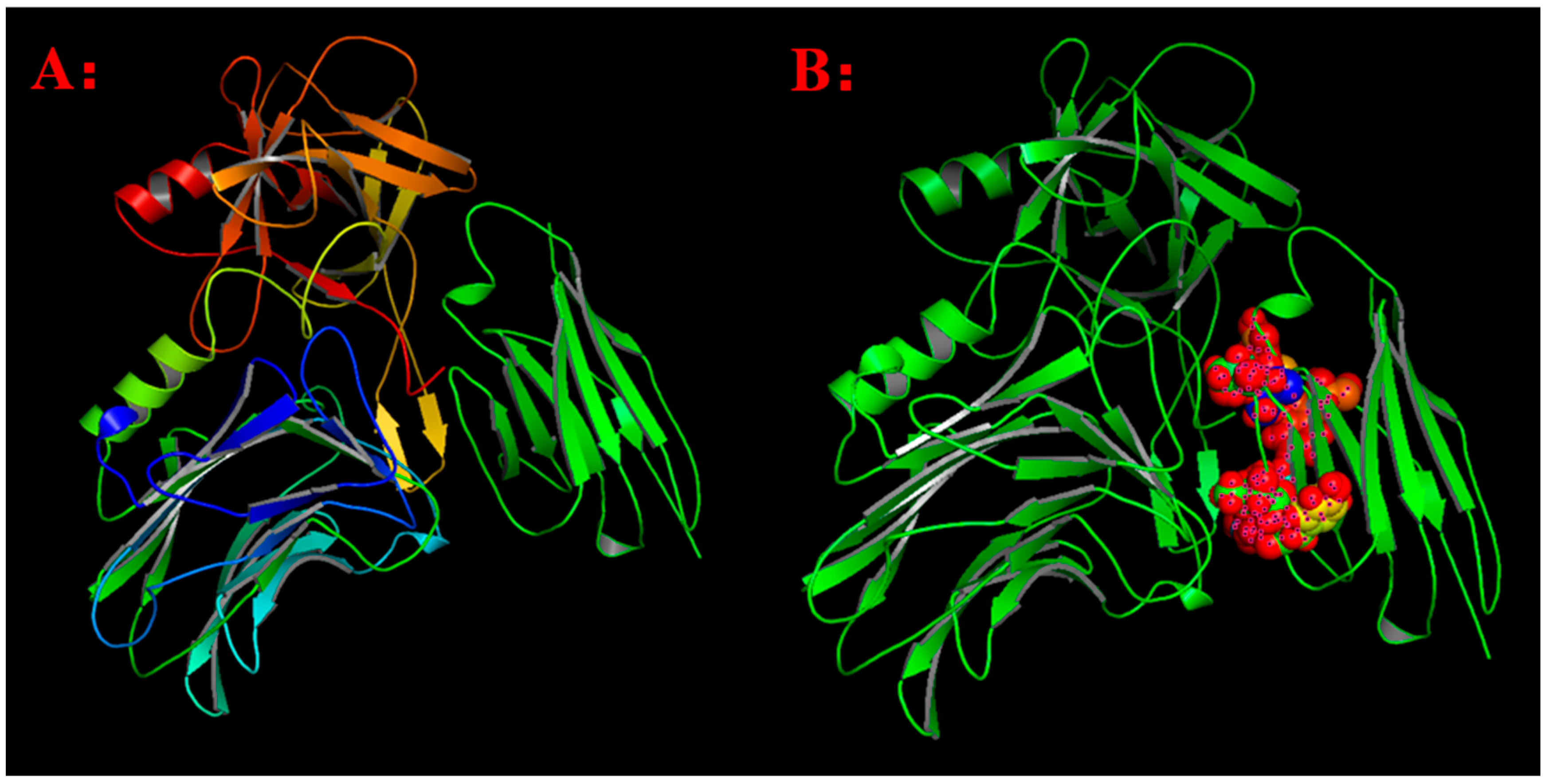
2.1. Prediction of Key Epitopes of Toxin Based on BoNT/A–HM Complex Structure
2.2. Design of Fc Mutants Based on Virtual Screening of Fc Mutation Library
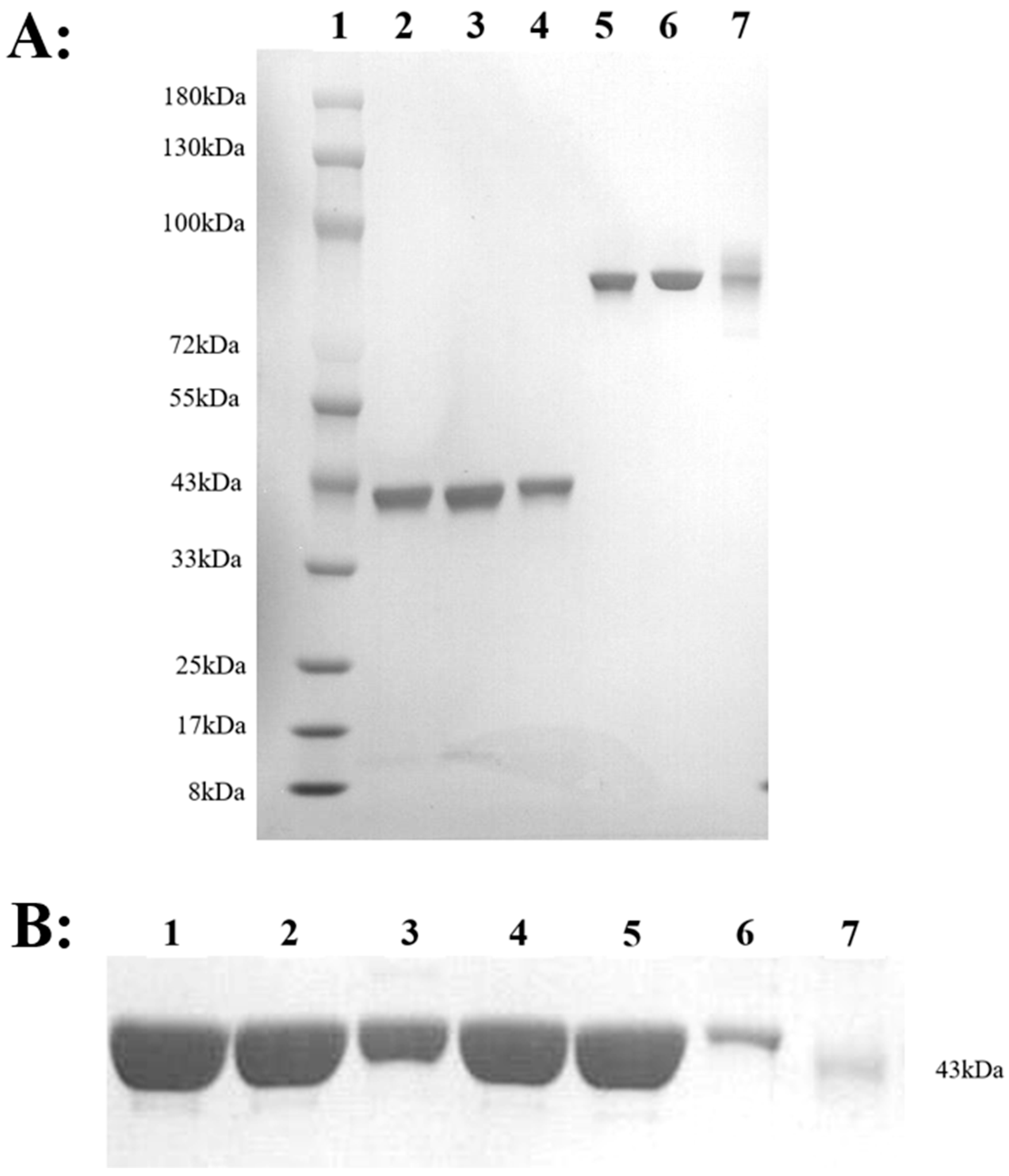
2.3. Expression, Identification and Stability of HM-Fc Mutants and BoNT/AHC Mutants
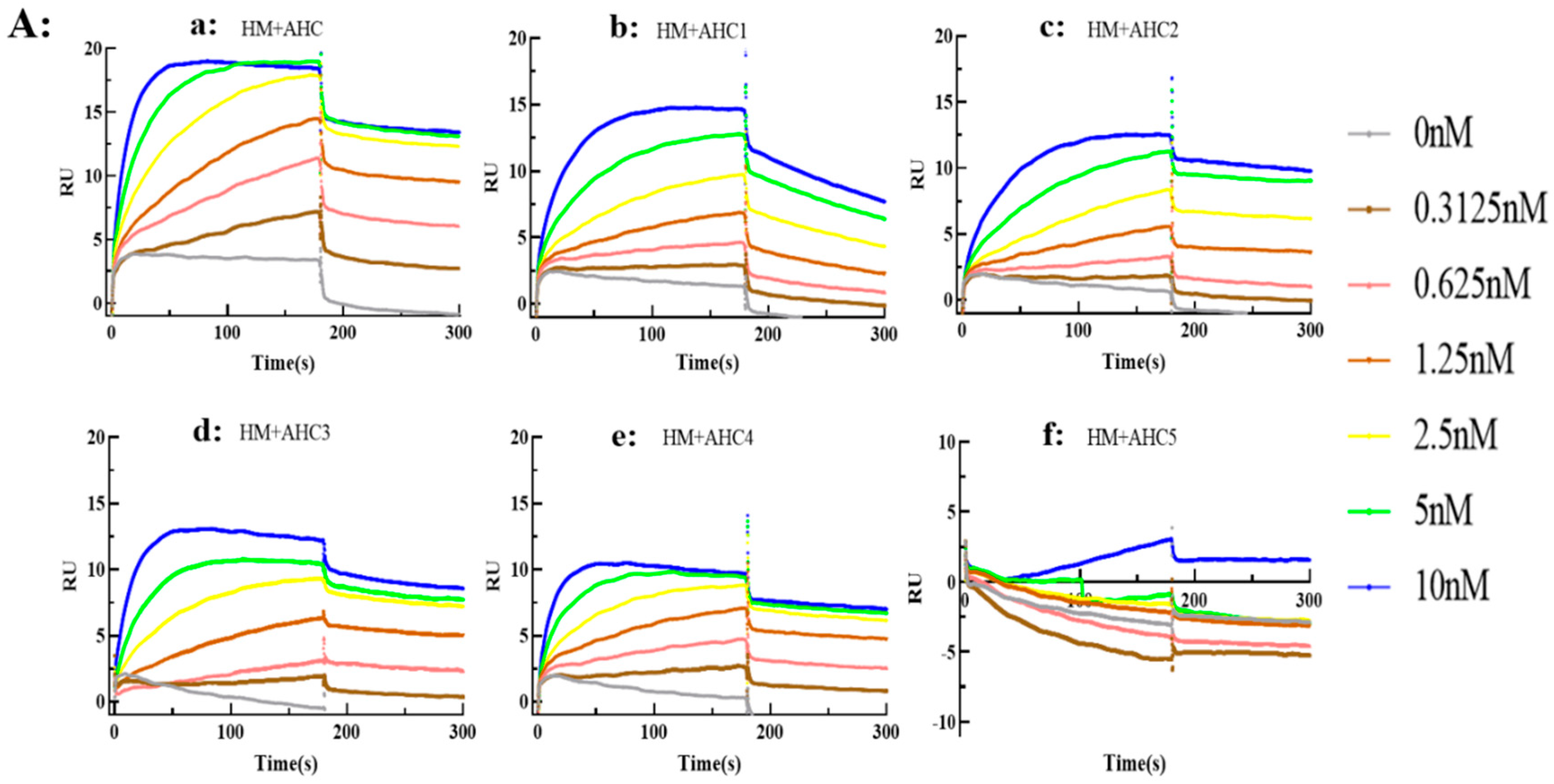
2.4. Characterization of Key Epitopes in BoNT/A Recognized by HMs or SV2C
2.5. Biological Effect of Antibodies to Antagonize the Toxin Receptor SV2C
2.6. In Vivo Protection Activity of the Antibodies in Human FcRn Transgenic Mice
2.7. Fc-Modified Antibodies Had Prolonged In Vivo Half-Life in Post-Injection Neutralizing Assay
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Nano-Antibody HM Structural Modeling
4.2. Nano-Antibody HM and BoNT/AHC Complex Structure Constructing
4.3. Mutant Design and Preparation of BoNT/AHC
4.4. Design, Expression and Purification of HM, HM-Fc5 and HM-Fc6
4.5. Purification of Expressed Antibodies
4.6. SPR Assays
4.7. In Vivo Protection Activity of Antibodies Against BoNT/AHC Toxin in Transgenic Mouse Model
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhury, S.; Baker, M.R.; Chatterjee, S.; Kumar, H. Botulinum Toxin: An Update on Pharmacology and Newer Products in Development. Toxins 2021, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagueny, A.; Burbaud, P. Mécanisme d’action, indication et résultats des traitements par la toxine botulinique [Mechanism of action, clinical indication and results of treatment of botulinum toxin]. Neurophysiol. Clin. 1996, 26, 216–226. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, K.S.; Acharya, K.R. A Comprehensive Structural Analysis of Clostridium botulinum Neurotoxin A Cell-Binding Domain from Different Subtypes. Toxins 2023, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Fabris, F.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Mechanism of Action. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 263, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Olson, M.E.; Eubanks, L.M.; Janda, K.D. Strategies to Counteract Botulinum Neurotoxin A: Nature’s Deadliest Biomolecule. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2322–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J. Serotype Features of 17 Suspected Cases of Foodborne Botulism in China 2019–2022 Revealed by a Multiplex Immuno-Endopep-MS Method. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 869874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosow, L.K.; Strober, J.B. Infant botulism: Review and clinical update. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 52, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, B.; Danino, D.; Levinsky, Y.; Levy, I.; Straussberg, R.; Dabaja-Younis, H.; Guri, A.; Almagor, Y.; Tasher, D.; Elad, D.; et al. Infant Botulism, Israel, 2007–2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, A.; Matur, Z.; Hanagasi, H.A.; Parman, Y. Iatrogenic botulism after botulinum toxin type A injections. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 33, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; et al. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Group on the Application of Botulinum Toxin Therapy; Parkinson’s Disease and Motor Disorders Group of the Neurology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Consensus of Chinese experts on the application of botulinum toxin therapy. Chin. J. Neurol. 2018, 51, 779–786. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X. Overview of the Current Status and Development Trends of Botulinum Antitoxin. Dis. Surveill. 2022, 37, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Investigational heptavalent botulinum antitoxin (HBAT) to replace licensed botulinum antitoxin AB and investigational botulinum antitoxin E. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2010, 59, 299. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, J.O.; Sherwood, L.J.; Collazo, M.T.; Garza, J.A.; Hayhurst, A. Llama single domain antibodies specific for the 7 botulinum neurotoxin serotypes as heptaplex immunoreagents. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Thompson, A.A.; Fan, Y.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Ho, M.; Pires-Alves, M.; Wilson, B.A.; Stevens, R.C.; Marks, J.D. A single-domain llama antibody potently inhibits the enzymatic activity of botulinum neurotoxin by binding to the noncatalytic alpha-exosite binding region. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Research progress on structural characteristics and preparation of nanobodies. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 32, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Tan, X.; Pang, X.; Li, M.; Hao, X. Latest progress in the application of nanobody technology. Chin. J. Bioeng. 2022, 38, 855–867. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Lin, Z.; Feng, J.; Peng, H.; Guo, R.; Han, G.; Geng, S.; Lang, X.; Sun, Y.; Shen, B.; et al. Identification of conformational core epitope Lys68 in C5a based on the 3-D modeling complex C5a and its functional antibody F20. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni-Kale, U.; Bhosle, S.; Kolaskar, A.S. CEP: A conformational epitope prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W168–W171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernille, H.A.; Morten, N.; Ole, L. Prediction of residues in discontinuous B-cell epitopes using protein 3D structures. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 2006, 15, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky, K.; Pupko, T.; Freund, N.T. Evaluation of the Ability of AlphaFold to Predict the Three-Dimensional Structures of Antibodies and Epitopes. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Mao, T.; Qiu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G. Exploring the spatial recognition relationship between epitopes and antibodies from COVID-19 Spike protein antigen antibody complex. Mod. Chin. Appl. Pharm. 2022, 39, 2850–2855. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, S.; Park, S.; Sohn, M.H.; Jo, M.; Ko, B.J.; Na, J.H.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, A.L.; Ha, K.; Woo, J.R.; et al. An Fc variant with two mutations confers prolonged serum half-life and enhanced effector functions on IgG antibodies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinn, S.; Vazquez-Lombardi, R.; Zimmermann, C.; Sapra, P.; Jermutus, L.; Christ, D. Advances in antibody-based therapy in oncology. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Qiao, C.; Feng, J.; Peng, F.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; et al. A Nanobody That Neutralizes Botulinum Toxin Type A. CN116925213b, 15 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, N.; Peng, F.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, S.; Xing, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Chen, G.; et al. A novel single-domain antibody obtained from immune Bactrian camels against botulinum toxin type A using SPR-based screening method. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Matteoli, M.; Montecucco, C. Neurotoxins affecting neuroexocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 717–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostindie, S.C.; Lazar, G.A.; Schuurman, J.; Parren, P.W.H.I. Avidity in antibody effector functions and biotherapeutic drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.J.; Cao, G.H.; Zhao, W.Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, X.B.; Qiu, H.Y.; Chen, D.D.; Tong, X.H.; et al. Epitope prime editing shields hematopoietic cells from CD123 immunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2024, 31, 1650–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; An, M.; Shen, H. Research progress on Fc domain modification of antibody drugs. Chin. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 31, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Kabat, E.A.; Wu, T.T. Identical V region amino acid sequences and segments of sequences in antibodies of different specificities. Relative contributions of VH and VL genes, minigenes, and complementarity-determining regions to binding of antibody-combining sites. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.Y.; Jiang, H. Investigating the relationship between structure and analgesic activity of crotalphine using alanine scanning mutagenesis. Lett. Biotechnol. 2020, 31, 710–713. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Zhuang, X. Translational pharmacokinetics of a novel bispecific antibody against Ebola virus (MBS77E) from animal to human by PBPK modeling & simulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 626, 122160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Interacting Molecules | Interaction Energy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| van der Waals Energy | Electrostatic Energy | Total Energy | |
| Fc-FcRn | −67.18 | −17.17 | −84.35 |
| Fc5-FcRn | −75.63 | −17.72 | −93.35 |
| Fc6-FcRn | −65.58 | −21.53 | −87.11 |
| Interacting Molecules | Boundary Area of Action (A2) * | Interface Functional Residues * | Number of Hydrogen Bonds | Number of Non Key Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fc-FcRn | 670:643 | 9:11 | 3 | 75 |
| Fc5-FcRn | 670:643 | 9:11 | 3 | 75 |
| Fc6-FcRn | 618:618 | 10:11 | 4 | 65 |
| Name | Amino Acid Sequence (1141 to 1200) |
|---|---|
| AHC | GSVMTTNIYL NSSLYRGTKF IIKKYASGNK DNIVRNNDRV YINVVVKNKE YRLATNASQA |
| AHC1 | GSVMTTNIYL NSSLARGTKF IIKKYASGNK DNIVRNNDRV YINVVVKNKE YRLATNASQA |
| AHC2 | GSVMTTNIYL NSSLYRGTKA AIKKYASGNK DNIVRNNDRV YINVVVKNKE YRLATNASQA |
| AHC3 | GSVMTTNIYL NSSLYRGTKF IIKKYASGNK DNIVRNNDRV YINAVVKNKE YRLATNASQA |
| AHC4 | GSVMTTNIYL NSSLYRGTKF IIKKYASGNK DNIVRNNDRV YINVVVKAAA YRLATNASQA |
| AHC5 | GSVMTTNIYL NSSLARGTKA AIKKYASGNK DNIVRNNDRV YINAVVKAAA YRLATNASQA |
| Time/Frequency | HM | HM-5 | HM-6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 °C | 0 h | 99.3% | 99.2% | 94.9% |
| 24 h | 99.1% | 99.2% | 93.8% | |
| 2 W | 99.3% | 99.2% | 95.7% | |
| 4 W | 99.3% | 99.2% | 94.5% | |
| 40 °C | 2 W | 99.4% | 99.2% | 95.4% |
| 4 W | 98.8% | 98.5% | 94.0% | |
| Freeze-thaw (−80 °C) | 1rd | 99.1% | 99.2% | 94.4% |
| 2rd | 99.1% | 99.2% | 94.3% | |
| 3rd | 99.0% | 99.2% | 94.3% | |
| pH 3.5 (4 °C) | 0 h | 99.5% | 99.5% | 99.4% |
| 4 h | 99.4% | 99.4% | 99.3% | |
| 24 h | 95.1% | 95.2% | 95.2% |
| Name | AHC | AHC1 | AHC2 | AHC3 | AHC4 | AHC5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HM | ka | (1/Ms) | (7.12 ± 0.02) × 106 | (2.91 ± 0.01) × 106 | (3.86 ± 0.01) × 106 | (5.67 ± 0.05) × 106 | (6.36 ± 0.03) × 106 | (6.41 ± 0.02) × 103 |
| Kd | (1/s) | (7.28 ± 0.01) × 10−5 | (2.35 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | (2.16 ± 0.02) × 10−4 | (1.39 ± 0.02) × 10−4 | (2.65 ± 0.03) × 10−4 | (1.27 ± 0.02) × 10−3 | |
| KD | (M) | (1.022 ± 0.007) × 10−11 | (8.076 ± 0.035) × 10−10 | (5.596 ± 0.055) × 10−11 | (2.451 ± 0.044) × 10−11 | (4.167 ± 0.053) × 10−11 | (1.981 ± 0.032) × 10−7 | |
| HM-Fc 5 | ka | (1/Ms) | (1.022 ± 0.007) × 10−11 | (2.72 ± 0.01) × 106 | (3.20 ± 0.02) × 106 | (7.27 ± 0.04) × 106 | (6.53 ± 0.03) × 106 | (1.08 ± 0.01) × 104 |
| kd | (1/s) | (9.60 ± 0.05) × 10−5 | (2.86 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | (1.09 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | (4.61 ± 0.03) × 10−4 | (8.01 ± 0.04) × 10−4 | (2.03 ± 0.02) × 10−3 | |
| KD | (M) | (1.943 ± 0.015) × 10−11 | (1.052 ± 0.006) × 10−9 | (3.406 ± 0.041) × 10−10 | (6.341 ± 0.05) × 10−11 | (1.227 ± 0.012) × 10−10 | (1.880 ± 0.025) × 10−7 | |
| HM-Fc 6 | Ka | (1/Ms) | (5.96 ± 0.03) × 106 | (1.69 ± 0.01) × 106 | (1.94 ± 0.01) × 106 | (8.64 ± 0.04) × 106 | (1.80 ± 0.01) × 106 | (4.31 ± 0.02) × 103 |
| kd | (1/s) | (4.08 ± 0.02) × 10−4 | (3.65 ± 0.02) × 10−3 | (1.15 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | (1.06 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | (1.09 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | (5.08 ± 0.05) × 10−6 | |
| KD | (M) | (6.846 ± 0.045) × 10−11 | (2.160 ± 0.018) × 10−9 | (5.928 ± 0.062) × 10−10 | (1.227 ± 0.015) × 10−10 | (6.056 ± 0.061) × 10−10 | (1.179 ± 0.015) × 10−9 | |
| SV2C | ka | (1/Ms) | (2.58 ± 0.03) × 105 | (2.11 ± 0.02) × 104 | (2.68 ± 0.03) × 104 | (6.78 ± 0.07) × 105 | (1.82 ± 0.02) × 105 | (4.00 ± 0.04) × 104 |
| kd | (1/s) | (0.014 ± 0.001) | (7.91 ± 0.08) × 10−4 | (0.0021 ± 0.0002) | (0.0149 ± 0.001) | (0.0054 ± 0.0003) | (0.0077 ± 0.0004) | |
| KD | (M) | (5.43 ± 0.43) × 10−8 | (3.75 ± 0.30) × 10−8 | (7.84 ± 0.78) × 10−8 | (2.20 ± 0.18) × 10−8 | (2.97 ± 0.21) × 10−8 | (1.93 ± 0.15) × 10−7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, S.; Hu, N.; Peng, F.; Mu, H.; Yi, Z.; Xing, C.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; et al. A Novel Anti-BoNT/A Neutralizing Antibody Possessed Overlapped Epitope with SV2 and Had Prolonged Half-Life In Vivo. Toxins 2025, 17, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080376
Peng S, Hu N, Peng F, Mu H, Yi Z, Xing C, Zhang L, Hu W, Zhou X, Wen Y, et al. A Novel Anti-BoNT/A Neutralizing Antibody Possessed Overlapped Epitope with SV2 and Had Prolonged Half-Life In Vivo. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080376
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Shangde, Naijing Hu, Fenghao Peng, Huirong Mu, Zihan Yi, Cong Xing, Liang Zhang, Wen Hu, Xinyi Zhou, Yan Wen, and et al. 2025. "A Novel Anti-BoNT/A Neutralizing Antibody Possessed Overlapped Epitope with SV2 and Had Prolonged Half-Life In Vivo" Toxins 17, no. 8: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080376
APA StylePeng, S., Hu, N., Peng, F., Mu, H., Yi, Z., Xing, C., Zhang, L., Hu, W., Zhou, X., Wen, Y., Feng, J., & Qiao, C. (2025). A Novel Anti-BoNT/A Neutralizing Antibody Possessed Overlapped Epitope with SV2 and Had Prolonged Half-Life In Vivo. Toxins, 17(8), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080376





