Dual Proteomics Strategies to Dissect and Quantify the Components of Nine Medically Important African Snake Venoms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Complexity and Diversity of Echis and Dendroaspis Venoms
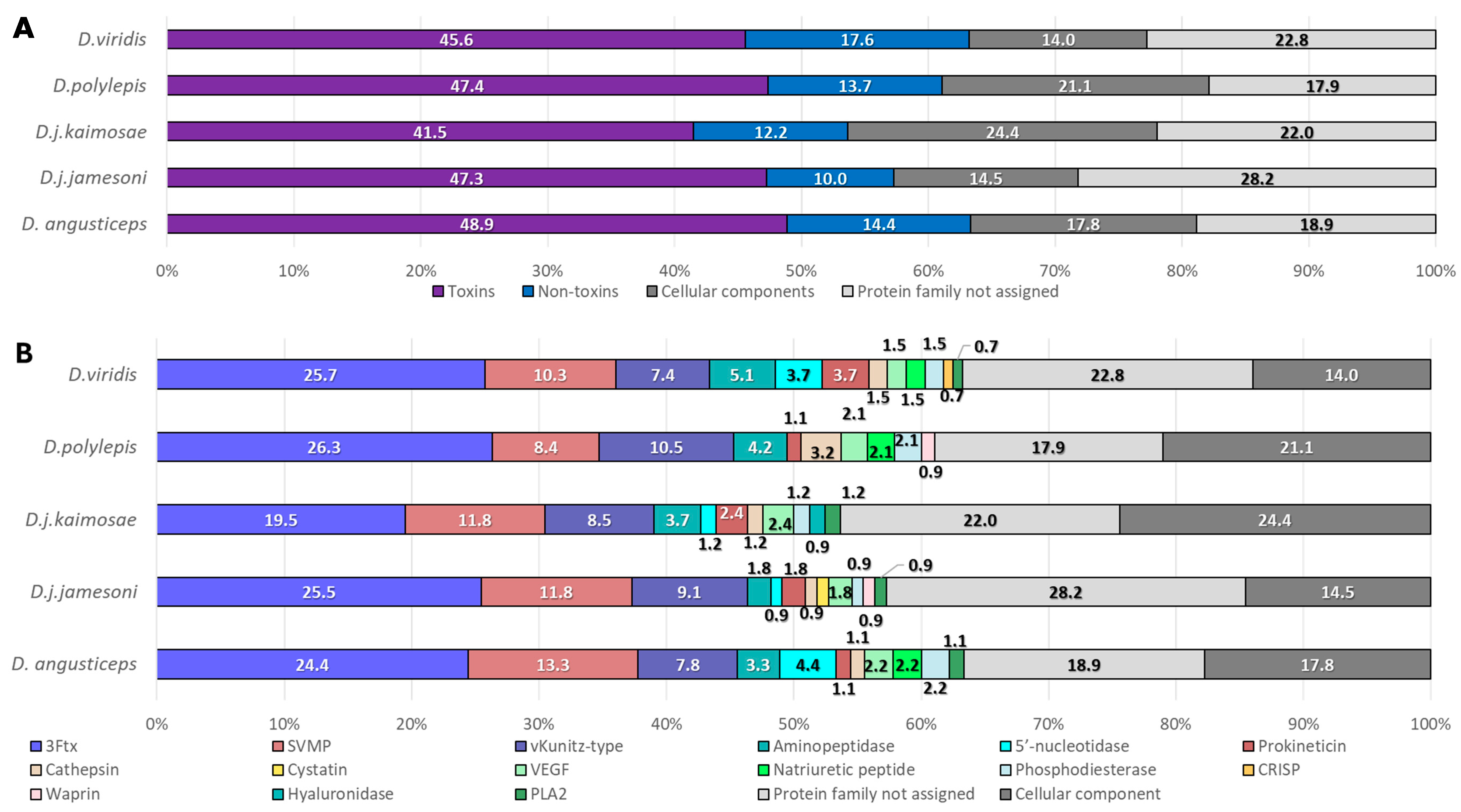
2.2. Proteomics Characterization of Dendroaspis Venoms
2.3. Proteomics Characterization of Echis Venoms
2.4. Proteomics Relative Toxin Quantification for Echis and Dendroaspis Venoms
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michael, G.C.; Grema, B.A.; Aliyu, I.; Alhaji, M.A.; Lawal, T.O.; Ibrahim, H.; Fikin, A.G.; Gyaran, F.S.; Kane, K.N.; Thacher, T.D.; et al. Knowledge of Venomous Snakes, Snakebite First Aid, Treatment, and Prevention among Clinicians in Northern Nigeria: A Cross-Sectional Multicentre Study. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 112, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The Global Burden of Snakebite: A Literature Analysis and Modelling Based on Regional Estimates of Envenoming and Deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrell, D.A.; Williams, D.J. Clinical Aspects of Snakebite Envenoming and Its Treatment in Low-Resource Settings. Lancet 2023, 401, 1382–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Current Perspective on Snake Venom Composition and Constituent Protein Families. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, A.; Utkin, Y. What Are the Neurotoxins in Hemotoxic Snake Venoms? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Calderón, L. An Overview of Lysine-49 Phospholipase A2 Myotoxins from Crotalid Snake Venoms and Their Structural Determinants of Myotoxic Action. Toxicon 2003, 42, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midtgaard, R. RepFocus—A Survey of the Reptiles of the World. Available online: www.Repfocus.Dk (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Abu Baker, M.A.; Al-Saraireh, M.; Amr, Z.; Amr, S.S.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebites in Jordan: A Clinical and Epidemiological Study. Toxicon 2022, 208, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanathasan, A.; Rodrigo, C.; Peranantharajah, T.; Coonghe, A. Saw-Scaled Viper Bites in Sri Lanka: Is It a Different Subspecies? Clinical Evidence from an Authenticated Case Series. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A.; NMcD, D.; Greenwood, B.M.; Ormerod, L.D.; Pope, H.M.; Watkins, B.J.; Prentice, C.R. Poisoning by Bites of the Saw-Scaled or Carpet Viper (Echis carinatus) in Nigeria. Q. J. Med. 1977, 46, 33–62. [Google Scholar]
- Závada, J.; Valenta, J.; Kopecký, O.; Stach, Z.; Leden, P. Black Mamba Dendroaspis Polylepis Bite: A Case Report. Prague Med. Rep. 2011, 112, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.C.; Cue, K.; Khan, R.; Gilbert, M.B.; Rahimi, J. Captive Black Mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) Bite Leading to Respiratory Failure. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 64, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalten, M.; Bakhuis, C.F.J.; Asaggau, I.; Wulfse, M.; van Binsbergen, M.F.; Arntz, E.R.A.N.; Troenokarso, M.F.; Oediet Doebe, J.L.R.; Mahamuud, U.; Belbachir, L.; et al. The Clinical Course and Treatment of Black Mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) Envenomations: A Narrative Review. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, J.; Weiler, S.; Meier, J. Envenomation by a Western Green Mamba (Dendroaspis viridis)—A Report of Three Episodes in Switzerland. Toxicon 2019, 168, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.J.; Gutiérrez, J.-M.; Calvete, J.J.; Wüster, W.; Ratanabanangkoon, K.; Paiva, O.; Brown, N.I.; Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A.; Rowley, P.D.; et al. Ending the Drought: New Strategies for Improving the Flow of Affordable, Effective Antivenoms in Asia and Africa. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1735–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumtecho, S.; Burlet, N.J.; Ljungars, A.; Laustsen, A.H. Towards Better Antivenoms: Navigating the Road to New Types of Snakebite Envenoming Therapies. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 29, e20230057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, Á.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Vargas, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, G. Assessment of Snake Antivenom Purity by Comparing Physicochemical and Immunochemical Methods. Biologicals 2013, 41, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for the Prevention and Clinical Management of Snakebite in Africa; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/204458 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Menzies, S.K.; Arinto-Garcia, R.; Amorim, F.G.; Cardoso, I.A.; Abada, C.; Crasset, T.; Durbesson, F.; Edge, R.J.; El-Kazzi, P.; Hall, S.; et al. ADDovenom: Thermostable Protein-Based ADDomer Nanoparticles as New Therapeutics for Snakebite Envenoming. Toxins 2023, 15, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H. Recombinant Snake Antivenoms Get Closer to the Clinic. Trends Immunol. 2024, 45, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, J.-M.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Laing, G.D. Neutralization of the Haemorrhagic Activities of Viperine Snake Venoms and Venom Metalloproteinases Using Synthetic Peptide Inhibitors and Chelators. Toxicon 2007, 49, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalante, T.; Franceschi, A.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Effectiveness of Batimastat, a Synthetic Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinases, in Neutralizing Local Tissue Damage Induced by BaP1, a Hemorrhagic Metalloproteinase from the Venom of the Snake Bothrops Asper. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.S.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Peptidomimetic Hydroxamate Metalloproteinase Inhibitors Abrogate Local and Systemic Toxicity Induced by Echis Ocellatus (Saw-Scaled) Snake Venom. Toxicon 2017, 132, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Torres, S.; Benard Valle, M.; Mackessy, S.P.; Menzies, S.K.; Casewell, N.R.; Ahmadi, S.; Burlet, N.J.; Muratspahić, E.; Sappington, I.; Overath, M.D.; et al. De Novo Designed Proteins Neutralize Lethal Snake Venom Toxins. Nature 2025, 639, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Venoms, Venomics, Antivenomics. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, D.J.; Calvete, J.J.; Sánchez, E.E.; Sanz, L.; Richards, K.; Curtis, R.; Boesen, K. Venom Variability and Envenoming Severity Outcomes of the Crotalus Scutulatus Scutulatus (Mojave Rattlesnake) from Southern Arizona. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2576–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsa, D.; Baiwir, D.; La Rocca, R.; Zimmerman, T.A.; Hanozin, E.; Grifnée, E.; Longuespée, R.; Meuwis, M.-A.; Smargiasso, N.; Pauw, E.D.; et al. Multi-Enzymatic Limited Digestion: The Next-Generation Sequencing for Proteomics? J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2501–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, F.G.; Redureau, D.; Crasset, T.; Freuville, L.; Baiwir, D.; Mazzucchelli, G.; Menzies, S.K.; Casewell, N.R.; Quinton, L. Next-Generation Sequencing for Venomics: Application of Multi-Enzymatic Limited Digestion for Inventorying the Snake Venom Arsenal. Toxins 2023, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shweiki, M.R.; Mönchgesang, S.; Majovsky, P.; Thieme, D.; Trutschel, D.; Hoehenwarter, W. Assessment of Label-Free Quantification in Discovery Proteomics and Impact of Technological Factors and Natural Variability of Protein Abundance. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1410–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, P.V.; Chelius, D.; Shaler, T.A. Identification and Relative Quantitation of Protein Mixtures by Enzymatic Digestion Followed by Capillary Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography−Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4741–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.C.; Nightingale, D.J.H.; Harrison, R.A.; Wagstaff, S.C. Isolation and Characterization of Renin-like Aspartic-Proteases from Echis Ocellatus Venom. Toxicon 2017, 137, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.F.; Nikolakis, Z.L.; Ivey, K.; Perry, B.W.; Schield, D.R.; Balchan, N.R.; Parker, J.; Hansen, K.C.; Saviola, A.J.; Castoe, T.A.; et al. Snakes on a Plain: Biotic and Abiotic Factors Determine Venom Compositional Variation in a Wide-Ranging Generalist Rattlesnake. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex Cocktails: The Evolutionary Novelty of Venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, A.; Pook, C.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Wüster, W. Coevolution of Diet and Prey-Specific Venom Activity Supports the Role of Selection in Snake Venom Evolution. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2443–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N. Last Decade Update for Three-Finger Toxins: Newly Emerging Structures and Biological Activities. World J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 10, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Structure, Function and Evolution of Three-Finger Toxins: Mini Proteins with Multiple Targets. Toxicon 2010, 56, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, S.W.; Williams, S.R.; Clark*, R.F. Dendrotoxin Poisoning in a Neurobiochemist. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, P.P.; Whitaker, A.N.; Sparrow, L.G.; de Jersey, J.; Winzor, D.J.; Watters, D.J.; Lavin, M.F.; Gaffney, P.J. Textilinins from Pseudonaja Textilis Textilis. Characterization of Two Plasmin Inhibitors That Reduce Bleeding in an Animal Model. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2000, 11, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, Y.M.; Lee, K.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Qiu, Y.; Wan, H.; Sohn, M.R.; Sohn, H.D.; Jin, B.R. Antifibrinolytic Role of a Bee Venom Serine Protease Inhibitor That Acts as a Plasmin Inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L. Twenty Years of Dendrotoxins. Toxicon 2001, 39, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Feng, J.; Wang, B.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z. BF9, the First Functionally Characterized Snake Toxin Peptide with Kunitz-Type Protease and Potassium Channel Inhibiting Properties. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2014, 28, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.-T.; Yang, W.-S.; He, Y.-W.; Feng, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, R.-M.; Ding, J.-P.; Cao, Z.-J.; Li, W.-X.; et al. Hg1, Novel Peptide Inhibitor Specific for Kv1.3 Channels from First Scorpion Kunitz-Type Potassium Channel Toxin Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13813–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweitz, H.; Bruhn, T.; Guillemare, E.; Moinier, D.; Lancelin, J.-M.; Béress, L.; Lazdunski, M. Kalicludines and Kaliseptine. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25121–25126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamitsu, S.; Kaoruko, S.; Yasushi, N.; Shigeru, K.; Makoto, M. Patient without Neurotoxic Symptom after Being Bitten by an Eastern Green Mamba (Dendroaspis angusticeps). J. Jpn. Assoc. Acute Med. 2011, 22, 777–781. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, S.; Petras, D.; Engmark, M.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Whiteley, G.; Albulescu, L.-O.; Kazandjian, T.D.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Rowley, P.; Wüster, W.; et al. The Medical Threat of Mamba Envenoming in Sub-Saharan Africa Revealed by Genus-Wide Analysis of Venom Composition, Toxicity and Antivenomics Profiling of Available Antivenoms. J. Proteom. 2018, 172, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, D.; Heiss, P.; Harrison, R.A.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Calvete, J.J. Top-down Venomics of the East African Green Mamba, Dendroaspis Angusticeps, and the Black Mamba, Dendroaspis Polylepis, Highlight the Complexity of Their Toxin Arsenals. J. Proteom. 2016, 146, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Lohse, B.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Unveiling the Nature of Black Mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) Venom through Venomics and Antivenom Immunoprofiling: Identification of Key Toxin Targets for Antivenom Development. J. Proteom. 2015, 119, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-da-Silva, A.; Butera, D.; Tanjoni, I. Importance of Snake Venom Metalloproteinases in Cell Biology: Effects on Platelets, Inflammatory and Endothelial Cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Local Tissue Damage. Biochimie 2000, 82, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A.; Soerensen, C.; op den Brouw, B.; Lister, C.; Dashevsky, D.; Arbuckle, K.; Gloria, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Casewell, N.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Differential Procoagulant Effects of Saw-Scaled Viper (Serpentes: Viperidae: Echis) Snake Venoms on Human Plasma and the Narrow Taxonomic Ranges of Antivenom Efficacies. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 280, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musch, T. Outline of an Anthropological Contribution to the Study of Snake Venom Variability: The Case of Echis Sp. Envenomation. Ethnobiol. Lett. 2014, 5, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipases A2: Unveiling the Secrets of a Functionally Versatile Group of Snake Venom Toxins. Toxicon 2013, 62, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Pan, H.; Liao, K.; Yang, M.; Huang, C. Snake Venom PLA2, a Promising Target for Broad-Spectrum Antivenom Drug Development. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6592820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Mitra, J.; Bhattacharyya, D. L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Venoms. Toxins Drug Discov. 2017, 13, 295–320. [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff, S.C.; Sanz, L.; Juárez, P.; Harrison, R.A.; Calvete, J.J. Combined Snake Venomics and Venom Gland Transcriptomic Analysis of the Ocellated Carpet Viper, Echis Ocellatus. J. Proteom. 2009, 71, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Wüster, W.; Cook, D.A.N.; Bolton, F.M.S.; King, S.I.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Harrison, R.A. Medically Important Differences in Snake Venom Composition Are Dictated by Distinct Postgenomic Mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9205–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Kalita, B.; Chanda, A.; Mukherjee, A.K. Proteomics and Antivenomics of Echis Carinatus Carinatus Venom: Correlation with Pharmacological Properties and Pathophysiology of Envenomation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A.; Wüster, W.; Wagstaff, S.C. Comparative Venom Gland Transcriptome Surveys of the Saw-Scaled Vipers (Viperidae: Echis) Reveal Substantial Intra-Family Gene Diversity and Novel Venom Transcripts. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, N.; Robinson, M.; Carranza, S. A Preliminary Analysis of Phylogenetic Relationships and Biogeography of the Dangerously Venomous Carpet Vipers, Echis (Squamata, Serpentes, Viperidae) Based on Mitochondrial DNA Sequences. Amphibia-Reptilia 2009, 30, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal Abidin, S.A.; Rajadurai, P.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Ahmad Rusmili, M.R.; Othman, I.; Naidu, R. Proteomic Characterization and Comparison of Malaysian Tropidolaemus Wagleri and Cryptelytrops Purpureomaculatus Venom Using Shotgun-Proteomics. Toxins 2016, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Species | D. angusticeps | D. j. jamesoni | D. j. kaimosae | D. polylepis | D. viridis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Trypsin | MELD | Trypsin | MELD | Trypsin | MELD | Trypsin | MELD | Trypsin | MELD |
| Peptide Spectrum Matches | 3395 | 5513 | 3684 | 7315 | 2837 | 4757 | 3728 | 2932 | 3311 | 5589 |
| Peptides | 622 | 1666 | 581 | 1940 | 513 | 1240 | 646 | 951 | 616 | 1701 |
| All proteins | 122 | 137 | 123 | 158 | 96 | 101 | 121 | 122 | 157 | 187 |
| Top proteins | 82 | 90 | 90 | 110 | 81 | 82 | 92 | 95 | 112 | 136 |
| Species | E. coloratus | E. leucogaster | E. p. leakeyi | E. romani | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Trypsin | MELD | Trypsin | MELD | Trypsin | MELD | Trypsin | MELD |
| Peptide Spectrum Matches | 7418 | 14632 | 5180 | 9461 | 4943 | 9364 | 6860 | 10377 |
| Peptides | 1715 | 4126 | 1033 | 2584 | 1118 | 3007 | 1536 | 3104 |
| All proteins | 130 | 144 | 112 | 140 | 115 | 136 | 108 | 124 |
| Top proteins | 98 | 121 | 65 | 89 | 74 | 87 | 87 | 96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Redureau, D.; Amorim, F.G.; Crasset, T.; Berger, I.; Schaffitzel, C.; Menzies, S.K.; Casewell, N.R.; Quinton, L. Dual Proteomics Strategies to Dissect and Quantify the Components of Nine Medically Important African Snake Venoms. Toxins 2025, 17, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050243
Redureau D, Amorim FG, Crasset T, Berger I, Schaffitzel C, Menzies SK, Casewell NR, Quinton L. Dual Proteomics Strategies to Dissect and Quantify the Components of Nine Medically Important African Snake Venoms. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050243
Chicago/Turabian StyleRedureau, Damien, Fernanda Gobbi Amorim, Thomas Crasset, Imre Berger, Christiane Schaffitzel, Stefanie Kate Menzies, Nicholas R. Casewell, and Loïc Quinton. 2025. "Dual Proteomics Strategies to Dissect and Quantify the Components of Nine Medically Important African Snake Venoms" Toxins 17, no. 5: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050243
APA StyleRedureau, D., Amorim, F. G., Crasset, T., Berger, I., Schaffitzel, C., Menzies, S. K., Casewell, N. R., & Quinton, L. (2025). Dual Proteomics Strategies to Dissect and Quantify the Components of Nine Medically Important African Snake Venoms. Toxins, 17(5), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050243







