Single-Dose IncobotulinumtoxinA in the Treatment of Early-Stage Knee Osteoarthritis: Results from a Preliminary Single-Arm Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
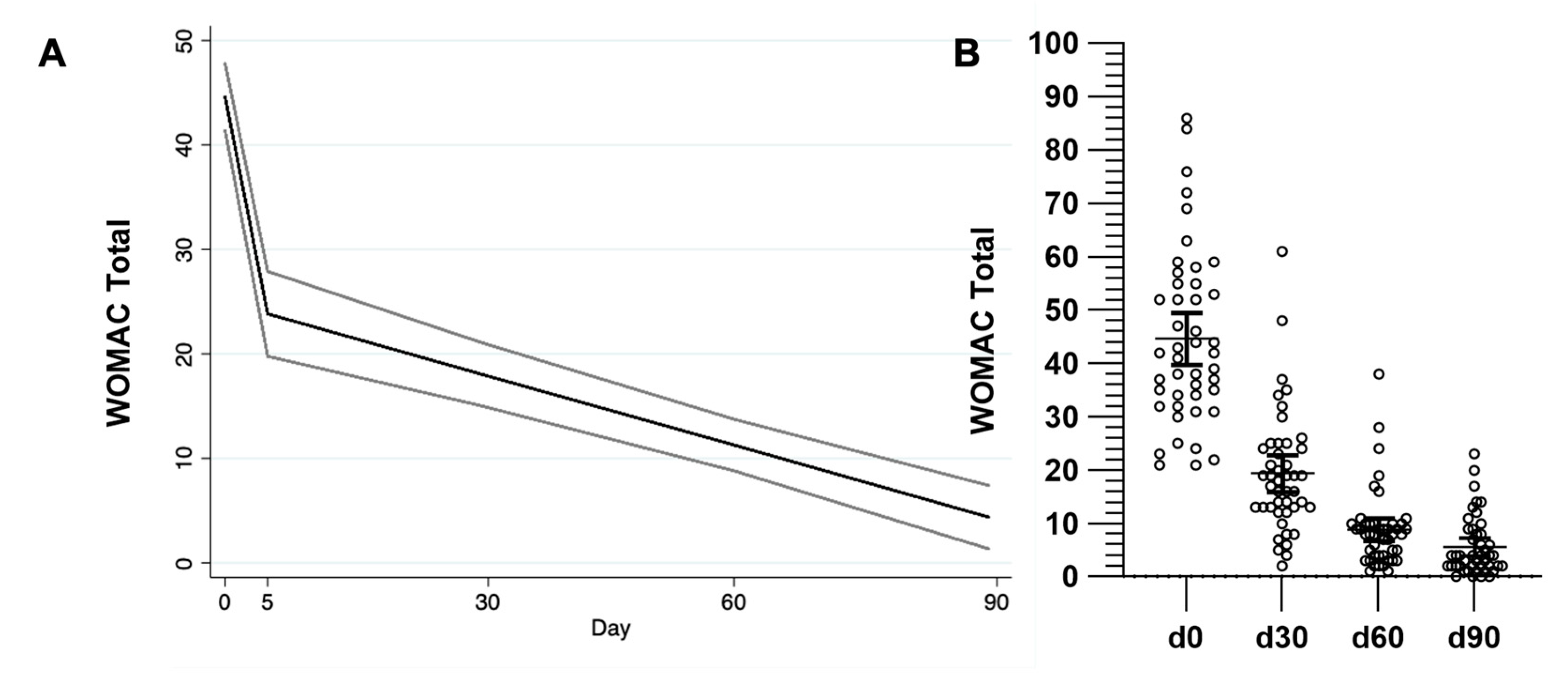
2.1. Therapeutic Effect in Pain, Stiffness, and Function (WOMAC)
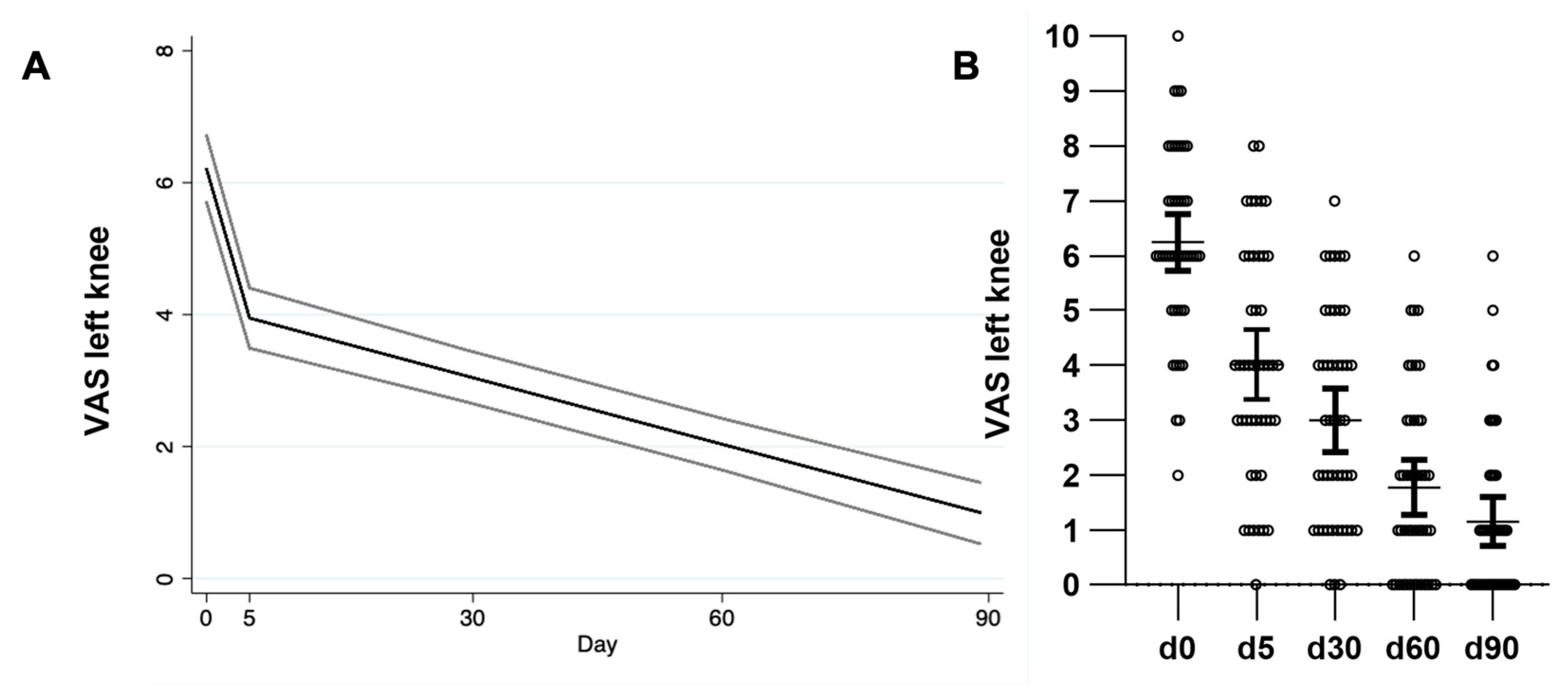
2.2. Therapeutic Effect in Referred Pain (VAS)
2.3. BoNT-A Effect on Muscular Strength of the Lower Limb
2.4. Generalized Linear Random Effect Model
3. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Design and Patients
5.2. Intervention
5.3. Clinical Evaluation
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.; Smith, E.; Hoy, D.; Carmona, L.; Wolfe, F.; Vos, T.; Williams, B.; Gabriel, S.; Lassere, M.; Johns, N.; et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Smith, E.; Hill, C.; Bettampadi, D.; Mansournia, M.A.; Hoy, D.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990–2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.H.; Lepus, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Raghu, H.; Mao, R.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Sokolove, J. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, C.B.; Hunter, D.J. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis: From mouse models to clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, B.R.; Saadat, P.; Basciani, R.M.; Agarwal, A.; Johnston, B.C.; Jüni, P. Visual Analogue Scale has higher assay sensitivity than WOMAC pain in detecting between-group differences in treatment effects: A meta-epidemiological study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, N.; Buchanan, W.W. A Preliminary Evaluation of the Dimensionality and Clinical Importance of Pain and Disability in Osteoarthritis of the Hip and Knee. Clin. Rheumatol. 1986, 5, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, M.; Droy, E.; Muscatelli, S.; Gagnier, J.J. Measures of Adult Knee Function. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72 (Suppl. S10), 219–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, K.; LaValley, M.P.; Jafarzadeh, S.R.; Felson, D. Does cartilage loss cause pain in osteoarthritis and if so, how much? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellgren, J.; Lawrence, J. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1957, 16, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermazi, A.; Hayashi, D.; Roemer, F.; Felson, D.; Wang, K.; Lynch, J.; Amin, S.; Torner, J.; Lewis, C.; Nevitt, M. Severe radiographic knee osteoarthritis e does Kellgren and Lawrence grade 4 represent end stage disease?—The MOST study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingleton, C.; Smart, K.; Moloney, N.; Fullen, B.; Doody, C. Pain sensitization in people with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Osani, M.C.; Vaysbrot, E.E.; Arden, N.K.; Bennell, K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Kraus, V.B.; Lohmander, L.S.; Abbott, J.H.; Bhandari, M.; et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanshan, N.; Krug, H. The use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of chronic joint pain: Clinical and experimental evidence. Toxins 2020, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, J.K.; Eisen, A.; Stoessl, A.J.; Calne, S.; Calne, D.B. Double-blind study of Botulinum Toxin in Spasmodic Torticollis. Lancet 1986, 328, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, B.; Machado, D. Treatment of Refractory Pain with Botulinum Toxins-An Evidence-Based Review. Pain Med. 2011, 12, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herd, C.P.; Tomlinson, C.L.; Rick, C.; Scotton, W.J.; Edwards, J.; Ives, N.J.; E Clarke, C.; Sinclair, A. Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of botulinum toxin for the prevention of migraine. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, R.; Juodzbalys, G. The Use of Botulinum Toxin A in the Management of Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Res. 2020, 11, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagna, A.; Attal, N. Botulinum toxin A and neuropathic pain: An update. Toxicon 2023, 232, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N.; de Andrade, D.C.; Adam, F.; Ranoux, D.; Teixeira, M.J.; Galhardoni, R.; Raicher, I.; Üçeyler, N.; Sommer, C.; Bouhassira, D. Safety and efficacy of repeated injections of botulinum toxin A in peripheral neuropathic pain (BOTNEP): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val, M.; Delcanho, R.; Ferrari, M.; Nardini, L.G.; Manfredini, D. Is Botulinum Toxin Effective in Treating Orofacial Neuropathic Pain Disorders? A Systematic Review. Toxins 2023, 15, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarpour, Y.; Jabbari, B. Botulinum toxin treatment of pain syndromes—An evidence based review. Toxicon 2018, 147, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Park, H.J. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Toxins 2017, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intiso, D. Therapeutic use of botulinum toxin in neurorehabilitation. J. Toxicol. 2012, 2012, 802893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Binder, A. Fighting neuropathic pain with botulinum toxin A. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 534–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, M.L.; Singh, J.A.; Dykstra, D. Long term effects of intra-articular botulinum toxin a for refractory joint pain. Neurotox. Res. 2006, 9, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, H.E.; Frizelle, S.; McGarraugh, P.; Mahowald, M.L. Pain behavior measures to quantitate joint pain and response to neurotoxin treatment in murine models of arthritis. Pain Med. 2009, 10, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Krug, H.; Dorman, C.; McGarraugh, P.; Frizelle, S.; Mahowald, M.; Garraugh, M. Analgesic effects of intra-articular botulinum toxin Type B in a murine model of chronic degenerative knee arthritis pain. J. Pain Res. 2010, 3, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A.; Mahowald, M.L.; Noorbaloochi, S. Intra-articular botulinum toxin A for refractory shoulder pain: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Transl. Res. 2009, 153, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, A.J.; Smith, J.; Dahm, D.L.; Sorenson, E.J.; Larson, D.R.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.D.; Dykstra, D.D.; Singh, J.A. Efficacy of Intra-Articular Botulinum Toxin Type A in Painful Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study. PM&R 2010, 2, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, L.-F.; Wu, C.-W.; Chou, C.-C.; Yang, S.-W.; Wu, S.-H.; Lin, Y.-J.; Hsu, W.-C. Effects of Botulinum Toxin Landmark-Guided Intra-articular Injection in Subjects with Knee Osteoarthritis. PM&R 2016, 8, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Tan, J.-W.; Flyzik, M.; Ma, X.-C.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.-Y. Effect of therapeutic exercise on knee osteoarthritis after intraarticular injection of botulinum toxin type a, hyaluronate or saline: A randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezasoltani, Z.; Azizi, S.; Najafi, S.; Sanati, E.; Dadarkhah, A.; Abdorrazaghi, F. Physical therapy, intra-articular dextrose prolotherapy, botulinum neurotoxin, and hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis: Randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2020, 43, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Jiang, G.-L.; DeGryse, R.; Turkel, C. Intra-articular onabotulinumtoxinA in osteoarthritis knee pain: Effect on human mechanistic pain biomarkers and clinical pain. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 46, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlindon, T.; Schmidt, U.; Bugarin, D.; Abrams, S.; Geib, T.; DeGryse, R.; Kim, K.; Schnitzer, T. Efficacy and safety of single-dose onabotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee: Results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.G.; Natour, J.; Nunes-Tamashiro, J.C.; Toffolo, S.R.; Rosenfeld, A.; Furtado, R.N.V. Comparison between intra-articular Botulinum toxin type A, corticosteroid, and saline in knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2019, 33, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazendam, A.; Ekhtiari, S.; Bozzo, A.; Phillips, M.; Bhandari, M. Intra-articular saline injection is as effective as corticosteroids, platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid for hip osteoarthritis pain: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, S.; Sanati, E.; Khademi, M.; Abdorrazaghi, F.; Mofrad, R.K.; Rezasoltani, Z. Intra-articular botulinum toxin type A for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Clinical trial. Toxicon 2019, 165, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Mahowald, M.L. Intra-articular botulinum toxin A as an adjunctive therapy for refractory joint pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving biologics: A report of two cases. Jt. Bone Spine 2009, 76, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, M.; Singh, J.; Dykstra, D. Report on Intraarticular Botulinum Toxin Type a for Refractory Joint Pain. J. Investig. Med. 2004, 52 Pt 5, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liles, S.C.; Bley, B.; White, D.K. The effects of exercise and intra-articular injections versus exercise alone for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A scoping review of the evidence. Osteoarthr. Cart. Open 2024, 6, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría De Salud. Prevención, Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de Rehabilitación en el Paciente Adulto con Osteoartrosis de Rodilla en los Tres Niveles de Atención. Secretaría de Salud. 2014. Available online: http://www.cenetec-difusion.com/CMGPC/IMSS-726-14/RR.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Altman, R.D.; Devji, T.; Bhandari, M.; Fierlinger, A.; Niazi, F.; Christensen, R. Clinical benefit of intra-articular saline as a comparator in clinical trials of knee osteoarthritis treatments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Semin. Arthritis. Rheum. 2016, 46, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría De Salud. Diagnóstico, Tratamiento y Prevención de Sobrepeso y Obesidad en el Adulto. Secretaría de Salud. 2008. Available online: http://www.facmed.unam.mx/sg/css/GPC/SIDSS-GPC/gpc/docs/IMSS-046-08-RR.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2024).

| Variable | n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Women | 37 (82.25) |
| Men | 8 (17.8%) | |
| Kellgren and Lawrence | Grade I | 10 (22.2%) |
| Grade II | 35 (77.8%) | |
| Age | 59.3 (18, 78) * | |
| BMI | Normal | 2 (4.4%) |
| Overweight | 27 (60%) | |
| Obese | 16 (35.6%) | |
| Comorbidities | Diabetes | 1 (2.2%) |
| Hypertension | 10 (22.2%) | |
| Diabetes and Hypertension | 6 (13.3%) | |
| n = 45 |
| Days | 0 | 5 | 30 | 60 | 90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS right mean, (SD) | 6.11 (1.94) | 3.68 (2.03) * | 2.86 (1.87) ** | 1.86 (1.67) ** | 1.15 (1.58) ** |
| VAS left mean, (SD) | 6.24 (1.72) | 4.02 (2.105) * | 3 (1.93) ** | 1.77 (1.67) ** | 1.15 (1.49) ** |
| WOMAC | |||||
| Total | 44.57 (16.3) | - | 19.33 (11.33) * | 8.82 (7.15) ** | 5.6 (5.53) ** |
| Pain | 17.95 (5.25) | - | 8.02 (3.87) ** | 4.42 (1.97) ** | 2.84 (1.9) ** |
| Stiffness | 3.8 (1.63) | - | 1.28 (1.14) ** | 0.51 (0.69) ** | 0.31 (0.55) ** |
| Function | 31.66 (12.19) | - | 14 (8.8) * | 6.06 (5.96) ** | 3.84 (4.6) ** |
| Extension right, (kg, SD) | 30.62 (11.53) | - | 39.06 (14.52) * | 41.93 (12.62) ** | 45.71 (13.96) ** |
| Flexion right (kg, SD) | 18.66 (7.61) | - | 29.94 (9.04) ** | 26.79 (9.24) ** | 29.95 (11.91) ** |
| Extension left, (kg, SD) | 28.91 (11.85) | - | 38.84 (15.33) ** | 40 (11.69) ** | 41.37 (11.57) ** |
| Flexion left (kg, SD) | 18.5 (7.34) | - | 24.33 (10.09) ** | 24.09 (7.91) ** | 26.31 (11.06) ** |
| Toxin | Toxin * Day | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| VAS right knee * n = 45 | Coef. | −2.31 ** | −0.03 ** |
| 95% CI | −2.81, −1.8 | −0.04, −0.02 | |
| VAS left knee * n = 44 | Coef. | −2.08 ** | −0.03 ** |
| 95% CI | −2.60, −1.57 | −0.04, −0.03 | |
| WOMAC * n = 45 | Coef. | 19.66 ** | −0.23 ** |
| 95% CI | −24.21, −15.11 | −0.29, −0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durán-Hernández, S.; Herrera-González, N.E.; Durán-Hernández, N.; Carnalla, M.; Castillejos-López, M.d.J.; Salinas-Lara, C. Single-Dose IncobotulinumtoxinA in the Treatment of Early-Stage Knee Osteoarthritis: Results from a Preliminary Single-Arm Clinical Trial. Toxins 2025, 17, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050216
Durán-Hernández S, Herrera-González NE, Durán-Hernández N, Carnalla M, Castillejos-López MdJ, Salinas-Lara C. Single-Dose IncobotulinumtoxinA in the Treatment of Early-Stage Knee Osteoarthritis: Results from a Preliminary Single-Arm Clinical Trial. Toxins. 2025; 17(5):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050216
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurán-Hernández, Sofia, Norma E. Herrera-González, Nayar Durán-Hernández, Martha Carnalla, Manuel de Jesús Castillejos-López, and Citlaltepetl Salinas-Lara. 2025. "Single-Dose IncobotulinumtoxinA in the Treatment of Early-Stage Knee Osteoarthritis: Results from a Preliminary Single-Arm Clinical Trial" Toxins 17, no. 5: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050216
APA StyleDurán-Hernández, S., Herrera-González, N. E., Durán-Hernández, N., Carnalla, M., Castillejos-López, M. d. J., & Salinas-Lara, C. (2025). Single-Dose IncobotulinumtoxinA in the Treatment of Early-Stage Knee Osteoarthritis: Results from a Preliminary Single-Arm Clinical Trial. Toxins, 17(5), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17050216





