Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom-Induced Nociceptive Responses Depend on TRPV1, Immune Cells, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
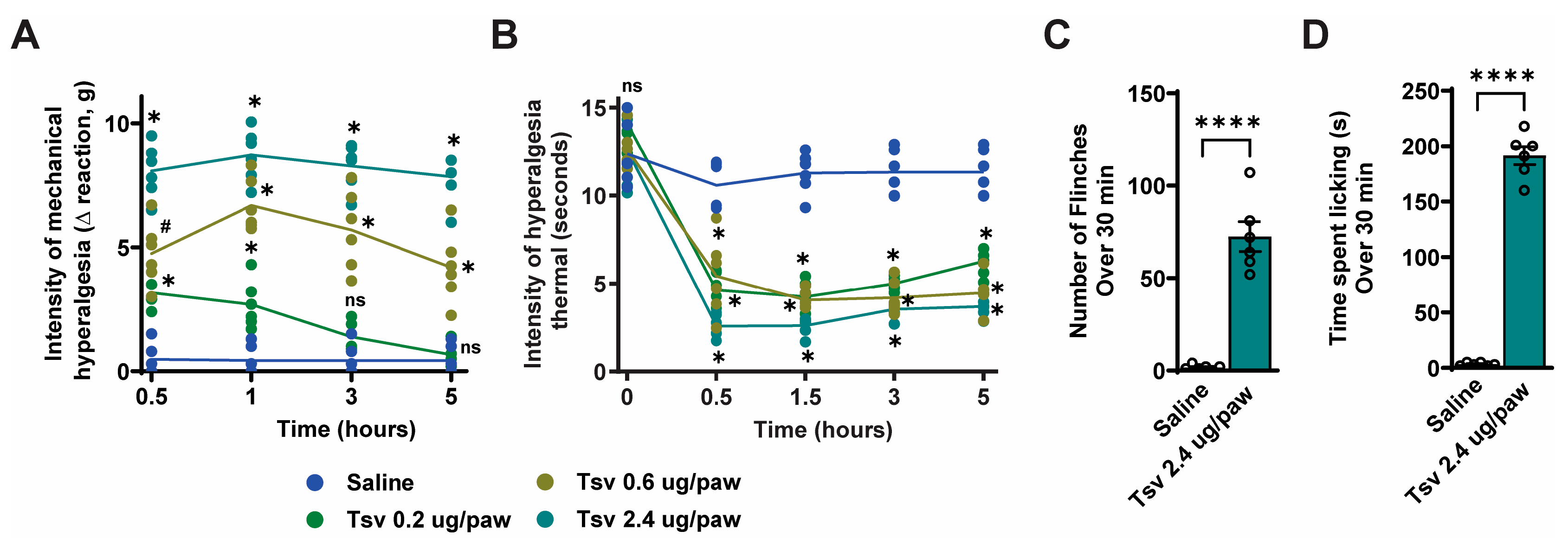
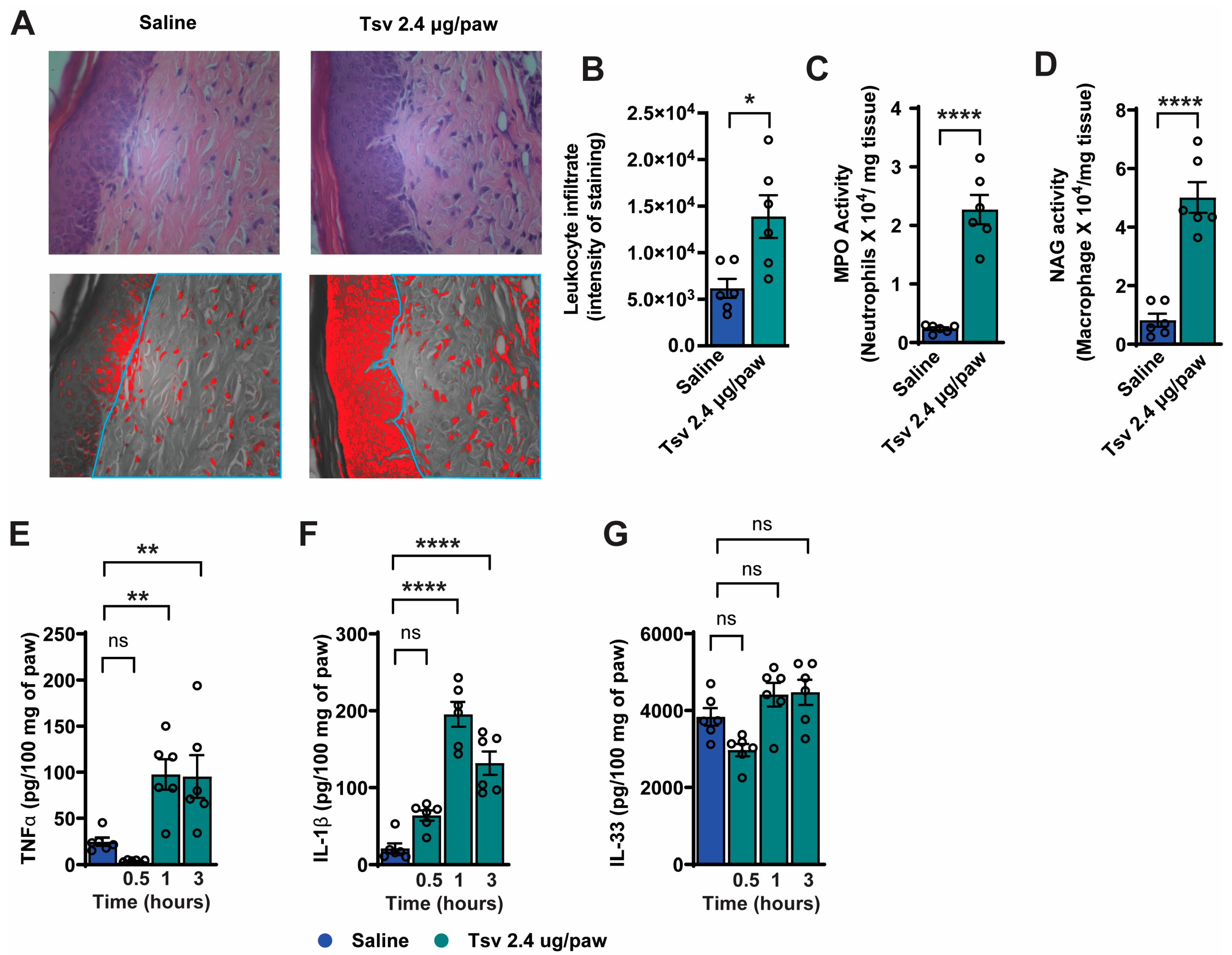
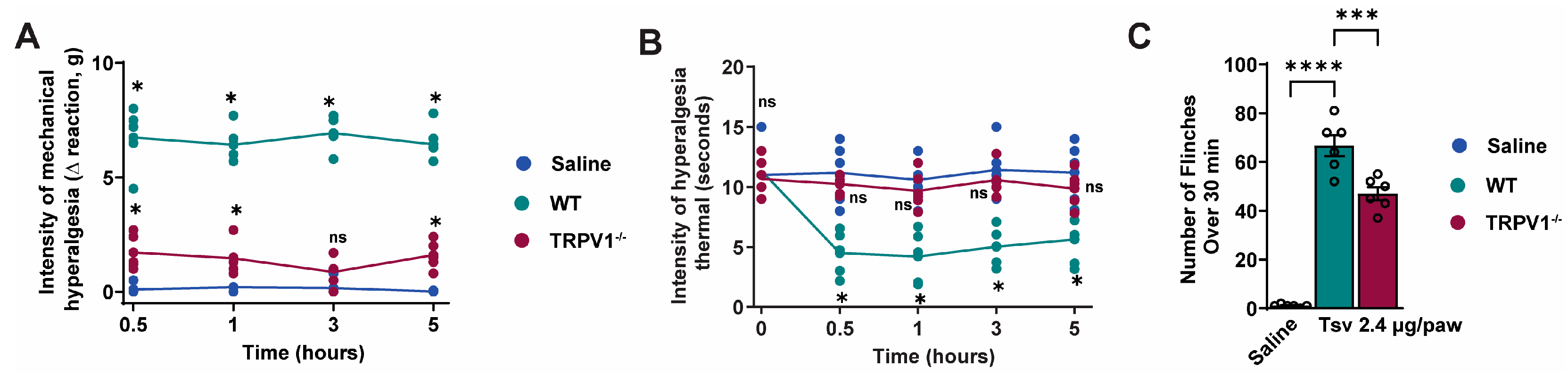
2.1. Tityus serrulatus Venom Induces Dose-Dependent Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia, Spontaneous Pain Behaviors, and Local Inflammatory Responses
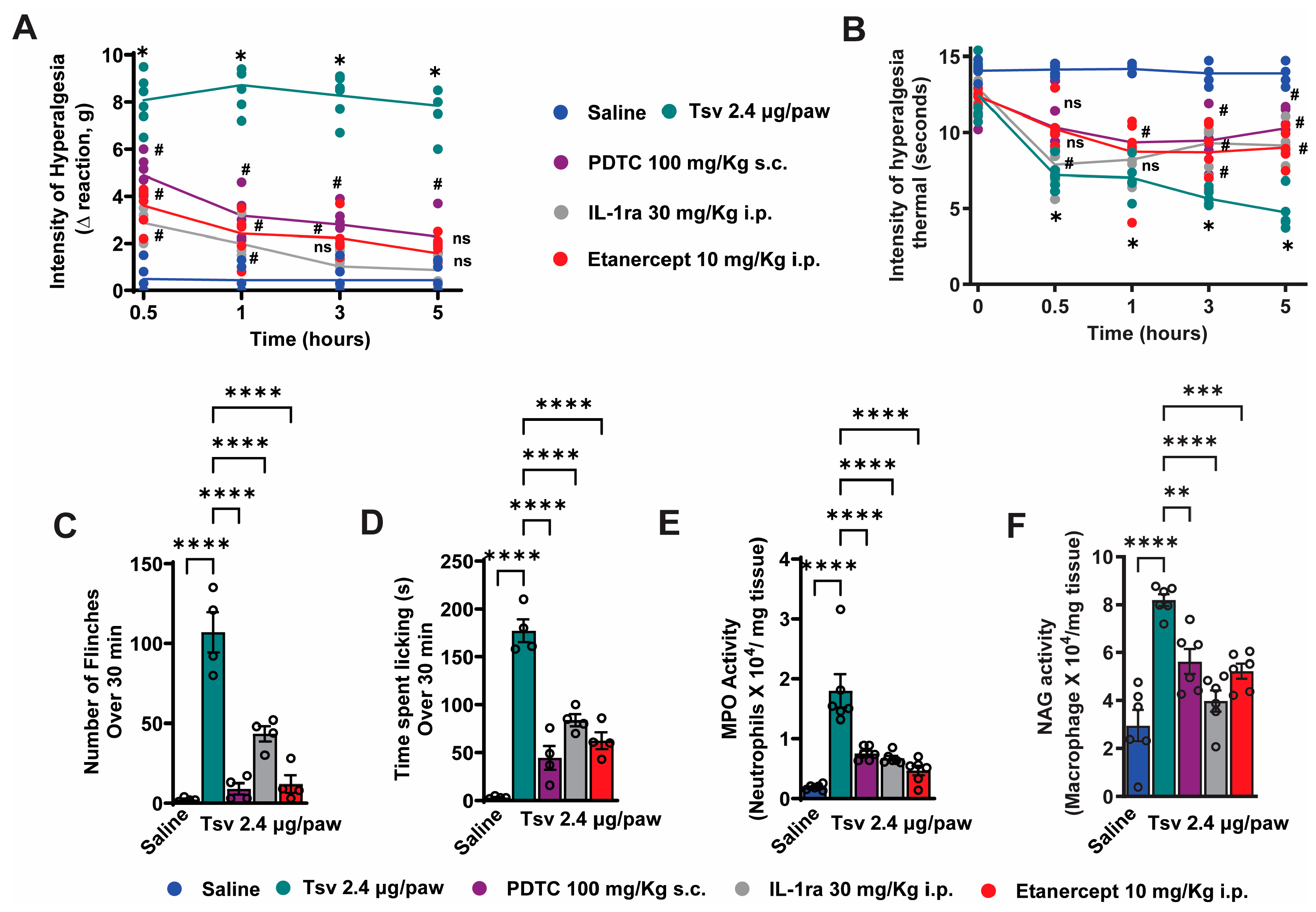
2.2. TNF-α, IL-1β and NFκB Inhibition Attenuates Tityus serrulatus Venom-Induced Hyperalgesia and Inflammatory Response
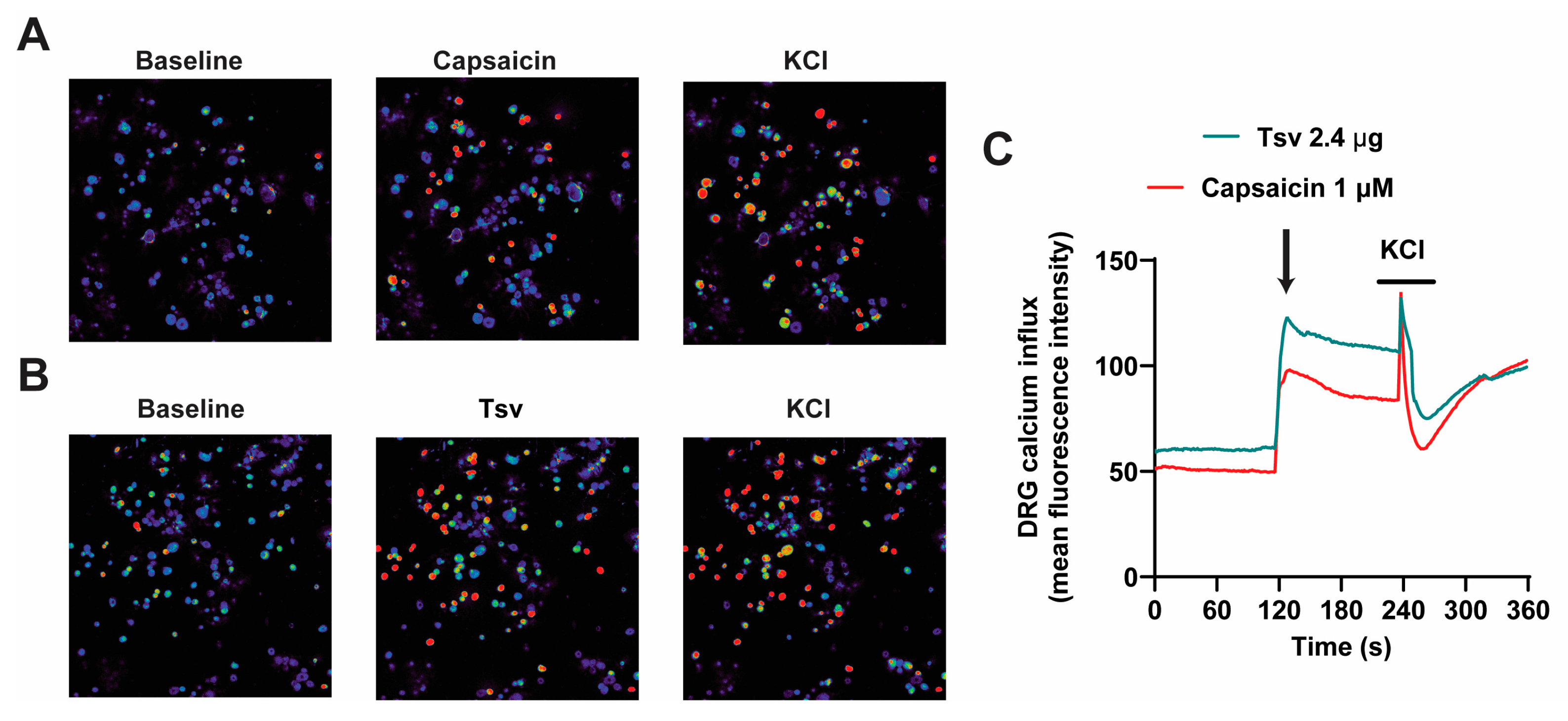
2.3. Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Neurons Are Activated by Tityus serrulatus Venom
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Tityus serrulatus Venom
5.3. Drugs and Compounds
5.4. Experimental Protocols
5.5. Mechanical Hyperalgesia Test
5.6. Thermal Hyperalgesia Test
5.7. Spontaneous Pain Behavior Test
5.8. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) and N-Acetylglucosaminidase Activity (NAG) Assays
5.9. Cytokine Measurement
5.10. Paw Tissue Histology
5.11. Immunofluorescence
5.12. Calcium Imaging
5.13. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, J.G.; Santos, G.C.; Procopio, R.E.L.; Arantes, E.C.; Bordon, K.C.F. Scorpion species of medical importance in the Brazilian Amazon: A review to identify knowledge gaps. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 27, e20210012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, N.B.; Magalhaes, A.C.M.; Bloch, C., Jr.; Beirao, P.S.L.; Silva, A.O.; Melani, R.D.; Barbosa, E.A.; Pires, O.R.; Schwartz, C.A. Characterization of the first two toxins isolated from the venom of the ancient scorpion Tityus (Archaeotityus) mattogrossensis (Borelli, 1901). J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 27, e20210035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, C.; Serna-Gonzalez, M.; Chang-Castillo, A.; Lomonte, B.; Bonilla, F.; Alfaro-Chinchilla, A.; Triana, F.; Sasa, M. Proteomic profile of the venom of three dark-colored Tityus (Scorpiones: Buthidae) from the tropical rainforests of Costa Rica. Acta Trop. 2023, 248, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.J.; Ellsworth, S.A.; Nystrom, G.S. A global accounting of medically significant scorpions: Epidemiology, major toxins, and comparative resources in harmless counterparts. Toxicon 2018, 151, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, W.M.; Gomes, J.; Fe, N.; Mendonca da Silva, I.; Lacerda, M.; Alencar, A.; Seabra de Farias, A.; Val, F.; de Souza Sampaio, V.; Cardoso de Melo, G.; et al. Perspectives and recommendations towards evidence-based health care for scorpion sting envenoming in the Brazilian Amazon: A comprehensive review. Toxicon 2019, 169, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Acosta de Patino, H.; Pascale, J.M.; Otero, R.; Miranda, R.J.; De Sousa, L.; Graham, M.R.; Gomez, A.; et al. Venom diversity in the Neotropical scorpion genus Tityus: Implications for antivenom design emerging from molecular and immunochemical analyses across endemic areas of scorpionism. Acta Trop. 2020, 204, 105346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Pinheiro Junior, E.L.; Bordon Kde, C.; Amorim, F.G.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Longhim, H.T.; Cremonez, C.M.; Oliveira, G.H.; Arantes, E.C. Tityus serrulatus venom—A lethal cocktail. Toxicon 2015, 108, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, R.J.G.; Brandao-Dias, P.F.P.; Leal, H.G.; Carmo, A.O.D.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.R.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E. Selected to survive and kill: Tityus serrulatus, the Brazilian yellow scorpion. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiezel, G.A.; Oliveira, I.S.; Reis, M.B.; Ferreira, I.G.; Cordeiro, K.R.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Arantes, E.C. The complex repertoire of Tityus spp. venoms: Advances on their composition and pharmacological potential of their toxins. Biochimie 2024, 220, 144–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cologna, C.T.; Marcussi, S.; Giglio, J.R.; Soares, A.M.; Arantes, E.C. Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom and toxins: An overview. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, I.S.; Alano-da-Silva, N.M.; Ferreira, I.G.; Cerni, F.A.; Sachett, J.A.G.; Monteiro, W.M.; Pucca, M.B.; Arantes, E.C. Understanding the complexity of Tityus serrulatus venom: A focus on high molecular weight components. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 30, e20230046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duzzi, B.; Silva, C.C.F.; Kodama, R.T.; Cajado-Carvalho, D.; Squaiella-Baptistao, C.C.; Portaro, F.C.V. New Insights into the Hypotensins from Tityus serrulatus Venom: Pro-Inflammatory and Vasopeptidases Modulation Activities. Toxins 2021, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Abri, S.; Al Rumhi, M.; Al Mahruqi, G.; Shakir, A.S. Scorpion Sting Management at Tertiary and Secondary Care Emergency Departments. Oman Med. J. 2019, 34, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerni, F.; Oliveira, I.; Cordeiro, F.; Bordon, K.; Ferreira, I.; Monteiro, W.; Arantes, E.; Cunha, T.; Pucca, M. The nociceptive response induced by different classes of Tityus serrulatus neurotoxins: The important role of Ts5 in venom-induced nociception. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, Y.D.; Reis, M.L.; Dellalibera-Joviliano, R.; Cunha, F.Q.; Donadi, E.A. Increased plasma levels of IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10 and TNF-alpha in patients moderately or severely envenomed by Tityus serrulatus scorpion sting. Toxicon 2003, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, M.M.; Pereira, M.E.; Amaral, C.F.; Rezende, N.A.; Campolina, D.; Bucaretchi, F.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Cunha-Melo, J.R. Serum levels of cytokines in patients envenomed by Tityus serrulatus scorpion sting. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, E.M.; Maciel, M.C.; Silva, A.C.; Reis, A.S.; Assuncao, A.K.; Fortes, T.S.; Silva, L.A.; Guerra, R.N.; Kwasniewski, F.H.; Nascimento, F.R. Immune cells recruitment and activation by Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom. Toxicon 2011, 58, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccal, K.F.; Bitencourt Cda, S.; Paula-Silva, F.W.; Sorgi, C.A.; de Castro Figueiredo Bordon, K.; Arantes, E.C.; Faccioli, L.H. TLR2, TLR4 and CD14 recognize venom-associated molecular patterns from Tityus serrulatus to induce macrophage-derived inflammatory mediators. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petricevich, V.L. Effect of Tityus serrulatus venom on cytokine production and the activity of murine macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petricevich, V.L.; Hernandez Cruz, A.; Coronas, F.I.; Possani, L.D. Toxin gamma from Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom plays an essential role in immunomodulation of macrophages. Toxicon 2007, 50, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccal, K.F.; Paula-Silva, F.W.; Bitencourt Cda, S.; Sorgi, C.A.; Bordon Kde, C.; Arantes, E.C.; Faccioli, L.H. PPAR-gamma activation by Tityus serrulatus venom regulates lipid body formation and lipid mediator production. Toxicon 2015, 93, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertazzi, D.T.; de Assis-Pandochi, A.I.; Talhaferro, V.L.; Caleiro Seixas Azzolini, A.E.; Pereira Crott, L.S.; Arantes, E.C. Activation of the complement system and leukocyte recruitment by Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2005, 5, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowy, D.B.; Makker, P.G.S.; Moalem-Taylor, G. Cutaneous Neuroimmune Interactions in Peripheral Neuropathic Pain States. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 660203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Interactions between the immune and nervous systems in pain. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.Q.; Poole, S.; Lorenzetti, B.B.; Ferreira, S.H. The pivotal role of tumour necrosis factor alpha in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 107, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccioli, L.H.; Souza, G.E.; Cunha, F.Q.; Poole, S.; Ferreira, S.H. Recombinant interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor induce neutrophil migration “in vivo” by indirect mechanisms. Agents Actions 1990, 30, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, W.A., Jr.; Guerrero, A.T.; Fukada, S.Y.; Valerio, D.A.; Cunha, T.M.; Xu, D.; Ferreira, S.H.; Liew, F.Y.; Cunha, F.Q. IL-33 mediates antigen-induced cutaneous and articular hypernociception in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2723–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, D.A.; Hohmann, M.S.; Mizokami, S.S.; Cunha, T.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Casagrande, R.; Ferreira, S.H.; Liew, F.Y.; Cunha, F.Q.; Verri, W.A., Jr. An interleukin-33/ST2 signaling deficiency reduces overt pain-like behaviors in mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, W.A., Jr.; Souto, F.O.; Vieira, S.M.; Almeida, S.C.; Fukada, S.Y.; Xu, D.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Guerrero, A.T.; Mattos-Guimaraes, R.B.; et al. IL-33 induces neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of anti-TNF therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Huang, Z.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhong, B.; et al. TRIM38 inhibits TNFalpha- and IL-1beta-triggered NF-kappaB activation by mediating lysosome-dependent degradation of TAB2/3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-kappaB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva-Santos, T.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Manchope, M.F.; Andrade, K.C.; Ferraz, C.R.; Bertozzi, M.M.; Artero, N.A.; Franciosi, A.; Badaro-Garcia, S.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; et al. Therapeutic activity of lipoxin A(4) in TiO(2)-induced arthritis in mice: NF-kappaB and Nrf2 in synovial fluid leukocytes and neuronal TRPV1 mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 949407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattori, V.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Ferraz, C.R.; Brasil-Silva, L.; Borghi, S.M.; Cunha, J.M.; Chichorro, J.G.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Maresin 2 is an analgesic specialized pro-resolution lipid mediator in mice by inhibiting neutrophil and monocyte recruitment, nociceptor neuron TRPV1 and TRPA1 activation, and CGRP release. Neuropharmacology 2022, 216, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Duan, K.L.; Shang, C.F.; Yu, H.G.; Zhou, Z. Calcium influx through hyperpolarization-activated cation channels (I(h) channels) contributes to activity-evoked neuronal secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, M.J.; Rosen, T.A.; Tominaga, M.; Brake, A.J.; Julius, D. A capsaicin-receptor homologue with a high threshold for noxious heat. Nature 1999, 398, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximiano, T.K.E.; Carneiro, J.A.; Fattori, V.; Verri, W.A. TRPV1: Receptor structure, activation, modulation and role in neuro-immune interactions and pain. Cell Calcium 2024, 119, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizgerd, J.P.; Spieker, M.R.; Doerschuk, C.M. Early response cytokines and innate immunity: Essential roles for TNF receptor 1 and type I IL-1 receptor during Escherichia coli pneumonia in mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Calixto-Campos, C.; Manchope, M.F.; Casagrande, R.; Clissa, P.B.; Baldo, C.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Jararhagin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia depends on TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and NFkappaB in mice. Toxicon 2015, 103, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Manchope, M.F.; Andrade, K.C.; Saraiva-Santos, T.; Franciosi, A.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Bagatim-Souza, J.; Borghi, S.M.; Candido, D.M.; Knysak, I.; et al. Peripheral mechanisms involved in Tityus bahiensis venom-induced pain. Toxicon 2021, 200, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, D.N.; Pereira, R.L.; Knysak, I.; Candido, D.M.; Kwasniewski, F.H. Edematogenic activity of scorpion venoms from the Buthidae family and the role of platelet-activating factor and nitric oxide in paw edema induced by Tityus venoms. Inflammation 2009, 32, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Westlund, K.N. Reactive oxygen species mediate TNFR1 increase after TRPV1 activation in mouse DRG neurons. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailhot, B.; Christin, M.; Tessandier, N.; Sotoudeh, C.; Bretheau, F.; Turmel, R.; Pellerin, E.; Wang, F.; Bories, C.; Joly-Beauparlant, C.; et al. Neuronal interleukin-1 receptors mediate pain in chronic inflammatory diseases. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Chiu, I.M. Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafers, M.; Sorkin, L.S.; Geis, C.; Shubayev, V.I. Spinal nerve ligation induces transient upregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 and 2 in injured and adjacent uninjured dorsal root ganglia in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 347, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pang, R.P.; Shen, K.F.; Zimmermann, M.; Xin, W.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, X.G. TNF-alpha enhances the currents of voltage gated sodium channels in uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons following motor nerve injury. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 227, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, R.; Nemoto, T.; Maruta, T.; Onizuka, S.; Yanagita, T.; Wada, A.; Murakami, M.; Tsuneyoshi, I. Up-regulation of NaV1.7 sodium channels expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells and rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 118, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obreja, O.; Rathee, P.K.; Lips, K.S.; Distler, C.; Kress, M. IL-1 beta potentiates heat-activated currents in rat sensory neurons: Involvement of IL-1RI, tyrosine kinase, and protein kinase C. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Peigneur, S.; Cunha, T.M.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Ts8 scorpion toxin inhibits the Kv4.2 channel and produces nociception in vivo. Toxicon 2016, 119, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, G.E.; Skattebol, A.; Possani, L.D.; Brown, A.M. Modification of Na channel gating by an alpha scorpion toxin from Tityus serrulatus. J. Gen. Physiol. 1989, 93, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.B., Jr.; Costa, K.A.; Bertollo, C.M.; Oliveira, A.C.; Rocha, L.T.; Souza, A.L.; Gloria, M.B.; Moraes-Santos, T.; Coelho, M.M. Pharmacological investigation of the nociceptive response and edema induced by venom of the scorpion Tityus serrulatus. Toxicon 2005, 45, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerni, F.A.; Pucca, M.B.; Peigneur, S.; Cremonez, C.M.; Bordon, K.C.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Electrophysiological characterization of Ts6 and Ts7, K(+) channel toxins isolated through an improved Tityus serrulatus venom purification procedure. Toxins 2014, 6, 892–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucca, M.B.; Bertolini, T.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Bordon, K.C.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Bonato, V.L.; Arantes, E.C. Immunosuppressive evidence of Tityus serrulatus toxins Ts6 and Ts15: Insights of a novel K(+) channel pattern in T cells. Immunology 2016, 147, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerni, F.A.; Pucca, M.B.; Amorim, F.G.; de Castro Figueiredo Bordon, K.; Echterbille, J.; Quinton, L.; De Pauw, E.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Isolation and characterization of Ts19 Fragment II, a new long-chain potassium channel toxin from Tityus serrulatus venom. Peptides 2016, 80, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, O.; L’Herondelle, K.; Lebonvallet, N.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Sakka, M.; Buhe, V.; Plee-Gautier, E.; Carre, J.L.; Lefeuvre, L.; Misery, L.; et al. TRPV1 and TRPA1 in cutaneous neurogenic and chronic inflammation: Pro-inflammatory response induced by their activation and their sensitization. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planells-Cases, R.; Garcia-Sanz, N.; Morenilla-Palao, C.; Ferrer-Montiel, A. Functional aspects and mechanisms of TRPV1 involvement in neurogenic inflammation that leads to thermal hyperalgesia. Pflug. Arch. 2005, 451, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujak, J.K.; Kosmala, D.; Szopa, I.M.; Majchrzak, K.; Bednarczyk, P. Inflammation, Cancer and Immunity-Implication of TRPV1 Channel. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Salvador, L.; Andres-Borderia, A.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.; Planells-Cases, R. Agonist- and Ca2+-dependent desensitization of TRPV1 channel targets the receptor to lysosomes for degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19462–19471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiariello, T.M.; Candido, D.M.; Oliveira, R.N.; Auada, A.V.V.; Fan, H.W. Captive Maintenance and Venom Extraction of Tityus serrulatus (Brazilian Yellow Scorpion) for Antivenom Production. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, e65737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogrul, A.; Gul, H.; Yesilyurt, O.; Ulas, U.H.; Yildiz, O. Systemic and spinal administration of etanercept, a tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor, blocks tactile allodynia in diabetic mice. Acta Diabetol. 2011, 48, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendele, A.M.; Chlipala, E.S.; Scherrer, J.; Frazier, J.; Sennello, G.; Rich, W.J.; Edwards, C.K., 3rd. Combination benefit of treatment with the cytokine inhibitors interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and PEGylated soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor type I in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 2648–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Fattori, V.; Zarpelon, A.C.; Borghi, S.M.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Carvalho, T.T.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, F.Q.; Cunha, T.M.; Casagrande, R.; et al. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits superoxide anion-induced pain and inflammation in the paw skin and spinal cord by targeting NF-kappaB and oxidative stress. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, T.M.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Vivancos, G.G.; Moreira, I.F.; Reis, S.; Parada, C.A.; Cunha, F.Q.; Ferreira, S.H. An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, S.M.; Carvalho, T.T.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Hohmann, M.S.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Vitexin inhibits inflammatory pain in mice by targeting TRPV1, oxidative stress, and cytokines. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, V.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Borghi, S.M.; Rossaneis, A.C.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. The specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator maresin 1 reduces inflammatory pain with a long-lasting analgesic effect. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1728–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, V.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Borghi, S.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Curcumin inhibits superoxide anion-induced pain-like behavior and leukocyte recruitment by increasing Nrf2 expression and reducing NF-kappaB activation. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco-Gonzalez, Y.; Fattori, V.; Domiciano, T.P.; Rossaneis, A.C.; Borghi, S.M.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Bernardy, C.C.F.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Repurposing of the Nootropic Drug Vinpocetine as an Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Agent: Evidence in a Mouse Model of Superoxide Anion-Triggered Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 6481812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Baddal, B.; Haarsma, R.; O’Seaghdha, M.; Yang, N.J.; Blake, K.J.; Portley, M.; Verri, W.A.; Dale, J.B.; Wessels, M.R.; et al. Blocking Neuronal Signaling to Immune Cells Treats Streptococcal Invasive Infection. Cell 2018, 173, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferraz, C.R.; Manchope, M.F.; Bertozzi, M.M.; Saraiva-Santos, T.; Andrade, K.C.; Franciosi, A.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Bagatim-Souza, J.; Borghi, S.M.; Cândido, D.M.; et al. Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom-Induced Nociceptive Responses Depend on TRPV1, Immune Cells, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Toxins 2025, 17, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070332
Ferraz CR, Manchope MF, Bertozzi MM, Saraiva-Santos T, Andrade KC, Franciosi A, Zaninelli TH, Bagatim-Souza J, Borghi SM, Cândido DM, et al. Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom-Induced Nociceptive Responses Depend on TRPV1, Immune Cells, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Toxins. 2025; 17(7):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070332
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerraz, Camila R., Marília F. Manchope, Mariana M. Bertozzi, Telma Saraiva-Santos, Ketlem C. Andrade, Anelise Franciosi, Tiago H. Zaninelli, Julia Bagatim-Souza, Sergio M. Borghi, Denise M. Cândido, and et al. 2025. "Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom-Induced Nociceptive Responses Depend on TRPV1, Immune Cells, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines" Toxins 17, no. 7: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070332
APA StyleFerraz, C. R., Manchope, M. F., Bertozzi, M. M., Saraiva-Santos, T., Andrade, K. C., Franciosi, A., Zaninelli, T. H., Bagatim-Souza, J., Borghi, S. M., Cândido, D. M., Cunha, T. M., Casagrande, R., Kwasniewski, F. H., & Verri, W. A. (2025). Tityus serrulatus Scorpion Venom-Induced Nociceptive Responses Depend on TRPV1, Immune Cells, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Toxins, 17(7), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070332





