Toxicity, Mitigation, and Chemical Analysis of Aflatoxins and Other Toxic Metabolites Produced by Aspergillus: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
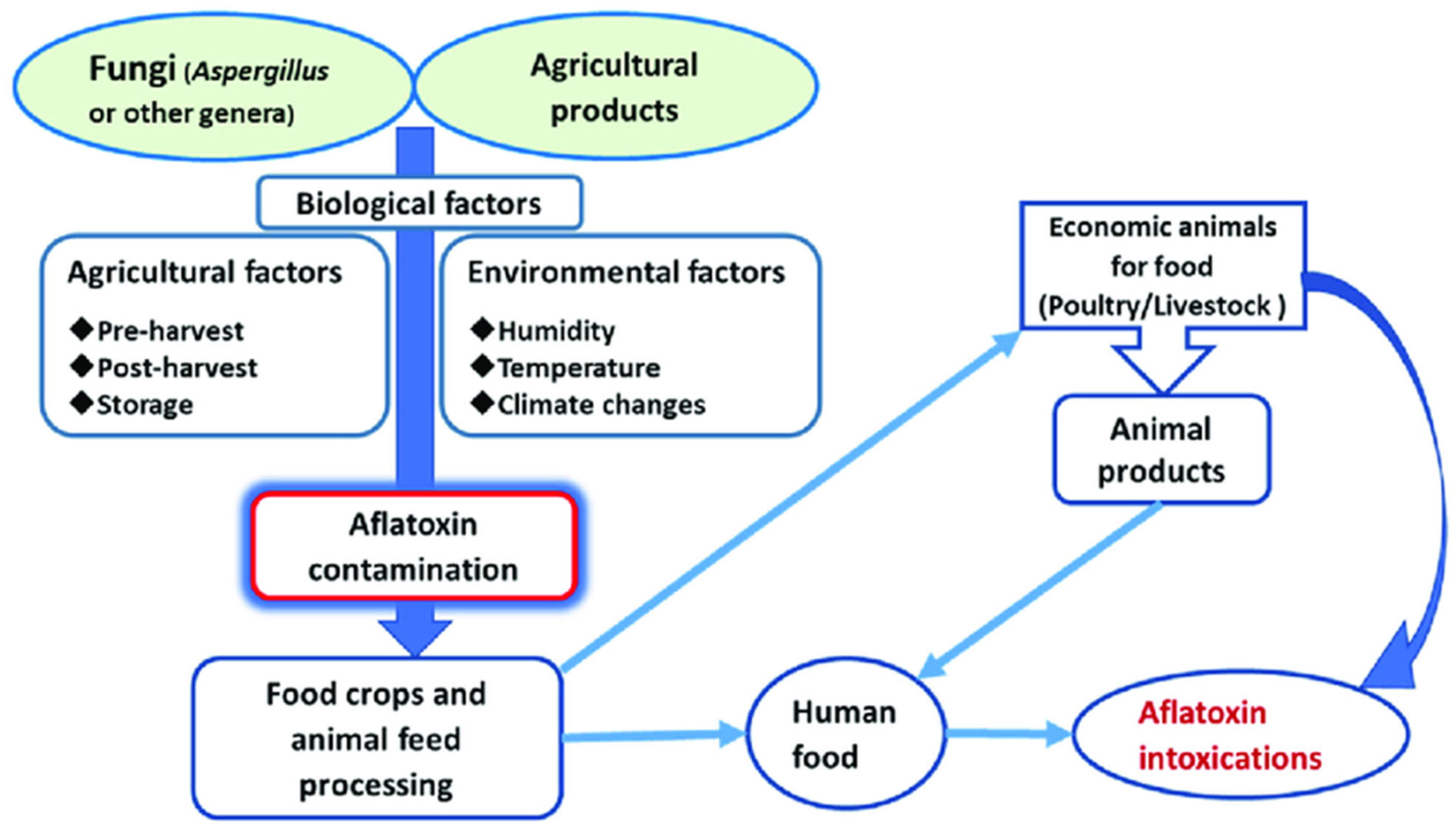
1. Introduction
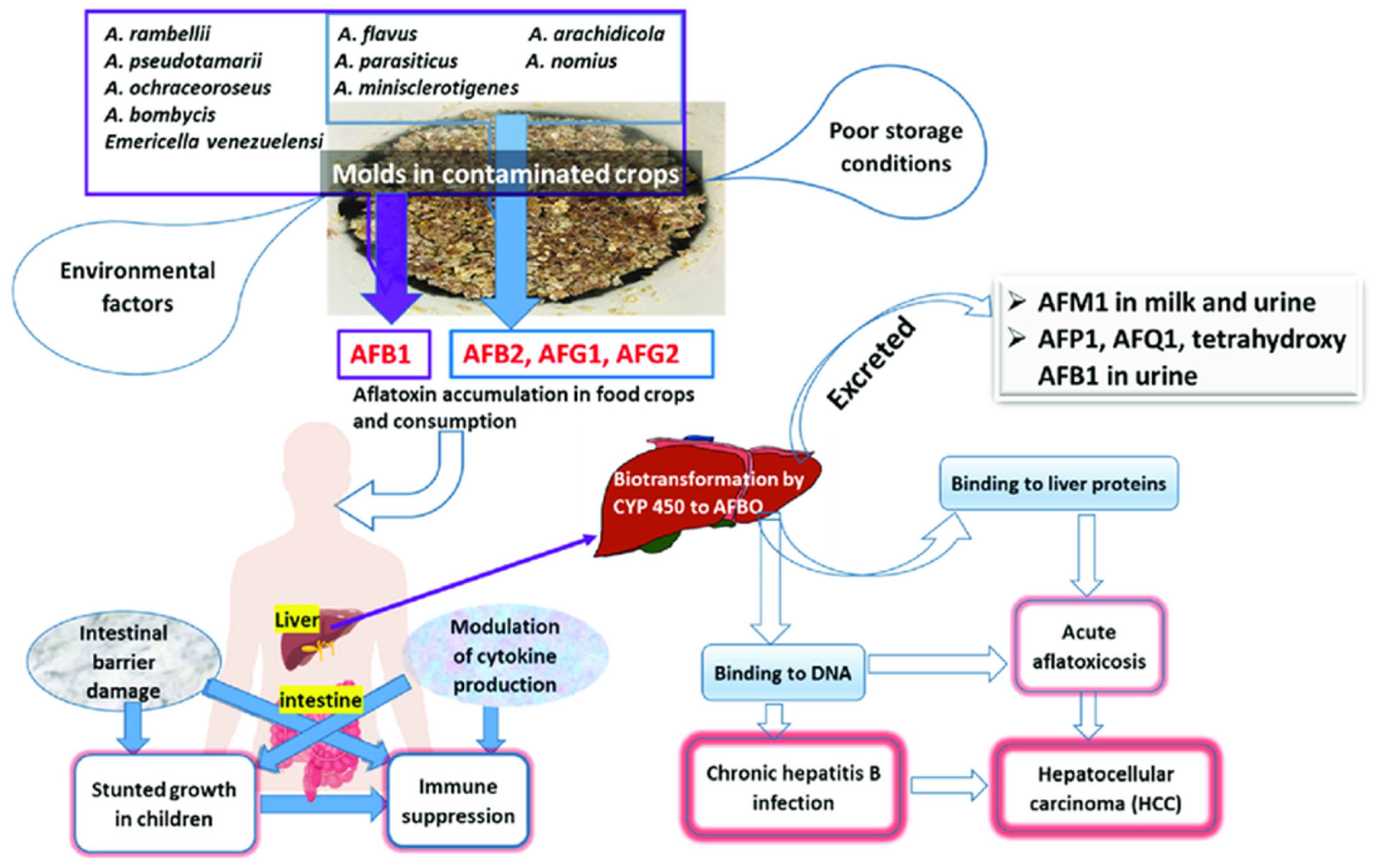
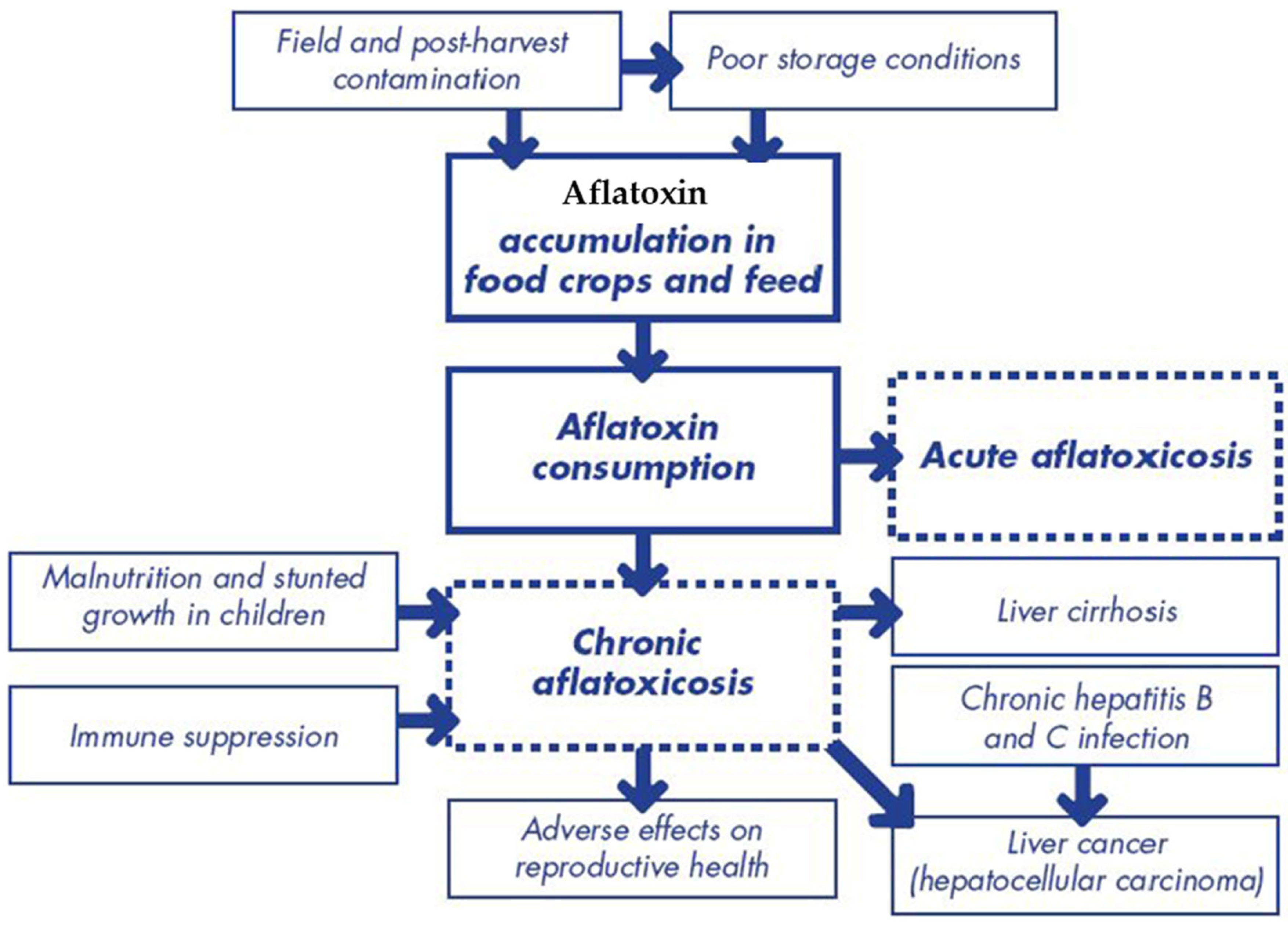
2. Toxicity of Aflatoxins and Other Toxic Metabolites
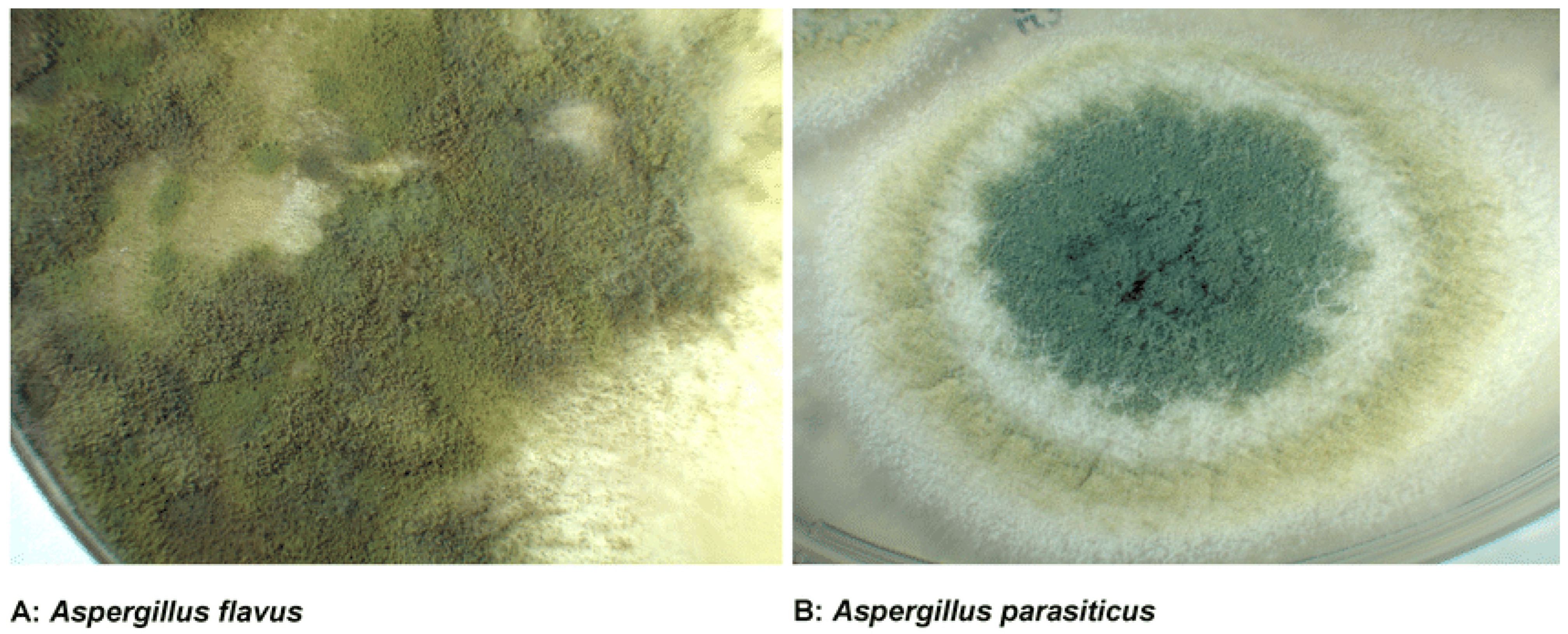
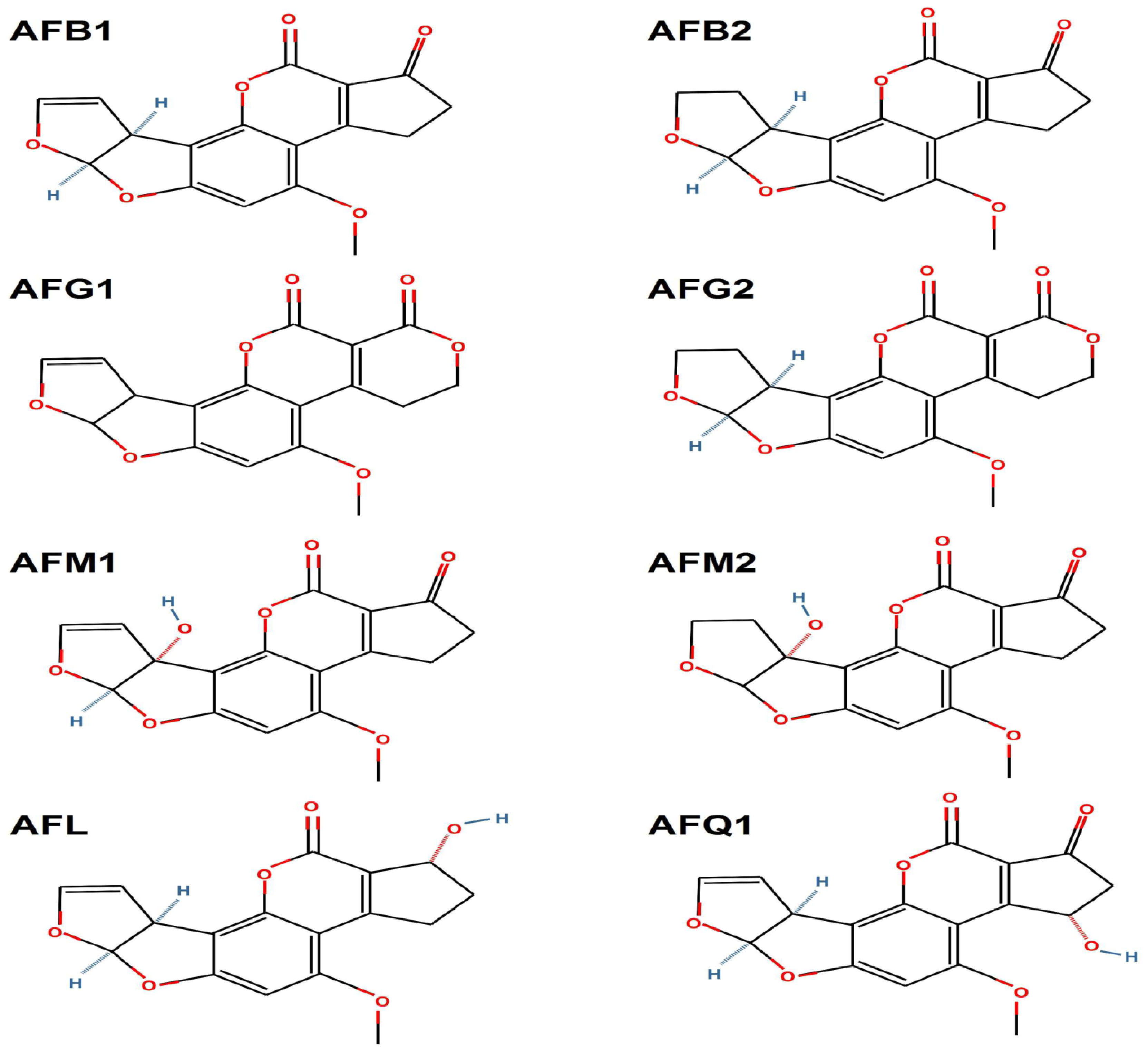
2.1. Chemical Structure and Classification of Aflatoxins
2.2. Mechanisms of Toxicity
2.3. Acute and Chronic Health Effects
2.4. Other Toxic Metabolites Produced by Aspergillus
2.5. Synergistic Effects of Multiple Mycotoxins
3. Health Risks Associated with Aflatoxin Exposure
3.1. Hepatotoxicity and Liver Cancer
3.2. Immunosuppression and Increased Susceptibility to Infections
3.3. Growth Impairment and Developmental Delays in Children
3.4. Economic Impact on Livestock and Poultry
3.5. Global Burden of Aflatoxin-Related Diseases
4. Mitigation Strategies for Aflatoxin Contamination
4.1. Pre-Harvest Interventions
4.2. Post-Harvest Management
4.3. Biological Control Methods
4.4. Physical and Chemical Detoxification
4.5. Integrated Management Approaches
5. Chemical Analysis of Aflatoxins and Toxic Metabolites
5.1. Sample Preparation Techniques
5.2. Chromatographic Methods
5.3. Immunoassays and Rapid Screening Methods
5.4. Emerging Technologies for Aflatoxin Detection
5.5. Challenges in Aflatoxin Analysis
6. Regulatory Framework and Global Perspectives
6.1. International Regulations and Standards
6.2. Challenges in Developing Countries
6.3. Role of International Organizations
6.4. Trade Implications and Economic Impact
6.5. Public Awareness and Education
7. Future Perspectives and Research Directions
7.1. Genetic Engineering and Crop Improvement
7.2. Nanotechnology in Aflatoxin Management
7.3. Integration of Omics Technologies
7.4. Climate Change and Aflatoxin Contamination
7.5. Global Collaboration and Capacity Building
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed (CXS 193-1995); FAO/WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Mitigating Aflatoxin Contamination in Food and Feed; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Aflatoxins (Vol. 100F). In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.Y.; Watson, S.; Routledge, M.N. Aflatoxin exposure and associated human health effects, a review of epidemiological studies. Food Saf. 2016, 4, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klich, M.A. Aspergillus flavus: The major producer of aflatoxin. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, F. Global burden of aflatoxin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: A risk assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkvold, G.P.; Arias, S.; Taschl, I.; Gruber-Dorninger, C. Mycotoxins in corn: Occurrence, impacts, and management. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 90, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraica, M.; Radic, B.; Lucic, A.; Pavlovic, M. Toxic effects of mycotoxins in humans. Bull. World Health Organ. 1999, 77, 754–766. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M.; Lema, A.G.; Ejeta, D.I.; Gowda, L. Global public health and economic concern due to aflatoxins. Glob. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2021, 1, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zahra, N.; Raza, M.H.; Hafeez, F.; Saeed, M.K.; Khan, S.A.; Saeed, A.; Shahzad, K. Impact of aflatoxins exposure on human health and its management strategies. Lahore Garrison Univ. J. Life Sci. 2023, 7, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyebamiji, Y.O.; Adebayo, I.; Umar, O.B.; Mohd Zaini, N.A.; Ismail, M.N. Occurrence, health implications, and management of aflatoxin in cereal: A current review. Egypt. J. Bot. 2024, 64, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shephard, G.S. Impact of mycotoxins on human health in developing countries. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2008, 25, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Pedroso, I.R. Mycotoxins in cereal-based products and their impacts on the health of humans, livestock animals and pets. Toxins 2023, 15, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, M.C. Aflatoxins as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28 (Suppl. S1), 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Guclu, H. Aflatoxin regulations in a network of global maize trade. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milki, S.; Abdeta, D. Public health impact of aflatoxin. J. Bacteriol. Mycol. Open Access. 2023, 11, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, P.C.; Sylla, A.; Diallo, M.S.; Castegnaro, M.; Hall, A.J.; Wild, C.P. The role of aflatoxins in initiating liver cancer in Ghana. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, G.A.; Brown, M.P. Genetics and physiology of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1998, 36, 329–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, D.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Cleveland, T.E. Molecular genetic analysis and regulation of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.L. Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses—An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Samson, R.A. Two new aflatoxin producing species, and an overview of Aspergillus section Flavi. Stud. Mycol. 2011, 69, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, K.; Cardwell, K.F.; Setamou, M.; Poehling, H.M. The influence of storage practices on aflatoxin contamination in maize in four agroecological zones of Benin, West Africa. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2000, 36, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Hubka, V.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Hong, S.B.; Nováková, A.; Chen, A.J.; Samson, R.A. Taxonomy of Aspergillus section Flavi and their production of aflatoxins, ochratoxins, and other mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groopman, J.D.; Egner, P.A.; Schulze, K.J.; Wu, L.S.F.; Merrill, R.; Mehta, S.; Christian, P. Aflatoxin exposure during pregnancy and neonatal outcomes in Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Huang, T.; Su, J.; Liang, F.; Wei, Z.; Liang, Y.; Kensler, T.W. Hepatocellular carcinoma and aflatoxin exposure in Zhuqing Village, Fusui County, People’s Republic of China. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2001, 10, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, P.C.; Collinson, A.C.; Cheung, Y.B.; Gong, Y.Y.; Hall, A.J.; Prentice, A.M.; Wild, C.P. Aflatoxin exposure in utero causes growth faltering in Gambian infants. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Jinap, S.; Pirouz, A.A.; Ahmad Faizal, A.R. Aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products, occurrence and recent challenges: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlangwiset, P.; Shephard, G.S.; Wu, F. Aflatoxins and growth impairment: A review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2011, 41, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Singh, R.K.; De, P.S.; Dey, A. Aflatoxins in feeds: Issues and concerns with safe food production. Indian J. Anim. Health 2022, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustom, I.Y.S. Aflatoxin in food and feed: Occurrence, legislation and inactivation by physical methods. Food Chem. 1997, 59, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.K.; Wilkinson, J.R.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Weaver, M.A.; Horn, B.W.; Accinelli, C. Ecology of Aspergillus flavus, regulation of aflatoxin production, and biocontrol strategies to reduce aflatoxin contamination. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 667, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, M.E. Impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoth, S. Improving the evidence base on aflatoxin contamination and exposure in Africa. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2016, 16, 1034–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Klich, M.A. Environmental and developmental factors influencing aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Mycoscience 2007, 48, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, R.; Kumar, M.; Leslie, J.F. Relative severity of aflatoxin contamination in groundnut, maize and rice and its management in Asia. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2007, 24, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, N.J.; Kumi, J.; Johnson, N.M.; Dotse, E.; Marroquin-Cardona, A.; Wang, J.S.; Jolly, P.E. Aflatoxin exposure in individuals consuming maize in Ghana: Impact of traditional maize processing methods. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2016, 16, 11012–11034. [Google Scholar]
- Bankole, S.A.; Adebanjo, A. Mycotoxins in food in West Africa: Current situation and possibilities of controlling it. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 2, 254–263. [Google Scholar]
- Gnonlonfin, G.J.B.; Hell, K.; Fandohan, P.; Siame, A.B. Mycotoxin contamination and toxigenic fungi associated with maize and groundnut in Benin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 122, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezekiel, C.N.; Sulyok, M.; Warth, B.; Krska, R. Multi-mycotoxin analysis in Nigerian maize and maize-based snacks. Mycotoxin Res. 2012, 28, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.; Naehrer, K. A three-year survey on the worldwide occurrence of mycotoxins in feedstuffs and feed. Toxins 2012, 4, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krska, R.; Welzig, E.; Boudra, H. Analysis of Fusarium toxins in feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, G.S. Aflatoxin and food safety: Recent African perspectives. Toxin Rev. 2009, 28, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kaale, L.D.; Kimanya, M.E.; Macha, I.J.; Mlalila, N. Aflatoxin contamination and recommendations to improve its control: A review. World Mycotoxin J. 2021, 14, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mahato, D.K.; Kamle, M.; Mohanta, T.K.; Kang, S.G. Aflatoxins: A global concern for food safety, human health and their management. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryden, W.L. Mycotoxin contamination of the feed supply chain: Implications for animal productivity and feed security. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2012, 173, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I.; Miller, J.D. A concise history of mycotoxin research. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7021–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.P.; Turner, P.C. The toxicology of aflatoxins as a basis for public health decisions. Mutagenesis 2002, 17, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Albores, A.; Arámbula-Villa, G.; Loarca-Piña, G.; González-Hernández, J.; Moreno-Martínez, E. Aflatoxins’ biodegradation in maize by Pleurotus ostreatus: Effect on toxicological activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnoli, C.; Monge, M.P.; Miazzo, R.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Magnoli, C.E.; Merkis, C.; Dalcero, A. Effect of low levels of aflatoxin B1 on performance, biochemical parameters, and aflatoxin B1 in broiler liver tissues in the presence of monensin. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagl, V.; Schwartz, H.; Krska, R.; Moll, W.D. Metabolism of the masked mycotoxin deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Hou, L. Aflatoxin exposure assessment and control strategies in China. Food Control 2016, 68, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruyck, K.; De Boevre, M.; Huybrechts, I.; De Saeger, S. Dietary mycotoxins, co-exposure, and carcinogenesis in humans: Short review. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2015, 766, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.B.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J.; Ferrer, E. Co-occurrence and risk assessment of mycotoxins in food and diet in Europe. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2050–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, P.E.; Jiang, Y.; Ellis, W.O.; Awuah, R.T.; Nnedu, O.; Phillips, T.D.; Williams, J.H. Determinants of aflatoxin levels in Ghanaians: Socioeconomic status, health, and food consumption patterns. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 771–789. [Google Scholar]
- Kortei, N.K.; Odamtten, G.T.; Agyekum, M.A. Mycotoxins and food safety: A review of the implications of climate change on aflatoxin production. Food Control 2021, 125, 107994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligeorgakis, C.; Magro, C.; Skendi, A.; Gebrehiwot, H.H.; Valdramidis, V.; Papageorgiou, M. Fungal and Toxin Contaminants in Cereal Grains and Flours: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojuri, O.T.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Eskola, M.K.; Šarkanj, B.; Babalola, D.A.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R.; Turner, P.C.; Degen, G.H. Biomonitoring of Dietary Mycotoxin Exposure and Associated Impact on the Gut Microbiome in Nigerian Infants. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, C.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Cotty, P.J. Diversity of aflatoxin-producing fungi and their impact on food safety in sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 174, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojuri, O.T.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Eskola, M.K.; Turner, P.C.; Degen, G.H. Mycotoxin Exposure Biomonitoring in Breastfed and Non-Exclusively Breastfed Nigerian Children. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106998. [Google Scholar]
- Akinrinlola, R.J.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Ayeni, K.I.; Oyeyemi, O.T.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R.; Ogunremi, O.R.; Oyeyemi, I.T. Prevalence and Health Risk Evaluations of Mycotoxins in Drinking Water Sources in Nigeria. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 31200–31214. [Google Scholar]
- Rushing, B.R.; Selim, M.I. Aflatoxin B1: A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food, occupational exposure, and detoxification methods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.F.; Girgin, G.; Baydar, T. Mycotoxin detection in animal-derived foodstuffs in Europe. Toxins 2019, 11, 545. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Mitchell, N.J. How climate change and regulation can affect the economics of mycotoxins. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.S.; Salleh, B. Aflatoxin detection methods and testing for contamination in peanuts: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3103–3116. [Google Scholar]
- Udomkun, P.; Wiredu, A.N.; Nagle, M.; Müller, J.; Vanlauwe, B.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Innovative technologies to manage aflatoxins in foods and feeds and the profitability of application—A review. Food Control. 2017, 76, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.M.; Kim, S.H.; Lovell, D.P.; Williams, J.H. Aflatoxin and fumonisin biomarkers: A review of exposure, genetic susceptibility, and cancer risk. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 233, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Benkerroum, N. Retrospective and prospective look at aflatoxin research and control: A review. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 791–810. [Google Scholar]
- Cotty, P.J.; Bayman, P.; Egel, D.S.; Elias, K.S. Agriculture, aflatoxins and Aspergillus. Genus Aspergillus 1994, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ayeni, K.I.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R.; Warth, B.; Ezekiel, C.N. Mycotoxins in Complementary Foods Consumed by Infants and Young Children within the First 18 Months of Life. Food Control 2023, 144, 109328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tong, E.; Wu, P.; Chen, J.; Zhao, D.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Qi, X.; et al. Occurrence and Exposure Assessment of Deoxynivalenol and Its Acetylated Derivatives from Grains and Grain Products in Zhejiang Province, China (2017–2020). Toxins 2022, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollay, C.; Kimanya, M.; Kassim, N.; Stoltzfus, R. Main Complementary Food Ingredients Contributing to Aflatoxin Exposure to Infants and Young Children in Kongwa, Tanzania. Food Control 2022, 135, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Meneely, J.P.; Haughey, S.A.; Dean, M.; Wall, P.; Zhang, G.; Baker, B.; Elliott, C.T. Risk Assessments for the Dietary Intake of Aflatoxins in Food: A Systematic Review (2016–2022). Food Control 2023, 149, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, A.; Izzo, L.; Pallarés, N.; Castaldo, L.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ritieni, A. Human Biomonitoring of T-2 Toxin, T-2 Toxin-3-Glucoside and Their Metabolites in Urine through High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2021, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M.I.; Cunha, S.C.; Rebai, I.; Fernandes, J.O. Algerian Workers’ Exposure to Mycotoxins—A Biomonitoring Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Wells, L.; Williams, C.; White, K.; De Santis, B.; Liu, Y.; Debegnach, F.; Miano, B.; Moretti, G.; Greetham, S.; et al. Assessment of Urinary Deoxynivalenol Biomarkers in UK Children and Adolescents. Toxins 2018, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpakpale, D.O.; Kraak, B.; Meijer, M.; Ayeni, K.I.; Houbraken, J.; Ezekiel, C.N. Fungal Diversity and Aflatoxins in Maize and Rice Grains and Cassava-Based Flour (Pupuru) from Ondo State, Nigeria. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, N.; Emam, W.A.; Gharib, A.F.; Nafea, O.E.; Zakaria, M. Assessment of Serum Aflatoxin B1 Levels in Neonatal Jaundice with Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency: A Preliminary Study. Mycotoxin Res. 2021, 37, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, M.C.; Atanda, O.O.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Sulyok, M.; Warth, B.; Beltrán, E.; Krska, R. Food Safety Assessment of Mycotoxins in Infant Formulas Consumed in Nigeria. Food Control 2020, 108, 106825. [Google Scholar]
- Samarajeewa, U.; Jayasena, D.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Jo, C.; Lee, S.K. Recent Advances in Mycotoxin Detection Techniques and the Crucial Role of Reference Materials. Food Control 2025, 142, 109274. [Google Scholar]
- Samarajeewa, U.; Jayasena, D.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Jo, C.; Lee, S.K. A Comprehensive Review of Mycotoxins: Toxicology, Detection, and Innovative Mitigation Strategies. Foods 2024, 13, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Samarajeewa, U.; Jayasena, D.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Jo, C.; Lee, S.K. Mitigation of Mycotoxins in Food—Is It Possible? Foods 2024, 13, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarajeewa, U.; Jayasena, D.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Jo, C.; Lee, S.K. A Review of Recent Innovative Strategies for Controlling Mycotoxins in Foods. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Samarajeewa, U.; Jayasena, D.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Jo, C.; Lee, S.K. The Impact of Mycotoxins in the Food Industry: Occurrence, Detection, and Mitigation Strategies. Foods 2024, 13, 1589. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Basu, M.S.; Rajendran, T.P. Mycotoxin research and mycoflora in some commercially important agricultural commodities. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senghor, L.A.; Ortega-Beltran, A.; Atehnkeng, J.; Callicott, K.A.; Cotty, P.J.; Bandyopadhyay, R. The atoxigenic biocontrol strain Aspergillus flavus AF36 uses competition to prevent aflatoxin contamination in U.S. commercial cotton. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, B.; Oswald, I.P. Mycotoxin co-contamination of food and feed: Meta-analysis of publications describing toxicological interactions. World Mycotoxin J. 2011, 4, 285–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, M.V.; Iamanaka, B.T.; Pitt, J.I.; Taniwaki, M.H. Fungi and mycotoxins in cocoa: From farm to chocolate. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 296, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Oswald, I.P.; Puel, O. The mycotoxin deoxynivalenol: Advances in molecular approach and future perspectives in toxicology. Toxins 2015, 7, 4747–4766. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, R.A.; Jebur, A.B.; Kang, W.; El-Demerdash, F.M. An overview on the major mycotoxins in food products: Characteristics, toxicity, and analysis. J. Future Foods 2022, 2, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, E.; Juan-García, A.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Interaction effects of mycotoxin mixtures on oxidative stress biomarkers in Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol 2014, 74, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajslova, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25%. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte, I.; Audenaert, K.; De Gelder, L. Biodegradation of mycotoxins: Tales from known and unexplored worlds. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uegaki, R. Aflatoxin contamination in food and its removal technologies. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2016, 6, 555–569. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, H.; Singh, N.K.; Gupta, R. Genetic and molecular mechanisms of resistance to aflatoxin contamination in crops. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyeye, S.A.O. Aflatoxigenic fungi and mycotoxins in food: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.P. Fungal secondary metabolism: Regulation, function, and drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardwell, K.F.; Cotty, P.J. Distribution of Aspergillus section Flavi among field soils from the four agroecological zones of the Republic of Benin, West Africa. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neme, K.; Mohammed, A. Mycotoxin occurrence in grains and the role of postharvest management as a mitigation strategy: A review. Food Control 2017, 78, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, M.M.; Huffaker, A.; Schmelz, E.A. OsMPK3 regulates metabolic defense responses to anthracnose infection in rice. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1984–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Identification and detoxification of mycotoxins using nanotechnology. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Redzwan, S.; Rosita, J.; Mohd Sokhini, A.; Norshakirin, M.H. Socio-demographic and socio-economic determinants of aflatoxin exposure in young adults. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, W.L. Mycotoxin contamination of the feed supply chain: Implications for animal productivity and feed security. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, I.M.G.; França, J.A.; Uliana, R. Assessment of aflatoxin contamination in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) from smallholder farms in Africa. Food Control 2021, 121, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Risk assessment of aflatoxins in food. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.P.P.; Mohd-Redzwan, S. Mycotoxin: Its impact on gut health and microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.I.; Hocking, A.D. Fungi and Food Spoilage, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Montesano, R.; Hall, J.; Wild, C.P. Aflatoxin exposure and cancer risk. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 263, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Phillips, T.D.; Jolly, C.M.; Stiles, J.K.; Jolly, P.E.; Aggarwal, D. Human aflatoxicosis in developing countries: A review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, C.C.H.; Marsh, G.M.; Wu, F. Population attributable risk of aflatoxin-related liver cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosnider, H.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Banziger, M.; Bhat, R.V.; Breiman, R.; Brune, M.N.; DeCock, K.; Dilley, A.; Groopman, J.; Hell, K.; et al. Workgroup report: Public health strategies for reducing aflatoxin exposure in developing countries. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.C.; Moore, S.E.; Hall, A.J.; Prentice, A.M.; Wild, C.P. Modification of immune function through exposure to dietary aflatoxin in Gambian children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, A.V.; Tonin, F.G.; Baptista, G.Z.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Chemical, enzymatic and biological methods for detoxification of aflatoxins in foods and feeds: A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 1758–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabak, B.; Dobson, A.D.; Var, I. Strategies to prevent mycotoxin contamination of food and animal feed: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanail, A.V.; Syku, L.; Malachová, A.; Krska, R. Simultaneous determination of major mycotoxins and their conjugated forms in cereals using a novel LC-MS/MS method. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnoli, C.; Monge, M.P.; Miazzo, R.; Dalcero, A. Dietary strategies to counteract the effects of mycotoxins: A review. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2011, 20, 377–393. [Google Scholar]
- Misihairabgwi, J.M.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Sulyok, M.; Shephard, G.S.; Krska, R. Mycotoxin contamination of foods in Southern Africa: A review of 100 years of research. Food Control 2019, 101, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Vermeulen, L.C.; Gavai, A.K.; Liu, C. Climate change impacts on aflatoxin B1 in maize and mycotoxin risks for human health. World Mycotoxin J. 2019, 12, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Munkvold, G.P. Cultural and genetic approaches to managing mycotoxins in maize. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.R.; Singh, D.; Singh, R. Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetables by microbial antagonists: A review. Biol. Control 2009, 50, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.Y.; Cardwell, K.; Hounsa, A.; Egal, S.; Turner, P.C.; Hall, A.J.; Wild, C.P. Dietary aflatoxin exposure and impaired child growth in Benin and Togo: A cross-sectional study. Br. Med. J. 2002, 325, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wogan, G.N.; Kensler, T.W.; Groopman, J.D. Present and future directions of translational research on aflatoxin and hepatocellular carcinoma. A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I. Mycotoxins in food: Detection and control. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12000–12007. [Google Scholar]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, toxicity, and analysis of major mycotoxins in food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohnal, V.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Metabolism of aflatoxins: Key enzymes and interindividual variability. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissonnier, G.M.; Pinton, P.; Laffitte, J.; Cossalter, A.M.; Gong, Y.Y.; Wild, C.P.; Oswald, I.P. Immunotoxicity of aflatoxin B1: Impairment of the cell-mediated response to vaccine antigen and modulation of cytokine expression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 231, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.N.; Raghavender, C.R.; Reddy, B.N.; Salleh, B. Biological control of Aspergillus flavus growth and subsequent aflatoxin B1 production in sorghum grains. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 4247–4250. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, R.; Rai, R.V.; Karim, A.A. Mycotoxins in food and feed: Present status and future concerns. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, M.A.; Abbas, H.K.; Jin, X.; Elliott, M.S.; Duke, S.O. Aflatoxin regulation in crops: A review of recent advances. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 964–973. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The 2020 update on aflatoxin regulations and risk assessment. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaike, S.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Bhatnagar, D. Aflatoxin regulation: An update on current practices and guidelines. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 435–450. [Google Scholar]
- Kensler, T.W.; Roebuck, B.D.; Wogan, G.N.; Groopman, J.D. Aflatoxin: A 50-year odyssey of mechanistic and translational toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120 (Suppl. S1), S28–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.P.; Gong, Y.Y. Mycotoxins and human disease: A largely ignored global health issue. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Impact Area | Public Health Impact | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Health Risks |
|
|
|
| |
| Chronic Exposure |
|
|
|
| |
| Childhood Stunting |
|
|
| Crop Losses |
|
|
| Trade Restrictions |
|
|
| Healthcare Burden |
|
|
| Case Study Examples |
|
|
| Mitigation Strategies |
|
|
| Agricultural Impact |
|
|
| Region | Countries Affected | Common Contaminated Crops | Prevalence | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Kenya, Nigeria, Ghana, Tanzania, Malawi, and Benin. | Maize, peanuts, and sorghum. | High prevalence; >50% of maize samples exceed regulatory limits in some areas. | Warm, humid climates; poor storage practices; limited regulatory enforcement. |
| Southeast Asia | India, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam, and Thailand. | Maize, rice, and peanuts. | High prevalence; frequent contamination in maize and peanuts. | Tropical climate; high humidity; inadequate post-harvest management. |
| Latin America | Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, and Honduras. | Maize, peanuts, and tree nuts. | Moderate to high prevalence; significant contamination in maize and peanuts. | Warm climates; variable agricultural practices; some regulatory challenges. |
| North America | United States (Southern states). | Maize, peanuts, and tree nuts. | Low to moderate prevalence; localized outbreaks in drought-affected areas. | Advanced agricultural practices; strict regulatory standards. |
| Europe | Serbia, Italy, Spain, and Romania. | Maize and cereals. | Low prevalence; occasional contamination due to climate change. | Strict regulatory enforcement; advanced storage and monitoring systems. |
| Middle East | Iran, Egypt, and Turkey. | Maize, pistachios, and figs. | Moderate prevalence; contamination in pistachios and figs. | Warm climates; variable storage conditions; limited regulatory enforcement. |
| East Asia | China and South Korea. | Maize, rice, and peanuts. | Moderate prevalence; contamination in maize and peanuts. | Variable climate; improving regulatory standards. |
| Disease | Associated Health Impact | Global Incidence (Estimate) | Regions Most Affected | Primary Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma—HCC) | Aflatoxin exposure is a leading cause of liver cancer. | 250,000–500,000 new cases annually. | Sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, and China. | Chronic exposure to aflatoxin, particularly in combination with HBV infection. |
| Acute Aflatoxicosis | Acute poisoning leading to liver damage, and in severe cases, death. | 10,000–20,000 cases annually. | Asia, Africa, and Latin America. | Consumption of aflatoxin-contaminated food (high levels). |
| Stunted Growth in Children | Aflatoxin exposure impairs childhood development and growth. | Millions of children at risk. | Sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia. | Chronic exposure to aflatoxins in food over extended periods. |
| Immune Suppression | Impaired immune system, leading to increased vulnerability to infections. | Significant regional impact. | Africa, Southeast Asia. | Long-term exposure to low levels of aflatoxins. |
| Liver Cirrhosis | Chronic liver damage and fibrosis due to prolonged exposure. | Thousands of cases annually. | High exposure areas such as sub-Saharan Africa. | Long-term exposure to aflatoxins. |
| Increased Mortality in HIV Patients | Aflatoxin exacerbates liver disease progression in HIV-infected individuals. | Unclear, but significant. | Sub-Saharan Africa. | Co-exposure to aflatoxins and HIV infection. |
| Pre-Harvest Interventions |
|
| Post-Harvest Management |
|
| Biological Control Methods |
|
| Physical and Chemical Detoxification |
|
| Integrated Management Approaches |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gemede, H.F. Toxicity, Mitigation, and Chemical Analysis of Aflatoxins and Other Toxic Metabolites Produced by Aspergillus: A Comprehensive Review. Toxins 2025, 17, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070331
Gemede HF. Toxicity, Mitigation, and Chemical Analysis of Aflatoxins and Other Toxic Metabolites Produced by Aspergillus: A Comprehensive Review. Toxins. 2025; 17(7):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070331
Chicago/Turabian StyleGemede, Habtamu Fekadu. 2025. "Toxicity, Mitigation, and Chemical Analysis of Aflatoxins and Other Toxic Metabolites Produced by Aspergillus: A Comprehensive Review" Toxins 17, no. 7: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070331
APA StyleGemede, H. F. (2025). Toxicity, Mitigation, and Chemical Analysis of Aflatoxins and Other Toxic Metabolites Produced by Aspergillus: A Comprehensive Review. Toxins, 17(7), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070331





