Incidence of Dysphagia and Comorbidities in Patients with Cervical Dystonia, Analyzed by Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
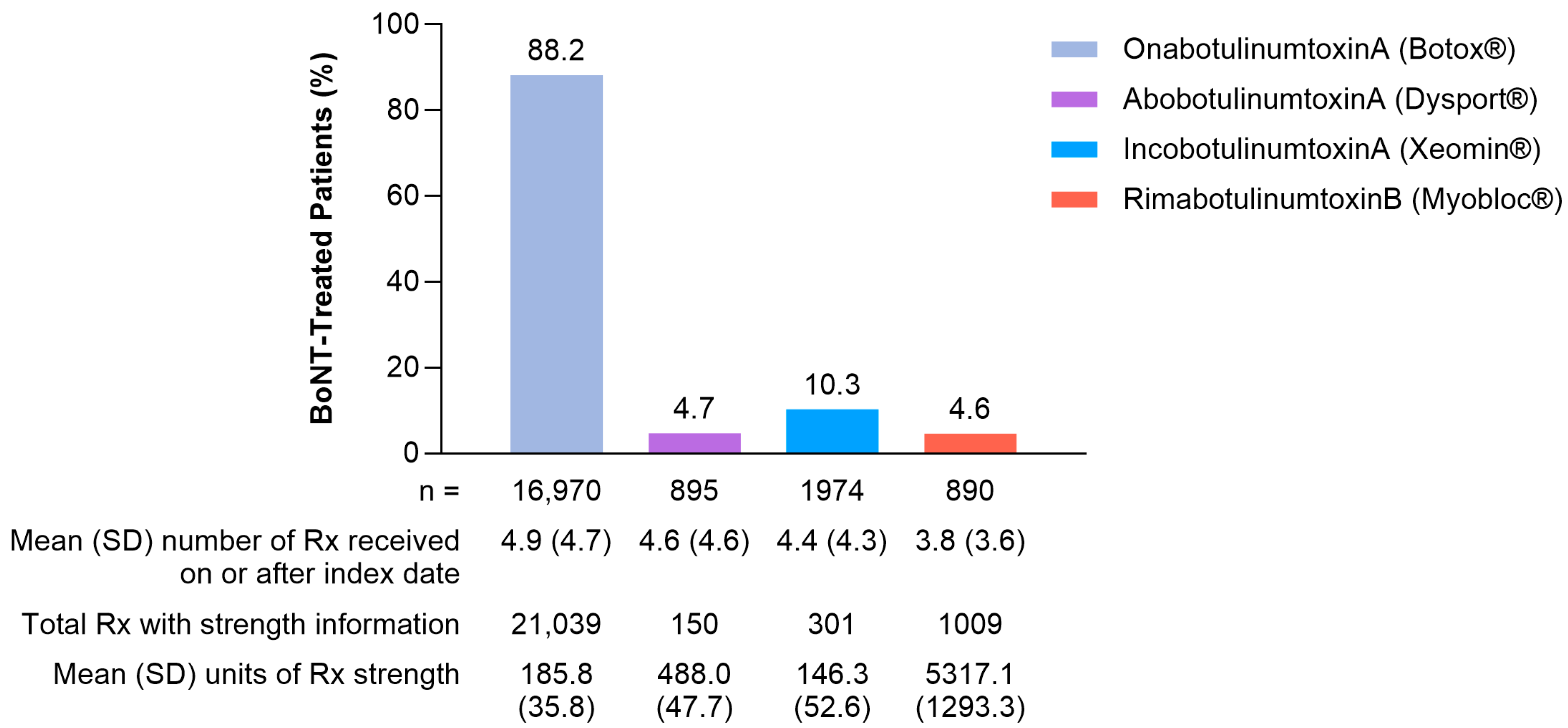
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Outcomes
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Design and Participants
5.2. Outcomes
5.3. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortiz, R.; Scheperjans, F.; Mertsalmi, T.; Pekkonen, E. The Prevalence of Adult-Onset Isolated Dystonia in Finland 2007–2016. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Bhatia, K.; Bressman, S.B.; DeLong, M.R.; Fahn, S.; Fung, V.S.C.; Hallett, M.; Jankovic, J.; Jinnah, H.A.; Klein, C.; et al. Phenomenology and Classification of Dystonia: A Consensus Update. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic-Berkmen, G.; Richardson, S.P.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Hallett, M.; Klein, C.; Wagle-Shukla, A.; Malaty, I.A.; Reich, S.G.; Berman, B.D.; Feuerstein, J.; et al. Current Guidelines for Classifying and Diagnosing Cervical Dystonia: Empirical Evidence and Recommendations. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloud, L.J.; Jinnah, H. Treatment Strategies for Dystonia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Abbruzzese, G.; Dressler, D.; Duzynski, W.; Khatkova, S.; Marti, M.J.; Mir, P.; Montecucco, C.; Moro, E.; Pinter, M.; et al. Practical Guidance for CD Management Involving Treatment of Botulinum Toxin: A Consensus Statement. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.M.; Hallett, M.; Ashman, E.J.; Comella, C.L.; Green, M.W.; Gronseth, G.S.; Armstrong, M.J.; Gloss, D.; Potrebic, S.; Jankovic, J.; et al. Practice Guideline Update Summary: Botulinum Neurotoxin for the Treatment of Blepharospasm, Cervical Dystonia, Adult Spasticity, and Headache Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 86, 1818–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, L.L.; Ostrem, J.L.; Bledsoe, I.O. FDA Approvals and Consensus Guidelines for Botulinum Toxins in the Treatment of Dystonia. Toxins 2020, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.F.; Comella, C.L.; Jankovic, J.; Lai, F.; Naumann, M. Long-term Treatment with Botulinum Toxin Type A in Cervical Dystonia Has Low Immunogenicity by Mouse Protection Assay. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, D.; Brashear, A.; Hauser, R.A.; Li, H.-I.; Boo, L.-M.; Brin, M.F.; The CD 140 Study Group. Efficacy, Tolerability, and Immunogenicity of OnabotulinumtoxinA in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial for Cervical Dystonia. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2012, 35, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Adler, C.H.; Charles, D.; Comella, C.; Stacy, M.; Schwartz, M.; Adams, A.M.; Brin, M.F. Primary Results from the Cervical Dystonia Patient Registry for Observation of OnabotulinumtoxinA Efficacy (CD PROBE). J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 349, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riski, J.E.; Homer, J.; Nashold, B.S. Swallowing Function in Patients with Spasmodic Torticollis. Neurology 1990, 40, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, J.; Riski, J.E.; Ovelmen-Levitt, J.; Nashold, B.S. Swallowing in Torticollis before and after Rhizotomy. Dysphagia 1992, 7, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella, C.L.; Tanner, C.M.; DeFoor-Hill, L.; Smith, C. Dysphagia after Botulinum Toxin Injections for Spasmodic Torticollis: Clinical and Radiologic Findings. Neurology 1992, 42, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, C.; Aydogdu, I.; Seçil, Y.; Kiylioglu, N.; Tarlaci, S.; Ozdemirkiran, T. Oropharyngeal Swallowing in Craniocervical Dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botox. Prescribing Information. AbbVie Inc. Available online: https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/botox_pi.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Dysport. Prescribing Information. Ipsen Biopharm Ltd. Available online: https://www.ipsen.com/websites/Ipsen_Online/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/10002305/DYS-US-004998_Dysport-PI-July-2020.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Myobloc. Prescribing Information. Solstice Neurosciences, LLC. Available online: https://www.myobloc.com/files/Myobloc-Prescribing-Information.pdf (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Xeomin. Prescribing Information. Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbH. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/125360s078lbl.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Single Treatment of DaxibotulinumtoxinA for Injection in Adults with Isolated Cervical Dystonia (ASPEN-1) (ASPEN-1). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03608397 (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Anandan, C.; Jankovic, J. Botulinum Toxin in Movement Disorders: An Update. Toxins 2021, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münchau, A.; Good, C.D.; McGowan, S.; Quinn, N.P.; Palmer, J.D.; Bhatia, K.P. Prospective Study of Swallowing Function in Patients with Cervical Dystonia Undergoing Selective Peripheral Denervation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 71, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.J.; Rivest, J.; Stell, R.; Steiger, M.J.; Cohen, H.; Thompson, P.D.; Marsden, C.D. Botulinum Toxin Treatment of Spasmodic Torticollis. J. R. Soc. Med. 1992, 85, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, C.; Jankovic, J. Botulinum Toxin Treatment in Parkinsonism. J. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 456, 122810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.O.; Nascimento, W.V.; Cassiani, R.A.; Silva, A.C.V.; Alves, L.M.T.; Alves, D.C.; Dantas, R.O. Prevalence of Non-Obstructive Dysphagia in Patients with Heartburn and Regurgitation. Clinics 2020, 75, e1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, M.; Ottenstein, L.; Atanelov, L.; Christian, A.B. Dysphagia after Stroke: An Overview. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2013, 1, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttrup, I.; Warnecke, T. Dysphagia in Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutschenko, A.; Klietz, M.; Paracka, L.; Kollewe, K.; Schulte-Sutum, A.; Janssen, T.; Schrader, C.; Wegner, F.; Dressler, D. Dysphagia in Cervical Dystonia Patients Receiving Optimised Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtipour, K.; Lee, H.S.; Ellenbogen, A.; Kazerooni, R.; Gross, T.M.; Hollander, D.A.; Gallagher, C.J. Dysphagia and Muscle Weakness Secondary to Botulinum Toxin Type A Treatment of Cervical Dystonia: A Drug Class Analysis of Prescribing Information. Toxins 2024, 16, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Barbano, R.; Moore, H.; Schwartz, M.; Zuzek, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Patel, A. OnabotulinumtoxinA Dosing, Disease Severity, and Treatment Benefit in Patients With Cervical Dystonia: A Cohort Analysis From CD PROBE. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 914486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, T.F.D.D.; Borges, V.; Ferraz, H.B. Specific Characteristics of the Medical History of Swallowing before and after Application of Botulinum Toxin in Patients with Cervical Dystonia. Clinics 2019, 74, e776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodic, G.E.; Joseph, M.; Fay, L.; Cozzolino, D.; Ferrante, R.J. Botulinum a Toxin for the Treatment of Spasmodic Torticollis: Dysphagia and Regional Toxin Spread. Head Neck 1990, 12, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.-H.; Kim, S.-B.; Hu, H.; An, H.-S.; Hidajat, I.J.; Lim, T.S.; Kim, H.-J. Ultrasonographic Study of the Submandibular Gland for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection. Dermatol. Surg. 2024, 50, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, G. Cervical Dystonia: A New Phenomenological Classification for Botulinum Toxin Therapy. Basal Ganglia 2011, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erro, R.; Picillo, M.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Barone, P. Improving the Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin for Cervical Dystonia: A Scoping Review. Toxins 2023, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipe, M.E.; Deppen, S.A.; Farjah, F.; Grogan, E.L. Developing Prediction Models for Clinical Use Using Logistic Regression: An Overview. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S574–S584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristic | Cohort 1: All CD Patients (N = 81,884) | Cohort 2: BoNT-Exposed (N = 19,244) | Cohort 3: BoNT-Unexposed (N = 61,154) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) age, years | 54.00 (16.21) | 56.92 (14.92) | 53.10 (16.55) |
| Age group, years, n (%) | |||
| 18–29 | 6496 (7.93) | 809 (4.20) | 5580 (9.12) |
| 30–39 | 10,893 (13.30) | 1869 (9.71) | 8851 (14.47) |
| 40–49 | 14,122 (17.25) | 3163 (16.44) | 10,643 (17.40) |
| 50–59 | 18,472 (22.56) | 4617 (23.99) | 13,388 (21.89) |
| 60–69 | 16,783 (20.50) | 4671 (24.27) | 11,853 (19.38) |
| 70–79 | 10,411 (12.71) | 2977 (15.47) | 7,286 (11.91) |
| ≥80 | 4707 (5.75) | 1138 (5.91) | 3553 (5.81) |
| Female, n (%) | 55,602 (67.90) | 14,249 (74.04) | 40,240 (65.80) |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| White | 63,014 (76.96) | 15,695 (81.56) | 46,112 (75.40) |
| African American | 5032 (6.15) | 701 (3.64) | 4296 (7.02) |
| Asian | 1215 (1.48) | 231 (1.20) | 974 (1.59) |
| Other/Unknown | 12,623 (15.42) | 2617 (13.60) | 9772 (15.98) |
| Characteristic | Cohort 1: All CD Patients (N = 81,884) | Cohort 2: BoNT-Exposed (N = 19,244) | Cohort 3: BoNT-Unexposed (N = 61,154) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predominant CD posture, n (%) | |||
| Laterocollis | 1470 (1.8) | 1027 (5.34) | 391 (0.64) |
| Torticollis | 7171 (8.76) | 2703 (14.05) | 4260 (6.97) |
| Unknown | 74,308 (90.75) | 16,277 (84.58) | 56,766 (92.82) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index, mean (SD) | 1.3 (2.1) | 1.4 (2.0) | 1.3 (2.1) |
| Comorbidities, within 180 days prior to index date, n (%) | |||
| Other types of dystonia | 5221 (6.38) | 2643 (13.73) | 2068 (3.38) |
| Chronic migraine a,b | 10,424 (12.7) | 4087 (21.2) | 5918 (9.6) |
| Neurological conditions that are known risk factors for dysphagia, n (%) | |||
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 12,796 (15.63) | 3209 (16.68) | 9321 (15.24) |
| Stroke | 4030 (4.92) | 1110 (5.77) | 2838 (4.64) |
| Parkinson’s disease | 2433 (2.97) | 1016 (5.28) | 1354 (2.21) |
| Multiple sclerosis | 867 (1.06) | 316 (1.64) | 517 (0.85) |
| Myasthenia gravis | 109 (0.13) | 20 (0.10) | 86 (0.14) |
| Huntington disease | 33 (0.04) | 13 (0.07) | 18 (0.03) |
| Wilson’s disease | 11 (0.01) | 7 (0.04) | 4 (0.01) |
| Lambert–Eaton syndrome | 3 (<0.01) | 2 (0.01) | 1 (<0.01) |
| Psychiatric comorbidities, n (%) | 22,997 (28.08) | 6207 (32.25) | 22,997 (28.08) |
| Anxiety | 17,028 (20.80) | 4497 (23.37) | 12,151 (19.87) |
| Depression | 14,062 (17.17) | 3993 (20.75) | 9711 (15.88) |
| Cohort 2: BoNT-Exposed (N = 19,244) | Cohort 3: BoNT-Unexposed (N = 61,154) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic, n (%) | With Dysphagia (n = 3144) | Without Dysphagia (n = 16,100) | With Dysphagia (n = 7378) | Without Dysphagia (n = 53,776) |
| Mean (SD) age, years | 60.43 (15.09) | 56.23 (14.71) | 59.27 (16.12) | 52.25 (16.43) |
| Age group, years | ||||
| 18–29 | 131 (4.17) | 678 (4.21) | 351 (4.76) | 5229 (9.72) |
| 30–39 | 181 (5.76) | 1688 (10.48) | 629 (8.53) | 8222 (15.29) |
| 40–49 | 391 (12.44) | 2772 (17.22) | 969 (13.13) | 9674 (17.99) |
| 50–59 | 691 (21.98) | 3926 (24.39) | 1562 (21.17) | 11,826 (21.99) |
| 60–69 | 779 (24.78) | 3892 (24.17) | 1697 (23.00) | 10,156 (18.89) |
| 70–79 | 675 (21.47) | 2302 (14.30) | 1373 (18.61) | 5913 (11.00) |
| ≥80 | 296 (9.41) | 842 (5.23) | 797 (10.80) | 2756 (5.12) |
| Other types of dystonia | 566 (18.00) | 2077 (12.90) | 515 (6.98) | 1553 (2.89) |
| Stroke | 370 (11.77) | 740 (4.60) | 781 (10.59) | 2057 (3.83) |
| Parkinson’s disease | 444 (14.12) | 572 (3.55) | 527 (7.14) | 827 (1.54) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 861 (27.39) | 2348 (14.58) | 2146 (29.09) | 7175 (13.34) |
| Psychiatric comorbidities (of the below) | 1216 (38.68) | 4991 (31.00) | 2693 (36.50) | 13,556 (25.21) |
| Anxiety | 853 (27.13) | 3644 (22.63) | 1979 (26.82) | 10,172 (18.92) |
| Depression | 856 (27.23) | 3137 (19.48) | 1742 (23.61) | 7969 (14.82) |
| Hospitalization/emergency room visit/urgent care visit within 180 days prior to index date | ||||
| Patients with ≥1 hospitalization | 522 (16.60) | 1215 (7.55) | 1485 (20.13) | 4730 (8.80) |
| Patients with ≥emergency room or urgent care visit | 954 (30.34) | 3308 (20.55) | 2616 (35.46) | 13,131 (24.42) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbano, R.L.; Jabbari, B.; Sadeghi, M.; Ukah, A.; Yue, E.; Becker Ifantides, K.; Huang, N.-Y.; Swope, D. Incidence of Dysphagia and Comorbidities in Patients with Cervical Dystonia, Analyzed by Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment Exposure. Toxins 2025, 17, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030148
Barbano RL, Jabbari B, Sadeghi M, Ukah A, Yue E, Becker Ifantides K, Huang N-Y, Swope D. Incidence of Dysphagia and Comorbidities in Patients with Cervical Dystonia, Analyzed by Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment Exposure. Toxins. 2025; 17(3):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030148
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbano, Richard L., Bahman Jabbari, Marjan Sadeghi, Ahunna Ukah, Emma Yue, Kimberly Becker Ifantides, Nuo-Yu Huang, and David Swope. 2025. "Incidence of Dysphagia and Comorbidities in Patients with Cervical Dystonia, Analyzed by Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment Exposure" Toxins 17, no. 3: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030148
APA StyleBarbano, R. L., Jabbari, B., Sadeghi, M., Ukah, A., Yue, E., Becker Ifantides, K., Huang, N.-Y., & Swope, D. (2025). Incidence of Dysphagia and Comorbidities in Patients with Cervical Dystonia, Analyzed by Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment Exposure. Toxins, 17(3), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030148






