Comparative Efficacy of Ribosome-Inactivating Protein-Containing Immunotoxins in 2D and 3D Models of Sarcoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of 3D Single Spheroids and Organoids from Sarcoma Cell Lines
2.2. TfR1, EGFR1 and Her2 Antigen Expression
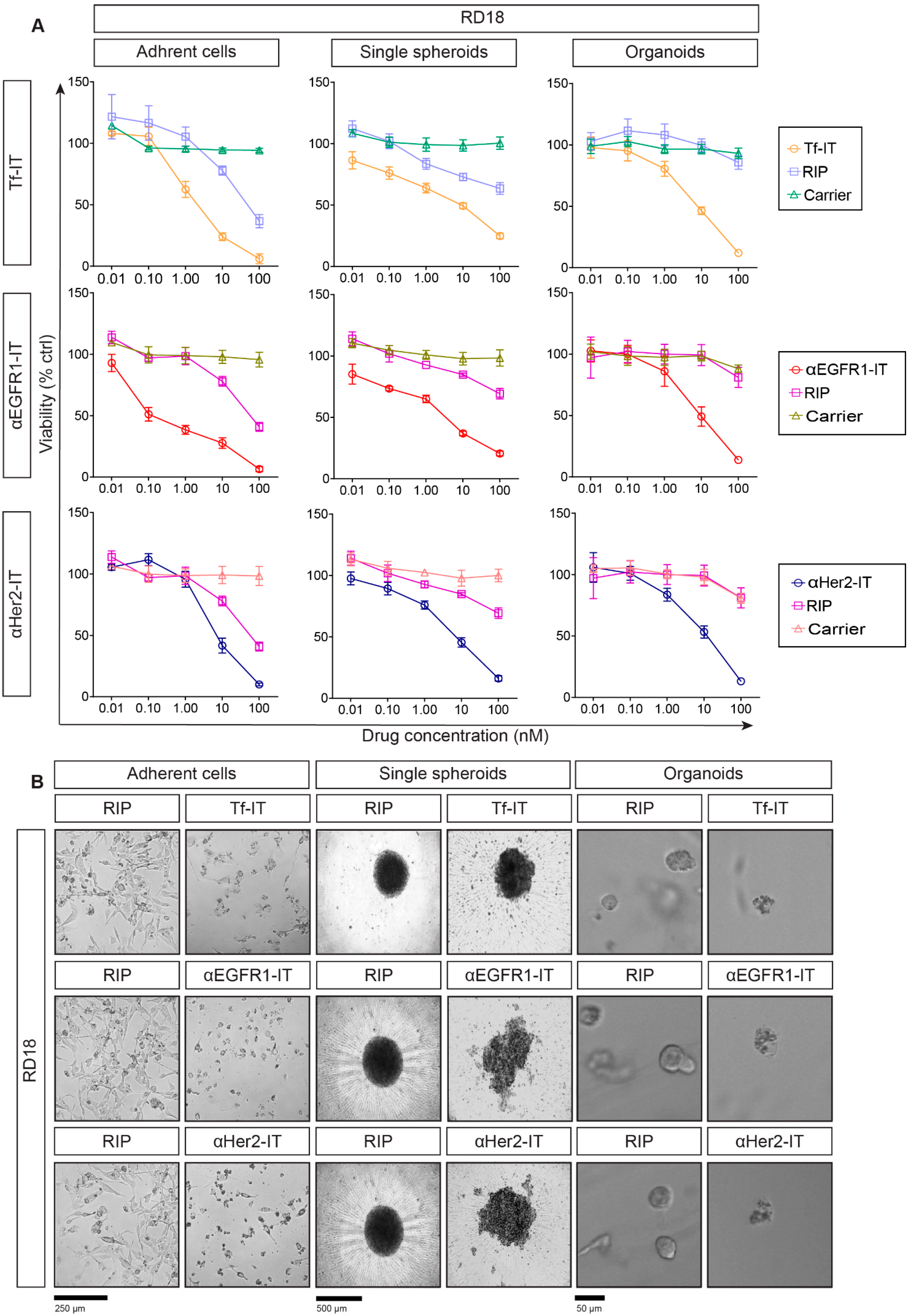
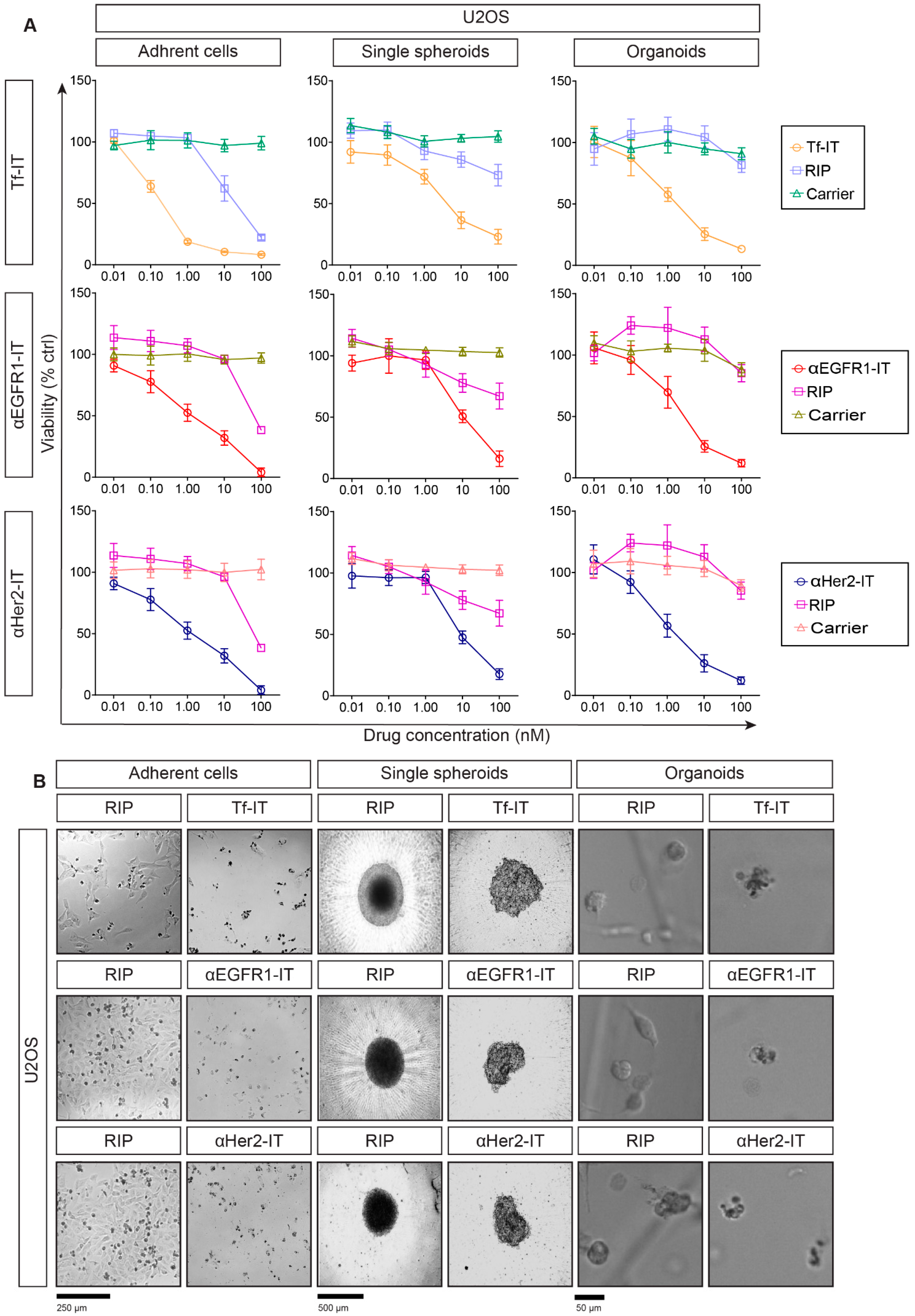
2.3. Selective Efficacy of RIP-Containing ITs in RD18- and U2OS-Derived Models
2.4. Evaluation of Cell Death Mechanisms Induced by the ITs in RD18 and U2OS 2D and 3D Models
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Culture of Adherent Cell Lines, Single Spheroids and Organoids
5.2. RIPs, Carriers and ITs
5.3. H&E and ki67 Immunohistochemistry
5.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
5.5. Viability Assays
5.6. Imaging
5.7. Caspase 3/7 Activation Assays
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Adherent cells |
| IC50 | Concentration inhibiting 50% of cell viability |
| ITs | Immunotoxins |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| Ocy | Ocymoidine |
| OR | Organoids |
| RIPs | Ribosome-inactivating proteins |
| SO6 | Saporin |
| SS | Single spheroids |
| Tf | Transferrin |
References
- Dyson, K.A.; Stover, B.D.; Grippin, A.; Mendez-Gomez, H.R.; Lagmay, J.; Mitchell, D.A.; Sayour, E.J. Emerging trends in immunotherapy for pediatric sarcomas. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Kim, H.S.; Han, I. Actual long-term survival after resection of stage III soft tissue sarcoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Bulk, J.; Verdegaal, E.M.; de Miranda, N.F. Cancer immunotherapy: Broadening the scope of targetable tumours. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Weng, A.; Mallinckrodt, B.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H.; Thakur, M. Immunotoxins constructed with ribosome-inactivating proteins and their enhancers: A lethal cocktail with tumor specific efficacy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 6584–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavell, D.J.; Flavell, S.U. Plant-Derived Type I Ribosome Inactivating Protein-Based Targeted Toxins: A Review of the Clinical Experience. Toxins 2022, 14, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Dai, R.; Xu, J.; Feng, H. Transferrin receptor-1 and VEGF are prognostic factors for osteosarcoma. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Brawley, V.S.; Hegde, M.; Robertson, C.; Ghazi, A.; Gerken, C.; Liu, E.; Dakhova, O.; Ashoori, A.; Corder, A.; et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) -Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells for the Immunotherapy of HER2-Positive Sarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.C.; de Mello, C.A.L.; Corassa, M.; Abdallah, E.A.; Urvanegia, A.C.; Alves, V.S.; Flores, B.C.T.C.P.; Díaz, M.; Nicolau, U.R.; Silva, V.S.E.; et al. EGFR expression in circulating tumor cells from high-grade metastatic soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin-S6: A useful tool in cancer therapy. Toxins 2013, 5, 1698–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubelin, C.; Muñoz-Garcia, J.; Griscom, L.; Cochonneau, D.; Ollivier, E.; Heymann, M.F.; Vallette, F.M.; Oliver, L.; Heymann, D. Three-dimensional in vitro culture models in oncology research. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunti, S.; Hoke, A.T.K.; Vu, K.P.; London, N.R., Jr. Organoid and Spheroid Tumor Models: Techniques and Applications. Cancers 2021, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünewald, T.G.; Alonso, M.; Avnet, S.; Banito, A.; Burdach, S.; Cidre-Aranaz, F.; Di Pompo, G.; Distel, M.; Dorado-Garcia, H.; Garcia-Castro, J.; et al. Sarcoma treatment in the era of molecular medicine. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Calafato, G.; Bortolotti, M.; Chiarelli Olivari, C.; Maiello, S.; Bolognesi, A. Antibody conjugates for sarcoma therapy: How far along are we? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, M.; Cortesi, M.; Zamagni, A.; Arienti, C.; Pignatta, S.; Tesei, A. Modeling neoplastic disease with spheroids and organoids. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels-Wells, T.R.; Penichet, M.L. Transferrin receptor 1: A target for antibody-mediated cancer therapy. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelaria, P.V.; Leoh, L.S.; Penichet, M.L.; Daniels-Wells, T.R. Antibodies Targeting the Transferrin Receptor 1 (TfR1) as Direct Anti-cancer Agents. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 607692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maennling, A.E.; Tur, M.K.; Niebert, M.; Klockenbring, T.; Zeppernick, F.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Meinhold-Heerlein, I.; Hussain, A.F. Molecular Targeting Therapy against EGFR Family in Breast Cancer: Progress and Future Potentials. Cancers 2019, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, D.; Zhang, B.; Xue, Y.; Shang, P. Transferrin receptor 1 in cancer: A new sight for cancer therapy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 916–931. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, C.; Polito, L.; Nanni, P.; Landuzzi, L.; Astolfi, A.; Nicoletti, G.; Rossi, I.; De Giovanni, C.; Bolognesi, A.; Lollini, P.L. HER/erbB receptors as therapeutic targets of immunotoxins in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J. Immunother. 2002, 25, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzola, M.; Bergamaschi, G.; Dezza, L.; D’Uva, R.; Ponchio, L.; Rosti, V.; Ascari, E. Cytotoxic activity of an anti-transferrin receptor immunotoxin on normal and leukemic human hematopoietic progenitors. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 536–541. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, N.; FitzGerald, D. Immunotoxin Therapies for the Treatment of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent Cancers. Toxins 2016, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świerczewska, M.; Sterzyńska, K.; Ruciński, M.; Andrzejewska, M.; Nowicki, M.; Januchowski, R. The response and resistance to drugs in ovarian cancer cell lines in 2D monolayers and 3D spheroids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidwell, T.R.; Røsland, G.V.; Tronstad, K.J.; Søreide, K.; Hagland, H.R. Metabolic flux analysis of 3D spheroids reveals significant differences in glucose metabolism from matched 2D cultures of colorectal cancer and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Metab. 2022, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Shihabi, A.; Tebon, P.J.; Nguyen, H.T.L.; Chantharasamee, J.; Sartini, S.; Davarifar, A.; Jensen, A.Y.; Diaz-Infante, M.; Cox, H.; Gonzalez, A.E.; et al. The landscape of drug sensitivity and resistance in sarcoma. Cell Stem Cell 2024, 31, 1524–1542.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, C.; Landuzzi, L.; Rossi, I.; De Giovanni, C.; Nicoletti, G.; Astolfi, A.; Pupa, S.; Menard, S.; Scotlandi, K.; Nanni, P.; et al. Expression of HER/erbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases and induction of differentiation by glial growth factor 2 in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 87, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, L.L.; Li, Y.J.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.H.; Ye, Z.M. Trastuzumab enhanced the cytotoxicity of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells against zoledronate-sensitized osteosarcoma cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Li, B.; Qiu, C.; He, M. miR-141-3p is a key negative regulator of the EGFR pathway in osteosarcoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 4461–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesen, J.; Brehm, H.; Stein, C.; Berges, N.; Pardo, A.; Fischer, R.; Ten Haaf, A.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Tur, M.K.; Barth, S. In vitro effects and ex vivo binding of an EGFR-specific immunotoxin on rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesen, J.; Stein, C.; Brehm, H.; Hehmann-Titt, G.; Fendel, R.; Melmer, G.; Fischer, R.; Barth, S. Novel EGFR-specific immunotoxins based on panitumumab and cetuximab show in vitro and ex vivo activity against different tumor entities. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 2079–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilbeam, K.; Wang, H.; Taras, E.; Bergerson, R.J.; Ettestad, B.; DeFor, T.; Borgatti, A.; Vallera, D.A.; Verneris, M.R. Targeting pediatric sarcoma with a bispecific ligand immunotoxin targeting urokinase and epidermal growth factor receptors. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 11938–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, N.N.; Barsky, S.H.; Dougherty, P.R.; Vallera, D.A. A bispecific EpCAM/CD133-targeted toxin is effective against carcinoma. Target Oncol. 2014, 9, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, J.Z.; Phillips, G.D.L.; Nitta, H.; Garsha, K.; Admire, B.; Kraft, R.; Dennis, E.; Vela, E.; Towne, P. Activity of trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in 3D cell culture. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 188, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Hoshi, H.; Higa, A.; Hiyama, G.; Tamura, H.; Ogawa, M.; Takagi, K.; Goda, K.; Okabe, N.; Muto, S.; et al. An In Vitro System for Evaluating Molecular Targeted Drugs Using Lung Patient-Derived Tumor Organoids. Cells 2019, 8, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balalaeva, I.V.; Sokolova, E.A.; Puzhikhina, A.D.; Brilkina, A.A.; Deyev, S.M. Spheroids of HER2-Positive Breast Adenocarcinoma for Studying Anticancer Immunotoxins In Vitro. Acta Naturae 2017, 9, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Phung, Y.; Feng, M.; Nagashima, K.; Zhang, J.; Broaddus, V.C.; Hassan, R.; Fitzgerald, D.; Ho, M. The development and characterization of a human mesothelioma in vitro 3D model to investigate immunotoxin therapy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golay, J.; Taylor, R.P. The Role of Complement in the Mechanism of Action of Therapeutic Anti-Cancer mAbs. Antibodies 2020, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lóssio, C.F.; Verbeke, I.; Verduijn, J.; Parakhonskiy, B.; Van der Meeren, L.; Chen, P.; De Zaeytijd, J.; Skirtach, A.G.; Van Damme, E.J.M. The type-1 ribosome-inactivating protein OsRIP1 triggers caspase-independent apoptotic-like death in HeLa cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Farini, V.; Battelli, M.G.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin induces multiple death pathways in lymphoma cells with different intensity and timing as compared to ricin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Pedrazzi, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Apoptosis and necroptosis induced by stenodactylin in neuroblastoma cells can be completely prevented through caspase inhibition plus catalase or necrostatin-1. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, A.; Partridge, L.J.; Davletov, B.; Hautbergue, G.M. The Use of Plant-Derived Ribosome Inactivating Proteins in Immunotoxin Development: Past, Present and Future Generations. Toxins 2017, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Surendranath, K.; Bora, N.; Surolia, A.; Karande, A.A. Ribosome inactivating proteins and apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.L.; Soragni, A. Patient-Derived Tumor Organoid Rings for Histologic Characterization and High-Throughput Screening. STAR Protoc. 2020, 1, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirpe, F.; Gasperi-Campani, A.; Barbieri, L.; Falasca, A.; Abbondanza, A.; Stevens, W.A. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from the seeds of Saponaria officinalis L. (soapwort), of Agrostemma githago L. (corn cockle) and of Asparagus officinalis L. (asparagus), and from the latex of Hura crepitans L. (sandbox tree). Biochem. J. 1983, 216, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Olivieri, F.; Battelli, M.G.; Barbieri, L.; Falasca, A.I.; Parente, A.; Del Vecchio Blanco, F.; Stirpe, F. Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RNA N-glycosidases) from the seeds of Saponaria ocymoides and Vaccaria pyramidata. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 228, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselaar, P.H.; van-Dijk, A.J.; de-Gast, G.C.; Polito, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Vooijs, W.C.; Verheul, A.F.; Krouwer, H.G.; Marx, J. Transferrin toxin but not transferrin receptor immunotoxin is influenced by free transferrin and iron saturation. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 32, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Massimo, A.M.; Di Loreto, M.; Pacilli, A.; Raucci, G.; D’Alatri, L.; Mele, A.; Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L.; Stirpe, F.; De Santis, R. Immunoconjugates made of an anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody and type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Saponaria ocymoides or Vaccaria pyramidata. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
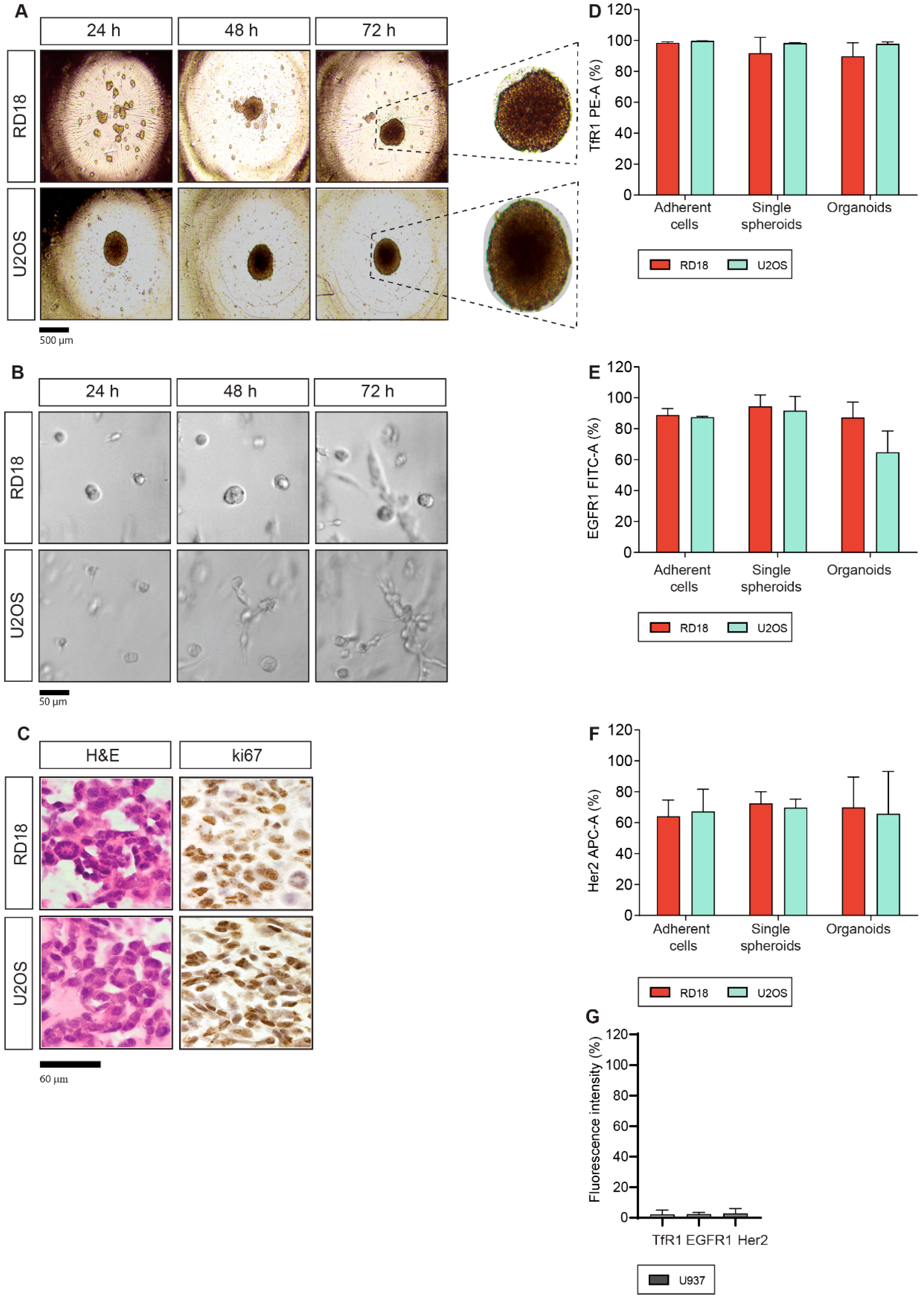

| Antigen Expression (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD18 | U2OS | Non-Target U937 | |||||
| AC | SS | OR | AC | SS | OR | AC | |
| TfR1 | 98.5 | 91.8 | 89.8 | 99.7 | 98.3 | 97.7 | 2.1 |
| EGFR1 | 88.9 | 94.4 | 87.3 | 87.5 | 91.6 | 64.8 | 2.3 |
| Her2 | 64.1 | 77.4 | 69.9 | 67.3 | 69.8 | 65.7 | 2.8 |
| IC50 (nM) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD18 | U2OS | Non-Target U937 | |||||
| AC | SS | OR | AC | SS | OR | AC | |
| SO6 | 24.2 | 314.6 | 740.6 | 13.1 | 473.3 | 236.8 | 470.7 |
| Tf-SO6 | 1.3 | 5.4 | 9.8 | 0.1 | 4.2 | 1.0 | >100 |
| Ocy | 58.9 | 751.9 | 1219 | 73.9 | 593.5 | 196.7 | 1076 |
| αEGFR1-Ocy | 0.3 | 2.8 | 9.1 | 1.3 | 12.1 | 1.8 | >100 |
| αHer2-Ocy | 8.8 | 6.8 | 28.8 | 3.7 | 11.1 | 0.7 | >100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calafato, G.; Bortolotti, M.; Polito, L.; Bolognesi, A. Comparative Efficacy of Ribosome-Inactivating Protein-Containing Immunotoxins in 2D and 3D Models of Sarcoma. Toxins 2025, 17, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060308
Calafato G, Bortolotti M, Polito L, Bolognesi A. Comparative Efficacy of Ribosome-Inactivating Protein-Containing Immunotoxins in 2D and 3D Models of Sarcoma. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060308
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalafato, Giulia, Massimo Bortolotti, Letizia Polito, and Andrea Bolognesi. 2025. "Comparative Efficacy of Ribosome-Inactivating Protein-Containing Immunotoxins in 2D and 3D Models of Sarcoma" Toxins 17, no. 6: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060308
APA StyleCalafato, G., Bortolotti, M., Polito, L., & Bolognesi, A. (2025). Comparative Efficacy of Ribosome-Inactivating Protein-Containing Immunotoxins in 2D and 3D Models of Sarcoma. Toxins, 17(6), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060308








